Optimal Thermal Treatment for Effective Copper Recovery in Waste Printed Circuit Boards by Physical Separation: Influence of Temperature and Gas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
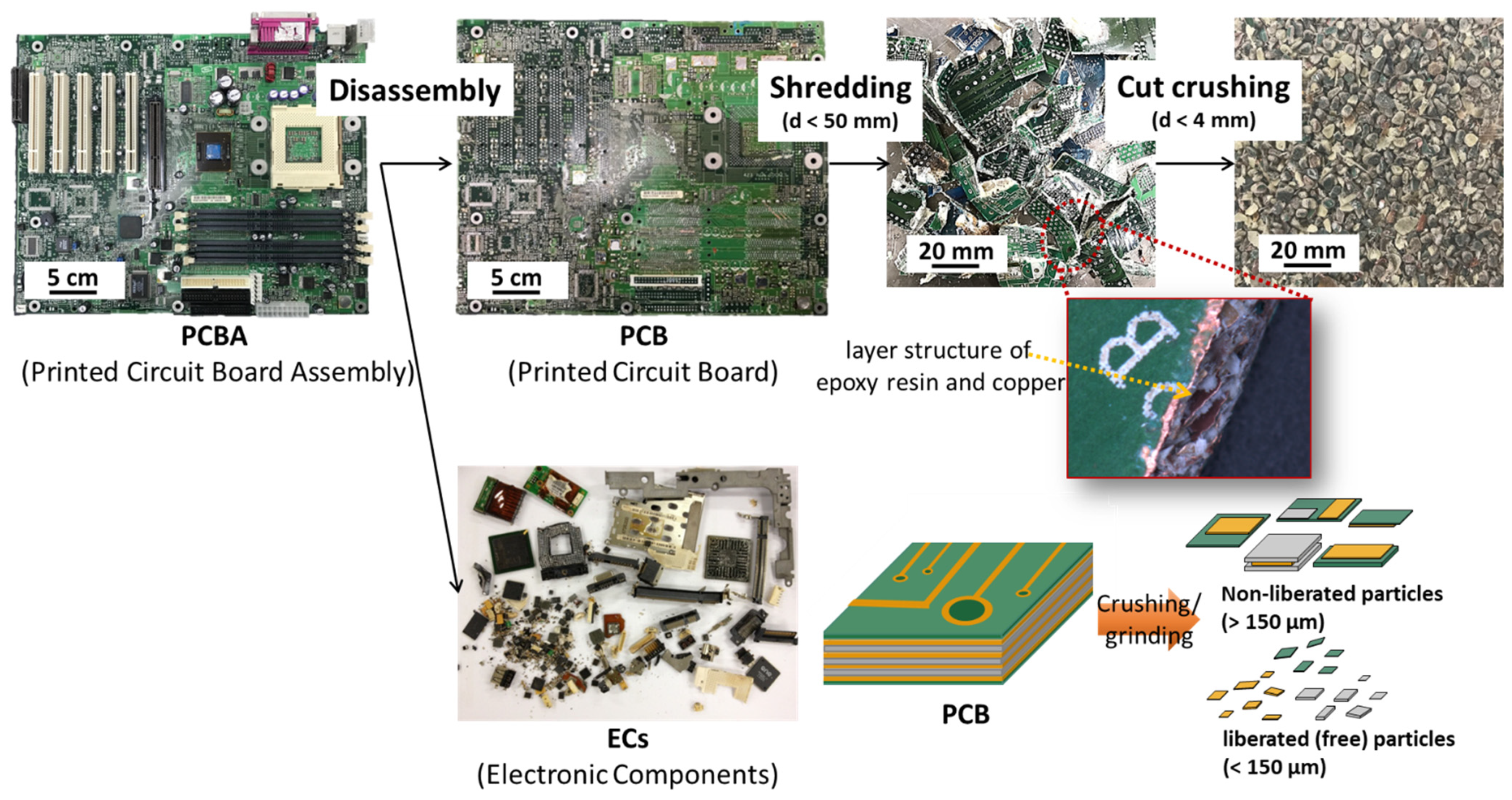
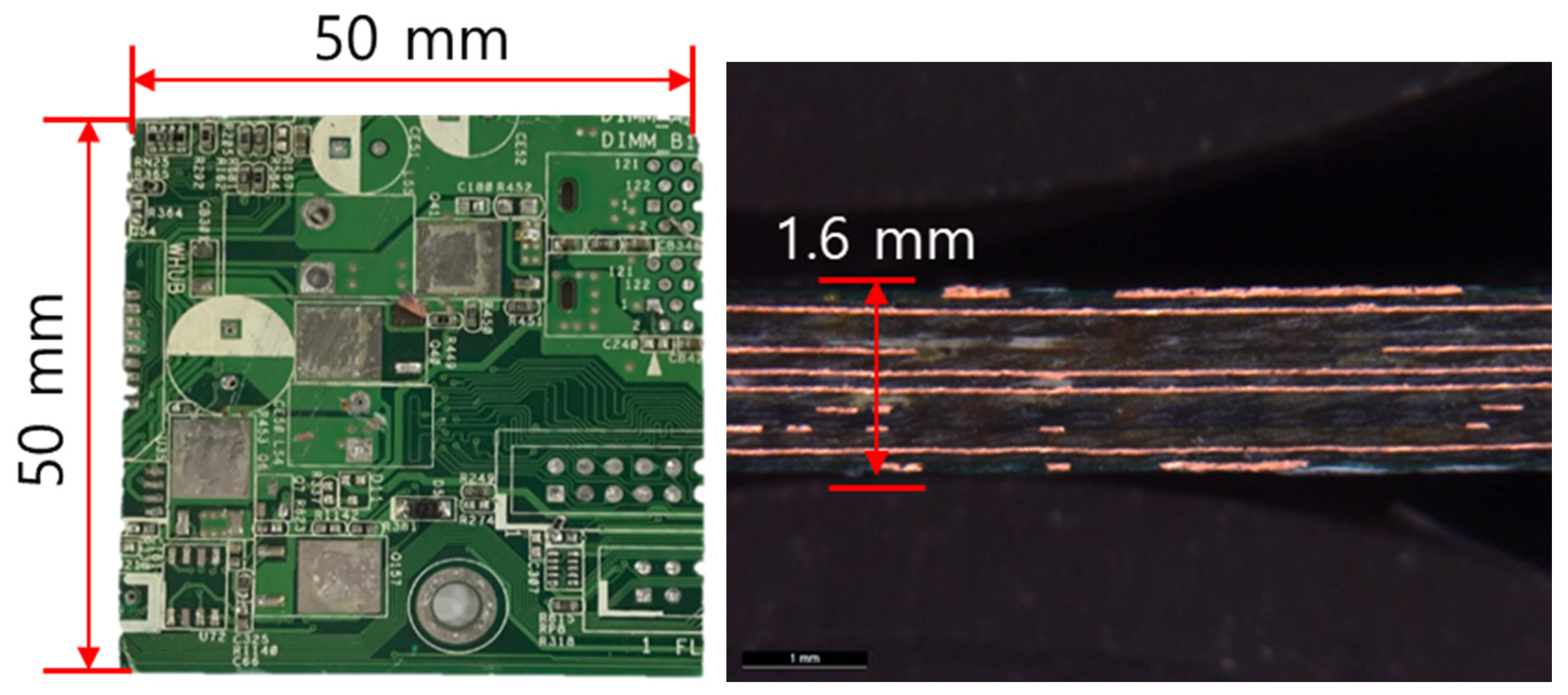
2.1. Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
2.2. Thermal Treatment Conditions
2.3. Evaluation of Flexible Strength and Degree of Liberation (DL)
2.4. Electrostatic Separation Experiment
3. Results
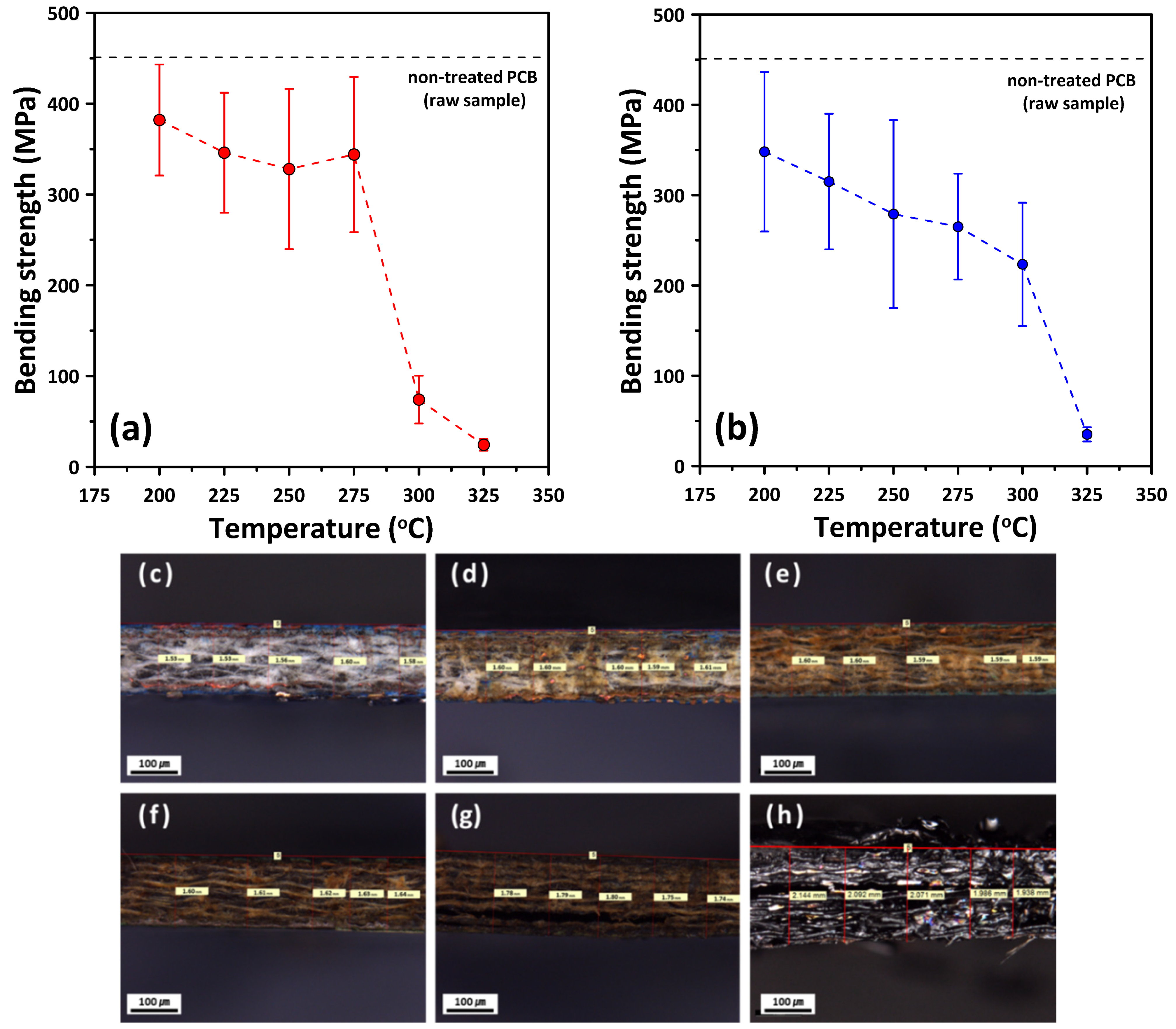
3.1. Thermal Behavior of the PCB
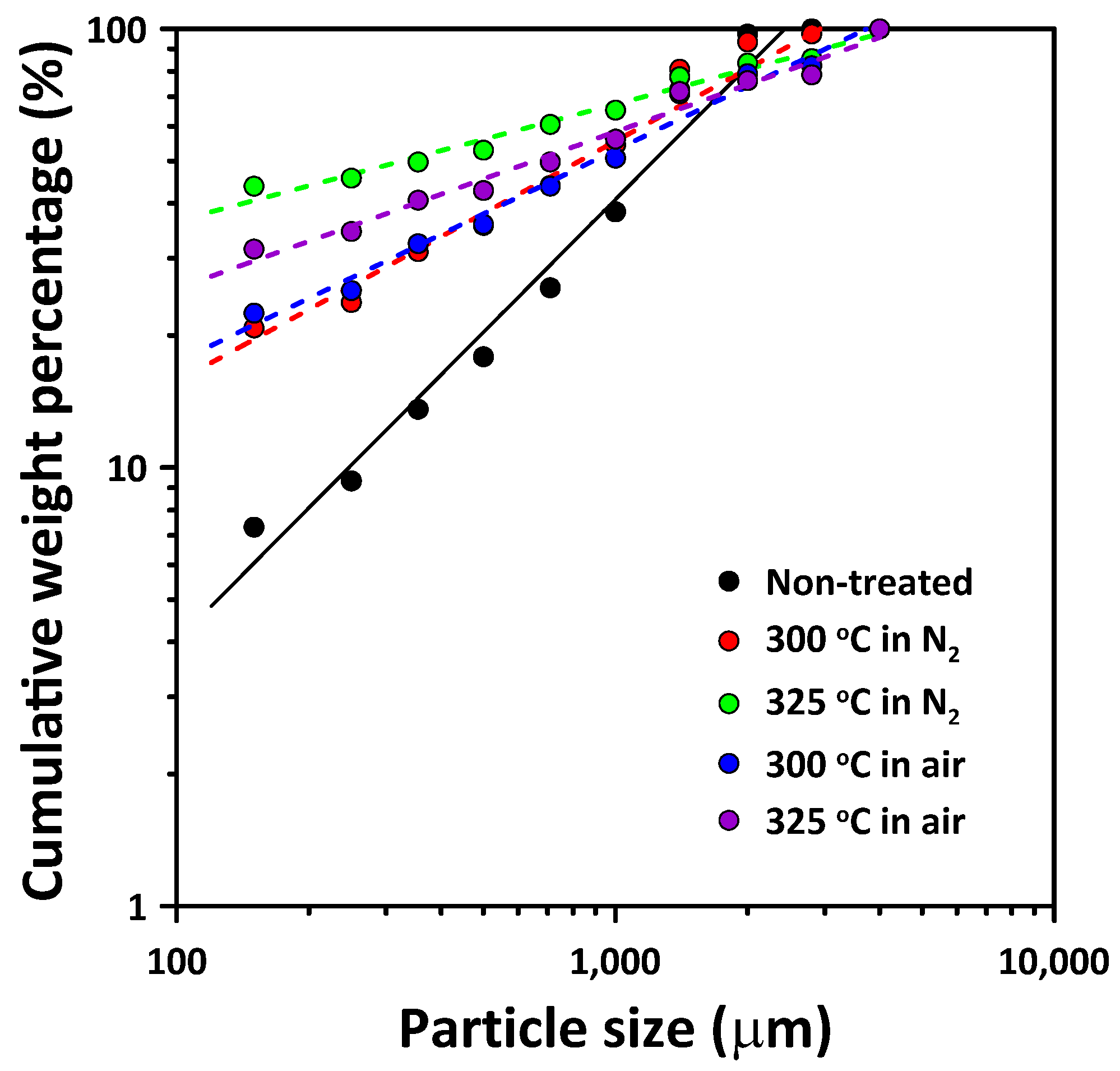
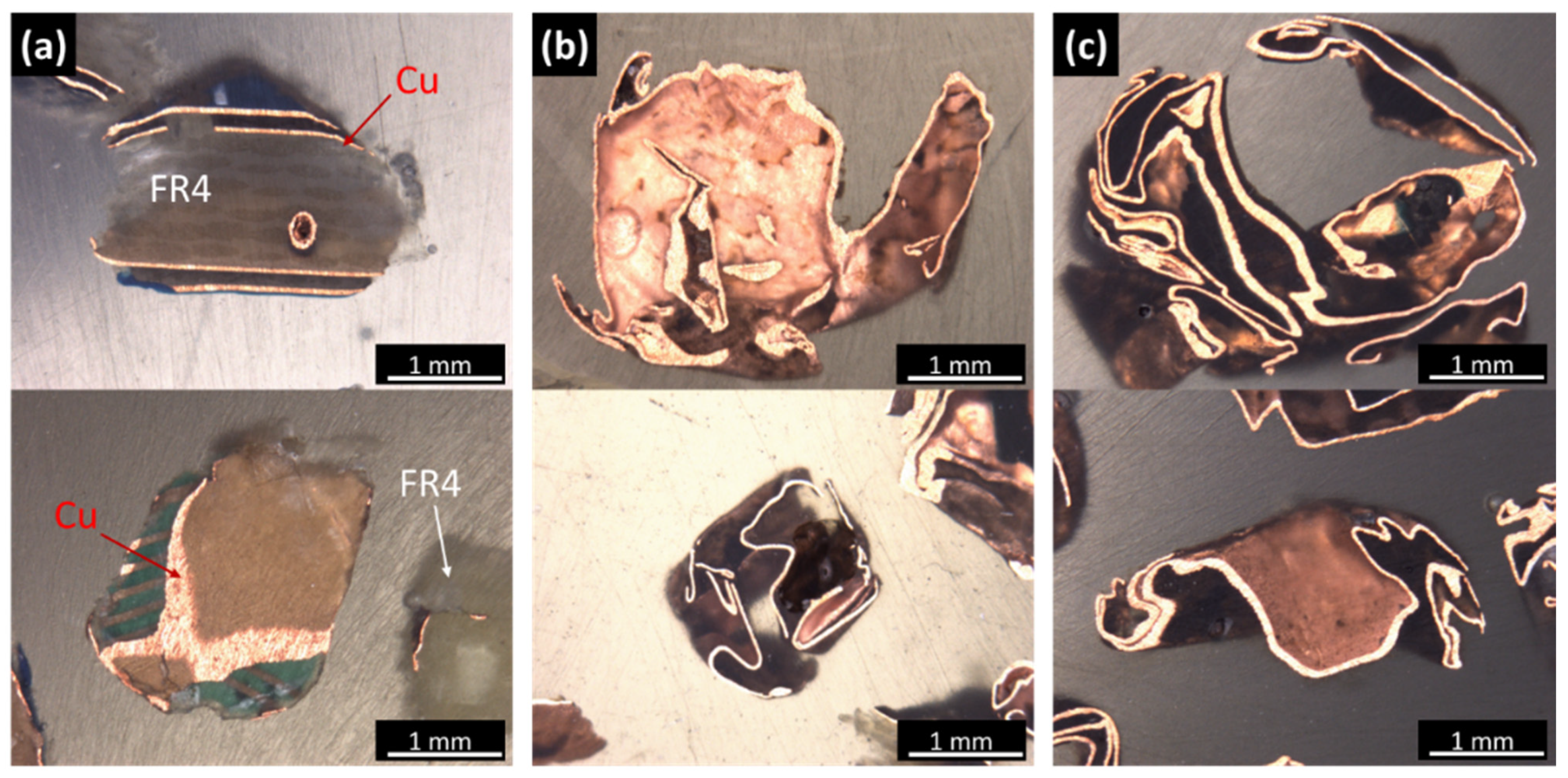
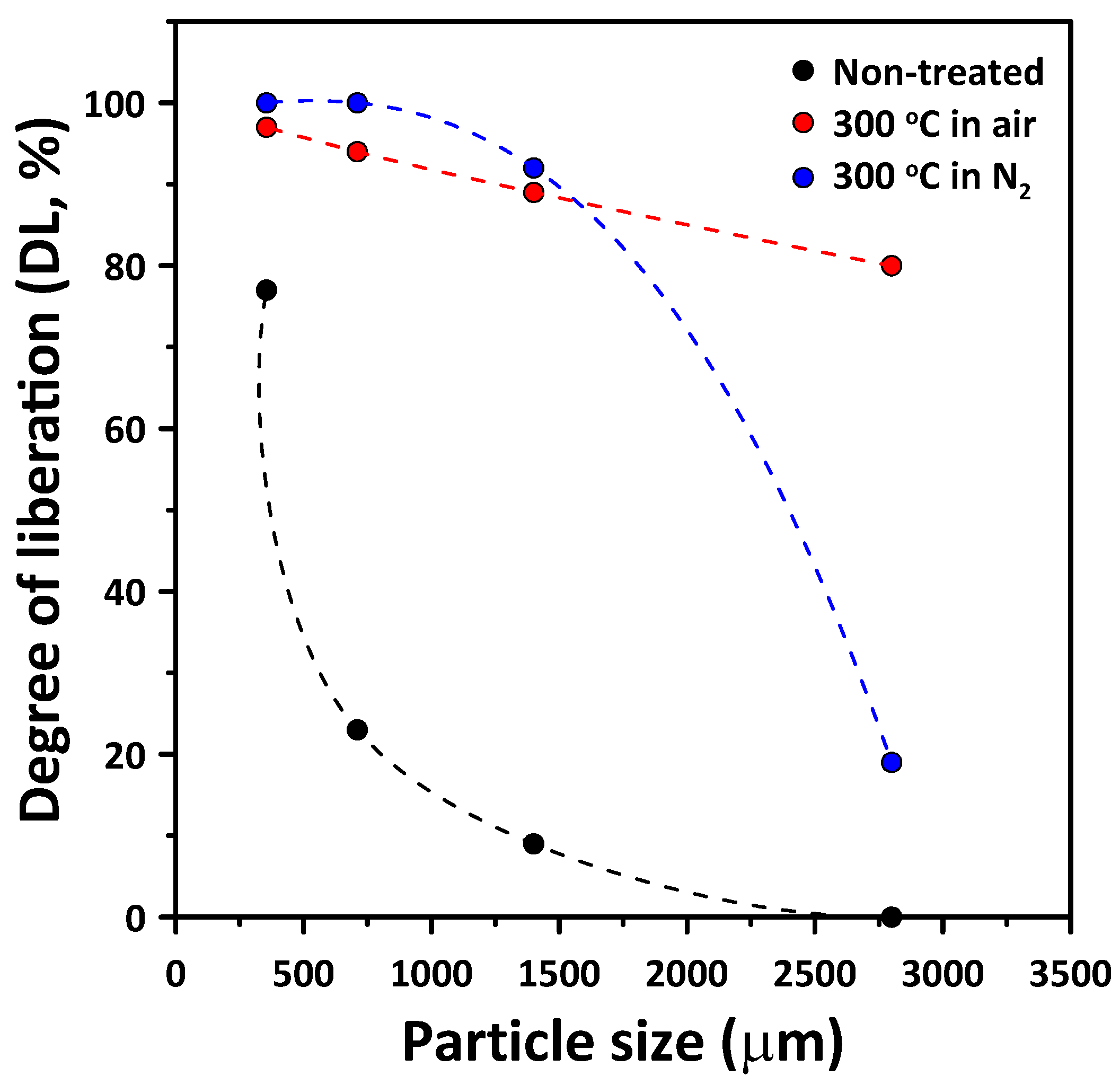
3.2. Comminution Behavior of Thermally Treated PCBs
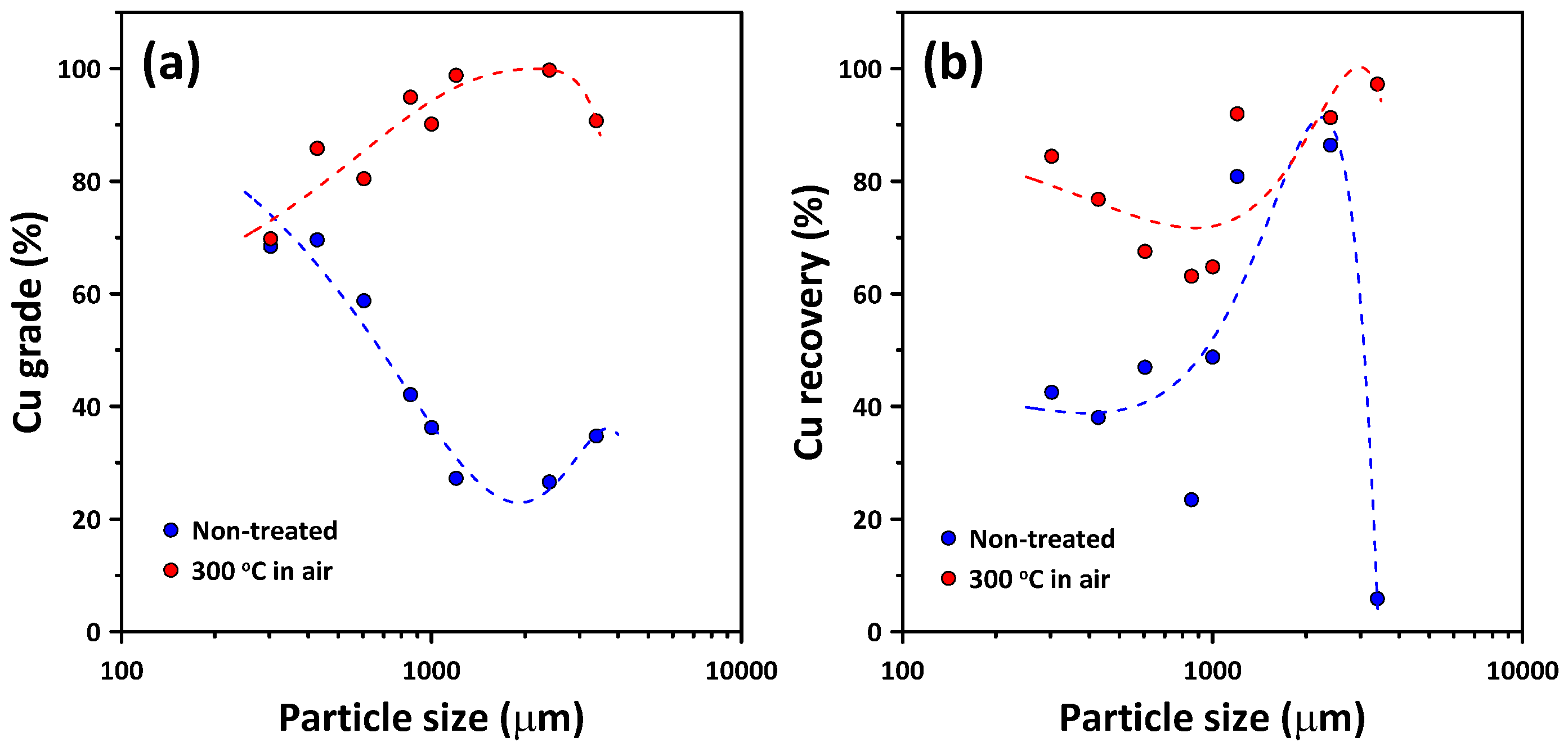
3.3. Cu Concentration by Electrostatic Separation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Xu, T.; Liu, J.; Wen, J.; Gong, S. Bioleaching metals from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) by Aspergil-lus niger: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardamone, G.F.; Ardolino, F.; Arena, U. About the environmental sustainability of the European management of WEEE plastics. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnamfard, A.; Salarirad, M.M.; Veglio, F. Process development for recovery of copper and precious metals from waste printed circuit boards with emphasize on palladium and gold leaching and precipitation. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2354–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Ono, H.; Dodbiba, G.; Yamaguchi, K. Evaluation of a recycling process for printed circuit board by physical separation and heat treatment. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Ghosh, M.; Parhi, P.; Mukherjee, P.; Mishra, B. Waste Printed Circuit Boards recycling: An extensive assessment of current status. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 94, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, A.; De La Mensbruge, L.; King, A.; Serranti, S.; Fiore, L.; Bonifazi, G. Non-destructive characterization of mechanically processed waste printed circuit boards-particle liberation analysis. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Fray, D.J. Recovery of high purity precious metals from printed circuit boards. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, S.; Han, S.; Han, Y.; Park, J. Silanol-rich ordered mesoporous silica modified thiol group for enhanced recovery performance of Au(III) in acidic leachate solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, L. Metallurgical recovery of metals from electronic waste: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 228–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hino, T.; Agawa, R.; Moriya, Y.; Nishida, M.; Tsugita, Y.; Araki, T. Techniques to separate metal from waste printed circuit boards from discarded personal computers. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2009, 11, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.-C. Disassembly and physical separation of electric/electronic components layered in printed circuit boards (PCB). J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucchiella, F.; D’Adamo, I.; Koh, S.L.; Rosa, P. Recycling of WEEEs: An economic assessment of present and future e-waste streams. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cilek, E.C.; Tuzci, G. Flotation behavior of native gold and gold-bearing sulfide minerals in a polymetallic gold ore. Part. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, G.J.; Emer, C. Coarse chalcopyrite recovery in a universal froth flotation machine. Miner. Eng. 2019, 134, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvas, F.P.; Correa, M.M.J.; Caldas, M.P.; de Moraes, V.T.; Espinosa, D.C.; Tenório, J.A. Printed circuit board recycling: Physical processing and copper extraction by selective leaching. Waste Manag. 2015, 46, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Hou, K.; Li, J.; Zhu, X. Examining the technology acceptance for dismantling of waste printed circuit boards in light of recycling and environmental concerns. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 92, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, S.; Han, Y.; Park, J. Apparatus for electronic component disassembly from printed circuit board assembly in e-wastes. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 144, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Forssberg, E. Mechanical recycling of waste electric and electronic equipment: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 99, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, H.; Guo, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y. Recycle Technology for Recovering Resources and Products from Waste Printed Circuit Boards. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1995–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veit, H.M.; De Pereira, C.C.; Bernardes, A.M. Using mechanical processing in recycling printed wiring boards. JOM 2002, 54, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Wang, H.; Liang, W.; Fu, J.; Yi, X. Liberation characteristic and physical separation of printed circuit board (PCB). Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, S.; Han, S.; Kim, B.; Kim, B.; Han, Y.; Park, J. Liberation Characteristics Assessment for Copper Component in PCB Comminution Product by Image Analysis. Mater. Trans. 2018, 59, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, G.; Ying-Shun, L.; Mai-Xi, L. Product characterization of waste printed circuit board by pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2008, 83, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wen, X.; Li, B.; Tao, D. Recovery of copper from waste printed circuit boards. Mining, Met. Explor. 2004, 21, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.D.; Ilankoon, I.M.S.K.; Dushyantha, N.; Chong, M.N. Assessment of Pre-Treatment Techniques for Coarse Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) Recycling. Minerals 2021, 11, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, H.R.; Singh, K.K.; Mankhand, T.R. Liberation of metal clads of waste printed circuit boards by removal of halogenated epoxy resin substrate using dimethylacetamide. Waste. Manag. 2017, 60, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.F.; Pan, M.W.; Lo, S.L. Hydrometallurgical metal recovery from waste printed circuit boards pretreated by microwave pyrolysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 163, 105090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Duan, H.; Yu, K.; Liu, L.; Wang, S. Characteristic of low-temperature pyrolysis of printed circuit boards subjected to various atmosphere. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Duan, H.; Yu, K.; Wang, S. Interfacial and Mechanical Property Analysis of Waste Printed Circuit Boards Subject to Thermal Shock. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2010, 60, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadi, P.; Xu, M.; Lin, C.S.; Hui, C.-W.; McKay, G. Waste printed circuit board recycling techniques and product utilization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 283, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, Z. Optimizing the operating parameters of corona electrostatic separation for recycling waste scraped printed circuit boards by computer simulation of electric field. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veit, H.M.; Diehl, T.R.; Salami, A.P.; Rodrigues, J.d.S.; Bernardes, A.M.; Tenório, J.A.S. Utilization of magnetic and electro-static separation in the recycling of printed circuit boards scrap. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y. Application of corona discharge and electrostatic force to separate metals and nonmetals from crushed particles of waste printed circuit boards. J. Electrost. 2007, 65, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Yan, G.; Li, J.; Xu, Z. Electrostatic Separation for Recycling Conductors, Semiconductors, and Nonconductors from Electronic Waste. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10556–10563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, H. TiO2-Coated Silica Foams by In-Situ Sol-Gel Reaction. Mater. Trans. 2011, 52, 2245–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barontini, F.; Marsanich, K.; Petarca, L.; Cozzani, V. Thermal Degradation and Decomposition Products of Electronic Boards Containing BFRs. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 4186–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.-L.; Lo, C.-C.; Ma, S.-Y. Characteristics of exhaust gas, liquid products, and residues of printed circuit boards using the pyrolysis process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 17, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janáčová, D.; Kolomazník, K.; Vašek, V.; Křenek, J.; Uhlířová, M. Separation of printed circuit board by temperature shock. In Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Conference on Heat Transfer, Thermal Engineering and Environment HTE’07, Athens, Greece, 25–27 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Koyanaka, S.; Endoh, S.; Ohya, H. Effect of impact velocity control on selective grinding of waste printed circuit boards. Adv. Powder Technol. 2006, 17, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, G.M.; Mario, M.; Javier, T.; Susana, T. Optimization of the recovery of plastics for recycling by density media separation cyclones. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncuk, A.; Stazi, V.; Akcil, A.; Yazici, E.Y.; Deveci, H. Aqueous metal recovery techniques from e-scrap: Hydrometallurgy in recycling. Miner. Eng. 2012, 25, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Sun, Q. Leaching behavior of copper from waste printed circuit boards with Brønsted acidic ionic liquid. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamberović, Ž.; Korać, M.; Ivšić, D.; Nikolić, V.; Ranitović, M. Hydrometallurgical process for extraction of metals from electronic waste-part I: Material characterization and process option selection. Metall. Mater. Eng. 2018, 15, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhao, P.; Chauhan, G.; Pant, K.; Nigam, K. Greener approach for the extraction of copper metal from electronic waste. Waste Manag. 2015, 57, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Operating Parameters | Operating Conditions |
|---|---|
| Supplied voltage (kV) | −30 |
| Rotation speed (rpm) | 30 |
| Distance of induction electrode (m) | 0.3 |
| Degree of induction electrode (o) | 20 |
| Distance of corona electrode (m) | 0.3 |
| Degree of corona electrode (o) | 60 |
| Relative humidity (%) | 35 ± 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, B.; Han, S.; Park, S.; Kim, S.; Jung, M.; Park, C.-H.; Jeon, H.-S.; Kim, D.-W.; Han, Y. Optimal Thermal Treatment for Effective Copper Recovery in Waste Printed Circuit Boards by Physical Separation: Influence of Temperature and Gas. Minerals 2021, 11, 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111213
Kim B, Han S, Park S, Kim S, Jung M, Park C-H, Jeon H-S, Kim D-W, Han Y. Optimal Thermal Treatment for Effective Copper Recovery in Waste Printed Circuit Boards by Physical Separation: Influence of Temperature and Gas. Minerals. 2021; 11(11):1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111213
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Boram, Seongsoo Han, Seungsoo Park, Seongmin Kim, Minuk Jung, Chul-Hyun Park, Ho-Seok Jeon, Dae-Weon Kim, and Yosep Han. 2021. "Optimal Thermal Treatment for Effective Copper Recovery in Waste Printed Circuit Boards by Physical Separation: Influence of Temperature and Gas" Minerals 11, no. 11: 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111213
APA StyleKim, B., Han, S., Park, S., Kim, S., Jung, M., Park, C.-H., Jeon, H.-S., Kim, D.-W., & Han, Y. (2021). Optimal Thermal Treatment for Effective Copper Recovery in Waste Printed Circuit Boards by Physical Separation: Influence of Temperature and Gas. Minerals, 11(11), 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111213






