Dissolution, Stability and Solubility of Tooeleite [Fe6(AsO3)4(SO4)(OH)4·4H2O] at 25–45 °C and pH 2–12
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Dissolution Experiments
2.4. Thermodynamic Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Analysis
3.2. XRD
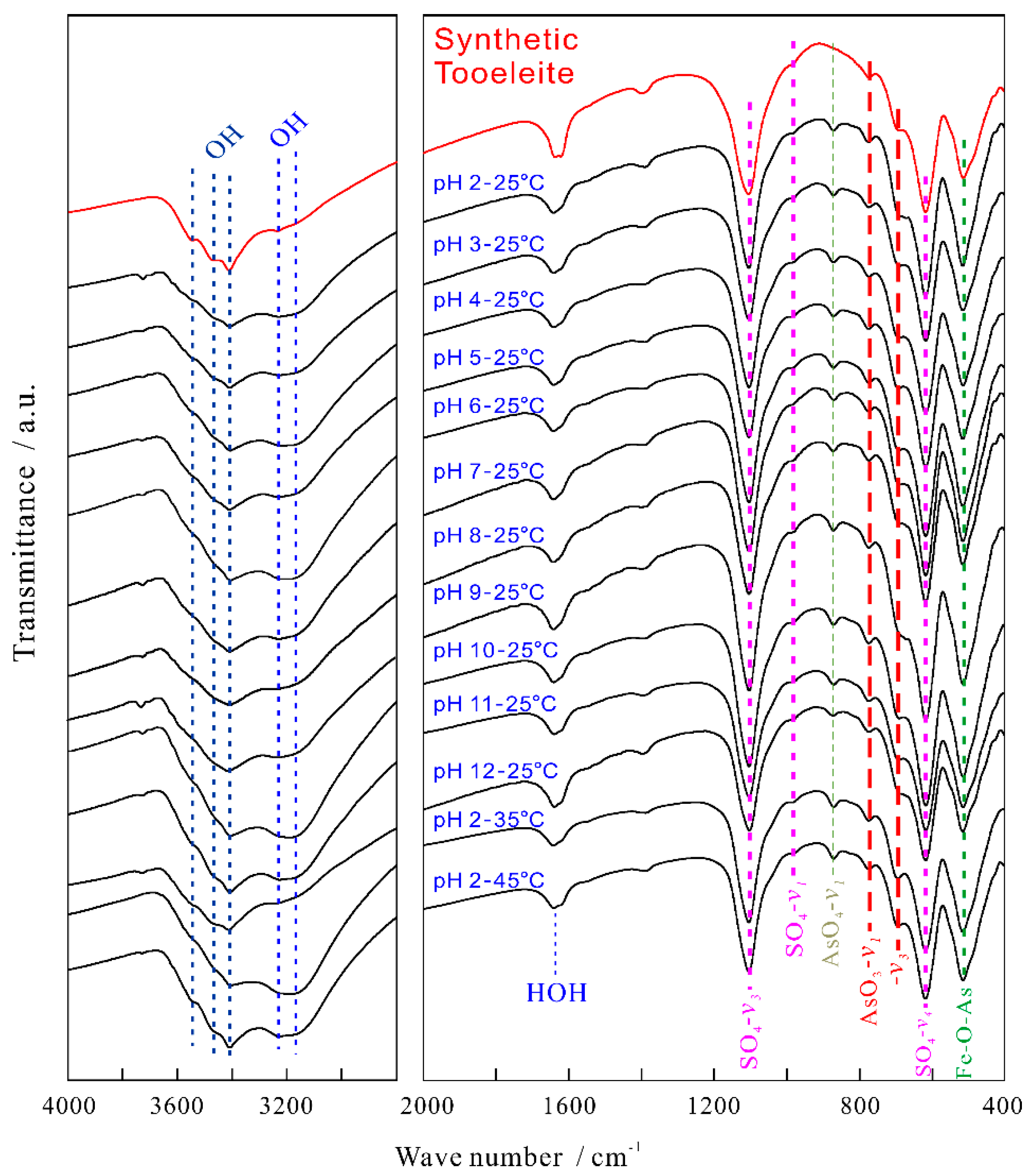
3.3. FT-IR
3.4. FE-SEM
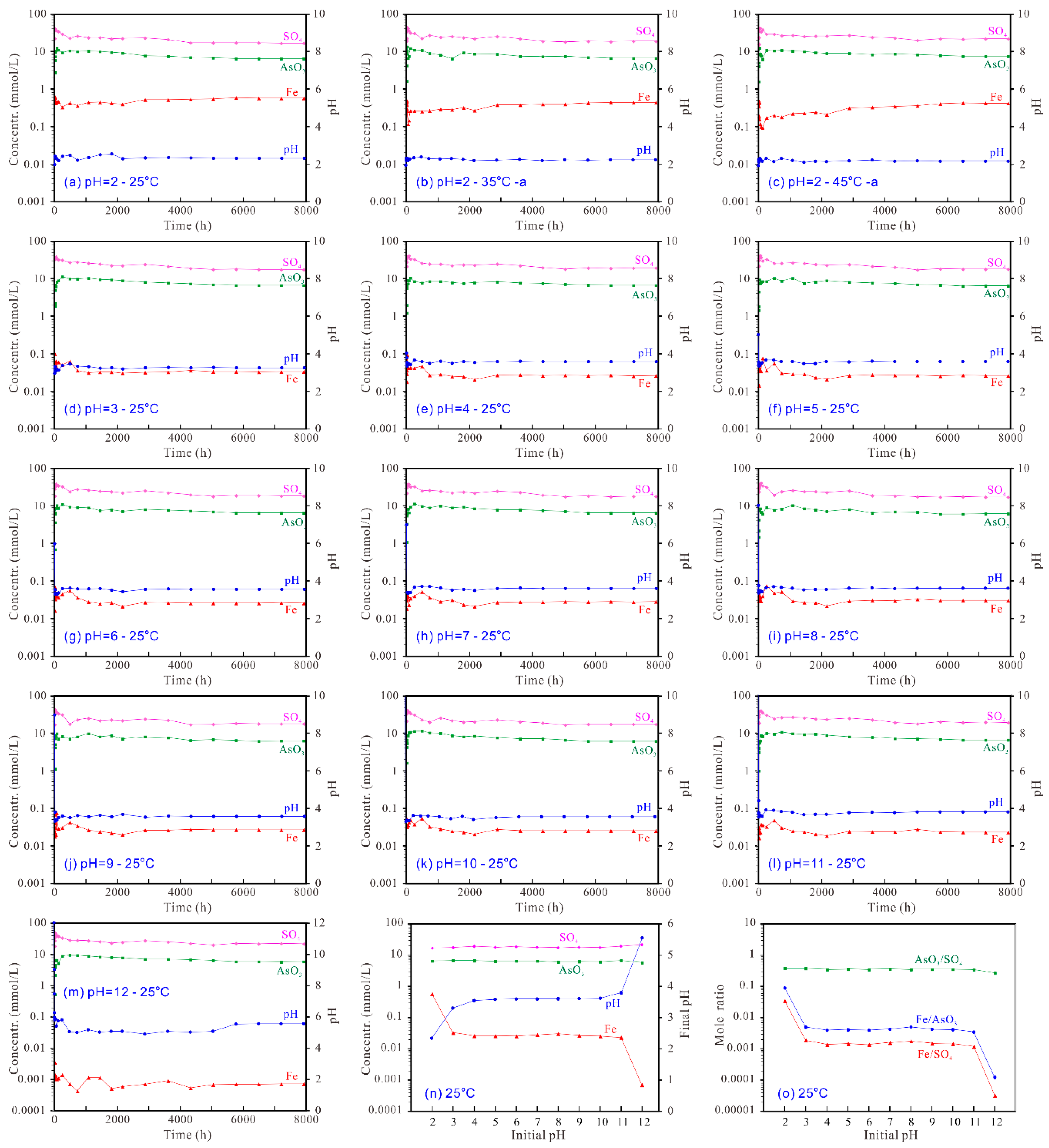
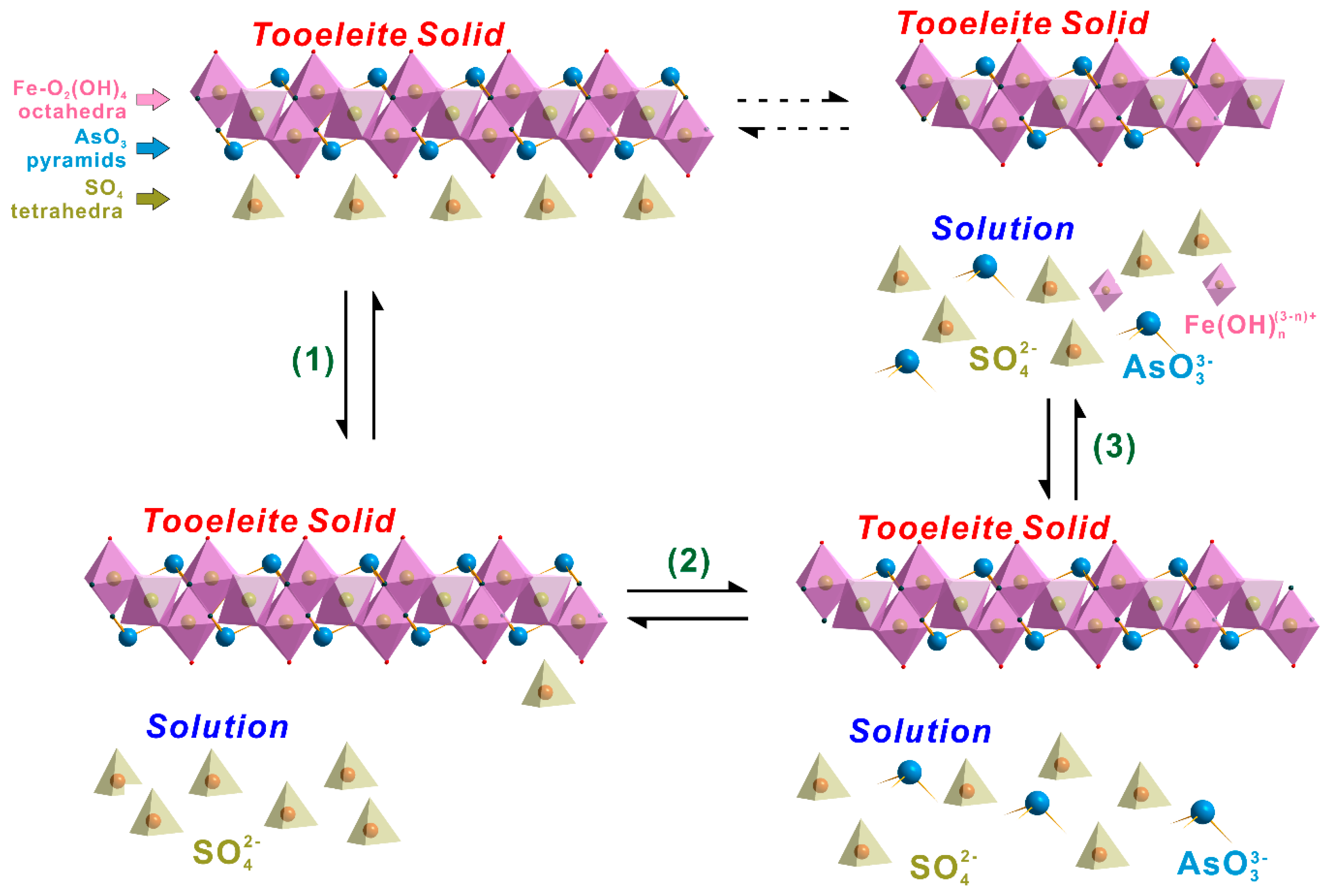
3.5. Evolution of the Aqueous Solutions and Dissolution Mechanism
3.6. Solubility Calculation
− ΔGfo[Fe6(AsO3)4(SO4)(OH)4·4H2O]
= 6 ΔGfo[Fe3+] + 4 ΔGfo[AsO33−] + ΔGfo[SO42−] + 4 ΔGfo[OH−]+ 4 ΔGfo[H2O] − ΔGro
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; fourth edition incorporating the first addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–541. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, M.A.; Signes-Pastor, A.J.; Argos, M.; Slaughter, F.; Pendergrast, C.; Punshon, T.; Gossai, A.; Ahsan, H.; Karagas, M.R. Assessment of human dietary exposure to arsenic through rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Nriagu, J.; Haack, S. Arsenic species and chemistry in groundwater of southeast Michigan. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 120, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paikaray, S.; Göttlicher, J.; Peiffer, S. As(III) retention kinetics, equilibrium and redox stability on biosynthesized schwertmannite and its fate and control on schwertmannite stability on acidic (pH 3.0) aqueous exposure. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, L.; Yue, M.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, H. Formation of tooeleite and the role of direct removal of As(III) from high-arsenic acid wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 320, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yan, Y.; Hu, K.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, D.; Li, Q.; Ye, B.; Chai, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; et al. Structural substitution for SO4 group in tooeleite crystal by As(V) and As(III) oxoanions and the environmental implications. Chemosphere 2018, 213, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Yue, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q. Enhanced stability of tooeleite by hydrothermal method for the fixation of arsenite. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 175, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Hallberg, K.B. Acid mine drainage remediation options: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 338, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olías, M.; Cánovas, C.R.; Nieto, J.M.; Sarmiento, A.M. Evaluation of the dissolved contaminant load transported by the Tinto and Odiel rivers (South West Spain). Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 1733–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egal, M.; Casiot, C.; Morin, G.; Parmentier, M.; Bruneel, O.; Lebrun, S.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F. Kinetic control on the formation of tooeleite, schwertmannite and jarosite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strains in an As(III)-rich acid mine water. Chem. Geol. 2009, 265, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovleva, E.; Mäkilä, E.; Salonen, J.; Sitarz, M.; Wang, S.; Sillanpää, M. Acid mine drainage (AMD) treatment: Neutralization and toxic elements removal with unmodified and modified limestone. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillot, F.; Morin, G.; Juillot, F.; Bruneel, O.; Casiot, C.; Ona-Nguema, G.; Wang, Y.; Lebrun, S.; Aubry, E.; Vlaic, G.; et al. Structure and reactivity of As(III)- and As(V)-rich schwertmannites and amorphous ferric arsenate sulfate from the Carnoulès acid mine drainage, France: Comparison with biotic and abiotic model compounds and implications for As remediation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 104, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, G.; Calas, G. Arsenic in soils, mine tailings, and former industrial sites. Elements 2006, 2, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, C.; Néel, C.; Bril, H. Minerals controlling arsenic and lead solubility in an abandoned gold mine tailings. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 263, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, G.; Juillot, F.; Casiot, C.; Bruneel, O.; Personneä, J.C.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F.; Leblanc, M.; Ildefonse, P.; Calas, G. Bacterial formation of tooeleite and mixed As(III) or As(V)-Fe(III) gels in the Carnoulès AMD, France. A XANES, XRD, and SEM study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Lin, J. Arsenic immobilization from aqueous solution by the precipitation of the pseudo-octahedral arsenate-substituted natroalunite solid solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhães, M.C.F. Arsenic: An environmental problem limited by solubility. Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 1843–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieré, R.; Sidenko, N.V.; Lazareva, E.V. The role of secondary minerals in controlling the migration of arsenic and metals from high-sulfide wastes (Berikul gold mine, Siberia). Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 1347–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordstrom, D.K.; Majzlan, J.; Konigsberger, E. Thermodynamic properties for arsenic minerals and aqueous Species. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2014, 79, 217–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Robins, R.G. A re-evaluation of the solubility and stability regions of calcium arsenites and calcium arsenates in aqueous solution at 25 °C. Min. Proc. Ext. Met. Rev. 1998, 18, 283–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paktunc, D.; Bruggeman, K. Solubility of nanocrystalline scorodite and amorphous ferric arsenate: Implications for stabilization of arsenic in mine wastes. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.L.; Bahfenne, S. Raman spectroscopic study of the arsenite minerals leiteite ZnAs2O4, reinerite Zn3(AsO3)2 and cafarsite Ca5(Ti,Fe,Mn)7(AsO3)12·4H2O. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frost, R.; Silmarilly, B. The mineral nealite Pb4Fe2+(AsO3)2Cl4·2H2O-A Raman spectroscopic study. Spectrosc. Lett. 2011, 44, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nieto, J.M.; Capitán, M.A.; Sáez, R.; Almodóvar, G.R. Beudantite: A natural sink for As and Pb in sulphide oxidation processes. Appl. Earth Sci. 2003, 112, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson-Edwards, K.A. Uptake and release of arsenic and antimony in alunite-jarosite and beudantite group minerals. Am. Mineral. 2019, 104, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cheng, H.; Frost, R.L.; Dong, F. The mineral tooeleite Fe6(AsO3)4SO4(OH)4·4H2O–An infrared and Raman spectroscopic study-environmental implications for arsenic remediation. Spectrochim. Acta A 2013, 103, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Deng, S.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, H.; Frost, R.L. Spectroscopic characterization and solubility investigation on the effects of As(V) on mineral structure tooeleite (Fe6(AsO3)4SO4(OH)4·H2O). Spectrochim. Acta A 2015, 134, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, T.; Robins, R.G. Confirmation that tooeleite is a ferric arsenite sulfate hydrate, and is relevant to arsenic stabilisation. Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Wu, C. Mineralogical research on synthesized tooeleite. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2012, 31, 901–906. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Opio, F.K.; Peacey, J.; Jamieson, H.E. Arsenic immobilization from industrial effluents. In One Century of the Discovery of Arsenicosis in Latin America (1914–2014): As 2014-Proceedings of the 5th International Congress on Arsenic in the Environment; CRC Press/Balkema: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 766–768. [Google Scholar]
- Morin, G.; Rousse, G.; Elkaim, E. Crystal structure of tooeleite, Fe6(AsO3)4SO4(OH)4·4H2O, a new iron arsenite oxyhydroxysulfate mineral relevant to acid mine drainage. Am. Mineral. 2007, 92, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesbron, F.P.; Williams, S.A. Tooeleite, a new mineral from the U.S. Mine, Tooele County, Utah. Mineral. Mag. 1992, 56, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cesbron, M.; Gaspar, J.; Bessler, K.E.; Magela, G. Process mineralogy of bacterial oxidized gold ore in São Bento Mine (Brasil). Hydrometallurgy 2006, 83, 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- Casiot, C.; Lebrun, S.; Morin, G.; Bruneel, O.; Personné, J.-C.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F. Sorption and redox processes controlling arsenic fate and transport in a stream impacted by acid mine drainage. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 347, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, F.; Deng, S. The removal of Arsenic(III) from acid mine drainage by mineral trap of tooeleite (Fe6(AsO3)4SO4(OH)4·4H2O). In An Interdisciplinary Response to Mine Water Challenges; Sui, W., Sun, Y., Wang, C., Eds.; China University of Mining and Technology Press: Xuzhou, China, 2014; pp. 671–674. [Google Scholar]
- Raghav, M.; Shan, J.; Sáez, A.E.; Ela, W.P. Scoping candidate minerals for stabilization of arsenic-bearing solid residuals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majzlan, J.; Dachs, E.; Benisek, A.; Koch, C.B.; Bolanz, R.; Göttlicher, J.; Steininger, R. Thermodynamic properties of tooeleite, Fe63+(As3+O3)4(SO4)(OH)4·4H2O. Chemie der Erde 2016, 76, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. Description of Input and Examples for PHREEQC Version 3, A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations; Techniques and Methods, Book 6, Chap. A43; U.S. Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 2013; pp. 1–497.
- Allison, J.D.; Brown, D.S.; Novo-Gradac, K.J. MINTEQA2/PRODEFA2, A Geochemical Assessment Model for Environmental Systems: Version 3.0 User’s Manual; Environmental Research Laboratory, Office of Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Athens, GA, USA, 1991; pp. 1–106.
- Boudia, S.; Zuddas, P.; Fernane, F.; Fiallo, M.; Sharrock, P. Mineralogical transformation during hydroxyapatite dissolution in simple aqueous solutions. Chem. Geol. 2018, 477, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, R.L.; Palmer, S.J.; Spratt, H.J.; Martens, W.N. The molecular structure of the mineral beudantite PbFe3(AsO4,SO4)2(OH)6-Implications for arsenic accumulation and removal. J. Mol. Struct. 2011, 1004, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, P.J.; Smith, A.M.L.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Dubbin, W.E.; Wright, K. Raman and IR spectroscopic studies of alunite-supergroup compounds containing Al, Cr3+, Fe3+ and V3+ at the B site. Can. Mineral. 2009, 47, 663–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loehr, T.M.; Plane, R.A. Raman spectra and structures of arsenious acid and arsenites in aqueous solution. Inorg. Chem. 1968, 7, 1708–1714. [Google Scholar]
- Tossell, J. Theoretical studies on arsenic oxide and hydroxide species in minerals and in aqueous solution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Bahfenne, S.; Frost, R.L. Raman spectroscopic study of the mineral finnemanite Pb5(As3+O3)3Cl. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, N.; Haseen, U. Development of polyacrylamide chromium oxide as anew sorbent for solid phase extraction of As(III) from food and environmental water samples. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 7311–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acero, P.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Gale, J.D. Influence of pH and temperature on alunite dissolution: Rates, products and insights on mechanisms from atomistic simulation. Chem. Geol. 2015, 419, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, L.; Accornero, M. Prediction of the thermodynamic properties of metal-arsenate and metal-arsenite aqueous complexes to high temperatures and pressures and some geological consequences. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1343–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Aquatic Chemistry, Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural Waters, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 976–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Nordstrom, D.K.; Archer, D.G. Arsenic thermodynamic data and environmental geochemistry. In Arsenic in Ground Water, 1st ed.; Welch, A.H., Stollenwerk, K.G., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; Chapter 1; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, D.; Palmer, C.D. Solid-solution aqueous-solution interactions between jarosite and its chromate analog. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 2841–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Speciation Reactions | log_K | Speciation Reactions | log_K |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3+ + H2O = FeOH2+ + H+ | −2.187 | Fe3+ + SO42− = FeSO4+ | 4.05 |
| Fe3+ + 2H2O = Fe(OH)2+ + 2H+ | −4.594 | Fe3+ + 2SO42− = Fe(SO4)2− | 5.38 |
| Fe3+ + 3H2O = Fe(OH)3 + 3H+ | −12.56 | H3AsO3 = AsO33− + 3H+ | −34.744 |
| Fe3+ + 4H2O = Fe(OH)4− + 4H+ | −21.588 | H3AsO3 = HAsO32− + 2H+ | −21.33 |
| 2Fe3+ + 2H2O = Fe2(OH)24+ + 2H+ | −2.854 | H3AsO3 = H2AsO3− + H+ | −9.29 |
| 3Fe3+ + 4H2O = Fe3(OH)45+ + 4H+ | −6.288 | H3AsO3 + H+ = H4AsO3+ | −0.305 |
| H+ + SO42− = HSO4− | 1.99 | Fe3+ + H2AsO3− = FeH2AsO32+ | 7.28 |
| Temp (°C) | Initial pH | Time (h) | Analytical Data (mmol/L) | log_IAP | Average log_IAP | ΔGfo [kJ/mol] | Average ΔGfo [kJ/mol] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Fe | AsO3 | SO4 | |||||||
| a25 | 2.00 | 6480 | 2.33 | 0.5747 | 6.4841 | 16.9276 | −200.29 | −200.28 | −5180.58 | −5180.54 |
| 7200 | 2.33 | 0.5770 | 6.4694 | 16.8184 | −200.27 | ±0.01 | −5180.47 | ±0.07 | ||
| 7920 | 2.33 | 0.5759 | 6.4347 | 16.8434 | −200.29 | −5180.58 | ||||
| 25 | 3.00 | 6480 | 3.30 | 0.0328 | 6.6603 | 17.3767 | −194.64 | −194.61 | −5148.31 | −5148.18 |
| 7200 | 3.30 | 0.0335 | 6.6109 | 17.4889 | −194.60 | ±0.03 | −5148.09 | ±0.13 | ||
| 7920 | 3.30 | 0.0333 | 6.6710 | 17.6698 | −194.61 | −5148.14 | ||||
| 25 | 4.00 | 6480 | 3.53 | 0.0265 | 6.6580 | 19.0295 | −193.19 | −193.18 | −5140.07 | −5140.01 |
| 7200 | 3.54 | 0.0258 | 6.5549 | 19.1262 | −193.21 | ±0.04 | −5140.19 | ±0.24 | ||
| 7920 | 3.54 | 0.0263 | 6.6403 | 19.1511 | −193.14 | −5139.77 | ||||
| 25 | 5.00 | 6480 | 3.57 | 0.0265 | 6.3787 | 17.8881 | −192.94 | −192.96 | −5138.61 | −5138.75 |
| 7200 | 3.57 | 0.0259 | 6.4427 | 17.8164 | −192.98 | ±0.02 | −5138.86 | ±0.14 | ||
| 7920 | 3.57 | 0.0261 | 6.4240 | 17.7509 | −192.97 | −5138.77 | ||||
| 25 | 6.00 | 6480 | 3.58 | 0.0258 | 6.4854 | 19.0389 | −192.92 | −192.92 | −5138.50 | −5138.50 |
| 7200 | 3.58 | 0.0259 | 6.4214 | 18.4713 | −192.91 | ±0.01 | −5138.47 | ±0.03 | ||
| 7920 | 3.58 | 0.0257 | 6.4561 | 18.5586 | −192.92 | −5138.53 | ||||
| 25 | 7.00 | 6480 | 3.58 | 0.0281 | 6.4668 | 17.7135 | −192.67 | −192.68 | −5137.07 | −5137.15 |
| 7200 | 3.58 | 0.0277 | 6.4961 | 17.8289 | −192.70 | ±0.02 | −5137.28 | ±0.13 | ||
| 7920 | 3.58 | 0.0279 | 6.5388 | 17.9692 | −192.67 | −5137.11 | ||||
| 25 | 8.00 | 6480 | 3.59 | 0.0305 | 6.0450 | 17.3829 | −192.50 | −192.44 | −5136.08 | −5135.77 |
| 7200 | 3.60 | 0.0304 | 6.1104 | 17.1334 | −192.42 | ±0.06 | −5135.63 | ±0.31 | ||
| 7920 | 3.60 | 0.0304 | 6.1050 | 17.1552 | −192.41 | −5135.59 | ||||
| 25 | 9.00 | 6480 | 3.60 | 0.0270 | 6.2265 | 17.8881 | −192.70 | −192.70 | −5137.25 | −5137.26 |
| 7200 | 3.60 | 0.0269 | 6.2906 | 17.9973 | −192.69 | ±0.01 | −5137.20 | ±0.08 | ||
| 7920 | 3.60 | 0.0268 | 6.2692 | 17.9442 | −192.71 | −5137.34 | ||||
| 25 | 10.00 | 6480 | 3.61 | 0.0255 | 6.1958 | 17.5825 | −192.78 | −192.78 | −5137.73 | −5137.71 |
| 7200 | 3.61 | 0.0257 | 6.1291 | 17.4172 | −192.78 | ±0.00 | −5137.72 | ±0.02 | ||
| 7920 | 3.61 | 0.0257 | 6.1531 | 17.5201 | −192.78 | −5137.69 | ||||
| 25 | 11.00 | 6480 | 3.79 | 0.0231 | 6.6203 | 19.4006 | −191.82 | −191.85 | −5132.25 | −5132.42 |
| 7200 | 3.78 | 0.0230 | 6.6536 | 19.5971 | −191.89 | ±0.04 | −5132.60 | ±0.18 | ||
| 7920 | 3.78 | 0.0232 | 6.7017 | 19.3788 | −191.85 | −5132.41 | ||||
| 25 | 12.00 | 6480 | 5.54 | 0.0007 | 5.8167 | 21.3715 | −193.66 | −193.64 | −5142.75 | −5142.63 |
| 7200 | 5.54 | 0.0007 | 5.7033 | 21.9048 | −193.64 | ±0.02 | −5142.60 | ±0.12 | ||
| 7920 | 5.54 | 0.0007 | 5.7794 | 21.7863 | −193.63 | −5142.54 | ||||
| a25 | 2.00 | 6480 | 2.30 | 0.5690 | 6.6309 | 17.1740 | −200.75 | −200.68 | −5183.20 | −5182.79 |
| 7200 | 2.30 | 0.5775 | 6.4895 | 17.0835 | −200.74 | ±0.13 | −5183.12 | ±0.74 | ||
| 7920 | 2.31 | 0.5834 | 6.6136 | 17.2332 | −200.55 | −5182.05 | ||||
| a25 | 2.00 | 6480 | 2.31 | 0.5792 | 6.5495 | 17.5388 | −200.62 | −200.64 | −5182.47 | −5182.58 |
| 7200 | 2.30 | 0.5811 | 6.6283 | 17.3954 | −200.72 | ±0.08 | −5183.04 | ±0.46 | ||
| 7920 | 2.31 | 0.5828 | 6.5549 | 17.3268 | −200.58 | −5182.23 | ||||
| b35 | 2.00 | 6480 | 2.28 | 0.4324 | 6.5589 | 18.5399 | −199.39 | −199.39 | ||
| 7200 | 2.28 | 0.4339 | 6.6456 | 19.0451 | −199.42 | ±0.03 | ||||
| 7920 | 2.28 | 0.4337 | 6.6616 | 18.6366 | −199.37 | |||||
| b35 | 2.00 | 6480 | 2.28 | 0.4393 | 6.5495 | 19.0233 | −199.40 | −199.35 | ||
| 7200 | 2.28 | 0.4361 | 6.7324 | 18.6459 | −199.33 | ±0.05 | ||||
| 7920 | 2.28 | 0.4412 | 6.7017 | 18.7800 | −199.33 | |||||
| c45 | 2.00 | 6480 | 2.23 | 0.4234 | 7.4958 | 21.4776 | −197.80 | −197.83 | ||
| 7200 | 2.23 | 0.4201 | 7.5279 | 21.7957 | −197.85 | ±0.03 | ||||
| 7920 | 2.23 | 0.4186 | 7.5172 | 21.6678 | −197.85 | |||||
| c45 | 2.00 | 6480 | 2.21 | 0.4627 | 7.3397 | 20.7354 | −197.81 | −197.80 | ||
| 7200 | 2.21 | 0.4643 | 7.4558 | 20.8944 | −197.79 | ±0.02 | ||||
| 7920 | 2.21 | 0.4623 | 7.3984 | 20.9225 | −197.82 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. Dissolution, Stability and Solubility of Tooeleite [Fe6(AsO3)4(SO4)(OH)4·4H2O] at 25–45 °C and pH 2–12. Minerals 2020, 10, 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100921
Zhu Z, Zhang J, Zhu Y, Liu J, Tang S, Zhang L, Wang Y. Dissolution, Stability and Solubility of Tooeleite [Fe6(AsO3)4(SO4)(OH)4·4H2O] at 25–45 °C and pH 2–12. Minerals. 2020; 10(10):921. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100921
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zongqiang, Jun Zhang, Yinian Zhu, Jie Liu, Shen Tang, Lihao Zhang, and Yaru Wang. 2020. "Dissolution, Stability and Solubility of Tooeleite [Fe6(AsO3)4(SO4)(OH)4·4H2O] at 25–45 °C and pH 2–12" Minerals 10, no. 10: 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100921
APA StyleZhu, Z., Zhang, J., Zhu, Y., Liu, J., Tang, S., Zhang, L., & Wang, Y. (2020). Dissolution, Stability and Solubility of Tooeleite [Fe6(AsO3)4(SO4)(OH)4·4H2O] at 25–45 °C and pH 2–12. Minerals, 10(10), 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100921





