Geochronology and Isotope Geochemistry of the Yingfang Pb-Zn-Ag Deposit: Implications for Large-Scale Metallogeny along the Northern Flank of the North China Craton
Abstract
1. Introduction
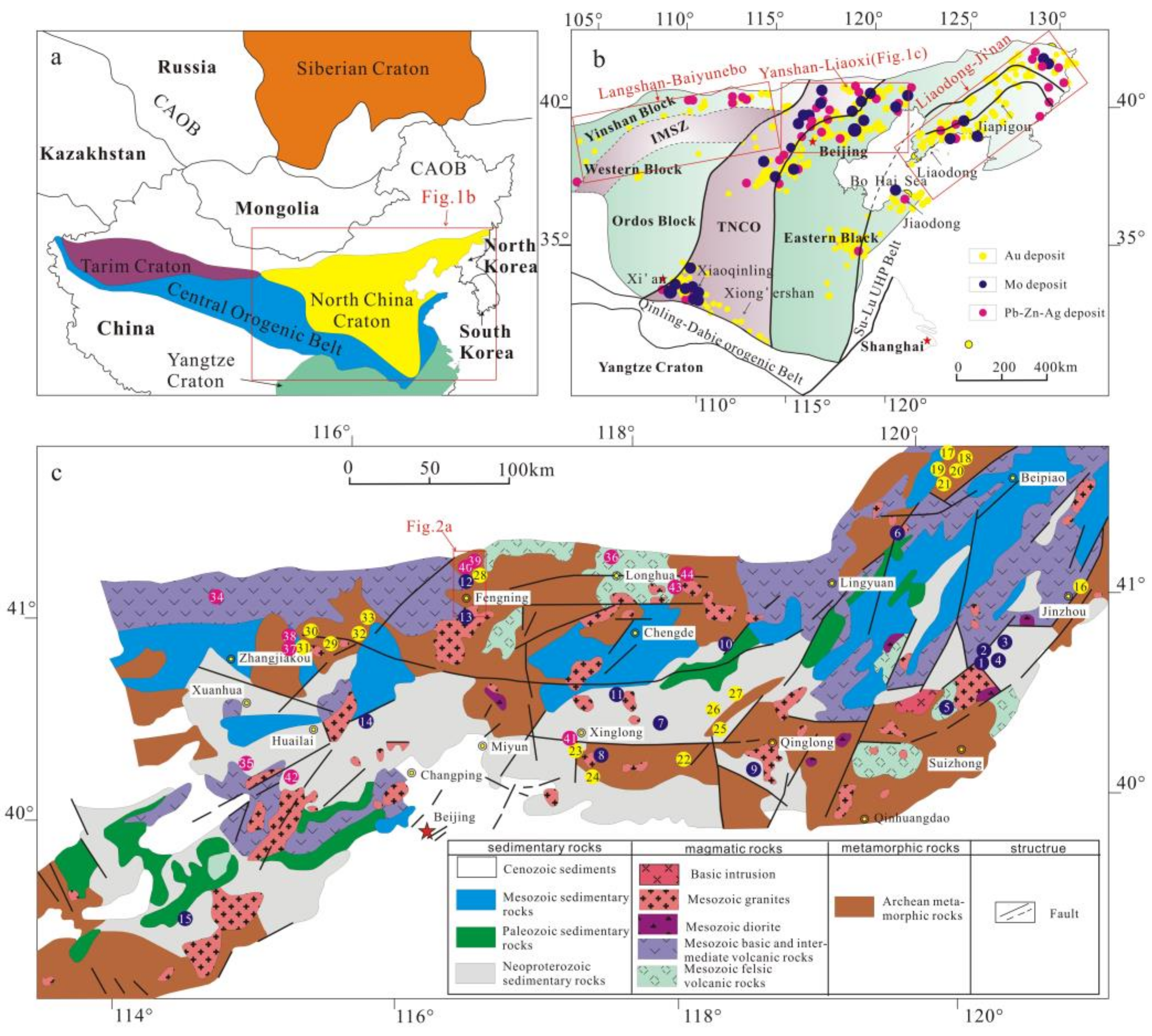
2. Geological Setting
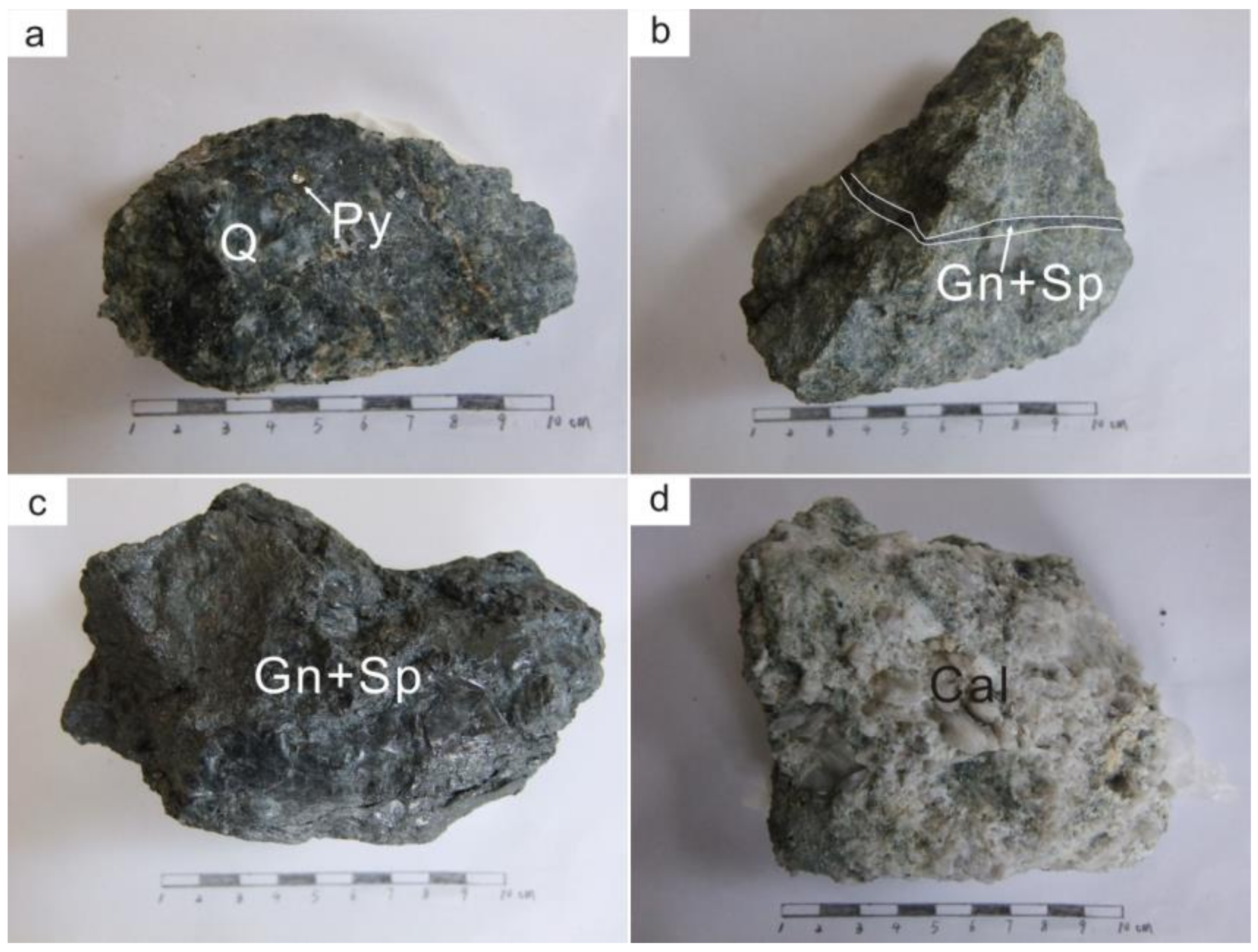
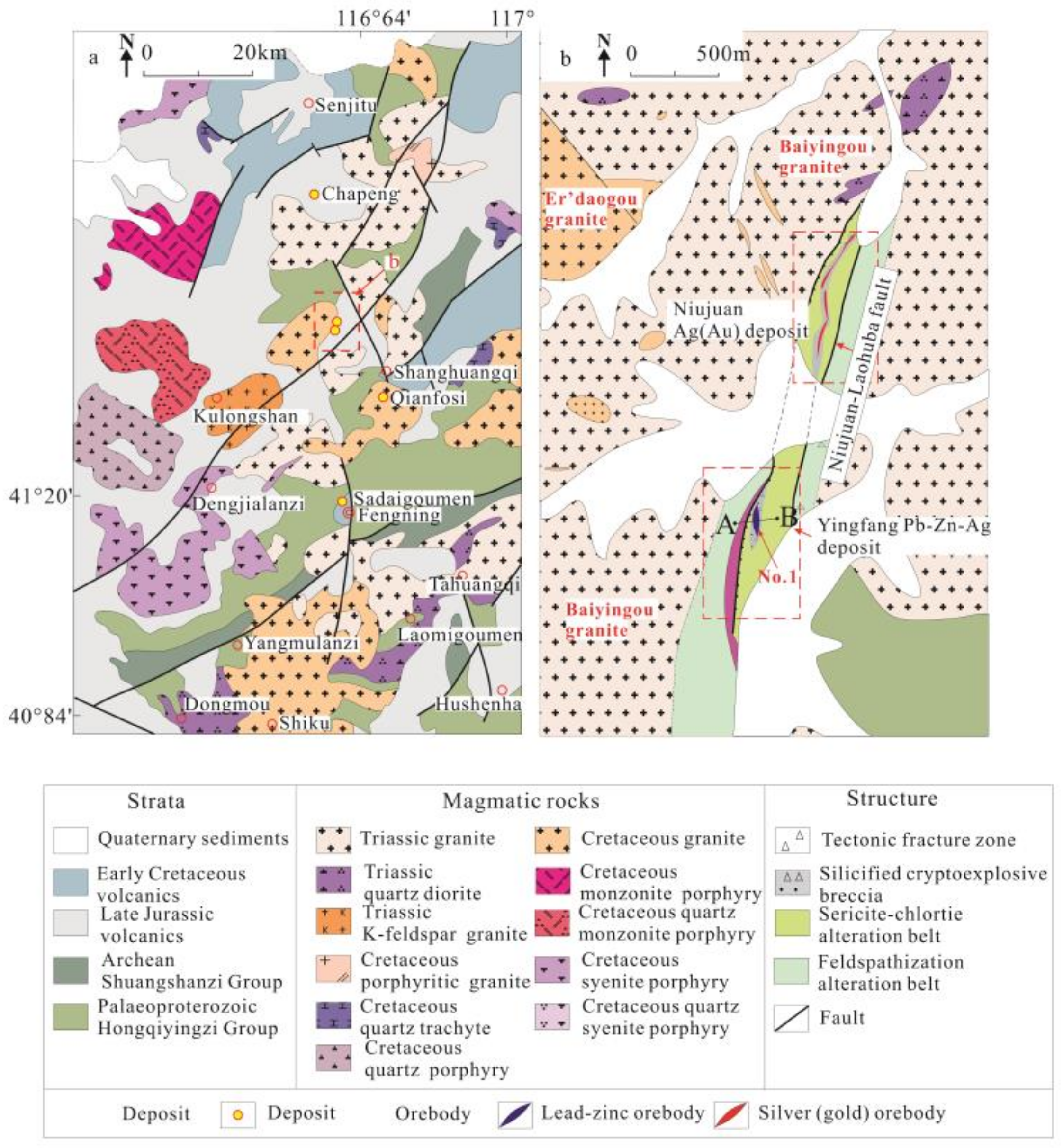
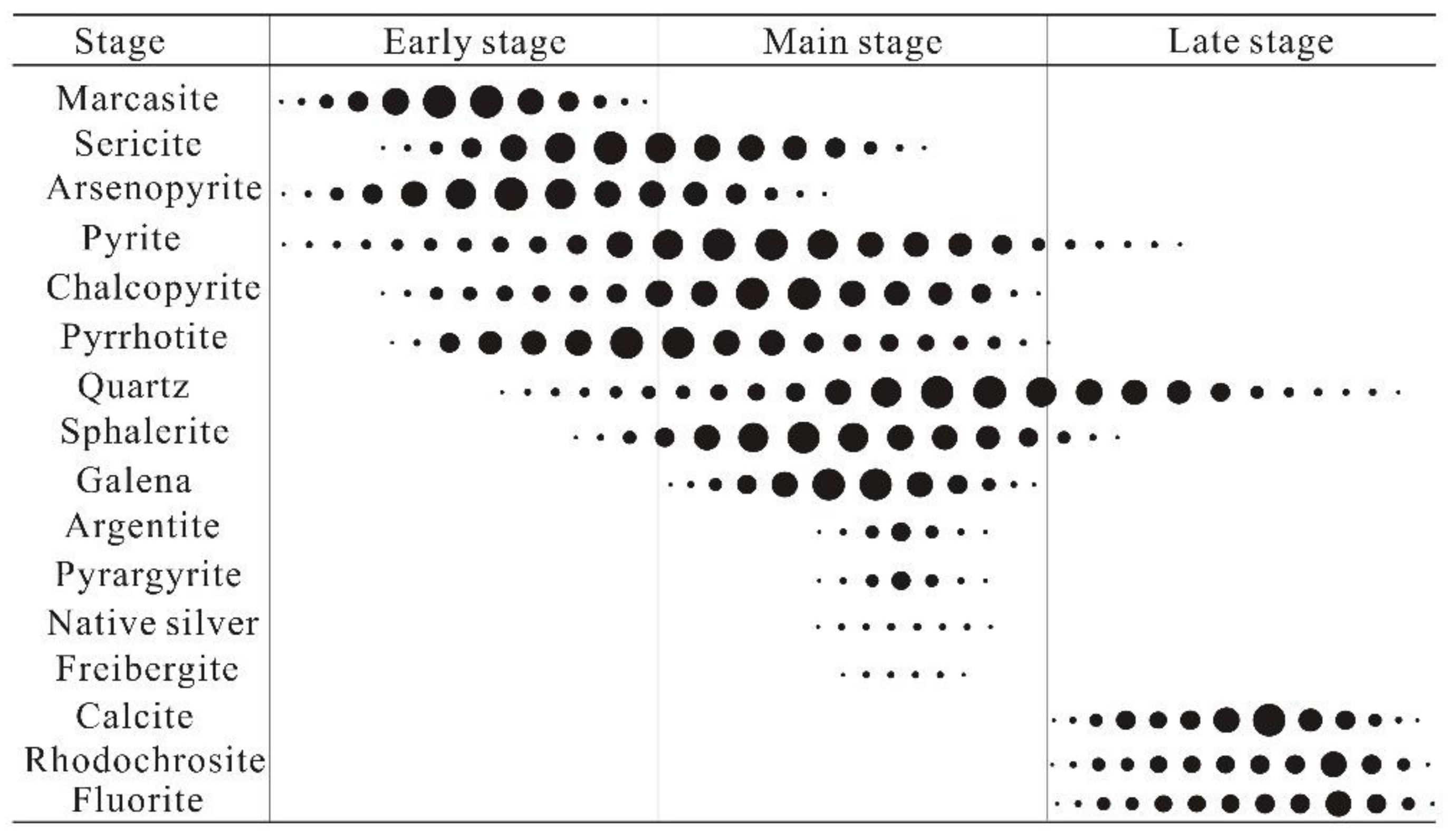
3. Orefield Geology
4. Sampling and Analytical Methods
4.1. Sampling
4.2. Analytical Methods
4.2.1. Rubidium-Strontium Isotopes
4.2.2. Sulfur and Lead Isotopic Analyses
5. Analytical Results
5.1. Rb-Sr Isochron Age
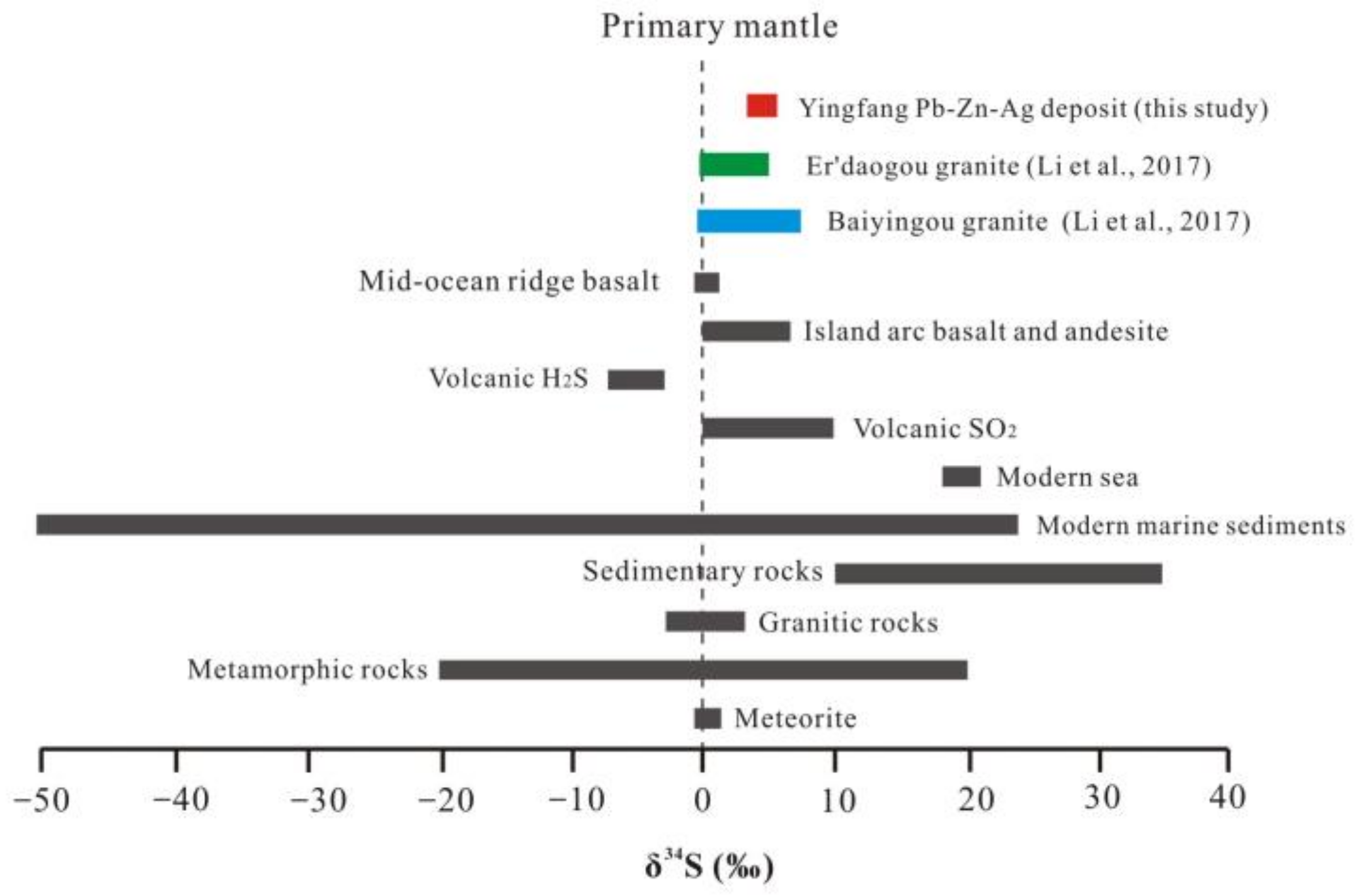
5.2. S and Pb Isotope Systematics
6. Discussion
6.1. Timing of Ore Mineralization
6.2. Origin of the Ore-Forming Constituents
6.3. Comparison with Other Deposits in the YLMB along the Northern Flank of the North China Craton (NCC)
6.4. The Tectonic Setting and Metallogenic Model
7. Conclusions
- The Rb-Sr isochron age of sulfides from the Yingfang deposit obtained in this study mark the timing of mineralization as 135.7 ± 4.1 Ma, and the ore-forming materials were primarily derived from crust, with minor input of mantle materials.
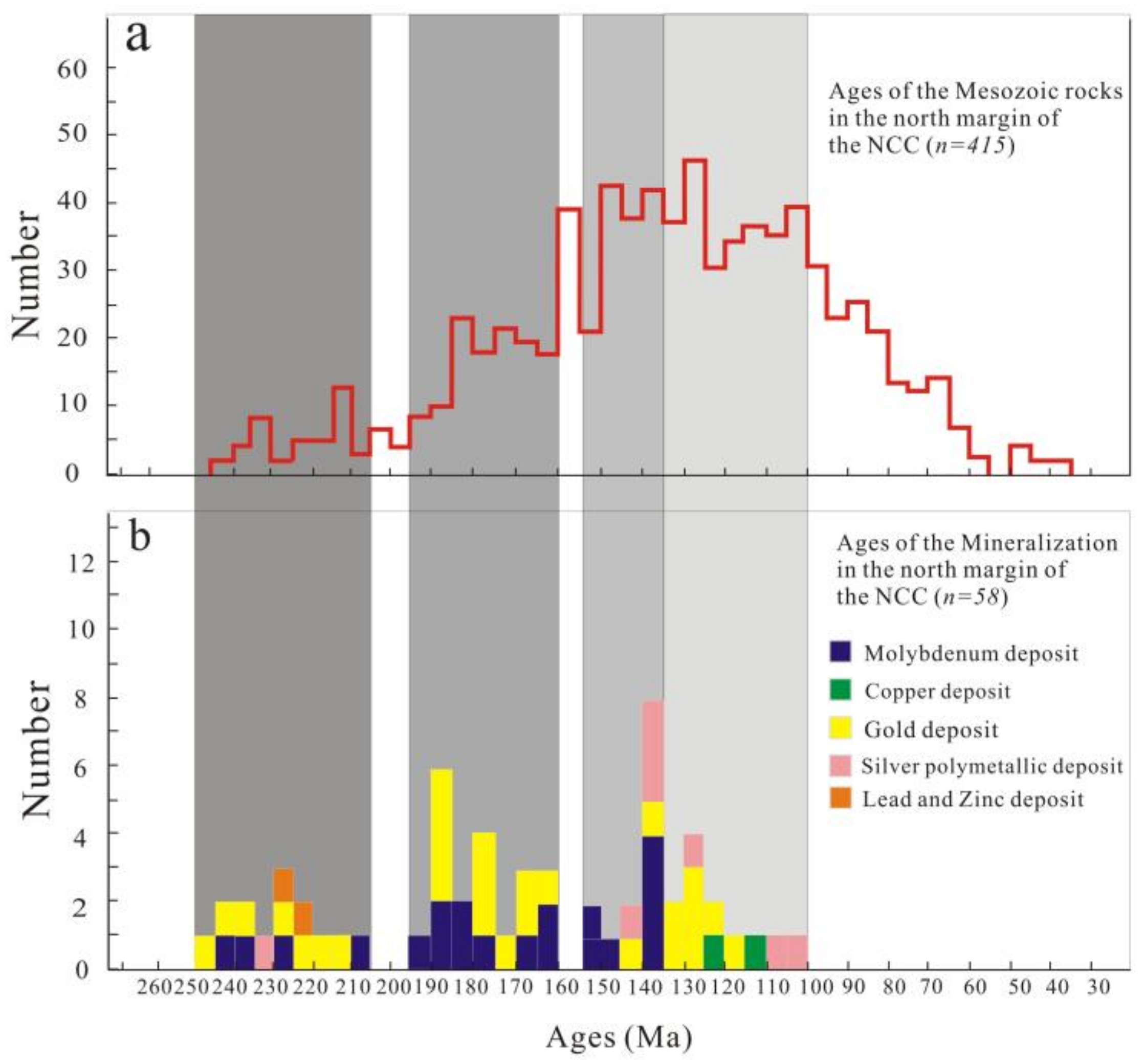
- Mesozoic magmatism and mineralization in the Yingfang deposit mainly took place at 245 and 145–135 Ma. The Pb-Zn-Ag mineralization is related to large-scale inhomogeneous lithosphere thinning beneath the NCC.
- The silver polymetallic deposits in the YLMB possess similar sources of ore-forming materials.
- The Mesozoic mineralization events in the northern flank of the NCC can be divided into the following four periods: 240–205 Ma, 190–160 Ma, 155–135 Ma, and 135–100 Ma.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mao, D.B.; Zhong, C.T.; Chen, Z.H.; Hu, X.D. On the metollogenic aspects of Pb-Zn-Ag deposits in the middle north flank of north china block. Prog. Precambrian Res. 2002, 25, 105–112, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.R.; Santosh, M. Metallogeny and craton destruction: Records from the North China Craton. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 376–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.R.; Santosh, M. Geodynamics of heterogeneous gold mineralization in the North China Craton and its relationship to lithospheric destruction. Gondwana Res. 2017, 50, 267–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Xue, C.J.; Wang, D.H.; Li, H.Q.; Lu, Y.F. A discussion on the regional mineralizing pedigree of the ore deposits in the northern flank of the North China. Geol. J. China Univ. 2003, 9, 520–535, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Peng, R.M.; Zhai, Y.S. Hydrothermal Mineralization on the Mesoproterozoic Passive Continental Flanks of China: A Case Study of the Langshan-Zhaertaishan Belt, Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2004, 78, 534–547. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, S.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, J. Re-Os and U-Pb geochronology of the Songbei porphyry-skarn Mo deposit, North China Craton: Implications for the Early Jurassic tectonic setting in eastern China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 181, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.C.; Cawood, P.A.; Wilde, S.A.; Sun, M.; Lu, L.Z. Metamorphism of basement rocks in the Central Zone of the North China Craton: Implications for Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution. Precambrian Res. 2000, 103, 55–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosh, M. Assembling North China Craton within the Columbia supercontinent: The role of double-sided subduct ion. Precambrian Res. 2010, 178, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.Z.; Mao, J.W.; Zhao, C.; Xie, G.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y. New U-Pb and Re-Os age data and the geodynamic setting of the Xiaojiayingzi Mo (Fe) deposit, western Liaoning province, Northeastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2009, 35, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.D. Ore Forming Geological Characteristics and Scientific Prospecting for Silver Deposits in North Hebei Province. Ph.D. Thesis, Central South University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2000. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.M. Silver Deposits and Their Metallogenic Geodynamics Setting in Yanshan Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeastern University, Shenyang, China, 2006. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.M.; Ye, Q.; Liu, W.J.; Wang, Z. Discussion on metallogenic regularities and dynamics of Mesozoic endogenous non-ferrous metals of Northern Hebei. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2011, 25, 98–104, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.J.; Li, S.R.; Mo, X.X.; Santosh, M. Isotope geochemistry and geochronology of the Niujuan silver deposit, northern North China Craton: Implications for magmatism and metallogeny in an extensional tectonic setting. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 90, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.X.; Li, W.S.; Wang, Z.L.; Ma, J.X.; Li, C.Y. Forecast for the deep mineralization of niujuan silver-gold deposit and yingfang silver-lead-zinc deposit in northern hebei province. Contrib. Geol. Miner. Resour. Res. 2012, 4, 450–457, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Chen, B.; Duan, X.X.; Wang, Z.Q. Geochronology and Ore Genesis of the Niujuan-Yingfang Pb-Zn-Ag Deposit in Fengning, Northern North China Craton: Constraints from Fluid Inclusions, H-O-S Isotopes and Fluorite Sr-Nd Isotopes. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2021, 32, 81–102. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Quan, H.; Han, Q.Y.; Ai, Y.F.; Lin, Y.C. The Features and Prospects of Metallogenesis of Polymetals, Gold and Silver in Yan-Liao Area of China; Geology Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1992; pp. 59–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Cope, T.D.; Lin, Y. Out-of-sequence thrusting in polycyclic thrust belts: An example from the mesozoic Yanshan belt, North China Craton: Out-of-sequence thrusting in the Yanshan. Tectonics 2016, 35, 2082–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Q.; Zheng, T. Destruction of the north China Craton. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 1565–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Zhu, R.X.; Santosh, M.; Ying, J.F.; Su, B.X.; Hu, Y. Episodic widespread magma underplating beneath the North China Craton in the Phanerozoic: Implications for craton destruction. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.B.; Zhong, C.T.; Chen, Z.H.; Hu, X.D. Structural analysis of metallogenic geological attributes for Pb-Zn-Ag deposits in northern Hebei province. Earth Sci. J. China Univ. Geosci. 1999, 24, 464–467, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.J.; Wang, J.B.; Wang, Y.W.; Zhu, H.P. Study of metallic fluid of caijiaying Pb-Zn-Ag Deposit. Miner. Depos. 2002, 21, 1037–1040, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.J.; Liu, H.T.; Zhang, D.H. Fluid inclusion’s characteristics of the Niujuan silve deposit in Fengning, Hebei, and its geological significance. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2007, 4, 36–40, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, S.M.; Hu, H.B.; Yang, Y. An analysis of geological age and materials source of the Niujuan Ag-Au polymetallic deposit in Chengde. Geol. China 2014, 41, 951–960, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, F.H.; Liu, H.L.; Zhao, Y.C.; Xie, L.; Xie, G.Q. Rb-Sr Isochron Ages of the Guzigou Pb-Zn-Ag Ore Deposits in the Chengde area, northern Hebei province. Miner. Depos. 2014, 33, 271–272. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Davis, G.A.; Zheng, Y.D.; Wang, C. Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Yanshan folds and thrust belt, with emphasis on Hehei and Liaoning Provinces, Northern China. GSA Memoir. 2001, 194, 171–197. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, H. Nonferrous metallic deposits in the northern Hebei Province–western Liaoning Province area. In Geology and Nonferrous Metallic Deposits in the Northern Flank of the North China Landmass and Its Adjacent; Rui, Ed.; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1994; pp. 383–471. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.G.; Wu, Z.H.; Cui, S.Q. Features of Mesozoic magmatic activities in the Yanshan area and their relations to intracontinental orogenesis. Geol. Rev. 1999, 45, 163–172, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.C.; Wang, C.G.; Feng, G.Q.; Li, Y.Q.; Song, Y.C.; Jia, G.N. Prospecting of Yangjiazhangzi ore deposit area. Miner. Depos. 2002, 21, 435–438. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.L.; Fan, P.; Zheng, Z.F.; Li, A.L. The Yangjiazhangzi-Bajiazi molybdenumpolymetal metallogenic belt in western Liaoning province: Characteristics of typical molybdenum deposits and prediction for exploration. Geol. Resour. 2009, 18, 110–115, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wong, W.H. The Mesozoic orogenic movements in eastern China. Geol. Bull. China 1929, 8, 33–44. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. The Mesozoic orogenic and tectonic evolution of the Yanshan area. Geol. Rev. 1990, 36, 1–13, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Xu, G.; Yang, Z.Y.; Hu, J.M. The Jurassic major tectonic events of the Yanshanian intraplate deformation belt. Geol. Bull. China 2004, 23, 854–862. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.X.; Yang, J.D.; Chen, J. The Sr and Nd isotopic variations of the Chinese Loess Plateau during the past 7 Ma: Implications for the East Asian winter monsoon and source areas of loess. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2007, 249, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesenmann, A.; Jäger, H.J.; Norman, A.L.; Krouse, H.R.; Brand, W.A. On-line sulfur-isotope determination using an elemental analyser coupled to a mass spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 2816–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. User’s Manual for Isoplot/EX Version 3.0. A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel; Berkeley Geochronology Center: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2003; Volume 4, pp. 1–71. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, T.; Darbyshire, D. Fluid inclusion Rb–Sr isochrons for dating mineral deposits. Nature 1981, 290, 578–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannon, J.C.; Podosek, F.A.; Mclimans, R.K. Alleghenian age of the Upper Mississippi Valley zinc-lead deposit determined by Rb-Sr dating of sphalerite. Nature 1992, 356, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, S.; Halliday, A.N.; Kesler, S.E.; Jones, H.D.; Kyle, J.R.; Lane, T.E. Rb–Sr dating of sphalerites from Mississippi Valley-type (MVT) ore deposits. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Chen, F.K.; Yang, J.H.; Fan, H.R. Single grain pyrite Rb-Sr dating of the Linglong gold deposit, eastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2008, 34, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.G.; Wu, G.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.F.; Luo, D.F. Rb-Sr isochron age of the Jiawula Pb-Zn-Ag deposit in the Manzhouli area and its geological significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 257–270, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.Y.; Li, S.R.; Santosh, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.J. Isotope geochemistry and geochronology of the Qiubudong silver deposit, central North China Craton: Implications for ore genesis and lithospheric dynamics. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 57, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Wang, G.G.; Chen, H.; Xu, Y.F.; Guan, S.J.; Pan, J.Y. An Early Paleozoic orogenic gold belt along the Jiang-Shao Fault, South China: Evidence from fluid inclusions and Rb-Sr dating of quartz in the Huangshan and Pingshui deposits. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 103, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.B.; Bagas, L.; Xing, S.W.; Zhang, S.T.; Wang, R.J.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Zou, Y.-F.; et al. Genesis of the stratiform Zhenzigou Pb, Zn deposit in the North China Craton: Rb-Sr and C-O-S-Pb isotope constraints. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 79, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, S.R.; Santosh, M.; Zhu, J.; Suo, X.J. Early Jurassic decratonic gold metallogenesis in the Eastern North China Craton: Constraints from S-Pb-C-D-O isotopic systematics and pyrite Rb-Sr geochronology of the Guilaizhuang Te-Au deposit. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 92, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.J.; Li, L.; Li, S.R.; Santosh, M.; Song, Y.X.; Alam, M. Rb–Sr geochronology and geochemistry of pyrite from the Shihu gold deposit, central North China Craton: Implication for the timing and genesis of gold mineralization. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 5779–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.B.; Huang, Z.L.; Xu, D.R.; Chen, J.; Xu, C.; Guan, T. Rb–Sr isotopic method on zinc–lead ore deposits: A review. Geotect. Metall. 2002, 26, 436–441, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Seal, R.R. Sulfur isotope geochemistry of sulfide minerals. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2006, 61, 633–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H. Isotopic properties of sulfur compounds in hydrothermal processes. Geochem. J. 1968, 2, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H.; Rye, R.O. Isotopes of sulfur and carbon. In Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits; Barnes, H.L., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 509–567. [Google Scholar]
- Hoefs, J. Stable Isotope Geochemistry, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 1–201. [Google Scholar]
- Ohmoto, H. Systematics of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits. Econ. Geol. 1972, 67, 551–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Chen, Y.C.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.S.; Qiao, C.J. Geochronology and fluid inclusion study of the Yinjiagou porphyry-skarn Mo-Cu-pyrite deposit in the East Qinling orogenic belt, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 79, 585–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H. Stable isotope geochemistry of ore deposits. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 1986, 16, 491–559. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Chen, J.F. Geochemistry of Stable Isotopes; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 1–316. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.C.; Wang, Z.M. Geotectonic features of Yanshan area in Hebei province. Reg. Geol. Chin. 1983, 3, 39–55, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kiyosu, Y. Sulfur isotopic fractionation among sphalerite, galena and sulfide ions. Geochem. Soc. Jpn. 1973, 7, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, C.S.; Mishra, B. Uniformity in sulfur isotope composition in the orogenic gold deposits from the Dharwar Craton, southern India. Miner. Depos. 2009, 44, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, G. Principles of Isotope Geology, 2nd ed.; Wiley Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 22–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.W.; Zhang, J.M.; Quan, H. The isotopic age of the Hongqiyingzi group in North Hebei province. Reg. Geol. China 1996, 2, 186–192. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Stacey, J.S.; Kramers, J.D. Approximation of terrestrial lead isotope evolution by a two-stage model. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1975, 26, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zartman, R.E.; Doe, B.R. Plumbotectonic—The model. Tectonophysics 1981, 75, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doe, B.R.; Zartman, R.E. Plumbotectonics of the phanerozoic. In Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits; Barnes, H.L., Ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 22–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, M.L.; Jiang, S.Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Ling, H.F. S-Pb isotope geochemistry and Rb-Sr geochronology of the Penglai gold field in the eastern Shandong Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 2525–2533, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.L. The Study on Metallogenic Series of Hydrocarbon Alkali-Fluids in Devonian in Xicheng Concentrated Mineralization Area, West Qinling, Gansu Province. Ph.D. Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2001; pp. 43–44, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.D.; Niu, S.Y.; Sun, A.Q.; Zhang, J.Z. Deep Sources of Ore-Forming Materials and the Metallogenesis of Mantle Branch Structure; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 1–256. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.F.; Santosh, M.; Li, S.R. He-Ar, S, Pb and O isotope geochemistry of the Dabaiyang gold deposit: Implications for the relationship between gold metallogeny and destruction of the North China Craton. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 116, 103229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.X.; Wang, Y.Z. Geology of Gold Ore Deposits in Hebei; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1994. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Tong, W.J. The geological characteristics and causes of the Guzigou silver polymetallic ore deposit in Chengde. Earth 2015, 6, 50–52, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Changzhi, W.U.; Lianxing, G.U.; Hui, F.; Zheng, Y.C.; Huang, J.H. Molybdenite Re-Os dating of Xintaimen molybdenum deposit in Yanshan-Liaoning metallogenic belt, North China. Miner. Depos. 2009, 28, 313–320, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.H.; Du, A.D.; Wu, C.Y.; Liu, L.S.; Sun, Y.L.; Zou, X.Q. Geochronology of molybdenum (copper) deposits in the north China platform: Re-Os age of molybdenite and its geological significance. Miner. Depos. 1996, 15, 289–297, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chu, S.X. Structure-magma-fluid Evolution and Mineralization of Yangjiazhangzi Molybdenum Ore Field in the Eastern Segment of Yan-liao Molybdenum Metallogenic Belt. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.L.; Ren, Y.S.; Yang, Y.S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.B.; Zhang, J.J.; Nie, W.D.; Wang, A.C.; Qu, W.J. Re-Os isotopic dating of molybdenite from Taipingcun Mo deposit in eastern Hebei and its geological significance. Glob. Geol. 2016, 35, 738–751, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Meng, X.Y.; Wu, F. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of intrusive rocks and its metallogenic significance in Sibozi-Liubozi molybdenum-copper deposit of Qinglong County, Hebei Province. Miner. Depos. 2012, 255–270, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.B.; Liu, J.M.; Ye, J.; Chen, F.K. Chalcopyrite Rb-Sr isochron age dating and its’ ore-forming significance in Shouwangfen copper deposit, Hebei province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2008, 24, 1353–1358, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.C.; Qin, Z.Y.; Lin, X.H.; Zhang, B.H.; Liu, X.B.; Zhang, X.; Guo, P.Z.; Han, F.; Qin, L.; Dai, J.Z. Zircon U-Pb ages of intrusive bodies in Dacaoping molybdenum ore district, Fengning Country, Hebei province. Miner. Depos. 2007, 26, 634–642, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.B.; Li, C.; Ceng, K.; Qu, W.J. Re-Os dating for molybdenite-bearing rock samples: Application in Dazhuangke molybdenum deposit in Beijing. Geoscience 2012, 26, 254–260, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Y. Metallogenic Model and Prospecting Direction Research of Qingchengzi Polymetallic Ore Field in Liaoning Province. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Nie, F.J.; Jiang, S.H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Sm-Nd isotopes of metamorphic volcanic rocks in the Qiaogou area of Beishan, Inner Mongolia. Acta Geol. Sin. 2004, 6, 807–812. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.J.; Liu, J.M.; Liu, H.T.; Sun, X.G.; Zhang, R.B.; Zhang, Z.L.; Qin, F. Study on ore-forming age and ore-forming fluid of Jiguanshan porphyry molybdenum deposit in Inner Mongolia. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2010, 26, 1423–1436. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, J.M.; Zeng, Q.D.; Chu, S.X.; Zhou, L.L.; Wu, G.B.; Gao, Y.Y.; Shen, W.J. Geological characteristics and molybdenite re-os age of Baituyingzi molybdenum copper deposit in eastern Inner Mongolia and its significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2013, 29, 241–254. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Zeng, Q.D.; Qu, W.J.; Liu, J.M.; Sun, X.G.; Zhang, R.B.; Chen, W.J.; Qin, F. Re-Os isotope age of molybdenite from Nianzigou molybdenum deposit in Inner Mongolia and its geological significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2009, 25, 212–218. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.Y.; Li, T.G.; Wu, W.H. Geochronology of Mo-Pb-Zn-Au mineralization system of Caosiyao superlarge porphyry in Xinghe County, Inner Mongolia and its geological significance. Miner. Depos. 2018, 37, 355–370. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Gu, X.X.; Dong, S.Y.; Cheng, W.B.; Huang, Z.Q.; Li, F.L.; Yang, W.L. Zircon U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os ages of Xishadegai molybdenum deposit in Inner Mongolia and their geological significance. Mineral. Petrol. 2011, 31, 33–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Wu, G.; Tao, H.; Wang, G.R.; Li, T.G.; Chen, J.Q.; Yang, N.N. Re_Os Isotope Age and Fluid Inclusion of Molybdenite in Dasuji Porphyry Molybdenum Deposit, Zhuozi County. Inn. Mong. Miner. Depos. 2014, 33, 1251–1267. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.H.; Jin, C.Z.; Li, L.C. 40Ar-39Ar Isotopic Dating for Paishanlou Gold Deposit and its Geological Implication. J. Northeast. Univ. 2008, 29, 1482–1485, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W.R. Contrast Study on Hadamengou Gold Deposit and Jinchanggouliang Gold Deposit, Inner Mongolia. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Miao, L.C.; Fan, W.M.; Zhai, M.G. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of the granitoid intrusions from Jinchanggouliang-Erdaogou gold orefield and its significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2003, 19, 71–80, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.M.; Xing, D.H.; Guo, S.Z.; Peng, Y.D.; Bian, X.F.; Tao, N. Lithogeochemistry and significance of the Xiduimiangou rock body in Jinchanggouliang, Inner Mongolia. Geol. Resour. 2009, 18, 134–139, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.J. Study on Gold Deposits Mineralization in Chifeng-Chaoyang Region, Northern Flank of North Craton. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Wang, R.J.; Nie, F.J.; Hu, J.Z.; Shi, C.L.; Zhang, S. Discovery of Indosinian Mineralization and Its Geological Significance in Jinchangyu Gold Deposit, eastern Hebei Province. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2011, 32, 125–128. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.C.; Ye, H.S.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, X.K.; Lu, D.Y.; Hu, H.B. Re-Os age of molybdenite from the Yu’erya Au deposit in eastern Hebei province and its geological significance. Geol. China 2014, 41, 1565–1576, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.Y.; Ye, H.S.; He, W. Geological characteristics and molybdenite Re-Os isotopic dating of Tangzhangzi gold (molybdenum) deposit in eastern Hebei Province. Miner. Depos. 2014, 33, 1366–1378, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zou, T.; Wang, Y.W.; Wang, J.B.; Zhang, H.Q.; Zhao, L.T.; Xie, H.J. Geochronology of the Xiayingfang Au deposit in eastern Hebei province. Geol. Explor. 2016, 52, 84–97, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Jinxing, B.O.; Chen, J. Geochronology of main intrusive rocks in Daxigou gold deposit, northern Hebei province and their tectonic-metallogenic singnificane. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 90, 1817–1834. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.H.; Nie, F.J. 40Ar/39Ar geochronology study on the alkaline intrusive complex and related gold deposits, northwestern Hebei, China. Geol. Rev. 2000, 46, 621–627, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.W.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, Z.H.; Yu, J.J.; Niu, B.G. Geodynamic settings of Mesozoic large-scale mineralization in the North China and adjacent areas: Implication from the highly precise and accurate ages of metal deposits. Sci. China Ser. D 2003, 46, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, C.J.; Goldfarb, R.J.; Qiu, Y.; Snee, L.; Miller, L.D.; Miller, M.L. Gold deposits of the northern flank of the North China Craton: Multiple late Paleozoic-Mesozoic mineralizing events. Miner. Depos. 2002, 37, 326–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.M.; Li, T.; Deng, J.F.; Su, S.G.; Liu, X.M. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age of the brittle-ductile shear zones in Hougou gold orefield, NW Hebei Province. Geotecton. Metallog. 2012, 36, 157–167, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.X.; Luo, G.L. 40Ar/39Ar ages of gold-bearing quartz veins and their geological significance in typical gold deposits of Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua gold field, Hebei province. Sci. Geol. Sin. 1994, 29, 151–158, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.F.; Tang, Z.L.; Luo, Z.H.; Zhao, W.H. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of the Tangzhangzi and Niuxinshan granites in eastern Hebei Province and its geological significance. Geol. Bull. China 2009, 10, 1458–1464. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Chai, P.; Wang, X.J.; Sha, D.M.; Shi, J.M. Re-Os dating of pyrite and its geological significance in Baiyun gold deposit, Liaodong rift valley. Geotecton. Metallog. 2016, 40, 731–738. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.H.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, Z.D.; Zhao, Y.X. On the determination of metallogenic age of gold deposits: A case study of Rb-Sr and U-Pb isotopic age of diagenesis and mineralization in Dandong area. Acta Geol. Sin. 2003, 1, 113–119. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.P.; Ai, Y.F. Discussion on the metallogenic age of Xiaotongjiapuzi gold deposit, Liaoning Province. Miner. Depos. 2002, 21, 53–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.M.; Han, Y.C.; Li, S.M. Formation age and geological significance of Wanquansi silver-gold deposit in Chicheng county, Hebei province. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2018, 39, 474–480. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.H.; Mao, D.B.; Zuo, Y.C.; Li, H.M.; Zhong, C.D.; Xiang, Z.Q. Mesozoic intrusive magmatism-related metallogenetic system in Beichagoumen area. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2004, 25, 224–228, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xue, C.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Lu, Y.F.; Li, H.Q. Metallogenic epochs of Au and Ag deposits in Qingchengzi ore-clustered area, eastern Liaoning Province. Miner. Depos. 2003, 22, 177–184. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Chen, J.F.; Xue, C.J. Geochronological framework and Pb, Sr isotope geochemistry of the Qingchengzi Pb–Zn–Ag–Au orefield, Northeastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2009, 35, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Sun, D.Y.; Ge, W.C.; Zhang, Y.B.; Grant, M.L.; Wilde, S.A.; Jahn, B.M. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.S. Geological Characteristics and Metallogenic Prediction of the Continental Lithosphere in East China and Its Adjugating Areas; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.H.; Wu, F.Y.; Wilde, S.A. A review of the geodynamic setting of large-scale late mesozoic gold mineralization in the north china craton: An association with lithospheric thinning. Ore Geol. Rev. 2003, 23, 125–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; Xie, G.Q.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, X.F.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, C.Q.; Li, Y.F. Mesozoic large-scale metallogenic pulses in North China and corresponding geodynamic settings. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2005, 21, 169–188. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Y. Some new ideas on tectonics of NE China and its neighboring areas. Geol. Rev. 1998, 44, 339–347. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zorin, Y.A. Geodynamics of the western part of the Mongolia-Okhotsk collisional belt, Trans-Baikal region (Russia) and Mongolia. Tectonophysics 1999, 306, 33–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.A.; Wang, C.; Zheng, Y.D.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, C.H.; Gehrels, G.E. The enigmatic Yinshan fold-and-thrust belt of northern China: New views on its intraplate contractional styles. Geology 1998, 26, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.R. What drove late Mesozoic extension of the northern China-Mongolia tract? Tectonophysics 2003, 369, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.F.; Zhao, G.C.; Su, S.G.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.H.; Li, F.N.; Zhao, X.G. Structure overlap and tectonic setting of Yanshan orogenic belt in Yanshan area. Geotecton. Metallog. 2005, 29, 157–165, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jahn, B.M.; Litvinovsky, B.A.; Zanvilevich, A.N.; Reichow, M. Peralkaline granitoid magmatism in the Mongolian–Transbaikalian Belt: Evolution, petrogenesis and tectonic significance. Lithos 2009, 113, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.C.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, M.T.; Huang, K.; Peng, Z. Regional heterogeneous temporal–spatial distribution of gold deposits in the North China Craton: A review. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 5646–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Nie, S. A Phanerozoic palin spastic reconstruction of China and its neighboring regions. In The Tectonic Evolution of Asia; Yin, A., Harrison, T.A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 442–485. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, R.F.; Lu, F.X.; Fan, J.Z. Metallogenic Series and Prospecting of the Metal Deposits in North Flank of the North China Craton; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 1–237. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.Y.; Santosh, M. The building of an Archean microcontinent: Evidence from the North China Craton. Gondwana Res. 2017, 50, 3–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Jahn, B.M.; Wilde, S.A.; Lo, C.H.; Yui, T.F.; Lin, Q.; Ge, W.C.; Sun, D.Y. Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China (I): Geochronology and petrogenesis. Lithos 2003, 66, 241–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Lin, J.Q.; Wilde, S.A.; Zhang, X.O.; Yang, J.H. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in eastern China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 233, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.X.; Chen, L.; Wu, F.Y.; Liu, J.L. Timing, scale and mechanism of the destruction of the North China Craton. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, R.J.; Santosh, M. The dilemma of the Jiaodong gold deposits: Are they unique? Geosci. Front. 2014, 5, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample No. | Mineral | Rb(ug/g) | Sr(ug/g) | 87Rb/86Sr | 87Sr/86Sr | 2σ * | (87Sr/86Sr)i |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9-46-5 | galena | 0.1269 | 1.564 | 0.2374 | 0.711364 | 10 | 0.71091 |
| 9-45-5 | galena | 0.2085 | 1.698 | 0.3621 | 0.711491 | 9 | 0.71080 |
| 9-46-1 | galena | 0.2513 | 1.085 | 0.6802 | 0.712246 | 8 | 0.71094 |
| 9-45-2 | galena | 0.2936 | 0.9142 | 0.9458 | 0.712615 | 11 | 0.71080 |
| 9-45-2 | sphalerite | 0.3927 | 0.2256 | 5.137 | 0.720768 | 9 | 0.71091 |
| Sample No. | Stage | Mineral | δ34SV-CDT (‰) * | δ34SH2S (‰) | 206Pb/204Pb | 207Pb/204Pb | 208Pb/204Pb | μ1 | ω2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9-45-3(g) | Stage Ⅱ | Galena | 3.3 | 2.9 | 16.956 | 15.461 | 37.722 | 9.41 | 41.07 |
| 9-45-3(s) | Stage Ⅱ | Sphalerite | 5.7 | 8.2 | 16.875 | 15.477 | 37.778 | 9.47 | 42.14 |
| 9-46-5(g) | Stage Ⅱ | Galena | 3.7 | 3.3 | 16.886 | 15.468 | 37.747 | 9.44 | 41.8 |
| 9-45-5(g) | Stage Ⅱ | Galena | 3.9 | 3.5 | 16.885 | 15.475 | 37.771 | 9.46 | 42.01 |
| 9-46-1(g) | Stage Ⅱ | Galena | 3.4 | 3.0 | 16.934 | 15.522 | 37.928 | 9.55 | 42.95 |
| 9-45-2(g) | Stage Ⅱ | Galena | 3.3 | 2.9 | 16.833 | 15.374 | 37.448 | 9.25 | 39.66 |
| 9-45-2(s) | Stage Ⅱ | Sphalerite | 5.8 | 8.3 | 16.863 | 15.422 | 37.604 | 9.35 | 40.74 |
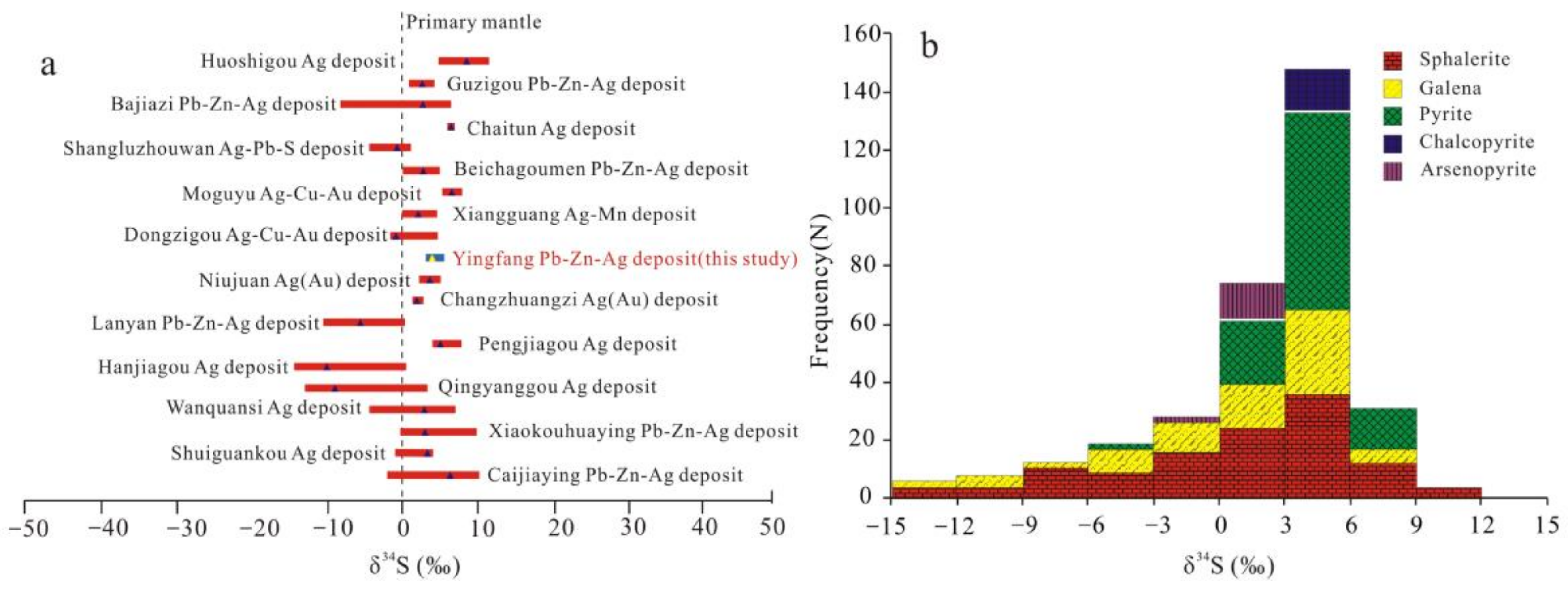
| Deposit | Species | δ34S (‰) | Pb | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean | 206Pb/204Pb | 207Pb/204Pb | 208Pb/204Pb | |||
| Yingfang | Pb-Zn-Ag | 3.2 to 5.8 | +4.07 | 16.89 | 15.46 | 37.71 | This paper |
| Caijiaying | Ag-Pb-Zn | −1.90 to 10.50 | +6.70 | 16.84 | 15.47 | 37.72 | [16] |
| Shuiguankou | Ag | −0.83 to 4.26 | +3.50 | 16.31 | 15.25 | 36.51 | [67] |
| Xiaokouhuaying | Ag-Pb-Zn | −0.13 to 10.14 | 3.20 | 17.15 | 15.34 | 37.39 | [67] |
| Wanquansi | Ag | −4.30 to 7.30 | +3.13 | 16.45 | 15.29 | 36.69 | [67] |
| Qingyanggou | Ag | −12.96 to 3.54 | −8.92 | 16.76 | 15.34 | 36.97 | [67] |
| Hanjiagou | Ag | −14.40 to 0.65 | −10.01 | 17.21 | 15.37 | 37.22 | [67] |
| Pengjiagou | Ag | 4.20 to 8.10 | +5.25 | 16.90 | 15.16 | 37.02 | [67] |
| Lanyan | Ag-Pb-Zn | −10.50 to 0.50 | −5.50 | 16.67 | 15.38 | 37.90 | [10] |
| Changzhuangzi | Ag-Au | 1.50 to 3.00 | +2.10 | 16.34 | 15.19 | 36.22 | [10] |
| Niujuan | Ag-Au | 2.4 to 5.30 | +3.84 | 16.89 | 15.48 | 37.79 | [13] |
| Dongzigou | Ag-Cu-Au | −1.49 to 4.90 | −0.70 | 15.63 | 15.09 | 35.59 | [10] |
| Xiangguang | Ag-Mn | 0.10 to 4.80 | +2.28 | 16.97 | 15.54 | 37.22 | [10] |
| Moguyu | Ag-Cu-Zn | 5.50 to 8.20 | +6.80 | 17.57 | 15.47 | 37.76 | [1] |
| Beichagoumen | Ag-Pb-Zn | 0.20 to 5.20 | +2.94 | 16.57 | 15.02 | 36.25 | [1] |
| Shangluzhouwan | Ag | −4.30 to 1.30 | −0.58 | 16.06 | 14.90 | 36.14 | [1] |
| Bajiazi | Ag-Pb-Zn | −8.20 to 6.70 | +2.90 | 16.27 | 15.23 | 36.46 | [16] |
| Guzigou | Ag-Pb-Zn | 0.89 to 4.32 | +2.68 | 16.37 | 15.20 | 36.43 | [68] |
| Huoshigou | Ag | 5.00 to 11.80 | +8.78 | - | - | - | [10] |
| Chaitun | Ag | 6.4 to 6.9 | +6.70 | - | - | - | [16] |
| Manhantu | Ag-Pb-Zn | - | - | 17.03 | 15.34 | 37.28 | [16] |
| Liujiaying | Ag-Pb-Zn | - | - | 16.38 | 15.22 | 36.73 | [16] |
| No. | Deposit | Mineralization System | Analytical Methods | Analytical Minerals | Age (Ma) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Songbei | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 184 ± 2.0 | [6] |
| 2 | Xintaimen | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 183 ± 3.0 | [69] |
| 3 | Lanjiagou | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 186.5 ± 0.7 | [70] |
| 4 | Yangjiazhangzi | Mo(Pb-Zn) | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 189.7 ± 2.8 | [71] |
| 5 | Bajiazi | Mo(Pb-Zn) | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 204.0 ± 0.5 | [9] |
| 6 | Xiaojiayingzi | Mo(Fe) | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 165.5 ± 4.6 | [9] |
| 7 | Taipingcun | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 164.110 ± 92 | [72] |
| 8 | Sibozi | Mo(Cu) | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 194 ± 1.0 | [73] |
| 9 | Xiaosigou | Cu(Mo) | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 122.83 ± 2.46 | [70] |
| 10 | Shouwangfen | Cu(Fe, Mo) | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 111 ± 5.3 | [74] |
| 11 | Sadaigoumen | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 237.0 ± 3.9 | [75] |
| 12 | Dacaoping | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 137.1 ± 2.6 | [75] |
| 13 | Dazhuangke | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 137.6 ± 3.7 | [76] |
| 14 | Dawan | Mo(Cu) | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 139.7 ± 6.2 | [70] |
| 15 | Yaojiagou | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 164.7 ± 2.3 | [77] |
| 16 | Xinling | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 221.3 ± 3.2 | [77] |
| 17 | Xiaodonggou | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 135.5 ± 1.5 | [78] |
| 18 | Jiguanshan | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 151.1 ± 1.3 | [79] |
| 19 | Kulitu | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 245.0 ± 4.3 | [80] |
| 20 | Nianzigou | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 154.3 ± 3.6 | [81] |
| 21 | Caosiyao | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 145.3 ± 1.0 | [82] |
| 22 | Xishadegai | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 225.4 ± 2.6 | [83] |
| 23 | Dasuji | Mo | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 223.5 ± 5.5 | [84] |
| 24 | Paishanlou | Au | SHRIMP U-Pb | Zircon | 126.1 ± 1.1 | [85] |
| 25 | Siping | Au | Rb-Sr | Quartz | 187 ± 4 | [2] |
| 26 | Jinchanggouliang | Au | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 131.45 ± 0.93 | [86] |
| 27 | Er’daogou | Au | SHRIMP U-Pb | Zircon | 126 ± 2.8 | [87] |
| 28 | Xiaotazigou | Au | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | Zircon | 239 ± 2 | [88] |
| 29 | Jinchangliang | Au | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 245 ± 1 | [89] |
| 30 | Nailingou | Au | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | Zircon | 125.5 ± 0.87 | [89] |
| 31 | Jinchangyu | Au | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 242.6 ± 6.8 | [90] |
| 32 | Toudaomenzigou | Au | 40Ar-39Ar | Potash feldspar | 217.3 ± 2.0 | [91] |
| 33 | Shuiquangou | Au | 40Ar-39Ar | Potash feldspar | 212.5 ± 0.4 | [91] |
| 34 | Yuerya | Au | Rb-Sr | Quartz | 168.4 ± 2.7 | [91] |
| 35 | Tangzhangzi | Au(Mo) | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 170.1 ± 1.6 | [92] |
| 36 | Xiayingfang | Au | Re-Os | Molybdenite | 164.2 ± 2.3 | [93] |
| 37 | Daxigou | Au | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | Zircon | 136.4 ± 0.7 | [94] |
| 38 | Dongping | Au | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | Zircon | 186.8 ± 0.3 | [95] |
| 39 | Dongping | Au | 40Ar-39Ar | Potash feldspar | 177.4 ± 5 | [96] |
| 40 | Zhongshangou | Au | 40Ar-39Ar | Potash feldspar | 131.45 | [97] |
| 41 | Shuijingtun | Au | 40Ar-39Ar | Quartz | 115.1 | [2] |
| 42 | Hougou | Au | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | Zircon | 187.6 ± 0.4 | [98] |
| 43 | Hougou | Au | 40Ar-39Ar | Potash feldspar | 177.6 ± 1.9 | [99] |
| 44 | Huangtuliang | Au | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | Zircon | 187.4 ± 0.3 | [95] |
| 45 | Niuxinshan | Au | 40Ar-39Ar | Quartz | 175.8 ± 3.1 | [100] |
| 46 | Baiyun | Au | Rb-Sr | Sulfides | 225.3 ± 7.0 | [101] |
| 47 | Erdaogou | Au | 40Ar-39Ar | Quartz | 140.6 ± 2.8 | [87] |
| 48 | Wulong | Au | Rb-Sr | Quartz | 120 ± 3 | [102] |
| 49 | Xiaotongjiabuzi | Au | 40Ar-39Ar | Sericite | 167 | [103] |
| 50 | Wanquansi | Ag | Rb-Sr | Sulfides | 144.1 ± 4.0 | [104] |
| 51 | Liangjiagou | Ag | Rb-Sr | Sulfides | 126–131.3 | [98] |
| 52 | Niujuan | Ag-Au | Sm-Nd | Fluorite | 139.2 ± 3.8 | [13] |
| 53 | Yingfang | Pb-Zn-Ag | Rb-Sr | Sulfides | 135.7 ± 4.1 | This study |
| 54 | Beichagoumen | Ag-Pb-Zn | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | Zircon | 138.5 ± 1.3 | [105] |
| 55 | Guzigou | Ag-Pb-Zn | Rb-Sr | Sulfides | 101 ± 4.7 | [24] |
| 56 | Gaojiabuzi | Ag | Rb-Sr | Quartz | 234 ± 14 | [106] |
| 57 | Zhenzigou | Pb-Zn | Rb-Sr | Sphalerite | 221 ± 12 | [107] |
| 58 | Xiquegou | Pb-Zn | Rb-Sr | Pyrite | 225 | [107] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Santosh, M.; Li, Y. Geochronology and Isotope Geochemistry of the Yingfang Pb-Zn-Ag Deposit: Implications for Large-Scale Metallogeny along the Northern Flank of the North China Craton. Minerals 2021, 11, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11040353
Liu X, Li L, Li S, Santosh M, Li Y. Geochronology and Isotope Geochemistry of the Yingfang Pb-Zn-Ag Deposit: Implications for Large-Scale Metallogeny along the Northern Flank of the North China Craton. Minerals. 2021; 11(4):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11040353
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoyan, Lin Li, Shengrong Li, M. Santosh, and Yujie Li. 2021. "Geochronology and Isotope Geochemistry of the Yingfang Pb-Zn-Ag Deposit: Implications for Large-Scale Metallogeny along the Northern Flank of the North China Craton" Minerals 11, no. 4: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11040353
APA StyleLiu, X., Li, L., Li, S., Santosh, M., & Li, Y. (2021). Geochronology and Isotope Geochemistry of the Yingfang Pb-Zn-Ag Deposit: Implications for Large-Scale Metallogeny along the Northern Flank of the North China Craton. Minerals, 11(4), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11040353








