Specific Mixing Energy of Cemented Paste Backfill, Part II: Influence on the Rheological and Mechanical Properties and Practical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tailings Characterization
2.2. Cemented Paste Backfill (CPB) Proportioning and Measurement of the Specific Mixing Energy (SME)
2.3. Rheological and Mechanical Characterisation of CPB
3. Results
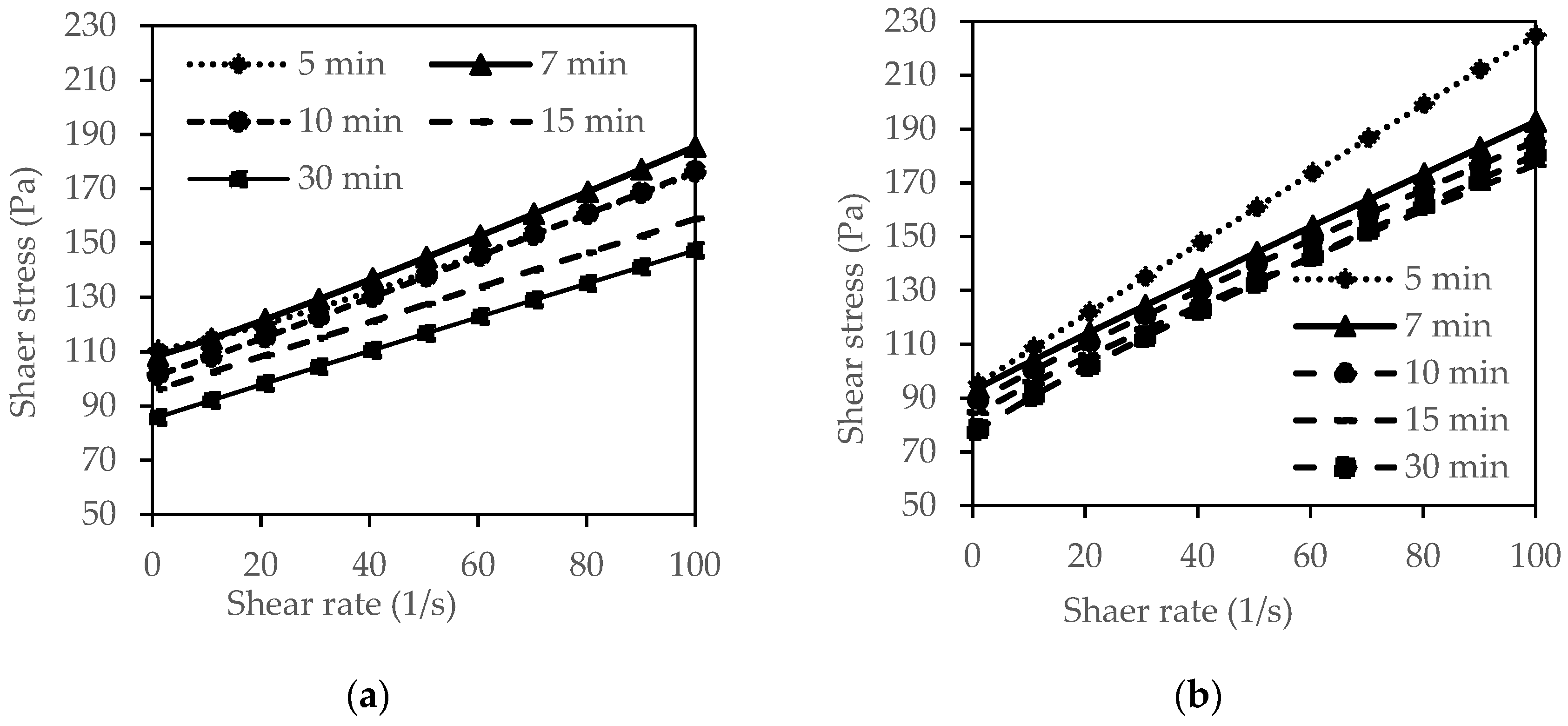
3.1. Effect of Mixing Time on the Rheological and Mechanical Properties of CPB
3.2. Effect of Mixing Speed on the Rheological and Mechanical Properties of CPB
3.3. Effect of the SME on the Rheological and Mechanical Properties of CPB
4. Discussion
4.1. Link between Consistency (K) and Flow Behavior (n) Indexes
4.2. Effect of the Type of Tailings on the Variation of the Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS) with the SME
4.3. Practical Application 1: Preliminary Prediction of the Change in Rheological Properties of CPB along the Distribution System
4.3.1. Assessing the Specific Energy Dissipation during CPB Transportation
4.3.2. Prediction of the Change in Yield Stress and Infinite Viscosity of CPB along the Pipeline
4.4. Practical Application 2: Assessment of Mixing Time during the Optimization Phase of CPB in the Laboratory
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassani, F.; Archibald, J. Mine Backfill (on CD-ROM); Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum: Montreal, QC, Canada, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Belem, T.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B. Mechanical behaviour of cemented paste backfill. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Conference of the Canadian Geotechnical Society, Montreal, QC, Canada, 15–18 October 2000; Volume 1, ISBN 0-920505-15-5. [Google Scholar]
- Landriault, D. The present state of paste fill in Canadian underground mining. In Proceedings of the 97th Annual General Meeting of CIM Rock Mechanics and Strata Control, Halifax, NS, Canada, 14–18 May 1995; pp. 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Landriault, D.; Verburg, R.; Cincilla, W.; Welch, D. Paste technology for underground backfill and surface tailings disposal applications. In Proceedings of the Short Course Notes in CIM Technical Workshop, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 27 April 1997; p. 120. [Google Scholar]
- Belem, T.; El Aatar, O.; Bussière, B.; Benzaazoua, M. Gravity-driven 1-D consolidation of cemented paste backfill in 3-m-high columns. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2016, 1, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tariq, A.; Yanful, E.K. A review of binders used in cemented paste tailings for underground and surface disposal practices. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 131, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Fall, M.; Belem, T. A contribution to understanding the hardening process of cemented pastefill. Miner. Eng. 2004, 17, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Belem, T.; Bussière, B.; Ouellet, S. Évolution des propriétés des remblais en pâte: Principaux paramètres d’influence. In Proceedings of the 20th Colloque en Contrôle de Terrain, Association Minière du Québec, Val d’Or, QC, Canada, 22–23 March 2005; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Ercikdi, B.; Kesimal, A.; Cihangir, F.; Deveci, H.; Alp, İ. Cemented paste backfill of sulphide-rich tailings: Importance of binder type and dosage. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, M. Study on the Homogenization Speed in a Tank Equipped with Maxblend Impeller. Master’s Thesis, École Polytechnique de Montréal, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, Q.; Boger, D. Application of rheology to solving tailings disposal problems. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1998, 54, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennberg, T.; Sellgren, A. Pumping evaluations with paste tailings thickened close to the surface disposal area. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on the Hydraulic Transport of Solids, Cape Town, South Africa, 7–10 May 2007; pp. 561–574. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, A. Pipeline transport of high-density slurries: A historical review of past mistakes, lessons learned and current technologies. Min. Technol. 2012, 121, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Ferron, R.D. Influence of high mixing intensity on rheology, hydration, and microstructure of fresh state cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 84, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Jennings, H. Influences of mixing methods on the microstructure and rheological behavior of cement paste. Adv. Cem. Based Mater. 1995, 2, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfill, P.; Swift, D. The effect of mixing on the rheology of cement-based materials containing high performance superplasticisers. In Proceedings of the Nordic Rheology Conference, Reykjavik, Iceland, 4–6 August 2004; pp. 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Schießl, P.; Mazanec, O.; Lowke, D. SCC and UHPC—Effect of Mixing Technology on Fresh Concrete Properties. In Advances in Construction Materials 2007; Grosse, C.U., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 513–522. [Google Scholar]
- Mazanec, O.; Lowke, D.; Schießl, P. Mixing of high-performance concrete: Effect of concrete composition and mixing intensity on mixing time. Mater. Struct. 2010, 43, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallevik, J.E.; Wallevik, O.H. Analysis of shear rate inside a concrete truck mixer. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 95, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dils, J.; De Schutter, G.; Boel, V. Influence of mixing procedure and mixer type on fresh and hardened properties of concrete: A review. Mater. Struct. 2012, 45, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fládr, J.; Bílý, P. Influence of mixing procedure on mechanical properties of high-performance concrete. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Fibre Concrete 2017, Prague, Czech Republic, 13–16 September 2017; Volume 246, p. 012012. [Google Scholar]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Ouellet, J.; Servant, S.; Newman, P.; Verburg, R. Cementitious backfill with high sulfur content physical, chemical, and mineralogical characterization. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesimal, A.; Yilmaz, E.; Ercikdi, B.; Alp, I.; Deveci, H. Effect of properties of tailings and binder on the short-and long-term strength and stability of cemented paste backfill. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 3703–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Fall, M.; Cai, S. Coupling temperature, cement hydration and rheological behaviour of fresh cemented paste backfill. Miner. Eng. 2013, 42, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohestani, B.; Belem, T.; Koubaa, A.; Bussière, B. Experimental investigation into the compressive strength development of cemented paste backfill containing Nano-silica. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 72, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhang, J.; Klein, B.; Zhou, N.; Dewit, B. Experimental characterization of the influence of solid components on the rheological and mechanical properties of cemented paste backfill. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 168, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouattara, D.; Belem, T.; Mbonimpa, M.; Yahia, A. Effect of superplasticizers on the consistency and unconfined compressive strength of cemented paste backfills. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 181, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouattara, D.; Yahia, A.; Mbonimpa, M.; Belem, T. Effects of superplasticizer on rheological properties of cemented paste backfills. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 161, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikonda, R.K.; Mamert, M.; Tikou, B. Specific mixing energy of cemented paste backfill: Part I. Laboratory determination and influence on the consistency. Minerals. submitted.
- Pullum, L. Pipelining tailings, pastes, and backfill. In Proceedings of the Paste 2007: The Tenth International Seminar on Paste and Thickened Tailings, Perth, Australia, 13–15 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, C.; Thieme, J.; Neuhäusler, U.; Jacobsen, C.; Kaulich, B.; Salome, M.; Susini, J. Spectromicroscopy of soil colloids. J. Phys. IV Fr. 2003, 104, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussot, P. Rhéophysique: La Matière dans Tous ses États; CNRS Éditions: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, E.; Belem, T.; Bussière, B.; Benzaazoua, M. Relationships between microstructural properties and compressive strength of consolidated and unconsolidated cemented paste backfills. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, M. Effect of Change in Mixing Time of Mixer on Wet Density, Dry Density, Workability and Compressive Strength of M-20 Grade Concrete. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2016, 5, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Wu, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X. The effects of mixing time on cement paste slurry transport and mechanical property. In Proceedings of the Paste 2017: The 20th International Seminar on Paste and Thickened Tailings, Beijing, China, 15–18 June 2017; pp. 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Mahboub, K.; Cutshaw, Q. Effects of Fresh Concrete Temperature and Mixing Time on Compressive Strength of Concrete. Mater. J. 2001, 98, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, C.; Vickery, J.; Backer, R.R. Transport of Total Tailings Paste Backfill: Results of Full-Scale Pipe Test Loop Pumping Tests. Report of Investigation RI 9593; United States Department of the Interior: District of Columbia, DC, USA, 1995.
- Gawu, S.K.; Fourie, A. Assessment of the modified slump test as a measure of the yield stress of high-density thickened tailings. Can. Geotech. J. 2004, 41, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejo, B.; Barrientos, A. Model for yield stress of quartz pulps and copper tailings. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2009, 93, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouattara, D.; Mbonimpa, M.; Belem, T. Rheological Properties of Thickened Tailings and Cemented Paste Tailings and the Effect of Mixture Characteristics on Shearing Behaviour. In Proceedings of the 63rd Canadian Geotechnical Conference and 1st Joint CGS/CNC-IPA Permafrost Specialty Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 12–16 September 2010; pp. 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Estimation model for yield stress of fresh uncemented thickened tailings: Coupled effects of true solid density, bulk density, and solid concentration. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 143, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.A.; Hutton, J.F.; Walters, K. An Introduction to Rheology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Zhou, X. Effect of high mixing intensity on rheological properties of cemented paste backfill. Minerals 2019, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, K.; Bier, T.A. Mechanisms of degradation in rheological properties due to pumping and mixing. Adv. Civ. Eng. Mater. 2014, 3, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creber, K.J.; McGuinness, M.; Kermani, M.F.; Hassani, F.P. Investigation into changes in pastefill properties during pipeline transport. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 163, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandanjon, P.-O.; de Larrard, F.; Dehousse, B.; Villain, G.; Maillot, R.; Laplante, P. Homogénéisation des bétons en centrale de fabrication discontinue. Influence du temps de malaxage et du mode d’introduction des additions minérales. Bull.-Lab. Des. Ponts Chaussées 2000, 228, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Chopin, D. Malaxage des Bétons à Hautes Performances et des Bétons Auto-Plaçants: Optimisation du Temps de Fabrication. Ph.D. Thesis, École Centrale de Nantes et Université de Nantes, Nantes, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lea, F. The Chemistry of Cement and Concrete; Chemical Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Van Kesteren, W.; Talmon, A.; Pennekamp, J.G.; Costello, M.; Flynn, W. Dredged material placement under non-segregating conditions. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth World Dredging Congress (WODCON XVIII), Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 27 May–1 June 2007; pp. 1559–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Pirouz, B.; Kavianpour, M.R.; Williams, P. Sheared and un-sheared segregation and settling behavior of fine sand particles in hyperconcentrated homogeneous sand-water mixture flows. J. Hydraul. Res. 2008, 46, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamee, P.K.; Aggarwal, N. Explicit equations for laminar flow of Bingham plastic fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2011, 76, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamee, P.K.; Aggarwal, N. Explicit equations for laminar flow of Herschel–Bulkley fluids. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 89, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.J.; Steffe, J.F. Comparison of friction factor equations for non-newtonian fluids in pipe flow. J. Food Process. Eng. 1986, 9, 93–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouattara, D.; Mbonimpa, M.; Yahia, A.; Belem, T. Assessment of rheological parameters of high density cemented paste backfill mixtures incorporating superplasticizers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björn, A.; de La Monja, P.S.; Karlsson, A.; Ejlertsson, J.; Svensson, B.H. Rheological characterization. Biogas 2012, 1, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Belem, T.; Benzaazoua, M.; El Aatar, O.; Yilmaz, E.; Belem, T.; Benzaazoua, M.; El Aatar, O.; Yilmaz, E. Effect of drainage and the pore water pressure dissipation on the backfilling sequencing. In Proceedings of the 23rd World Mining Congress, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–15 August 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hane, I.; Belem, T.; Benzaazoua, M.; Maqsoud, A. Laboratory investigation into the compressive strength of cemented paste tailings aggregate fills. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Underground Mining Technology, Sudbury, ON, Canada, 11–13 October 2017; pp. 363–373. [Google Scholar]
- Fall, M.; Benzaazoua, M.; Ouellet, S. Experimental characterization of the influence of tailings fineness and density on the quality of cemented paste backfill. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Belem, T.; Ouellet, S.; Fall, M. Utilisation du remblai en pâte comme support de terrain. Partie II: Comportement à court, a moyen et à long terme. In Proceedings of the Après-Mines, Nancy, France, 5–7 February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Belem, T.; Bussiere, B. Chemical factors that influence the performance of mine sulphidic paste backfill. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzaiene, R. On the Flow Mechanics of Mine Backfill Slurries in Pipelines; McGill University Libraries: Montréal, QC, Canada, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.; Chen, Q.; Fourie, A.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Q. Pressure drop in pipe flow of cemented paste backfill: Experimental and modeling study. Powder Technol. 2018, 333, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiantzas, J.D. Explicit power formula for the Darcy–Weisbach pipe flow equation: Application in optimal pipeline design. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2008, 134, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, L.F. Friction factors for pipe flow. Trans. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. 1944, 66, 671–684. [Google Scholar]
- Darby, R. Determination and Utilization of Rheological Properties for Prediction of Flow Behavior of Pseudohomogeneous Slurries. In Proceedings of the 9th ITCOST, STA, Carson City, NV, USA, 21–22 March 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Csizmadia, P.; Till, S. The Effect of Rheology Model of an Activated Sludge on to the Predicted Losses by an Elbow. Period. Polytech. Mech. Eng. 2018, 62, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, K.C.; Addie, G.R.; Sellgren, A.; Clift, R. Slurry Transport Using Centrifugal Pumps; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, A. High density slurry and paste tailings, transport systems. In Proceedings of the International Platinum Conference: Platinum Adding Value, Sun City, South Africa, 3–7 October 2004; pp. 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ouattara, D. Étude Expérimentale des Propriétés Rhéologiques Et Mécaniques des Remblais Miniers en Pâte Cimentés Incorporant des Superplastifiants. Ph.D. Thesis, Université du Québec en Abitibi-Témiscamingue, Rouyn-Noranda, QC, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kalonji, K. Étude des Propriétés Rhéologiques et du Transport du Remblai Cimenté en Pâte en Conditions Nordiques. Master’s Thesis, Université du Québec en Abitibi-Témiscamingue, Rouyn-Noranda, QC, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Cai, S.-J.; Huang, G. Coupled effect of cement hydration and temperature on rheological properties of fresh cemented tailings backfill slurry. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 2954–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalonji, K.; Mbonimpa, M.; Belem, T.; Benzaazoua, M.; Beya, F.; Ouellet, S. Preliminary investigation of the effect of temperature and salinity on the rheological properties of fresh cemented paste backfills. In Proceedings of the 68th Canadian Geotechnical Conference and 7th Canadian Permafrost Conference, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 21–23 September 2015; pp. 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Xiapeng, P.; Fall, M.; Haruna, S. Sulphate induced changes of rheological properties of cemented paste backfill. Miner. Eng. 2019, 141, 105849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalonji, K.; Mbonimpa, M.; Belem, T.; Benzaazoua, M.; Beya, F.K.; Ouellet, S. Calage D’un Modèle Numérique de Prédiction de L’évolution de la Température Pendant le Transport du Remblai en Pâte Cimenté. In Proceedings of the 69th Conférence Canadienne de Géotechnique: GéoVancouver 2016, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2–5 October 2016. [Google Scholar]











| Variable Mixing Parameters | Constant Mixing Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPB-T1 | ||||||
| Mixtures Mixing time (min) | M01 5 | M02 7 | M03 10 | M04 15 | M05 30 | Mixing speed (166 rpm) Load mass (4.7 kg) |
| Mixtures Mixing speed (rpm) | M06 91 | M07 166 | M08 282 | Mixing time (5 min) Load mass (4.7 kg) | ||
| CPB-T2 | ||||||
| Mixtures Mixing time (min) | M09 5 | M10 7 | M11 10 | M12 15 | M13 30 | Mixing speed (166 rpm) Load mass (4.2 kg) |
| Mixtures Mixing speed (rpm) | M14 91 | M15 166 | M16 282 | Mixing time (5 min) Load mass (4.2 kg) | ||
| Parameters | Values | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mixing time t (min) | 7 | Infinite viscosity (Pa.s) | 0.92 |
| Mixing speed (rpm) | 166 | Hydraulic diameter D (m) | 0.15 |
| Load mass of mixer m (Kg) | 4.7 | Pipeline length L (m) | 6445 |
| Yield stress (Pa) | 106 | Mean flow velocity U (m/s) | 1 |
| Consistency index K (Pa.sn) | 1.2 | Bulk Density (Kg/m3) | 2043 |
| Flow index n (-) | 0.97 | Solids content Cw (%) | 75 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dikonda, R.K.; Mbonimpa, M.; Belem, T. Specific Mixing Energy of Cemented Paste Backfill, Part II: Influence on the Rheological and Mechanical Properties and Practical Applications. Minerals 2021, 11, 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111159
Dikonda RK, Mbonimpa M, Belem T. Specific Mixing Energy of Cemented Paste Backfill, Part II: Influence on the Rheological and Mechanical Properties and Practical Applications. Minerals. 2021; 11(11):1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111159
Chicago/Turabian StyleDikonda, Reagan Kabanga, Mamert Mbonimpa, and Tikou Belem. 2021. "Specific Mixing Energy of Cemented Paste Backfill, Part II: Influence on the Rheological and Mechanical Properties and Practical Applications" Minerals 11, no. 11: 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111159
APA StyleDikonda, R. K., Mbonimpa, M., & Belem, T. (2021). Specific Mixing Energy of Cemented Paste Backfill, Part II: Influence on the Rheological and Mechanical Properties and Practical Applications. Minerals, 11(11), 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11111159







