Optimization of Operating Parameters on Dry Grinding of Calcite in a Stirred Media Mill Using the Box-Behnken Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Method
2.3. Experiment Design
3. Results and Discussion
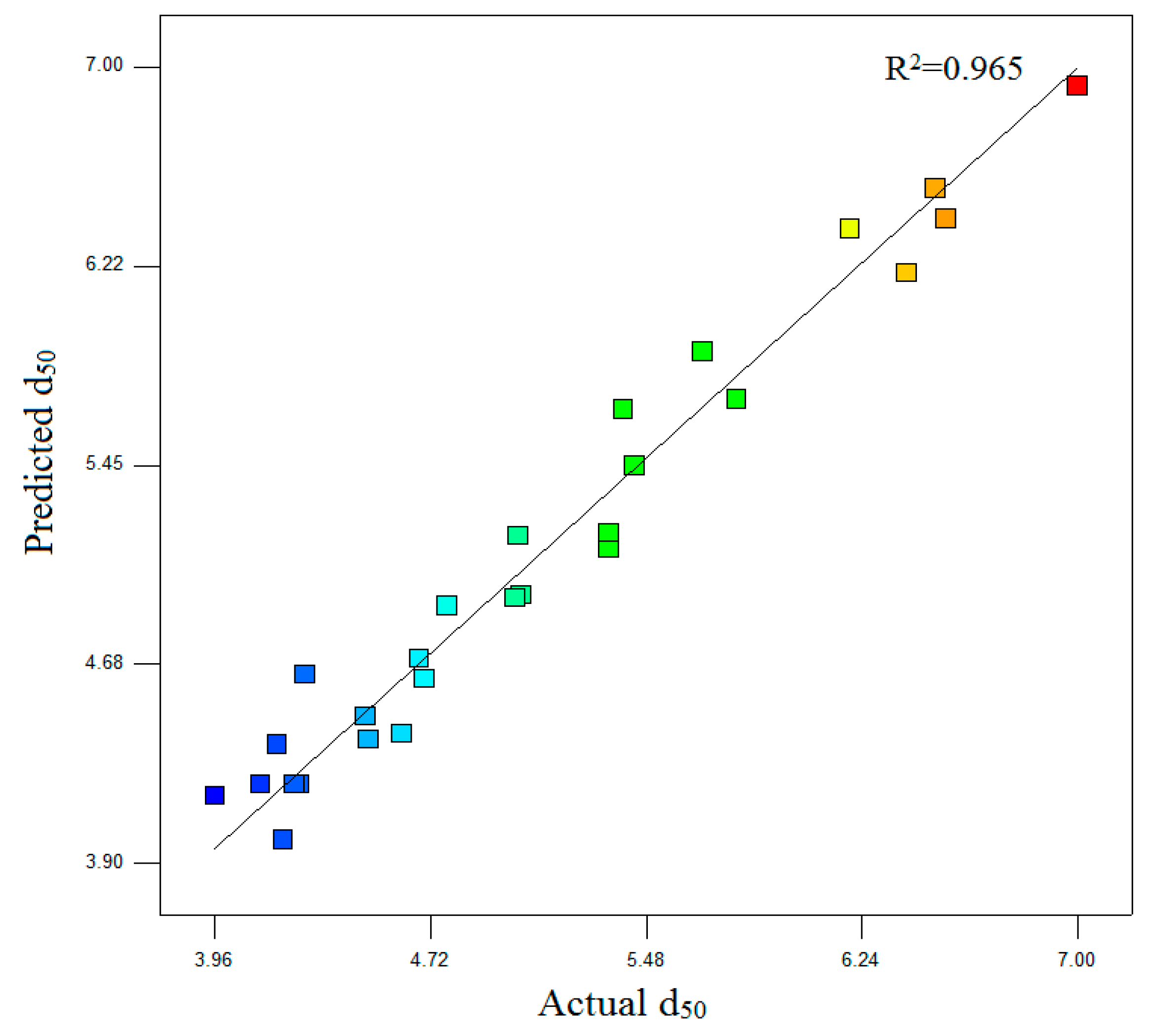
3.1. Models and ANOVA Analysis
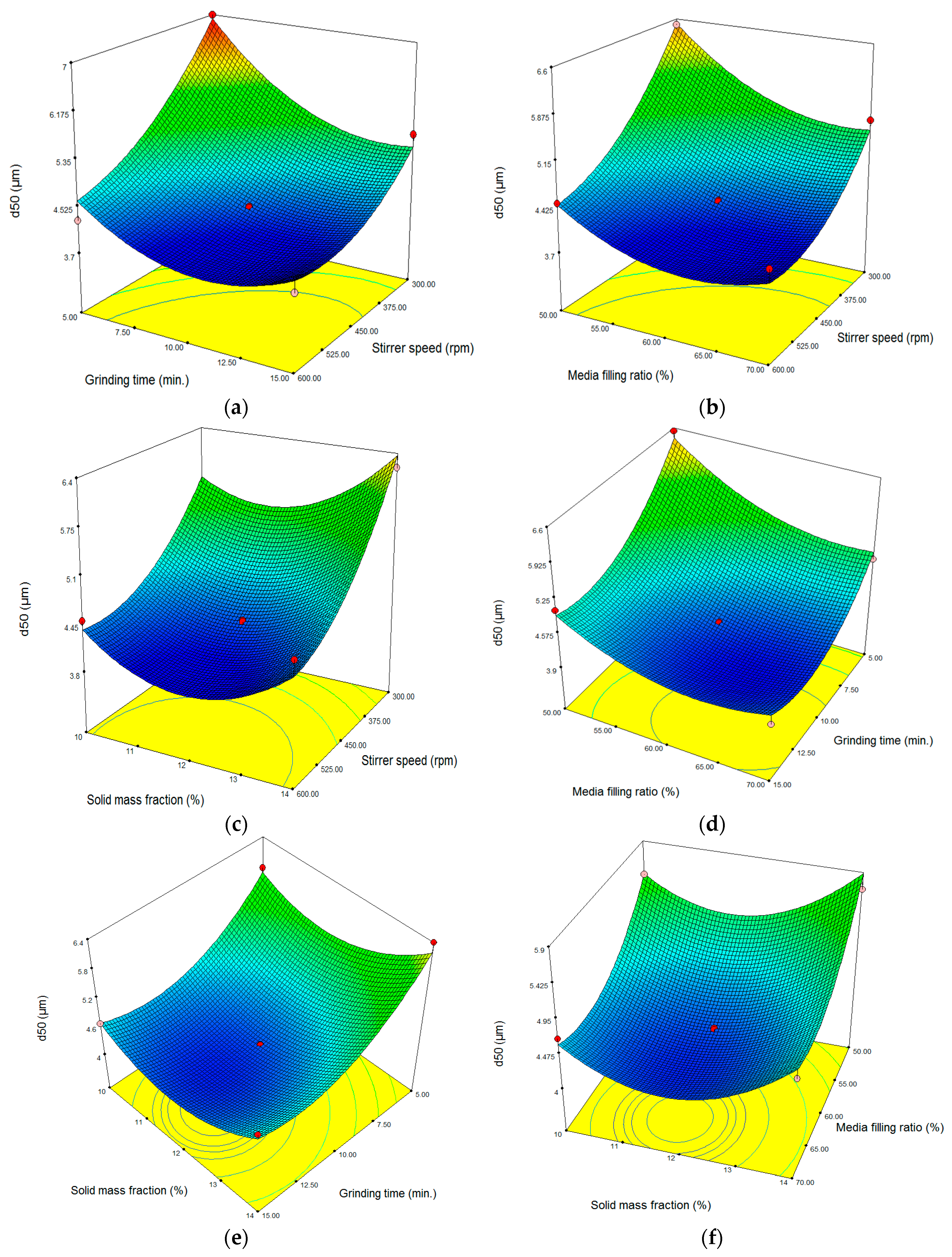
3.2. Three-Dimensional (3D) Response Surface Plots of the Factors
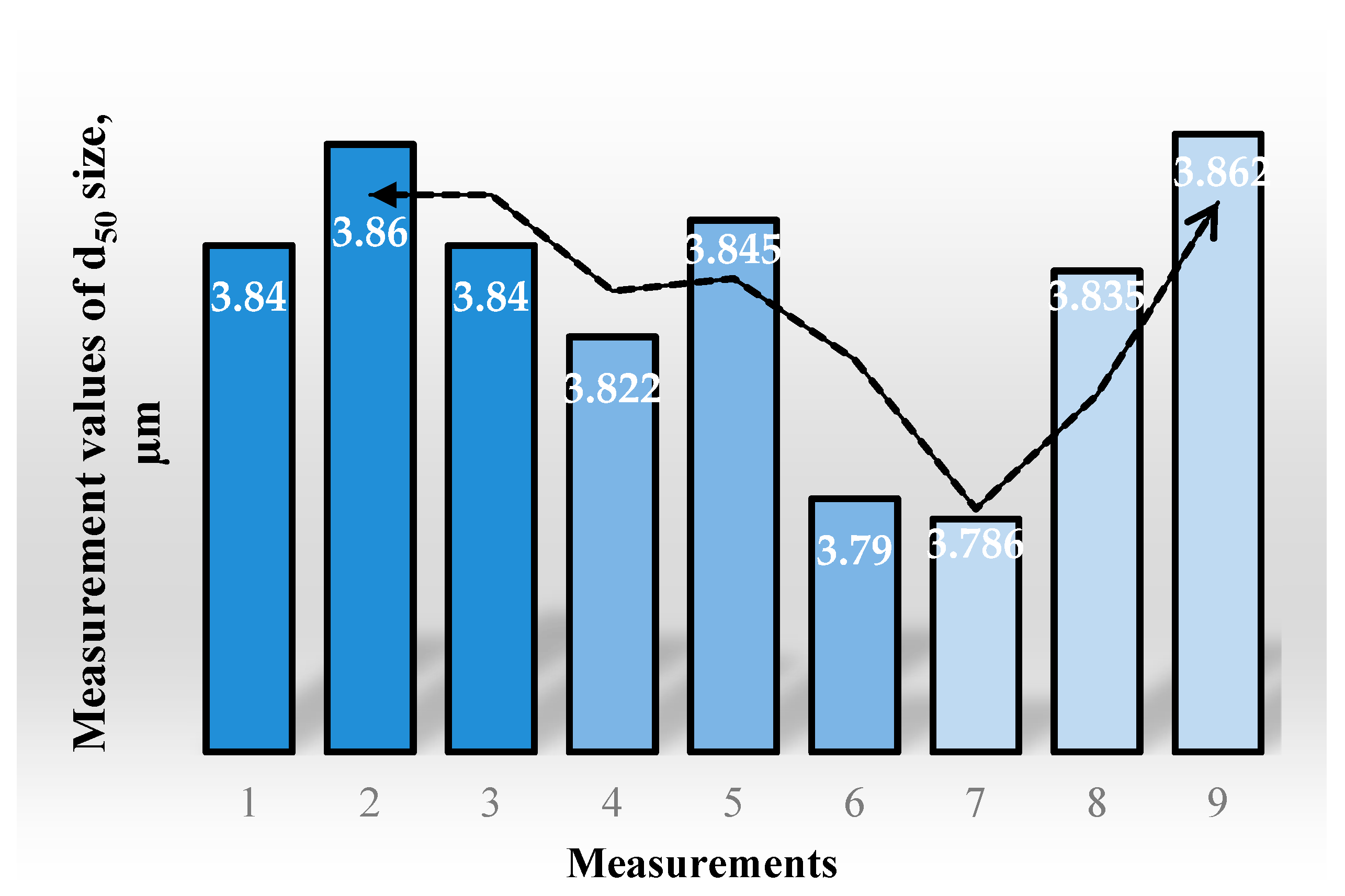
3.3. Optimization and Verification Tests
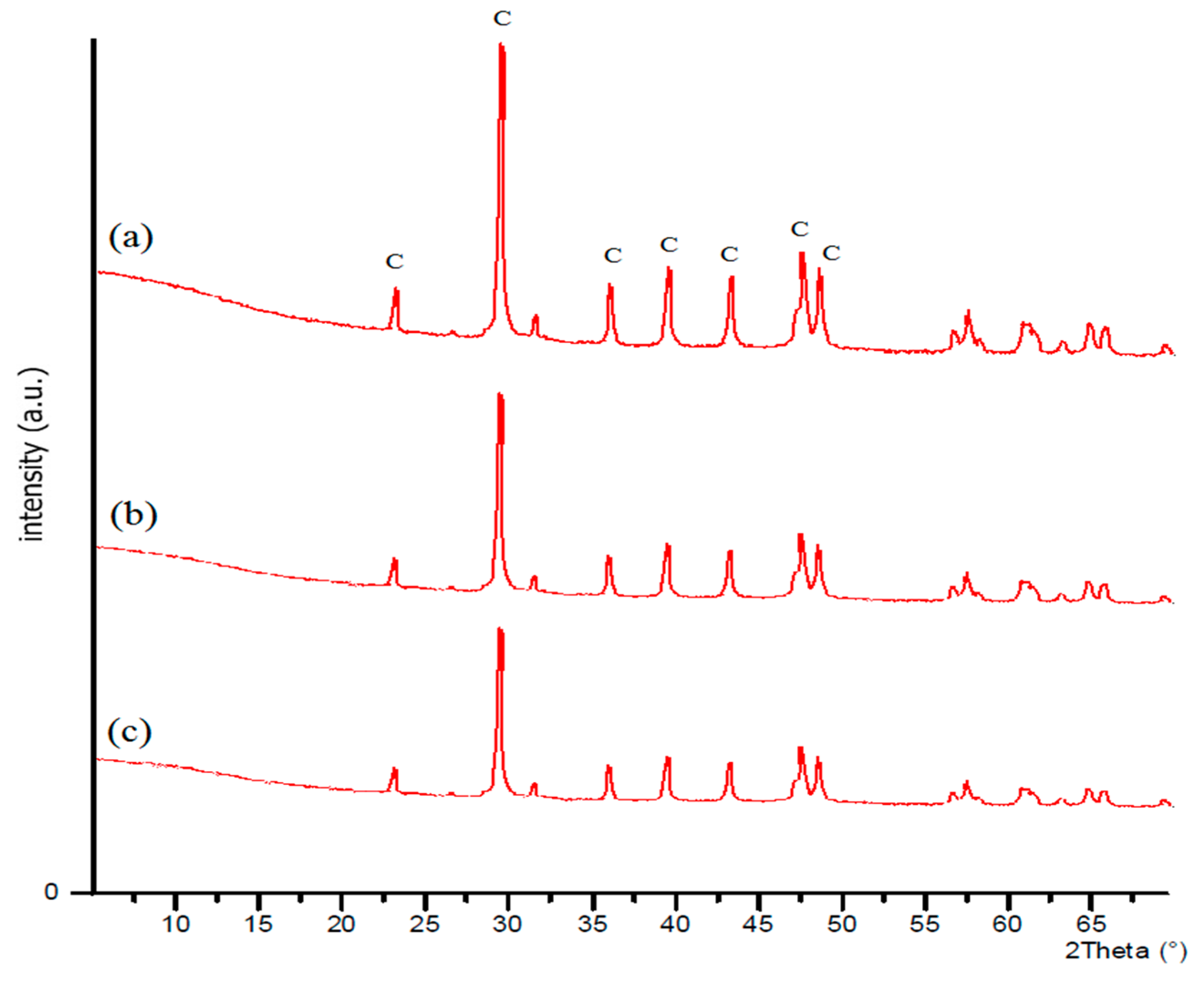
3.4. XRD Analysis
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rungruang, P.; Grady, B.P.; Supaphol, P. Surface-modified calcium carbonate particles by admicellar polymerization to be used as filler for isotactic polypropylene. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 275, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, J.; Tao, N.; Yu, K.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Z. Influence of octadecyl dihydrogen phosphate on the formation of active super-fine calcium carbonate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 272, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.C.; Jeong, S.B.; Yang, S.Y.; Chae, Y.B.; Kim, H.S. The changes in surface properties of the calcite powder with stearic acid treatment. Mater. Trans. 2009, 50, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deodhar, S.; Shanmuganathan, K.; Patra, P.; Fan, Q.; Calvert, P.; Warner, S. Technical Papers in Composites, Convention and Trade Show. In Polypropylene Based Novel Flame Retardant Nanocomposite Composition; American Composite Manufacturers Association: St Louis, MO, USA, 2006; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Tao, X.; Gao, C.; Zheng, Q. Studies on the steady and dynamic rheological properties of poly(Dimethyl-Siloxane) filled with calcium carbonate based on superposition of its relative functions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 1590–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilevneli, C.C.; Kızgut, S.; Toroğlu, I.; Çuhadaroğlu, D.; Yiğit, E. Open and closed circuit dry grinding of cement mill rejects in a pilot scale vertical stirred mill. Powder Technol. 2004, 139, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraman, O.Y. Dry fine grinding of calcite powder by stirred mill. Part. Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prziwara, P.; Hamilton, L.D.; Breitung-Faes, S.; Kwade, A. Impact of grinding aids and process parameters on dry stirred media milling. Powder Technol. 2018, 335, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, O.; Benzer, H.; Enderle, U. Effects of operating parameters on the efficiency of dry stirred milling. Miner. Eng. 2013, 43, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucsi, G.; Rácz, Á.; Mádai, V. Mechanical activation of cement in stirred media mill. Powder Technol. 2013, 235, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rácz, Á.; Csőke, B. Application of the product related stress model for product dispersity control in dry stirred media milling. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 157, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prziwara, P.; Breitung-Faes, S.; Kwade, A. Impact of powder flow behavior on continuous fine grinding in dry operated stirred media mills. Miner. Eng. 2018, 128, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orumwense, O.A. The Effect of Media Type on Regrinding with Stirred Mills; SME Annual Meeting: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Celep, O.; Yazıcı, E.Y. Ultra fine grinding of silver plant tailings of refractory ore using vertical stirred media mill. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 3412–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouattara, S.; Frances, C. Grinding of calcite suspensions in a stirred media mill: Effect of operational parameters on the product quality and the specific energy. Powder Technol. 2014, 255, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jankovic, A. Variables affecting the fine grinding of minerals using stirred mills. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Forssberg, E.; Sachweh, J. Dry fine comminution in a stirred media mill- MaxxMill®. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2004, 74, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasundara, C.T.; Yang, R.Y.; Yu, A.B.; Rubenstein, J. Effects of disc rotation speed and media loading on particle flow and grinding performance in a horizontal stirred mill. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 96, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamey, R.G. Production of Organic Pigment Nanoparticles by Stirred Media Milling. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Holmes, R.; Pease, J. The Latest Developments in Fine and Ultrafine Grinding Technologies, XXIII; International Mineral Processing Congress: Istanbul, Turkey, 2006; pp. 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lichter, J.K.H.; Davey, G. Advances in Comminution. In Selection and Size of Ultrafine and Stirred Grinding Mills; Komar Kawatra, S., Ed.; Society for Mining Metallurgy and Exploration Inc.: Denver, CO, USA, 2006; pp. 69–86. [Google Scholar]
- Celep, O.; Aslan, N.; Alp, I.; Tasdemir, G. Optimization of some parameters of stirred mill for ultra fine grinding of refractory Au/Ag ores. PowderTechnol. 2011, 208, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson-Cook, C.M.; Borror, C.M.; Montgomery, D.C. Response surface design evaluation and comparison. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2009, 139, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Palaniandy, S.; Hilden, M.; Powell, M. Calculating breakage parameters of a batch vertical stirred mill. Miner. Eng. 2017, 111, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, C.E.; Hansuld, R.; Kelebek, S.; Aghamirian, M. Behaviour of ilmenite as a gangue mineral in the benzohydroxamic flotation of a complex pyrochlore-bearing ore. Miner. Eng. 2017, 109, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirboga, S.; Öner, M. Investigating the effect of ultrasonic irradiation on synthesis of calcium carbonate using Box–Behnken experimental design. Powder Technol. 2017, 308, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celep, O.; Altinkaya, P.; Yazici, E.Y.; Deveci, H. Thiosulphate leaching of silver from an arsenical refractory ore. Miner. Eng. 2018, 122, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, D.; Venugopal, R. Optimization of the process parameters for fine coal–oil agglomeration process using waste mustard oil. Powder Technol. 2019, 346, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariyan, K.; Hosseini, M.R.; Ahmadi, A.; Zahiri, A. Optimization and kinetics of oxalic acid treatment of feldspar for removing the iron oxide impurities. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, S.; Ahmadi, A.; Hosseini, M.R.; Nasab, M.M. Optimization of continuous air-assisted solvent extraction for treating dilute Cu leach solutions using response surface methodology. Miner. Eng. 2019, 13, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.L.; Bruns, R.E.; Ferreira, H.S.; Matos, G.D.; David, J.M.; Brandão, G.C.; da Silva, E.G.; Portugal, L.A.; dos Reis, P.S.; Souza, A.S.; et al. Box–Behnken design: An alternative for the optimization of analytical methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, R.H.; Montgomery, D.C. Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, A.C.; Donev, A.N. Optimum Experimental Designs; University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Jankovic, A. Media stress intensity analysis for vertical stirred mills. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katircioglu-Bayel, D.; Ozkan, S.G.; Toraman, O.Y. Effect of operating parameters on the breakage process of calcite in a stirred media mill. Min. Metall. Explor. 2019, 36, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wang, Y.; Forssberg, E. Parameter effects on wet ultrafine grinding of limestone through slurry rheology in stirred media mill. Powder Technol. 2006, 161, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochalin, V.N.; Sagar, A.; Gour, S.; Gogotsi, Y. Manufacturing nanosized fenofibrate by salt assisted milling. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
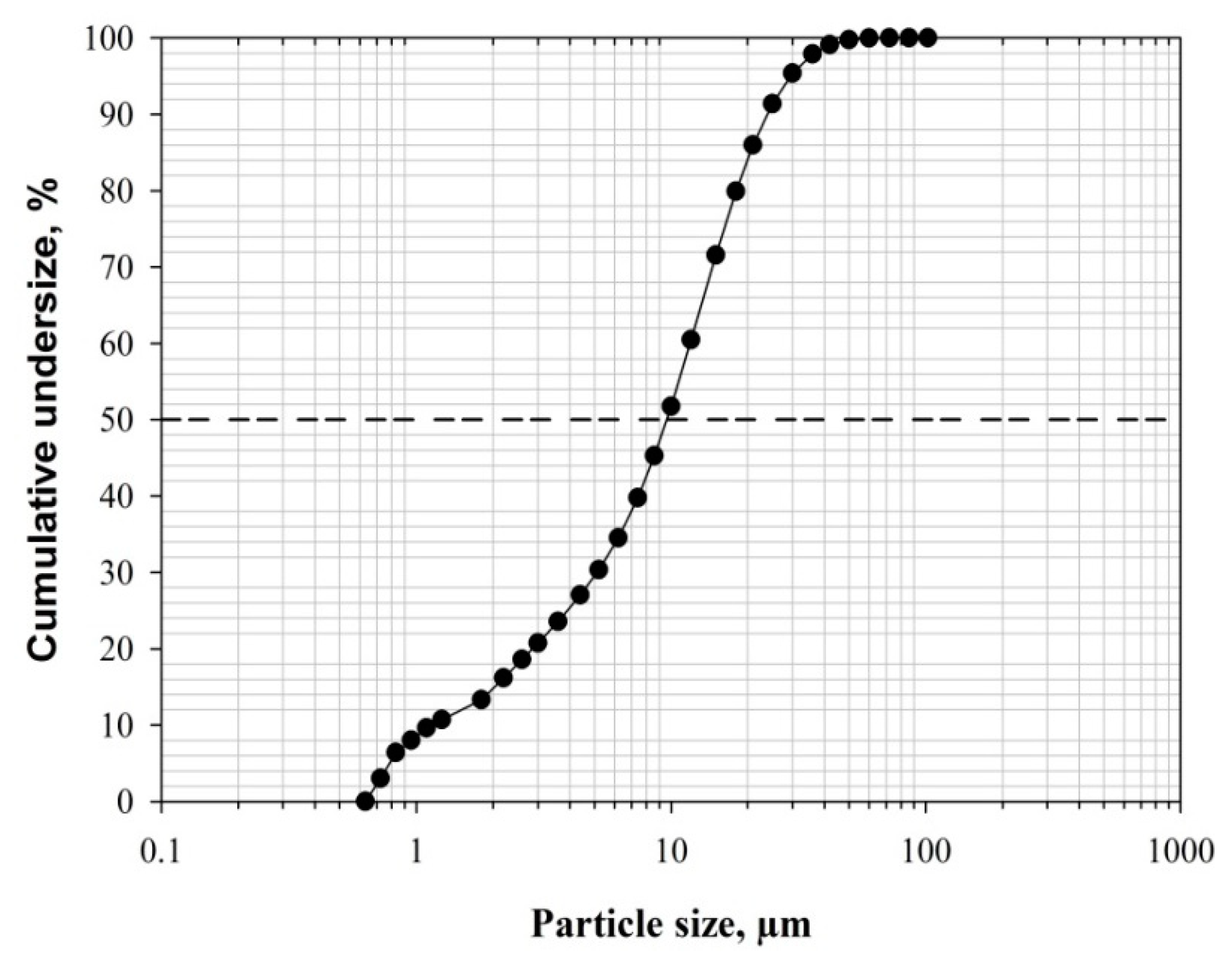
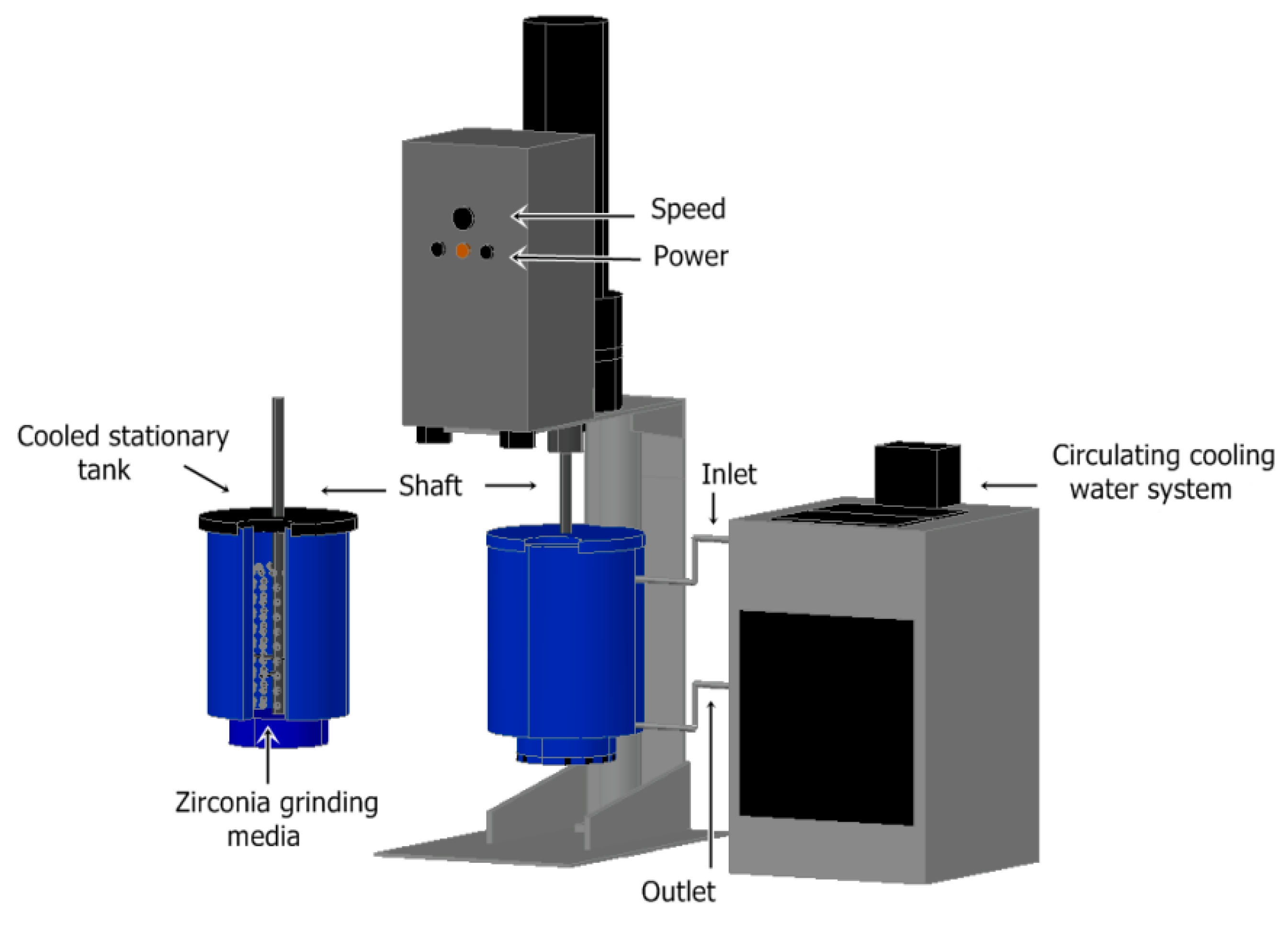
| Constituent | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Chemical composition | |
| CaCO3 | 99.5 |
| MgCO3 | 0.2 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.01 |
| SiO2 | 0.01 |
| Al2O3 | 0.02 |
| LOI * | 0.26 |
| Physical properties | |
| Average particle size, d50 (μm) | 11 |
| Specific gravity (kg/m3) | 2700 |
| Factors | Factor Code | Coded Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (−) | Center (0) | High (+) | ||
| Stirrer speed, SS (rpm) | X1 | 300 | 450 | 600 |
| Grinding time, GT (min.) | X2 | 5 | 10 | 15 |
| Media filling ratio, MFR (%) | X3 | 50 | 60 | 70 |
| Solid mass fraction, SMF (%) | X4 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
| Run | Coded Levels of Factors | Real Factors | Actual Results | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | SS | GT | MFR | SMF | |
| rpm | min | % | % | μm | |||||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 600 | 10 | 50 | 12 | 4.49 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 450 | 10 | 70 | 10 | 4.7 |
| 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 600 | 10 | 60 | 14 | 4.62 |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 450 | 15 | 70 | 12 | 4.18 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 450 | 10 | 50 | 14 | 5.68 |
| 6 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 300 | 15 | 60 | 12 | 5.35 |
| 7 | 0 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 450 | 5 | 60 | 10 | 5.8 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 450 | 10 | 50 | 10 | 5.44 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 450 | 10 | 60 | 12 | 4.12 |
| 10 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 600 | 10 | 70 | 12 | 4.2 |
| 11 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 450 | 15 | 60 | 14 | 5.02 |
| 12 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 300 | 10 | 60 | 14 | 6.2 |
| 13 | 1 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 600 | 10 | 60 | 10 | 4.5 |
| 14 | −1 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 300 | 10 | 60 | 10 | 5.4 |
| 15 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 300 | 10 | 50 | 12 | 6.5 |
| 16 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 300 | 5 | 60 | 12 | 7.01 |
| 17 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 450 | 15 | 50 | 12 | 5.04 |
| 18 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 300 | 10 | 70 | 12 | 5.35 |
| 19 | 0 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 450 | 15 | 60 | 10 | 4.68 |
| 20 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 600 | 15 | 60 | 12 | 3.96 |
| 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 450 | 10 | 60 | 12 | 4.26 |
| 22 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 600 | 5 | 60 | 12 | 4.28 |
| 23 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 450 | 10 | 60 | 12 | 4.24 |
| 24 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 450 | 5 | 60 | 14 | 6.4 |
| 25 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 450 | 5 | 70 | 12 | 5.03 |
| 26 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 450 | 10 | 70 | 14 | 4.78 |
| 27 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 450 | 5 | 50 | 12 | 6.54 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 18.48 | 14 | 1.32 | 23.60 | <0.0001 |
| Residual | 0.67 | 12 | 0.056 | ||
| Total | 19.15 | 26 | |||
| Model Summary | |||||
| R-sq. | R-sq. (adj) | ||||
| 0.965 | 0.9241 | ||||
| Optimum Actual Result | Optimum Predicted Result | |
|---|---|---|
| d50 (µm) | 3.96 | 3.83 |
| Energy consumption (kWh/ton) | 34.5 | 26.9 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katircioglu-Bayel, D. Optimization of Operating Parameters on Dry Grinding of Calcite in a Stirred Media Mill Using the Box-Behnken Design. Minerals 2020, 10, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10030251
Katircioglu-Bayel D. Optimization of Operating Parameters on Dry Grinding of Calcite in a Stirred Media Mill Using the Box-Behnken Design. Minerals. 2020; 10(3):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10030251
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatircioglu-Bayel, Diler. 2020. "Optimization of Operating Parameters on Dry Grinding of Calcite in a Stirred Media Mill Using the Box-Behnken Design" Minerals 10, no. 3: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10030251
APA StyleKatircioglu-Bayel, D. (2020). Optimization of Operating Parameters on Dry Grinding of Calcite in a Stirred Media Mill Using the Box-Behnken Design. Minerals, 10(3), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10030251





