Recovery of Iron from Mill Scale by Reduction with Carbon Monoxide
Abstract
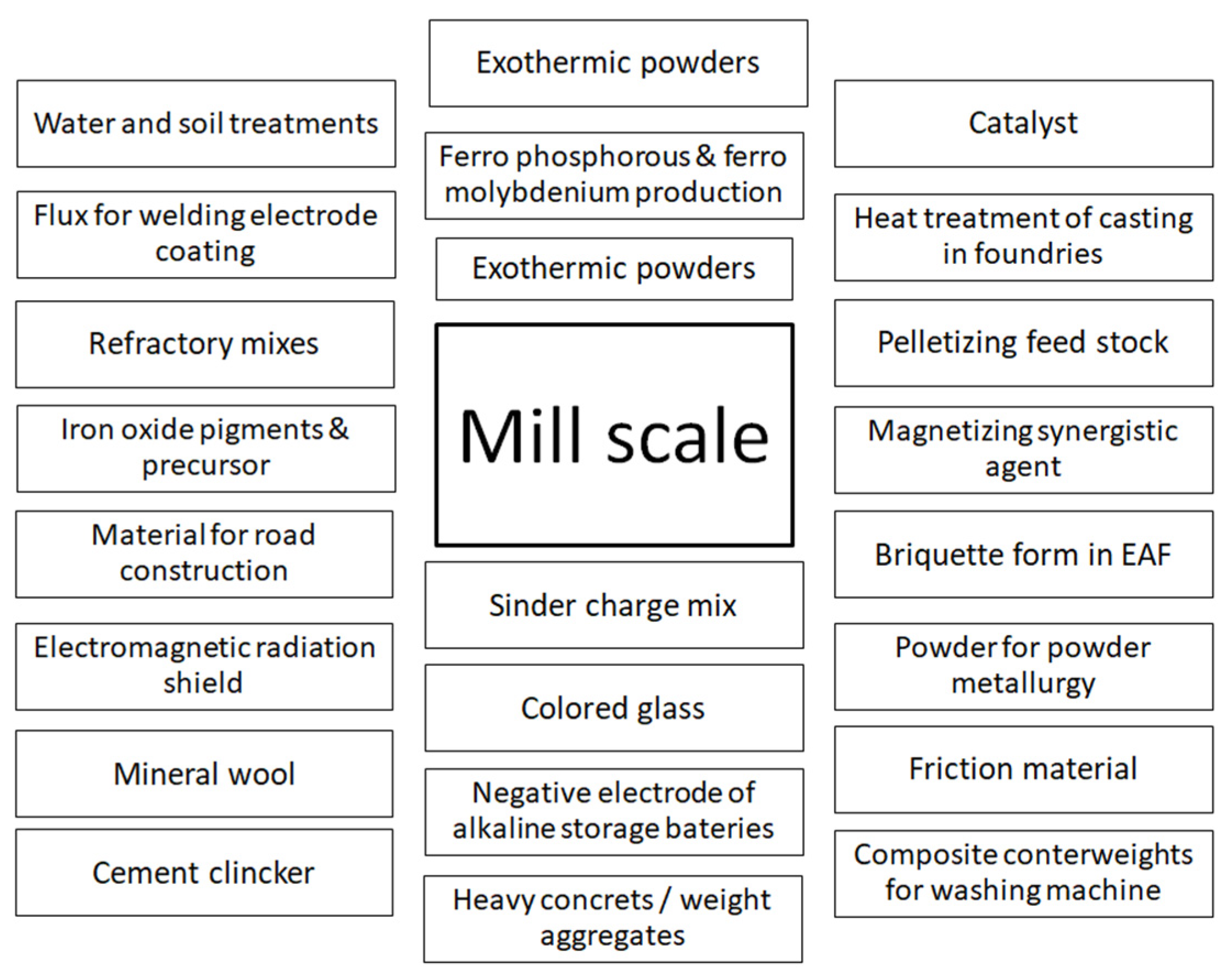
1. Introduction
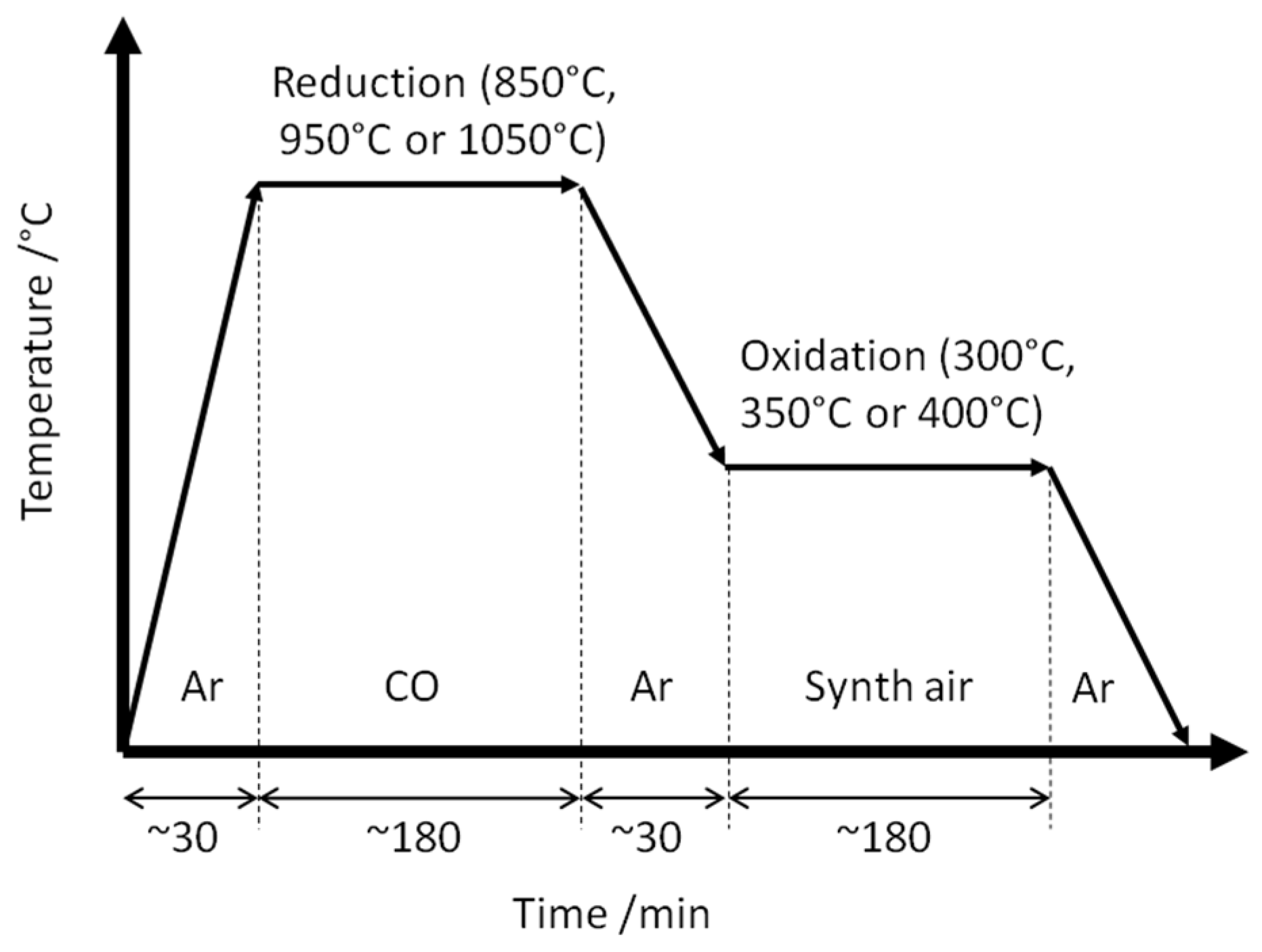
2. Materials and Methods
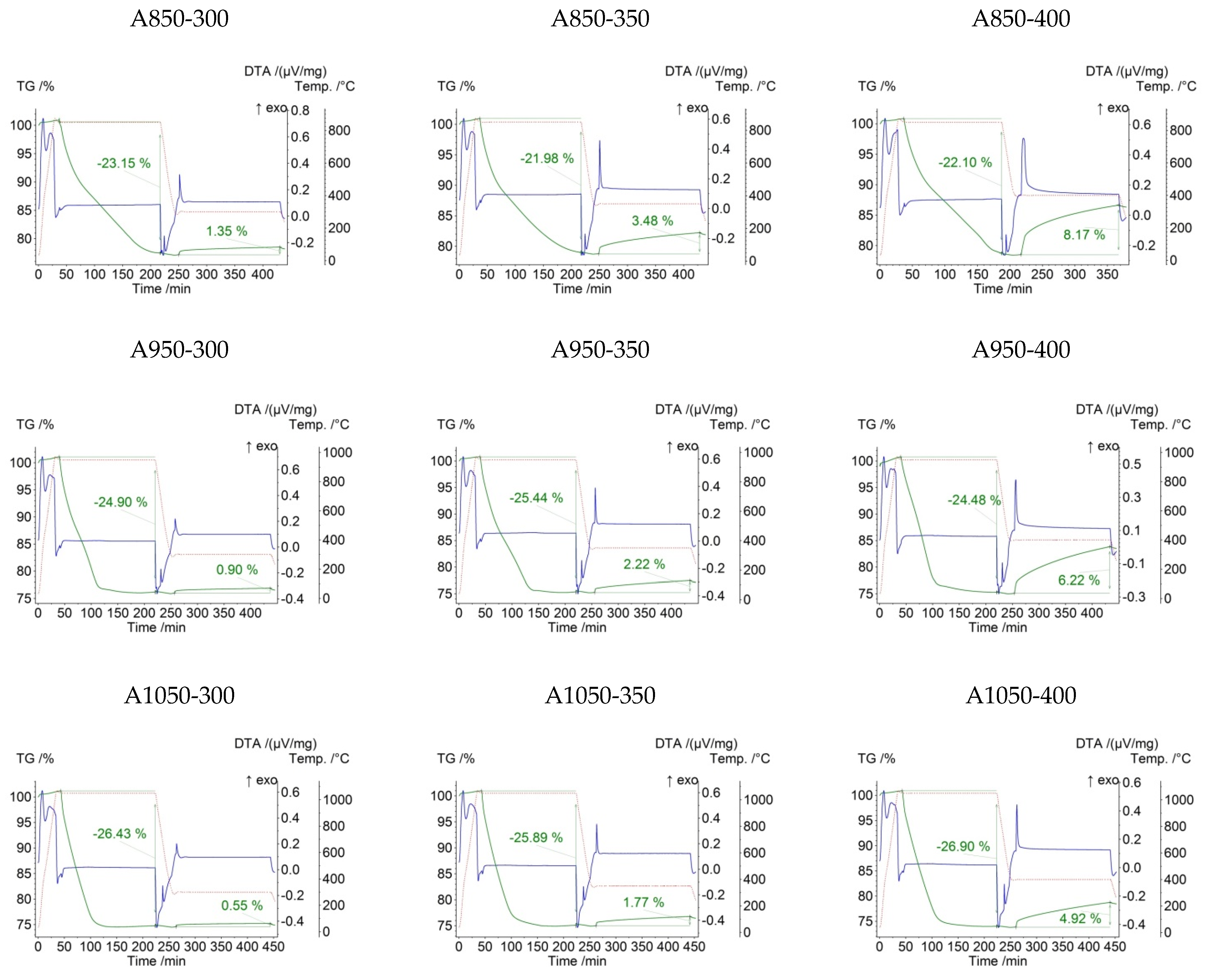
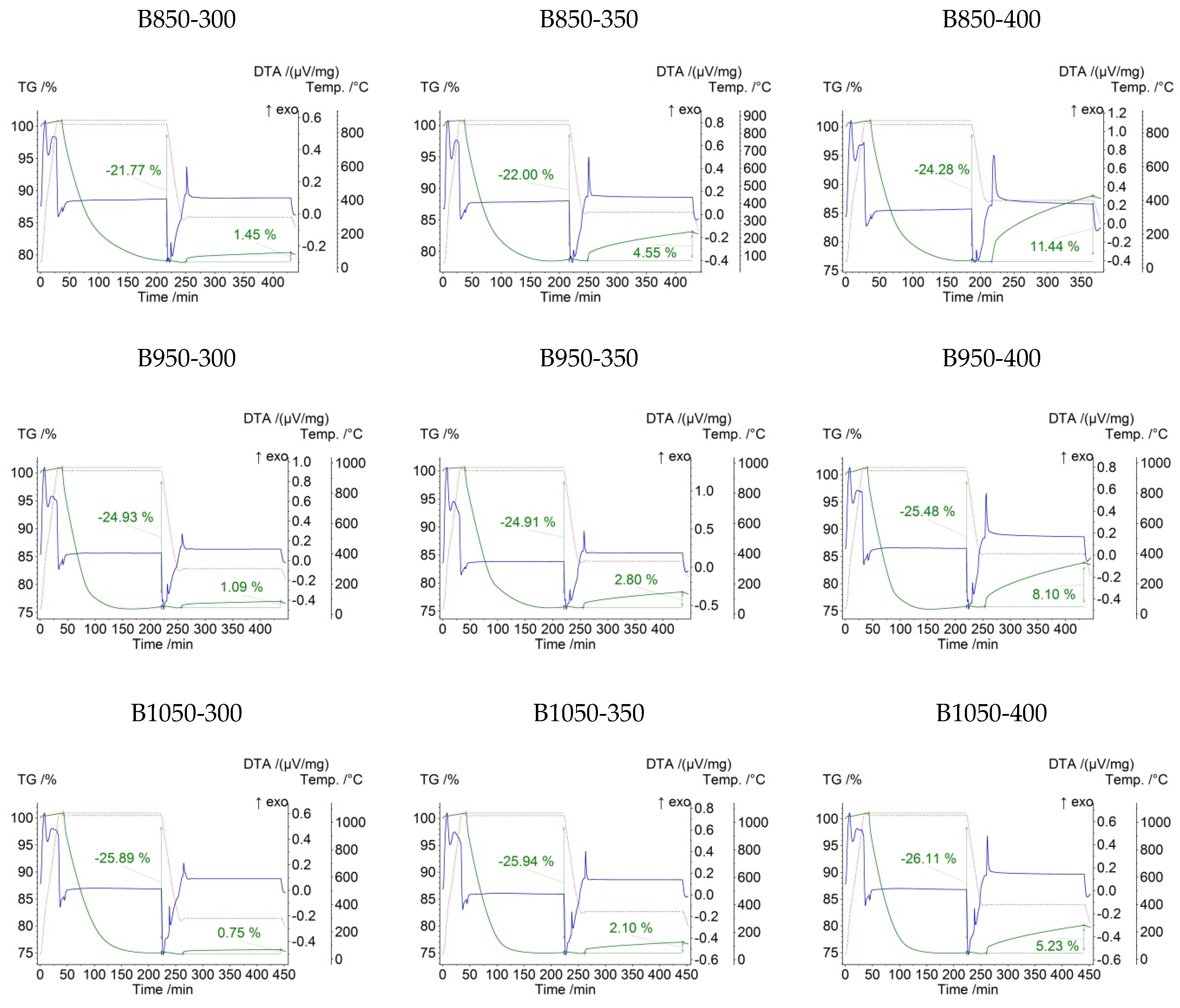
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EU Commission. Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives (Waste Framework Directive, R1 Formula in Footnote of Attachment II). Available online: http://eur-lex.Europa.Eu/lexuriserv (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- Sellitto, M.A.; Murakam, F.K. Destination of the waste generated by a steelmaking plant: A case study in Latin America. Aestimum 2020, 77, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecko, J.; Stachura, R.; Niesler, M.; Bernasowski, M.; Klimczyk, A. Utilisation of metallurgical sludge by multi-layer sintering. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2017, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, N.C.C.; Villegas, E.A.; Mansur, M.B. Management of solid wastes from steelmaking and galvanizing processes: A brief review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 102, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, I.G.; Palmer, J.P.; Barratt, P.A. 9 Steel Industry Raw Materials and Wastes. Stud. Environ. 1993, 56, 253–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, T.A.; Colla, V.; Algermissen, D.; Granbom, H.; Martini, U.; Morillon, A.; Pietruck, R.; Rosendahl, S. Reuse and Recycling of By-Products in the Steel Sector: Recent Achievements Paving the Way to Circular Economy and Industrial Symbiosis in Europe. Metals 2020, 10, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Wang, X. CO2 Utilization in the Ironmaking and Steelmaking Process. Metals 2019, 9, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jikar, P.; Dhokey, N. Overview on production of reduced iron powder from mill scale waste. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 4324–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Fernández, Á.M.; Torres, V.M. Hydrometallurgical Processes for the Recovery of Metals from Steel Industry By-Products: A Critical Review. J. Sustain. Met. 2020, 6, 505–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyzanowski, M.; Beynon, J.H.; Farrugia, D.C.J. Oxide Scale Behavior in High Temperature Metal Processing; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; ISBN 978-3-527-32518-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, R.; Dehiya, S.; Pandel, U.; Banerjee, M. Utilization of Low Grade Coal for Direct Reduction of Mill Scale to Obtain Sponge Iron: Effect of Reduction Time and Particle Size. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 11, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umadevi, T.; Brahmacharyulu, A.; Karthik, P.; Mahapatra, P.C.; Prabhu, M.; Ranjan, M. Recycling of steel plant mill scale via iron ore sintering plant. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2012, 39, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.; Ahmed, A.; El-Fawkhry, M. Conversion of Mill Scale Waste into Valuable Products via Carbothermic Reduction. J. Met. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roy, B.N. Conversion of rolling mill scale into sponge iron powder. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2016, 8, 31348–31351. [Google Scholar]
- Murthy, Y.I.; Agarwal, A.; Pandey, A. Characterization of Mill Scale for Potential Application in Construction Industry. Indian J. Eng. 2017, 14, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Khaerudini, D.S.; Chanif, I.; Insiyanda, D.R.; Destyorini, F.; Alva, S.; Pramono, A. Preparation and Characterization of Mill Scale Industrial Waste Reduced by Biomass-Based Carbon. J. Sustain. Met. 2019, 5, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanin, V.N.; Ikornikov, D.M.; Andreev, D.E.; Sachkova, N.V.; Yukhvid, V.I. Mill scale recycling by SHS metallurgy for production of cast ferrosilicon and ferrosilicoaluminium. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 558, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.I.; López, F.A.; Torralba, J.M. Production of sponge iron powder by reduction of rolling mill scale. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2012, 39, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.iron-consortium.org/assets/files/sief/UsesDescription_MillScale_20140108.pdf (accessed on 9 May 2021).
- Available online: https://www.koeppern-international.com/uploads/media/HBI_-_Hot_Briquetting_of_Direct_Reduced_Iron.pdf (accessed on 9 May 2021).
- Morris, A. Iron Resources and Direct Iron Production. Encycl. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2001, 4302–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozwiak, W.; Kaczmarek, E.; Maniecki, T.; Ignaczak, W.; Maniukiewicz, W. Reduction behavior of iron oxides in hydrogen and carbon monoxide atmospheres. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 326, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaballah, N.M.; Zikry, A.F.; Khalifa, M.G.; Farag, A.B.; El-Hussiny, N.A.; Shalabi, M.E.H. Production of Iron from Mill Scale Industrial Waste via Hydrogen. Open J. Inorg. Non-Met. Mater. 2013, 03, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Benchiheub, O.; Mechachti, S.; Serrai, S.; Khalifa, M.G. Elaboration of iron powder from mill scale. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2010, 1, 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Zhu, H.; Peng, J.; Kannan, C.S.; Chen, J.; Dai, L.; Liu, P. Preparation of Reduced Iron Powders from Mill Scale with Microwave Heating: Optimization Using Response Surface Methodology. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.; Peng, J. Preparation of reduced iron powder using combined distribution of wood-charcoal by microwave heating. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 613, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechachti, S.; Benchiheub, O.; Serrai, S.; Shalabi, M.E.H. Preparation of iron Powders by Reduction of Rolling Mill Scale. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2013, 4, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, C.; Dhokey, N.B. Study of Kinetics of Mill Scale Reduction: For PM Applications. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2015, 68, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, S.; De-Ren, W.; Ye-Dong, H.; Hui-Bin, Q.; Gao, W. Reduction of oxide scale on hot-rolled strip steels by carbon monoxide. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3500–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Li, J.; Tan, N.; He, Y.-Q.; Zhang, S.-G. Reduction of oxide scale on hot-rolled steel by hydrogen at low temperature. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 15116–15124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, N.; Desgranges, C.; Poquillon, D.; Lafont, M.-C.; Monceau, D. Iron Oxidation at Low Temperature (260–500 °C) in Air and the Effect of Water Vapor. Oxid. Met. 2010, 73, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henshall, G.A. Numerical Predictions of Dry Oxidation of Iron and Low-Carbon Steel at Moderately Elevated Temperatures. MRS Proc. 1996, 465, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krungkarnchana, H.; Kongvarhodom, C. Low Temperature Corrosion: Oxidation of Carbon Steel and Stainless Steel in Air. Appl. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2018, 12, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.ispatguru.com/mill-scale/ (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- Stephenson, R.L. Direct Reduced Iron—Technology and Economics of Production and Use; The Iron and Steel Society of AIME: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Patisson, F.; Mirgaux, O. Hydrogen Ironmaking: How it Works. Metals 2020, 10, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheshukov, O.; Mikheenkov, M.; Vedmid’, L.; Nekrasov, I.; Egiazaryan, D. Mechanism of Ion-Diffusion Solid-Phase Reduction of Iron Oxides of Technogenic Origin in the Presence of the Liquid Phase and without it. Metals 2020, 10, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tleugabulov, S.M.; Abikov, S.B.; Koishina, G.M.; Tatybaev, M.K. Fundamentals and Prospects of the Development of Reduction Steelmaking. Russ. Met. (Metally) 2018, 2018, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chufarov, G.I.; Men, A.N.; Balakirev, V.F. Thermodynamics of Metal Oxide Reduction Processes; Metallurgy: Moscow, Russia, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Longbottom, R.J.; Kolbeinsen, L. Iron Ore Reduction with CO and H2 Gas Mixtures—Thermodynamic and Kinetic Modelling. In Proceedings of the 4th Ulcos Seminar—New Direct Reduction (DR), Essen, Germany, 1–2 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Li, B.; Guo, H.; Yang, W.; Li, S.; Guo, J. Thermodynamic Study on Reduction of Iron Oxides by H2 + CO + CH4 + N2 Mixture at 900 °C. Energies 2020, 13, 5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe’s Dictionary of Applied Chemistry, 4th ed.; Longmans, Green and Co.: London, UK, 1950; Volume X, pp. 327–329.
- Hosseini, S.G.; Eslami, A. Investigation on the Reaction of Powdered Tin as a Metallic Fuel with Some Pyrotechnic Oxidizers. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2011, 36, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrie, T.M.; Kopf, P.W.; Toby, S. Kinetics of the reaction of some pyrophoric metals with oxygen. J. Phys. Chem. 1967, 71, 3842–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.P.; Borland, W.; Mardon, P.G. Pyrophoricity of Fine Metal Powders. Powder Met. 1976, 19, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelo, P.C.; Subramanian, R. Powder Metallurgy: Science, Technology and Applications; PHI Learning Private Limited: Delhi, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ellern, H. Military and Civilian Pyrotechnics; Chemical Publishing Company INC: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.ispatguru.com/direct-reduced-iron/ (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- Sista, K.S.; Dwarapudi, S.; Nerune, V.P. Direct Reduction Recycling of Mill Scale through Iron Powder Synthesis. ISIJ Int. 2019, 59, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Element | C | O | Al | Si | Ca | Mn | Fe | Cr | Cu | Ti | S | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass/% | 0.03 | 12.23 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.40 | 0.53 | 85.38 | 0.10 | 0.43 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0.03 |
| σ | ±0.01 | ±2.66 | ±0.06 | ±0.12 | ±0.10 | ±0.06 | ±0.20 | ±0.02 | ±0.06 | ±0.08 | ±0.01 | ±0.01 |
| Phase | Fe | FeO | Fe3O4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average mass fraction/% | 0.85 | 47.81 | 51.34 |
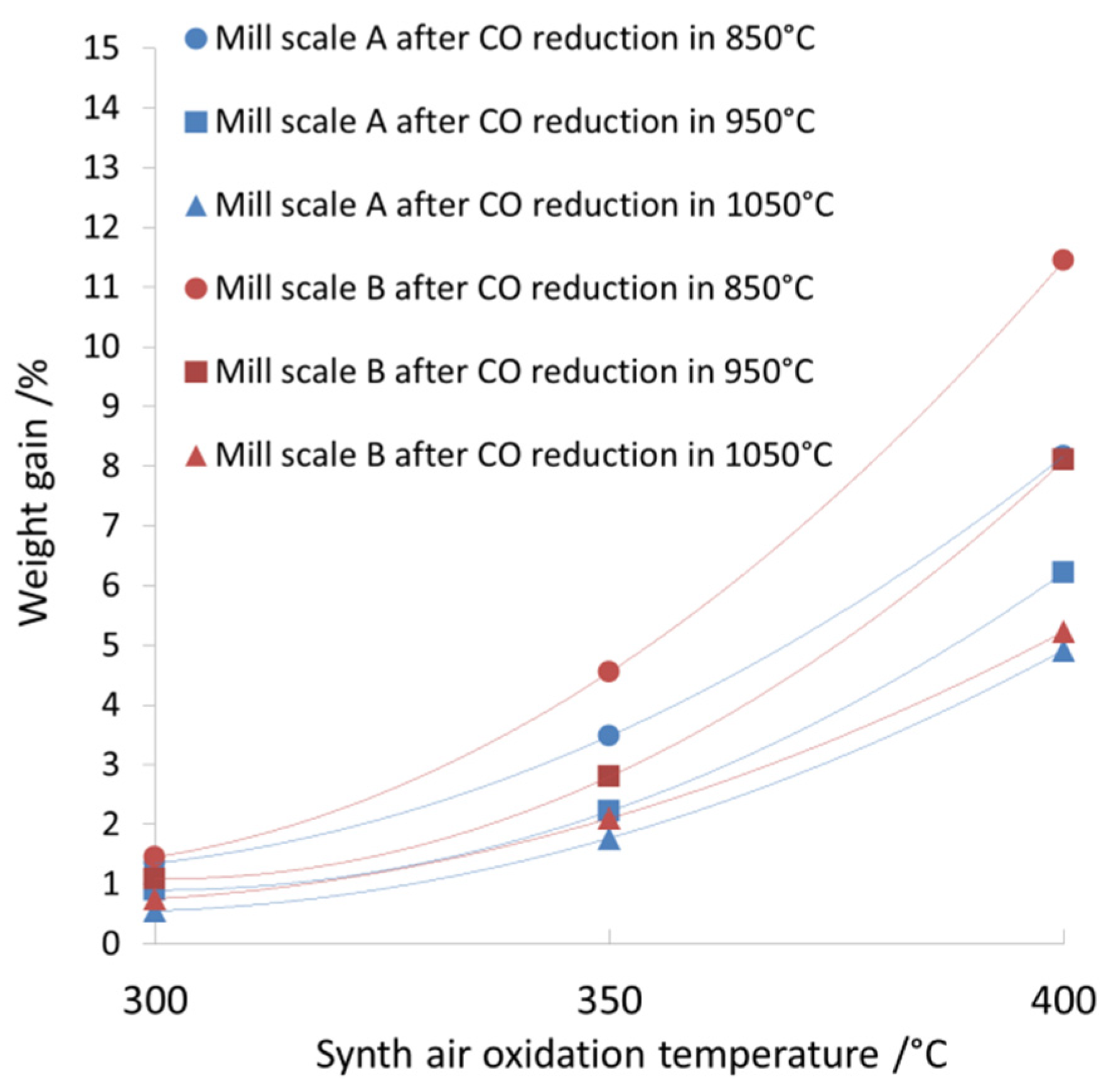
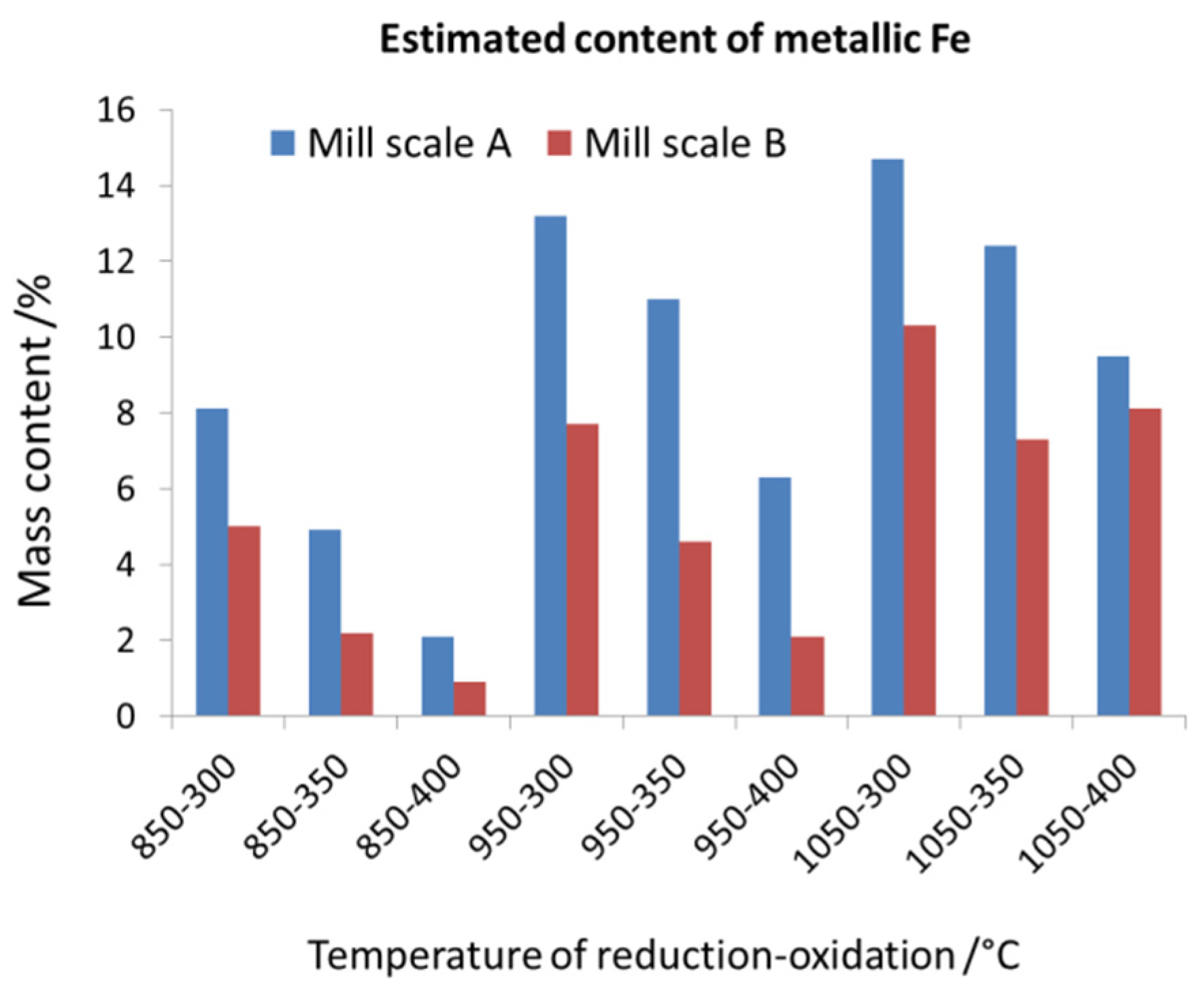
| Sample Denotation | Sample Weight /g | Temperature /°C | Mass Change /% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduction | Oxidation | Reduction | Oxidation | ||
| Fraction A | |||||
| A850-300 | 0.2054 | 850 | 300 | −23.15 | 1.35 |
| A850-350 | 0.1911 | 850 | 350 | −21.98 | 3.48 |
| A850-400 | 0.2039 | 850 | 400 | −22.10 | 8.17 |
| A950-300 | 0.1912 | 950 | 300 | −24.90 | 0.90 |
| A950-350 | 0.2067 | 950 | 350 | −25.44 | 2.22 |
| A950-400 | 0.2247 | 950 | 400 | −24.48 | 6.22 |
| A1050-300 | 0.2024 | 1050 | 300 | −26.43 | 0.55 |
| A1050-350 | 0.1932 | 1050 | 350 | −25.89 | 1.77 |
| A1050-400 | 0.2207 | 1050 | 400 | −26.90 | 4.92 |
| Fraction B | |||||
| B850-300 | 0.1957 | 850 | 300 | −21.77 | 1.45 |
| B850-350 | 0.1940 | 850 | 350 | −22.00 | 4.55 |
| B850-400 | 0.2140 | 850 | 400 | −24.28 | 11.44 |
| B950-300 | 0.1950 | 950 | 300 | −24.93 | 1.09 |
| B950-350 | 0.2136 | 950 | 350 | −24.91 | 2.80 |
| B950-400 | 0.1927 | 950 | 400 | −25.48 | 8.10 |
| B1050-300 | 0.1945 | 1050 | 300 | −25.89 | 0.75 |
| B1050-350 | 0.2076 | 1050 | 350 | −25.94 | 2.10 |
| B1050-400 | 0.2200 | 1050 | 400 | −26.11 | 5.23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nowacki, K.; Maciąg, T.; Lis, T. Recovery of Iron from Mill Scale by Reduction with Carbon Monoxide. Minerals 2021, 11, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11050529
Nowacki K, Maciąg T, Lis T. Recovery of Iron from Mill Scale by Reduction with Carbon Monoxide. Minerals. 2021; 11(5):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11050529
Chicago/Turabian StyleNowacki, Krzysztof, Tomasz Maciąg, and Teresa Lis. 2021. "Recovery of Iron from Mill Scale by Reduction with Carbon Monoxide" Minerals 11, no. 5: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11050529
APA StyleNowacki, K., Maciąg, T., & Lis, T. (2021). Recovery of Iron from Mill Scale by Reduction with Carbon Monoxide. Minerals, 11(5), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11050529






