Hydrometallurgical Recovery and Process Optimization of Rare Earth Fluorides from Recycled Magnets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Demagnetization
2.2.2. Comminution
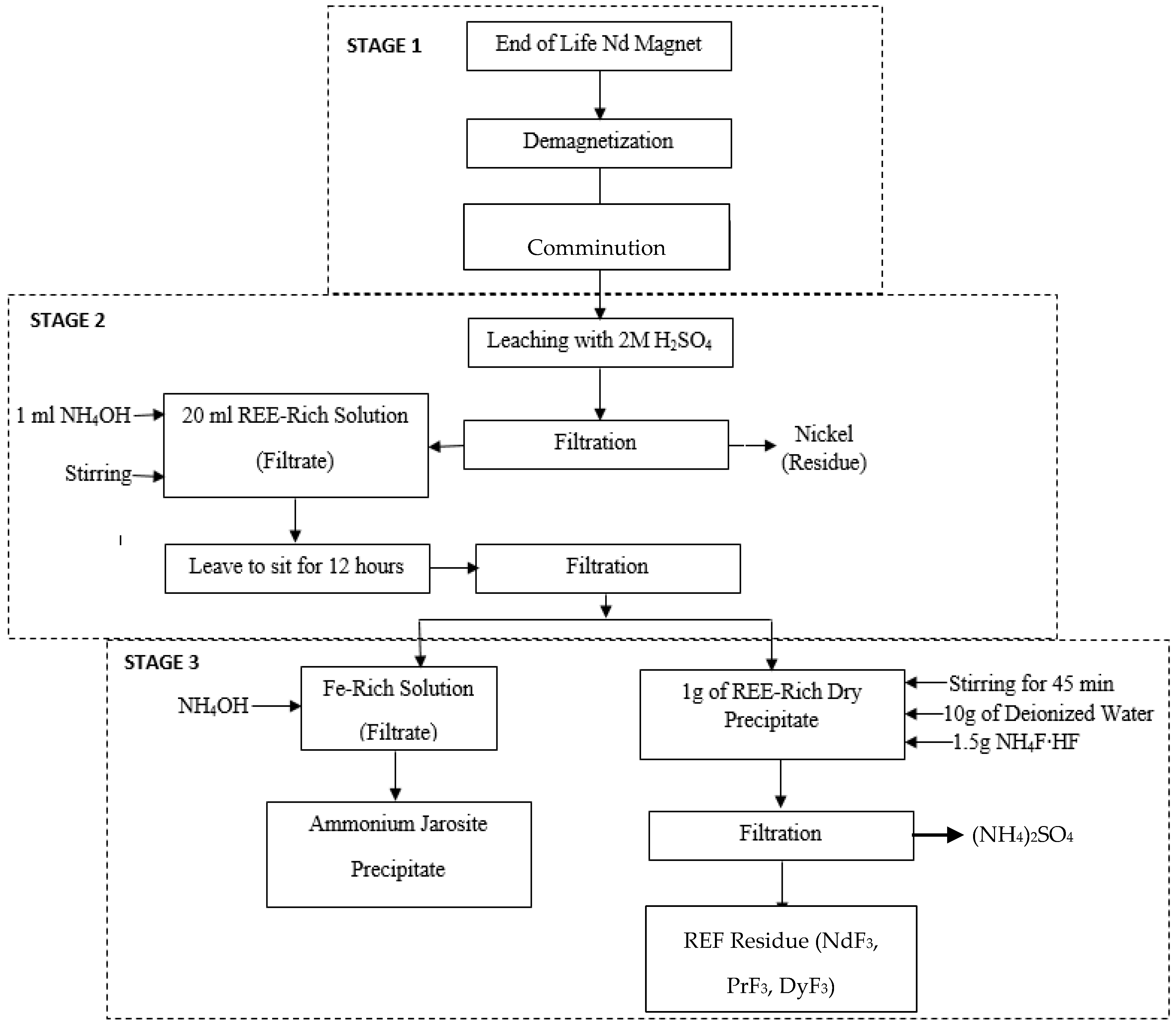
2.3. Hydrometallurgical Processing
2.4. Modelling of REF Recovery
2.5. Material Characterization
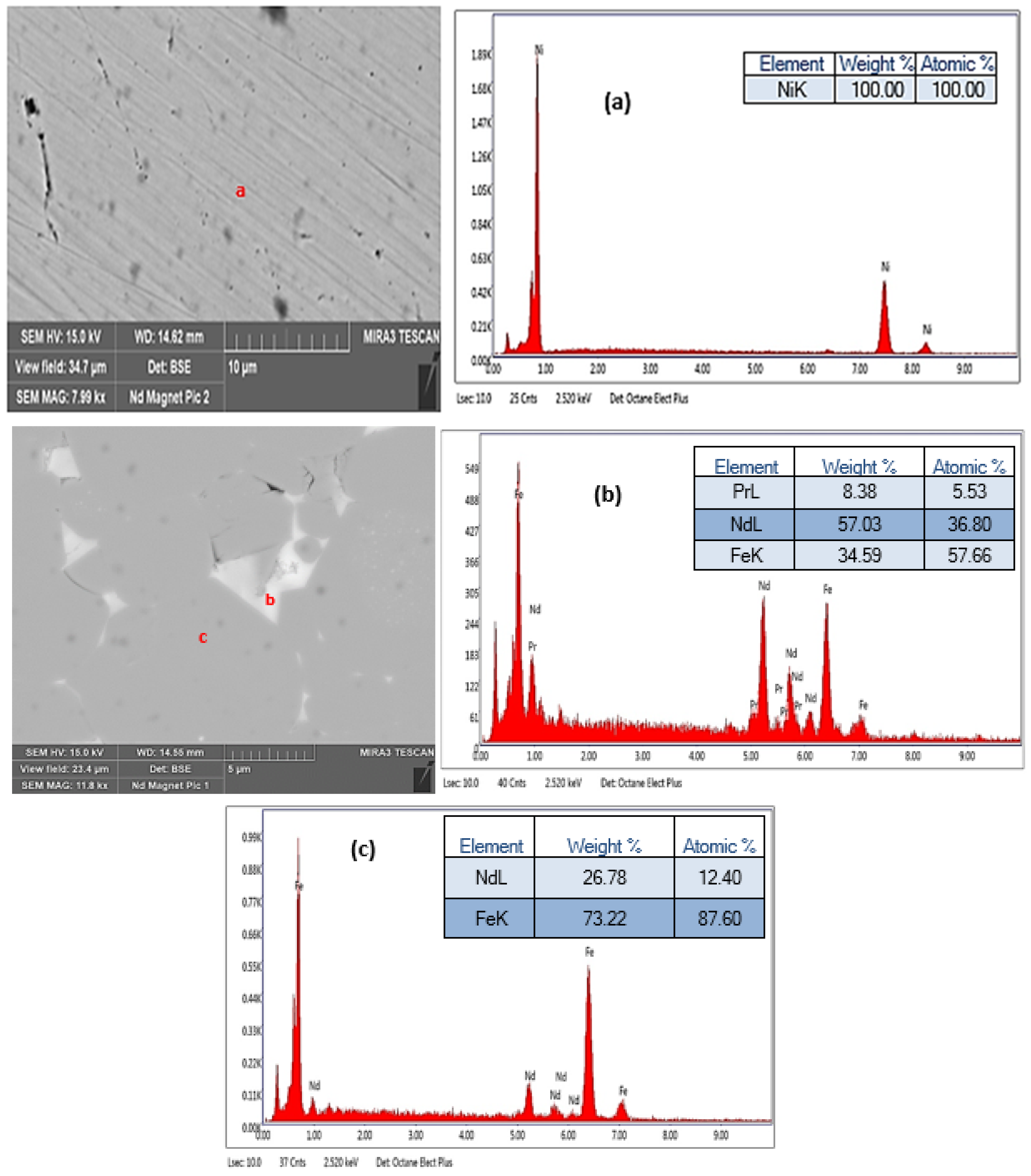
2.5.1. SEM/EDX
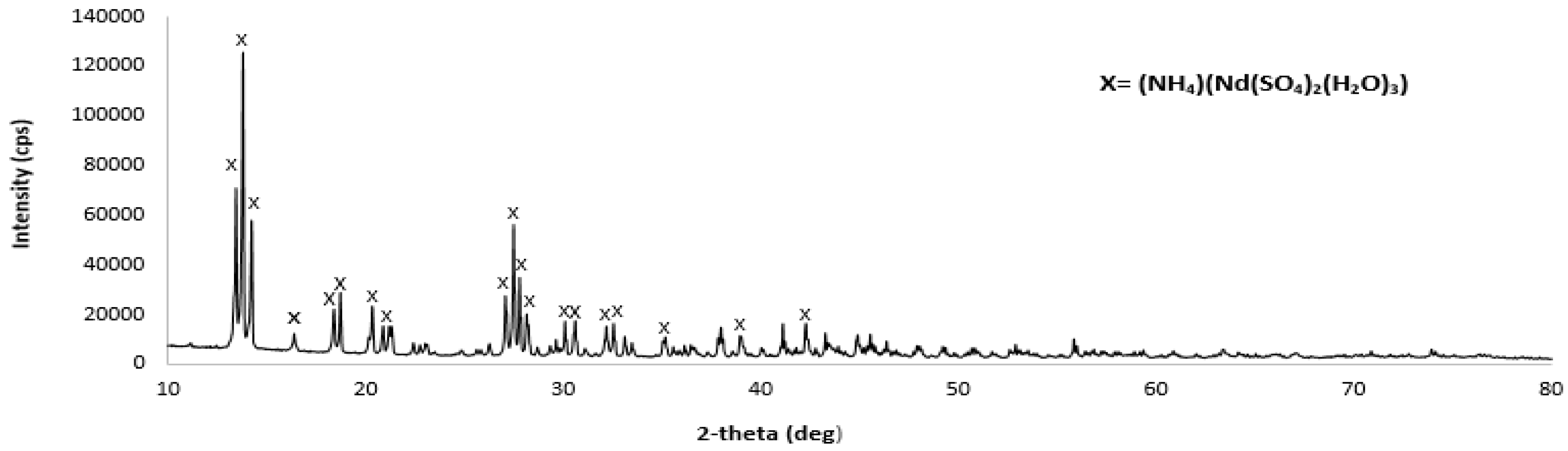
2.5.2. XRD
2.5.3. ICP-OES
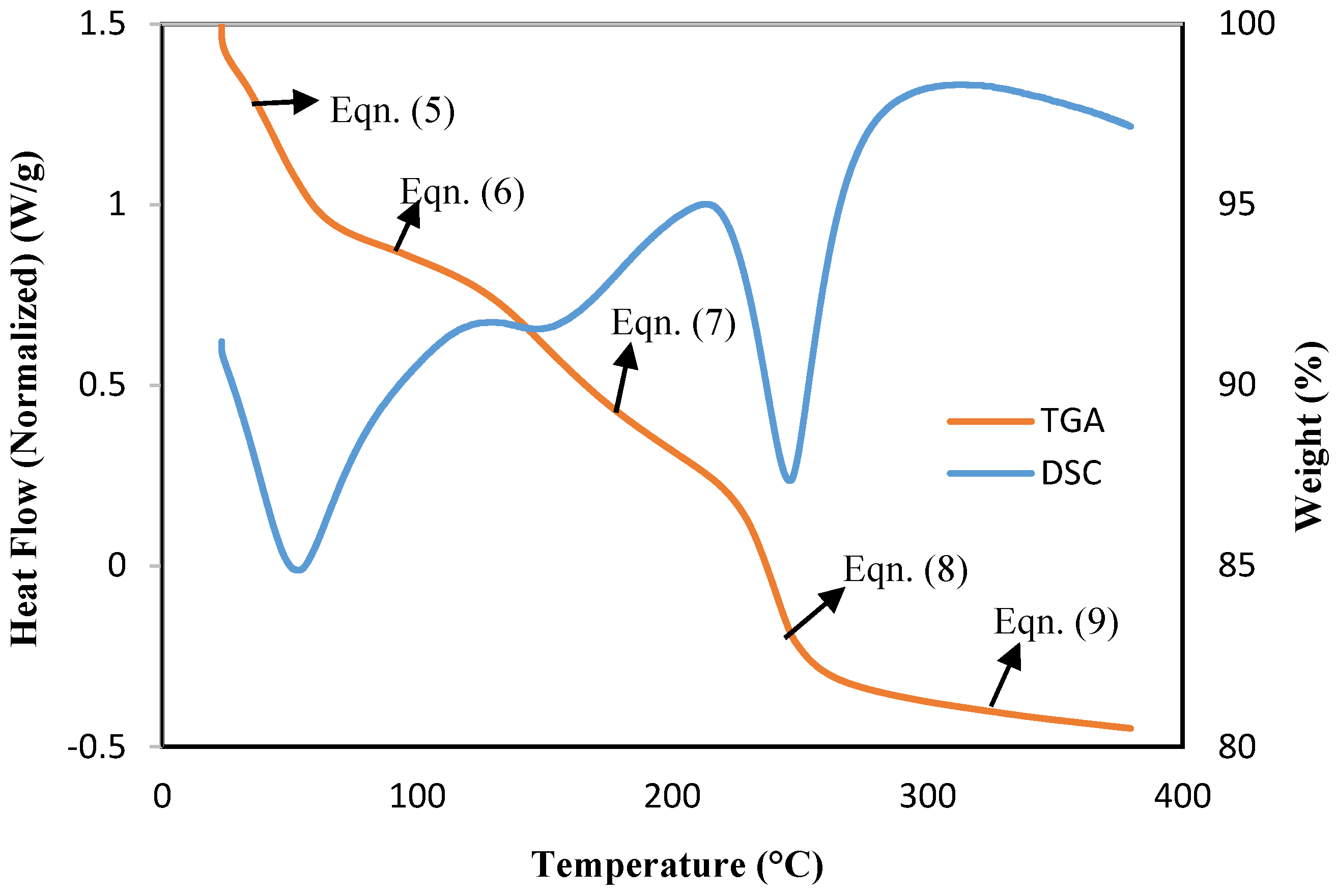
2.5.4. TGA-DSC
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Granulometry
3.2. SEM-EDX Analysis
3.3. XRD Results
3.4. ICP Results
3.5. TGA-DSC Results
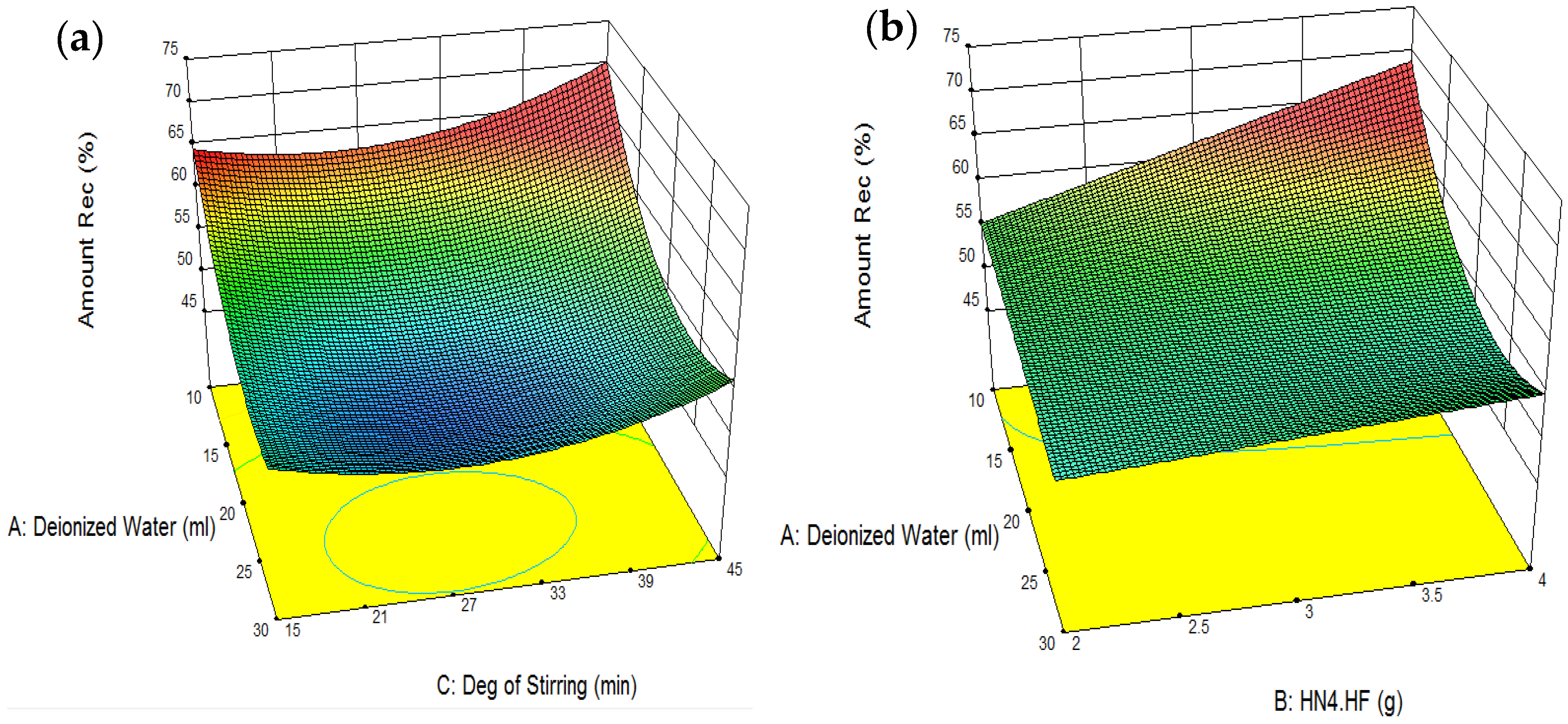
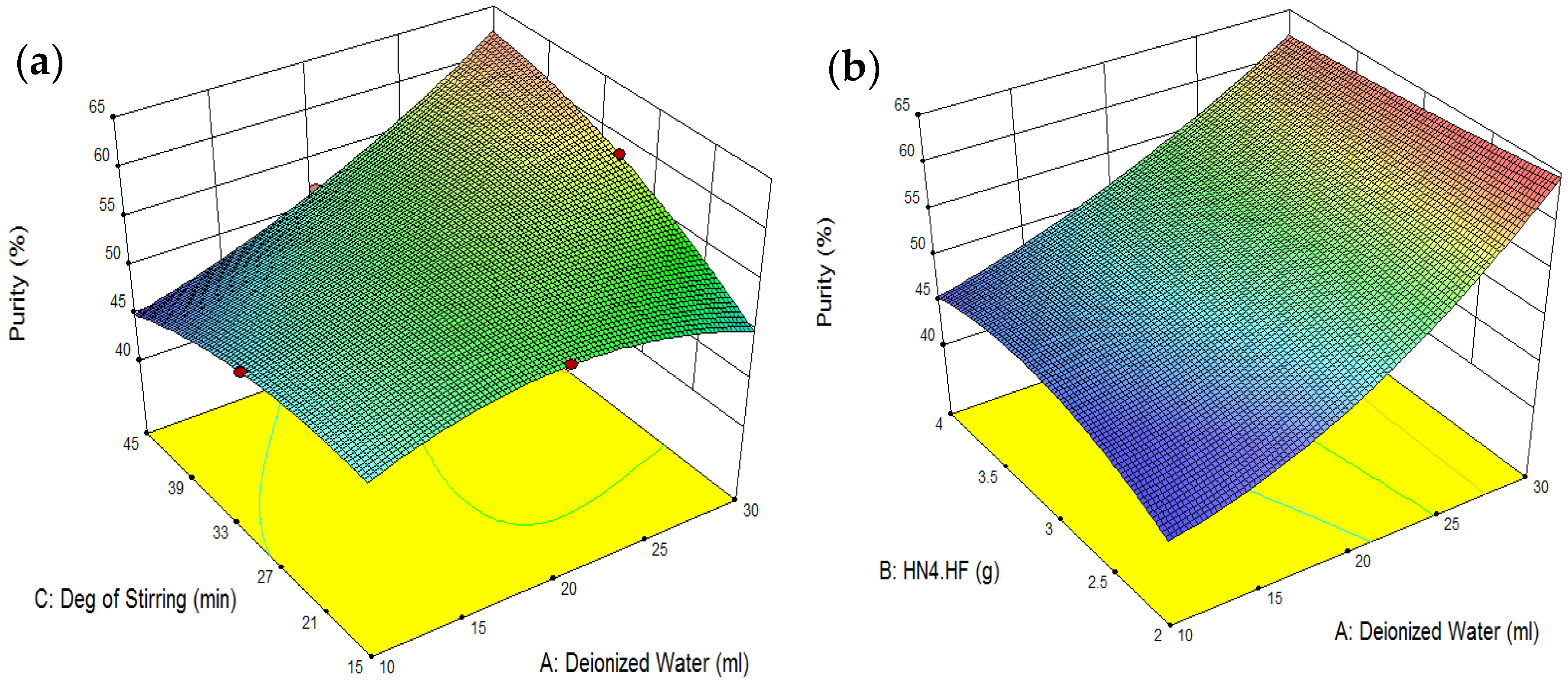
4. Model Development and Process Optimization Using RSM
| Amount of Deionized Water Used: 30 mL | REF Recovery: 56.23% |
| NH4F·HF Added: 4 g | |
| Degree of Stirring: 45 min | REF Purity: 62.42% |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Sheridan, R.; Güth, K.; Gauß, R.; Gutfleisch, O.; Buchert, M.; Binnemans, K. REE recovery from end-of-life NdFeB permanent magnet scrap: A critical review. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 122–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, A.; Lusty, P. Rare Earth Elements; British Geological Survey: Nottingham, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ueberschaar, M.; Rotter, V.S. Enabling the recycling of rare earth elements through product design and trend analyses of hard disk drives. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2015, 17, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal, M.A.R.; Borra, C.R.; Guo, M.; Blanpain, B.; Van, G.T. Hydrometallurgical recycling of NdFeB magnets: Complete leaching, iron removal and electrolysis. J. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademaker, J.H.; Kleijn, R.; Yang, Y. Recycling as a strategy against rare earth element criticality: A systemic evaluation of the potential yield of NdFeB magnet recycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10129–10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepf, V. Rare Earth Elements: A New Approach to the Nexus of Supply, Demand and Use: Exemplified along the Use of Neodymium in Permanent Magnets; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, A. Handbook of Modern Ferromagnetic Materials; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; p. 649. [Google Scholar]
- Rotter, V.S.; Chancerel, P.; Ueberschaar, M. Recycling-oriented product characterization for electric and electronic equipment as a tool to enable recycling of critical metals. In Rewas; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, R.T.; Diaz, L.A.; Imholte, D.D.; Lister, T.E. Economic assessment for recycling critical metals from hard disk drives using a comprehensive recovery process. JOM 2017, 69, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.; Bras, B. Rare earth metal recycling, sustainable systems and technology. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium, Dana Point, CA, USA, 16–18 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, M.; Oki, T.; Koyama, K.; Narita, H.; Oishi, T. Recycling of rare earths from scrap. In Handbook on the Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths; Bunzli, J.C.G., Pecharsky, V.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 43, pp. 159–211. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, C.D.; Anderson, C.G.; Taylor, P.R. A survey of recycled rare earths metallurgical processing. In Proceedings of the 51st Annual Conference of Metallurgists of CIM, Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 30 Septembere–3 October 2012; pp. 411–422. [Google Scholar]
- Graedel, T.E.; Allwood, J.; Birat, J.P.; Reck, B.K.; Sibley, S.F.; Sonnemann, G.; Buchert, M.; Hagelüken, C. Recycling Rates of Metals—A Status Report; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Reck, B.K.; Graedel, T.E. Challenges in metal recycling. Science 2012, 337, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggert, R.; Wadia, C.; Anderson, C.; Bauer, D.; Fields, F.; Meinert, L.; Taylor, P. Rare earths: Market disruption, innovation, and global supply chains. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2016, 41, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goonan, T.G. Rare Earth Elements—End Use and Recyclability; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2011.
- Lyman, J.W.; Palmer, G.R. Recycling of Neodymium Iron Boron Magnet Scrap; University of Michigan Library: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, R.J.; Reisman, D.J. Rare Earth Elements: A Review of Production, Processing, Recycling, and Associated Environmental Issues; US EPA Region: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Majzlan, J.; Stevens, R.; Boerio-Goates, J.; Woodfield, B.F.; Navrotsky, A.; Burns, P.C.; Crawford, M.K.; Amos, T.G. Thermodynamic properties, low-temperature heat-capacity anomalies, and single-crystal X-ray refinement of hydronium jarosite,(H3O)Fe3(SO4)2(OH)6. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2004, 31, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; López-Delgado, A.; López, F.A. A kinetic study of the thermal decomposition of ammoniojarosite. J. Mater. Sci. 1998, 33, 5821–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutrizac, J.E. Converting jarosite residues into compact hematite products. JOM 1990, 42, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.V.; Jayawant, D.V.; Iyer, N.S.; Koppiker, K.S. Separation of neodymium from lighter rare earths using alkyl phosphonic acid, PC 88A. Hydrometallurgy 1993, 34, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, J.S. The Recovery of Rare Earth Oxides from A Phosphoric Acid Byproduct. Part 4. The Preparation of Magnet-Grade Neodymium Oxide from The Light Rare Earth Fraction; Mintek: Randburg, South Africa, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Horng, J.S.; Hoh, Y.C. The separation of neodymium by quaternary amine from didymium nitrate solution. J. Less Common Met. 1989, 149, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, C.A.; Ciminelli, V.S.T. Process development for the recovery of high-grade lanthanum by solvent extraction. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 73, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika, S.; Nagaphani, K.B.; Lakshmi, K.M.; Ramachandra, R.B. Solvent extraction and separation of rare earths from phosphoric acid solutions with TOPS 99. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 110, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, N.; Devi, N.; Mishra, S. Solvent extraction of neodymium (III) from acidic nitrate medium using Cyanex 921 in kerosene. J. Rare Earths 2012, 30, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hefny, N.E. Kinetics and mechanism of extraction and stripping of neodymium using a Lewis cell. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2007, 46, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Lee, G.-S. Solvent extraction of neodymium ions from hydrochloric acid solution using PC88A and saponified PC88A. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 46, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, R.; Jeon, H.; Lee, M. Solvent extraction separation of Pr and Nd from chloride solution containing La using Cyanex 272 and its mixture with other extractants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 98, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhi, Y. Effective solvent extraction of La, Ce and Pr from hydrochloric acid with a novel extractant N, N-dihexyloxamic acid. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 92, 1596–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, L.; Deng, Y.; Li, D. Application of [A336][P507]/[P204] on High Selective Extraction and Separation of Rare Earths (III) from Mechanism to Techniques. In Proceedings of the 52nd Conference of Metallurgists (COM), Montreal, QC, Canada, 27–31 October 2013; pp. 367–374. [Google Scholar]
- Rout, A.; Kotlarska, J.; Dehaen, W.; Binnemans, K. Liquid–liquid extraction of neodymium(iii) by dialkylphosphate ionic liquids from acidic medium: The importance of the ionic liquid cation. Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: NMR spectra of the ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 16533–16541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeil, J.; Malek, S. The production of rare earth elements group via tributyl phosphate extraction and precipitation stripping using oxalic acid. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, S1532–S1539. [Google Scholar]
- Belova, V.V.; Voshkin, A.A.; Kholkin, A.I.; Payrtman, A.K. Solvent extraction of some lanthanides from chloride and nitrate solutions by binary extractants. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 97, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, I.M.; Goode, J.R.; Moldoveanu, G.; Rayat, M.S. Rare Earth Elements Symposium. In Proceedings of the 52nd Conference of Metallurgists (COM), Montreal, QC, Canada, 27–31 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Liao, C.; Jia, J.; Wang, M.; Li, B. Comparison of economical and technical indices on rare earth separation processes of bastnasite by solvent extraction. J. Rare Earths 1999, 17, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy, N.; Gupta, C.K. Extractive Metallurgy of Rare Earths; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; p. 869. [Google Scholar]
- Sarfo, P. Recovery of Rare Eearth Elements by Advanced Processing Technologies. Ph.D. Thesis, Montana Tech, Butte, MT, USA, October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sarfo, P.; Wyss, G.; Ma, G.; Das, A.; Young, C. Carbothermal reduction of copper smelter slag for recycling into pig iron and glass. Miner. Eng. 2017, 107, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfo, P.; Das, A.; Wyss, G.; Young, C. Recovery of metal values from copper slag and reuse of residual secondary slag. Waste Manag. 2017, 70, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Behnken, D.W. Some new three level designs for the study of quantitative variables. Technometrics 1960, 2, 455–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.A.; Santelli, R.E.; Oliveira, E.P.; Villar, L.S.; Escaleira, L.A. Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 2008, 76, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stat-Ease, Inc. Stat-Ease® DOE Software. 2003. Available online: https://www.hearne.software/Resources/Design-Ease/softoverview.aspx (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- Ingemarsson, L.; Halvarsson, M. Sem/edx Analysis of Boron; High Temperature Corrosion Centre-Chalmer University of Technology: Gothenburg, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Das, G.K.; Anand, S.; Acharya, S.; Das, R.P. Preparation and decomposition of ammoniojarosite at elevated temperatures in H2O–(NH4)2SO4–H2SO4 media. Hydrometallurgy 1995, 38, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.L.; Wills, R.-A.; Kloprogge, J.T.; Martens, W. Thermal decomposition of ammonium jarosite (NH4)Fe3(SO4)2(OH)6. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2006, 84, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunda, W.; Veltman, H. Decomposition of jarosite. Metall. Trans. B 1979, 10, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spratt, H.; Rintoul, L.; Avdeev, M.; Martens, W. The thermal decomposition of hydronium jarosite and ammoniojarosite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 15, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Composition | Dy | Fe | Nd | Pr | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (%) | 2.89 | 1.22 | 52.95 | 7.41 | 35.53 |
| Standard | Run | Volume of Deionized Water (mL) | Amount of NH4·HF (g) | Degree of Stirring (mins) | REE Recovery (%) | Purity of REF Residue (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1 | 30 | 2 | 30 | 46.76 | 60.59 |
| 8 | 2 | 30 | 3 | 45 | 55.58 | 63.26 |
| 10 | 3 | 20 | 4 | 15 | 53.15 | 54.01 |
| 7 | 4 | 10 | 3 | 45 | 63.03 | 46.12 |
| 4 | 5 | 30 | 4 | 30 | 49.63 | 58.38 |
| 17 | 6 | 20 | 3 | 30 | 47.16 | 56.93 |
| 3 | 7 | 10 | 4 | 30 | 64.09 | 49.66 |
| 1 | 8 | 10 | 2 | 30 | 50.44 | 45.52 |
| 12 | 9 | 20 | 4 | 45 | 55.41 | 51.84 |
| 16 | 10 | 20 | 3 | 30 | 49.67 | 53.08 |
| 5 | 11 | 10 | 3 | 15 | 57.48 | 51.19 |
| 11 | 12 | 20 | 2 | 45 | 54.65 | 48.59 |
| 15 | 13 | 20 | 3 | 30 | 50.09 | 54.94 |
| 14 | 14 | 20 | 3 | 30 | 52.74 | 51.39 |
| 6 | 15 | 30 | 3 | 15 | 52.13 | 50.85 |
| 9 | 16 | 20 | 2 | 15 | 53.56 | 50.65 |
| 13 | 17 | 20 | 3 | 30 | 51.38 | 57.42 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarfo, P.; Frasz, T.; Das, A.; Young, C. Hydrometallurgical Recovery and Process Optimization of Rare Earth Fluorides from Recycled Magnets. Minerals 2020, 10, 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10040340
Sarfo P, Frasz T, Das A, Young C. Hydrometallurgical Recovery and Process Optimization of Rare Earth Fluorides from Recycled Magnets. Minerals. 2020; 10(4):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10040340
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarfo, Prince, Thomas Frasz, Avimanyu Das, and Courtney Young. 2020. "Hydrometallurgical Recovery and Process Optimization of Rare Earth Fluorides from Recycled Magnets" Minerals 10, no. 4: 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10040340
APA StyleSarfo, P., Frasz, T., Das, A., & Young, C. (2020). Hydrometallurgical Recovery and Process Optimization of Rare Earth Fluorides from Recycled Magnets. Minerals, 10(4), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10040340




