Evolution and Li Mineralization of the No. 134 Pegmatite in the Jiajika Rare-Metal Deposit, Western Sichuan, China: Constrains from Critical Minerals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Background
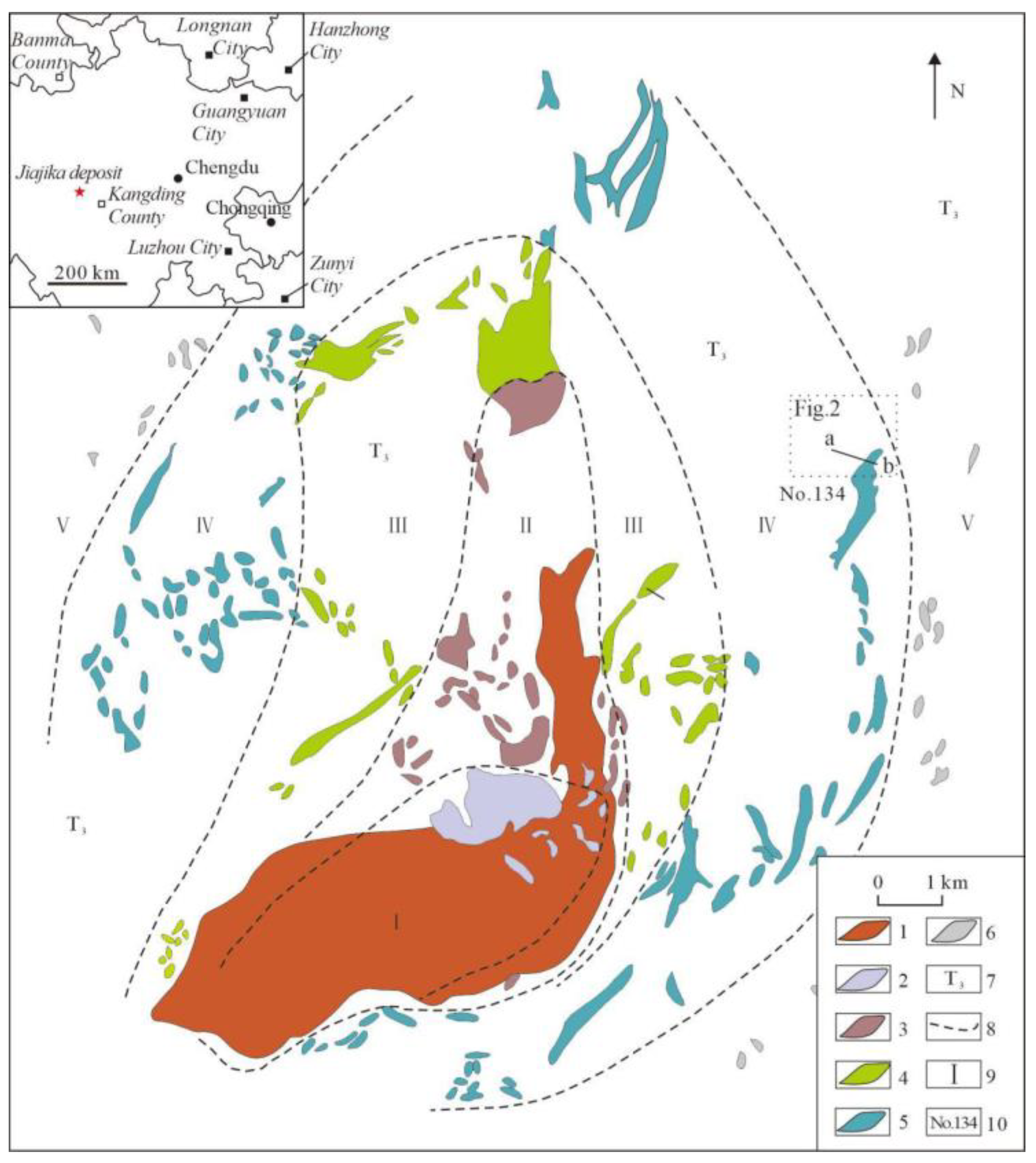
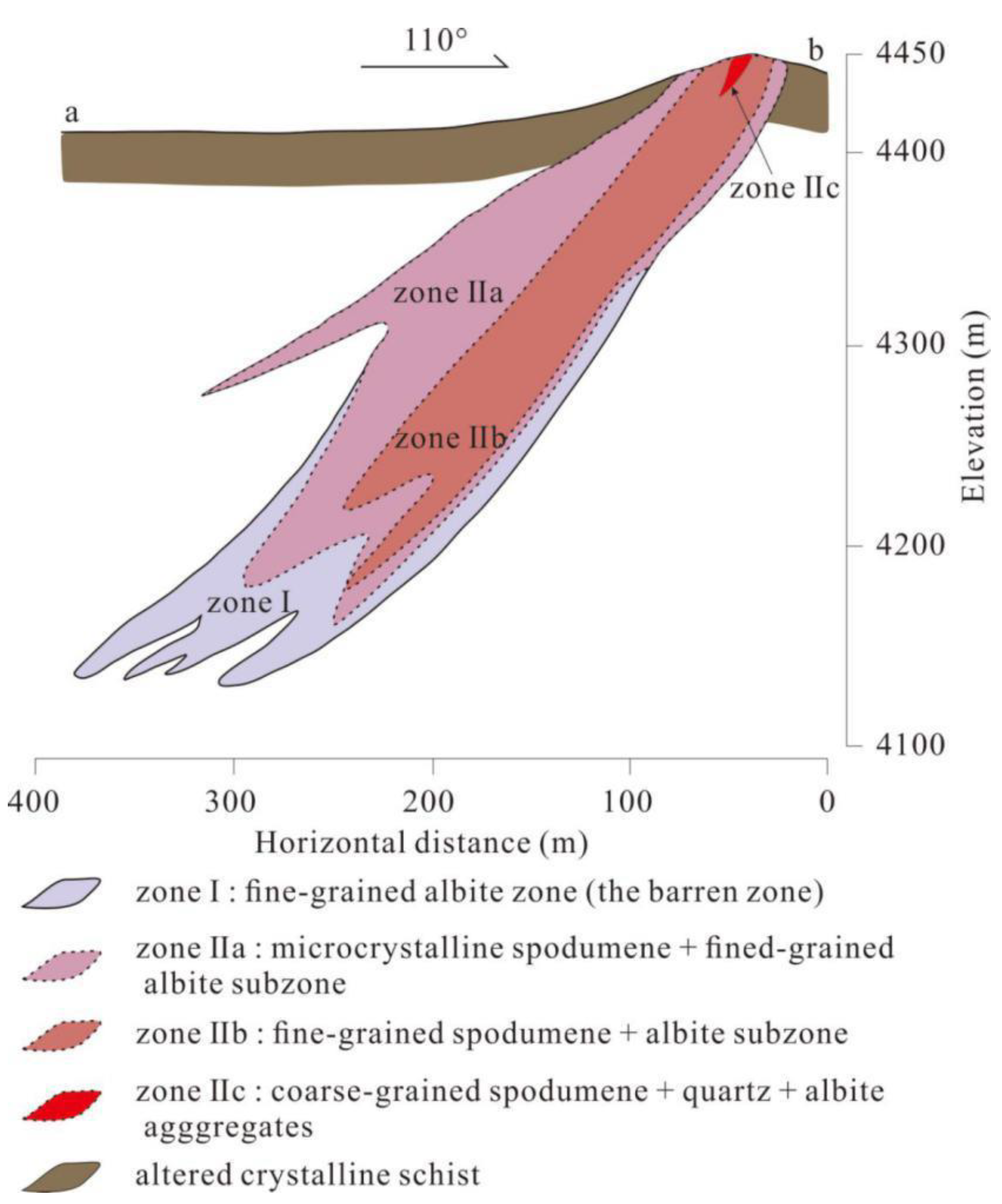
3. Results
3.1. Petrographic Characteristics of the No. 134 Pegmatite
3.1.1. Zone I (The Barren Zone: Fine-Grained Quartz–Albite Zone)
3.1.2. Zone IIa: Microcrystalline Spodumene + Fine-Grained Albite Subzone
3.1.3. Zone IIb: Medium- to Fine-Grained Spodumene + Albite Subzone
3.1.4. Zone IIc: Coarse-Grained Spodumene + Quartz + Albite Aggregates
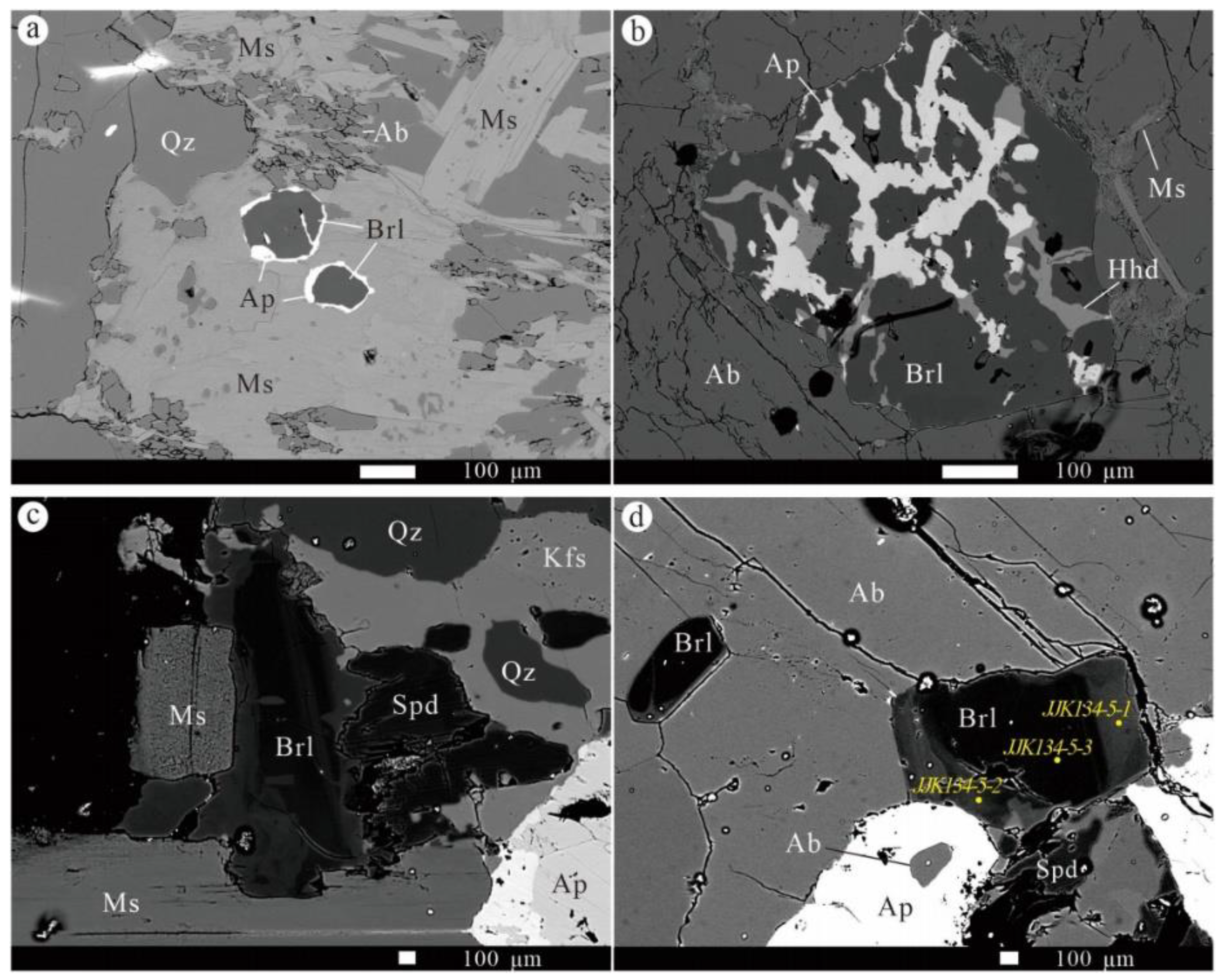
3.2. Mineralogical Characteristics of the No. 134 Pegmatite
3.2.1. Spodumene
3.2.2. Other Lithium Minerals
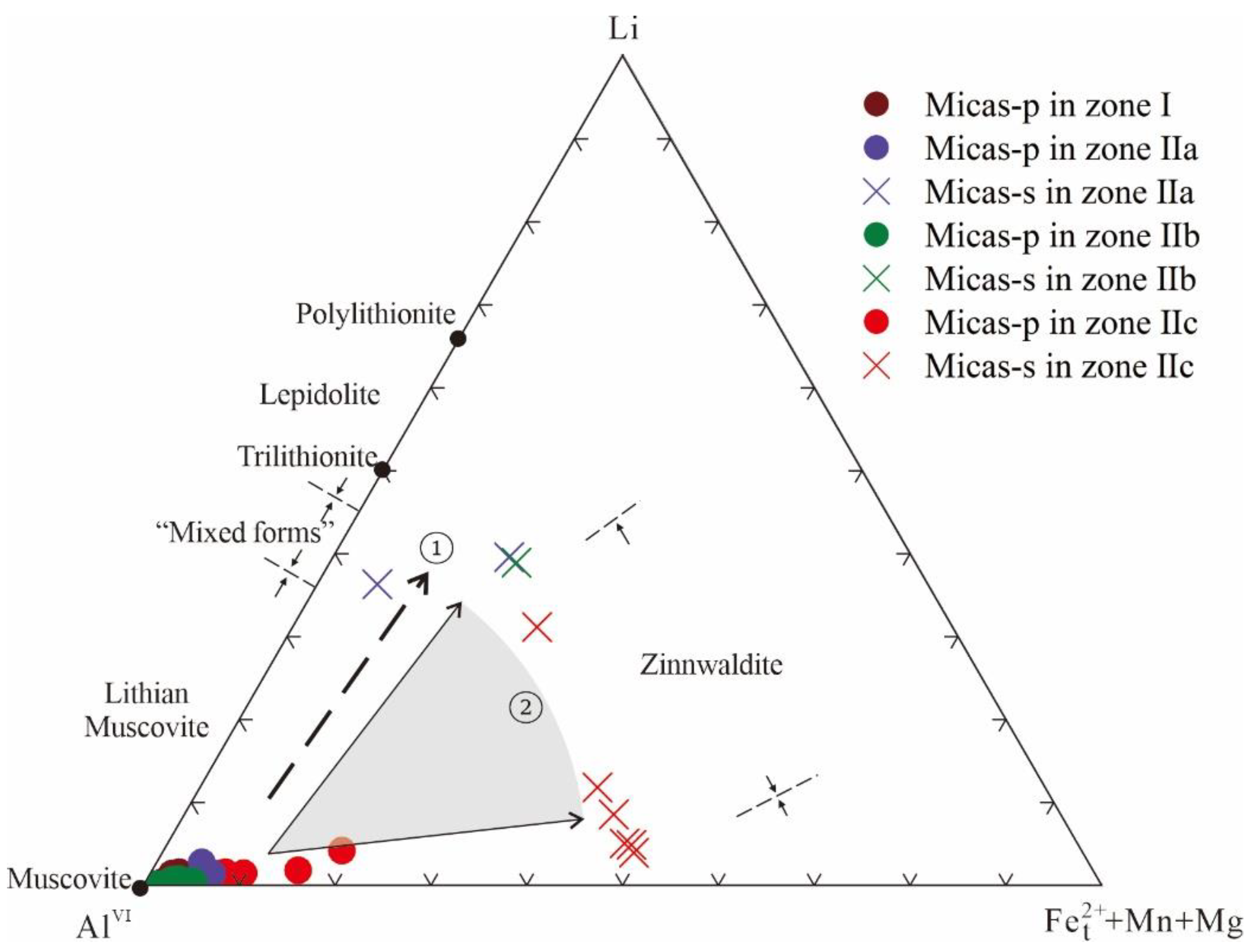
3.2.3. Micas
3.2.4. Beryl
4. Discussion
4.1. Li-Saturated Pegmatite-Forming Melt
4.2. Evolution of the Jiajika No. 134 Pegmatite
4.2.1. Magmatic–Hydrothermal Evolution
4.2.2. P-T Conditions

4.3. Effect of Undercooling on Rock Texture
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Černý, P.; Simpson, F.M. The Tanco Pegmatite at Bernic Lake, Manitoba: X, Pollucite. Can. Miner. 1978, 16, 325–333. [Google Scholar]
- Stilling, A.; Cerny, P.; Vanstone, P.J. The Tanco pegmatite at Bernic Lake, Manitoba. XVI. Zonal and bulk compositions and their petrogenetic significance. Can. Miner. 2006, 44, 599–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lichtervelde, M.; Linnen, R.L.; Salvi, S.; Beziat, D. The role of metagabbro rafts on tantalium mineralization in the Tanco granitic pegmatite, Manitoba. Can. Miner. 2006, 44, 625–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lichtervelde, M.; Salvi, S.; Béziat, D.; Linnen, R.L. Textural Features and Chemical Evolution in Tantalum Oxides: Magmatic Versus Hydrothermal Origins for Ta Mineralization in the Tanco Lower Pegmatite, Manitoba, Canada. Econ. Geol. 2007, 102, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Che, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, H. Geochemical evolution and late re-equilibration of NaCs-rich beryl from the Koktokay #3 pegmatite (Altai, NW China). Eur. J. Miner. 2009, 21, 795–809. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Wang, R.; Hu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X. Chemical evolution of Nb-Ta oxides and zircon from the Koktokay No. 3 granitic pegmatite, Altai, northwestern China. Miner. Mag. 2004, 68, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Qin, K.; Tang, D.; Wang, C.; Tian, Y.; Sakyi, P.A. Mineralogy of the Koktokay No. 3 pegmatite, Altai, NW China: Implications for evolution and melt-fluid processes of rare-metal pegmatites. Eur. J. Miner. 2015, 27, 433–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontak, D.J.; Kyser, T.K. Nature and origin of an LCT-suite pegmatite with late-stage sodium enrichment, Brazil Lake, Yarmouth County, Nova Scotia. II. Implications of stable isotopes (δ18O, δD) for magma source, internal crystallization and nature of sodium matasomatism. Can. Miner. 2009, 47, 745–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, S.E. Mineralogy of spodumene pegmatites and related rocks in the tin–spodumene belt of north Carolina and south Carolina, USA. Can. Miner. 2012, 50, 1589–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, R.; Menuge, J.F. The Origin of Spodumene Pegmatites Associated With the Leinster Granite In Southeast Ireland. Can. Miner. 2016, 54, 847–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaeter, D.; Barros, R.; Menuge, J.F.; Chew, D.M. The magmatic–hydrothermal transition in rare-element pegmatites from southeast Ireland: LA-ICP-MS chemical mapping of muscovite and columbite–tantalite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 240, 98–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, R.; Keater, D.; Menuge, J.F.; Škoda, R. Controls on chemical evolution and rare element enrichment in crystallising al-bite-spodumene pegmatite and wallrocks: Constraints from mineral chemistry. Lithos 2020, 352, 105289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černý, P. Characteristics of Pegmatite Deposits of Tantalum. Lanthan. Tantalum Niobium 1989, 7, 195–239. [Google Scholar]
- Černý, P.; Ercit, T.S. The classification of granitic pegmatites revisited. Can. Miner. 2005, 43, 2005–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.K.; Chou, I.-M.; Yuan, S.; Burruss, R.C. Observations on the crystallization of spodumene from aqueous solutions in a hy-drothermal diamond-anvil cell. Geofluids 2013, 13, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.F.; Fu, X.F.; Liang, B.; Yuan, L.P.; Pan, M.; Tang, Y. Formation ages of granite and X03 pegmatite vein in Jiajika, western Sichuan, and their geological significance. Miner. Depos. 2015, 34, 1199–1208, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.F.; Wu, S.X. Geological study of Jiajika granite-pegmatite lithium deposit in Kangding, Sichuan. Restricted Data 1984. (In Chinese without English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.K.; Chou, I.-M. An occurrence of metastable cristobalite in spodumene-hosted crystal-rich inclusions from Jiajika pegmatite deposit, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 171, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.H.; Li, J.K.; Fu, X.F. 40Ar/39Ar dating for the Jiajika pegmatite-type rare metal deposit in western Sichuan and its significance. Geochemica 2005, 34, 541–547. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.H.; Liu, S.B.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C.H.; Sun, Y.; Dai, H.Z.; Li, J.K.; Dai, J.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhao, T.; et al. Exploration progress and development suggestion for the large-scale mining base of strategic critical mineral resources in western Sichuan. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 98, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.H.; Fu, X.F. Breakthrough in lithium ore prospecting in the periphery of the Jiajika deposit, Sichuan. Rock Miner. Anal. 2013, 32, 987, (In Chinese without English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.J.; Fu, X.F.; Wang, D.H.; Hao, X.F.; Yuan, L.P.; Pan, M. Geological characteristics and metallogeny of Jiajika-style rare metal deposits. Miner. Depos. 2015, 34, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.K.; Chou, I.M. Homogenization Experiments of Crystal-Rich Inclusions in Spodumene from Jiajika Lithium Deposit, China, under Elevated External Pressures in a Hydrothermal Diamond-Anvil Cell. Geofluids 2017, 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnis, A. Mineral Replacement Reactions. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2009, 70, 87–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnis, A.; Austrheim, H. Fluid-induced processes: Metasomatism and metamorphism. Geofluids 2010, 10, 254–269. [Google Scholar]
- Bobos, I.; Vieillard, P.; Charoy, B.; Noronha, F.; Bobos-Radu, I. Alteration of spodumene to cookeite and its pressure and temperature stability conditions in Li-bearing aplite-pegmatites from northern Portugal. Clays Clay Miner. 2007, 55, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Huang, X.-L.; Xu, Y.-G.; Wang, R.-C.; Wang, H.; Yuan, C.; Ma, Q.; Sun, X.-M.; Chen, L.-L. Mineralogical constraints on the magmatic–hydrothermal evolution of rare-elements deposits in the Bailongshan granitic pegmatites, Xinjiang, NW China. Lithos 2020, 352, 105208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, D.; Burt, D.M. Alteration of spodumene, montebrasite and lithiophilite in pegmatites of the White Picacho District, Arizona. Am. Miner. 1982, 67, 97–113. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, P.; Fontan, F.; Fransolet, A.M. Intercrystalline cation partitioning between minerals of the trip-lite-zwieselite-magniotriplite and the triphylite-lithiophilite series in granitic pegmatites. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 1994, 118, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigley, J.E.; Brown, G.E. Lithiophilite formation in granitic pegmatites: A reconnaissance experimental study of phosphate crystallization from hydrous aluminosilicate melts. Am. Miner. 1986, 71, 356–366. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, C.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Hatert, F.; Xia, Q.; Yue, X.; Wang, W. Insights into post-magmatic metasomatism and Li circulation in granitic systems from phosphate minerals of the Nanping No. 31 pegmatite (SE China). Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 91, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.; Wang, R.; Hu, H. Electron-Microprobe Compositions and Genesis of Beryls from the Nanping No. 31 Granitic Peg-matite (Fujian Province, Southeastern China). Geol. J. China Univ. 2009, 15, 496–505. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, D.B. Petrogenesis of lithium-rich pegmatites. Am. Miner. 1978, 63, 970–980. [Google Scholar]
- London, D.; Morgan, G.B. The Pegmatite Puzzle. Elements 2012, 8, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.L. Confusion by design. Nat. Cell Biol. 1993, 366, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabelek, P.I.; Whittington, A.G.; Sirbescu, M.-L.C. The role of H2O in rapid emplacement and crystallization of granite pegmatites: Resolving the paradox of large crystals in highly undercooled melts. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 2010, 160, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneta, V.; Baker, D.R.; Minarik, W. Evidence for lithium-aluminosilicate supersaturation of pegmatite-forming melts. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 2015, 170, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeister, A.M.; Whittington, A.G.; Pertermann, M. Transport properties of high albite crystals, near-endmember feldspar and pyroxene glasses, and their melts to high temperature. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 2009, 158, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.R. The escape of pegmatite dikes from granitic plutons: Constraints from new models of viscosity and dike propagation. Can. Miner. 1998, 36, 255–263. [Google Scholar]
- Maneta, V.; Baker, D.R. Exploring the effect of lithium on pegmatitic textures: An experimental study. Am. Miner. 2014, 99, 1383–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliff, B.L.; Papike, J.J.; Shearer, C.K. Fractionation trends in mica and tourmaline as indicators of pegmatite internal evolution: Bob Ingersoll pegmatite, Black Hills, South Dakota. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliff, B.L.; Papike, J.J.; Shearer, C.K. Petrogenetic relationships between pegmatite and granite based on geochemistry of muscovite in pegmatite wall zones, Black Hills, South Dakota, USA. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 1915–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foord, E.E.; Černý, P.; Jackson, L.L.; Sherman, D.M.; Eby, R.K. Mineralogical and geochemical evolution of micas from miarolitic pegmatites of the anorogenic pikes peak batholith, Colorado. Miner. Pet. 1995, 55, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesquera, A.; Torres-Ruiz, J.; Gil-Crespo, P.P.; Velilla, N. Chemistry and genetic implications oftourmaline and Li-F-Cs micas from the Valdeflores area (Cáceres, Spain). Am. Miner. 1999, 84, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R.; Roda-Robles, E.; Pesquera, A.; Lima, A. Chemical variation and significance of micas from the Fregeneda-Almendra pegmatitic field (Central-Iberian Zone, Spain and Portugal). Am. Miner. 2011, 96, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoy, B. Beryllium speciation in evolved granitic magmas: Phosphates versus silicates. Eur. J. Miner. 1999, 11, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černý, P.; Anderson, A.J.; Tomascak, P.B.; Chapman, R. Geochemical and morphological features of beryl from the Bikita gra-nitic pegmatite, Zimbabwe. Can. Miner. 2003, 41, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uher, P.; Chudík, P.; Bačík, P.; Vaculovič, T.; Galliová, M. Beryl composition and evolution trends: An example from granitic pegmatites of the beryl-columbite subtype, Western Carpathians, Slovakia. J. Geosci. 2010, 55, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Neiva, A.M.R. Micas, feldspars and columbite-tantalite minerals from the zoned granitic lepidolite-subtype pegmatite at Namivo, Alto Ligonha, Mozambique. Eur. J. Miner. 2013, 25, 967–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, M.A. Trace element chemistry of lithium-rich micas from rare-element granitic pegmatites. Miner. Pet. 1995, 55, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda-Robles, E.; Pesquera, A.; Gil-Crespo, P.P.; Ruiz, J.T.; de Parseval, P. Mineralogy and geochemistry of micas from the Pinilla de Fermoselle pegmatite (Zamora, Spain). Eur. J. Miner. 2006, 18, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda-Robles, E.; Keller, P.; Pesquera, A.; Fontan, F. Micas of the muscovite–lepidolite series from Karibib pegmatites, Namibia. Miner. Mag. 2007, 71, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kile, D.E.; Foord, E.E. Micas from the pikes peak batholith and its cogenetic granitic pegmatites, Colorado: Optical properties, compostion, and correlation with pegmatite evolution. Can. Miner. 1998, 36, 463–482. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Qin, K.; Tang, D.; Ding, J.; Guo, Z. Mineralogy and significance of micas and feldspars from the Koktokay No. 3 pegmatite rare-element deposit, Altai. Acta Pet. Sin. 2013, 29, 3004–3022, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- London, D. Experimental phase equilibria in the system LiAlSiO4-SiO2-H2O: A petrogenetic grid for lithium-rich pegmatites. Am. Miner. 1984, 69, 995–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Chakoumakos, B.C.; Lumpkin, G.R. Pressure-temperature constraints on the crystallization of the Harding pegmatite, Taos County, New Mexico. Can. Miner. 1990, 28, 287–298. [Google Scholar]
- Černý, P.; Ferguson, R.B. The Tanco pegmatite at Bernic Lake, Manitoba. IV. Petalite and spodumene relations. Can. Miner. 1972, 11, 660–678. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R.J.; Bühamnn, D.; Bullen, W.D.; Scogings, A.J.; Bruin, D.D. Unusual spodumene pegmatites from the Late Kibaran of southern Natal, South Africa. Ore. Geol. Rev. 1994, 9, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoy, B.; Noronha, F.; Lima, A. Spodumene-petalite-eucryptite: Mutual relationships and pattern of alteration in Li-rich aplite-pegmatite dykes from Northern Portugal. Can. Miner. 2001, 39, 729–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, D. Ore-forming processes within granitic pegmatites. Ore. Geol. Rev. 2018, 101, 349–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, H.M.; Knoper, M.W.; Belyanin, G.A.; Safonov, O.G.; Schmidt, C. Petalite postdating spodumene in pegmatite as a consequence of the-2.02 Ga meteorite impact in the Vredefort structure, southern Africa. Lithos 2020, 105760, 376–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X. Ore-Forming Process of Jiajika-Type Granitic Pegmatite Lithium Deposits in Songpan-Garze Orgentic Belt. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- London, D. Internal differentiation of rare-element pegmatites; A synthesis of recent research. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Papers 1990, 246, 35–50. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.K. Mineralizing mechanism and continental geodynamics of typical pegmatite deposits in western Sichuan, China. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Holdaway, M.J. Stability of andalusite and the aluminum silicate phase diagram. Am. J. Sci. 1971, 271, 97–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, W.B.S.; Webber, K.L. Pegmatite genesis: State of the art. Eur. J. Miner. 2008, 20, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, D. A petrologic assessment of internal zonation in granitic pegmatites. Lithos 2014, 184, 74–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofgren, G.E.; Donaldson, C.H. Curved branching crystals and differentiation in comb-layered rocks. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 1975, 49, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.R.; Freda, C. Ising models of undercooled binary system crystallization; Comparison with experimental and pegmatite textures. J. Am. Miner. 1999, 84, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.R.; Freda, C. Eutectic crystallization in the undercooled Orthoclase-Quartz-H2O system: Experiments and simulations. Eur. J. Miner. 2001, 13, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, D. Granitic pegmatites: An assessment of current concepts and directions for the future. Lithos 2005, 80, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, D. The origin of primary textures in granitic pegmatites. Can. Miner. 2009, 47, 697–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, K.L.; Simmons, W.B.; Falster, A.U.; Foord, E.E. Cooling rates and crystallization dynamics of shallow level pegma-tite-aplite dikes, San Diego County, California. Am. Miner. 1999, 84, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenn, P.M. The nucleation and growth of alkali feldspars from hydrous melts. Can. Miner. 1977, 15, 135–161. [Google Scholar]
- Lofgren, G. An experimental study of plagioclase crystal morphology; Isothermal crystallization. Am. J. Sci. 1974, 274, 243–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirbescu, M.-L.C.; Hartwick, E.E.; Student, J.J. Rapid crystallization of the Animikie Red Ace Pegmatite, Florence County, northeastern Wisconsin: Inclusion microthermometry and conductive-cooling modeling. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 2008, 156, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirbescu, M.-L.C.; Leatherman, M.A.; Student, J.J.; Beehr, A.R. Apatite textures and compositions as records of crystallization processes in the Animikie Red Ace pegmatite dike, Wisconsin, USA. Can. Miner. 2009, 47, 725–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.B.; London, D. Crystallization of the Little Three layered pegmatite-aplite dike, Ramona District, California. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 1999, 136, 310–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.K. Research developments of crystallization dynamics for pegmatite texture. Front. Earth. Sci. 2012, 19, 165–172, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Manning, D.A.C. The effect of fluorine on liquidus phase relationships in the system Qz-Ab-Or with excess water at 1 kb. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 1981, 76, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, D.; Morgan, G.B.; Hervig, R.L. Vapor-undersaturated experiments with Macusani glass+H2O at 200 MPa, and the internal differentiation of granitic pegmatites. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 1989, 102, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, D.; Morgan, G.B.; Babb, H.A.; Loomis, J.L. Behavior and effects of phosphorus in the system Na2O-K2O-Al2O3-SiO2-P2O5-H2O at 200 MPa (H2O). Contrib. Miner. Pet. 1993, 113, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, D. Estimating Abundances of Volatile and Other Mobile Components in Evolved Silicic Melts Through Mineral-Melt Equilibria. J. Pet. 1997, 38, 1691–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.B.; Acosta-Vigil, A.; London, D. Diffusive equilibration between hydrous metaluminous-peraluminous haplogranite liquid couples at 200 MPa (H2O) and alkali transport in granitic liquids. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 2008, 155, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-S.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.-G.; Cempírek, J.; Wang, H.; Ma, J.-L.; Wei, G.-J.; Huang, T.-Y.; Zhu, G.-H.; Zhang, L. Geochronology, petrology, and lithium isotope geochemistry of the Bailongshan granite-pegmatite system, northern Tibet: Implications for the ore-forming potential of pegmatites. Chem. Geol. 2021, 584, 120484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, D. Holmquistite as a guide to pegmatitic rare metal deposits. Econ. Geol. 1986, 81, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnen, R.L.; van Lichtervelde, M.; Černý, P. Granitic Pegmatites as Sources of Strategic Metals. Elements 2012, 8, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černý, P.; Meintzer, R.E.; Anderson, A.J. Extreme fractionation in rare-element granitic pegmatites: Selected examples of data and mechanisms. Can. Miner. 1985, 23, 381–421. [Google Scholar]



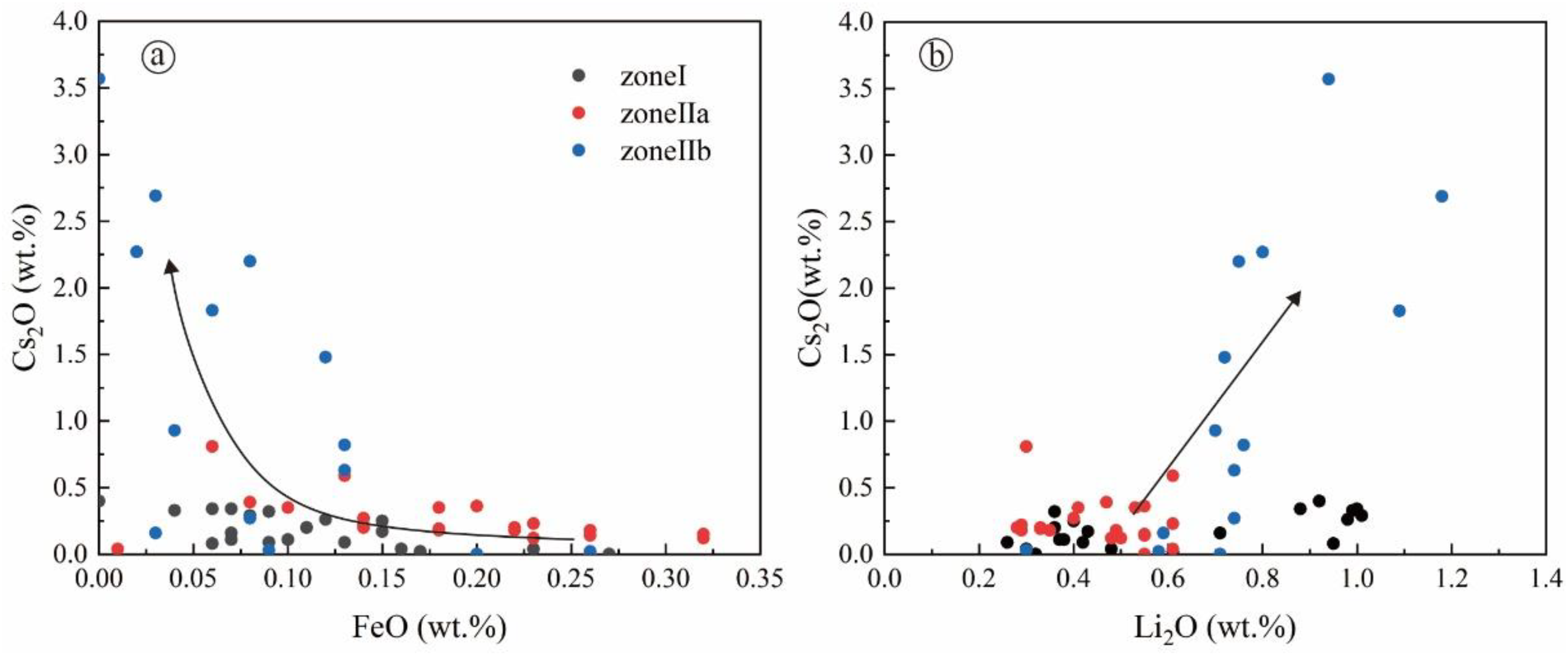
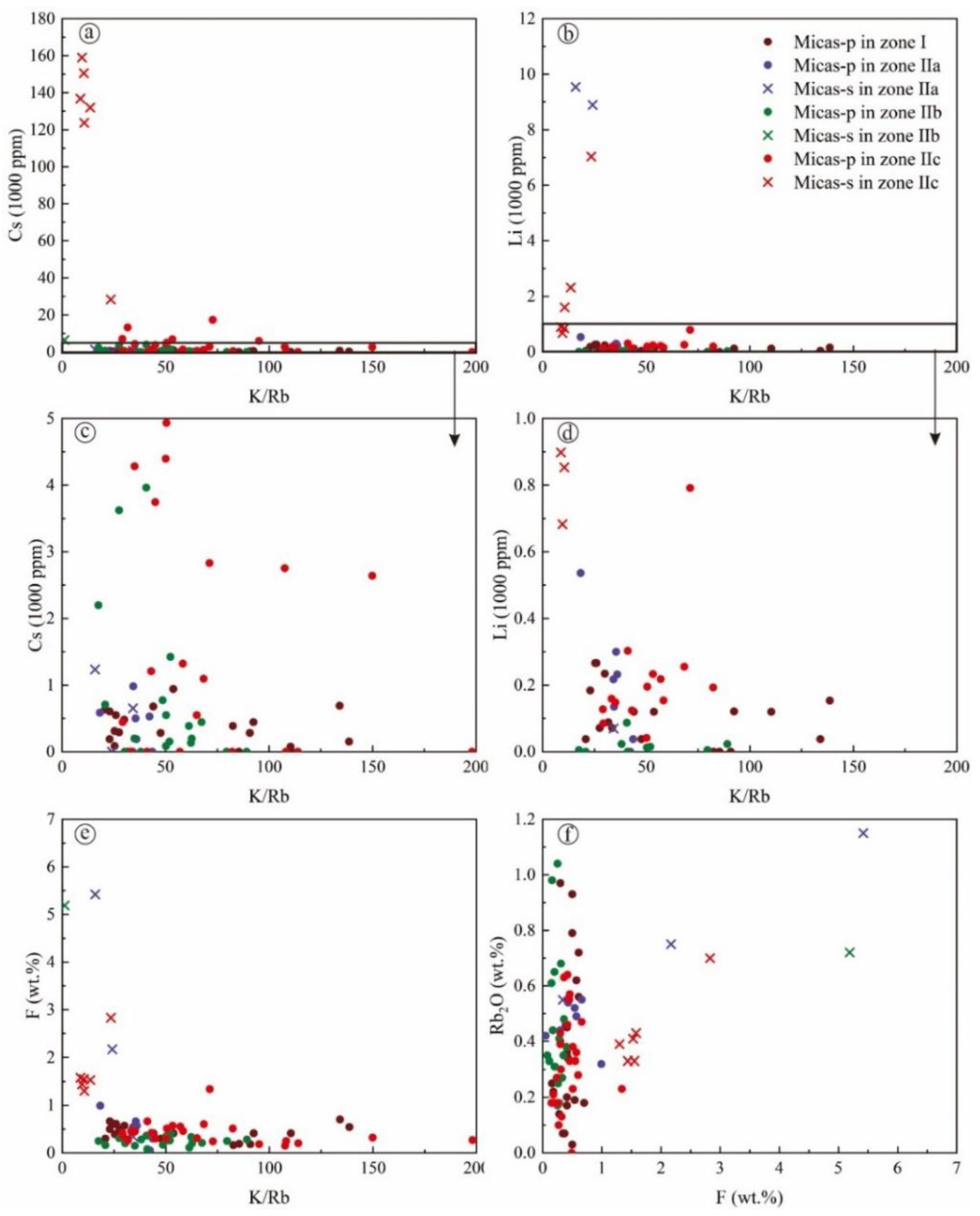

| Lithological Zones | Zone I | Zone IIa | Zone IIb | Zone IIc | Magmatic→Hydrothermal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K-feldspar | 2 | 30 | 10 | + |  | |||
| albite | 50 | 7–15 | 35 | 20 |  | |||
| quartz | 10–30 | 10–25 | 18 | 25 |  | |||
| muscovite | 10–20 | 5–20 | 10 | 10 |  | |||
| spodumene | 25 | 20 | 40 |  |  | |||
| beryl | ++ | + |  | |||||
| hydroxylherderite | + |  | ||||||
| CGM | + | + | + | + |  | |||
| lithiophilite | + | + |  | |||||
| lepidolite | + | + | + |  | ||||
| apatite | ++ | ++ | ++ | + |  | |||
| fairfieldite | + | + |  | |||||
| rhodochrosite | + | + |  | |||||
| cookeite | ++ | ++ | + |  | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Yan, Q.; Xiong, X.; Li, P.; Deng, J. Evolution and Li Mineralization of the No. 134 Pegmatite in the Jiajika Rare-Metal Deposit, Western Sichuan, China: Constrains from Critical Minerals. Minerals 2022, 12, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12010045
Wang Z, Li J, Chen Z, Yan Q, Xiong X, Li P, Deng J. Evolution and Li Mineralization of the No. 134 Pegmatite in the Jiajika Rare-Metal Deposit, Western Sichuan, China: Constrains from Critical Minerals. Minerals. 2022; 12(1):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12010045
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhen, Jiankang Li, Zhenyu Chen, Qinggao Yan, Xin Xiong, Peng Li, and Jingyi Deng. 2022. "Evolution and Li Mineralization of the No. 134 Pegmatite in the Jiajika Rare-Metal Deposit, Western Sichuan, China: Constrains from Critical Minerals" Minerals 12, no. 1: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12010045
APA StyleWang, Z., Li, J., Chen, Z., Yan, Q., Xiong, X., Li, P., & Deng, J. (2022). Evolution and Li Mineralization of the No. 134 Pegmatite in the Jiajika Rare-Metal Deposit, Western Sichuan, China: Constrains from Critical Minerals. Minerals, 12(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12010045