Natural and Anthropogenic Origin of Metals in Lacustrine Sediments; Assessment and Consequences—A Case Study of Wigry Lake (Poland)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Laboratory Research
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology. Experientia Supplementum; Luch, A., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 101, pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Trace Elements in Human Nutrition and Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/37931 (accessed on 19 January 2021).
- Sharma, R.K.; Agrawal, M. Biological effects of heavy metals: An overview. J. Environ. Biol. 2005, 26, 301–313. [Google Scholar]
- Bernhoft, R.A. Mercury Toxicity and Treatment: A Review of the Literature. J. Environ. Public Health 2012, 460508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assi, M.A.; Hezmee, M.N.M.; Haron, A.W.; Sabri, M.Y.M.; Rajion, M.A. The detrimental effects of lead on human and animal health. Vet. World 2016, 9, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmytryk, A.; Tuhy, Ł.; Samoraj, M.; Chojnacka, K. Biological Functions of Cadmium, Nickel, Vanadium, and Tungsten. In Recent Advances in Trace Elements; Chojnacka, K., Saeid, A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, S.J. What Is a “Heavy Metal”? J. Chem. Educ. 1997, 74, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffus, J.H. “Heavy metals”—A meaningless term? (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, R.; Astin, K.B.; Herbert, R.J.H. ‘Heavy metal’—time to move on from semantics to pragmatics? J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E. What are heavy metals? Long-standing controversy over the scientific use of the term ‘heavy metals’—proposal of a comprehensive definition. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2018, 100, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, R.H. Metalloids. J. Chem. Educ. 1982, 59, 526–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.R.; Marshall, W.J. Heavy metal poisoning and its laboratory investigation. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1999, 36, 267–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, R.E. Which Elements Are Metalloids? J. Chem. Educ. 2013, 90, 1703–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.M.; Holtzmann, M. Heavy metal—music, not science. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomons, W.; Förstner, U. Metals in the Hydrocycle; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, P.W. The regulation of heavy metal concentrations in natural aquatic systems. In Heavy Metals in the Environment; Vernet, J.-P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 95–123. [Google Scholar]
- Belzunce Segarra, M.J.; Helios-Rybicka, E.; Prego, R. Distribution of heavy metals in the River Ulla and its estuary (North-West Spain). Oceanol. Stud. 1997, 26, 139–152. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, F.; Jiantong, L.; Bangding, X.; Xiaoguo, C.; Xiaoqing, X. Mobilization Potential of Heavy Metals: A Comparison between River and Lake Sediments. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2005, 161, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerregaard, P.; Andersen, C.B.I.; Andersen, O. Ecotoxicology of Metals—Sources, Transport, and Effects on the Ecosystem. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, 4th ed.; Gunnar, F.N., Fowler, B.A., Nordberg, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 425–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquery, M.; Welbourn, P.M. The relationship between metal concentration and organic matter in sediments and metal concentration in the aquatic macrophyte Eriocaulon septangulare. Water Res. 1995, 29, 2094–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bilali, L.; Rasmussen, P.E.; Hall, G.E.M.; Fortin, D. Role of sediments composition in trace metal distribution in lake sediments. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasby, G.P.; Szefer, P.; Geldon, J.; Warzocha, J. Heavy-metal pollution of sediments from Szczecin Lagoon and the Gdansk Basin, Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 330, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.Y.; Aris, A.Z.; Zakaria, M.P. Spatial Variability of Metals in Surface Water and Sediment in the Langat River and Geochemical Factors That Influence Their Water-Sediment Interactions. Sci. World J. 2012, 652150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Paul, S.C.; Shaari, F.I.; Rak, A.E.; Ahmad, R.B.; Kadir, W.R. Geostatistical Distribution and Contamination Status of Heavy Metals in the Sediment of Perak River, Malaysia. Hydrology 2019, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, K.; Mohan, V.R.; Szefer, P. Evaluation of metal contamination in coastal sediments of the Bay of Bengal, India: Geochemical and statistical approaches. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylmann, W.; Łysek, K.; Kinder, M.; Pempkowiak, J. Regional Pattern of Heavy Metal Content in Lake Sediments in Northeastern Poland. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 216, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriata-Potasznik, A.; Szymczyk, S.; Skwierawski, A.; Glińska-Lewczuk, K.; Cymes, I. Heavy Metal Contamination in the Surface Layer of Bottom Sediments in a Flow-Through Lake: A Case Study of Lake Symsar in Northern Poland. Water 2016, 8, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matys Grygar, T.; Popelka, J. Revisiting geochemical methods of distinguishing natural concentrations and pollution by risk elements in fluvial sediments. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 170, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.A., Jr. Assessing the toxicity of freshwater sediments. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1991, 10, 1585–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riba, I.; García-Luque, E.; Blasco, J.; DelValls, T.A. Bioavailability of heavy metals bound to estuarine sediments as a function of pH and salinity values. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2003, 15, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlf, W.; Drost, W.; Heise, S. Incorporation of metal bioavailability into regulatory frameworks—metal exposure in water and sediment. J. Soils Sediments 2009, 9, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonge, M.; Teuchies, J.; Meire, P.; Blust, R.; Bervoets, L. The impact of increased oxygen conditions on metal-contaminated sediments part I: Effects on redox status, sediment geochemistry and metal bioavailability. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, A.; Li, M.; Zhang., X. Effect of pH, Temperature, Dissolved Oxygen, and Flow Rate of Overlying Water on Heavy Metals Release from Storm Sewer Sediments. J. Chem. 2013, 434012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Z.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.; Cui, F.; Zhu, M.; Shen, L.; Hu, L. Effects of sediment geochemical properties on heavy metal bioavailability. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paiva Magalhães, D.; da Costa Marques, M.R.; Baptista, D.F.; Buss, D.F. Metal bioavailability and toxicity in freshwaters. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Håkanson, L. An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control. A Sedimentological Approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, R.; Stoner, J.H. Pb in Particulates from the Lower Atmosphere of the Eastern Atlantic. Nature 1973, 245, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoller, W.H.; Gladney, E.S.; Duce, R.A. Atmospheric Concentrations and Sources of Trace Metals at the South Pole. Science 1974, 183, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, M. The Importance of Enrichment Factor (EF) and Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo) to Evaluate the Soil Contamination. J. Geol. Geophys. 2016, 5, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimoh, A.; Agbaji, E.B.; Ajibola, V.O.; Funtua, M.A. Application of Pollution Load Indices, Enrichment Factors, Contamination Factor and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals Pollution of Soils of Welding Workshops at Old Panteka Market, Kaduna-Nigeria. Open J. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 4, 011–019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loska, K.; Cebula, J.; Pelczar, J.; Wiechuła, D.; Kwapiliński, J. Use of Enrichment, and Contamination Factors Together with Geoaccumulation Indexes to Evaluate the Content of Cd, Cu, and Ni in the Rybnik Water Reservoir in Poland. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1997, 93, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malsiu, A.; Shehu, I.; Stafilov, T.; Faiku, F. Assessment of Heavy Metal Concentrations with Fractionation Method in Sediments and Waters of the Badovci Lake (Kosovo). J. Environ. Public Health 2020, 3098594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keresztesi, Á.; Nita, I.-A.; Birsan, M.-V.; Bodor, Z.; Pernyeszi, T.; Micheu, M.M.; Szép, R. Assessing the variations in the chemical composition of rainwater and air masses using the zonal and meridional index. Atmos. Res. 2020, 237, 104846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzebońska, M.; Gruszecka-Kosowska, A.; Kostka, A. Chemistry and Microbiology of Urban Roof Runoff in Kraków, Poland with Ecological and Health Risk Implications. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłos, A.; Rajfur, M.; Wacławek, M. Application of enrichment factor (EF) to the interpretation of results from the biomonitoring studies. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2011, 18, 171–183. [Google Scholar]
- Reimann, C.; de Caritat, P. Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for elements in the environment: Regional geochemical survey versus enrichment factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 337, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matschullat, J.; Ottenstein, R.; Reimann, C. Geochemical background—can we calculate it? Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobelo-García, A.; Prego, R. Heavy metal sedimentary record in a Galician Ria (NW Spain): Background values and recent contamination. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; Filzmoser, P.; Garret, R.G. Background and threshold: Critical comparison of methods of determination. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 346, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gałuszka, A. Different Approaches in Using and Understanding the Term “Geochemical Background”—Practical Implications for Environmental Studies. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2007, 16, 389–395. [Google Scholar]
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.M. Geochemical background—an environmental perspective. Mineralogia 2011, 42, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, T.T.T.; Cappuyns, V.; Swennen, R.; Phung, N.K. From geochemical background determination to pollution assessment of heavy metals in sediments and soils. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bábek, O.; Matys Grygar, T.; Faměra, M.; Hron, K.; Nováková, T.; Sedláček, J. Geochemical background in polluted river sediments: How to separate the effects of sediment provenance and grain size with statistical rigour? Catena 2015, 135, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Z.; Xu, F.; Jiang, Z.; Li, A.; Yin, X. Environmental background values of trace elements in sediments from the Jiaozhou Bay catchment, Qingdao, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turekian, K.K.; Wedephol, K.H. Distribution of the Elements in Some Major Units of the Earth’s Crust. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1961, 72, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.A., Jr. Sediment quality criteria in use around the world. Limnology 2002, 3, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.L.; MacDonald, D.D.; Keenleyside, K.A.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Field, L.J. A Preliminary Evaluation of Sediment Quality Assessment Values for Freshwater Ecosystems. J. Great Lakes Res. 1996, 22, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.D.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Berger, T.A. Development and Evaluation of Consensus-Based Sediment Quality Guidelines for Freshwater Ecosystems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Połujański, A. Wandering around the Augustów Governorate for Research Purposes; Drukarnia Gazety Codziennej: Warszawa, Poland, 1859. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Kulwieć, K. Lake Wigry Physiography Materials. Pamiętnik Fizyograficzny 1904, 18, 1–42. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Lityński, A. General data on the Wigry lakes complex. Sprawozdania Stacji Hydrobiologicznej na Wigrach 1922, 1, 11–14. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Lityński, A. Limnological studies on Wigry Lake. I. Limnographic part. Archiwum Hydrobiologii i Rybactwa 1926, 1, 1–78. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Dembowska, S.; Dembowski, J. Morphometric measurements of Wigry lakes complex. 1. Uklejowa Bay and Białe Lake. Archiwum Hydrobiologii i Rybactwa 1922, 1, 15–21. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Dembowska, S.; Dembowski, J. Morphometric measurements of Wigry lakes complex. 2. Wigierki Bay. Archiwum Hydrobiologii i Rybactwa 1924, 1, 7–9. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Dembowska, S.; Dembowski, J. Morphometric measurements of Wigry lakes complex. 3. Eastern part of Wigierki Bay. Archiwum Hydrobiologii i Rybactwa 1927, 2, 160–165. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Stangenberg, M. Chemical Composition of Deep Sediments in the lakes of Suwałki Region; Rozprawy i Sprawozdania, Instytut Badawczy Lasów Państwowych: Warszawa, Poland, 1938. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Stangenberg, M. Nitrogen and carbon in the bottom-deposits of lakes and in the soils under carp-ponds. Verh. Int. Ver. Limnol. 1949, 10, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, J.I. Bottom sediments of the lakes of various trophic type. Ekol. Pol. A 1969, 17, 611–662. [Google Scholar]
- Czeczuga, B.; Gołębiewski, Z. Ecological changes in Wigry Lake in the post-glacial period. Part I. Chemical investigations. Polskie Archiwum Hydrobiologii 1976, 23, 189–205. [Google Scholar]
- Czeczuga, B.; Kossacka, W. Ecological changes in Wigry Lake in the post-glacial period. Part II. Investigations of the Cladoceran stratigraphy. Polskie Archiwum Hydrobiologii 1977, 24, 259–277. [Google Scholar]
- Woroniecka-Stasiak, A. Chemical composition of interstitial waters in bottom sediments of some Polish lakes of the Wigry group (Northern Poland). Acta Hydrobiol. 1980, 22, 347–360. [Google Scholar]
- Falk, K.O. Wigry and Huta Waters–Toponomastic Study; Almqvist & Wiksell: Uppsala, Sweden, 1941. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Kamiński, M. Lake Wigry, the lake “adopted” by International Association of Theoretical and Applied Limnology (SIL “Lake Adoption” Project). Pol. J. Ecol. 1999, 47, 215–224. [Google Scholar]
- Król, K. Obituary—Prof. Jacek Rutkowski (1934–2016). Geochronometria 2017, 44, 1-1. [Google Scholar]
- Niewolak, S. The Evaluation of the Contamination Degree and the Sanitary and Bacteriological State of the Waters in the Czarna Hańcza River in the Region of Suwałki and Wigry National Park. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 1998, 7, 229–241. [Google Scholar]
- Niewolak, S. Evaluation of Pollution and the Sanitary-Bacteriological State of Lake Wigry, Poland. Part I. Pelagic Waters of Lake Wigry. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 1999, 8, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Niewolak, S. Evaluation of Pollution and the Sanitary-Bacteriological State of Lake Wigry, Poland. Part II. Near-shore Waters of Lake Wigry. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 1999, 8, 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Niewolak, S. Bacteriological Monitoring of Lake Water in Wigry National Park in the Summer. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 1999, 8, 231–249. [Google Scholar]
- Niewolak, S. Bacteriological Monitoring of River Water Quality in the North Area of Wigry National Park. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2000, 9, 291–299. [Google Scholar]
- Niewolak, S.; Opieka, A. Potentially Pathogenic Microorganisms in Water and Bottom Sediments in the Czarna Hańcza River. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2000, 9, 183–194. [Google Scholar]
- Niewolak, S. The Evaluation of the Degree of Pollution and Sanitary-Bacteriological State of Surface Water in Wigry Lake, North-East Poland. Part III. Waters of Hanczanska Bay and the Areas Adjoing Wigry Lake. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2001, 10, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrowicz, W.P. The malacofauna of the upper Holocene lacustrine sediments of Wigry Lake (N Poland). Folia Malacol. 2000, 8, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brzeziński, T.; Kołodziejczyk, A. Distribution of Potamopyrgus antipodarum (Gray, 1843) in waters of the Wigry National Park (NE Poland) and the effect of selected habitat factors on its occurrence. Folia Malacol. 2001, 9, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czeczuga, B.; Kozłowska, M. Fertility of Eudiaptomus, Bosmina and Daphnia (Crustacea) Representatives in Lake of Varied Trophic States in the Suwałki District. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2002, 11, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlyta, J.; Pazdur, A.; Piotrowska, N.; Poręba, G.; Sikorski, J.; Szczepanek, M.; Król, K.; Rutkowski, J.; Hałas, S. Isotopic investigations of uppermost sediments from Lake Wigry (NE Poland) and its environment. Geochronometria 2004, 23, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kupryjanowicz, M. Postglacial Development of Vegetation in the Vicinity of the Wigry Lake. Geochronometria 2007, 27, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paprocka, A. Stable Carbon and Oxygen Isotopes in Recent Sediments of Lake Wigry, NE Poland: Implications for Lake Morphometry and Environmental Changes. Terrestrial Ecol. 2007, 1, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, N.; Hajdas, I.; Bonani, G. Construction of the Calendar Timescale for Lake Wigry (NE Poland) Sediments on the Basis of Radiocarbon Dating. Radiocarbon 2007, 49, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zawisza, E.; Szeroczyńska, K. The Development History of Wigry Lake as Shown by Subfossil Cladocera. Geochronometria 2007, 27, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzymulska, D.; Żurek, S. Subfossil vegetation of near-shores mires from the vicinity of the Wigry Lake (NE Poland). In Proceedings of the 12th International Palynological Congress (IPC-12), Bonn, Germany, 30 August–5 September 2008; pp. 70–71. [Google Scholar]
- Rutkowski, J.; Aleksander-Kwaterczak, U.; Prosowicz, D.; Żurek, S.; Piotrowska, N.; Krzysztofiak, L. On paleo-Wigry Lake (NE Poland) and its sediments covered contemporary by peats. In Anthropogenic and Natural Transformations of Lakes; Bajkiewicz-Grabowska, E., Borowiak, D., Eds.; Department of Limnology, University of Gdańsk, Polish Limnological Society: Gdańsk, Poland, 2008; Volume 2, pp. 167–169. [Google Scholar]
- Drzymulska, D.; Fiłoc, M.; Kupryjanowicz, M. Reconstruction of landscape paleohydrology using the sediment archives of three dystrophic lakes in northeastern Poland. J. Paleolimnol. 2014, 51, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, J.; Król, K.; Krzysztofiak, L.; Prosowicz, D. Recent sediments of the Wigry Lake (Bryzgiel Basin). Limnol. Rev. 2002, 2, 353–362. [Google Scholar]
- Rutkowski, J.; Rudowski, S.; Pietsch, K.; Król, K.; Krzysztofiak, L. Sediments of Lake Wigry (NE Poland) in the light of high-resolution seismic (seismoacoustic) survey. Limnol. Rev. 2002, 2, 363–371. [Google Scholar]
- Rutkowski, J.; Król, K.; Krzysztofiak, L.; Prosowicz, D. Recent sediments of Wigry Lake (Szyja Basin), NE Poland. Limnol. Rev. 2003, 3, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Rutkowski, J. Sediments of Wigry Lake. Rocznik Augustowsko-Suwalski 2004, IX, 19–37. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Rutkowski, J.; Pietsch, K.; Król, K.; Rudowski, S.; Krzysztofiak, L. High-resolution seismic survey in the Wigry Lake (NE Poland). Peribalticum 2005, 9, 147–162. [Google Scholar]
- Osadczuk, A.; Rutkowski, J.; Krzysztofiak, L. Variability of southern part of Lake Wigry bottom (NE Poland) in the light of survey using the Rox-Ann acoustic system. Prace Komisji Paleogeografii Czwartorzędu PAU 2006, III, 179–185. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Rutkowski, J.; Król, K.; Szczepańska, J. Lithology of the Profundal Sediments in Słupiańska Bay (Wigry Lake, NE Poland)—Introduction to Interdisciplinary Study. Geochronometria 2007, 27, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rutkowski, J.; Prosowicz, D.; Aleksander-Kwaterczak, U.; Krzysztofiak, L. Profundal sediments of Wigry Lake (NE Poland). In Anthropogenic and Natural Transformations of Lakes; Bajkiewicz-Grabowska, E., Borowiak, D., Eds.; Department of Limnology, University of Gdańsk, Polish Limnological Society: Gdańsk, Poland, 2008; Volume 2, pp. 171–173. [Google Scholar]
- Prosowicz, D.; Helios-Rybicka, E. Trace metals in recent bottom sediments of Lake Wigry (Bryzgiel Basin). Limnol. Rev. 2002, 2, 323–332. [Google Scholar]
- Migaszewski, Z.M.; Gałuszka, A.; Pasławski, P. Baseline versus background concentrations of trace elements in sediments of Lake Wigry, NE Poland. Limnol. Rev. 2003, 3, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Migaszewski, Z.M.; Gałuszka, A.; Pasławski, P. The use of the barbell cluster ANOVA design for the assessment of environmental pollution: A case study, Wigierski National Park, NE Poland. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 133, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosowicz, D. Trace Metals and Their Chemical Forms of Bonding in Bottom Sediments of Lake Wigry. Ph.D. Thesis, AGH University of Science and Technology, Kraków, Poland, 2006. (In Polish). [Google Scholar]
- Aleksander-Kwaterczak, U.; Prosowicz, D. Distribution of Cd and Pb in the lake sediments cores from the Hańczańska Bay (Wigry Lake, NE Poland). Limnol. Rev. 2007, 7, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Helios-Rybicka, E.; Kostka, A. Distribution of Fe, Mn and Zn in Bottom Sediments of Wigierskie Basin—Wigry Lake (NE Poland). Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2007, 16, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Kostka, A.; Prosowicz, D.; Helios-Rybicka, E. Use of GIS for Spatial Analysis of Heavy Metals Distribution in the Bottom Sediments of Wigry Lake (NE Poland). Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2008, 17, 307–312. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksander-Kwaterczak, U.; Prosowicz, D.; Rutkowski, J.; Szczepańska, J. Changes of Selected Micro-Pollution Concentrations in the Long Carbonate Sediment Cores of the Southern Part of Wigry Lake (NE Poland). Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2009, 18, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Kostka, A. Assessment of Spatial Variability of Trace Metals in Bottom Sediments of Lake Wigry Using GIS Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, AGH University of Science and Technology, Kraków, Poland, 2009. (In Polish). [Google Scholar]
- Aleksander-Kwaterczak, U.; Kostka, A. Lead in the environment of Lake Wigry (NE Poland). Limnol. Rev. 2011, 11, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostka, A.; Leśniak, A. Spatial and geochemical aspects of heavy metal distribution in lacustrine sediments using the example of Lake Wigry (Poland). Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksander-Kwaterczak, U.; Kostka, A.; Leśniak, A. Multiparameter assessment of select metal distribution in lacustrine sediments. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 512–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, J. Simple gravity sampler for taking cores from lake sediments. In Anthropogenic and Natural Transformation of Lakes; Kubiak, J., Bajkiewicz-Grabowska, E., Eds.; Agricultural University of Szczecin, Polish Limnological Society: Szczecin, Poland, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 108–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey, M.H.; Thompson, M.; Hale, M. Objective evaluation of precision requirements for geochemical analysis using robust analysis of variance. J. Geochem. Explor. 1992, 44, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, M.H. Sampling and analytical quality control (SAX) for improved error estimation in the measurement of Pb in the environment using robust analysis of variance. Appl. Geochem. 1993, 8, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LKSD-1 to LKSD-4 Lake Sediment Samples; CCRMP, CANMET Mining and Mineral Sciences Laboratories: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2003; Available online: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/sites/www.nrcan.gc.ca/files/mineralsmetals/pdf/mms-smm/tect-tech/ccrmp/cer-cer/lksd-1-eng.pdf (accessed on 19 January 2021).
- Burrough, P.A.; McDonnell, R.A. Principles of Geographical Information Systems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksander-Kwaterczak, U.; Zdechlik, R. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of interstitial water and overlying water in the lacustrine environment. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stumm, W.; Baccini, P. Man-Made Chemical Perturbation of Lakes. In Lakes: Chemistry, Geology and Physics; Lerman, A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 91–126. [Google Scholar]
- Helios-Rybicka, E. Phase-specific bonding of heavy metals in sediments of the Vistula River, Poland. Appl. Geochem. 1993, 2, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helios-Rybicka, E.; Jędrzejczyk, B. Preliminary studies on mobilisation of copper and lead from contaminated soils and readsorption on competing sorbents. Appl. Clay Sci. 1995, 10, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prego, R.; Bezlunce Segarra, M.J.; Helios-Rybicka, E.; Barciela, M.C. Cadmium, manganese, nickel and lead contents in surface sediments of the lower Ulla River and its estuary (northwest Spain). Bol. Inst. Esp. Oceanogr. 1999, 15, 495–500. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffery, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metals levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstner, U.; Ahlf, W.; Calmano, W.; Kersten, M. Sediment criteria development. Contributions from environmental geochemistry to water quality management. In Sediments and Environmental Geochemistry: Selected Aspects and Case Histories; Heling, D., Rothe, P., Förstner, U., Stoffers, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, K. Preliminary results of lacustrine chalk survey from Lake Wigry. Sprawozdania z Czynności i Posiedzeń PAU 1998, LXI, 112–114. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Lis, J.; Pasieczna, A. Geochemical Atlas of Poland on a scale 1:2,500,000; Państwowy Instytut Geologiczny: Warszawa, Poland, 1995. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Balistrieri, L.S.; Murray, J.W.; Paul, B. The cycling of iron and manganese in the water column of Lake Sammamish, Washington. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 510–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, T.; Wehrli, B. Geochemical-Focusing of Manganese in Lake Sediments—An Indicator of Deep-Water Oxygen Conditions. Aquat. Geochem. 1997, 2, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, A.M.; Elatrash, A.M.; Ghattas, N.K. The Co-Precipitation of Manganese by Iron(III) Hydroxide. J. Radioanal. Chem. 1969, 2, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawecki, K.; Zdanowski, B.; Dunalska, J. Seasonal changes in phosphorous concentrations in the waters of Lake Wigry. Limnol. Rev. 2003, 3, 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Zdanowski, B. Precipitation of phosphorus in the zone of river and lake water mixing: R. Hańcza and lake Wigry (North-East Poland). Pol. J. Ecol. 2003, 51, 143–154. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, V.; Martin, M.; Persson, P.; Lerda, C.; Said-Pullicino, D.; Magnacca, G.; Celi, L. Inorganic and organic P retention by coprecipitation during ferrous iron oxidation. Geoderma 2019, 348, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton-Taylor, J.; Davison, W. Redox-driven cycling of trace elements in lakes. In Physics and Chemistry of Lakes; Lerman, A., Imboden, D., Gat, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 217–263. [Google Scholar]
- Łącka, B.; Starnawska, E.; Kuźniarski, M.; Chróst, L. Mineralogy and geochemistry of the Lake Gościąż Holocene sediments. In Lake Gościąż, Central Poland. A Monographic Study; Ralska-Jasiewiczowa, M., Goslar, T., Madeyska, T., Starkel, L., Eds.; W. Szafer Institute of Botany, Polish Academy of Sciences: Kraków, Poland, 1998; pp. 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- Ber, A. Stratigraphy of the Quaternary of the Suwałki Lakeland and its substrate based on recent data. Kwart. Geol. 1989, 33, 463–478. [Google Scholar]
- Fjeld, E.; Rognerud, S.; Steinnes, E. Influence of Environmental Factors on Heavy Metal Concentration in Lake Sediments in Southern Norway Indicated by Path Analysis. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1994, 51, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graney, J.R.; Halliday, A.N.; Keeler, G.J.; Nriagu, J.O.; Robbins, J.A.; Norton, S.A. Isotopic record of lead pollution in lake sediments from the northeastern United States. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1715–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojakowska, I.; Krasuska, J.; Retka, J.; Wiłkomirski, B. Lead concentration and the content of selected macroelements in lake sediments in Poland. J. Elem. 2014, 3, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gäbler, H.-E. Mobility of heavy metals as a function of pH of samples from an overbank sediment profile contaminated by mining activities. J. Geochem. Explor. 1997, 58, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbe, J.; Sobczyński, T.; Elbanowska, H.; Siepak, J. Speciation of Heavy Metals in Bottom Sediments of Lakes. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 1999, 8, 331–339. [Google Scholar]
- Sobczyński, T.; Siepak, J. Speciation of Heavy Metals in Bottom Sediments of Lakes in the Area of Wielkopolski National Park. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2001, 10, 463–474. [Google Scholar]
- Juśkiewicz, W.W.; Marszelewski, W.; Tylmann, W. Differentiation of the concentration of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants in lake sediments depending on the catchment management (Lake Gopło case study). Bull. Geogr. Phys. Geogr. 2015, 8, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kļaviņš, M.; Briede, A.; Kļaviņa, I.; Rodinov, V. Metals in sediments of lakes in Latvia. Environ. Int. 1995, 21, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognerud, S.; Hongve, D.; Fjeld, E.; Ottesen, R.T. Trace metal concentrations in lake and overbank sediments in southern Norway. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepane, V.; Varvas, M.; Viitak, A.; Alliksaar, T.; Heinsalu, A. Sedimentary record of heavy metals in Lake Rõuge Liinjärv, southern Estonia. Estonian J. Earth Sci. 2007, 56, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustsson, A.; Peltola, P.; Bergbäck, B.; Saarinen, T.; Haltia-Hovi, E. Trace metal and geochemical variability during 5500 years in the sediment of Lake Lehmilampi, Finland. J. Paleolimnol. 2010, 44, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





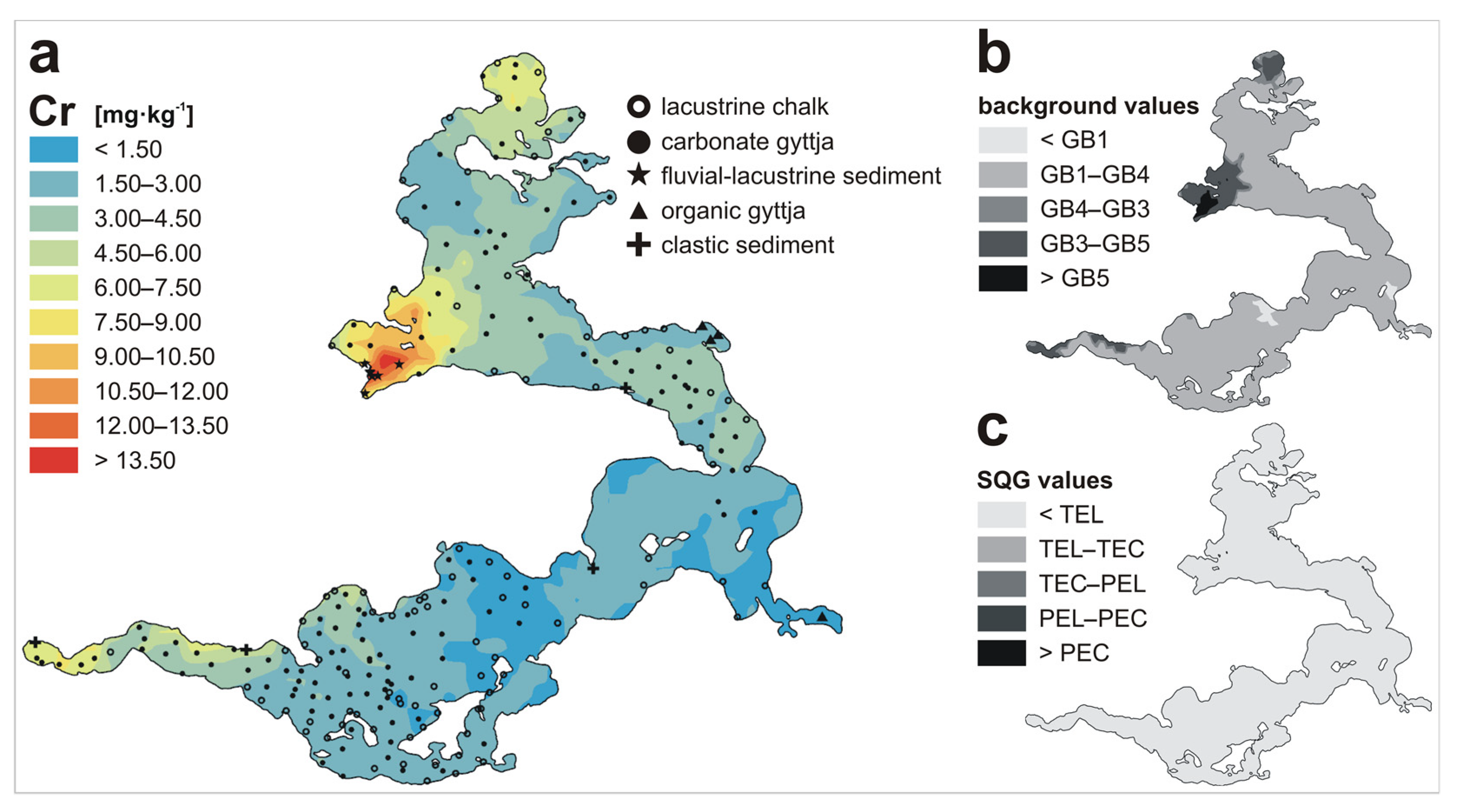

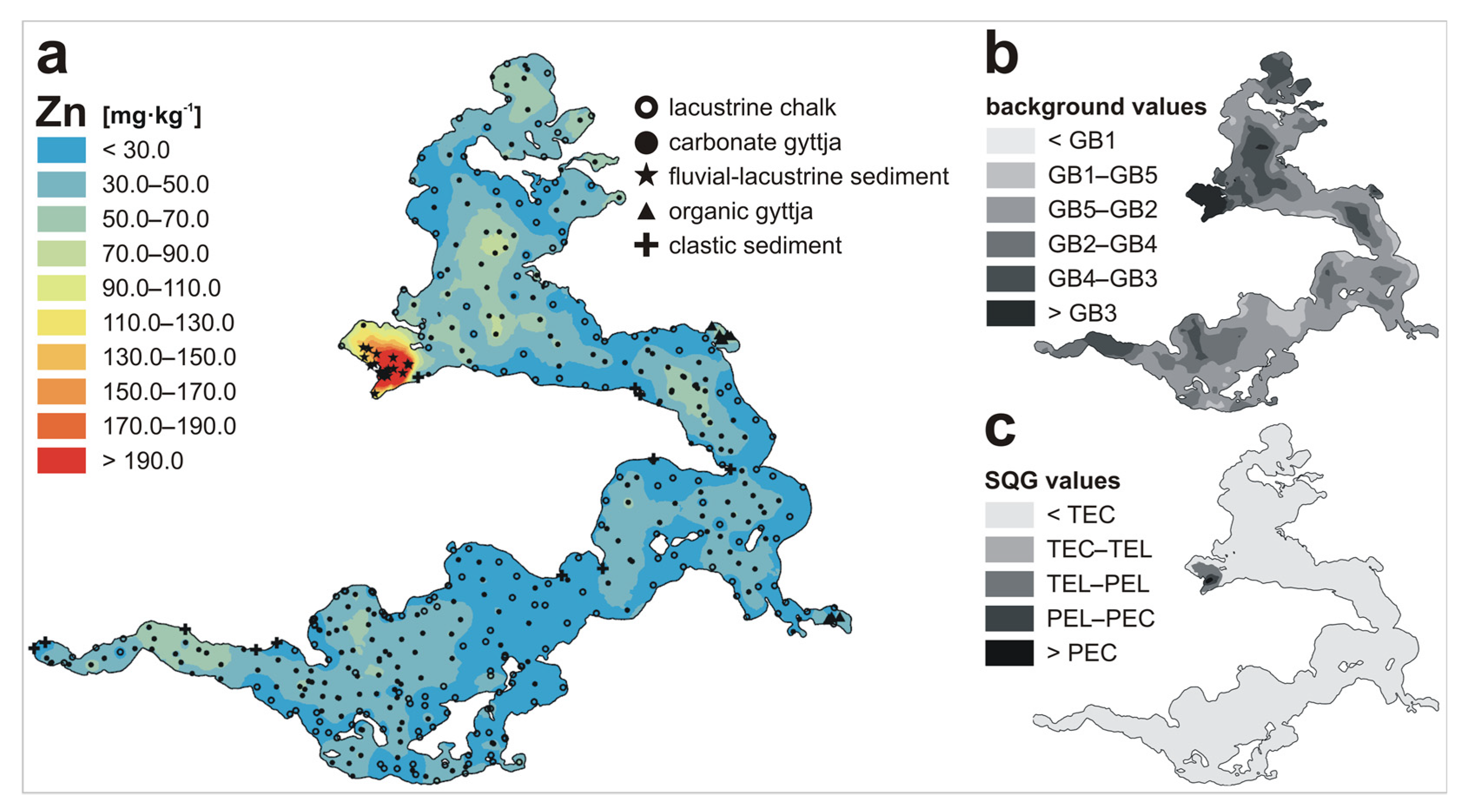

| Metal | LKSD-4 * | ICP-MS | ICP-AES | AAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg·kg−1 | ||||
| Cd | 1.9 | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.3 |
| Cu | 31.0 | 29.8 ± 1.7 | 28.5 ± 1.6 | 30.5 ± 2.6 |
| Mn | 420 | 412 ± 7.9 | - | 405 ± 12 |
| Pb | 91 | 101 ± 3.8 | 99 ± 4.5 | 81.8 ± 5.1 |
| Zn | 195 | 202 ± 9.6 | 200 ± 4.0 | 190 ± 11 |
| Metal | Lacustrine Chalk | Carbonate Gyttja | Fluvial-lacustrine Sediment | Organic Gyttja | Clastic Sediment | All Sediments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg·kg−1 | |||||||
| Cd | n | 98 | 149 | 17 | 4 | 3 | 271 |
| Min | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.160 | 0.120 | 0.006 | 0.003 | |
| Max | 0.557 | 0.870 | 3.060 | 0.620 | 0.633 | 3.060 | |
| Mean | 0.133 | 0.340 | 1.077 | 0.338 | 0.236 | 0.310 | |
| Cr | n | 88 | 136 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 239 |
| Min | 0.20 | 0.42 | 4.07 | 0.82 | 3.39 | 0.20 | |
| Max | 4.31 | 12.25 | 22.61 | 7.78 | 4.15 | 22.61 | |
| Mean | 1.48 | 3.69 | 16.17 | 3.63 | 3.73 | 3.24 | |
| Cu | n | 102 | 144 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 261 |
| Min | 0.02 | 0.20 | 12.27 | 3.07 | 0.08 | 0.02 | |
| Max | 8.97 | 26.27 | 59.70 | 10.30 | 6.55 | 59.70 | |
| Mean | 2.24 | 6.78 | 41.56 | 6.68 | 2.34 | 5.87 | |
| Fe | n | 200 | 217 | 21 | 9 | 12 | 459 |
| Min | 80 | 484 | 5863 | 2542 | 581 | 80 | |
| Max | 5588 | 10,654 | 32,857 | 15,876 | 3181 | 32,857 | |
| Mean | 983 | 3670 | 18,377 | 7529 | 1496 | 3191 | |
| Mn | n | 200 | 216 | 21 | 9 | 12 | 458 |
| Min | 18 | 56 | 142 | 86 | 28 | 18 | |
| Max | 206 | 1698 | 1373 | 372 | 85 | 1698 | |
| Mean | 94 | 354 | 518 | 230 | 51 | 238 | |
| Pb | n | 72 | 64 | 14 | 5 | 7 | 162 |
| Min | 36.2 | 46.8 | 35.6 | 62.3 | 7.0 | 7.0 | |
| Max | 88.1 | 84.7 | 107.5 | 79.4 | 63.8 | 107.5 | |
| Mean | 71.6 | 60.6 | 78.2 | 71.4 | 21.8 | 65.7 | |
| Zn | n | 200 | 213 | 21 | 9 | 12 | 455 |
| Min | 4.6 | 7.1 | 84.5 | 6.2 | 3.1 | 3.1 | |
| Max | 103.4 | 119.3 | 632.1 | 105.9 | 60.2 | 632.1 | |
| Mean | 17.8 | 44.6 | 339.2 | 62.7 | 14.7 | 46.0 | |
| Metal | GB1 1 | GB2 2 | GB3 3 | GB4 4 | GB5 5 | TEL 6 | TEC 7 | PEL 8 | PEC 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg·kg−1 | |||||||||
| Cd | 0.003 * | - | 0.631 | 0.500 | 0.035 | 0.596 | 0.99 | 3.53 | 4.98 |
| Cr | 0.99 | - | 6.08 | 5.00 | 11.00 | 37.3 | 43.4 | 90 | 111 |
| Cu | 0.5 | <1.0–4.0 | 11.1 | 6.0 | 4.0 | 35.7 | 31.6 | 197 | 149 |
| Fe | 344 | 100–13,800 | 5640 | 1000 | 3800 | - | - | - | - |
| Mn | 82 | 53–2046 | 493 | 500 | 1100 | - | - | - | - |
| Pb | 0.2 | 4.0–8.0 | 70.9 | 10.0 | 9.0 | 35 | 35.8 | 91.3 | 128 |
| Zn | 4.0 | 2.0–36.0 | 73.5 | 48.0 | 20.0 | 123 | 121 | 315 | 459 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kostka, A.; Leśniak, A. Natural and Anthropogenic Origin of Metals in Lacustrine Sediments; Assessment and Consequences—A Case Study of Wigry Lake (Poland). Minerals 2021, 11, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11020158
Kostka A, Leśniak A. Natural and Anthropogenic Origin of Metals in Lacustrine Sediments; Assessment and Consequences—A Case Study of Wigry Lake (Poland). Minerals. 2021; 11(2):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11020158
Chicago/Turabian StyleKostka, Anna, and Andrzej Leśniak. 2021. "Natural and Anthropogenic Origin of Metals in Lacustrine Sediments; Assessment and Consequences—A Case Study of Wigry Lake (Poland)" Minerals 11, no. 2: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11020158
APA StyleKostka, A., & Leśniak, A. (2021). Natural and Anthropogenic Origin of Metals in Lacustrine Sediments; Assessment and Consequences—A Case Study of Wigry Lake (Poland). Minerals, 11(2), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11020158







