Challenges Related to the Processing of Fines in the Recovery of Platinum Group Minerals (PGMs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
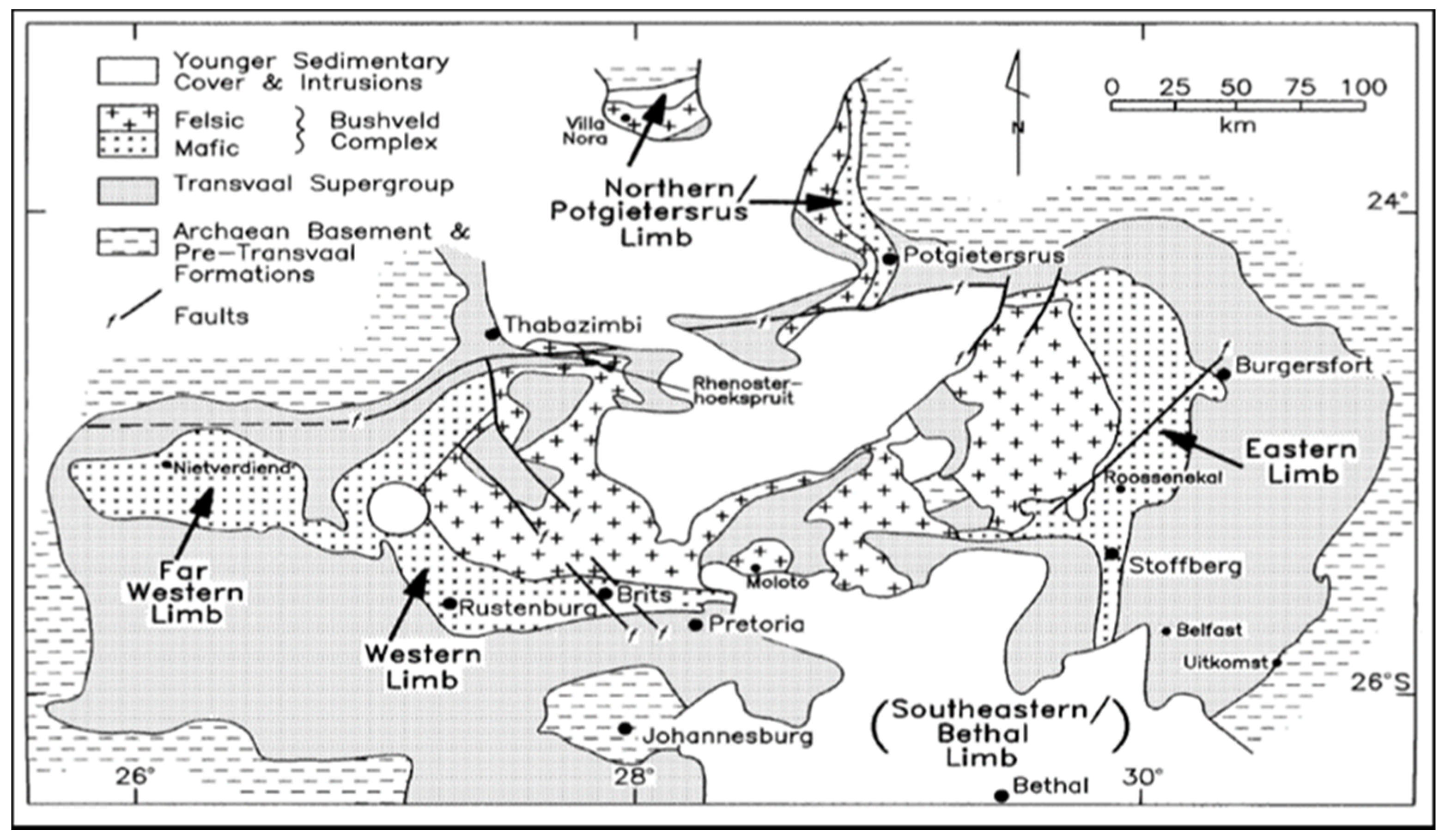
2. Mineralogy
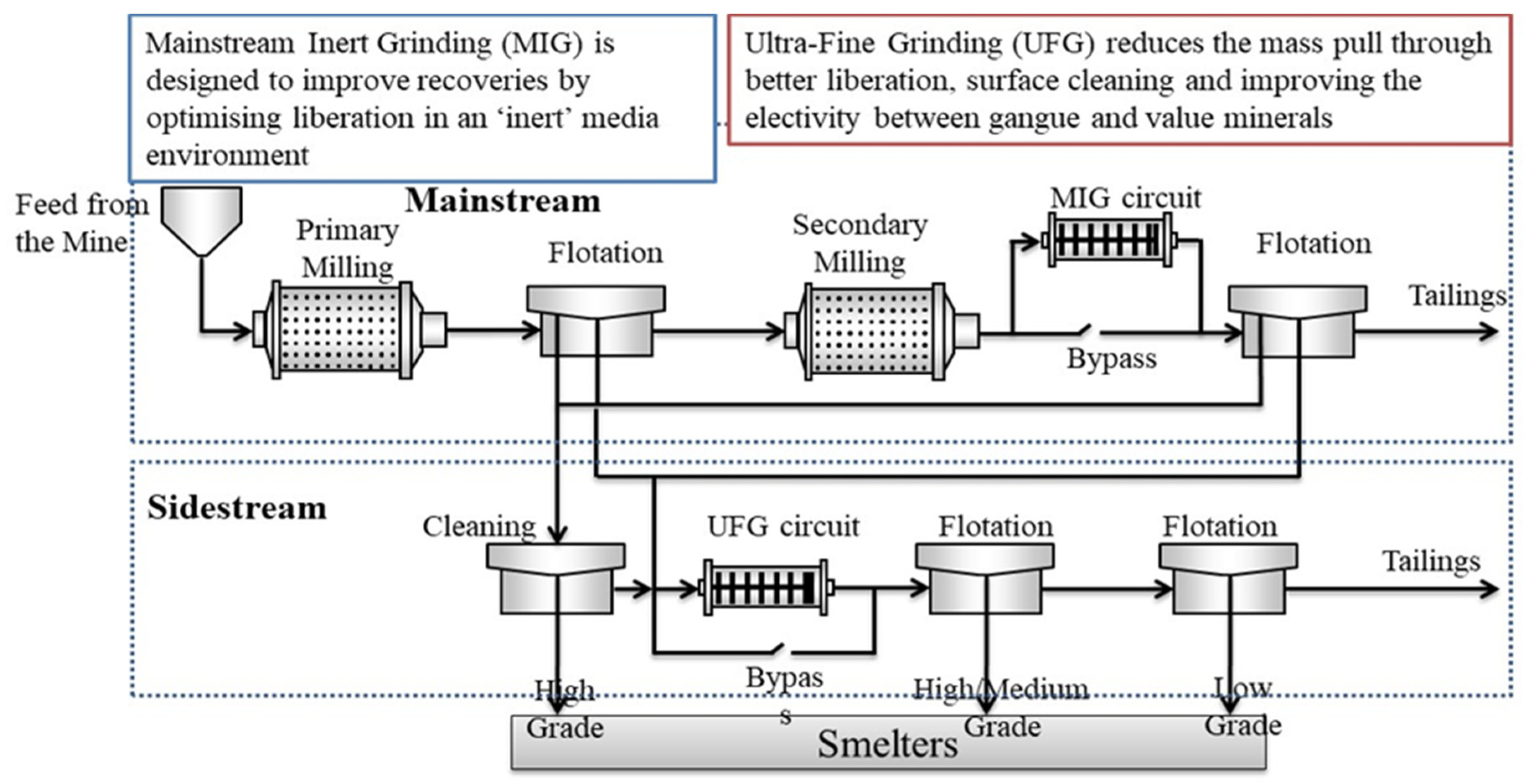
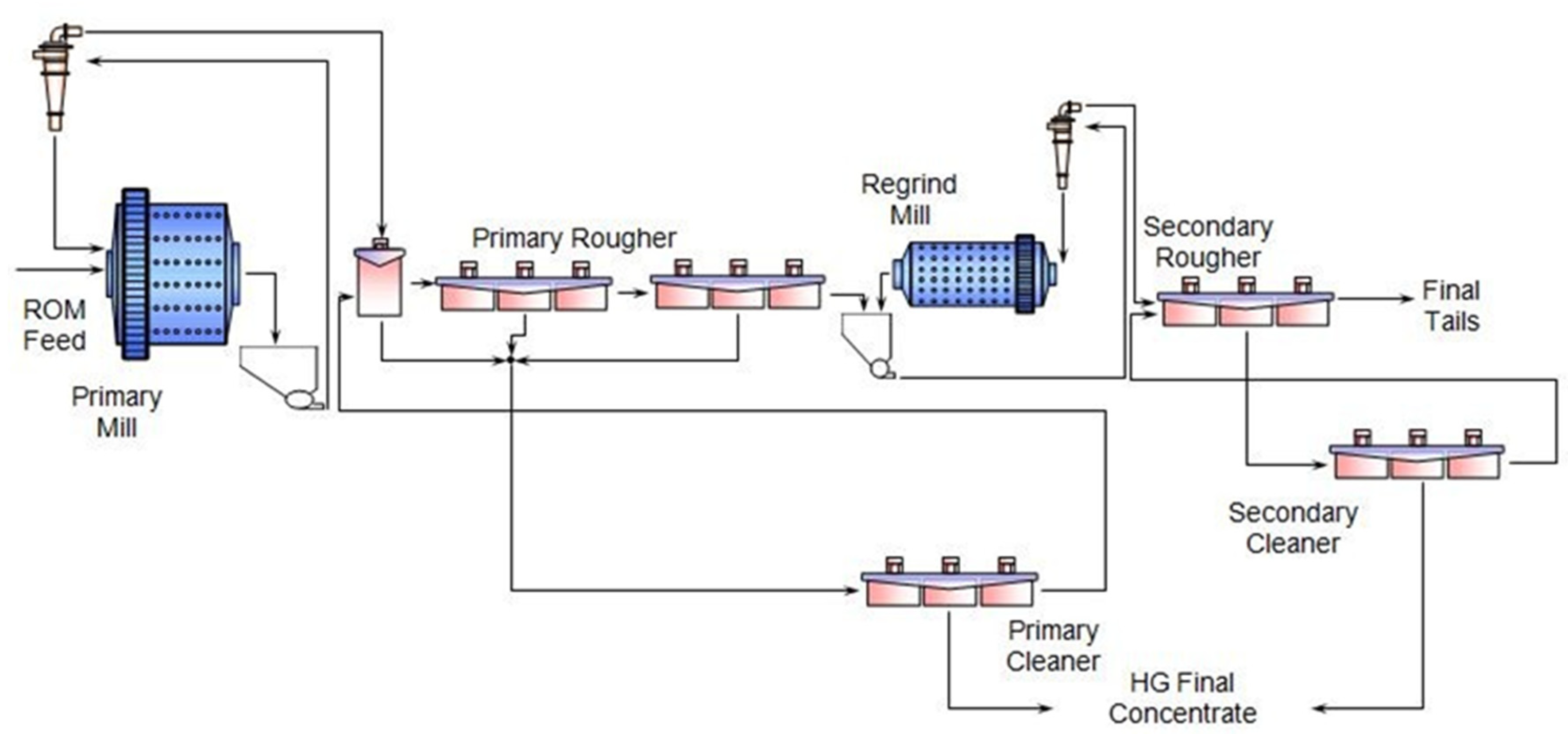
3. Comminution
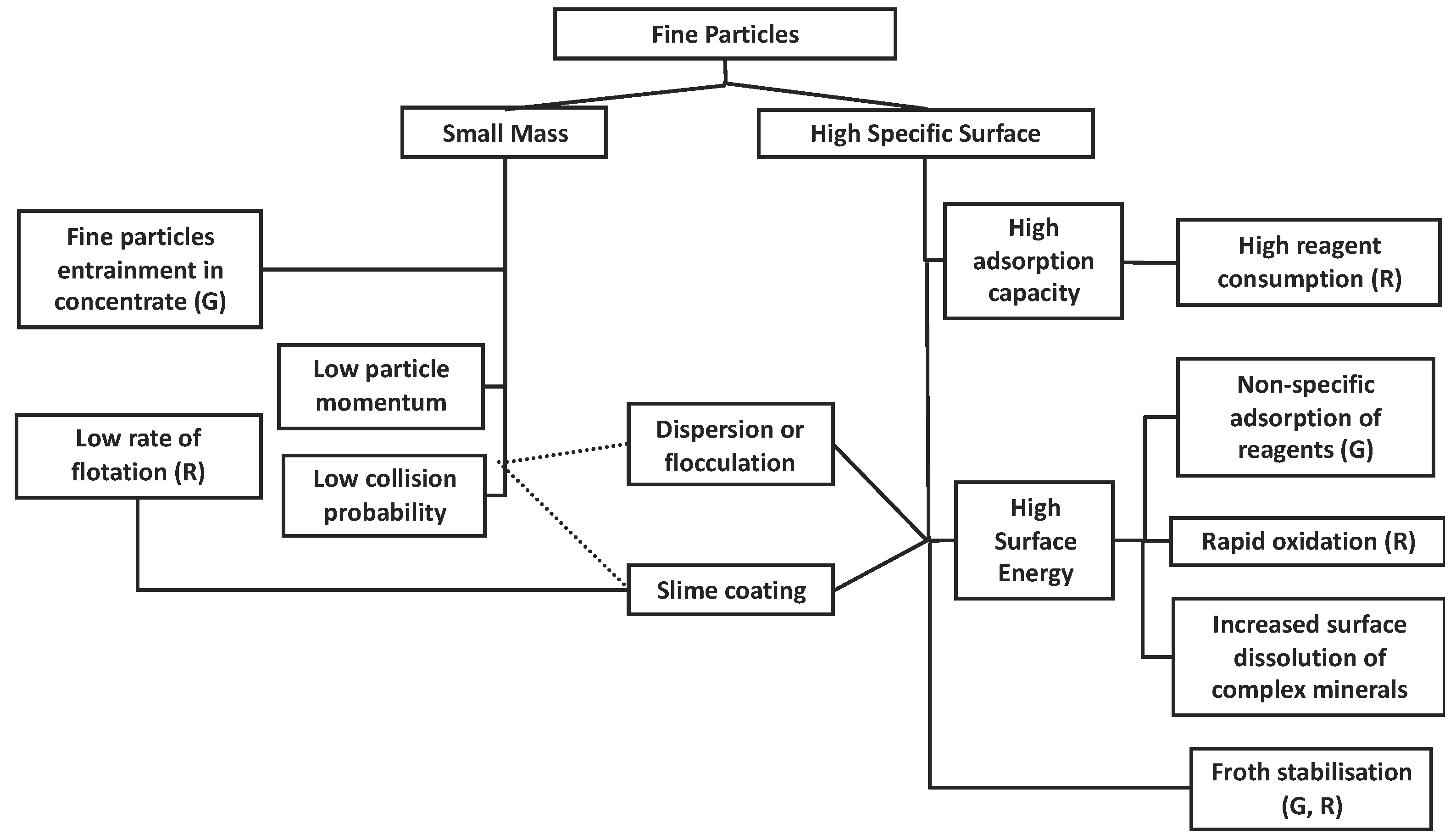
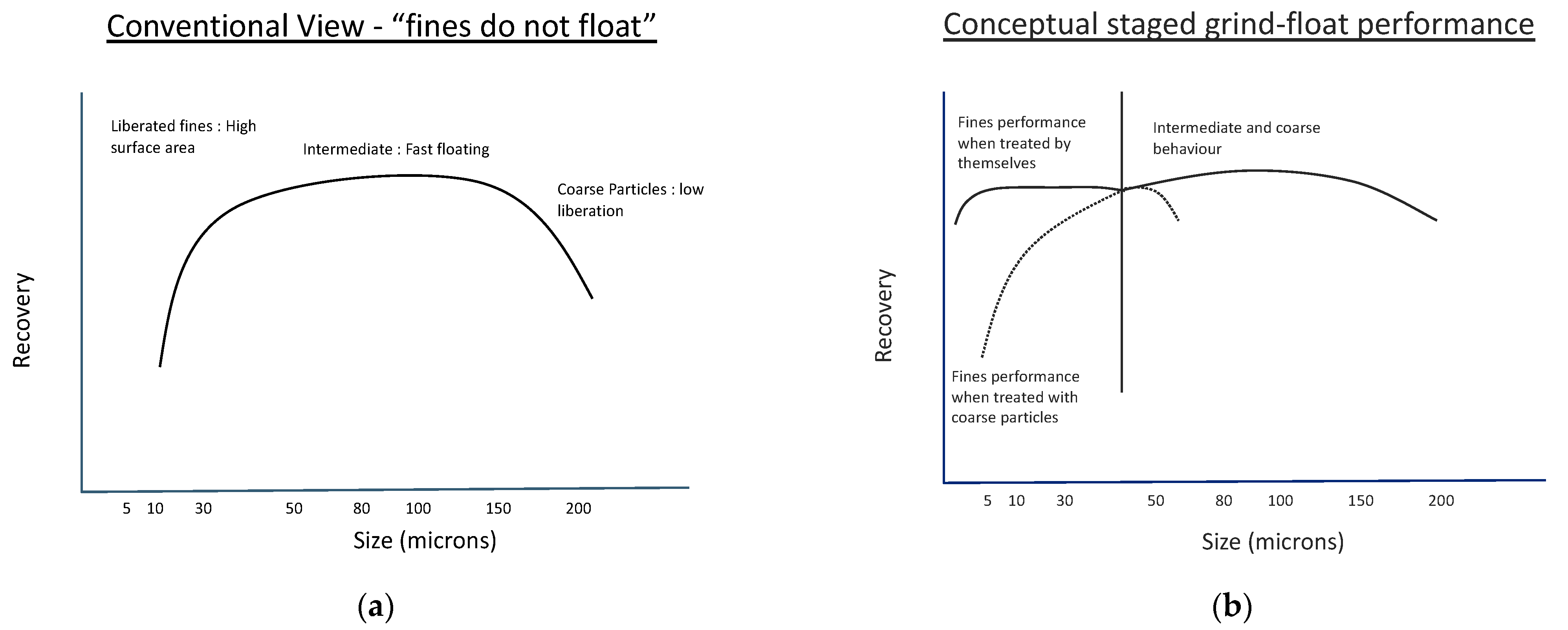
4. Flotation
5. Entrainment
6. Rheology and Slimes Coatings
6.1. Rheology
6.2. Slimes Coatings
6.3. Mitigation of Rheological and Slimes Effects in PGM Flotation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trahar, W.J.; Warren, L.J. The floatability of very fine particles—A review. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1976, 3, 103–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerstenau, D.W. Fine Particle Flotation. In Fine Particle Processing; Somasundaran, P., Ed.; The American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical and Petroleum Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 669–705. [Google Scholar]
- Shackleton, N.J.; Mokoena, D.M.; Malysiak, V. Fundamental study of fine PGE particle flotation. In Proceedings of the XXVII International Minerals Processing Congress, New Delhi, India, 24–28 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Grano, S.R.; Wong, P.; Skinner, W.; Johnson, N.W.; Ralston, J. The effect of autogenous and ball mill grinding on the chemical environment and flotation of the copper ore of Mount ISA Mines Ltd. In Proceedings of the III Latin-American Congress on Froth Flotation, Concepcion, Chile, 20–23 November 1994; pp. 351–388. [Google Scholar]
- Pease, J.D.; Curry, D.C.; Young, M.F. Designing flotation circuits for high fines recovery. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rule, C.M.; Plint, N. What will the typical PGM concentrator look like? In Proceedings of the 8th International Comminution Symposium, Comminution’12, Cape Town, South Africa, 17–20 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Engelbrecht, J. Potential changes in the physical beneficiation processes that can improve the recovery grade or costs for the platinum group metals. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Platinum Conference: A Catalyst for Change 2012, Sun City, South Africa, 19–21 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jameson, G.J. The effect of surface liberation and particle size on flotation rate constants. Miner. Eng. 2012, 36–38, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyn, J.J. Developing a Framework for the Design of the Milling and Rougher Circuits for a Platinum-Bearing UG2 Ore. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Valenta, M.M. Balancing reagent suite to optimize grade and recovery. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawthorn, R.G.; Webb, S.J. Connectivity between western and eastern limbs of the Bushveld Complex. Tectonophysics 2001, 330, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rule, C.M. Energy considerations in the current PGM processing flowsheet utilizing new technologies. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2008, 108, 30–46. [Google Scholar]
- Cawthorn, R.G. Seventy-fifth Anniversary of the Discovery of the Platiniferous Merenskv Reef: The largest platinum deposits in the world. Platin. Met. Rev. 1999, 43, 146. [Google Scholar]
- Cawthorn, R.G. The platinum and palladium resources of the bushveld complex. S. Afr. J. Sci. 1999, 95, 48–489. [Google Scholar]
- Schouwstra, R.P.; Kinloch, E.D.; Lee, C.A. A short geological review of the Bushveld Complex. Platin. Met. Rev. 2000, 44, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, C.; Alexandrova, T. The geological occurrence, mineralogy, and processing by flotation of platinum group minerals (PGMs) in South Africa and Russia. Minerals 2021, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermaak, C.F. The Platinum Group Metals: A Global Perspective; Mintek: Randburg, South Africa, 1995; p. 247. [Google Scholar]
- Shackleton, N.J. Surface Characterization and Flotation Behavior of the Platinum and Palladium Arsenide, Telluride and Sulphide Mineral Species. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Malysiak, V.; Shackleton, N.J. Private, Personal Communication, 2010.
- Shackleton, N.J.; Malysiak, V.; Theron, E.H.W.; Dicks, P.F. Where chemistry and mineralogy meet during PGE and BMS flotation. In Proceedings of the XXX International Mineral Processing Congress, Cape Town, South Africa, 18–22 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Napier-Munn, T.J.; Morrell, S.; Morrison, R.D.; Kojovic, T. Mineral Comminution Circuits—Their Operation and Operation; Julius Kruttschnitt Mineral Research Centre: Indooroopilly, Australia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Pease, J.D.; Curry, D.C.; Barnes, K.E.; Young, M.F.; Rule, C. Transforming flow sheet design with inert grinding media—The IsaMill. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Mineral Processors, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 17–19 January 2006; pp. 231–249. [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne, G.; Powell, M.S. Benchmarking comminution energy consumption for the processing of copper and gold ores. Miner. Eng. 2014, 65, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rule, C. Stirred milling—New comminution technology in the PGM industry. In Proceedings of the 4th International Platinum Conference, Platinum in Transition ‘Boom or Bust’, Sun City, South Africa, 11–14 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rule, C.; Schouwstra, R.P. Process mineralogy delivering significant value at anglo platinum concentrator operations. In Proceedings of the 10th International Congress for Applied Mineralogy (ICAM), Trondheim, Norway, 1–5 August 2011; Broekmans, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Humphries, G.; Rule, C.; Wolmarans, E. The development of a process flowsheet for the new Anglo Platinum PPRust north concentrator; incorporating HPGR technology. In Proceedings of the International Platinum Conference ‘Platinum Surges Ahead’, Sun City, South Africa, 8–12 October 2006; The Southern African Institute of Mining Metallurgy: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Morley, C.T. Plant Layout Considerations for High Pressure Grinding Rolls; Procemin: Santiago, Chile, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, N.A.; Shackleton, N.J.; Malysiak, V.; O’Connor, C.T. The effect of using different comminution procedures on the flotation of Platinum-Group Minerals. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelunxen, P.; Meadows, D. Not another HPGR trade-off study! Miner. Metall. Process. 2011, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M. Energy Efficient Mineral Liberation Using HPGR Technology. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Patzelt, N.; Klymowsky, R.I.B.; Knecht, J.; Burchardt, E. High-pressure grinding rolls for gold/copper applications. In Advances in Comminution; Kawatra, S.K., Ed.; Society for Mining Metallurgy & Exploration: Englewood, CO, USA, 2006; pp. 51–68. [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne, G.R.; Hilden, M.; van der Meer, F. Improved characterisation of ball milling energy requirements for HPGR products. Miner. Eng. 2017, 116, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rule, C.M. Stirred milling—New comminution technology in the PGM industry. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2011, 111, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Rule, C.M. Stirred milling at Anglo American Platinum. In Proceedings of the International Autogenous Grinding and High Pressure Grinding Roll Technology, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 25–28 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, M.; Mainza, A.N.; Powell, M.S.; Bradshaw, D.J.; Knopjes, B. Quantifying the influence of classification with the 3-product cyclone on liberation and recovery of PGMs in UG2 ore. Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowett, A. The formation and disruption particle-bubble aggregates in flotation. In Proceedings of the Fine Particles Processing: International Symposium on Fine Particles Processing, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24–28 February 1980; American Institute of Mining: New York, NY, USA, 1980; Volume l, pp. 720–753. [Google Scholar]
- Trahar, W. Rational interpretation of the role of particle size in flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1981, 8, 289–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D. Role of bubble size in flotation of coarse and fine particles. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 741–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Dukhin, S.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. The inertial hydrodynamic interaction of particles and rising bubbles with mobile surfaces. J. Colloid Interfacial Sci. 1998, 197, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. Particle-bubble collision models—A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 85, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirjavainen, V. Review and analysis of factors controlling the mechanical flotation of gangue minerals. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1996, 46, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savassi, O.N.; Alexander, D.J.; Franzidis, J.P.; Manlapig, E.V. An empirical model for entrainment in industrial flotation plants. Miner. Eng. 1998, 11, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudin, A.M.; Schuhmann, R., Jr.; Schlechten, A.W. Flotation kinetics, II. The effect of size on the behaviour of galena particles. J. Phys. Chem. 1942, 46, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, R.M.; Kelsall, D.F.; Trahar, W.J. The effect of particle size on the activation and flotation of sphalerite. Proc. Australas. Inst. Min. Metall. 1975, 254, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Trahar, W.J. The selective flotation of galena from sphalerite with special reference to the effects of particle size. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1976, 3, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, G.J. Physical aspects of fine particle flotation. In Principles of Mineral Flotation. The Wark Symposium; Series 40; Jones, M.H., Woodcock, J.T., Eds.; The Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Carlton, Australia, 1984; pp. 215–232. [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyam, T.V.; Forssberg, K.S.E. Froth stability, particle entrainment and drainage in flottaion–A review. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1988, 23, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, T.; Ralston, J.; Fornasiero, D. The limits of fine particle flotation. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 420–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokhpay, S.; Filippov, L.; Fornasiero, D. Flotation of fine particles: A review. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Aldrich, C. Effect of particle size on flotation performance of complex sulphide ores. Miner. Eng. 1999, 12, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.N.; Read, A.D. The treatment of slimes. Miner. Sci. Eng. 1971, 3, 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Deglon, D.A. The effect of agitation on the flotation of platinum ores. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matis, K.A.; Gallios, G.P.; Kydros, K.A. Separation of fines by flotation techniques. Sep. Technol. 1993, 3, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pease, J.D.; Young, M.F.; Curry, D.; Johnson, N.W. Improving Fines Recovery by Grinding Finer; MetPlant: Perth, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Corin, K.C.; Bezuidenhout, J.C.; O’Connor, C.T. The role of dithiophosphate as a co-collector in the flotation of a platinum group mineral ore. Miner. Eng. 2012, 36–38, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S. The Relationship between Froth Recovery and Froth Structure. Ph.D. Thesis, Ian Wark Research Institute, Mawson Lakes, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Szatkowski, M.; Freyburger, W. Kinetics of flotation with fine bubbles. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. 1985, 94, C61–C70. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, V. An investigation of sub-processes in equilibrium froths (1): The mechanisms of detachment and drainage. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1991, 31, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, M.; Harris, M.C.; Deglon, D.A. The effect of energy input on the flotation of a platinum ore in a pilot-scale oscillating grid flotation cell. Miner. Eng. 2017, 110, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Johnson, N.W.; Franzidis, J.P. Modelling of entrainment in industrial flotation cells: Water recovery and degree of entrainment. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, N.M.; Pinto, T.C.; Tavares, A.C.; Sweet, J. The entrainment effect on the performance of iron ore reverse flotation. Miner. Eng. 2016, 96–97, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, M.P.; Roy, R. A case study of optimizing UG2 flotation performance. Part 1: Bench, pilot and plant scale factors which influence Cr2O3 entrainment in UG2 flotation. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadzean, B.; Pani, S.; Wiese, J.; O’ Connor, C.T. The interactive effects of chemical and process parameters on the flotation performance of a UG2 ore. Miner. Eng. 2015, 70, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.; Harris, P.J.; Wiese, J.G.; Bradshaw, D.J. Mineralogical characterisation of naturally floatable gangue in Merensky Reef ore flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2009, 93, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, M.; Liu, D. The critical role of pulp density on flotation separation of nickel-copper sulfide from fine serpentine. Minerals 2018, 8, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molifie, A. Investigating the Use of Sodium Silicate to Improve the Flotation Performance of Altered PGE Ores. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Silva, M.; Wiese, J.; O’Connor, C.T. An investigation into the role of froth phase in controlling chromite in the flotation of UG2 ore using laboratory column flotation cell. Miner. Eng. 2013, 55, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, M.P. A case study of optimizing UG2 flotation performance. Part 2: Modelling improved PGM recovery and Cr2O3 rejection at Northam’s UG2 concentrator. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharaj, L.; Loveday, B.K.; Pocock, J. Gravity separation of a UG-2 ore secondary sample for the reduction of chromite minerals. Miner. Eng. 2012, 30, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achaye, I.; Wiese, J.; McFadzean, B. Effect of mineral particle size on froth stability. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadzean, B.; Marozva, T.; Wiese, J. Flotation frother mixtures: Decoupling the sub-processes of froth stability, froth recovery and entrainment. Miner. Eng. 2016, 85, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyabeze, W.; McFadzean, B. Adsorption of copper sulphate on PGM-bearing ores and its influence on froth stability and flotation kinetics. Miner. Eng. 2016, 92, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, N.; Forster, J.; Bobicki, E.R. Slurry rheology in mineral processing unit operations: A critical review. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 2102–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndlovu, B.; Becker, M.; Forbes, E.; Deglon, D.; Franzidis, J.-P. The influence of phyllosilicate mineralogy on the rheology of mineral slurries. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndlovu, B.N.; Burdukova, E.; Becker, M.; Deglon, D.; Franzidis, J.P.; Laskowski, J.S. The effects of chrysotile mineralogical properties on the rheology of chrysotile suspensions. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdukova, E.; Becker, M.; Ndlovu, B.; Mokgethi, D.; Deglon, D. Relationship between slurry rheology and its mineralogical content. In Proceedings of the 24th International Mineral Processing Congress, Beijing, China, 24–28 September 2008; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 2169–2178. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, M.; Yorath, G.; Ndlovu, B.; Harris, M.; Deglon, D.; Franzidis, J.P. A rheological investigation of the behaviour of two Southern African platinum ores. Miner. Eng. 2013, 49, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.N.; Napier-Munn, T.J. Effects of slurry rheology on industrial grinding performance. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2002, 65, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, I.; Tupper, G.; Mainza, A. Towards a mechanistic model for slurry transport in tumbling mills. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimha, M.; Mainza, A.; Holtham, P.; Powell, M.; Brennan, M. A semi-mechanistic model of hydrocyclones–Developed from industrial data and inputs from CFD. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 133, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, C.W.; Meyer, C.J.; Deglon, D.A. The development of a cavern model for mechanical flotation cells. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabalala, N.Z.P.; Harris, M.; Leal Filho, L.S.; Deglon, D.A. Effect of slurry rheology on gas dispersion in a pilot-scale mechanical flotation cell. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1448–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, J.; Fornaserio, D. Effect of MgO minerals on pentlandite flotation. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Minerals Processing Congress, Istanbul, Turkey, 3–8 September 2006; Onal, G., Acarkan, N., Celik, M.S., Arslan, F., Atesok, G., Guney, A., Sirkeci, A.A., Yuce, A.E., Perek, K.T., Eds.; Promed Advertising Ltd: Istanbul, Turkey, 2006; pp. 750–755. [Google Scholar]
- Farrokhpay, S. The importance of rheology in mineral flotation: A review. Miner. Eng. 2012, 36–38, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.J.; Franzidis, J.P.; Manlapig, E.V. Froth recovery measurement in plant scale flotation cells. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaman, D.R.; Franzidis, J.P.; Manlapig, E.V. Bubble load measurement in the pulp zone of industrial flotation machines—A new device for determining the froth recovery of attached particles. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2004, 74, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yianatos, J.B.; Moys, M.H.; Contreras, F.A.V. Froth recovery of industrial flotation cells. Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzidis, J.P.; Harris, M.C. Froth recovery factor—What is it and why is it so difficult to measure? Can. Metall. Q. 2010, 49, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.N.; Zheng, X.F. The rheology of flotation froths. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2003, 69, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Farrokhpay, S.; Runge, K.; Shi, F. Determining the significance of flotation variables on froth rheology using a central composite rotatable design. Powder Technol. 2016, 287, 216–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Runge, K.; Shi, F.; Farrokhpay, S. Effect of flotation froth properties on froth rheology. Powder Technol. 2016, 294, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Runge, K.; Shi, F.; Farrokhpay, S. Effect of froth rheology on froth and flotation performance. Miner. Eng. 2018, 115, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Runge, K.; Shi, F.; Farrokhpay, S. Effect of flotation conditions on froth rheology. Powder Technol. 2018, 340, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Boger, D.V. Application of rheology to solving tailings disposal problems. Miner. Eng. 1998, 24, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, N.J.; Malysiak, V.; O’Connor, C.T. Surface characteristics and flotation behaviour of platinum and palladium tellurides. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 1232–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, N.J.; Malysiak, V.; O’Connor, C.T. Surface characteristics and flotation behaviour of platinum and palladium arsenides. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2007, 85, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molifie, A.; McFadzean, B.; Becker, M.; Geldenhuys, S. Investigating the use of sodium metasilicate to improve the flotation performance of altered PGE ores. In Proceedings of the XXVIII International Mineral Processing Congress, Cape Town, South Africa, 18–22 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ndlovu, B.; Forbes, E.; Farrokhpay, S.; Becker, M.; Bradshaw, D.; Deglon, D. A preliminary rheological classification of phyllosilicate group minerals. Miner. Eng. 2014, 55, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, P.S.; Berg, J.C. Poly(acrylic acid) as a rheology modifier for dense alumina dispersions in high ionic strength environments. Colloids Surf. A 2010, 362, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearse, M.J. An overview of the use of chemical reagents in mineral processing. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Lee, W.; Kim, S. Effect of grinding aids on the kinetics of fine grinding energy consumed of calcite powders by a stirred ball mill. Adv. Powder Technol. 2009, 20, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosa, E.S.; Saleh, A.M.; Taha, T.A.; El-Molla, A.M. Effect of chemical additives on flow characteristics of coal slurries. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2008, 42, 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, V.; Singh, A.; Pillay, K. Improved flotation of PGM tailings with a high-shear hydrodynamic cavitation device. Miner. Eng. 2019, 137, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mineral Name | Merensky Reef | UG2 Reef | Platreef |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volume % | |||
| Pyroxene | 55–60 | 15–30 | 30–40 |
| Feldspar | 30–40 | 3–9 | 18 |
| Chromite | 6 | 50–75 | - |
| Talc | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Serpentine | 2–3 | 1 | 5 |
| Amphibole | 1–2 | <1 | 4 |
| Chlorite | 1–2 | <1 | 4 |
| Mica | <1 | <1 | 1 |
| BMS | <1 | <1 | 2 |
| Other * | 1–2 | <1 | 5 |
| Minerals | Merensky Reef | UG2 Reef | Platreef |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volume % | |||
| Pentlandite | 35 | 44–52 | 27 |
| Pyrrhotite | 46 | 26–35 | 52 |
| Chalcopyrite | 20 | 21 | 19 |
| Class | Minerals | Merensky Reef | UG2 Reef | Platreef |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume % | ||||
| PGM Alloys | Ferroplatinum Pt Alloy Pd Alloy | 40 | 40 | 11–30 |
| Electrum (Au) | 2 | 0.2 | 3 | |
| Arsenides | Pt-arsenides Pd-arsenides | 4 | 0.1–1 | 1–20 |
| PGE-sulphurarsenides | 3 | 0.8–7 | 16–35 | |
| PGM sulphides | PtPd-sulphide Pt-sulphide PtRh-sulphide | 16 | 40–60 | 1–7 |
| Tellurides | Pt-tellurides Pd-tellurides | 35 | 0.5–5 | 20–50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corin, K.C.; McFadzean, B.J.; Shackleton, N.J.; O’Connor, C.T. Challenges Related to the Processing of Fines in the Recovery of Platinum Group Minerals (PGMs). Minerals 2021, 11, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11050533
Corin KC, McFadzean BJ, Shackleton NJ, O’Connor CT. Challenges Related to the Processing of Fines in the Recovery of Platinum Group Minerals (PGMs). Minerals. 2021; 11(5):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11050533
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorin, Kirsten C., Belinda J. McFadzean, Natalie J. Shackleton, and Cyril T. O’Connor. 2021. "Challenges Related to the Processing of Fines in the Recovery of Platinum Group Minerals (PGMs)" Minerals 11, no. 5: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11050533
APA StyleCorin, K. C., McFadzean, B. J., Shackleton, N. J., & O’Connor, C. T. (2021). Challenges Related to the Processing of Fines in the Recovery of Platinum Group Minerals (PGMs). Minerals, 11(5), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11050533