Cleaner Production of Chromium Oxide from Low Fe(II)-Chromite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Data Correlation Analysis Methods
3. Results
3.1. Modeling
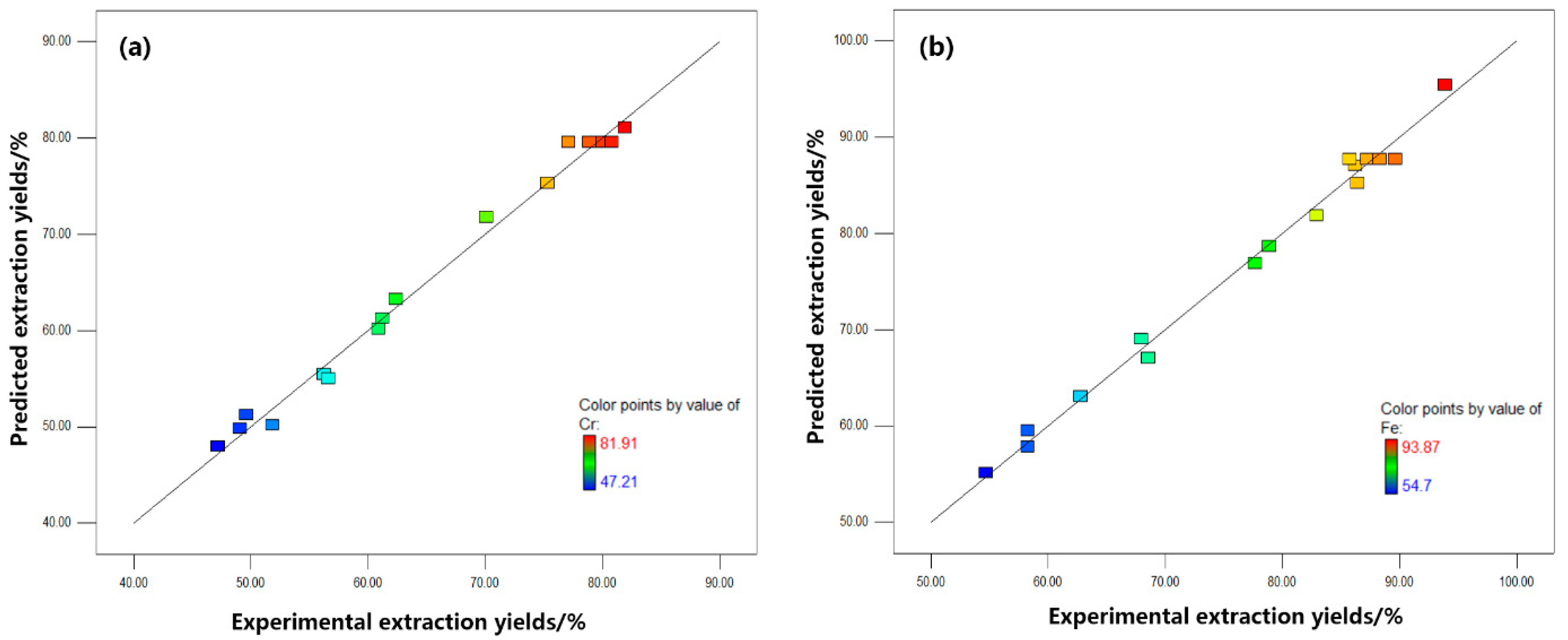
3.2. Model Validation
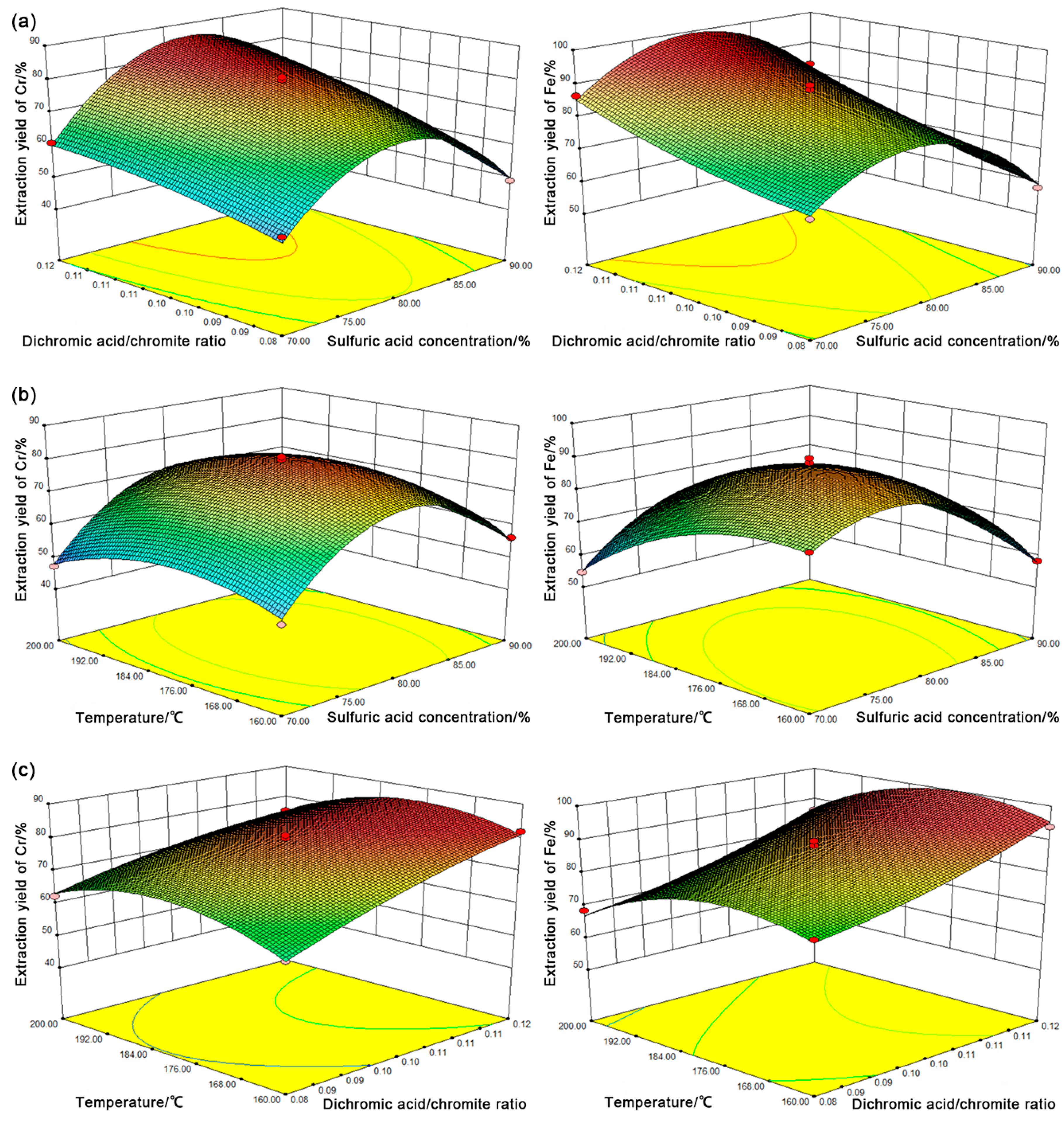
3.3. Optimization
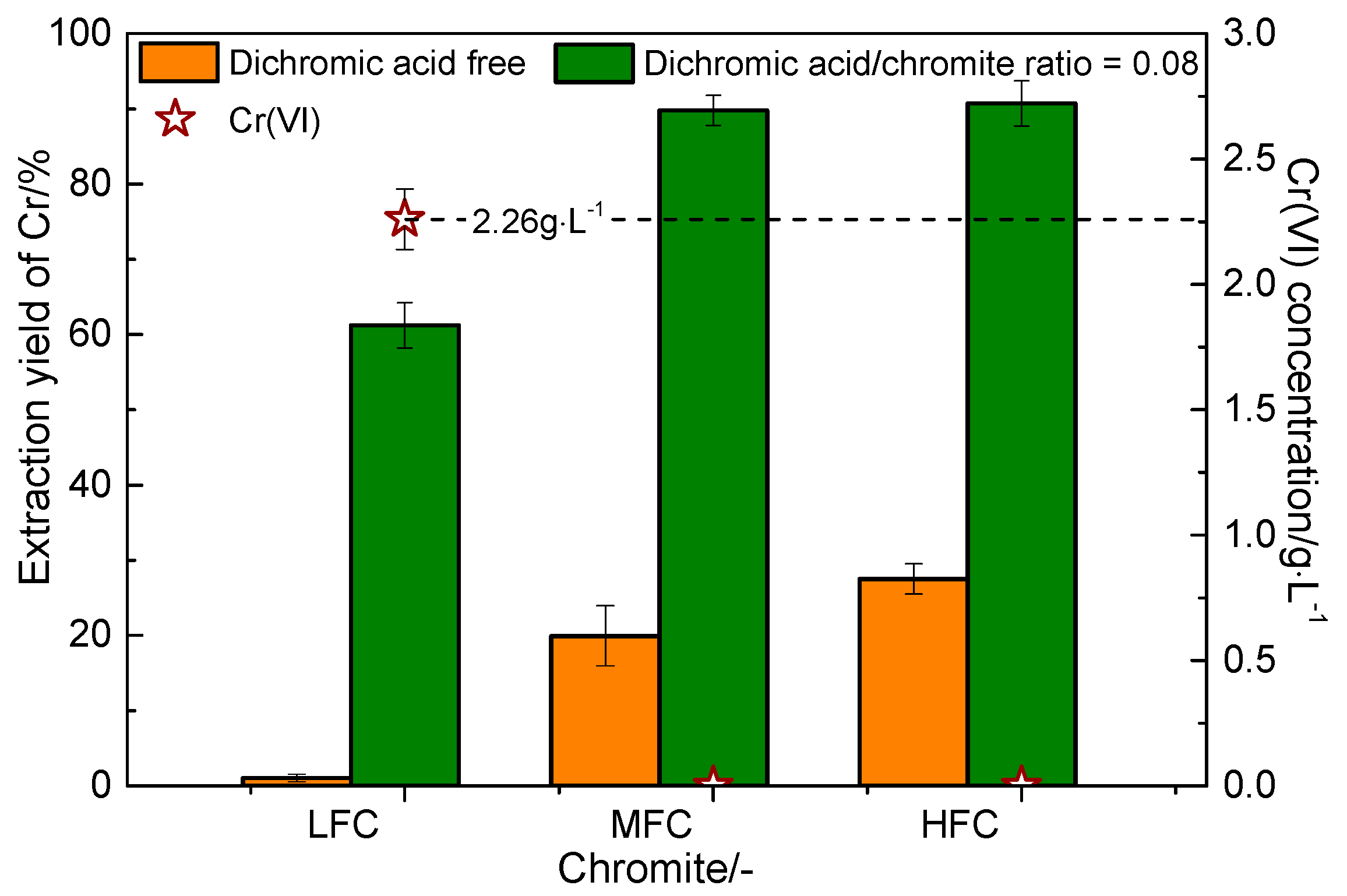
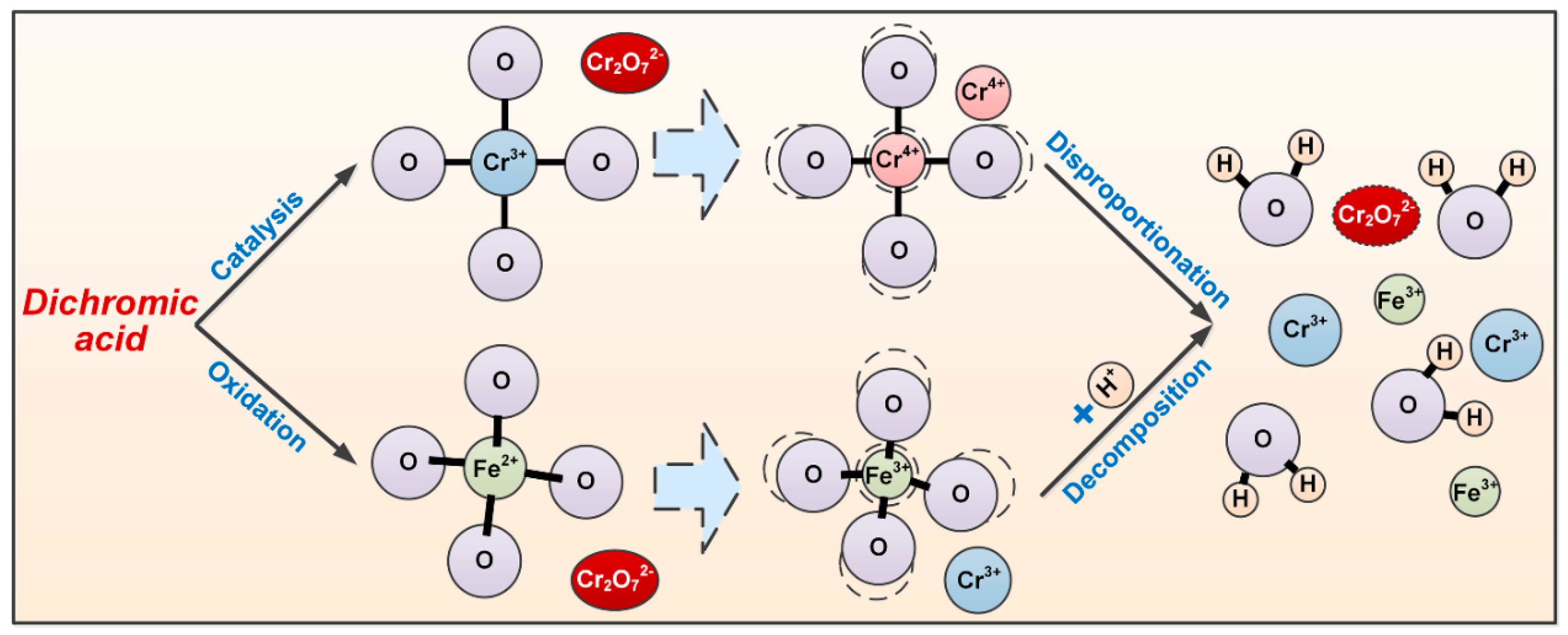
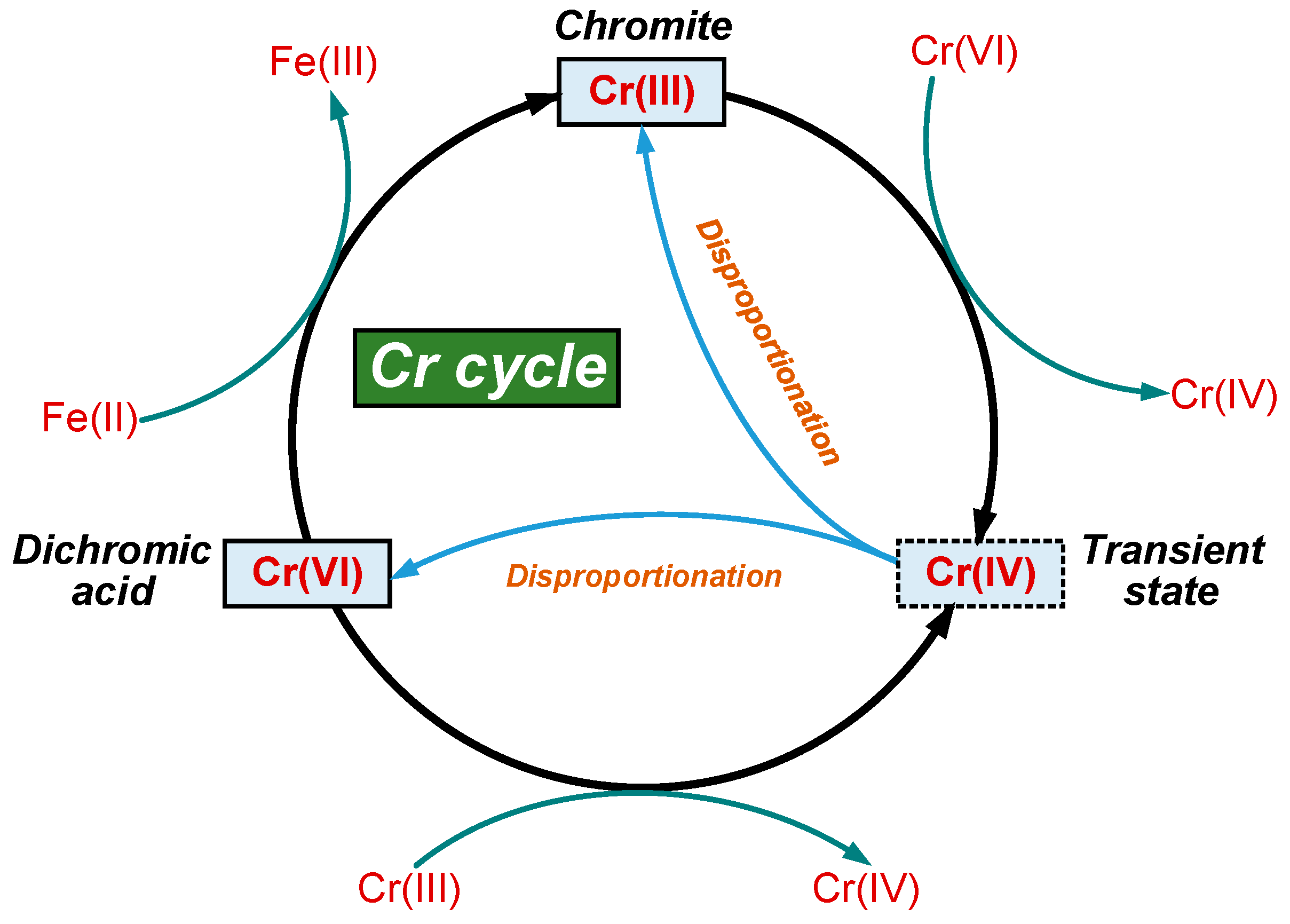
3.4. Effect of Dichromic Acid
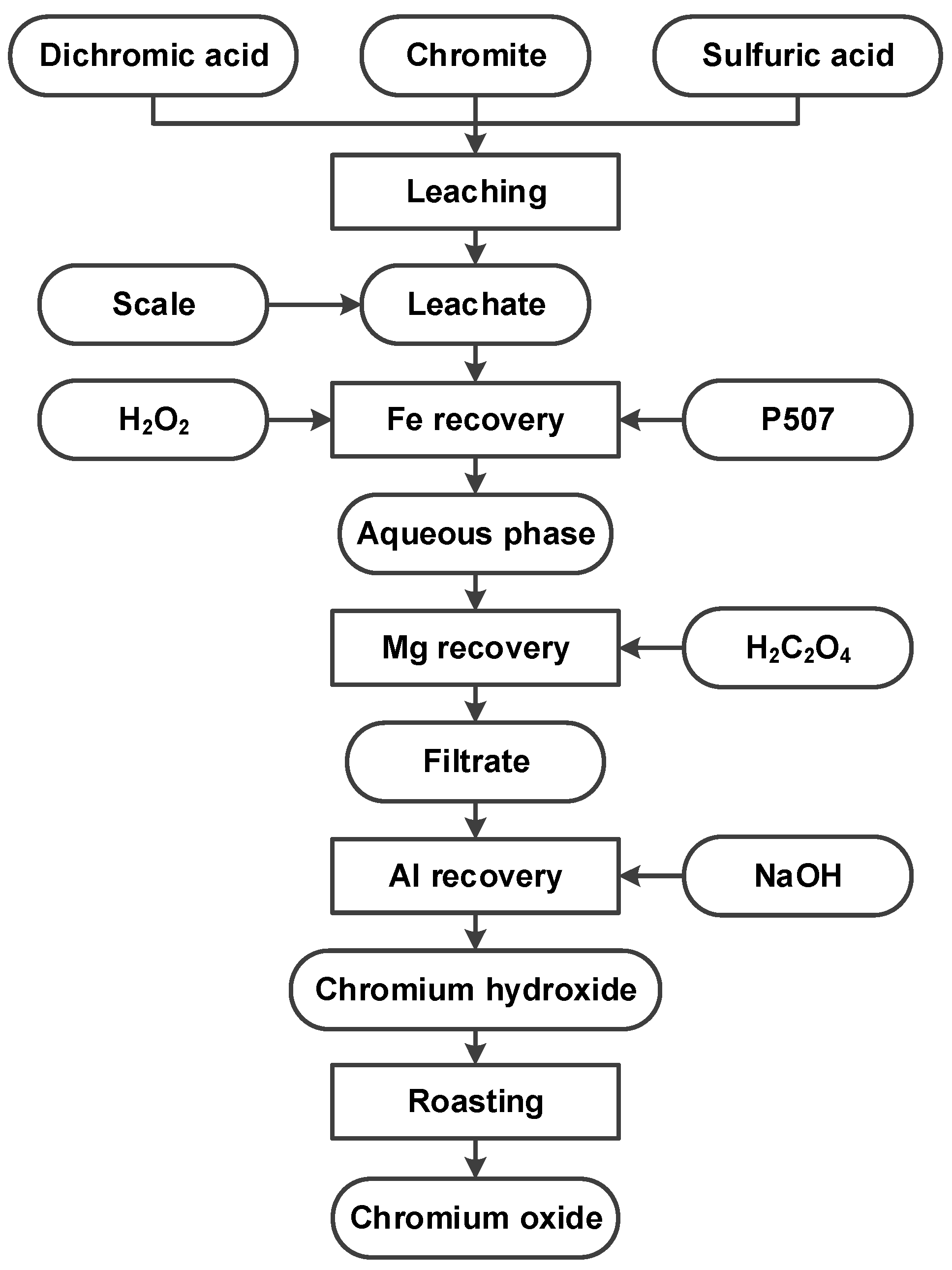
3.5. Product Preparation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TC | Turkish chromite |
| RSM | Response surface methodology |
| BBD | Box-Behnken design |
| C | Sulfuric acid concentration |
| r | Dichromic acid/chromite ratio |
| T | Processing temperature |
| ICP-OES | Inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry |
| LFC | low Fe(II)-chromite |
| MFC | Medium Fe(II)-chromite |
| HFC | High Fe(II)-chromite |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| CSM | Crystallographica Search-Match |
| Powder Diffraction File | |
| ICDD | International Centre for Diffraction Data |
| SEM-EDS | Scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| R2 | Coefficient of determination |
| Adj. R2 | Adjusted coefficient of determination |
| Pred. R2 | Predicted coefficient of determination |
| RCr | Extraction yields of Cr |
| RFe | Extraction yields of Fe |
| RCr(exp) | Experimental extraction yields of Cr |
| RFe(exp) | Experimental extraction yields of Fe |
| C.V.% | Coefficients of variance |
References
- Feng, H.; Li, H.B.; Jiang, Z.H.; Zhang, T.; Dong, N.; Zhang, S.C.; Han, P.D.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Z.G. Designing for high corrosion-resistant high nitrogen martensitic stainless steel based on DFT calculation and pressurized metallurgy method. Corros. Sci. 2019, 158, 108081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Song, S.; Xue, Z.; Nath, M. Formation mechanisms and leachability of hexavalent chromium in Cr2O3-containing refractory castables of electric arc furnace cover. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2019, 50, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Shao, Z.B.; Liu, C.J.; Jiang, M.F.; Li, X.T.; Zevenhoven, R.; Saxén, H. Preparation of Cu–Cr alloy powder by mechanical alloying. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 607, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleli, N.; Demir, A. Chromite. Environmental Materials and Waste, 1st ed.; Prasad, M.N.V., Shih, K., Eds.; The Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016; pp. 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Demand analysis and prediction of world chrome resource. Res. Ind. 2016, 18, 87–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, S.; Eyuboglu, C.; Morcali, M.; Özbey, S.; Sucuoglu, Y. Production of chromium oxide from Turkish chromite concentrate using ethanol. High Temp. Mater. P-US. 2015, 34, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcali, M.H.; Eyuboglu, C.; Aktas, S. Synthesis of nanosized Cr2O3 from Turkish chromite concentrates with sodium borohydride (NaHB4) as reducing agent. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 157, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, S.L.; Xu, H.B.; Du, H.; Zhang, Y. Decomposition of chromite ore by oxygen in molten NaOH–NaNO3. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 95, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarkadaş, G.; Yildiz, K. Effects of mechanical activation on the soda roasting of chromite. Can. Metall. Quart. 2013, 48, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaños-Benítez, V.; Hullebusch, E.D.V.; Lens, P.N.L.; Quantin, C.; Vossenberg, J.V.D.; Subramanian, S.; Sivry, Y. (Bio)leaching Behavior of Chromite Tailings. Minerals-Basel 2018, 8, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Nagendran, R. Fractionation behavior of heavy metals in soil during bioleaching with Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Pan, Z.Y.; Lang, J.M.; Xu, J.M.; Zheng, Y.G. Bioleaching of chromium from tannery sludge by indigenous Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, T.H.; Williams, T.D.; Eales, G.J. Toxicity of cadmium, hexavalent chromium and copper to marine fish larvae (Cyprinodon variegatus) and copepods (Tisbe battagliai). Mar. Environ. Res. 1994, 38, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beukes, J.P.; Preez, S.P.D.; Zyl, P.G.V.; Paktunc, D.; Fabritius, T.; Päätalo, M.; Cramer, M. Review of Cr(VI) environmental practices in the chromite mining and smelting industry-Relevance to development of the Ring of Fire, Canada. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 874–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loock-Hattingh, M.M.; Beukes, J.P.; Zyl, P.G.V.; Tiedt, L.R. Cr(VI) and conductivity as indicators of surface water pollution from ferrochrome production in South Africa: Four case studies. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2015, 46, 2315–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, R.J.; Gardea-Torresdey, L.J.; Tiemann, J.K.; Gomez, E.; Arteaga, S.; Rascon, E.; Parsons, G.J. Uptake and effects of five heavy metals on seed germination and plant growth in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). B. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 66, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Mou, Q.Q.; Zeng, Q.; Yue, Y. Experimental study on precipitation behavior of spinels in stainless steel-making slag under heating treatment. Processes 2019, 7, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Li, J.L.; Mou, Q.Q.; Zhu, H.Y.; Xue, Z.L. Effect of FeO on spinel crystallization and chromium stability in stainless steel-making slag. JOM 2019, 71, 2331–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.Z.; Tang, Y.Y.; Lee, P.H.; Liu, C.S.; Shih, K.M.; Li, F.B. Detoxification and immobilization of chromite ore processing residue in spinel-based glass-ceramic. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, M.; Song, S.; Garbers-Craig, A.M.; Li, Y. Phase evolution with temperature in chromium-containing refractory castables used for waste melting furnaces and Cr(VI) leachability. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 20391–20398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.J.; Cao, L.H.; Jiang, M.F.; Li, B.K.; Saxén, H.; Zevenhoven, R. Shear-force based stainless steel slag modification for chromium immobilization. ISIJ Int. 2019, 59, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.J.; Gao, T.C.; Gao, L.; Saxén, H.; Zevenhoven, R. Remediation of stainless steel slag with MnO for CO2 mineralization. Process Saf. Environ. 2019, 127, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geelhoed, J.S.; Meeussen, J.C.L.; Roe, M.J.; Hillier, S.; Thomas, R.P.; Farmer, J.G.; Paterson, E. Chromium remediation or release? Effect of iron(II) sulfate addition on chromium(VI) leaching from columns of chromite ore processing residue. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 3, 3206–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, M.C.; Farmer, J.G.; Anderson, P.; Paterson, E.; Hillier, S.; Lumsdon, D.G.; Bewley, R.J.F. Calcium polysulfide remediation of hexavalent chromium contamination from chromite ore processing residue. Sci. Total. Environ. 2006, 364, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Ludwig, R.D. Treatment of hexavalent chromium in chromite ore processing solid waste using a mixed reductant solution of ferrous sulfate and sodium dithionite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6208–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.J.; Shi, P.Y.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, M.F.; Zhang, Q.S.; Zevenhoven, R.; Saxén, H. Sulfuric acid leaching kinetics of South African chromite. Int. J. of Miner. Metall. Mater. 2015, 22, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.F.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.J.; Shi, P.Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, D.P.; Saxén, H.; Zevenhoven, R. Sulfuric acid leaching of South African chromite. Part 2: Optimization of leaching conditions. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 130, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.J.; Shi, P.Y.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, M.F.; Zhang, Q.S.; Saxén, H.; Zevenhoven, R. Sulfuric acid leaching of South African chromite. Part 1: Study on leaching behavior. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 130, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shi, P.Y.; Jiang, M.F. Advances towards a clean hydrometallurgical process for chromite. Miner. Basel 2016, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Qi, J.; Jiang, M.F. Experimental study on sulfuric acid leaching behavior of chromite with different temperature. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 361–363, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.J.; Yang, D.P.; Shi, P.Y.; Jiang, M.F.; Li, B.K.; Saxén, H.; Zevenhoven, R. A cleaner method for preparation of chromium oxide from chromite. Process Saf. Environ. 2017, 105, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, W.J.; Heinrichs, M. The attack of chromite by sulphuric acid. Can. J. Chem. 1960, 38, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geveci, A.; Topkaya, Y.; Ayhan, E. Sulfuric acid leaching of Turkish chromite concentrate. Miner. Eng. 2002, 15, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardar, E.; Eric, R.H.; Letowski, F.K. Acid leaching of chromite. Mine. Eng. 1994, 7, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Vimala, R.; Das, N. Biosorption of Zn(II) onto Pleurotus platypus: 5-Level Box-Behnken design, equilibrium, kinetic and regeneration studies. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 64, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeganathan, P.M.; Venkatachalam, S.; Karichappan, T.; Ramasamy, S. Model development and process optimization for solvent extraction of polyphenols from red grapes using Box-Behnken design. Prep. Biochem. Biotech. 2014, 44, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Shao, Z.B.; Leng, Q.C.; Zhang, X.D.; Liu, C.J.; Li, B.K.; Jiang, M.F. Preparation of Cu–Cr alloy powder by heat mechanical alloying and Box-Behnken design based optimization. Powder Technol. 2017, 321, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.J.; Li, B.K.; Zevenhoven, R.; Saxén, H.; Jiang, M.F. Recovery of chromium from residue of sulfuric acid leaching of chromite. Process Saf. Environ. 2018, 113, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaari, J. Molecular dynamics simulations of vacancy diffusion in chromium(III) oxide, hematite, magnetite and chromite. Solid State Ion. 2015, 270, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourabet, M.; El Rhilassi, A.; El Boujaady, H.; Bennani-Ziatni, M.; El Hamri, R.; Taitai, A. Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by adsorption on Apatitic tricalcium phosphate using Box-Behnken design and desirability function. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 4402–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tathavakar, V.D.; Antony, M.P.; Jha, A. The physical chemistry of thermal decomposition of South African chromite minerals. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2005, 36, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.H.; Luo, C.; Chen, J.H.; Hou, X.M. High-performance chromite by structure stabilization treatment. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2020, 27, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.J.; Li, B.K.; Jiang, M.F. Decomposition mechanism of chromite in sulfuric acid-dichromic acid solution. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 2017, 24, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
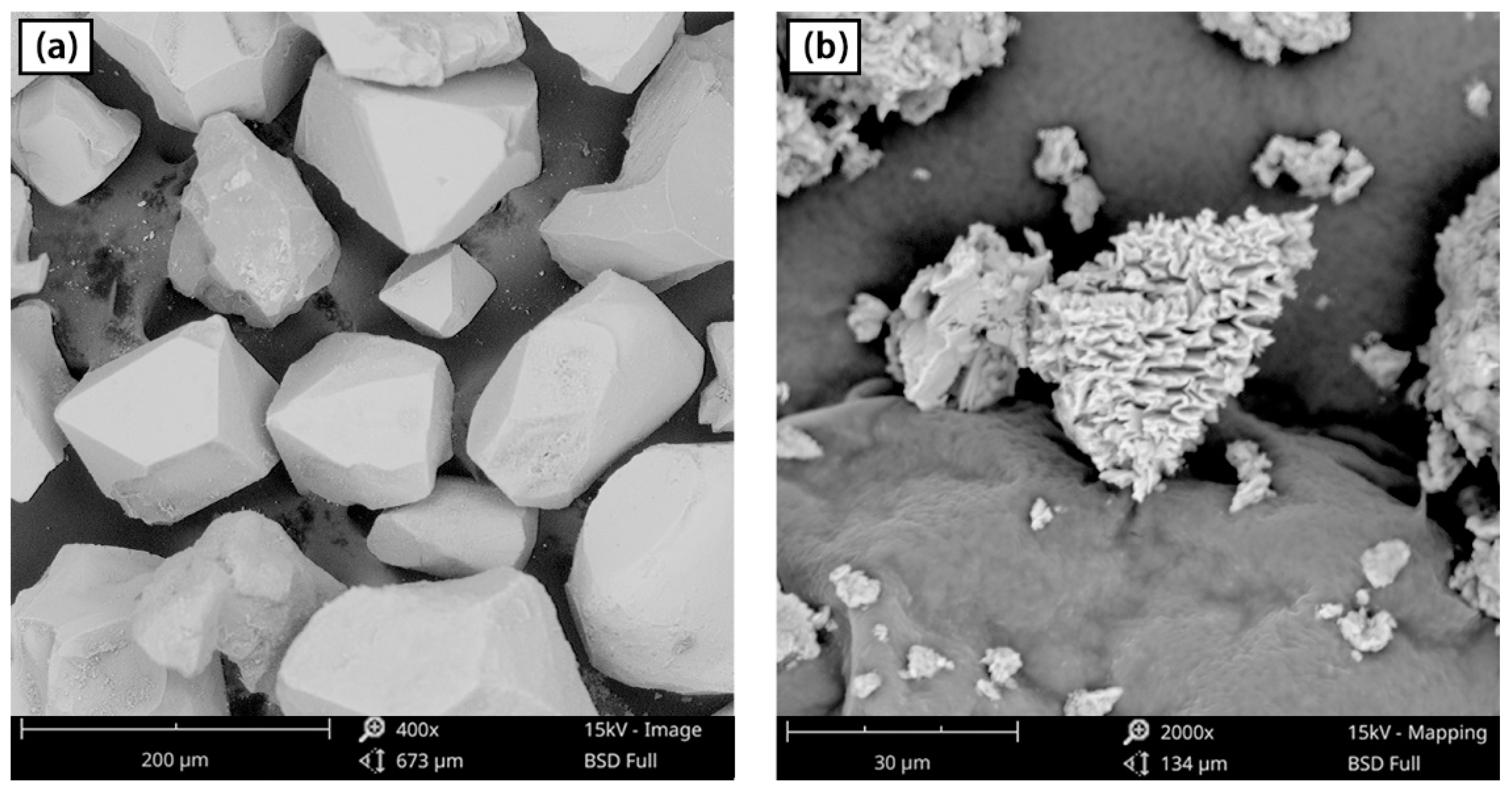
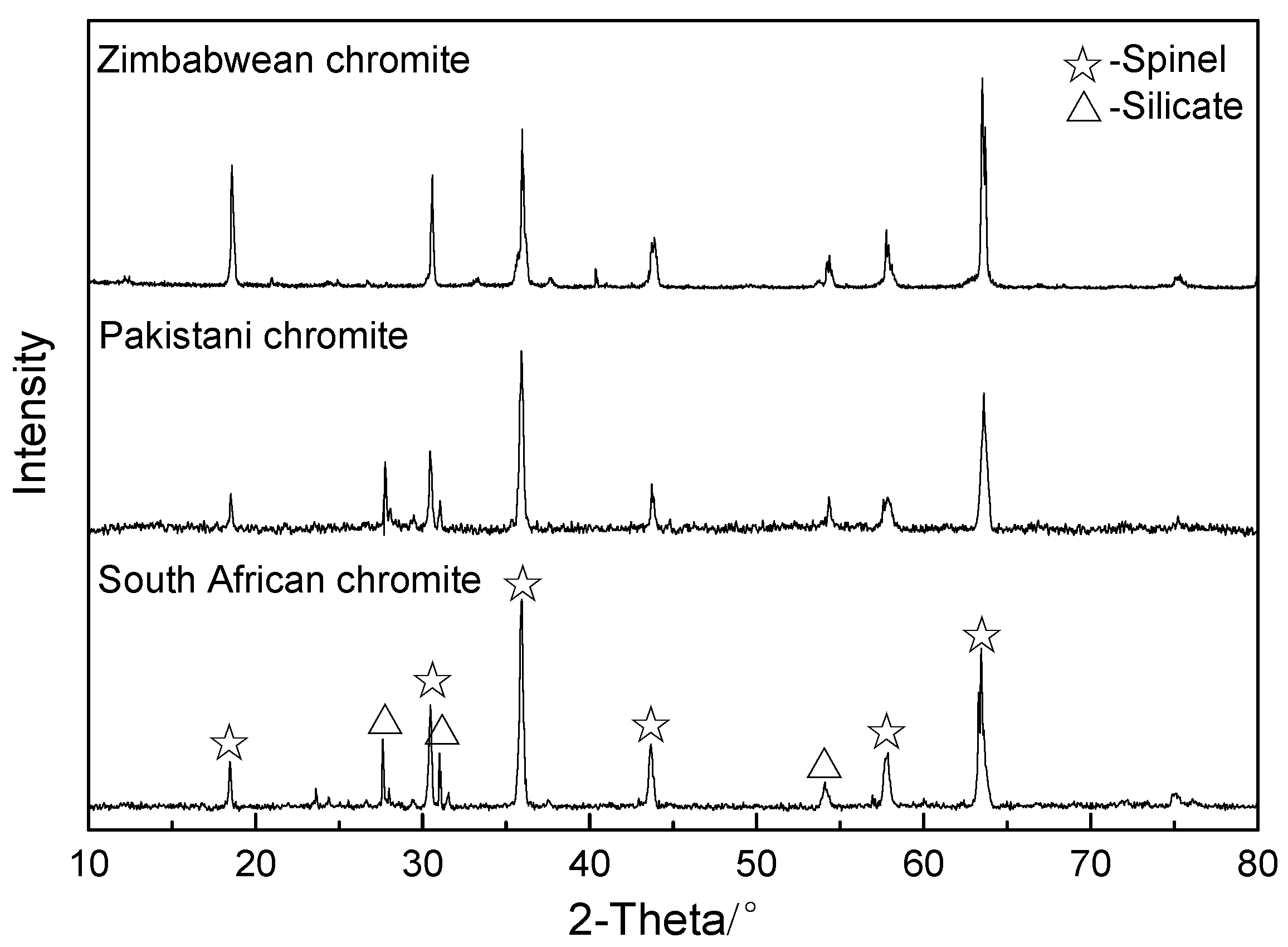

| Chromite | FeO | Fe2O3 | Cr2O3 | Al2O3 | MgO | SiO2 | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zimbabwean chromite (LFC) | 1.52 | 21.56 | 45.95 | 12.05 | 6.40 | 2.80 | 9.72 |
| Pakistani chromite (MFC) | 6.67 | 5.34 | 42.29 | 13.01 | 19.75 | 6.67 | 6.27 |
| South African chromite (HFC) | 18.69 | 5.22 | 45.18 | 13.25 | 8.87 | 6.79 | 2.00 |
| Standard Order | Actual and Coded Level of Variables | RCr(exp)/% | RFe(exp)/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/% (X1) | r/- (X2) | T/°C (X3) | |||
| 1 | 90 (+1) | 0.10 (0) | 160 (−1) | 56.25 | 58.26 |
| 2 | 70 (−1) | 0.08 (−1) | 180 (0) | 51.84 | 67.97 |
| 3 | 90 (+1) | 0.10 (0) | 200 (+1) | 56.63 | 62.77 |
| 4 | 80 (0) | 0.08 (−1) | 200 (+1) | 62.37 | 68.56 |
| 5 | 90 (+1) | 0.12 (+1) | 180 (0) | 70.08 | 82.92 |
| 6 | 80 (0) | 0.08 (−1) | 160 (−1) | 61.22 | 77.69 |
| 7 | 80 (0) | 0.10 (0) | 180 (0) | 79.97 | 87.40 |
| 8 | 70 (−1) | 0.10 (0) | 200 (+1) | 47.21 | 54.70 |
| 9 | 80 (0) | 0.10 (0) | 180 (0) | 77.11 | 87.24 |
| 10 | 90 (+1) | 0.08 (−1) | 180 (0) | 49.08 | 58.26 |
| 11 | 80 (0) | 0.10 (0) | 180 (0) | 78.91 | 85.74 |
| 12 | 80 (0) | 0.10 (0) | 180 (0) | 80.77 | 88.31 |
| 13 | 70 (−1) | 0.10 (0) | 160 (−1) | 49.63 | 78.9 |
| 14 | 70 (−1) | 0.12 (+1) | 180 (0) | 60.89 | 86.44 |
| 15 | 80 (0) | 0.12 (+1) | 160 (−1) | 81.91 | 93.87 |
| 16 | 80 (0) | 0.10 (0) | 180 (0) | 80.82 | 89.66 |
| 17 | 80 (0) | 0.12 (+1) | 200 (+1) | 75.33 | 86.21 |
| Source | Cr | Fe | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum of Square | df | Mean Square | F Value | p-Value Prob. > F | Sum of Square | df | Mean Square | F Value | p-Value Prob. > F | |
| Model | 2608.23 | 9 | 289.80 | 83.70 | <0.0001 | 2607.88 | 9 | 289.76 | 100.07 | <0.0001 |
| C | 63.11 | 1 | 63.11 | 18.23 | 0.0037 | 83.21 | 1 | 83.21 | 28.73 | 0.0011 |
| r | 507.21 | 1 | 507.21 | 146.50 | <0.0001 | 740.36 | 1 | 740.36 | 255.68 | <0.0001 |
| T | 6.98 | 1 | 6.98 | 2.01 | 0.1988 | 166.35 | 1 | 166.35 | 57.45 | 0.0001 |
| Cr | 35.70 | 1 | 35.70 | 10.31 | 0.0148 | 9.58 | 1 | 9.58 | 3.31 | 0.1118 |
| CT | 1.96 | 1 | 1.96 | 0.57 | 0.4763 | 206.07 | 1 | 206.07 | 71.16 | <0.0001 |
| rT | 14.94 | 1 | 14.94 | 4.31 | 0.0764 | 0.54 | 1 | 0.54 | 0.19 | 0.6788 |
| C2 | 1627.52 | 1 | 1627.52 | 470.08 | <0.0001 | 1057.61 | 1 | 1057.61 | 365.25 | <0.0001 |
| r2 | 14.93 | 1 | 14.93 | 4.31 | 0.0765 | 18.15 | 1 | 18.15 | 6.27 | 0.0408 |
| T2 | 232.16 | 1 | 232.16 | 67.06 | <0.0001 | 280.62 | 1 | 280.62 | 96.91 | <0.0001 |
| Element | Standard Deviation | Mean | Coefficient of Variance (C.V.%) | R2 | Adj. R2 | Pred. R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 1.86 | 65.88 | 2.82 | 0.9908 | 0.9790 | 0.9055 |
| Fe | 1.70 | 77.35 | 2.20 | 0.9923 | 0.9824 | 0.9225 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.; Shi, P.; Sun, L.; Jiang, M.; Saxen, H.; Zevenhoven, R. Cleaner Production of Chromium Oxide from Low Fe(II)-Chromite. Minerals 2020, 10, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10050460
Zhao Q, Liu C, Shi P, Sun L, Jiang M, Saxen H, Zevenhoven R. Cleaner Production of Chromium Oxide from Low Fe(II)-Chromite. Minerals. 2020; 10(5):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10050460
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Qing, Chengjun Liu, Peiyang Shi, Lifeng Sun, Maofa Jiang, Henrik Saxen, and Ron Zevenhoven. 2020. "Cleaner Production of Chromium Oxide from Low Fe(II)-Chromite" Minerals 10, no. 5: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10050460
APA StyleZhao, Q., Liu, C., Shi, P., Sun, L., Jiang, M., Saxen, H., & Zevenhoven, R. (2020). Cleaner Production of Chromium Oxide from Low Fe(II)-Chromite. Minerals, 10(5), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10050460