Leaching of Chalcopyrite under Bacteria–Mineral Contact/Noncontact Leaching Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Leaching Bacteria
2.2. Microorganism Culture
2.3. Mineral Sample
2.4. Experimental Procedure
2.5. Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
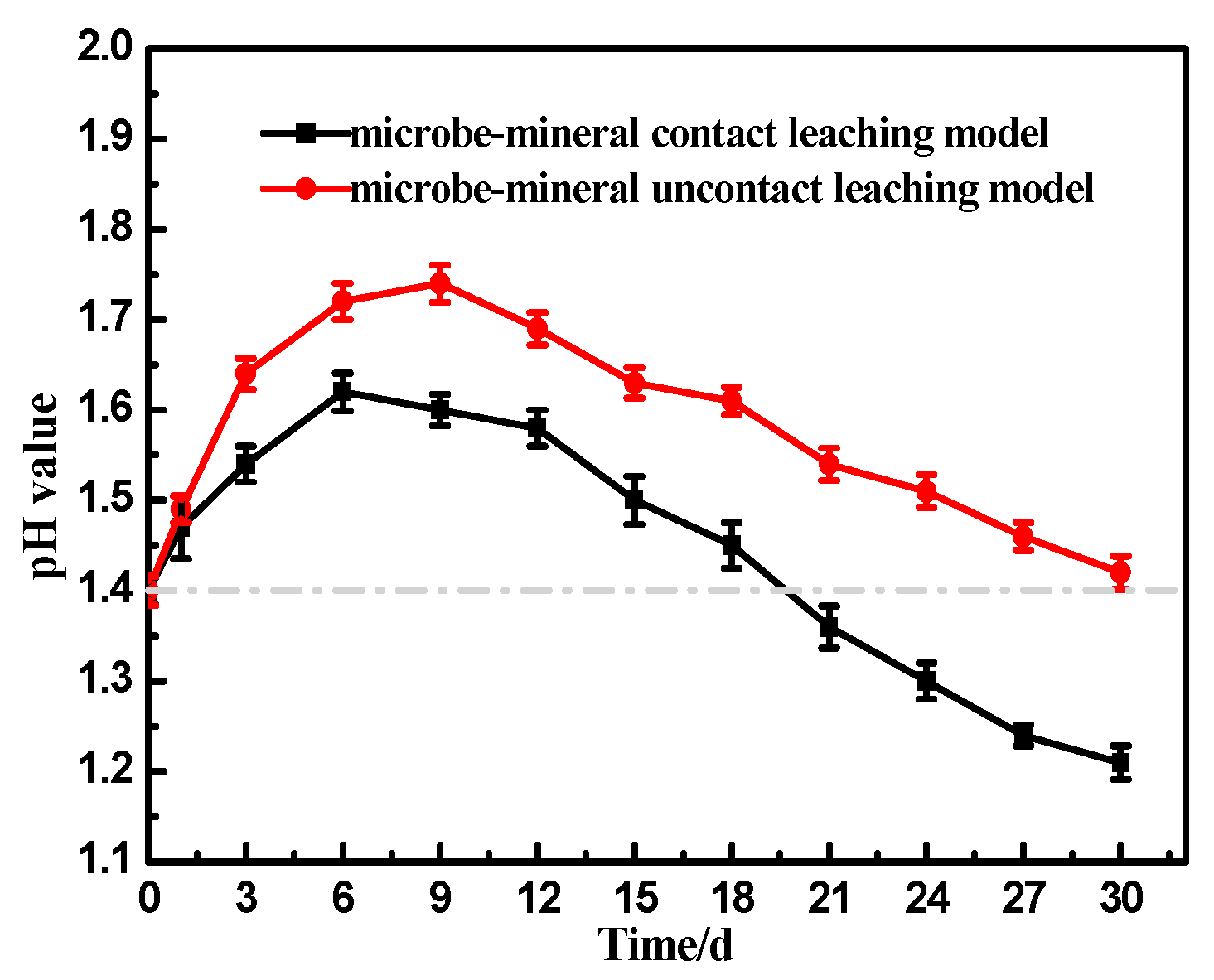
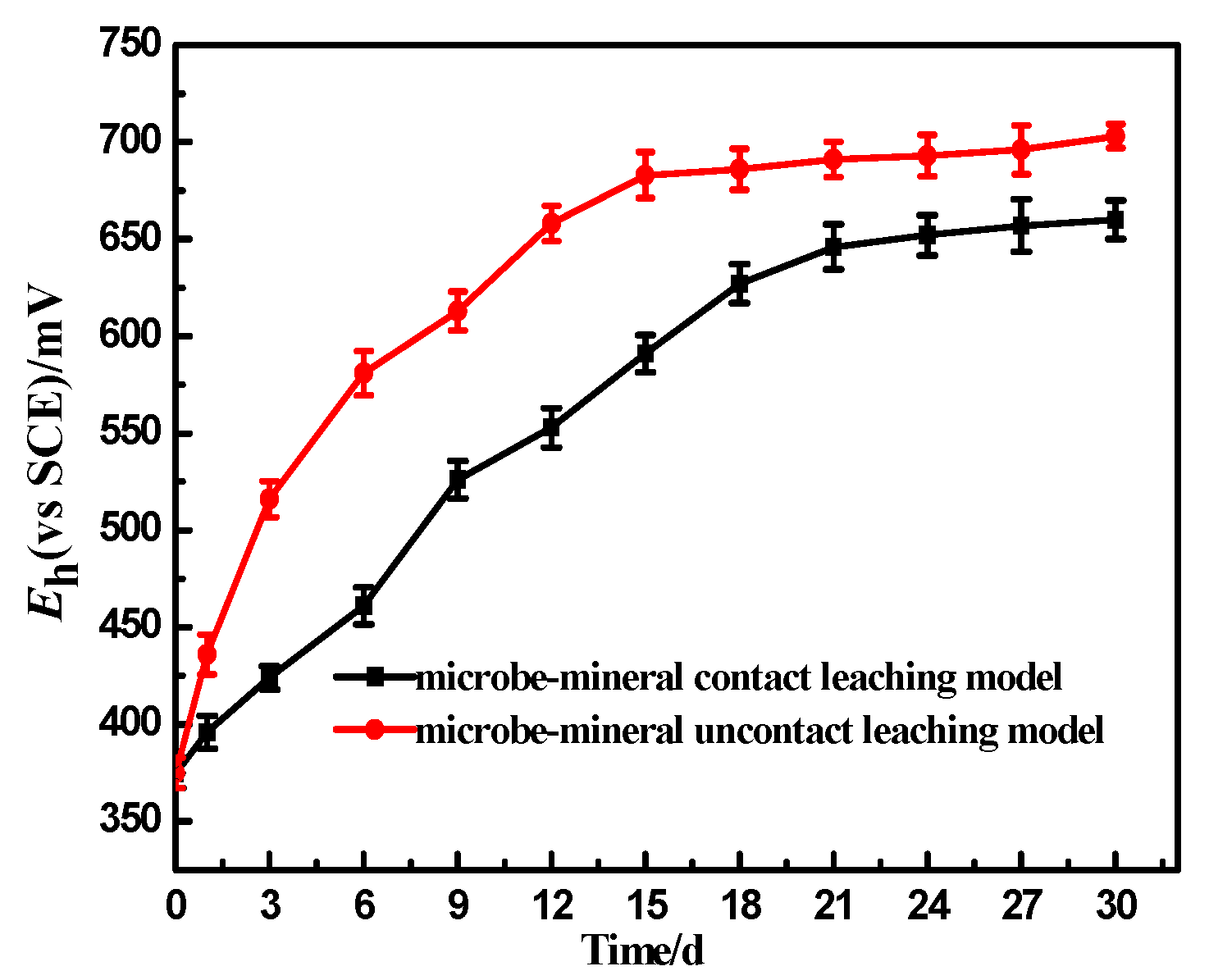
3.1. pH and Potential Change
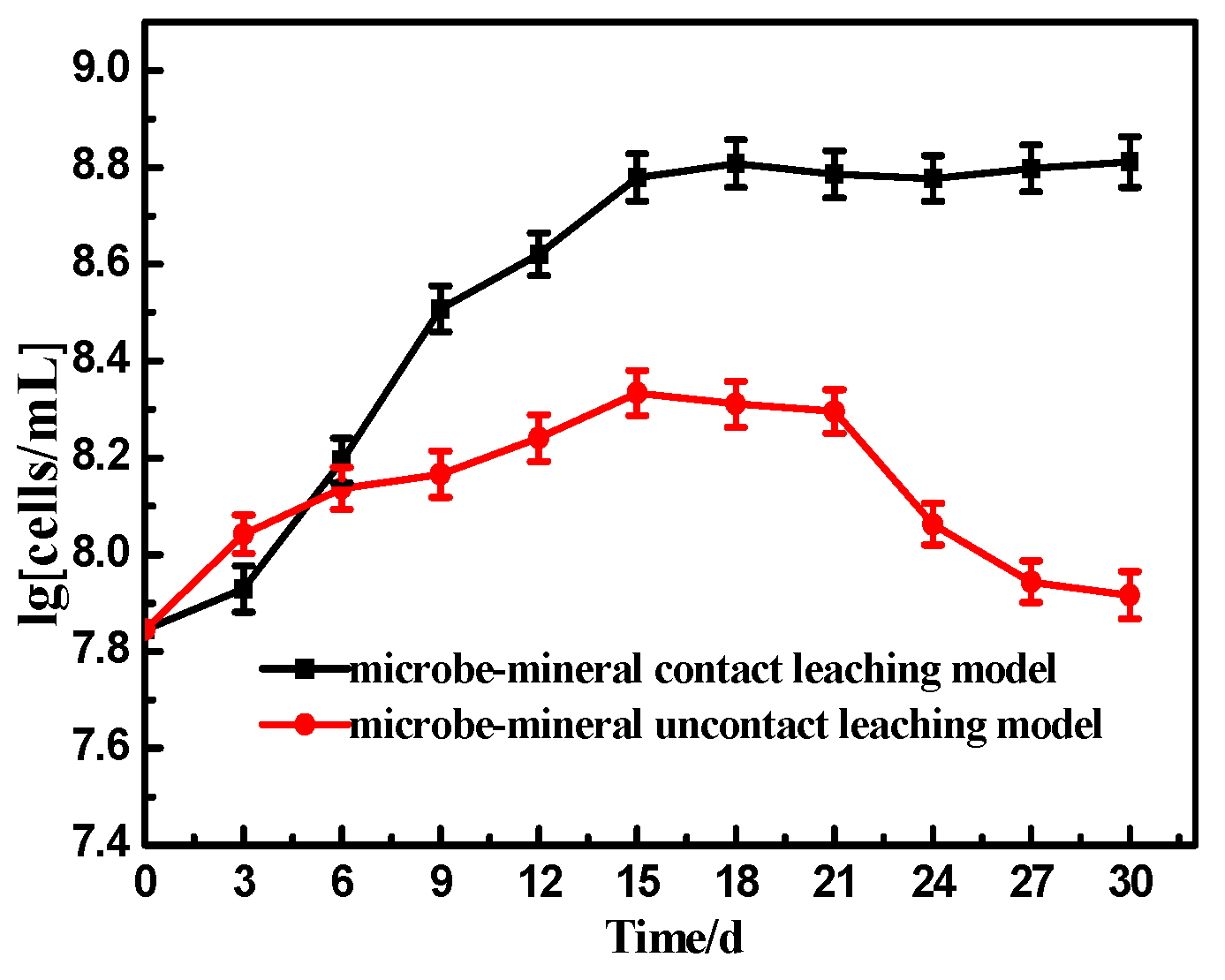
3.2. Bacterial Concentration Change
3.3. Copper Leaching Efficiency
3.4. Discussion
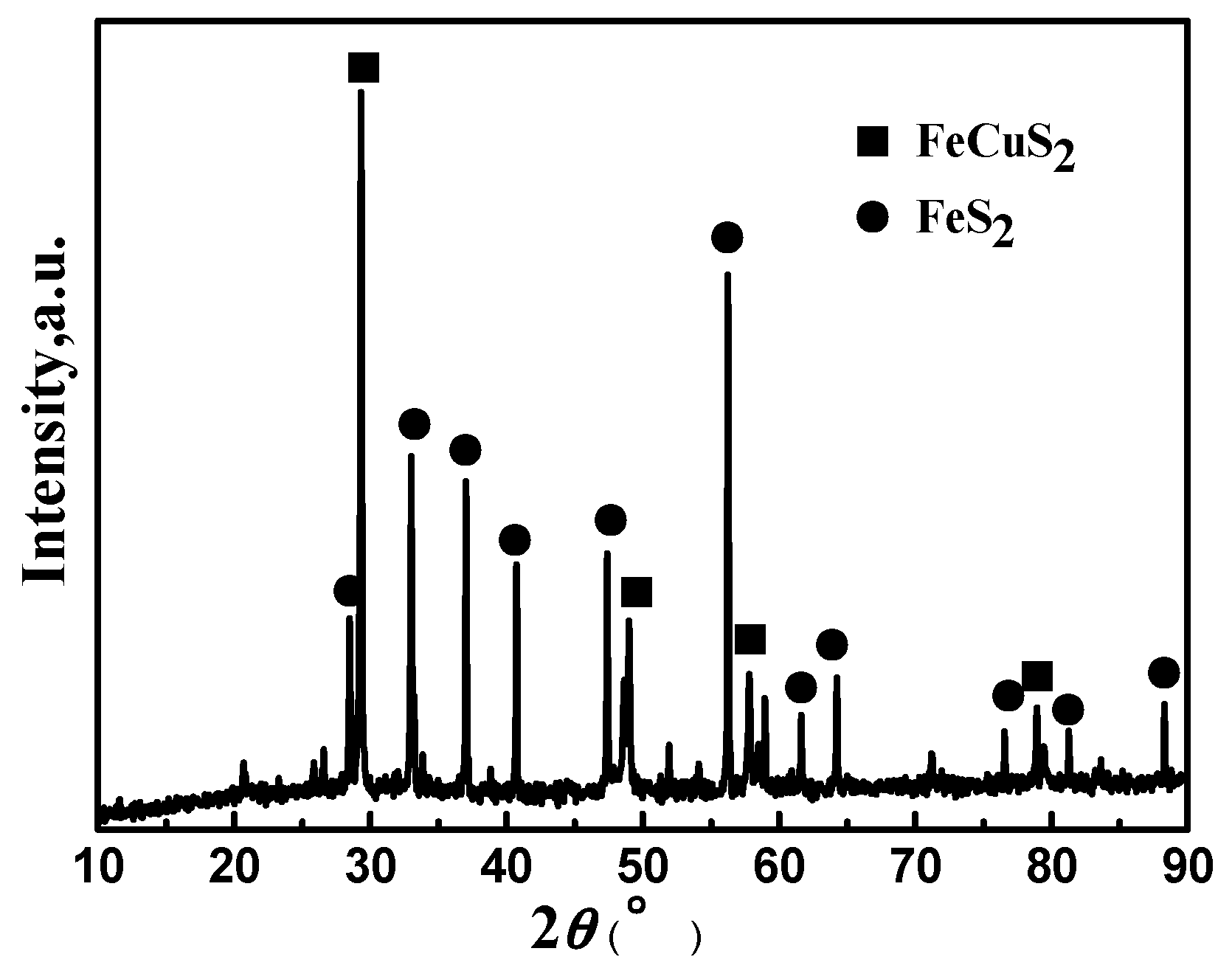
3.4.1. XRD Analysis of Leaching Residue
3.4.2. SEM Analysis of Leaching Residue
3.4.3. FTIR Analysis of Leaching Residue
3.4.4. Model of Bioleaching Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brierley, J.A. Acdidophilic thermophilic archaebacteria: Potential application for metals recovery. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1990, 75, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, J.; Dixon, D.G. Competitive bioleaching of pyrite and chalcopyrite. Hydrometallurgy 2006, 83, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, J.A.; Brierley, C.L. Present and future commercial applications of biohydrometallurgy. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 59, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, M.P.; Ehrlich, H.L. Microbial formation and degradation of minerals. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 1964, 6, 153–206. [Google Scholar]
- Tributsch, H. Direct versus indirect bioleaching. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 59, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crundwell, F.K. How do bacteria interact with minerals? Hydrometallurgy 2003, 71, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, C.L. Biohydrometallurgical prospects. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroyoshi, N.; Kitagawa, H.; Tsunekawa, M. Effect of solution composition on the optimum redox potential for chalcopyrite leaching in sulfuric acid solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 91, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauber, C. A critical review of the surface chemistry of acidic ferric sulphate dissolution of chalcopyrite with regards to hindered dissolution. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2008, 86, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, H.M.; Heimala, S.; Riekkola-Vanhanen, M.L.; Puhakka, J.A. Chalcopyrite concentrate leaching with biologically produced ferric sulphate. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, D.E.; Johnson, B.D. Biomining; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 287–301. [Google Scholar]
- Yohana, R.; Ballester, A.; María, L.B.; Felisa, G.; Jesús, A.M. Study of bacterial attachment during the bioleaching of pyrite, chalcopyrite, and sphalerite. Geomicrobiology 2003, 20, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Harmer, S.; Chen, M. Synchrotron X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study of the chalcopyrite leached by moderate thermophiles and mesophiles. Miner. Eng. 2014, 69, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcil, A.; Ciftci, H.; Deveci, H. Role and contribution of pure and mixed cultures of mesophiles in bioleaching of a pyritic chalcopyrite concentrate. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Schaffie, M.; Manafi, Z.; Ranjbar, M. Electrochemical bioleaching of high grade chalcopyrite flotation concentrates in a stirred bioreactor. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Klauber, C.; Kougianos, A.; Watling, H.R.; Van-Bronswijk, W. An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of the mechanism of oxidative dissolution of chalcopyrite. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 71, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutrizac, J.E. Elemental sulphur formation during the ferric chloride leaching of chalcopyrite. Hydrometallurgy 1990, 23, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremaninezhad, A.; Dixon, D.G.; Asselin, E. Kinetics of the ferric–ferrous couple on anodically passivated chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) electrodes. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 125–126, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Wen, J.; Gao, H.; Wang, D. Chalcopyrite bioleaching by moderate thermophilic bacteria and surface passivation. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2010, 41, 1234–1236. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Yang, H.; Tong, L.; Zhong, C.; Zhao, Y. Control method of chalcopyrite passivation in bioleaching. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 2255–2260. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Pan, H.; Tong, L.; Liu, Y. Formation process of biological oxide film on chalcopyrite crystal surface. Acta Metall. Sin. 2012, 48, 1145–1152. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Lu, J.; Zhu, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, R.; Li, Q.; Xu, Z. Preliminary study on surface properties of iron sulfate formed by microbially Induced mineralization. Geol. J. China Univ. 2005, 2, 194–198. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Henao, D.M.O.; Godoy, M.A.M. Jarosite pseudomorph formation from arsenopyrite oxidation using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Lu, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, R.; Li, Q. SEM study on jarosite mediated by thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Geol. J. China Univ. 2005, 11, 234–238. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Liang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhou, L. Effect of Fe(III) supply rate on the formation of amorphous schwertmannite. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2011, 2, 256–262. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Daoud, J.; Karamanev, D. Formation of jarosite during Fe2+ oxidation by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Konno, H. Morphology of jarosite-group compounds precipitated from biologically and chemically oxidized Fe ions. Can. Mineral. 2000, 38, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Zhou, L.X. Effect of sludge dissolved organic matter on oxidation of ferrous iron and sulfur by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2006, 171, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tong, L.; Xia, Y.; Yang, H.; Auwalu, A. Microbial synergy and stoichiometry in heap biooxidation of low-grade porphyry arsenic-bearing gold ore. Extremophiles 2020, 24, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Yang, H.; Chen, S. Conditions for biosorption measuring on chalcopyrite surface. J. Northeast. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2010, 31, 999–1002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bevilaqua, D.; Lette, A.L.L.C.; Garcia, J.O.; Tuovinen, O.H. Oxidation of chalcopyrite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans in shake flasks. Process Biochem. 2002, 38, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremaninezhad, A.; Asselin, E.; Dixon, D.G. Electrochemical evaluation of the surface of chalcopyrite during dissolution in sulfuric acid solution. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 5041–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauber, C.; Parker, A.; Van-Bronswijk, W.; Watling, H. Sulphur speciation of leached chalcopyrite surfaces as determined by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2001, 62, 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, W.; Gehrke, T. Extracellular polymeric substances mediate bioleaching/biocorrosion via interfacial processes involving iron(III) ions and acidophilic bacteria. Res. Microbiol. 2006, 157, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.A.; Rossman, G.R.; Schugar, H.J.; Gray, H.B. Magnetic behavior and infrared spectra of jarosite, basic iron sulfate, and their chromate analogs. J. Solid State Chem. 1975, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaroff, N.; Sigal, W.; Wasserman, A. Iron oxidation and precipitation of ferric hydroxysulfates by resting Thiobacillus ferrooxidans cells. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 43, 924–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marel, H.W.; Beutelspacher, H. Atlas of Infrared Spectroscopy of Clay Minerals and Their Admixtures; Elsevier Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1976; p. 396. [Google Scholar]


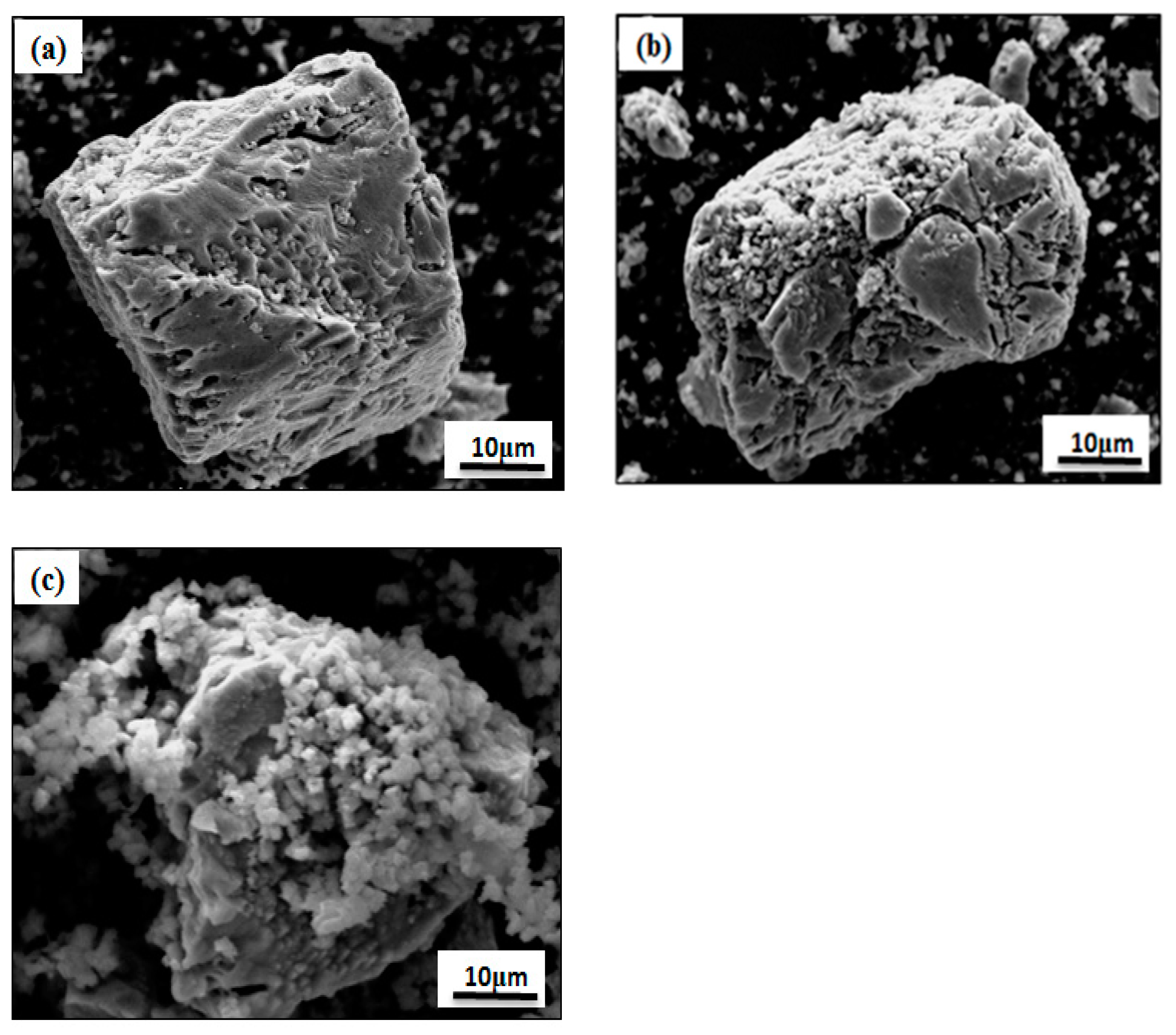
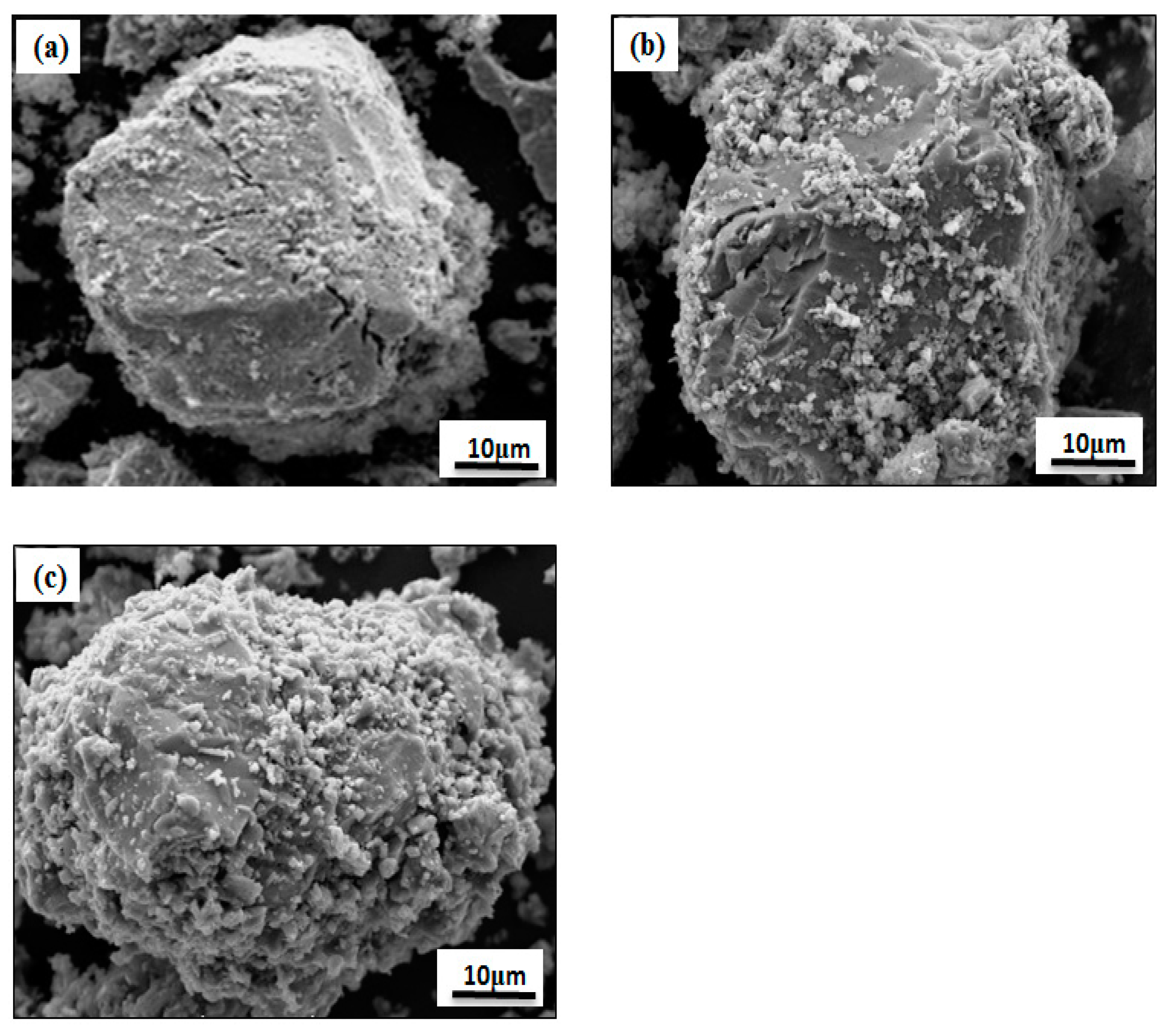
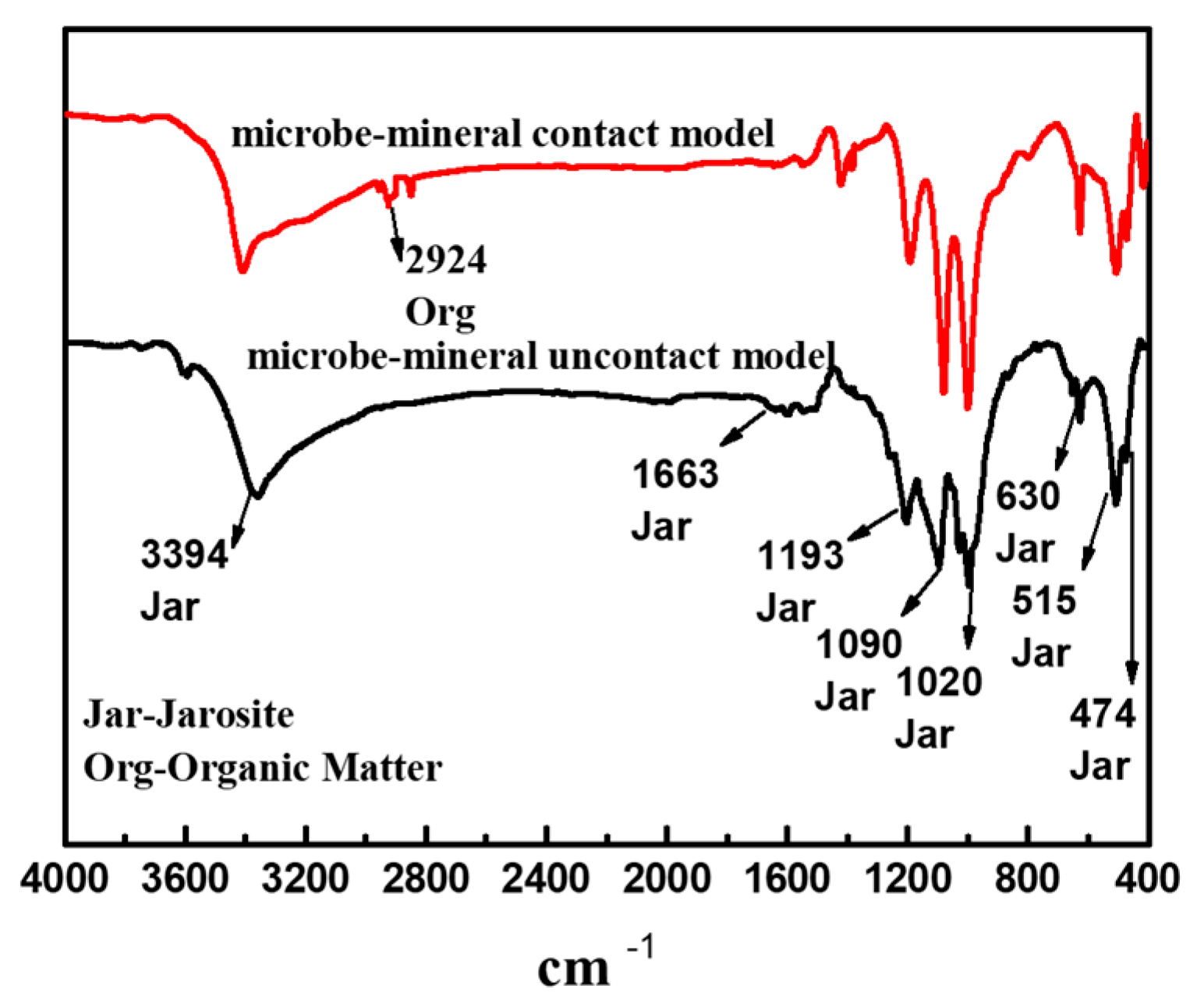
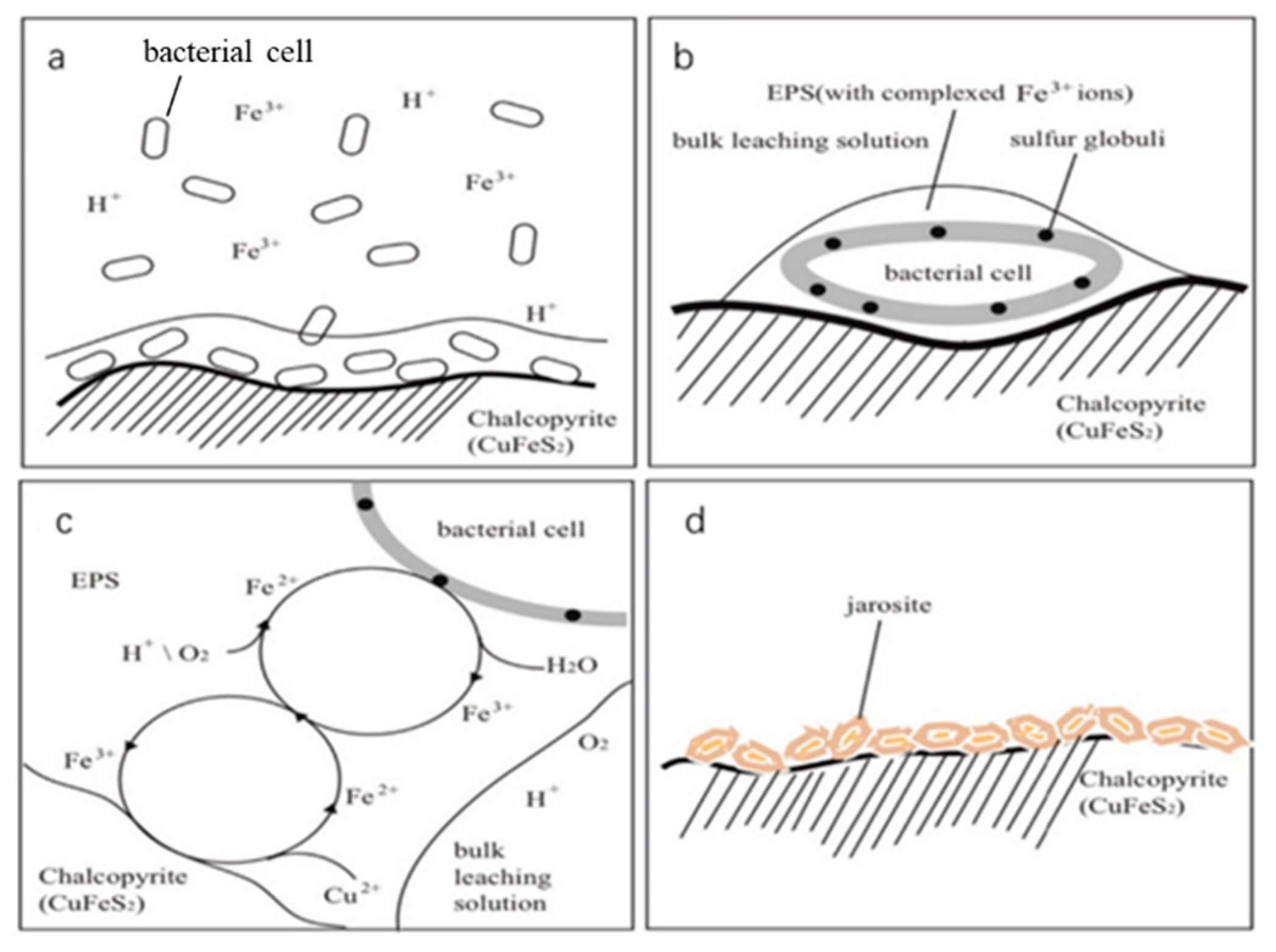
| Element | Cu | Fe | S | SiO2 | CaO | Al2O3 | MgO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content, % | 13.82 | 37.50 | 39.76 | 2.72 | 0.79 | 0.40 | 0.15 |
| Particle Size | >75 μm | 75–45 μm | 45–37 μm | <37 μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content, % | 1.12 | 9.53 | 20.16 | 69.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, P.; Yang, H.; Luan, Z.; Sun, Q.; Ali, A.; Tong, L. Leaching of Chalcopyrite under Bacteria–Mineral Contact/Noncontact Leaching Model. Minerals 2021, 11, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030230
Ma P, Yang H, Luan Z, Sun Q, Ali A, Tong L. Leaching of Chalcopyrite under Bacteria–Mineral Contact/Noncontact Leaching Model. Minerals. 2021; 11(3):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030230
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Pengcheng, Hongying Yang, Zuochun Luan, Qifei Sun, Auwalu Ali, and Linlin Tong. 2021. "Leaching of Chalcopyrite under Bacteria–Mineral Contact/Noncontact Leaching Model" Minerals 11, no. 3: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030230
APA StyleMa, P., Yang, H., Luan, Z., Sun, Q., Ali, A., & Tong, L. (2021). Leaching of Chalcopyrite under Bacteria–Mineral Contact/Noncontact Leaching Model. Minerals, 11(3), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030230





