Microstructure and Pb2+ Adsorption Properties of Blast Furnace Slag and Fly Ash based Geopolymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Geopolymer Synthesis
2.3. Microstructure Analysis
2.4. Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
- [Na+] = Na+ concentration in exchangeable solution (mg/L)
- V = Exchangeable solution volume (L)
- m = Mass
- MW = Molecular weight
2.5. Batch Adsorption Operation
- C0 = Initial concentration of heavy metal solution (mg/L)
- Ce = Remaining equilibrium or final concentration (mg/L)
- V = Solution volume (L)
- m = Mass of adsorbent (g)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mineralogical Analyses
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.4. Physical Adsorption of Gases by the BET Method
3.5. CEC
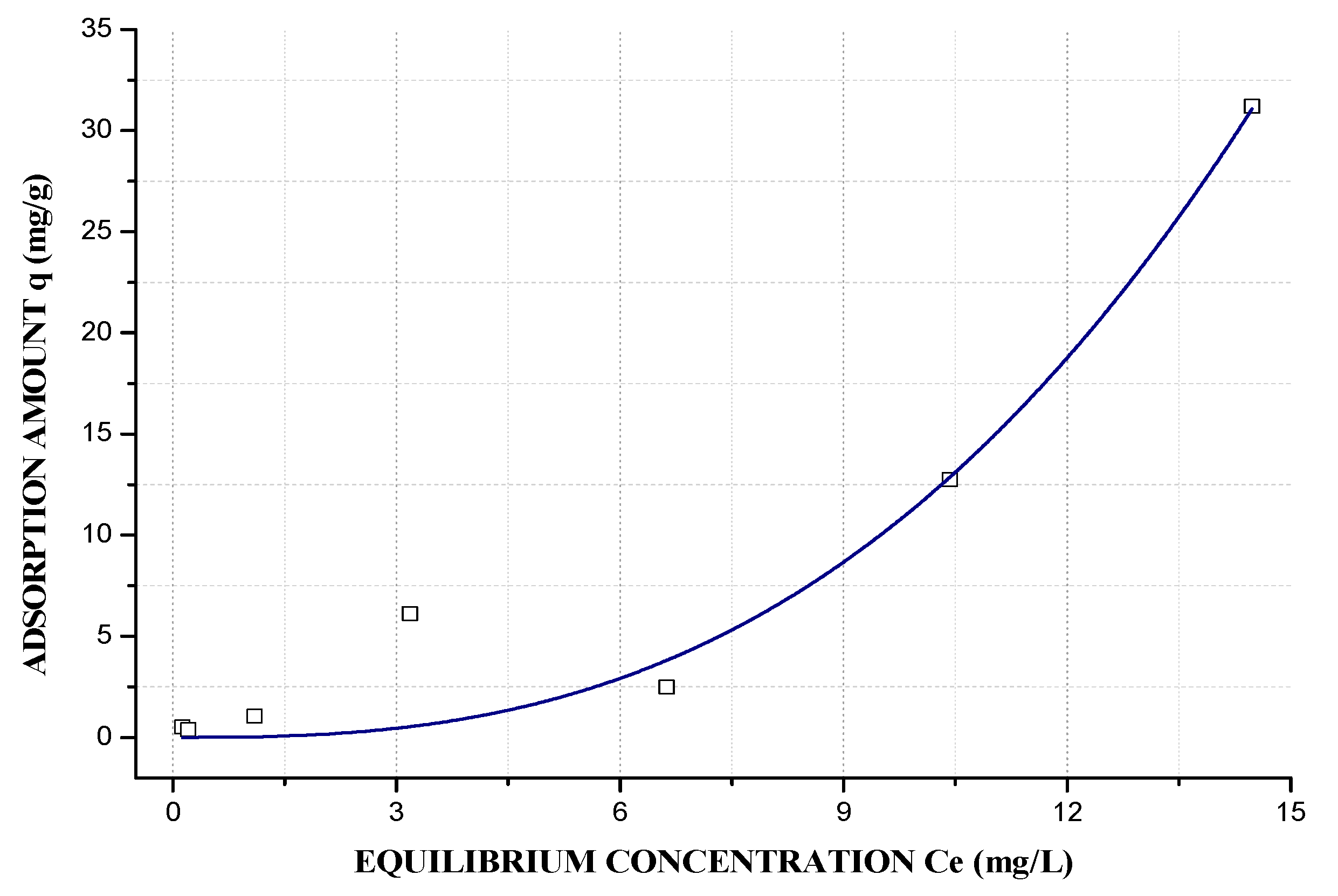
3.6. Adsorption Potential for Pb2+ Ions
3.7. Langmuir–Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De la Peña, M.E.; Ducci, J.; Zamora, V. Tratamiento de Aguas Residuales en México; IDB-TN-512; Banco Interamericano de Desarrollo: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Cardona-Gutiérrez, A.F.; Cabañas-Vargas, D.D.; Zepeda-Pedreguera, A. Evaluación del poder biosorbente de cáscara de naranja para la eliminación de metales pesados, Pb (II) y Zn (II). Ingeniería 2013, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bumanis, G.; Novais, R.M.; Carvalheiras, J.; Bajare, D.; Labrincha, J.A. Metals removal from aqueous solutions by tailored porous waste-based granulated alkali-activated materials. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 179, 105147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onutai, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Thavorniti, P.; Jiemsirilers, S. Removal of Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Cd2+ from wastewater using fly ash based geopolymer as an adsorbent. Key Eng. Mater. 2018, 773, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeng-Gyasi, E. Sources of lead exposure in various countries. Rev. Environ. Health 2019, 34, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dignam, T.; Kaufmann, R.B.; LeStourgeon, L.; Brown, M.J. Control of lead sources in the United States, 1970–2017: Public health progress and current challenges to eliminating lead exposure. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 176, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, D.M.; Maurer, J.R. Assessment of Lead Contamination Sources Exposing California Condors; Species Conservation and Recovery Program report 2003-02; California Department of Fish and Game Habitat Conservation Planning Branch: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.Y.; Chen, T.; Yu, J.; Qin, D.P.; Chen, L. Lead contamination and its potential sources in vegetables and soils of Fujian, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2012, 34, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, Y.C.; Vergara, I.; Torres, O.E.; Díaz, M.; González, E.E. Contaminación por metales pesados: Implicaciones en salud, ambiente y seguridad alimentaria. Rev. Ing. Investig. Y Desarro. 2016, 16, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, N.C.; Hatzidaki, E.G.; Belivanis, S.; Tzanakakis, G.N.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Lead toxicity update. A brief review. Med. Sci. Monit. 2005, 11, 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Rivas, S.C.; Ramos-Clamont Montfort, G. Descontaminación de arsénico, cadmio y plomo en agua por biosorción con Saccharomyces cerevisiae. TIP Rev. Espec. En Cienc. Quím. Biol. 2018, 21, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohod, C.V.; Dhote, J. Review of heavy metals in drinking water and their effect on human health. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2013, 2, 2992–2996. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, S.; Griswold, W. Human health effects of heavy metals: Briefs for citizens. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jan, A.T.; Azam, M.; Siddiqui, K.; Ali, A.; Choi, I.; Haq, Q.M.R. Heavy metals and human health: Mechanistic insight into toxicity and counter defense system of antioxidants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 29592–29630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez Vázquez, R.G. Efecto de los Metales Pesados en la Salud Humana. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad de Pinar del Río “Hermanos Saíz Montes de Oca”, Pinar del Río, Cuba, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Caviedes Rubio, D.I.; Muñoz Calderón, R.A.; Perdomo Gualtero, A.; Rodríguez Acosta, D.; Sandoval Rojas, I.J. Tratamientos para la remoción de metales pesados comúnmente presentes en aguas residuales industriales. Una revisión. Rev. Ing. Y Reg. 2015, 13, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bapat, S.A.; Jaspal, D.K. Parthenium hysterophorus: Novel adsorbent for the removal of heavy metals and dyes. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2016, 2, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlock, M.M.; Howerton, B.S.; Atwood, D.A. Chemical precipitation of heavy metals from acid mine drainage. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4757–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efome, J.E.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Lan, C.Q. Effects of operating parameters and coexisting ions on the efficiency of heavy metal ions removal by nano-fibrous metal-organic framework membrane filtration process. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres Gaviria, L.F.; Ocampo Vélez, J.C.; Socarrás Cárdenas, A. Reducción del nivel de potasio en vinaza de destilería utilizando resinas de intercambio iónico. Rev. Investig. Agrar. Y Ambient. 2018, 10, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfferich, F. Ion. Exchange; Hill, M., Ed.; Dover Publications, INC.: New York, NY, USA, 1995; ISBN 0-486-68784-8. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, I.S.; Silva, D.L.; Pereira, T.B.; Gonzálves, G.R.F.; Veríssimo, L.A.A.; Veloso, C.M.; Bonomo, R.C.F.; Fontan, R.C.I. Capture of lectins from jackfruit (Artocarpus integrifolia) seeds in a single step using a supermacroporous ion exchange cryogel. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quim. 2019, 18, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Guzmán, F.J. Study of Geopolymer Adsorbents Prepared from Metakaolin and Rice Husk Silica for Targeting to Heavy Metal Capture. Ph.D. Thesis, Nagaoka University of Technology, Nagaoka, Japan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Guo, L.; Ren, D.; Duan, P. Novel composites based on geopolymer for removal of Pb (II). Mater. Lett. 2018, 239, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaquirán-Caicedo, M.A.; Mejía de Gutiérrez, R. Synthesis of ceramic materials from ecofriendly geopolymer precursors. Mater. Lett. 2018, 230, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers. J. Therm. Anal. 1991, 37, 1633–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Introduction of Geopolymers. Geopolymers. Structure, Processing, Properties and Industrial Applications, 1st ed.; Provis, J.L., van Deventer, J.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; ISBN 9781845694494. [Google Scholar]
- Liew, Y.M.; Heah, C.Y.; Mohd Mustafa, A.B.; Kamarudin, H. Structure and properties of clay-based geopolymer cements: A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 83, 595–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymer. Chemistry & Applications, 2nd ed.; Institut Geopolymere: Saint-Quentin, France, 2008; ISBN 2-9514820-1-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, R.; Mehrotra, S.P. Influence of granulated blast furnace slag on the reaction, structure and properties of fly ash based geopolymer. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, A.; Karakoç, M.B. The resistance of blast furnace slag- and ferrochrome slag-based geopolymer concrete against acid attack. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Heponiemi, A.; Runtti, H.; Pesonen, J.; Yliniemi, J.; Lassi, U. Application of alkali-activated materials for water and wastewater treatment: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 271–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, S.; Panigrahi, R.; Sahu, P. Effect of silica fume on the properties of fly ash geopolymer concrete. Lect. Notes Civ. Eng. 2019, 25, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltue, T.; Suddeepong, A.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Samingthong, W.; Arulrajah, A.; Rashid, A.S.A. Strength development of recycled concrete aggregate stabilized with fly ash-rice husk ash based geopolymer as pavement base material. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liang, G.; Xu, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhai, M. Influence of rice husk ash on the waterproof properties of ultrafine fly ash based geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 208, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, R.; Khan, M.I. Supplementary Cementing Materials; Engineering Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 37, ISBN 978-3-642-17865-8. [Google Scholar]
- Riveros Olivares, B. Tratamiento de Aguas Residuales Municipales en la Ciudad de México. Bachelor´s Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma De México, Mexico City, Mexico, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Petrakis, E.; Karmali, V.; Bartzas, G.; Komnitsas, K. Grinding kinetics of slag and e ff ect of final particle size on the compressive strength of Alkali. Minerals 2019, 9, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. Standard Specifications for Wire Cloth and Sieves for Testing Purposes; ASTM E11—95; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Leyva Ramos, R.; Medellín Castillo, N.A.; Guerrero Coronado, R.M.; Berber Mendoza, M.S.; Aragón Piña, A.; Jacobo Azuara, A. Intercambio iónico de Plata (I) en solución acuosa sobre clinoptilolita. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2005, 21, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Mendoza-Castillo, D.I.; Reynel-Ávila, H.E. Adsorption Processes for Water Treatment and Puri Cation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 9783319581354. [Google Scholar]
- Jeppu, G.P.; Clement, T.P. A modified Langmuir-Freundlich isotherm model for simulating pH-dependent adsorption effects. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2012, 129–130, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komnitsas, K.; Bartzas, G.; Karmali, V.; Petrakis, E.; Witold, K.; Grzegorz, P.; Jaroslaw, K. Assessment of alkali activation potential of a Polish Ferronickel slag. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharaki, D.; Komnitsas, K.; Perdikatsis, V. Use of analytical techniques for identification of inorganic polymer gel composition. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 2715–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigil de la Villa Mencía, R.; Goiti, E.; Ocejo, M.; García Giménez, R. Synthesis of zeolite type analcime from industrial wastes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, A.A.; Shamsuddin, M.R.; Khan, M.I.; Rabat, N.E.; Zulfiqar, M.; Man, Z.; Siame, J.; Azizli, K.A. A review on geopolymers as emerging materials for the adsorption of heavy metals and dyes. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, M.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. Alkali activation of fly ash: Effect of the SiO2/Na2O ratio. Part I: FTIR study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 106, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadsden, J.A. Infrared Spectra of Minerals and Related Inorganic Compounds; Butterworths: London, UK, 1975; ISBN 0-408-70665-1. [Google Scholar]
- Yousuf, M.; Mollah, A.; Hess, T.R.; Tsai, Y.N.; Cocke, D.L. An FTIR and XPS investigations of the effects of carbonation on the solidification/stabilization of cement based systems-Portland type V with zinc. Cem. Concr. Res. 1993, 23, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M. Impact of alkali cations on properties of metakaolin and metakaolin/slag geopolymers: Microstructures in relation to sorption of 134 Cs radionuclide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovtun, M.; Kearsley, E.P.; Shekhovtsova, J. Cement and Concrete Research Chemical acceleration of a neutral granulated blast-furnace slag activated by sodium carbonate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 72, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. Mid-Infrared spectroscopic studies of alkali-activated fly ash structure. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 86, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Carrasco, M.; Puertas, F. Waste glass in the geopolymer preparation. Mechanical and microstructural characterisation. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 90, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yu, Q.L.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Reaction kinetics, gel character and strength of ambient temperature cured alkali activated slag-fly ash blends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 80, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, X.L.; Wang, J.X.; Liu, C.Z.; Lai, Y.M.; Hong, Z.K.; Zheng, J.P. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of alkali-activated slag-fly ash-metakaolin cementitious materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 155, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Provis, J.L.; Bullen, F.; Reid, A.; Zhu, Y. Quantitative kinetic and structural analysis of geopolymers. Part 1. the activation of metakaolin with sodium hydroxide. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 539, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimohammadi, A.; Provis, J.L.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Time-Resolved and spatially-resolved infrared spectroscopic observation of seeded nucleation controlling geopolymer gel formation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 357, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, T.R.; Foletto, E.L.; Dotto, G.L.; Jahn, S.L. Preparation of mesoporous geopolymer using metakaolin and rice husk ash as synthesis precursors and its use as potential adsorbent to remove organic dye from aqueous solutions. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavia, D.L.; Lampman, G.M.; Kriz, G.S.; Vyvyan, J.R. Introduction to Spectroscopy, 4th ed.; Harcourt College Publishers: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-495-11478-9. [Google Scholar]
- Albella, J.M.; Cintas, A.M.; Miranda, T.; Serratosa, J.M. Introducción a la Ciencia de Materiales. Técnicas de Preparación y Caracterización; Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas: Madrid, Spain, 1993; ISBN 84-00-07343-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L.; Rose, V.; Mejía De Gutierrez, R. Evolution of binder structure in sodium silicate-activated slag-metakaolin blends. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Kirkpatrick, R.J.; Poe, B.; McMillan, P.F.; Cong, X. Structure of Calcium Silicate Hydrate (C-S-H): Near-, mid-, and far-infrared spectroscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 82, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereshchagina, T.A.; Kutikhina, E.A.; Solovyov, L.A.; Vereshchagin, S.N.; Mazurova, E.V.; Chernykh, Y.Y.; Anshits, A.G. Synthesis and structure of analcime and analcime-zirconia composite derived from coal fly ash cenospheres. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 258, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wan, S.; Zheng, R.; Tong, J.; Hou, H.; Wang, T. Synthesis and characterization of geopolymer composites based on gasification coal fly ash and steel slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, K.J.; Brown, P.L.; Byrne, R.H.; Gajda, T.; Hefter, G.; Leuz, A.; Sjöberg, S.; Wanner, H. Chemical speciation of environmentally significant metals with inorganic ligands. Part 3: The Pb2+ + OH−, Cl−, CO32−, SO42−, and PO43− Systems (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 2425–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.C.; Loganathan, P.; Nguyen, T.V.; Kandasamy, J.; Naidu, R.; Vigneswaran, S. Adsorptive removal of five heavy metals from water using blast furnace slag and fly ash. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 20430–20438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komnitsas, K.; Zaharaki, D.; Bartzas, G.; Alevios, G. Adsorption of Scandium and Neodymium on Biochar derived after low-temperature pyrolysis of sawdust. Minerals 2017, 7, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaaer, M.; Zaharaki, D.; Komnitsas, K. Microstructural characteristics and adsorption potential of a zeolitic tuff–metakaolin geopolymer. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 56, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Aseno, N. Una Nueva Generación de Carbones Activados de Altas Prestaciones Para Aplicaciones Medioambientales. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Oviedo, Oviedo, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Giles, C.H.; MacEwan, T.H.; Nakhwa, S.N.; Smith, D. Studies in adsorption. Part XI. A system of classification of solution adsorption isotherms and its use in diagnosis of adsorption mechanisms and in measurement of specific surface areas of solids. Chem. Soc. 1960, 3973–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zboon, K.; Al-Harahsheh, M.S.; Hani, F.B. Fly ash-based geopolymer for Pb removal from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
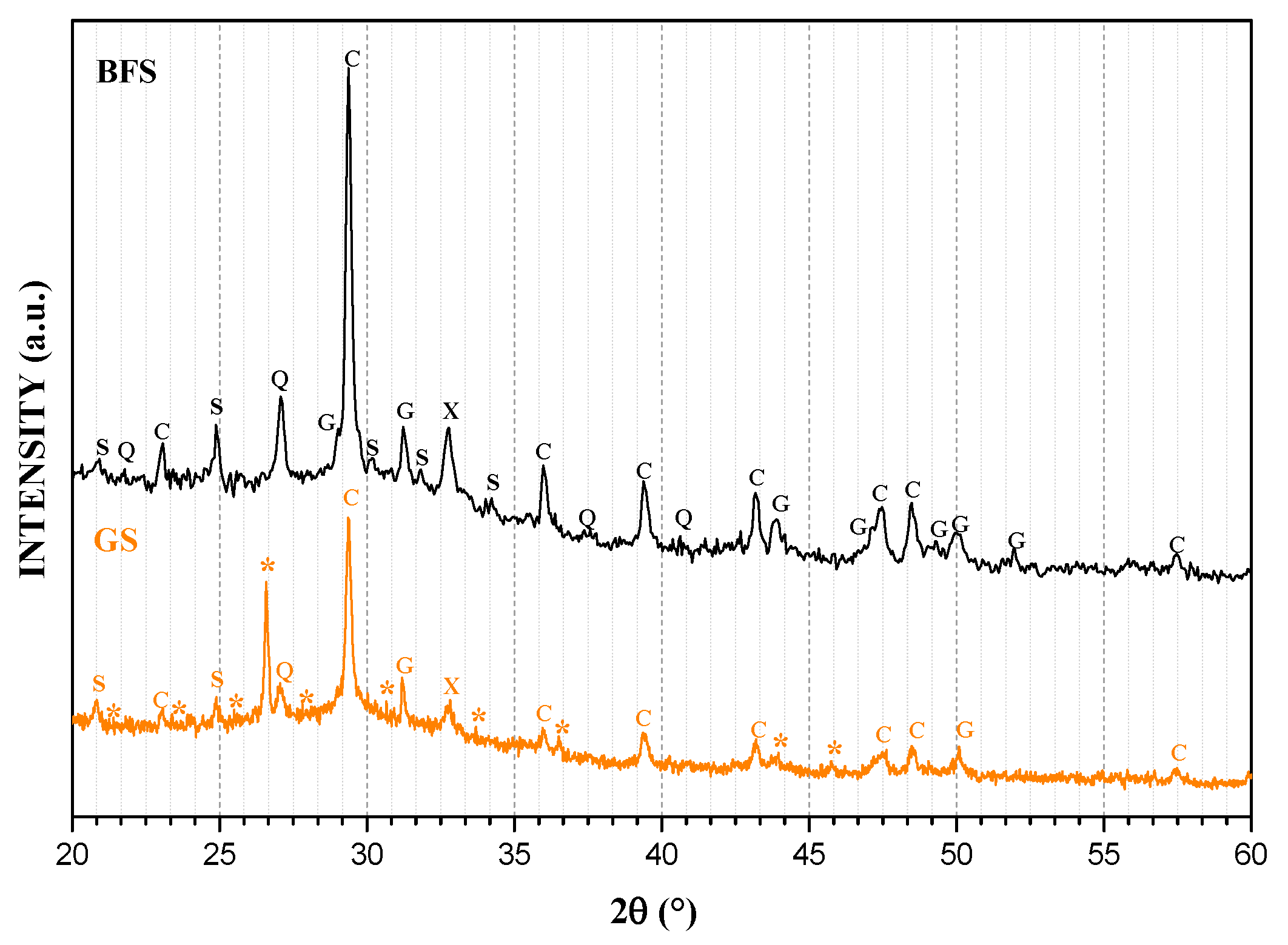
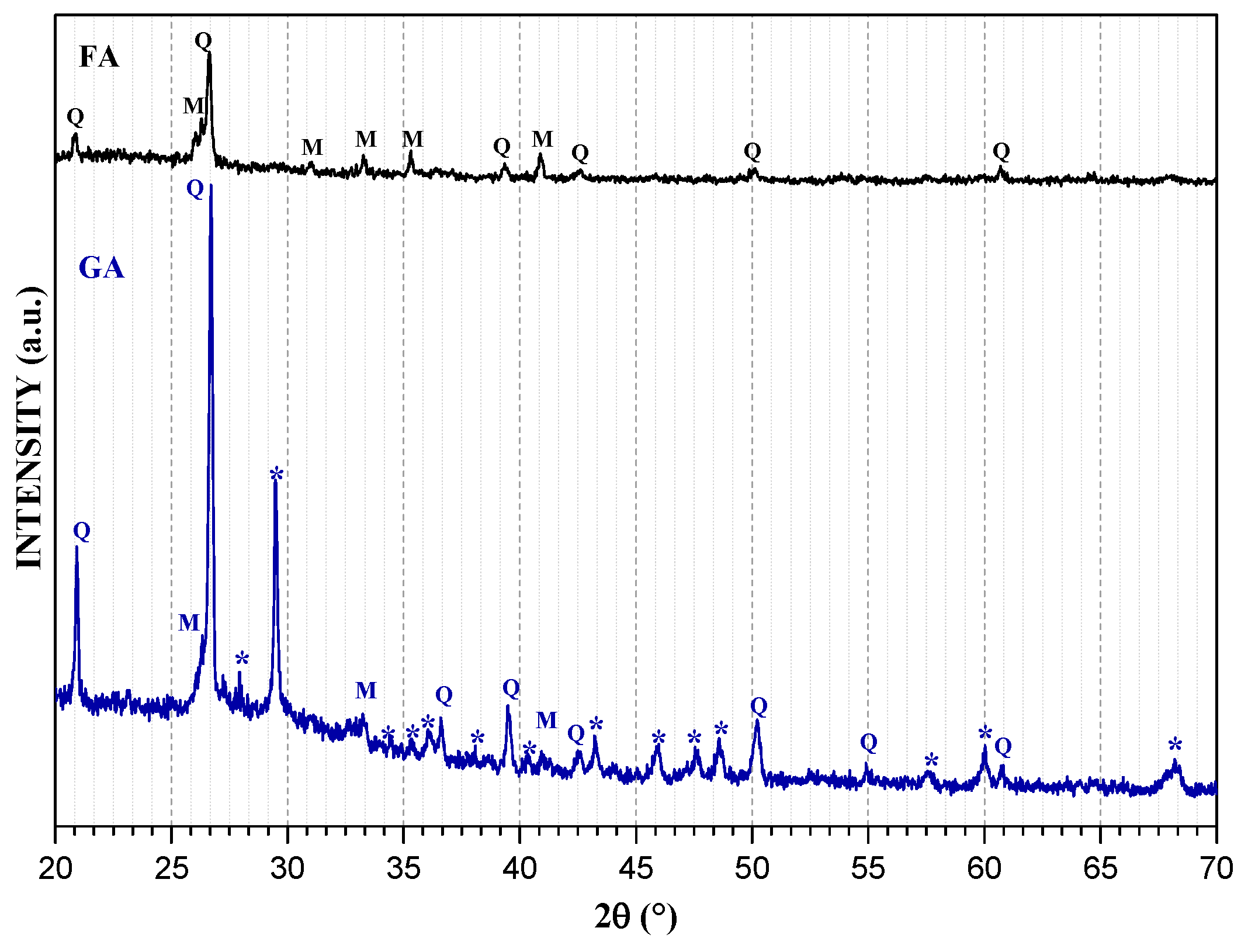

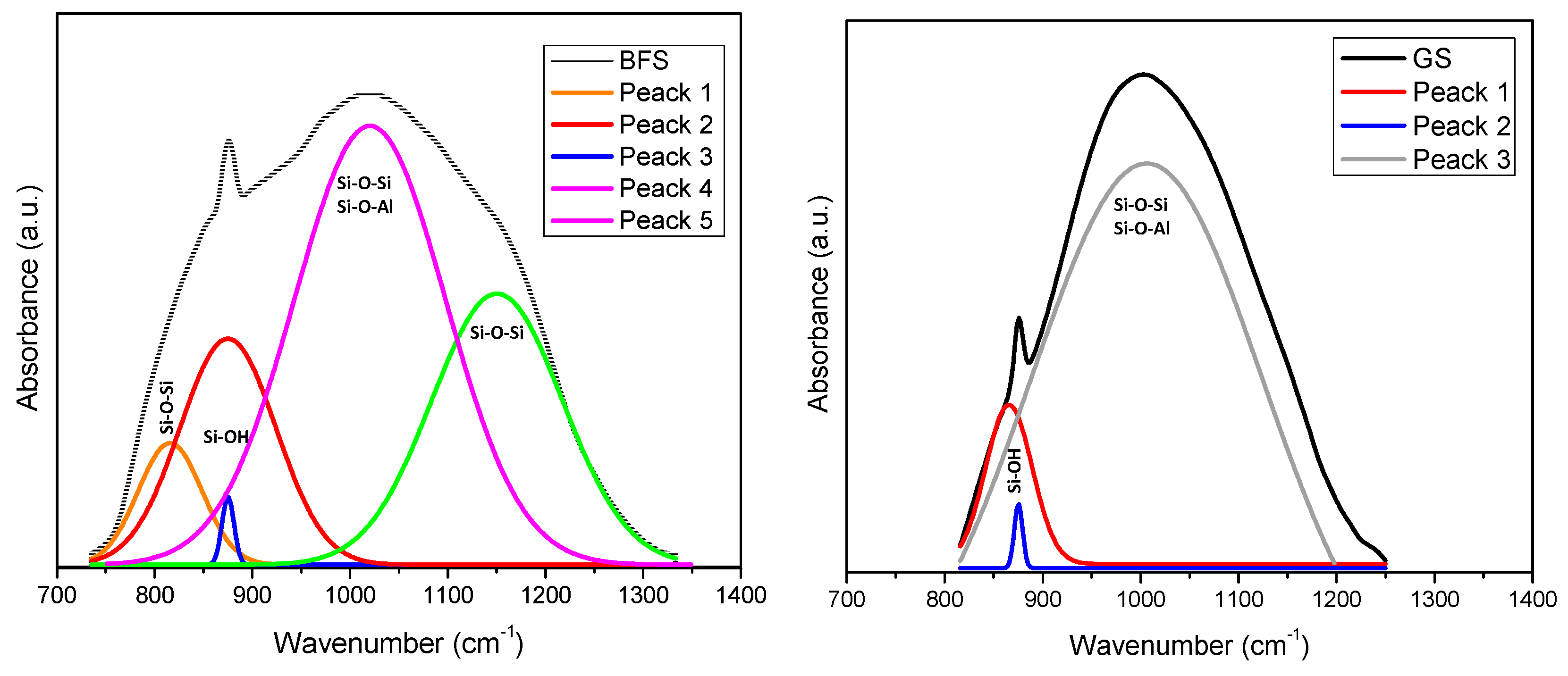
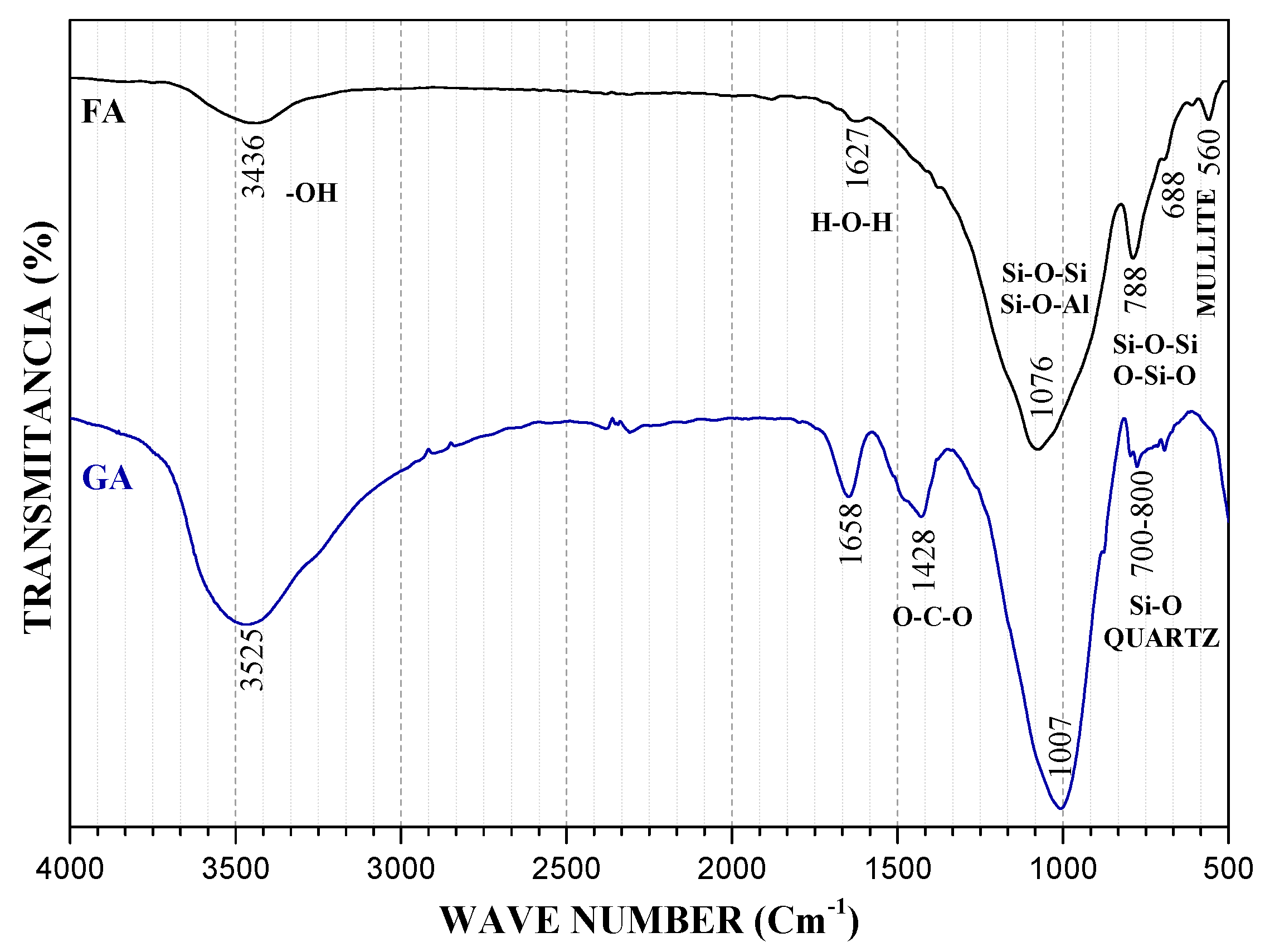
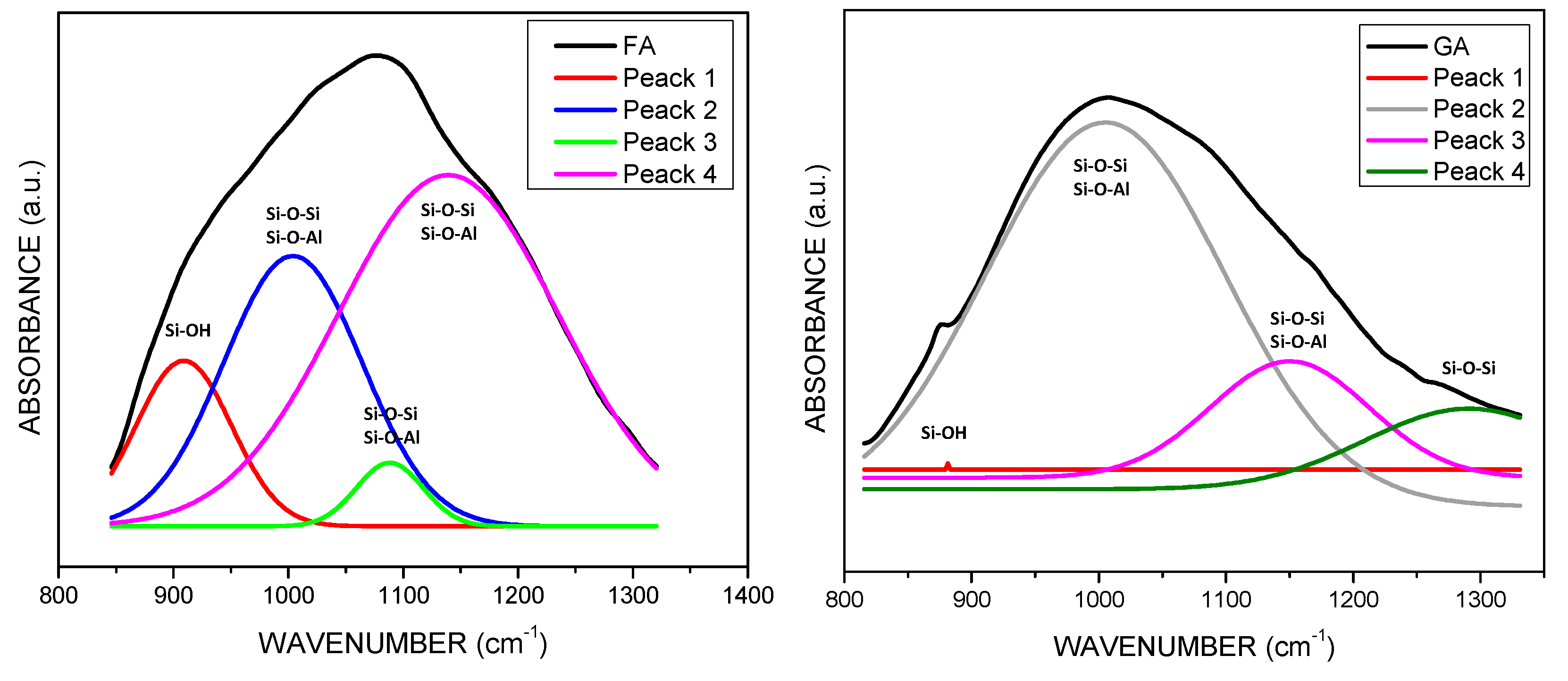


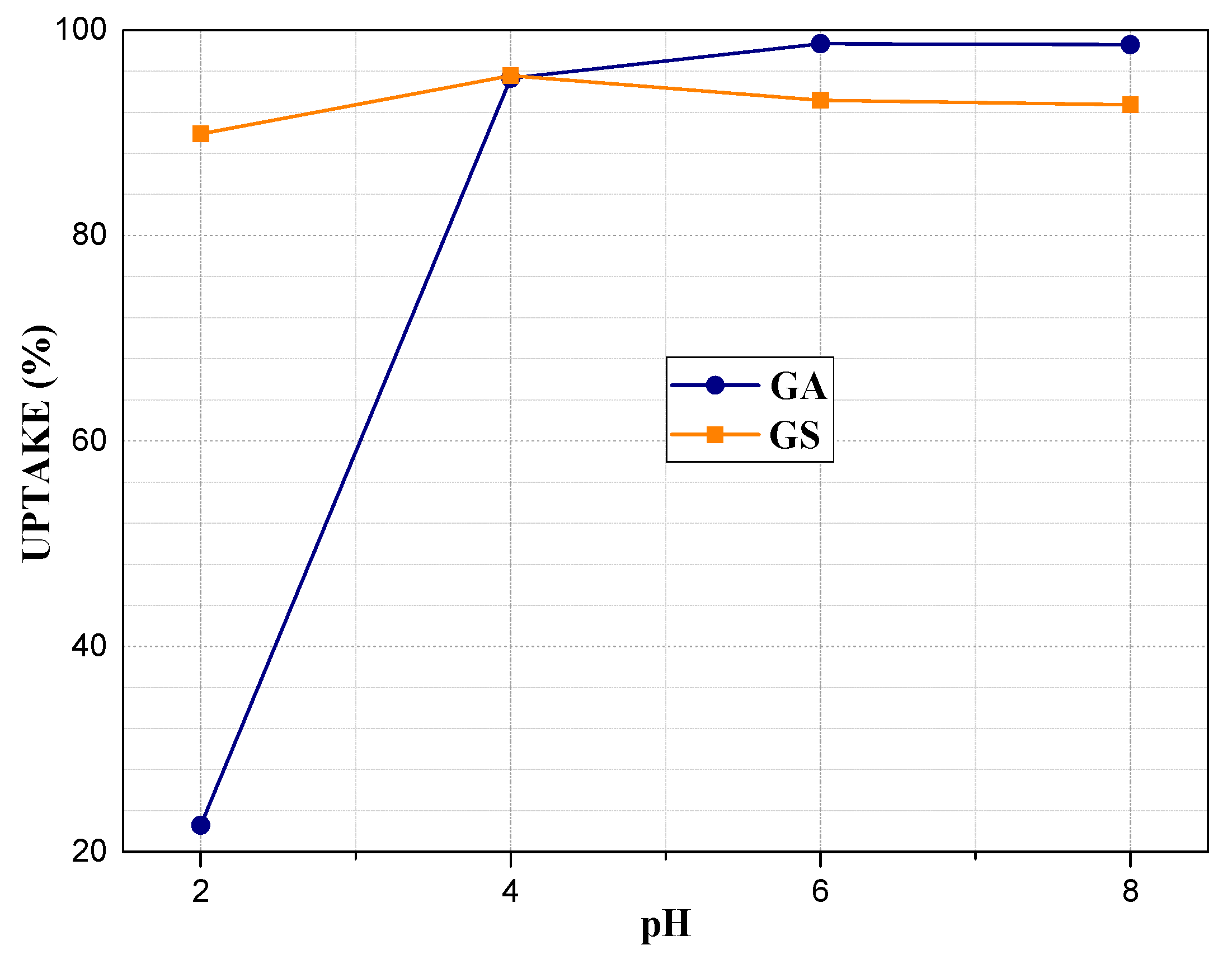
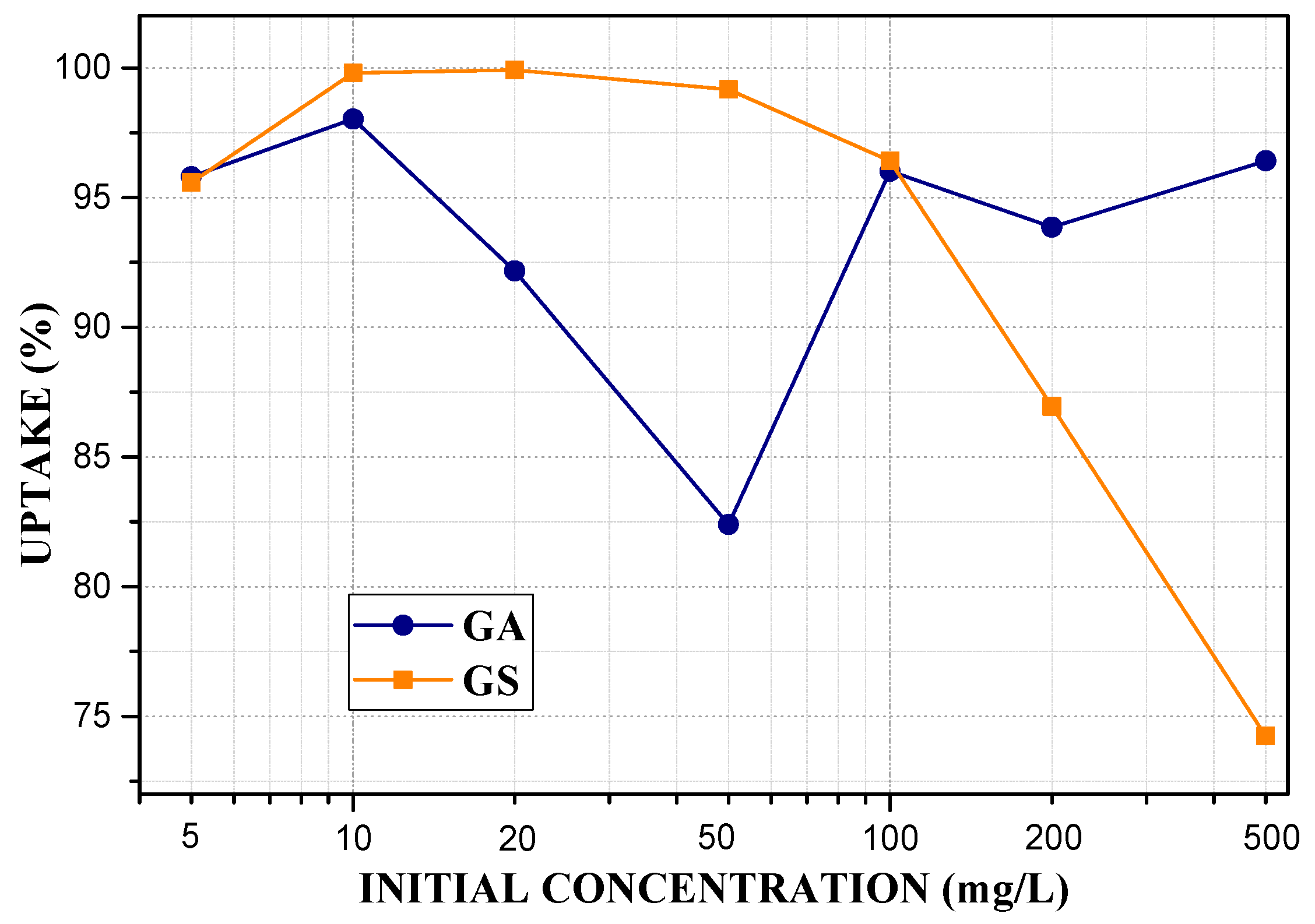
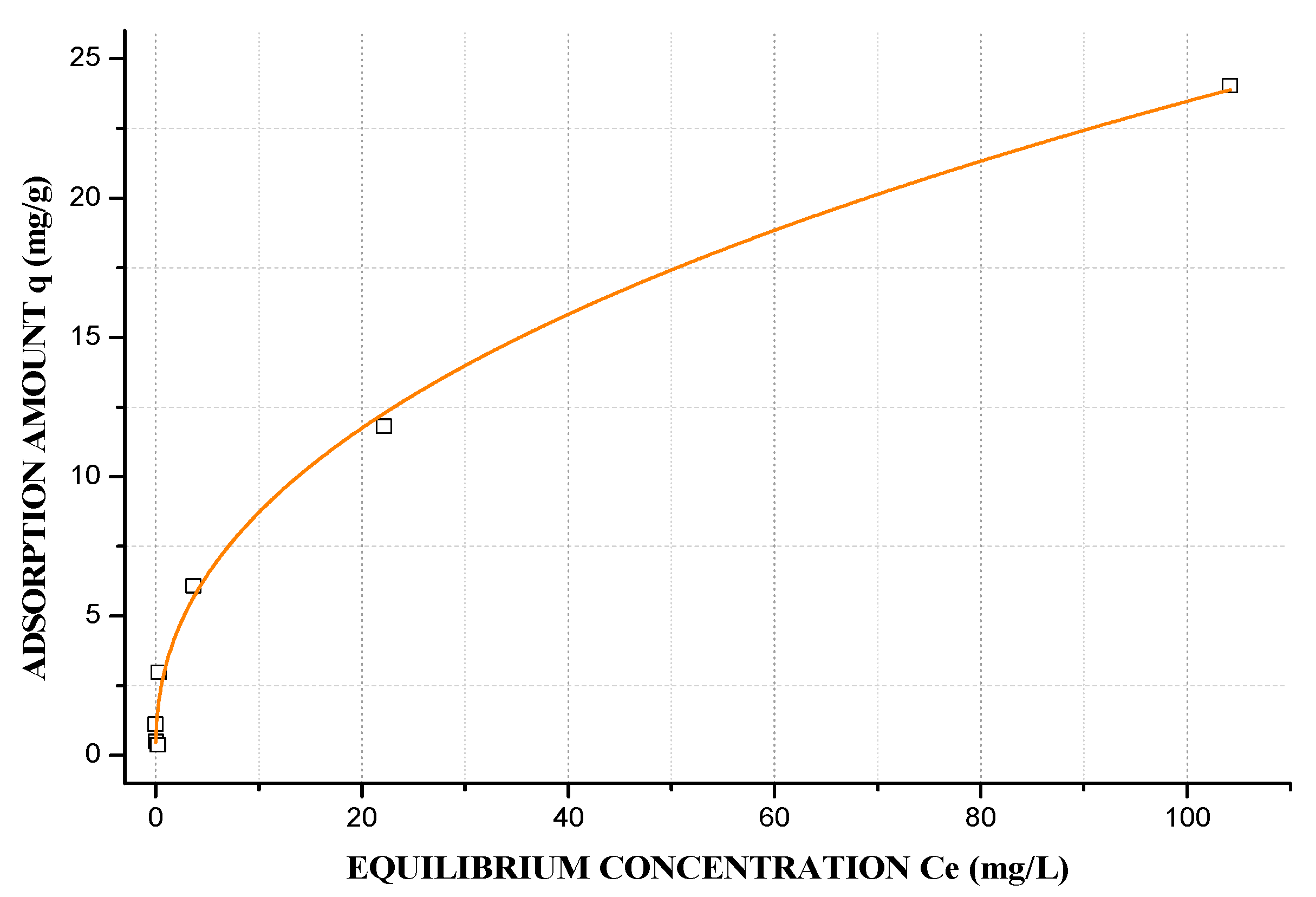
| Sample | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Na2O | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | K2O | P2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BFS | 32.6 | 10.9 | 9.12 | 0.99 | 1.16 | 0.47 | 8.73 | 34.9 | 0.74 | 0.05 |
| FA | 61.9 | 19.3 | 0.79 | 1.49 | 4.29 | 0.08 | 2.0 | 8.28 | 1.0 | 0.11 |
| Phase ID | Phase Name | Chemical Formula | ICDD-PDF 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | Calcite | Ca(CO3) | 00-001-0837 |
| S | Calcium silicate | Ca2SiO4 | 00-072-2297 |
| G | Calcium aluminosilicate (Gehlenite) | Ca2(Al(Al Si)O7 | 00-073-2041 |
| X | Magnesite | MgCO3 | 00-085-2348 |
| Q | Quartz | SiO2 | 00-046-1045 |
| M | Mullite | Al6Si2O13 | 00-001-0613 |
| * | CASH and NASH gels | ||
| Chabasite-Ca | Al3.6Ca1.76H19.74O33.87Si8.4 | 96-901-4473 | |
| Chantalite | Al2CaH4O8Si | 96-900-8283 | |
| Analcime | Al2H4Na1.862O13.667Si4 | 96-900-9956 | |
| Ussignite | AlHNa2O9Si3 | 96-901-6499 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medina, T.J.; Arredondo, S.P.; Corral, R.; Jacobo, A.; Zárraga, R.A.; Rosas, C.A.; Cabrera, F.G.; Bernal, J.M. Microstructure and Pb2+ Adsorption Properties of Blast Furnace Slag and Fly Ash based Geopolymers. Minerals 2020, 10, 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10090808
Medina TJ, Arredondo SP, Corral R, Jacobo A, Zárraga RA, Rosas CA, Cabrera FG, Bernal JM. Microstructure and Pb2+ Adsorption Properties of Blast Furnace Slag and Fly Ash based Geopolymers. Minerals. 2020; 10(9):808. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10090808
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedina, T. J., S. P. Arredondo, R. Corral, A. Jacobo, R. A. Zárraga, C. A. Rosas, F. G. Cabrera, and J. M. Bernal. 2020. "Microstructure and Pb2+ Adsorption Properties of Blast Furnace Slag and Fly Ash based Geopolymers" Minerals 10, no. 9: 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10090808
APA StyleMedina, T. J., Arredondo, S. P., Corral, R., Jacobo, A., Zárraga, R. A., Rosas, C. A., Cabrera, F. G., & Bernal, J. M. (2020). Microstructure and Pb2+ Adsorption Properties of Blast Furnace Slag and Fly Ash based Geopolymers. Minerals, 10(9), 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10090808







