Temporal–Spatial Separation of Cu from Mo in the Jiama Porphyry Copper–Polymetallic Deposit, Southern Tibet, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
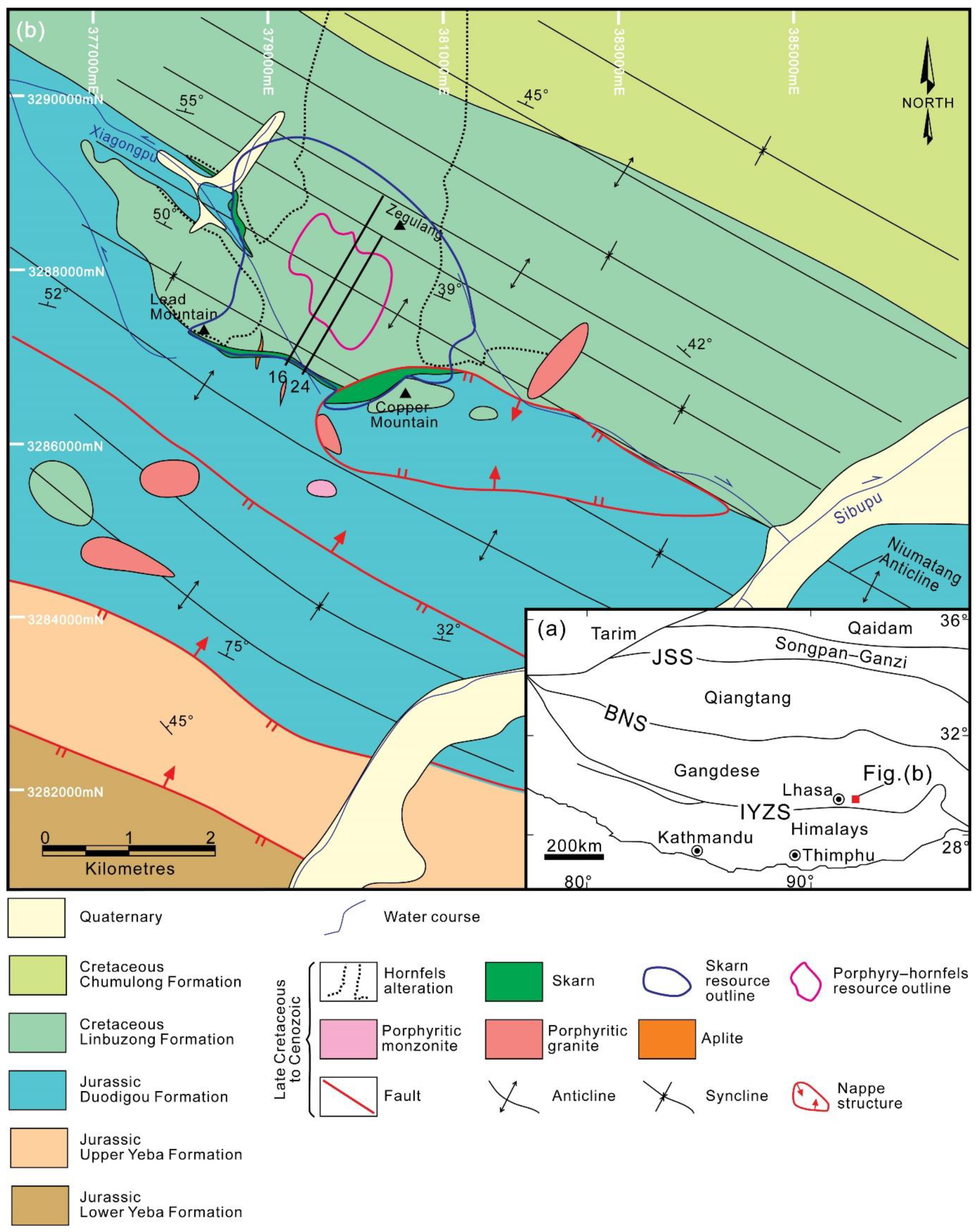
2. Geological Setting and Ore Deposit Geology
3. Relationship between Cu and Mo Mineralization at the Contact between the Jiama Porphyry and Hornfels
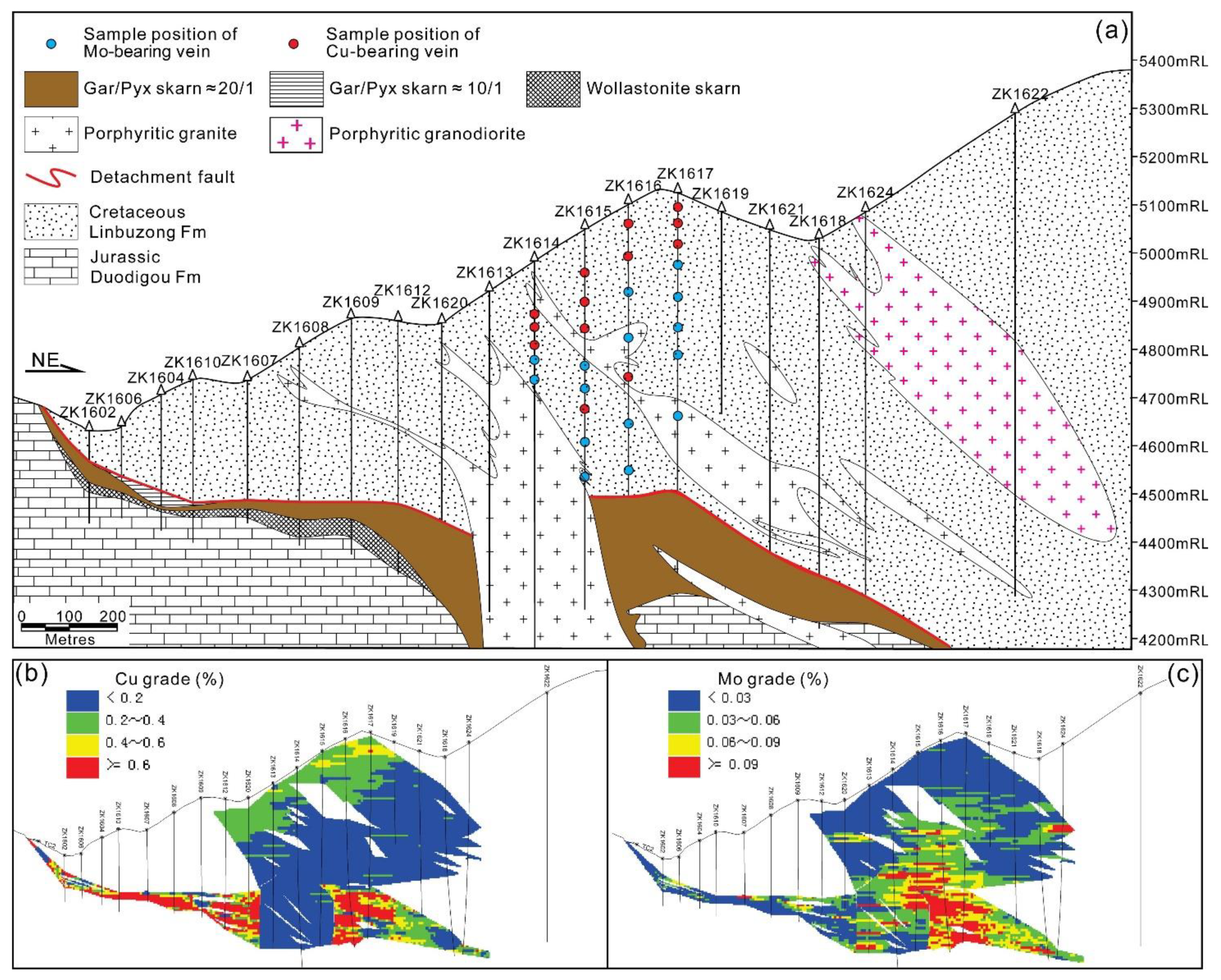
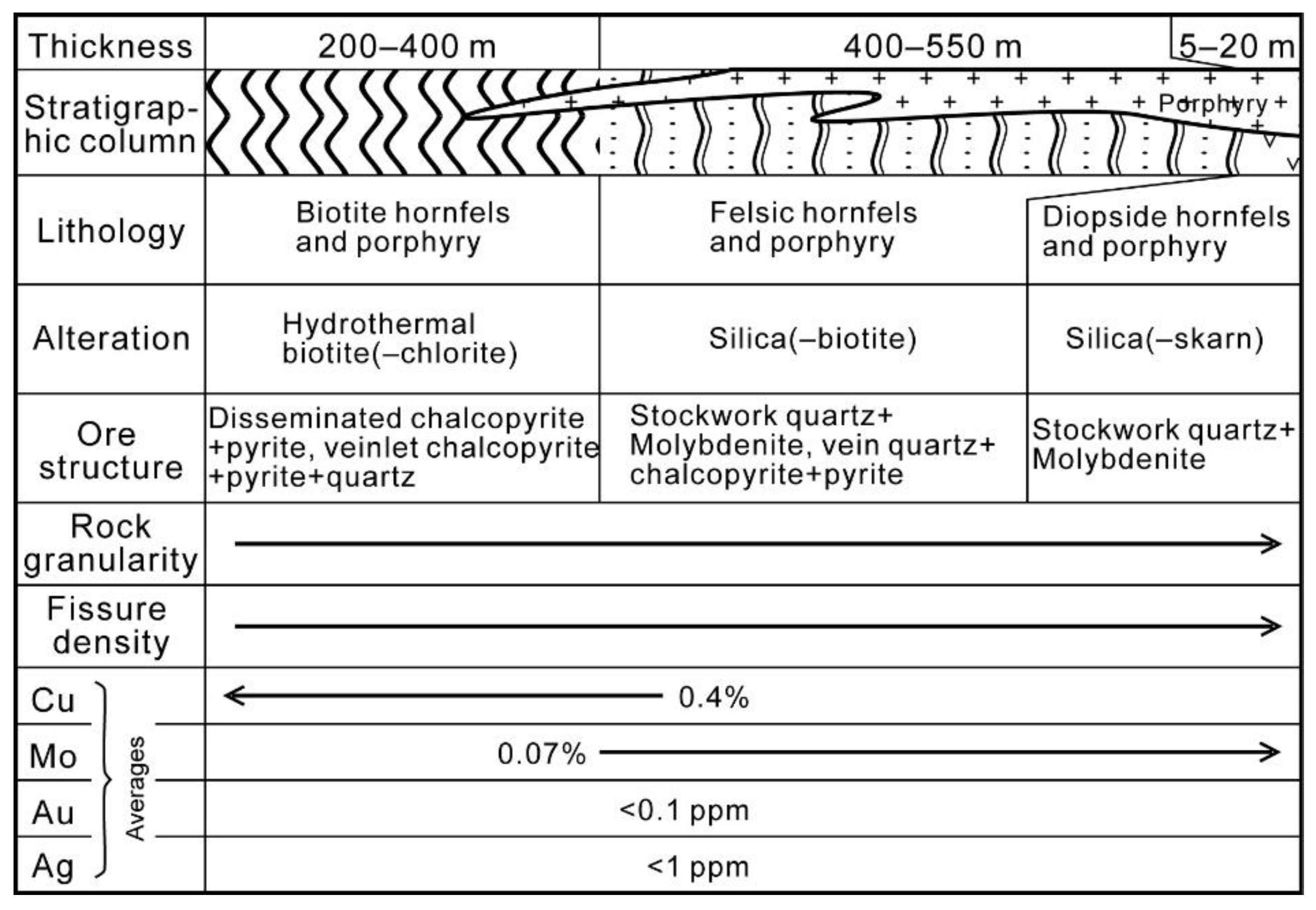
3.1. Spatial Relationships
3.2. Temporal Relationships
3.2.1. Characteristics of the Cu Stages
3.2.2. Characteristics of the Mo Stages
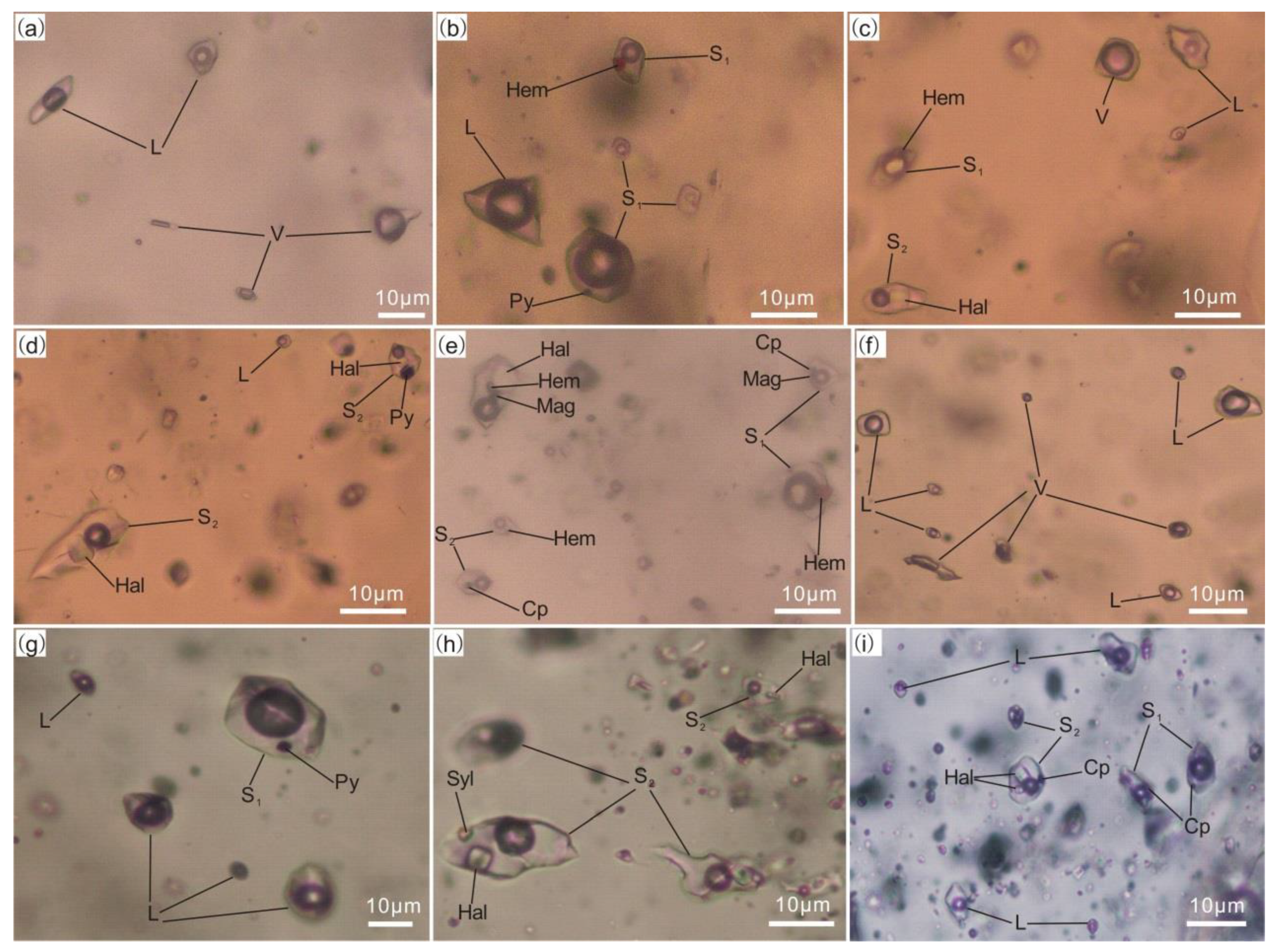
4. Fluid Inclusions Study
4.1. Sample Selection
4.2. Analytical Methods
4.2.1. Petrography and Microthermometry
4.2.2. Laser Micro-Raman Spectra Analyses
4.2.3. SR–XRF Analyses
4.3. Analytical Results
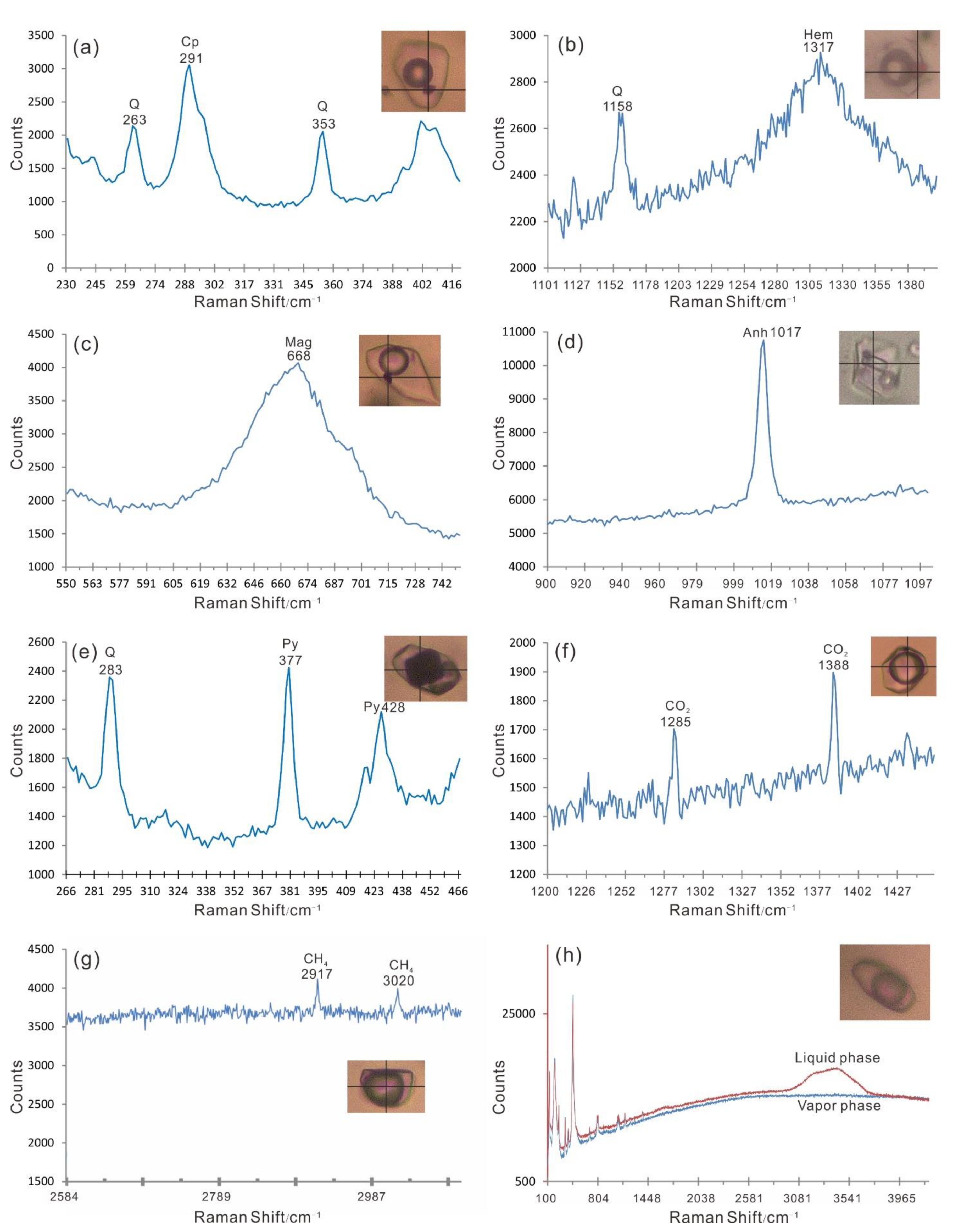
4.3.1. Petrography and Microthermometry
4.3.2. Laser Micro-Raman Spectra
4.3.3. SR–XRF Mapping
5. Discussion
5.1. Magmatic Metal Fractionation and Magma Evolution
5.2. P–T Conditions and Phase Separation
5.3. Transport and Precipitation of Metals
5.4. Influence of Wall-Rock Permeability on Metal Transport
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, J.; Tang, J.; Mason, R.; Zheng, W.; Ying, L. Zircon U-Pb Age and Deformation Characteristics of the Jiama Porphyry Copper Deposit, Tibet: Implications for Relationships between Mineralization, Structure and Alteration. Resour. Geol. 2014, 64, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Thoms, C.; Tang, J.X.; Tong, Q.X. Mapping white mica alteration associated with the Jiama porphyry-skarn Cu de-posit, central Tibet using field SWIR spectrometry. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 108, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-R.; Guo, N.; Tang, J.-X.; Shi, W.-X.; Ran, F.-Q. Garnet Characteristics Associated with Jiama Porphyry-Skarn Cu Deposit 1# Skarn Orebody, Tibet, Using Thermal Infrared Spectroscopy. Minerals 2020, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.X.; Wang, D.H.; Wang, X.W.; Zhong, K.H.; Ying, L.J.; Zheng, W.B.; Li, F.J.; Guo, N.; Qin, Z.P.; Yao, X.F.; et al. Geological features and metallogenic model of the Jiama copper–polymetallic deposit in Tibet. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2010, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, L.J.; Wang, D.H.; Tang, J.X.; Chang, Z.S.; Qu, W.J.; Zheng, W.B.; Wang, H. Re2O3 dating of molybdenite from the Jiama copper polymetallic deposit in Tibet and its metallogenic significance. Acta Geol. Sin. 2010, 84, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, L.; Wang, C.; Tang, J.; Wang, D.; Qu, W.; Li, C. Re–Os systematics of sulfides (chalcopyrite, bornite, pyrite and pyrrhotite) from the Jiama Cu–Mo deposit of Tibet, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 79, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Lin, B.; Zheng, W.B.; Song, Y.; Tang, P.; Zhang, Z.B.; Gao, X. The characteristics of alteration and mineralization and geochronology of ore-bearing porphyry in south pit of Jiama copper-polymetallic deposit, Tibet. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 953–967. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.B.; Tang, J.X.; Chang, Z.S.; Li, F.J.; Yao, X.F. Geological and geochemical characteristics and genesis of the Jiama polymetallic copper deposit in Tibet. Geol. Explor. 2010, 46, 985–992. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.B.; Chen, Y.C.; Tang, J.X.; Chang, Z.S.; Wang, X.W.; Ying, L.J.; Li, F.J.; Wang, H.; Tang, X.Q. Discovery of the tubu-lar ore body in Jiama ore district, Tibet and its geological significance. Miner. Depos. 2011, 30, 207–218. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.B.; Tang, J.X.; Zhong, K.H.; Ying, L.J.; Leng, Q.F.; Ding, S.; Lin, B. Geology of the Jiama porphyry cop-per-polymetallic system, Lhasa Region, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 74, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.H.; Li, L.; Zhou, H.W.; Bai, J.G.; Li, W.; Zhong, W.T.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Lan, J.Q.; Zheng, F.S.; Huang, X.Y.; et al. Features of Jiama–Kajunguo thrust–gliding nappe tectonic system in Tibet. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2012, 33, 411–423. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.W.; Tang, J.X.; Qin, Z.P.; Peng, H.J.; Li, A.G.; Yang, K.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.C. Origin and evolution of ore–forming fluids from Jiama copper polymetallic deposit in Tibet. Miner. Depos. 2011, 30, 231–246. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.B.; Chen, Y.C.; Song, X.; Tang, J.X.; Ying, L.J.; Li, F.J.; Tang, X.Q. Element distribution of Jiama copper–polymetallic deposit in Tibet and its geological significance. Miner. Depos. 2010, 29, 775–784. [Google Scholar]
- Susak, N.J.; Crerar, D.A. Factors controlling mineral zoning in hydrothermal ore deposits. Econ. Geol. 1982, 77, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.R.; Gregory, M.J.; Rebagliati, M.C.; Payne, J.G.; Oliver, J.L.; Roberts, K. Geology and magmatic–hydrothermal evolution of the giant Pebble porphyry copper–gold–molybdenum deposit, Southwest Alaska. Econ. Geol. 2013, 108, 437–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sasaki, M. Hydrothermal Alteration and Mineralization of Middle Jurassic Dexing Porphyry Cu-Mo Deposit, Southeast China. Resour. Geol. 2007, 57, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, P.B.; Einaudi, M.T. The Bingham Canyon Porphyry Cu-Mo-Au Deposit. I. Sequence of Intrusions, Vein Formation, and Sulfide Deposition. Econ. Geol. 2010, 105, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Guillong, M.; Heinrich, C.A. Separation of Molybdenum and Copper in Porphyry Deposits: The Roles of Sulfur, Redox, and pH in Ore Mineral Deposition at Bingham Canyon. Econ. Geol. 2012, 107, 333–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Tang, J.X.; Zheng, W.B.; Duan, J.L.; Song, J.L.; Yang, C. Mechanism of metal precipitation in Dabu porphyry Cu-Mo deposit, Quxu Country, Tibet. Miner. Depos. 2015, 34, 81–97. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Zheng, W.B.; Chen, Y.C.; Tang, J.X.; Leng, Q.F.; Tang, P.; Ding, S.; Zhou, Y. Discussion on the mechanism of sep-aration of copper and molybdenum in Jiama porphyry deposit system, Tibet. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2017, 33, 495–514. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Hou, Z.; White, N.C.; Chang, Z.; Li, Z.; Song, Y. Geology of the post-collisional porphyry copper–molybdenum deposit at Qulong, Tibet. Ore Geol. Rev. 2009, 36, 133–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-L.; Chu, M.-F.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Lo, C.-H.; Lee, T.-Y.; Lan, C.-Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Tibetan tectonic evolution inferred from spatial and temporal variations in post-collisional magmatism. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2005, 68, 173–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.L.; Chu, M.F.; Ji, J.Q.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Pearson, N.J.; Liu, D.Y.; Lee, T.Y.; Lo, C.H. The nature and timing of crustal thickening in southern Tibet: Geochemical and zircon Hf isotopic constraints from post-collisional adakites. Tectonophysics 2009, 477, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Cook, N.J. Metallogenesis of the Tibetan collisional orogeny: A review and introduction to the special issue. Ore Geol. Rev. 2009, 36, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Zheng, Y.C.; Yang, Z.M.; Rui, Z.Y.; Zhao, Z.D.; Jiang, S.H.; Qu, X.M.; Sun, Q.Z. Contribution of mantle compo-nents within juvenile lower–crust to collisional zone porphyry Cu systems in Tibet. Miner. Depos. 2013, 48, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Yang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Kemp, A.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Tang, J.; Yang, Z.; Duan, L. A genetic linkage between subduction- and collision-related porphyry Cu deposits in continental collision zones. Geology 2015, 43, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.X.; Hou, Z.Q.; Niu, Y.L.; Dong, G.C.; Qu, X.M.; Zhao, Z.D.; Yang, Z.M. Mantle contributions to crustal thickening dur-ing continental collision: Evidence from Cenozoic igneous rocks in southern Tibet. Lithos 2007, 96, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Wang, L.; Li, R.; Yuan, S.; Ji, W.; Yin, F.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B. Tectonic evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 53, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.X.; Duo, J.; Liu, H.F.; Lang, X.H.; Zhang, J.S.; Zheng, W.B.; Ying, L.J. Minerogenetic series of ore deposit in the east part of the Gangdise Metallogenic Belt. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2012, 33, 393–410. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Richards, J.P.; Hou, Z.; Yang, Z.; Dufrane, S.A. Increased Magmatic Water Content--The Key to Oligo-Miocene Porphyry Cu-Mo Au Formation in the Eastern Gangdese Belt, Tibet. Econ. Geol. 2014, 109, 1315–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Richards, J.P.; Hou, Z.-Q.; Yang, Z.-M.; Gou, Z.-B.; Dufrane, S.A. Increasing Magmatic Oxidation State from Paleocene to Miocene in the Eastern Gangdese Belt, Tibet: Implication for Collision-Related Porphyry Cu-Mo Au Mineralization. Econ. Geol. 2014, 109, 1943–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yang, W.; Ji, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Z. Deep root of a continent–continent collision belt: Evidence from the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling (CCSD) deep borehole in the Sulu ultrahigh-pressure (HP–UHP) metamorphic terrane, China. Tectonophysics 2009, 475, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Harrison, T.M.; Ryerson, F.J.; Wenji, C.; Kidd, W.S.F.; Copeland, P. Tertiary structural evolution of the Gangdese Thrust System, southeastern Tibet. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1994, 99, 18175–18201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Harrison, T.M. Geologic evolution of the Himalyan–Tibetan Orogen. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 211–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.C.; Pan, G.T.; Zhao, Z.D.; Lee, H.Y.; Kang, Z.Q.; Liao, Z.L.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, G.M.; Dong, G.C.; Liu, B. Early Cretaceous subduction–related adakite–like rocks in the Gangdese, south Tibet: Products of slab melting and subsequent melt–peridotite interaction? J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 34, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.C.; Zhao, Z.D.; Niu, Y.L.; Mo, X.X.; Chung, S.L.; Hou, Z.Q.; Wang, L.Q.; Wu, F.Y. The Lhasa Terrane: Record of a mi-crocontinent and its histories of drift and growth. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 301, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.-Q.; Gao, Y.-F.; Qu, X.-M.; Rui, Z.-Y.; Mo, X.-X. Origin of adakitic intrusives generated during mid-Miocene east–west extension in southern Tibet. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 220, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.X.; Zheng, W.B.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, D.H.; Ying, L.J.; Qin, Z.P. The deep porphyry prospecting breakthrough and its significance in the Jiama copper polymetallic deposit, Tibet. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2013, 43, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, C.W. Magmas and hydrothermal fluids. In Geochemistry of Hydrothermal ore Deposits, 2nd ed.; Barnes, H.L., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 71–136. [Google Scholar]
- Furman, T.; Graham, D. Erosion of lithospheric mantle beneath the East African Rift system: Geochemical evidence from the Kivu volcanic province. Lithos 1999, 48, 237–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, P.A.; Holland, H.D. The partitioning of copper and molybdenum between silicate melts and aqueous fluids. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevin, P.L. Redox and compositional parameters for interpreting the granitoid metallogeny of Eastern Australia: Implica-tions for gold–rich ore systems. Resour. Geol. 2004, 54, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.P. Discussion of: The link between reduced porphyry copper deposits and oxidized magmas. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 126, 643–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Huang, R.-F.; Li, H.; Hu, Y.-B.; Zhang, C.-C.; Sun, S.-J.; Zhang, L.-P.; Ding, X.; Li, C.-Y.; Zartman, R.E.; et al. Porphyry deposits and oxidized magmas. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 97–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenstern, J.B. Carbon dioxide in magmas and implications for hydrothermal systems. Miner. Depos. 2001, 36, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, C.A.; Günther, D.; Audétat, A.; Ulrich, T.; Frischknecht, R. Metal fractionation between magmatic brine and vapor, determined by microanalysis of fluid inclusions. Geology 1999, 27, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driesner, T.; Heinrich, C.A. The system H2O–NaCl. Part 1: Correlation formulae for phase relations in temperature–pressure–composition space from 0 to 1000 °C, 0 to 5000 bar, and 0 to 1 XNaCl. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 4880–4901. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, C.A.; Driesner, T.; Stefansson, A.; Seward, T.M. Magmatic vapour contraction and the transport of gold from porphyry to epithermal ore deposits. Geology 2004, 32, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams–Jones, A.E.; Heinrich, C.A. Vapour transport of metals and the formation of magmatic–hydrothermal ore depos-its. Econ. Geol. 2005, 100, 1287–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajacz, Z.; Hanley, J.J.; Heinrich, C.A.; Halter, W.E.; Guillong, M. Diffusive re-equilibration of quartz–hosted silicate melt and fluid inclusions: Are all metal concentrations unmodified? Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 3013–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundy, J.D.; Mavrogenes, J.; Tattitch, B.C.; Sparks, S.; Gilmer, A. Generation of porphyry copper deposits by gas–brine reaction in volcanic arcs. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungall, J.; Brenan, J.M.; Godel, B.; Barnes, S.; Gaillard, F. Transport of metals and sulphur in magmas by flotation of sulphide melt on vapour bubbles. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, L. Introduction to Ore–Forming Processes; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2005; p. 373. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Gammons, C.; Williams-Jones, A. Experimental study of copper(I) chloride complexing in hydrothermal solutions at 40 to 300 °C and saturated water vapor pressure. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 2949–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele–MacInnis, M.; Han, L.; Lowell, R.P.; Rimstidt, J.D.; Bodnar, R.J. The role of fluid phase immiscibility in quartz disso-lution and precipitation in sub–seafloor hydrothermal systems. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 321–322, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, R.O. Conceptual models of brine evolution in magmatic–hydrothermal systems. US Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 1987, 1350, 1487–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Sillitoe, R.H. Porphyry Copper Systems. Econ. Geol. 2010, 105, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.-J.; Zhong, H.; Bai, Z.-J.; Zhang, Z.-K.; Wu, C.-Q. High-sulfidation veins in the Jiama porphyry system, South Tibet. Miner. Depos. 2021, 56, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinert, L.D. Skarn zonation and fluid evolution in the Groundhog Mine, Central mining district, New Mexico. Econ. Geol. 1987, 82, 523–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinert, L.D. Skarns and skarn deposits. Geosci. Can. 1992, 19, 145–162. [Google Scholar]
- Meinert, L.D.; Dipple, G.M.; Nicolescu, S.; Hedenquist, J.W.; Thompson, J.F.H.; Goldfarb, R.J.; Richards, J.P. World Skarn Deposits. One Hundredth Anniv. Vol. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Tang, J.X.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, W.B.; Leng, Q.F.; Zhong, W.T.; Ying, L.J. Preliminary study of fissure system in Jiama porphyry deposit of Tibet and its significance. Miner. Depos. 2012, 31, 579–589. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.P.; Tang, J.X. Rock types and genetic significance of hornfels and location prediction of concealed porphyry bodies in Jiama copper polymetallic deposit, Tibet. Miner. Depos. 2011, 30, 1017–1038. [Google Scholar]



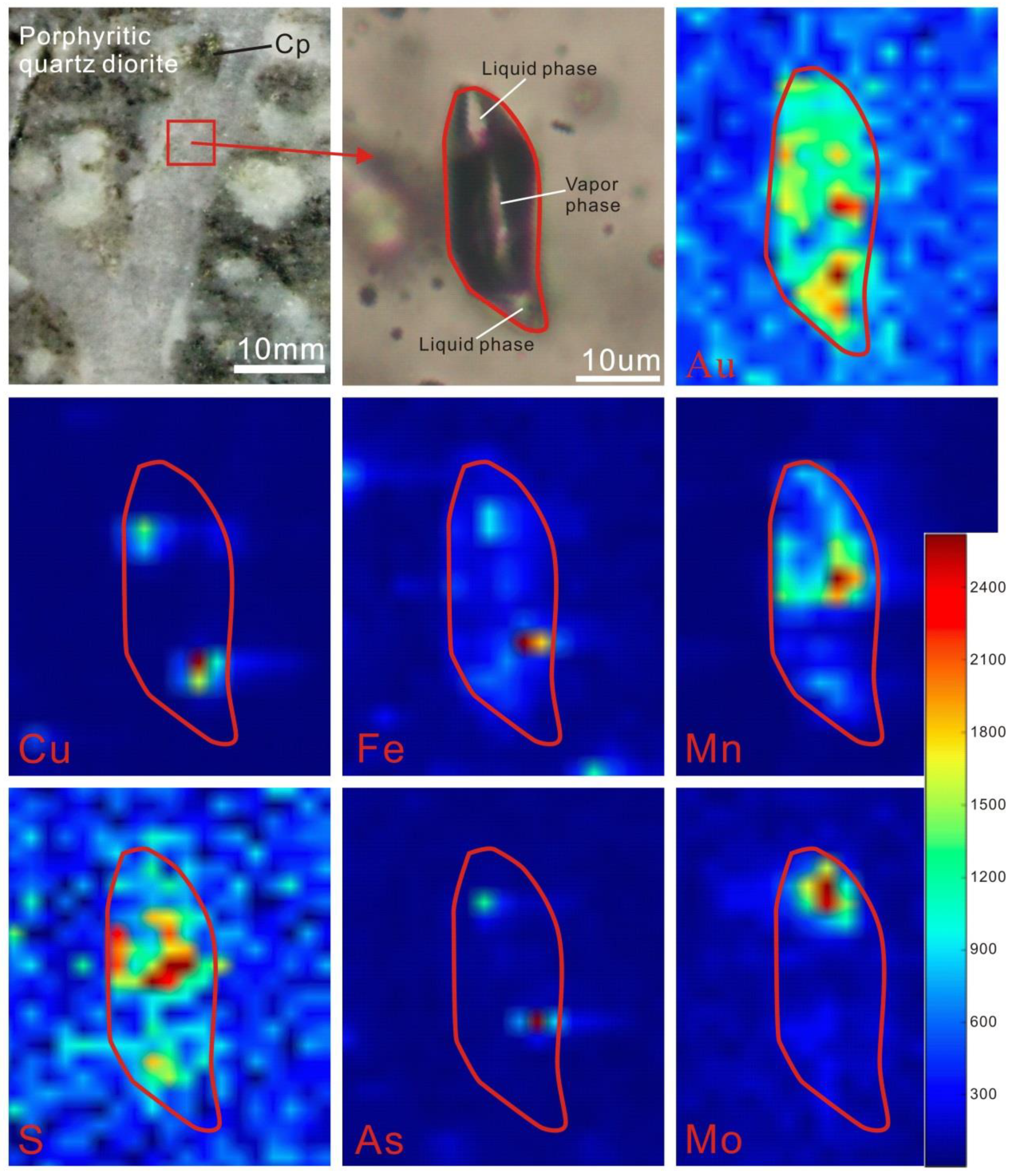

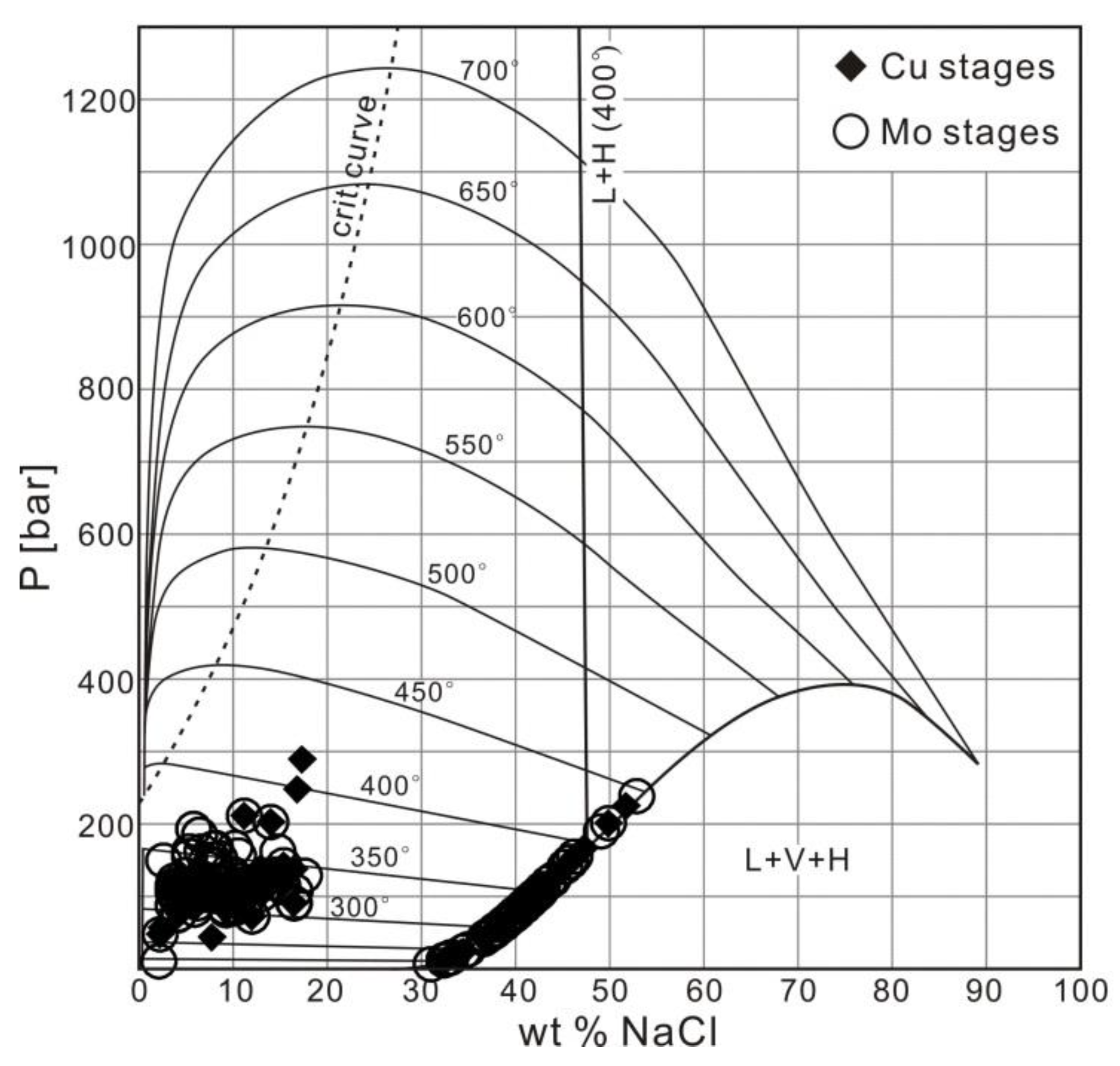
| Fluid Inclusion Type | Homogenization Temperature Range (°C) | Pressure Range (bar) | Salinity Range (NaCl Equiv.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-bearing quartz veins | |||
| L-type | 229°–478° | 43–292 | 1.2–16.4% |
| V-type | 328°–415° | 82–195 | 4.3–9.5% |
| S1-type | 317°–451° | 72–250 | 5.9–16% |
| S2-type | 198°–436° | 11–227 | 31.7–51.3% |
| Mo-bearing quartz veins | |||
| L-type | 189°–427° | 9–213 | 1.1–16.7% |
| V-type | 328°–415° | 82–195 | 1.6–9.2% |
| S1-type | 317°–387° | 72–153 | 3.1–15.7% |
| S2-type | 163°–445° | 5–241 | 30.3–52.4% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, W.; Wang, Y. Temporal–Spatial Separation of Cu from Mo in the Jiama Porphyry Copper–Polymetallic Deposit, Southern Tibet, China. Minerals 2021, 11, 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060609
Zheng W, Wang Y. Temporal–Spatial Separation of Cu from Mo in the Jiama Porphyry Copper–Polymetallic Deposit, Southern Tibet, China. Minerals. 2021; 11(6):609. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060609
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Wenbao, and Yiyun Wang. 2021. "Temporal–Spatial Separation of Cu from Mo in the Jiama Porphyry Copper–Polymetallic Deposit, Southern Tibet, China" Minerals 11, no. 6: 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060609
APA StyleZheng, W., & Wang, Y. (2021). Temporal–Spatial Separation of Cu from Mo in the Jiama Porphyry Copper–Polymetallic Deposit, Southern Tibet, China. Minerals, 11(6), 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060609






