Abstract
Field, petrological and mineral chemistry for meta-volcanic rocks from the Aravalli sequence (Aravalli Craton, India) are presented. Field evidence such as volcanic flows and suspect pillow lava structures, dominant Fe-tholeiite lava flows intercalated with quartzites and argillaceous sediments, indicate rift tectonic environment. Primary mineralogy was obliterated during post-magmatic processes such as metamorphism corresponding to the greenschist to lower amphibolite facies conditions. The rock’s mineral composition was overprinted by plagioclase–chlorite–amphibole–epidote assemblage. The relicts of clinopyroxene were observed. The P-T estimation indicates a temperature of 550–600 °C for the pressure ranging from 3.0 to 7.0 kbar for the majority of amphiboles and 8.0–10.7 kbar for the minority. Geochemically, these rocks are komatiitic (picritic) and high-Fe tholeiitic basalts with 45.06−59.2 wt.% SiO2 and MgO content from 5 to 22.4 wt.% and Mg# of 17 to 71. They show large-ion lithophile elements (LILE) and light rare-earth elements (LREE) enrichment. Chondrite normalized rare-earth elements (REE) patterns for the Aravalli lava are moderately enriched with (La/Sm)N = 1.1−3.85, (La/Yb)N from 1.49 (komatiites) to 14.91 (komatiitic basalts). The trace element systematics with the negative Nb, P and Zr anomalies reflect their derivation from enriched sub-continental lithospheric sources, although minor crustal contamination cannot be ruled out. Aravalli rocks are considered to represent the transition from continental rift magmatism to shallow submarine eruption.
1. Introduction
The granite–greenstone belts, preserved in ancient cratonic nuclei of continents, provide significant geological evidence for the evolution of the Earth in its early stages [1,2,3]. Archean greenstone belts are predominantly composed of variably metamorphosed and deformed ultramafic-mafic to felsic volcanic and silici-clastic sedimentary rocks [4,5].
Volcanogenic and volcano-sedimentary rocks of the Archean to Proterozoic greenstone belts are best known from South Africa (Barberton Greenstone Belt), Australia (Pilbara Craton), and western Greenland (Iska Greenstone Belt) but also from the Indian sub-continent, where a few greenstone complexes were recognized including an Aravalli craton with an Aravalli-Delhi Fold Belt in northwestern part of India.
The Aravalli Mountain Range of Rajasthan is an 800-km long mountain belt, with a long geological history from the Archean to Neoproterozoic period [6]. The presence of two generations of greenstone belts was identified [7]. The polycyclic Proterozoic orogenic processes, involving crustal thickening and thermal perturbations, successively obscured many of their original mineralogical features, thus all relics of the original structures are particularly valuable objects for these genetic investigations.
The occurrence of metamorphosed komatiitic (picritic) with suspect pillow lava and lava flows in association with Fe-tholeiites, quartzites, basal conglomerate, calcareous and argillaceous meta-sediments are recorded from the Aravalli mafic-ultramafic magmatic sequence [8], and are similar to the Archean Bundelkhand craton in Central India [9]. The remnants of basalt volcanism preserved as suspect pillow and lava flow structures were discovered in natural outcrops between the Nathdwara and Delwara towns, north of Udaipur city. These rocks document the proximity to the ancient eruption center and textural features formed during rapid solidifying processes.
This contribution presents new comprehensive mineral chemical data along with the earlier results for our geochemical investigations based on whole rock major and trace element composition, in order to characterize alteration processes and to understand the metamorphic conditions, petrogenesis and evolution of the mafic lavas. Particular emphasis is placed on the determination of the mineral composition of metamorphic assemblage, which has not yet been accurately performed on the Aravalli rocks. The studied meta-basalt samples were collected from near the Kajiawas and Matata villages, south of Nathdwara town, shown as a star in Figure 1. The meta-volcanic rocks are intercalated with conglomerate, grit and arkosic horizons at the base, followed by quartzitic and phyllitic units. The conglomerates contain clasts derived from the Banded Gneissic Complex (BGC) basement, the grit and arkoses also have more derivatives of granitic rocks from the BGC, probably indicating lesser transportation and quick deposition of these meta-sediments. This is followed by the deposition of a more mature quartzitic horizon, indicating longer transportation to lose the feldspars and concentration of clean-washed quartz grains. This horizon is followed by the phyllitic sequence, probably indicating a deepening of the basin. All through the described sedimentary sequence, meta-basalts are observed as intercalated with these sediments, probably indicating a rift tectonic environment for the eruption of the studied basalt [8,10].
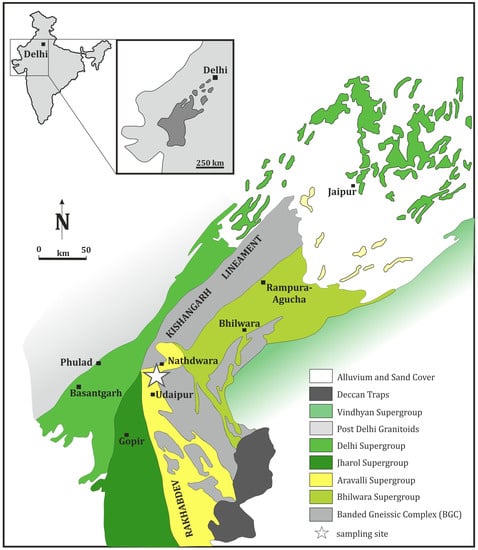
Figure 1.
Simplified regional geological map of the Aravalli–Delhi orogeny after [20].
2. Materials and Methods
The existence of the 3.7–3.5 Ga old Aravalli proto-continent is present in the Aravalli region (Northwest India), confirmed by detrital zircons in the sediments [11,12,13,14]. The initial stage of the continental growth took place in Paleoarchean and continued during the Proterozoic period. This long-lasting process of cratonization resulted due to the generation of poly-phase granite–gneiss terrains, represented by the Banded Gneissic Complex (BGC) [15]. It is believed that the BGC became stabilized at ~2.5 Ga and then was overlain by two Proterozoic supra-crustal complexes: The Aravalli and Delhi Super-groups, formed in 2.3–1.4 Ga in extensional regimes. These two Aravalli and Delhi orogenic belts evolved one after the other, separately in space and time, comprising together the Aravalli Mountain Range. Geochronological data indicate ca. 1.72–1.0 Ga ages for the polyphase deformation and metamorphism related to the collision and the subsequent orogenesis [7]. The relationship between the BGC basement rocks and the cover is contentious, similarly as in many strongly deformed Proterozoic fold belts. The typical granite–greenstone belt sequences of the Aravalli Super-group are associated with gneisses of the BGC basement.
The Aravalli Mountain Range have been assigned to three litho-stratigraphical units, which correspond to three independent geological cycles [10,15,16,17]: (1) crystalline basement of Rajasthan, known as the Banded Gneissic Complex (BGC), (2) Aravalli Super-group, and (3) the youngest Meso-Neoproterozoic Delhi Super-group (Figure 1).
The Aravalli Super-group has an unconformable relationship with BGC all along the entire margin of the Aravalli fold belt. The Aravalli Super-group has been additionally subdivided into three lithological Formations: The Delwara Fm., Jhamarkotra Fm. and Zawar Fm. The lowest Delwara Formation north of Udaipur comprises a thick sequence of mafic and ultra-mafic (komatiitic) volcanic rocks [8,11], generally referred to as the Delwara–Nathdwara volcanic sequence [7]. Based on the available radiogenic data of komatiite and tholeiite of 2.3 Ga was determined as the initial age of rifting of the BGC basement and eruption of the basal Aravalli volcanic sequence [16,18]. Collectively, geochronological data, based on Nd isotopic values, suggest that komatiitic and tholeiitic rocks erupted between 2.3–1.8 Ga from enriched and heterogeneous mantle source regions as part of the sub-continental lithospheric mantle of the Aravalli Craton [7,16]. The rocks of the Aravalli super-group have undergone later greenschist (in the southern part) to upper-amphibolite grade metamorphism in the northern part [17] and have undergone three main phases of folding [19].
The studied samples come from the same structural unit—The Aravalli Super-group. Electron microprobe analysis (EPMA) of mineral chemistry was undertaken using a CAMECA SX 100 (equipped with wavelength dispersive spectrometry) instrument in the Electron Microprobe Laboratory of the Inter-Institute Analytical Complex for Minerals and Synthetic Substances in the University of Warsaw and the Polish Geological Institute. Analyses on polished thin sections were performed with 15 kV accelerating voltage and a beam current of 10 nA. Collected natural and synthetic silicates and oxides were used for calibration. Raw data were corrected by the ZAF method which includes corrections for atomic number effects (Z), absorption (A) and fluorescence (F).
The whole-rock samples were analyzed for major elements and some trace elements in the Polish Geological Institute-National Research Institute (PIG-NRI) laboratory. Major elements and trace element analyses for Ba, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Rb, Sr, V, Y, Zn, and Zr were analyzed by the X-ray fluorescence (XRF) technique but REE and the selected trace elements Nb, Hf, Ta, W, Tl, Bi, Ga, Ge, Sn, Sb, Cs, Th and U were analyzed using inductively-coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) at the Polish Geological Institute, Warsaw.
3. Results
3.1. Field Occurrence
Meta-volcanic rocks from the basal Aravalli sequence in Rajasthan are best exposed between Nathdwara and Delwara, north of Udaipur city (Figure 1). The supra-crustal rocks of Aravalli sequence have undergone greenschist to lower-amphibolite facies metamorphism and polyphase deformation. These relatively high magnesium rocks occur at the contact of the basal Aravalli sequence with BGC (Figure 1). At some places, however, the amphibolites derived from meta-basalts have preserved relict pillow lava structures (Figure 2a,b). This is the first report of suspect pillow lava structures within the basal volcanic rocks of the Aravalli super-group with a spinifex-like texture, now occurring as fibrous amphiboles, observed on the surface of the pillows pile (Figure 2c,d). The suspect pillow lava outcrops were found on the top of the Nathdwara hills around Kajiawas village. They are formed in a separated 1.0–1.5-m high to 0.5–0.8-m wide band of a hard black pile of pillow-like lava sequence. This pillow-covered crust, about 2.0–5.0 cm thick, is enriched in platy, fibrous or acicular-like post-pyroxene amphibole crystals, around 0.5–2.0 cm long and 0.1–0.2 cm wide in a glassy matrix. The internal part of the pillows is coarser grained, composed of dark green to dark grey and black minerals of amphibolite composition.
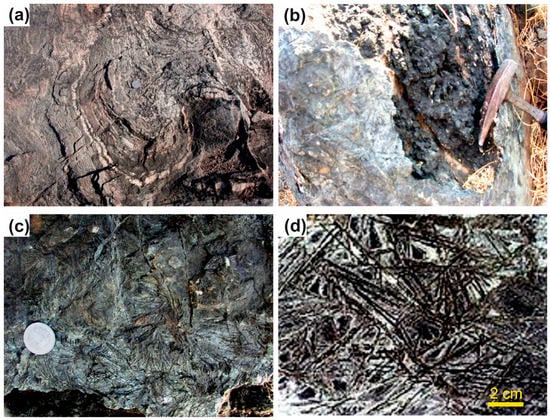
Figure 2.
Field photographs showing morphology of the pillow lava outcrops at the Aravalli area. (a) pillow structures showing deformation, (b) oval shape of the pillow lava in the Aravalli area with visible spinifex-like texture on the surface, (c,d) fibrous and platy amphibole on the Aravalli pillow lava surface. Note the hammer and the coin for scale.
3.2. Mineral Chemistry of the Suspect Pillow Lava
The greenschist to amphibolite facies metamorphism and secondary alteration obliterated the primary mineralogy. These meta-basalts are characterized by mineral assemblage including: amphibole ± plagioclase ± chlorite ± epidote ± ilmenite ± hematite ± sulphides. The amphibolites range from coarse- to medium-grained, with a pillow-like lava surface.
The suspect pillow lava from Aravalli has a preserved, fibrous, spinifex-like texture (Figure 2c,d). Such type of crystal arrangement develops as a result of large thermal gradients, coupled with conductive and radiative heat transfer within olivine or/and pyroxene crystals fixed in the cool upper layers of the lava flows [21,22]. All samples collected from natural outcrops are found to consist of amphibolite facies mineral assemblage, dominantly comprising crystals of calcic amphibole (Figure 3a–d) with only single pyroxene relicts accompanied with plagioclase (Figure 4a,b), apatite, ilmenite, chlorite (Figure 3d or Figure 4a) and epidote (Figure 4c,d) with allanite (Figure 4c). Small baddeleyite grains were also observed.
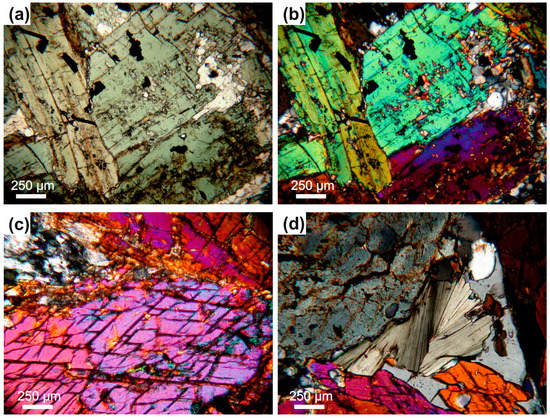
Figure 3.
Photomicrographs of the studied samples from the Aravalli area. (a–c) pseudomorphic large Ca-amphibole grains making spinifex-like texture in Aravalli pillow lava, (d) retrogressive Mg chlorite after amphibole.
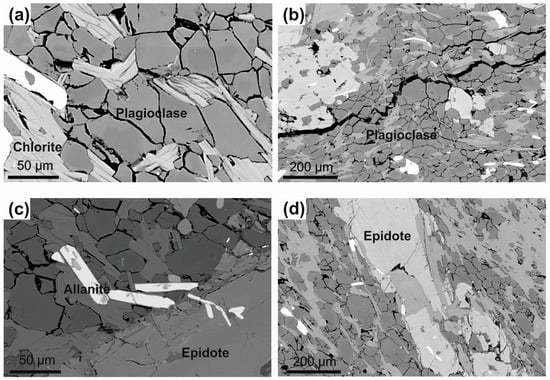
Figure 4.
Backscattered-Electron (BSE) micrographs of the studied samples from the Aravalli area. (a) retrogressive Mg chlorite with plagioclase grains, (b) euhedral plagioclase grains, (c,d) accessory allanite and epidote after plagioclase.
3.2.1. Amphibole
Euhedral, elongated Ca-amphiboles with visible zonation, which resulted in variable content of Fe and Mg, but also SiO2, are dominant minerals from the pillow-like lava basalts. The slender amphibole crystals have a radial orientation to random and intersecting arrangement, giving rise to spherylitic-type/or spinifex-type textures. The rocks contain predominantly large euhedral green-colored amphibole grains (Figure 3a–c) with randomly oriented ilmenite intergrowths, spinel and apatite within amphibole crystals. An amphibole composition from the collected Aravalli pillow lava samples was projected onto an amphibole classification diagram according to the nomenclature of [23] (Figure 5; Table S1). The EPMA data indicate that amphibole compositions are straddled between magnesio-hornblende and pargasite with a pronounced fluctuation of alkali content visible in the A* value. A core–rim relationship was observed in some places. A wide range of Mg# (defined as Mg/(Mg + Fe2+)) from 0.40 to 0.82 is observed, where the samples from the inner part of the pillow-like lava (AR-6C and AR-6E) are less magnesian than that of the outer zones (AR-6A and AR-6A(2)). The Si content ranges from 6.11 to 7.23 apfu. The content of titanium is always low, in the range of 0.17 to 0.44 wt.% of TiO2 with a single-grain content above 1 wt.%. The analytical data show a variable Al2O3 content, ranging from 7.2 to 17.1 wt.%. These variable alumina and Ti contents are not related to the pillow lava zone.
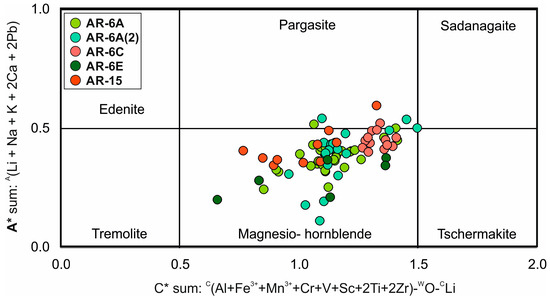
Figure 5.
Ca-amphiboles chemistry from the ortoamphibolites from the Aravalli. Plot of the EMPA data in the calcic amphibole classification diagram [23]. A* A(Li+ Na + K + 2Ca + 2Pb); C* C(Al + Fe3+ + Mn3+ + Cr + V + Sc + 2Ti + 2Zr) − WO − CLi.
3.2.2. Pyroxene
The only fragments of primary pyroxene grains were preserved within larger amphibole crystals. All pyroxene grains were substituted by amphibole during the metamorphism of the pillow lava. They were observed in microprobe, thus only eight points of this relict group were analyzed (Table S2). Pyroxenes from two samples analyzed have an igneous origin, varying from augite (dominant) to pigeonite and clinoenstatite, classified after [24] (Figure 6a). The augite relicts with a relatively small array of Ca (0.486–0.509 apfu; Table S2) have Mg# ranges from 0.55 to 0.74. The Cr content is below detection limit, but they have some amount of Na (0.11 to 0.48 wt.% Na2O), reflecting aegirine molecules, as detected for alkali basalts.
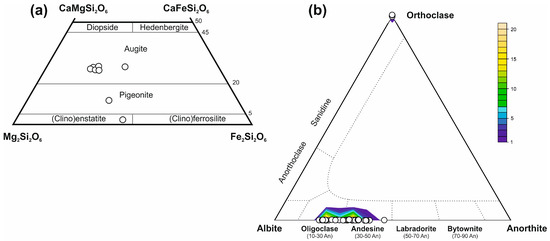
Figure 6.
(a) pyroxene chemistry of the orthoamphibolites from the Aravalli area, plot of the EPMA data in the pyroxene classification diagram after [20], (b) plagioclase chemistry of the orthoamphibolites from the Aravalli area, plot of the EMPA data in the feldspar classification diagram.
3.2.3. Feldspar
These minerals, found as plagioclase and K-feldspar, were observed through the 47-point analysis (Figure 6b; Table S3). Some of the currently recognized plagioclases remnants, due to the recrystallization to other minerals like epidote, are igneous, which is proven by their original euhedral tabular habit. There is also a dominant group of fine-grained feldspars, probably of metamorphic origin. Plagioclase represents a variable chemical composition with a mostly alkaline character and the visible metamorphic deformation. Microprobe analyses indicate almost equal amounts of andesine and oligoclase with two graphically pronounced maxima for An33 and An20 plagioclase composition (Figure 6b; Table S3). It is not possible to observe a clear core–rim relationship since most analyzed crystals are heterogeneous with a random composition or a homogeneous composition. The presence of a secondary potassium feldspar is also detected.
3.2.4. Chlorite
Chlorite is also common in some parts of pillow lava samples (Figure 3d or Figure 4a). This mineral phase results from thermal modifications and/or the replacement of primary Fe–Mg pyroxene or amphibole minerals. The analyses of a total of 25 points was conducted (Table S4). The EPMA data document a small dispersion (variation in the analysis of the composition of the same sample) with a uniform Fe# parameter Fe/[Mg + Fe] = 34–40 mol%. This is considered to be a typical feature of Fe, Mg- chlorite with composition corresponding to that of ripidolite, based on [25]’s classification, used by [26] in an excel spreadsheet. No significant variation is found in the mineral core–rim relation, as the minerals were found to have a homogeneous composition. This metamorphic mineral originates in low metamorphic grades, restricted to greenschist facies.
3.2.5. Ilmenite
The TiO2 content of the ilmenite from Aravalli pillow lava varies from 51.08 wt.% to 53.08 wt.%, which is close to the theoretical ilmenite 52.75 wt.% composition. The minor variations could be due to the leaching of other cations. The FeO content of the ilmenite varies from 43.56 wt.% to 46.57 wt.%. The large range of FeO in the ilmenite could be due to hematite exsolutions. The MnO content of ilmenite in different sections of the pillow varies from 2.25 wt.% to 3.97 wt.% or 1.45 wt.% to 2.03 wt.%, while the MgO content varies from 0.04 wt.% to 0.08 wt.%. with one higher content of 0.276 wt.%. (Table S5) The presence of significant amounts of manganese indicates that the Aravalli ilmenite constitutes a solid solution series with pyrophanite and smaller amounts of geikelite. As a result of these solid solutions, the TiO2 content of ilmenite reveals some variation in comparison to an ideal value. The amounts of V2O5, Al2O3, Cr2O3, NiO, ZnO are not significant or below the detection limit. Whereas typical igneous ilmenite from mafic and ultramafic rocks has 0.5 wt.% to 10 wt.% of MgO and less than 1 wt.% of MnO, it is apparent that the ilmenite from Aravalli pillow lava represents igneous grains that have been compositionally modified by diffusion processes during metamorphism [27].
3.3. Geothermo-Barometers
The amphiboles, as a mineral phase stable over a wide range of pressure and temperature from 1 to 23 kbar and 400 to 1150 °C [28], are an effective tool used for the estimation of P-T conditions of various Ca-amphibole-bearing rocks. The P-T parameters are usually determined based on the composition of amphibole-plagioclase pairs or amphibole-liquid calibration or amphibole-only calculation. This last option, independent of magma composition, was tested in Aravalli samples. The lava pillows contain different forms of amphibole (Figure 3 and Figure 4), accompanied or not accompanied with plagioclase of oligoclase to andesine composition, which suggests that these rocks did not achieve a state of equilibrium.
There are several successfully tested thermometers and barometers designed mostly for the igneous system. A few amphibole-only formulas allow us to approximate a range of pressure and temperature of metamorphic rocks. In these equations, the Ca–amphibole composition has to be calculated on the basis of 23 oxygen anhydrous mineral formula (Table S6).
The Ti thermometer of [29] applied to a magmatic system can be also used for sub-solidus hornblende. The temperatures, obtained according to their semi-empirical equation in most of the Aravalli analysis (Table S6), suggest a range of 600–550 °C (Figure 7a). These amphiboles were formed by the sub-solidus alteration of cumulus minerals, thus the Ti content was dependent on the availability of the Ti bearing phase (ilmenite). Consequently, the amphiboles may not contain the maximum amount of Ti and the thermometer may yield a minimum temperature [29].
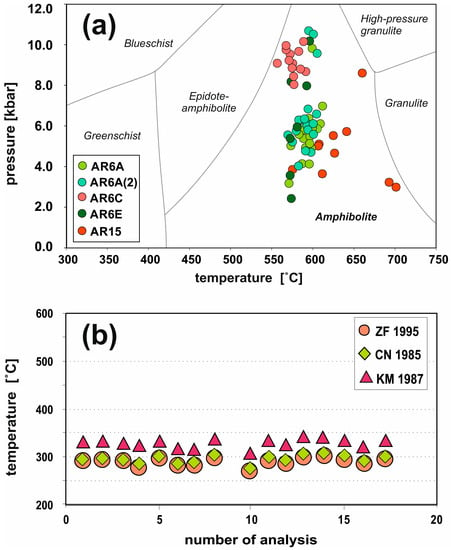
Figure 7.
(a) P-T condition estimation after [29,32] (b) pressure and temperature conditions of metamorphic processes calculated on chlorite formation conditions after ZF [38], KM [39] and CN [40].
The correlation between Al in hornblende and pressure was examined by the formula of [29,30,31] (Table S6).
An additional two formulas were also tested. Single-phase barometers, working with the total aluminum content of amphibole of [32] (Table S6), also provide two stages and falling in the ranges of pressure 3.0–7.0 (but mostly in the range of 5.0–6.0 kbar) and 8.0–10.7 kbar, mainly for the AR-6C sample, from the inner part of the pillow lava (Figure 7a). In contrast to the formula of [33], this showed a wider range of the pressure—4–14 kbar and 14–18 kbar. Some of them seem to be overstated, as they are too high (Table S6).
On the other hand, according to [34], amphiboles with Si of 7.3 (apfu) or less are generally considered magmatic and Si higher than 7.3 (apfu) is not a truly magmatic amphibole. In these terms, the Aravalli amphibole crystals plot as igneous, far off of the metamorphic field (Figure 8a). They display a variation of Si content and a sum of Na, Ca, K, whose particular values overlap with the population commonly found in magmatic arc amphiboles. The case of this (Na + Ca + K vs. Si) relationship should be explained, rather, as an indicator of meta-igneous origin. The amphibolite facies metamorphism recrystallized the probable reach of pyroxene protolith. An almost-analogous diagram (Na + K) vs. Si is used as a discriminator of protolith for ortho- vs. para-amphibolite [35].
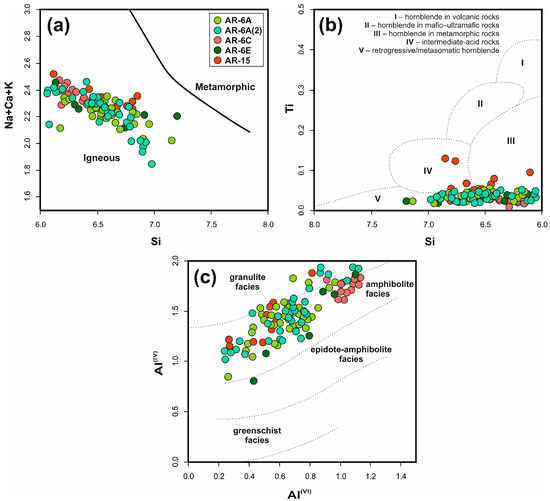
Figure 8.
Discrimination diagrams for hornblendes from the Aravalli area ortoamphibolites. (a) Na + Ca + K vs. Si diagram, (b) Si vs. Ti diagram for hornblendes after [36], (c) AlVI vs. AlIV diagram after [37].
The condition of amphibole formation shows that they crystallized in a medium-temperature regime, typical for retrogressive changes. This is confirmed by the low Ti content in amphibole grains from pillow lava, which places them in the field of the metamorphic rocks or even amphiboles resulting from metasomatic processes (Figure 8b) [36].
More detailed conclusions can be drawn from the AlIV vs. AlVI diagram (Figure 8c) [37], where amphiboles from pillow-like lava are located within the field of amphibolite facies, but they can be divided into two groups: high Al amphiboles close to granulite facies borders and lower-Al amphiboles, clearly showing a retrogressive trend with decreasing temperature. Metasomatism is documented by the occurrences of the feldspathic and chloritic veins within the most-altered zones.
Complementarily, the chlorite-bearing altered parts of amphiboles were used for the chlorite thermometry, defining the last stage of metamorphic evolution. The studied chlorites based on crystal–chemical classifications have constant ripidolite compositions with (Fe/(Fe + Mg), which range from 0.364 to 0.433 (Table S4). The Fe-chlorite crystallization temperatures were calculated on a basis of three different calibration methods by [38,39,40] that indicate similar temperature ranges from 330 ± 16 °C to 290 ± 8 °C (Figure 7b). These temperature ranges refer to greenschist facies metamorphism (typically 300–450 °C and 1–4 kbar pressures), and the most characteristic minerals in metabasalt remain as chlorite, actinolite composition amphibole, and Na rich plagioclase (albite) ± epidote.
3.4. Geochemistry of Aravalli Pillow Lava
Some samples from the pillow-like lava surface have high loss on ignition (LOI), suggesting that hydrothermal alteration was significant and excludes the use of these samples for further considerations. This is confirmed by the presence of the secondary minerals, such as calcite, chlorite and epidote, which were identified in veinlets. The inner part of pillow lava represents one sample (AR-6C), whose composition is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Major and trace element averages for AR-6C sample and tholeiites, komatiitic basalts and komatiites from Aravalli area.
To place mineralogical data of the suspect pillow lava into a geochemical context, we briefly present and summarize data on komatiite, komatiitic basalts and tholeiites from [10]. The tholeiite–komatiite suite indicates a relatively wide compositional range with SiO2 content of 45.06−59.2 wt.% and a Mg# [MgO/(MgO + FeOtot) × 100] ratio of 17–71. All rocks are classified dominantly as sub-alkali basalt and andesitic basalts based on [41] (Figure 9a). The “andesitic” nomenclature is not supported by the mineralogy and other geochemical parameters but only as an expression of higher silica abundance. Similar silica levels in basal volcanic rocks have also been reported by [8]. On the classification diagram after [42], rocks plot a gradual transition from komatiites, komatiitic basalts up to high-Mg and high-Fe tholeiite fields (Figure 9b), with tholeiitic affinity based on high FeO content. Rocks from the Aravalli sequence also reveal variable MgO content: 3.9–7.9 wt.% for tholeiites, 9.0–11.9 wt.% for komatiitic basalts and 19.6–22.4 wt.% for komatiites. The AR-6C sample from inner part of the pillow-like lava is characterized by a relatively high MgO 11.03 wt.% and plots on the border of the komatiitic basalts and high Mg-tholeiites (Figure 9b).
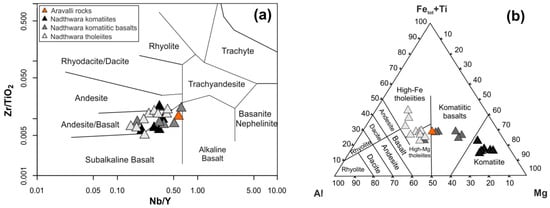
Figure 9.
(a) Zr/TiO2 vs Nb/Y plot after [41], (b) Al-(Fetot + Ti)-Mg diagram after [42] for the AR-6C sample and Nathdwara volcanic rocks (data from [10]).
Most of the trace elements in a function of immobile Zr show a perfect linear trend (Figure 10). Only Rb does not show linear variation, which can be attributed to some degree of elemental mobility during metamorphism. A broad negative correlation between MgO and Zr suggests the role of the fractional crystallization process.
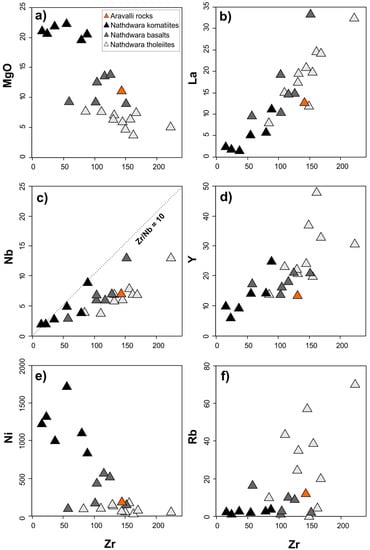
Figure 10.
Bivariate plots of Zr (as an index of fractionation) versus selected elements for the AR-6C sample and Nathdwara rocks (data from [10]). (a) major oxide (MgO) vs. Zr, (b–f) trace elements (La, Nb, Y, Ni, Rb) vs. Zr.
All of the mafic volcanic rocks exhibit REE patterns with LREE enrichment (Figure 11 normalizing values from [43]), where tholeiites exhibit La/SmN = 1.54–2.85 and La/YbN = 2.23–10.90, komatiitic basalts 1.74–3.85, 5.78–14.91 and komatiites 1.11–2.37, 1.49–4.30 respectively. The new Aravalli sample AR-6C indicates La/SmN = 2.3 and La/YbN = 7.73, similar to the tholeiites and komatiitic basalts. In terms of the multi-element plots normalized against enriched mid-ocean ridge basalts (E-MORB) [44] (Figure 11), the Aravalli tholeiite and the komatiitic basalt samples plot parallel the E-MORB, i.e., along or above the normalized ratio line 1 for most of the incompatible trace elements, indicating their derivation from enriched mantle sources similar to those for the E-MORB (Figure 11), however, the Aravalli samples have prominent negative anomalies for Nb, P, Sr and to some extent Eu and Ti, commonly observed in continental rift volcanics [45].
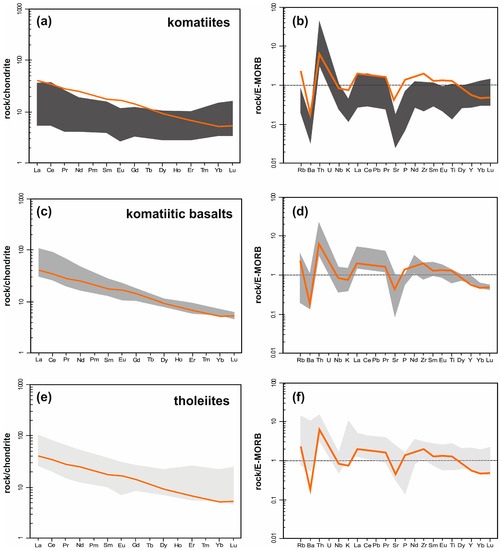
Figure 11.
(a,c,e) chondrite-normalized REE patterns for komatiite, komatiitic basalts and tholeiite respectively (normalizing values after [43]), (b,d,f) E-MORB normalized multielement spider diagrams (normalizing values after [44]) for the komatiite, komatiitic basalts and tholeiite respectively (data from [10]), REE and multi-element patterns of AR-6C (brown line) shown for comparison.
However, the komatiitic samples plot mostly below the normalized ratio line 1, indicating their derivation from less enriched mantle sources by higher degrees of partial melting compared to the tholeiite and komatiitic basalt samples, although depicting similar depletion of Nb, Sr, Eu, P and Ti, like the tholeiite and komatiitic basalt, indicating rift tectonic environment [10]. The tectonic interpretation is confirmed by the Zr/Y vs. Zr plot [46] where the Aravalli samples plot within or close to the “Within-Plate Basalt” field (Figure 12).
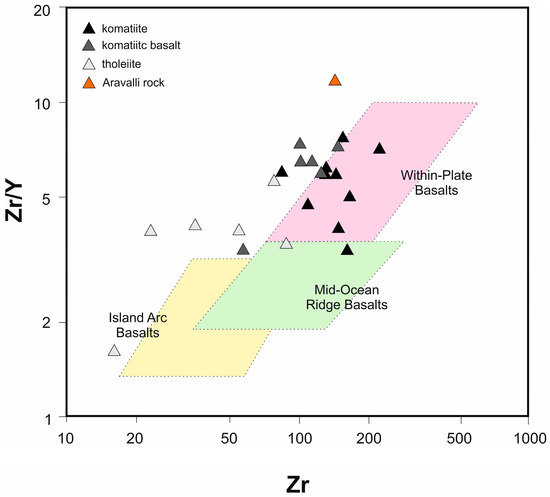
Figure 12.
Zr/Y vs. Zr diagram after [46].
4. Discussion
Geotectonic settings: The basal sequence of Aravalli is composed of mafic, ultramafic and komatiitic volcanites [8,10]. The geochemical criteria used in previous publications (i.e., La/Nb = 1 and Nb/Y = 0.3 [47] have suggested (in the case of komatiite) a simple connection of magmatism with the mantle plume and oceanic plateau basalt source. On the other hand, the komatiitic basalts and tholeiites resemble arc basalts with a typical La/Nb ratio of ca. 3. However, [16] based on lithological consideration, overall, the geology, petrology and geochemical arguments, including similar incompatible trace element ratios for continental rift basalt and arc basalt, link Aravalli volcanic rocks with rift-related magmatism. Furthermore, arc basalt indicates an overall relatively lower abundance of the incompatible trace elements compared to rift basalt, but arc basalt has similar multi-element patterns and arc basalts frequently contain positive Eu and Sr anomalies because of plagioclase accumulation, whereas these (Sr and Eu) have negative anomalies in rift basalt as in the case of Aravalli basalt [10]. Aravalli rocks, presented in this study, show general enrichment of LREE and LILE patterns and pronounced negative Nb, Sr, Eu, P and Ti anomalies, which are characteristic of many continental flood basalt suites, dyke swarms and rift volcanics [10,48,49,50].
Mineralogy: the mineralogy of the Aravalli rocks contributes towards understanding the geotectonic environment, whether the Aravalli meta-volcanic rocks are rift or subduction related. The subduction-related komatiite and their origin in shallower melting regimes is possible through the incorporation of significant amounts of H2O. Most of the komatiites contain hydrous amphiboles, but they are products of metamorphism rather than indicators of the real high H2O content of magma. Thus, the determination of the possible water content in the system can be possible only on the basis of primary minerals. In the case of Aravalli pillow lava, the only mineral that may indicate the crystallization environment is the clino-pyroxene relicts. The first experimental studies indicating the possible high H2O content in komatiites come from Barberton komatiites [51,52], where augite with high Wo content (>0.4) was found as the only pyroxene. The experiments, carried out after the addition of water, displayed a very good match with a natural augite composition. On the contrary, the anhydrous experiments produced two pyroxenes, both pigeonite and augite (with lower CaO content of Wo = 0.3–0.35). Taking into account that the pyroxene relics found in Aravalli pillow lava had both augite and subordinate pigeonite and even enstatite compositions, and that the augite has a low Ca content (Wo about 0.3), it can be stated that their crystallization took place in an anhydrous environment, considered as associated to the mantle plume. Based on the chemical composition of amphiboles, which are the result of metamorphism, it can be stated that the rocks within this area were subjected to later temperatures not in excess of 550–600 °C and pressures in the range of 3.0–7.0 kbar for the majority of amphiboles and 8.0–10.7 kbar for the minority, typical of amphibolite facies metamorphism.
Textural relationship: distinctive spinifex-like texture on a weathered Aravalli pillow lava surface consists of long, platy or fibrous phenocrysts of amphibole, however, olivine spinifex-texture is usually typical of komatiite lavas from most greenstone Archean belts worldwide. In the case of Aravalli, the mineralogical composition of rocks with a spinifex type textures has been strongly perturbed through repetitive episodes of regional metamorphism over millions of years, as well as hydrothermal and weathering changes. Primary minerals such as pyroxene, of which relics were observed at places, are replaced by secondary minerals such as chlorite and Ca-amphibole and carbonates. These Aravalli rock features were, at first, thought to have a komatiitic affinity by their resemblance to other spinifex textured komatiitic occurrences in the world, i.e., [53,54,55], but their geochemical composition indicates komatiitic/tholeiitic affinity with MgO content ranges up to 22 wt.%, reported by [10] and a wide range of SiO2 (45.06−59.2 wt.%). A few cases of spinifex-textured volcanic rocks are reported in the world literature, with significantly variable geochemical compositions compared to those of typical komatiites, e.g., in volcanic rocks with Ca-amphibole spinifex from the province of Musgraves in Western Australia [56] or platy pyroxene spinifex in the Boundle Volcanic Member of the Meekatharra Formation [57]. These rocks have moderate to high MgO content and show that spinifex texture occurs over a broad compositional spectrum. The formation of preferentially-oriented crystals typical of platy spinifex cannot be attributed exclusively to the nature or composition of the komatiite liquid. An explanation for its origin is related to specific physical conditions that prevailed during the crystallization of the upper part of the lava flow. The experiments [58] demonstrate that spinifex is a natural consequence of crystallization in the thermal gradient of a hot, dry and ultramafic lava flow. The large crystals are oriented perpendicular to the cooling front. The fibrous and skeletal post-pyroxene amphibole showed that this mineral was growing rapidly, under high degrees of undercooling [58]. To form pillows in true high Mg-rich komatiites, a lower local flow rate is required [59]. Such low flow rates are in conflict with the high flow velocities generally assumed for komatiites, and hence explains the rarity of submarine komatiite pillow lavas. In the case of Aravalli, a whole rock geochemistry documents tholeiites. Thus, these relatively small pillow forms may document a sub-marine or shallower lake-like eruption environment. The proposed model by [16], for the geotectonic evolution of the Aravalli belt, is consistent with the rifting model of [60], suggesting deep mantle plume melting of mantle material and the thinning of lithosphere, ultimately leading to continental rifting. Magmas may reach the surface as flood basalts.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2075-163X/10/7/638/s1. Table S1: Results of the EPMA analyses of Aravalli amphibole, Table S2: Results of the EPMA analyses of Aravalli pyroxene, Table S3: Results of the EPMA analyses of Aravalli feldspar, Table S4: Results of the EPMA analyses of Aravalli chlorite, Table S5: Results of the EPMA analyses of Aravalli ilmenite, Table S6: Results of the P-T condition estimations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W., E.K., A.G. and T.A.; methodology, E.K., J.W., and A.G. software, A.G.; validation, J.W., and T.A., formal analysis, J.W., E.K., and A.G.; investigation, J.W., T.A., E.K., A.G., resources, T.A. and J.W.; data curation, J.W., T.A.; writing—original draft preparation, J.W., E.K., A.G., writing—A.G.; visualization, A.G., E.K.; supervision, J.W., and T.A. project administration, J.W.; funding acquisition, J.W.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work benefited from Indo-Polish Joint Research Project of Department of Science & Technology, New Delhi (No. INT/POL/P-14/05) to T.A. & J.W. This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education (Poland) grant number 62.9012.2012.000 for J.W. in 2020.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Lidia Jeżak for her help in performing EPMA analyses at the Electron Microprobe Laboratory of the Inter-Institute Analytical Complex for Minerals and Synthetic Substances in University of Warsaw and Grzegorz Zielinski for qualitative and quantitative analysis of elemental composition using a WDS equipment with CAMECA SX 100 electron microprobe at Polish Geological Institute in Warsaw, Poland.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- De Wit, M.J.; Ashwal, L.D. Greenstone belts: What are they? South. Afr. J. Geol. 1995, 98, 505–520. [Google Scholar]
- Kerrich, R.; Polat, A.; Wyman, D.; Hollings, P. Trace element systematics of Mg to Fe–tholeiitic basalt suites of the Superior Province: Implications for Archean mantle reservoirs and greenstone belt genesis. Lithos 1999, 46, 163–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, A. Growth of Archean continental crust in oceanic island arcs. Geology 2012, 40, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condie, K.C. TTG and adakites: Are they both slab melts? Lithos 2005, 80, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condie, K.C.; Kröner, A. The building blocks of continental crust: Evidence for a major change in the tectonic setting of continental growth at the end of the Archean. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, H.C.; Prasad, B.R.; Kumar, P. Structure and Tectonics of the Indian Continental Crust and Its Adjoining Region: Deep Seismic Studies, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Fareeduddin; Banerjee, D.M. Aravalli craton and its mobile belts: An update. Episodes 2020, 43, 88–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Rajamani, V. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the basal Aravalli Volcanics near Nathdwara, Rajasthan, India. Precambrian Res. 1991, 49, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, V.P.; Arima, M.; Pati, J.K.; Kaneko, Y. Petrology and Geochemistry of metamorphosed basaltic pillow lava and basaltic komatiite in the Mauranipur area: Subduction related volcanism in the Archean Buldenkhand Craton, central India. J. Miner. Petrol. Sci. 2006, 102, 191–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Tarney, J. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Late Archaean Aravalli Volcanics, basement enclaves and granitoids, Rajasthan. Precambrian Res. 1994, 65, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, K.; Macdaugall, J.D.; Roy, A.B.; Murali, A.V. Sm-Nd evidence for 3.3 Ga old rock in Rajasthan, north-western India. Precambrian Res. 1990, 48, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenbeck, M.; Goswami, J.N. An ion-probe single zircon 207Pb/206Pb age from Mewar Gneiss at Jhamarkotra, Rajasthan. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 2135–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.B.; Kröner, A. Single zircon evaporation ages constraining the growth of the Archaean Aravalli craton, northwestern Indian shield. Geol. Mag. 1996, 133, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.B.; Kröner, A.; Laul, V. Detrital zircons constraining basement age in a late Archaean greenstone belt of south-eastern Rajasthan, India. Curr. Sci. 2001, 81, 407–410. [Google Scholar]
- Heron, A.M. Geology of Central Rajputana. Geol. Surv. India. Mem. 1953, 79, 389. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, T.; Dragusanu, C.; Tanaka, T. Provenance of Proterozoic Basal Aravalli mafic volcanic rocks from Rajasthan, Northwestern India: Nd isotopes evidence for enriched mantle reservoirs. Precambrian Res. 2008, 162, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Deb, M.; Tarney, J.; Raza, M. Proterozoic mafic volcanism in the Aravalli-Delhi Orogen, north-western India: Geochemistry and tectonic framework. J. Geol. Soc. India 2008, 72, 93–111. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, M.; Sarkar, S.C. Proterozoic tectonic evolution and metallogenesis in the Aravalli–Delhi orogenic Complex, Northwestern India. Precambrian Res. 1990, 46, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naha, K.; Halyburton, R.V. Early Precambrian stratigraphy of central and southern Rajasthan. Precambrian Res. 1974, 1, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugden, T.J.; Deb, M.; Windley, B.F. The tectonic setting of mineralisation in the Proterozoic Aravalli Delhi Orogenic belt, NW India. In Developments in Precambrian Geology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; Volume 8, pp. 367–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, M.; Fowler, A.D. The origin of spinifex texture in komatiites. Nature 1999, 397, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouquain, S.; Arndt, N.T.; Faure, F.; Libourel, G. An experimental study of pyroxene crystallization during rapid cooling in a thermal gradient: Application to komatiites. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 5, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hawthorne, F.C.; Oberti, R.; Harlow, G.E.; Maresch, W.V.; Martin, R.F.; Schumacher, J.C.; Welch, M.D. Nomenclature of the amphibole supergroup. Am. Mineral. 2012, 97, 2031–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, N. Nomenclature of pyroxenes. Mineral. J. 1989, 14, 198–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, M.H. A new review of the chlorites. Mineral. Mag. 1954, 30, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindle, A.G. Mineral Recalculation Software of Chlorite (Chlorite.xls). Available online: http://www.open.ac.uk/earth-research/tindle/AGTWebPages/AGTSoft.html (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- Cassidy, K.F.; Groves, D.I.; Binns, R.A. Manganoan ilmenite formed during regional metamorphism of Archean mafic and ultramafic rocks from Western Australia. Can. Mineral. 1988, 26, 999–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Blundy, J.D.; Holland, T.J. Calcic amphibole equilibria and a new amphibole-plagioclase geothermometer. Contrib. Mineral. Petr. 1990, 104, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otten, M.T. The origin of brown hornblende in the Artfjället gabbro and dolerites. Contrib. Mineral. Petr. 1984, 86, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarstrom, J.M.; Zen, E.A. Aluminum in hornblende: An empirical igneous geobarometer. Am. Mineral. 1986, 71, 1297–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Hollister, L.S.; Grissom, G.C.; Peters, E.K.; Stowell, H.H.; Sisson, V.B. Confirmation of the empirical correlation of Al in hornblende with pressure of solidification of calc-alkaline plutons. Am. Mineral. 1987, 72, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- Mutch, E.J.F.; Blundy, J.D.; Tattich, B.C.; Cooper, F.J.; Brooker, R.A. An experimental study of amphibole stability in low-pressure granitic magmas and a revised Al-in-hornblende geobarometer. Contrib. Mineral. Petr. 2016, 171, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczynski, M.J.; Grove, T.L.; Behrens, H. Amphibole stability in primitive arc magmas: Effects of temperature, H2O content, and oxygen fugacity. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2012, 164, 317–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivas, A.R. Geochemical evidence for magmatic fluids in porphyry copper mineralization. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1982, 78, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Han, C.M.; Xiao, W.J.; Su, B.X.; Ding, J.X.; Song, S.H. Geochemical and zircon U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopic constraints on the origin of supracrustal rocks from the mid-Qilian terrane: A comparison between supracrustal rocks on the two sides of the eastern segment of the Altyn Tagh Fault. Precambrian Res. 2017, 294, 284–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.J.; Bai, R.X.; Chen, W. Genetic Mineralogy, 1st ed.; University of Geosciences Press: Beijing, China, 1990; pp. 1–161. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.Y.; Sun, D.S.; Yin, H.A. Genetic Mineralogy and Prospecting Mineralogy, 1st ed.; University of Chongqing Publishing House: Chongqing, China, 1987; pp. 1–872. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zang, W.; Fyfe, W.S. Chloritization of the hydrothermally altered bedrock at the Igarape Bahia gold deposit, Carajas, Brasil. Miner. Deposita 1995, 30, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranidiotis, P.; MacLean, W.H. Systematics of chlorite alteration at the Phelps Dodge massive sulfide deposit, Matagami, Quebec. Econ. Geol. 1987, 82, 1898–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathelineau, M.; Nieva, D. A chlorite solid solution geothermometer. Contrib. Mineral. Petr. 1985, 91, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winchester, J.A.; Floyd, P.A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements. Chem. Geol. 1977, 20, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.S. A new cation plot for classifying subalkalic volcanic rocks. In Ontario Division Mines, Miscellaneous Paper; Ministry of Natural Resources: Toronto, Canada, 1976; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Boynton, W.V. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies. In Rare Earth Element Geochemistry, 1st ed.; Henderson, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 63–114. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Tarney, J. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Garhwal volcanics: Implications for evolution of the north Indian lithosphere. Precambrian Res. 1991, 50, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A.; Norry, M.J. Petrogenetic implications of Ti, Zr, Y, and Nb variations in volcanic rocks. Contrib. Mineral. Petr. 1979, 69, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condie, K.C. Mafic crustal xenoliths and the origin of the lower continental crust. Lithos 1999, 46, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.N.; Morrison, M.A.; Dickin, A.P.; Hendry, G.L. Continental flood basalt … Arachnids rule OK? In Continental Basalts and Mantle Xenoliths, 1st ed.; Hawkesworth, C.J., Morry, M.J., Eds.; Shiva: Nantwich, UK, 1983; pp. 158–185. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, B.L.; Tarney, J. Chemistry of the sub-continental mantle: Inferences from Archean and Proterozoic dykes and continental flood basalts. In Continental Basalts and Mantle Xenoliths, 1st ed.; Hawkesworth, C.J., Morry, M.J., Eds.; Shiva: Nantwich, UK, 1983; pp. 209–229. [Google Scholar]
- Dupuy, C.; Dostal, J. Trace element geochemistry of some continental tholeiites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1984, 67, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parman, S.W.; Dann, J.C.; Grove, T.L.; De Wit, M.J. Emplacement conditions of komatiite magmas from the 3.49 Ga Komati Formation, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1997, 150, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parman, S.W.; Grove, T.L. Komatiites in the plume debate. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap. 2005, 388, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Viljonen, M.J.; Viljonen, R.P. The geology and geochemistry of the lower ultramafic unit of the Onverwacht group and proposed new class of igneous rocks. Spec. Publ. Geol. Soc. S. Afr. 1969, 2, 55–85. [Google Scholar]
- Arndt, N.T.; Nisbet, E.G. Komatiites. What is 350 a komatiite. In Komatiites, 1st ed.; Arndt, N.T., Nisbet, E.G., Eds.; George Allen & Unwin: London, UK, 1982; pp. 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Arndt, N.T.; Lesher, C.M.; Barnes, S.J. Komatiite, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 1–196. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, H.M.; Werner, M.; Smithies, R.H.; Evins, P.M.; Kirkland, C.L.; Kelsey, D.E.; Hand, M.; Collins, A.; Pirajno, F.; Wingate, M.T.D.; et al. The Geology of the West Musgrave Province and the Bentley Supergroup—A Field Guide; Geological Survey of Western Australia: Adelaide, Australia, 2011; pp. 1–125. [Google Scholar]
- Lowrey, J.R.; Ivanic, T.J.; Wyman, D.A.; Roberts, M.P. Platy pyroxene: New insights into Spinifex texture. J. Petrol. 2017, 58, 1671–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, F.; Arndt, N.; Libourel, G. Formation of spinifex texture in komatiites: An experimental study. J. Petrol. 2006, 47, 1591–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staude, S.; Jones, T.J.; Markl, G. The textures, formation and dynamics of rare high-MgO komatiite pillow lavas. Precambrian Res. 2020, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.; McKenzie, D. Magmatism at rift zones: The generation of volcanic continental margins and flood basalts. J. Geoph. Res. 1989, 94, 7685–7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).