Leaching Chalcocite in Chloride Media—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fundamentals
3. Operational Variables
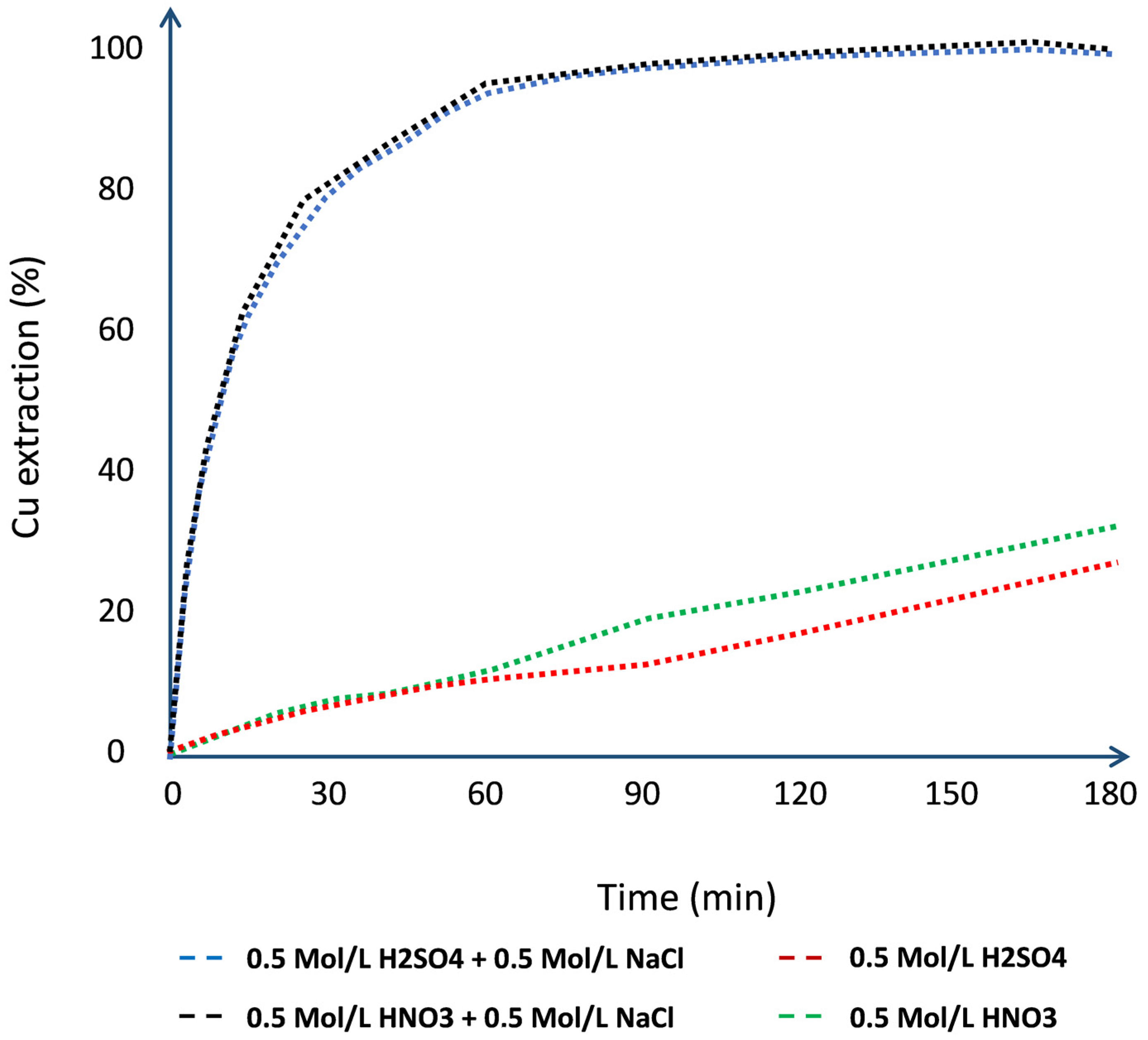
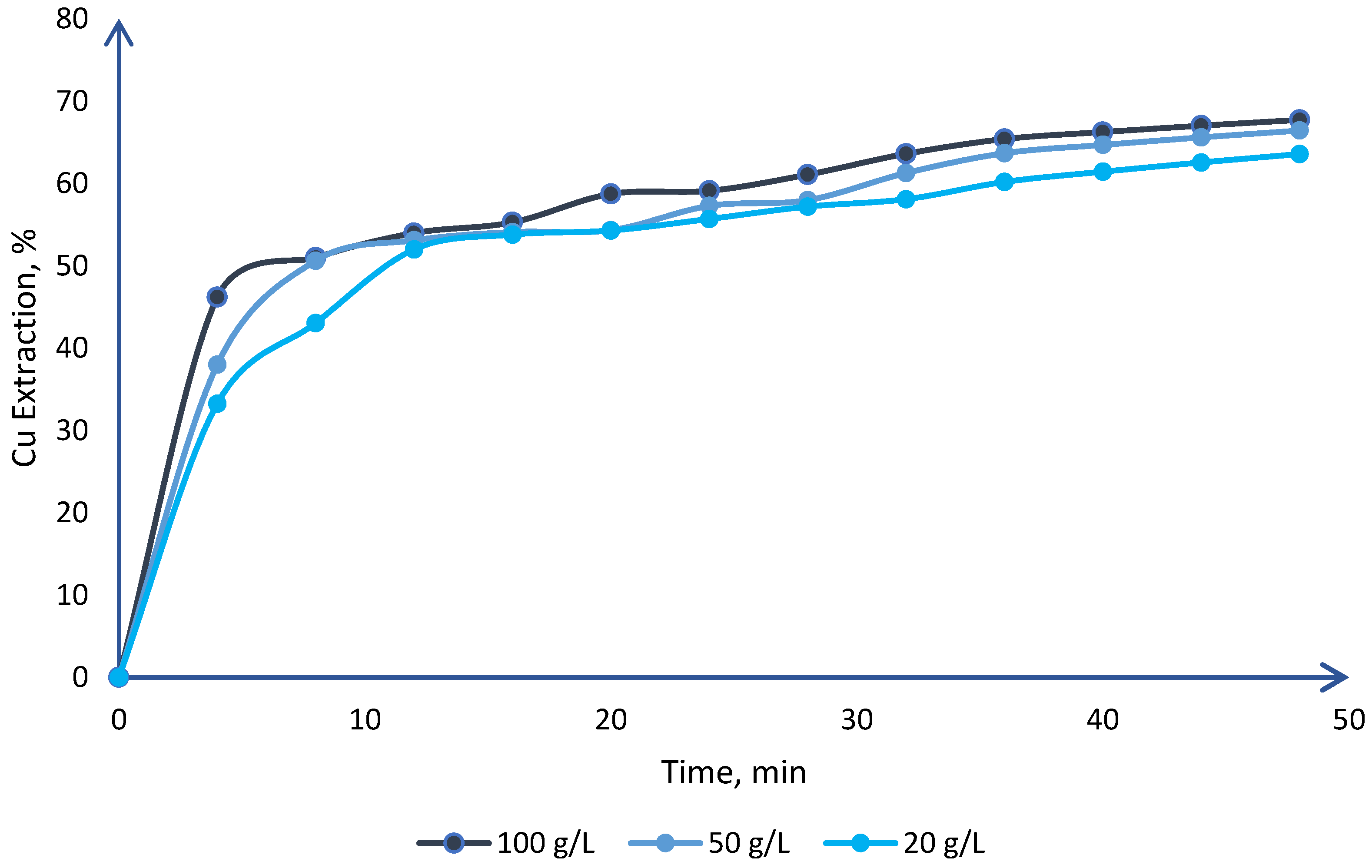
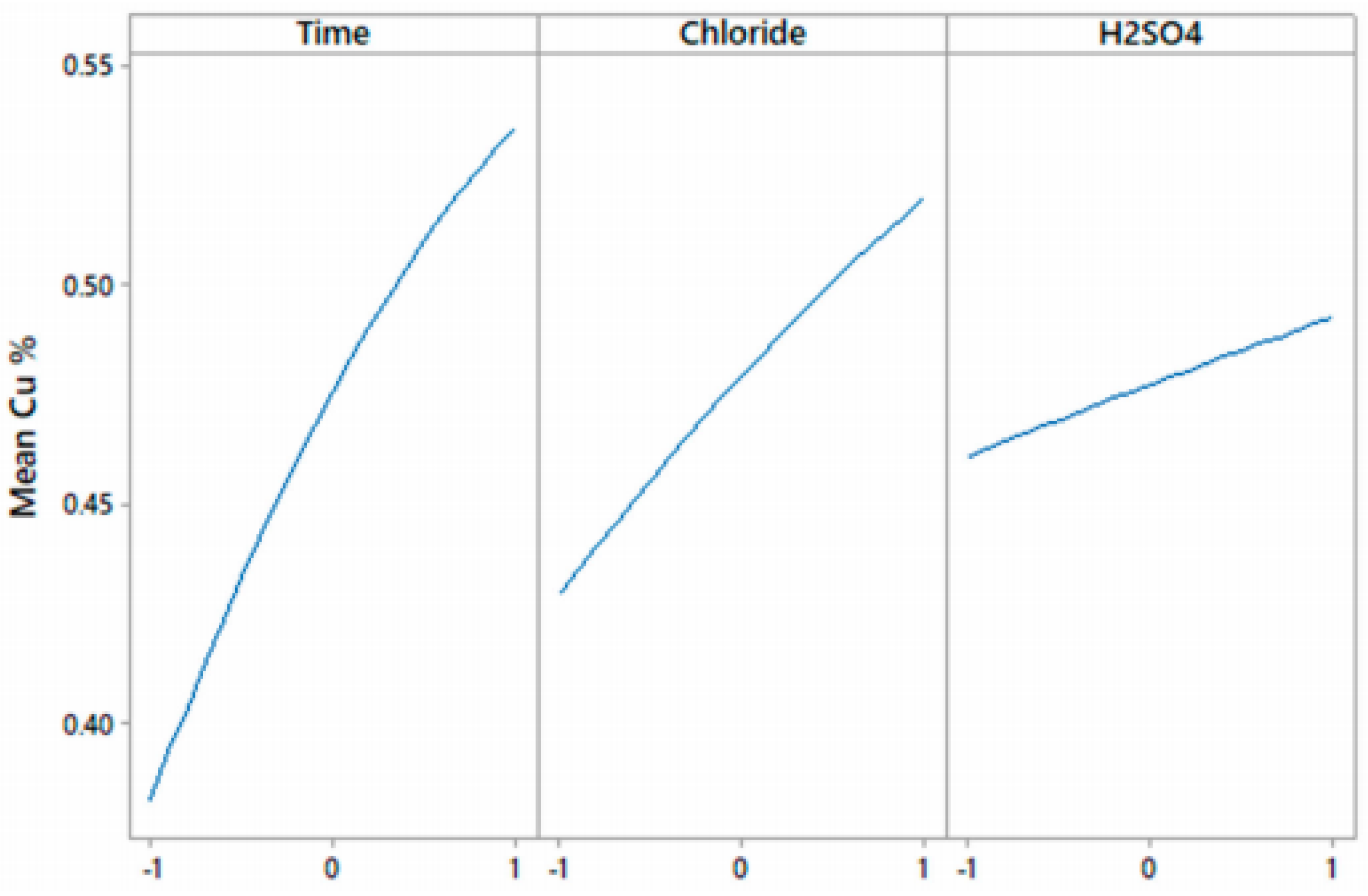
3.1. Effect on Chloride Concentration
3.2. Effect on Stirring Speed
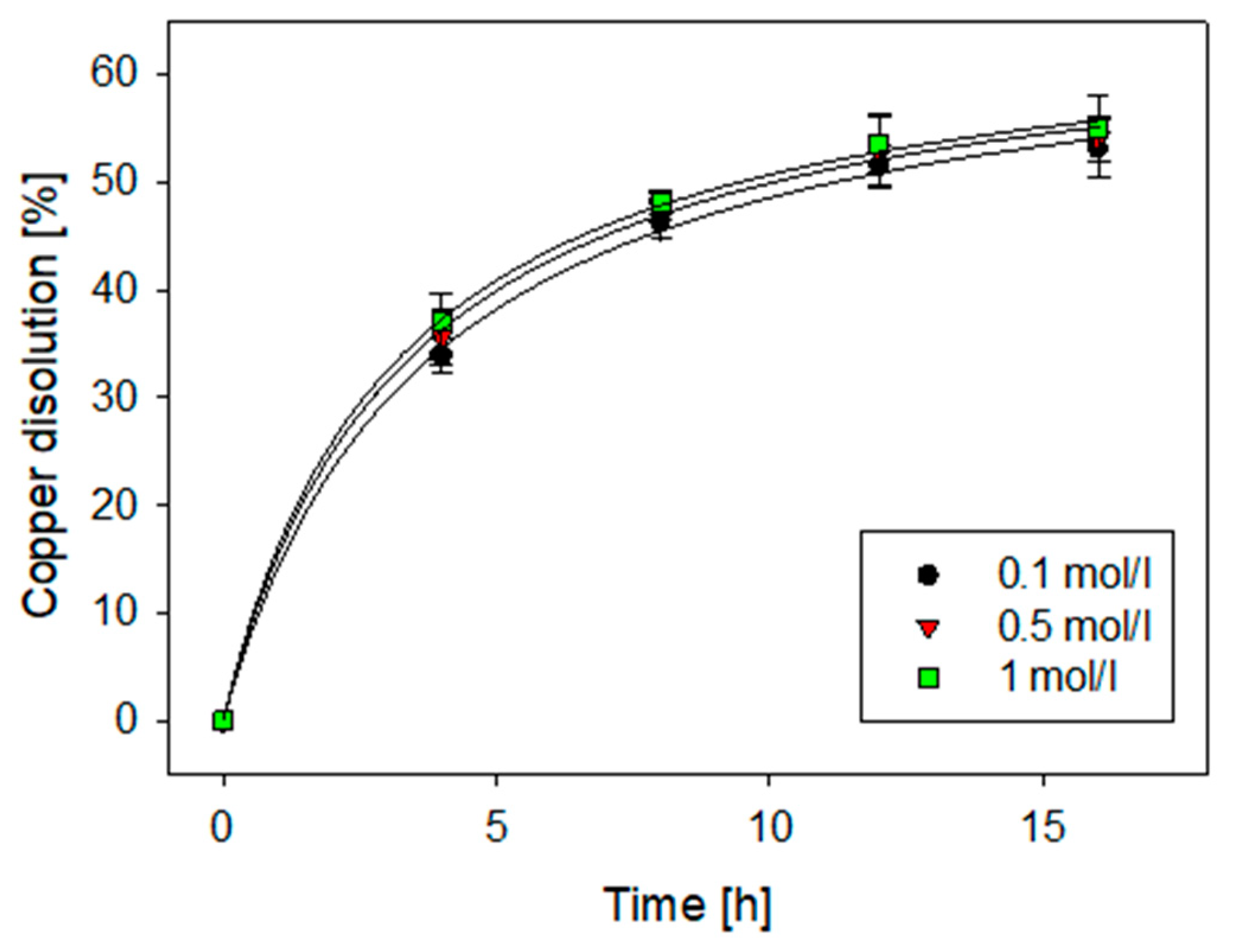
3.3. Effect on Acid Concentration
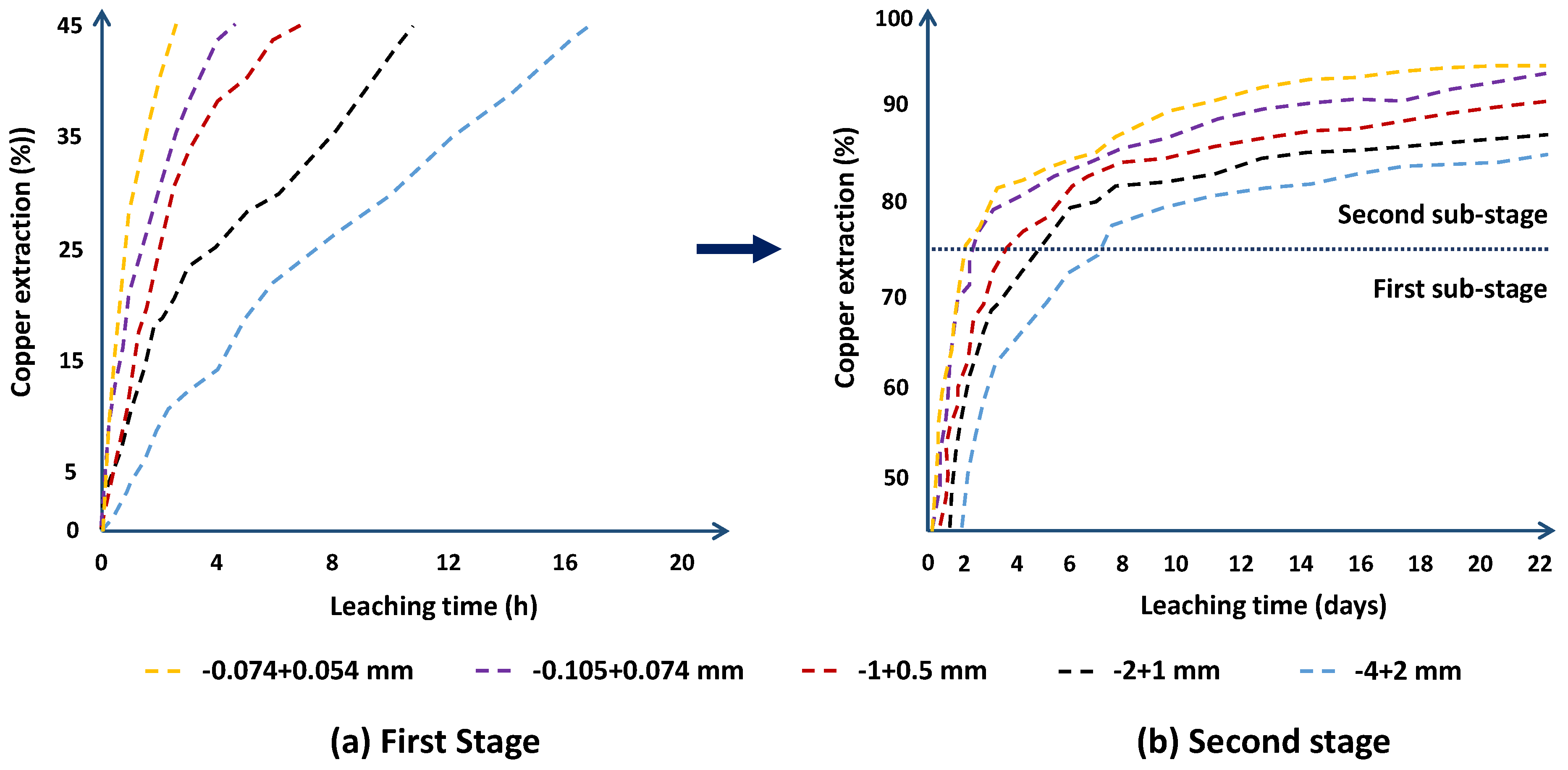
3.4. Particle Size Effect
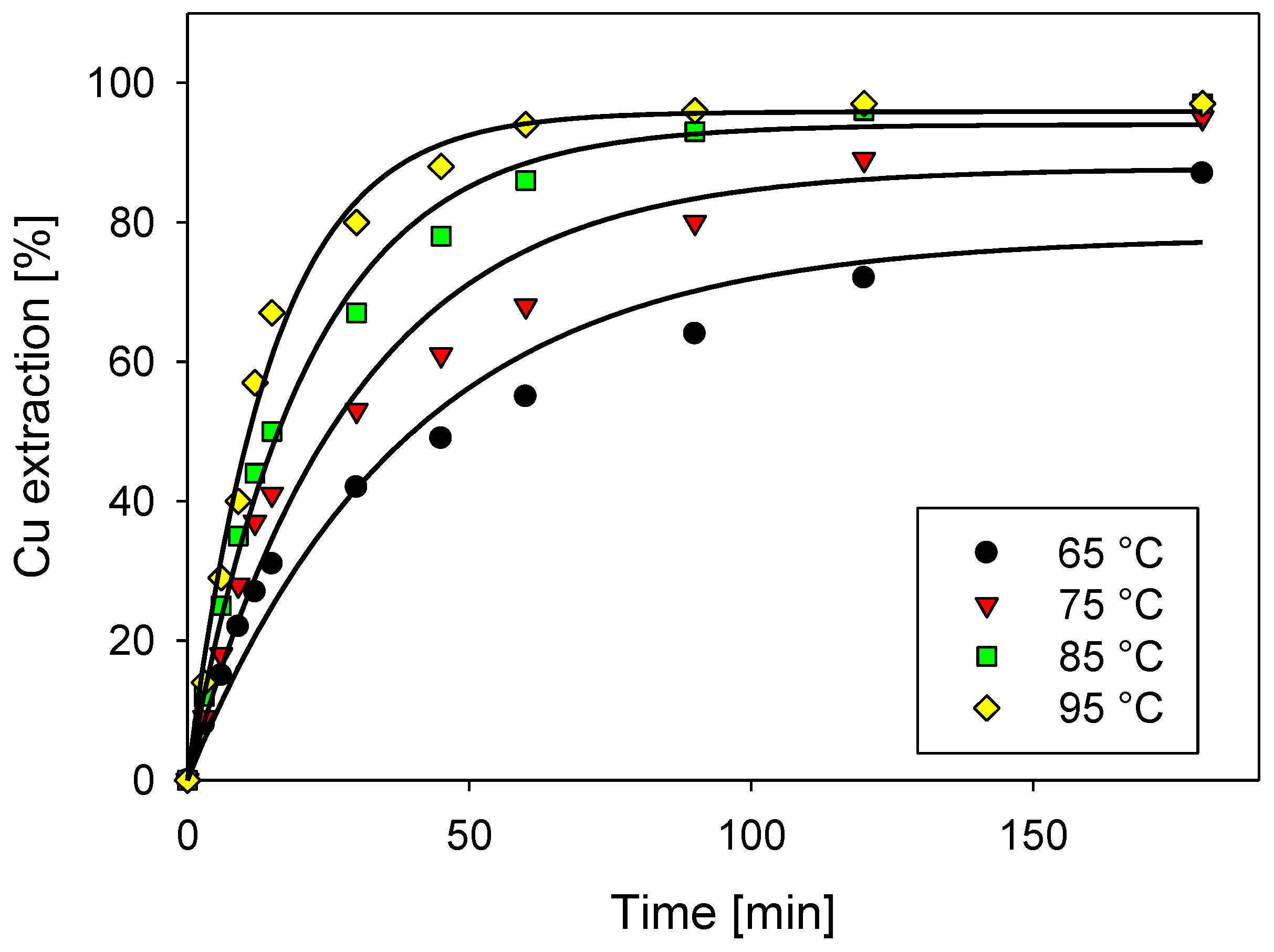
3.5. Effect of Temperature
3.6. Effect of Redox Potential
3.7. Effect of Oxidizing Agents
3.7.1. Air
3.7.2. Ferric Ions
3.7.3. MnO2
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bogdanović, G.D.; Petrović, S.; Sokić, M.; Antonijević, M.M. Chalcopyrite leaching in acid media: A review. Metall. Mater. Eng. 2020, 26, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong Thao, N.T.; Tsuji, S.; Jeon, S.; Park, I.; Tabelin, C.B.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N. Redox potential-dependent chalcopyrite leaching in acidic ferric chloride solutions: Leaching experiments. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 194, 105299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taboada, M.E.; Hernández, P.C.; Padilla, A.P.; Jamett, N.E.; Graber, T.A. Effects of Fe+2 and Fe+3 in Pretreatment and Leaching on a Mixed Copper Ore in Chloride Media. Metals 2021, 11, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, M.D.; Sarı, Z.A.; Nizamoğlu, H. Pressure leaching of chalcopyrite with oxalic acid and hydrogen peroxide. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 118, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutrizac, J. Elemental sulphur formation during the ferric chloride leaching of chalcopyrite. Hydrometallurgy 1990, 23, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, G.M.; Eksteen, J.J. A critical review of the passivation and semiconductor mechanisms of chalcopyrite leaching. Miner. Eng. 2020, 154, 106401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, R.; Coyle, V.E.; Bond, A.M.; Chen, M.; Bhargava, S.K.; Jones, L.A. A scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM) study of the interfacial solution chemistry at polarised chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) and chalcocite (Cu2S). Electrochem. Commun. 2020, 115, 106730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres Albornoz, D.A. Copper and Manganese Extraction Through Leaching Processes, Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena. 2021. Available online: https://repositorio.upct.es/bitstream/handle/10317/9373/data_C.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Hidalgo, T.; Verrall, M.; Beinlich, A.; Kuhar, L.; Putnis, A. Replacement reactions of copper sulphides at moderate temperature in acidic solutions. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 123, 103569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domic, E.M. A Review of the Development and Current Status of Copper Bioleaching Operations in Chile: 25 Years of Successful Commercial Implementation. In Biomining; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 81–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani, Y.; Becker, M.; Mainza, A.; Franzidis, J.-P.; Petersen, J. Large particle effects in chemical/biochemical heap leach processes—A review. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1172–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phyo, H.A.; Jia, Y.; Tan, Q.; Zhao, S.; Liang, X.; Ruan, R.; Niu, X. Effect of particle size on chalcocite dissolution kinetics in column leaching under controlled Eh and its implications. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2020, 56, 676–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, N.; Briceño, W.; Pérez, K.; Cánovas, M.; Trigueros, E.; Sepúlveda, R.; Hernández, P. Leaching of pure chalcocite in a chloride media using sea water and waste water. Metals 2019, 9, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watling, H.R. The bioleaching of sulphide minerals with emphasis on copper sulphides—A review. Hydrometallurgy 2006, 84, 81–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.G.; Ginting, A.R.; O’Connor, B. A thermoanalytical study of the oxidation of chalcocite. J. Therm. Anal. 1994, 41, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, H.T. The crystal structures of low chalcocite and djurleite. Zeitschrift Krist.-Cryst. Mater. 1979, 150, 299–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.L.; Fayazuddin, M.; Frost, R.L.; Endo, T. Electron paramagnetic resonance and optical absorption spectral studies on chalcocite. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2007, 68, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanda, B.C.; Eksteen, J.J.; Oraby, E.A. Kinetics of chalcocite leaching in oxygenated alkaline glycine solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 178, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-W. High Chalcocite Cu2S: A Solid-Liquid Hybrid Phase. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 085703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.; Lee, J.Y. Production of chalcocite by selective chlorination of chalcopyrite using cuprous chloride. Miner. Metall. Process. 2017, 34, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, R.S.; Liddell, K.C. Mechanism of anodic dissolution of chalcocite in hydrochloric acid solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1990, 29, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yang, X.; Wen, J.; Wang, D. Semiconductor-Microbial Mechanism of Selective Dissolution of Chalcocite in Bioleaching. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 18279–18288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.; Sepúlveda, R.; Araya, G.; Guzmán, D.; Toro, N.; Pérez, K.; Rodríguez, M.; Navarra, A. Leaching of white metal in a NaCl-H2SO4 system under environmental conditions. Minerals 2019, 9, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Lawson, F. The kinetics of leaching chalcocite in acidic oxygenated sulphate-chloride solutions. Hydrometallurgy 1991, 27, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.G.; Ginting, A.; O’Connor, B.H. Quantitative determination of phases present in oxidised chalcocite. J. Therm. Anal. 1997, 50, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posfai, M.; Buseck, P.R. Djurleite, digenite, and chalcocite: Intergrowths and transformations. Am. Mineral. 1994, 79, 308–315. [Google Scholar]
- Saldaña, M.; Neira, P.; Flores, V.; Robles, P.; Moraga, C. A Decision Support System for Changes in Operation Modes of the Copper Heap Leaching Process. Metals 2021, 11, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bampole, D.L.; Luis, P.; Mulaba-Bafubiandi, A.F. Sustainable copper extraction from mixed chalcopyrite–chalcocite using biomass. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 2170–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostelmann, H.; Southam, G. The biogeochemical reactivity of phosphate during bioleaching of bornite-chalcocite ore. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 104, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Qiu, G.; Gao, J.; Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Ding, J. Bioleaching of chalcocite by mixed microorganisms subjected to mutation. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2009, 16, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, M.J.; Davidson, M.R.; Schwarz, M.P. A model for heap bioleaching of chalcocite with heat balance: Bacterial temperature dependence. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 1239–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, M.J.; Davidson, M.R.; Schwarz, M.P. A model for heap bioleaching of chalcocite with heat balance: Mesophiles and moderate thermophiles. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 85, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, J.; Dixon, D.G. The dynamics of chalcocite heap bioleaching. In Hydrometallurgy; Young, C., Alfantazi, A., Anderson, C., James, A., Dreisinger, D.B., Harris, B., Eds.; In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium Honoring Professor Ian M. Ritchie; TMS Publishers: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, J.; Dixon, D.G. Modeling and Optimization of Heap Bioleach Processes. In Biomining; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 153–176. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Wen, J.-K.; Chen, B.-W.; Yao, G.-C.; Wang, D.-Z. Control of redox potential by oxygen limitation in selective bioleaching of chalcocite and pyrite. Rare Met. 2014, 33, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yin, H.; Deng, J.; Qiu, G. Interaction mechanism between marmatite and chalcocite in acidic (microbial) environments. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 191, 105217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolorunduro, S.A. Kinetics of Leaching of Chalcocite in Acid Ferric Sulfate Media: Chemical and Bacterial Leaching, University of British Columbia. 1999. Available online: https://open.library.ubc.ca/soa/cIRcle/collections/ubctheses/831/items/1.0078730 (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Miki, H.; Nicol, M.; Velásquez-Yévenes, L. The kinetics of dissolution of synthetic covellite, chalcocite and digenite in dilute chloride solutions at ambient temperatures. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 105, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, X.; Ruan, R.; Tan, Q.; Jia, Y.; Sun, H. Study on the second stage of chalcocite leaching in column with redox potential control and its implications. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 155, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palencia, I.; Romero, R.; Mazuelos, A.; Carranza, F. Treatment of secondary copper sulphides (chalcocite and covellite) by the BRISA process. Hydrometallurgy 2002, 66, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, W.W.; Flores, F.A.; Henderson, J.A. Comparison of chalcocite dissolution in the oxygenated, aqueous sulfate and chloride systems. Miner. Eng. 1992, 5, 817–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemzadeh, M.; Liu, W. The response of sulfur chemical state to different leaching conditions in chloride leaching of chalcocite. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 192, 105245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, K.; Jeldres, R.; Nieto, S.; Salinas-Rodríguez, E.; Robles, P.; Quezada, V.; Hernández-Ávila, J.; Toro, N. Leaching of pure chalcocite in a chloride media using waste water at high temperature. Metals 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saldaña, M.; Rodríguez, F.; Rojas, A.; Pérez, K.; Angulo, P. Development of an empirical model for copper extraction from chalcocite in chloride media. Hem. Ind. 2020, 74, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, G. Chloride assisted leaching of chalcocite by oxygenated sulphuric acid via Cu(II)-OH-Cl. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, D.; Trigueros, E.; Robles, P.; Leiva, W.H.; Jeldres, R.I.; Toledo, P.G.; Toro, N. Leaching of Pure Chalcocite with Reject Brine and MnO2 from Manganese Nodules. Metals 2020, 10, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszer, A.; Wódka, J.; Chmielewski, T.; Matuska, S. Covellinisation of copper sulphide minerals under pressure leaching conditions. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 137, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veltman, H.; Pellegrini, S.; Mackiw, V.N. Direct acid pressure leaching of chalcocite concentrate. JOM 1967, 19, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, J.; Aye, K.T.; Breuer, P.; Meakin, R. The dissolution of covellite and chalcocite in cyanide solutions. The dissolution of covellite and chalcocite in cyanide solutions. In Proceedings of the World Gold 2011: 50th Annual Conference of Metallurgists of CIM, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2–5 October 2011; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shantz, R.; Fisher, W.W. The kinetics of the dissolution of chalcocite in alkaline cyanide solution. Metall. Trans. B 1977, 8, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, Y.; Katoh, M.; Asai, S. Leaching kinetics of copper from natural chalcocite in alkaline Na4EDTA solutions. Metall. Trans. B 1991, 22, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomášek, J.; Neumann, L. Dissolution of secondary copper sulphides using complex-forming agents (EDTA, EDA). Part II: Chalcocite dissolution in EDTA and EDA. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1982, 9, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herreros, O.; Quiroz, R.; Viñals, J. Dissolution kinetics of copper, white metal and natural chalcocite in Cl2/Cl− media. Hydrometallurgy 1999, 51, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.C.; Abarzúa, E.; Padilla, R. Oxygen pressure leaching of white metal. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 86, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraga, G.A.; Jamett, N.E.; Hernández, P.C.; Graber, T.A.; Taboada, M.E. Chalcopyrite Leaching with Hydrogen Peroxide and Iodine Species in Acidic Chloride Media at Room Temperature: Technical and Economic Evaluation. Metals 2021, 11, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldaña, M.; Toro, N.; Castillo, J.; Hernández, P.; Navarra, A. Optimization of the heap leaching process through changes in modes of operation and discrete event simulation. Minerals 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- COCHILCO. Proyeccion Agua Mineria del Cobre 2019–2030; COCHILCO: Santiago, Chile, 2020; Available online: https://www.cochilco.cl/Listado%20Temtico/proyeccion%20agua%20mineria%20del%20cobre%202019-2030%20VF.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Whiteside, L.S.; Goble, R.J. Structural and compositional changes in copper sulfides during leaching and dissolution. Can. Mineral. 1986, 24, 247–258. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, R.; Zou, G.; Zhong, S.; Wu, Z.; Chan, B.; Wang, D. Why Zijinshan copper bioheapleaching plant works efficiently at low microbial activity—Study on leaching kinetics of copper sulfides and its implications. Miner. Eng. 2013, 48, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, M.; Basson, P. The anodic behaviour of covellite in chloride solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 172, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.C.; Honores, S.; Padilla, R. Leaching kinetics of digenite concentrate in oxygenated chloride media at ambient pressure. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1998, 29, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herreros, O.; Viñals, J. Leaching of sulfide copper ore in a NaCl–H2SO4–O2 media with acid pre-treatment. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 89, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemzadeh, M.; Dixon, D.G.; Liu, W. Modelling the kinetics of chalcocite leaching in acidified cupric chloride media under fully controlled pH and potential. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 189, 105114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, K.; Toro, N.; Saldaña, M.; Salinas-Rodríguez, E.; Robles, P.; Torres, D.; Jeldres, R.I. Statistical Study for Leaching of Covellite in a Chloride Media. Metals 2020, 10, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashemzadeh, M.; Dixon, D.G.; Liu, W. Modelling the kinetics of chalcocite leaching in acidified ferric chloride media under fully controlled pH and potential. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 186, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, P. Estudio del Equilibrio Sólido-Líquido de Sistemas Acuosos de Minerales de Cobre Con Agua de Mar, Aplicado A Procesos de Lixiviación, Universidad de Antofagasta. 2013. Available online: https://intranetua.uantof.cl/docs/carreras/tesis_pia_hernandez.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Schlesinger, M.; King, M.; Sole, K.; Davenport, W. Extractive Metallurgy of Copper, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; ISBN 9780080967899. [Google Scholar]
- Velásquez-Yévenes, L. The Kinetics of the Dissolution of Chalcopyrite in Chloride Media, Murdoch University. 2009. Available online: https://researchrepository.murdoch.edu.au/id/eprint/475/ (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Dutrizac, J.E. The leaching of sulphide minerals in chloride media. Hydrometallurgy 1992, 29, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, N.; Pérez, K.; Saldaña, M.; Jeldres, R.I.; Jeldres, M.; Cánovas, M. Dissolution of pure chalcopyrite with manganese nodules and waste water. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 9, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, H.; Abdollahy, M.; Mostoufi, N. Kinetics of chemical leaching of chalcocite from low-grade copper ore: Size-distribution behavior. J. Min. Environ. 2015, 6, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro Villarroel, N.R. Optimización de Parámetros Para la Extracción de Elementos Desde Minerales en Medios Ácido, Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena. 2020. Available online: https://repositorio.upct.es/handle/10317/8504 (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Chang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Wang, J.; Qin, W. Effect of temperature-induced phase transitions on bioleaching of chalcopyrite. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 2183–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kawashima, N.; Li, J.; Chandra, A.P.; Gerson, A.R. A review of the structure, and fundamental mechanisms and kinetics of the leaching of chalcopyrite. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 197, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Granata, G. The Effect of Aeration on Chalcocite Heap Leaching. In Extraction; Davis, B., Moats, M., Wang, S., Gregurek, D., Kapusta, J., Battle, T., Schlesinger, M., Alvear, G., Jak, E., Goodall, G., Eds.; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, N.B.; Madhuchhanda, M.; Rao, K.S.; Rath, P.C.; Paramguru, R.K. Oxidation of chalcopyrite in the presence of manganese dioxide in hydrochloric acid medium. Hydrometallurgy 2000, 57, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczuk, P.B.; Manaig, D.O.; Drivenes, K.; Snook, B.; Aasly, K.; Kleiv, R.A. Galvanic leaching of seafloor massive sulphides using MnO2 in H2SO4-NaCl media. Minerals 2018, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, D.; Ayala, L.; Jeldres, R.I.; Cerecedo-Sáenz, E.; Salinas-Rodríguez, E.; Robles, P.; Toro, N. Leaching Chalcopyrite with High MnO2 and Chloride Concentrations. Metals 2020, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

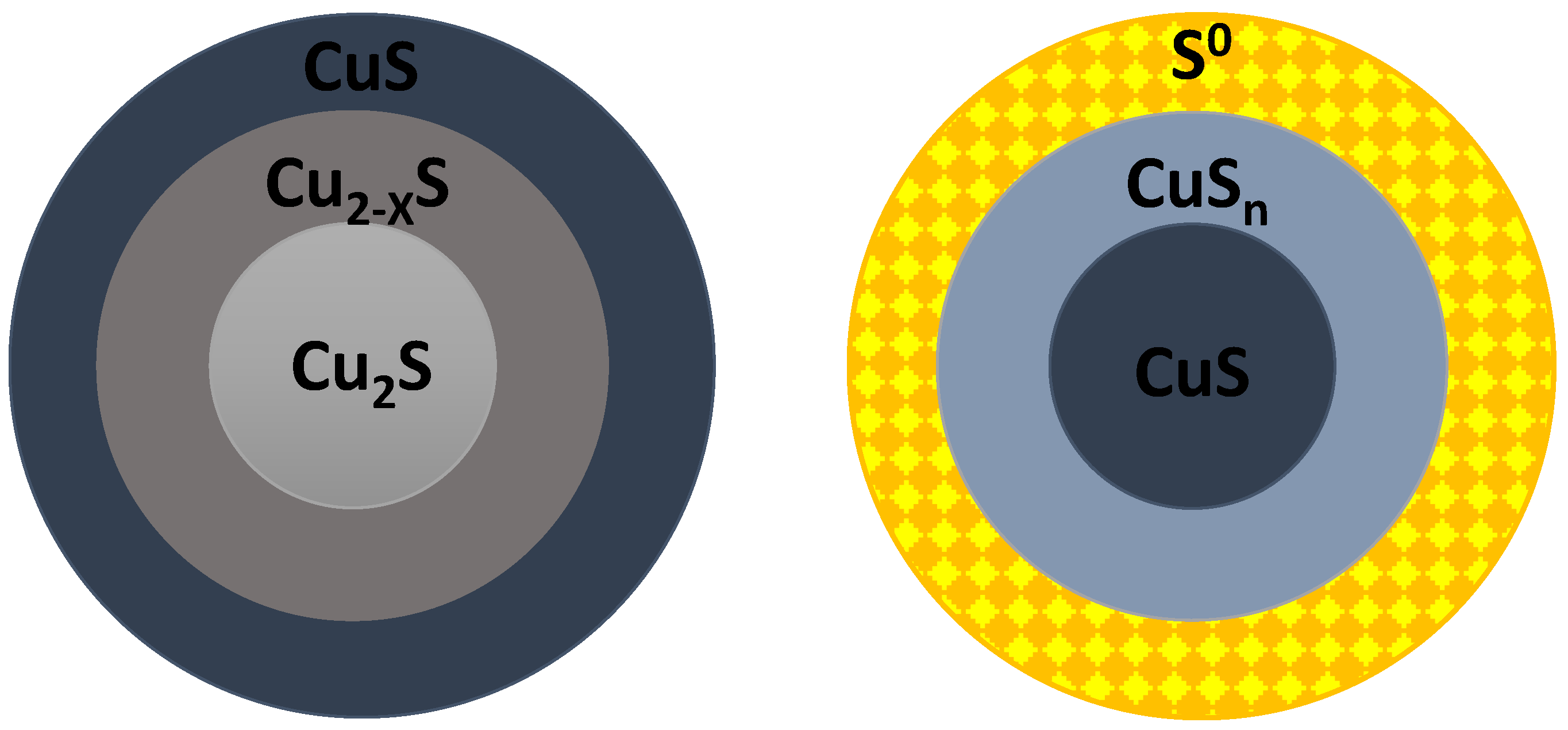
| Mineral | Composition | System | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chalcocite (low T) | Cu1.99–2S | Monoclinic | T < 105 °C |
| Chalcocite (high T) | Cu1.98–2S | Hexagonal | ~105 °C < T < ~425 °C |
| Chalcocite (high P and T) | Cu2S | Tetragonal | 1 kbar < P, T < 500 °C |
| Djurleite | Cu1.93–1.96S | Monoclinic | T < 93 °C |
| Digenite (low T) | Cu1.75–1.8S | Cubic | Metastable |
| Digenite (high T) | Cu1.73–2S | Cubic | 83 °C < T |
| Anilite | Cu1.75S | Orthorhombic | T < 72 °C |
| Investigation | Leaching Agent | Parameters Evaluated | Temperature (°C) | Reference | Max Cu Extraction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The kinetics of leaching chalcocite (synthetic) in acidic oxygenated sulfate–chloride solutions | NaCl, H2SO4, HCl, HNO3, and Fe3+ | Oxygen flow, stirring speed, temperature, acid concentration, ferric ion concentration, chloride concentration, and particle size | 65–94 | [24] | 97 |
| Leaching kinetics of digenite concentrate in oxygenated chloride media at ambient pressure | CuCl2, HCl, and NaCl | Effect of stirring speed, oxygen flow, cupric ion concentration, chloride concentration, acid concentration, and temperature effect | 50–100 | [61] | 95 |
| Leaching of sulfide copper ore in a NaCl–H2SO4–O2 media with acid pre-treatment | NaCl and H2SO4 | Chloride concentration, effect of agitation with compressed air, percentage of solids, and particle size | 20 | [62] | 78 |
| The kinetics of dissolution of synthetic covellite, chalcocite, and digenite in dilute chloride solutions at ambient temperatures | HCl, Cu2+, and Fe3+ | Potential redox effect, chloride concentration, acid concentration, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and pyrite effect | 35 | [38] | 98 |
| Leaching of pure chalcocite in a chloride media using seawater and wastewater | NaCl, H2SO4, and Cl− from seawater and wastewater | Chloride and acid concentration | 25 | [13] | 68 |
| Modeling the kinetics of chalcocite leaching in acidified cupric chloride media under fully controlled pH and potential | HCl, CuCl2, NaCl, KCl, CaCl2, and MgCl2 | Chloride concentration, cupric concentration, particle size, and temperature | 25–65 | [63] | 98 |
| Leaching of pure chalcocite in a chloride medium using wastewater at high temperature | H2SO4 and Cl− from wastewater | Temperature effect | 65–95 | [43] | 97 |
| The response of the sulfur chemical state to different leaching conditions in chloride leaching of chalcocite | FeCl3, CuCl2, and HCl | Chloride concentration, temperature, and potential redox effect. | 35–55 | [42] | 88 |
| Leaching of pure chalcocite with reject brine and MnO2 from manganese nodules | H2SO4, MnO2, and Cl− from seawater and wastewater | MnO2, chloride, and acid concentration | 25 | [46] | 71 |
| Experimental Parameters | Low | Medium | High |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time (h) | 4 | 8 | 12 |
| Cl− concentration (g/L) | 20 | 50 | 100 |
| H2SO4 (mol/L) | 0.5 | 1 | 2 |
| Experimental Conditions and Results | [13] | [46] |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 25 | 25 |
| Particle size of Cu2S (μm) | −147 + 104 | −147 + 104 |
| H2SO4 concentration (mol/L) | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| MnO2/Cu2S ratio (w/w) | - | 0.25/1 |
| Dissolution in seawater after 4 h (%) | 32.8 | 35.6 |
| Dissolution in reject brine after 4 h (%) | 36 | 40 |
| Dissolution in seawater after 48 h (%) | 63.4 | 64.7 |
| Dissolution in reject brine after 48 h (%) | 64.6 | 66.2 |
| Parameters | First Stage | Second Stage |
|---|---|---|
| Chloride concentration | Increases dissolution kinetics | Help prevent passivation |
| Stirring rate | It is not relevant | It is not relevant |
| Acid concentration | A low concentration of H2SO4 (0.02 mol/L) is sufficient to dissolve the mineral. | Increases dissolution kinetics |
| The same results are obtained between 0.1 and 1 mol/L of H2SO4. | ||
| Particle size | Increase in dissolution kinetics. | Slight increase in dissolution kinetics |
| Temperature | Significantly accelerates dissolution | Significantly accelerates dissolution |
| Helps prevent passivation | ||
| Redox potential | Low redox potential is required (≥500 mV) | High redox potential values are required (>650 mV) |
| Oxidizing agents (air, Fe3+, MnO2) | Increases dissolution kinetics by adding low concentrations | Increases dissolution kinetics, but only at high concentrations |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toro, N.; Moraga, C.; Torres, D.; Saldaña, M.; Pérez, K.; Gálvez, E. Leaching Chalcocite in Chloride Media—A Review. Minerals 2021, 11, 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111197
Toro N, Moraga C, Torres D, Saldaña M, Pérez K, Gálvez E. Leaching Chalcocite in Chloride Media—A Review. Minerals. 2021; 11(11):1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111197
Chicago/Turabian StyleToro, Norman, Carlos Moraga, David Torres, Manuel Saldaña, Kevin Pérez, and Edelmira Gálvez. 2021. "Leaching Chalcocite in Chloride Media—A Review" Minerals 11, no. 11: 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111197
APA StyleToro, N., Moraga, C., Torres, D., Saldaña, M., Pérez, K., & Gálvez, E. (2021). Leaching Chalcocite in Chloride Media—A Review. Minerals, 11(11), 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111197








