Evaluation of Efficiencies of Locally Available Neutralizing Agents for Passive Treatment of Acid Mine Drainage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Synthetic Acid Mine Drainage Preparation
2.3. Characterization of Neutralizing Agents
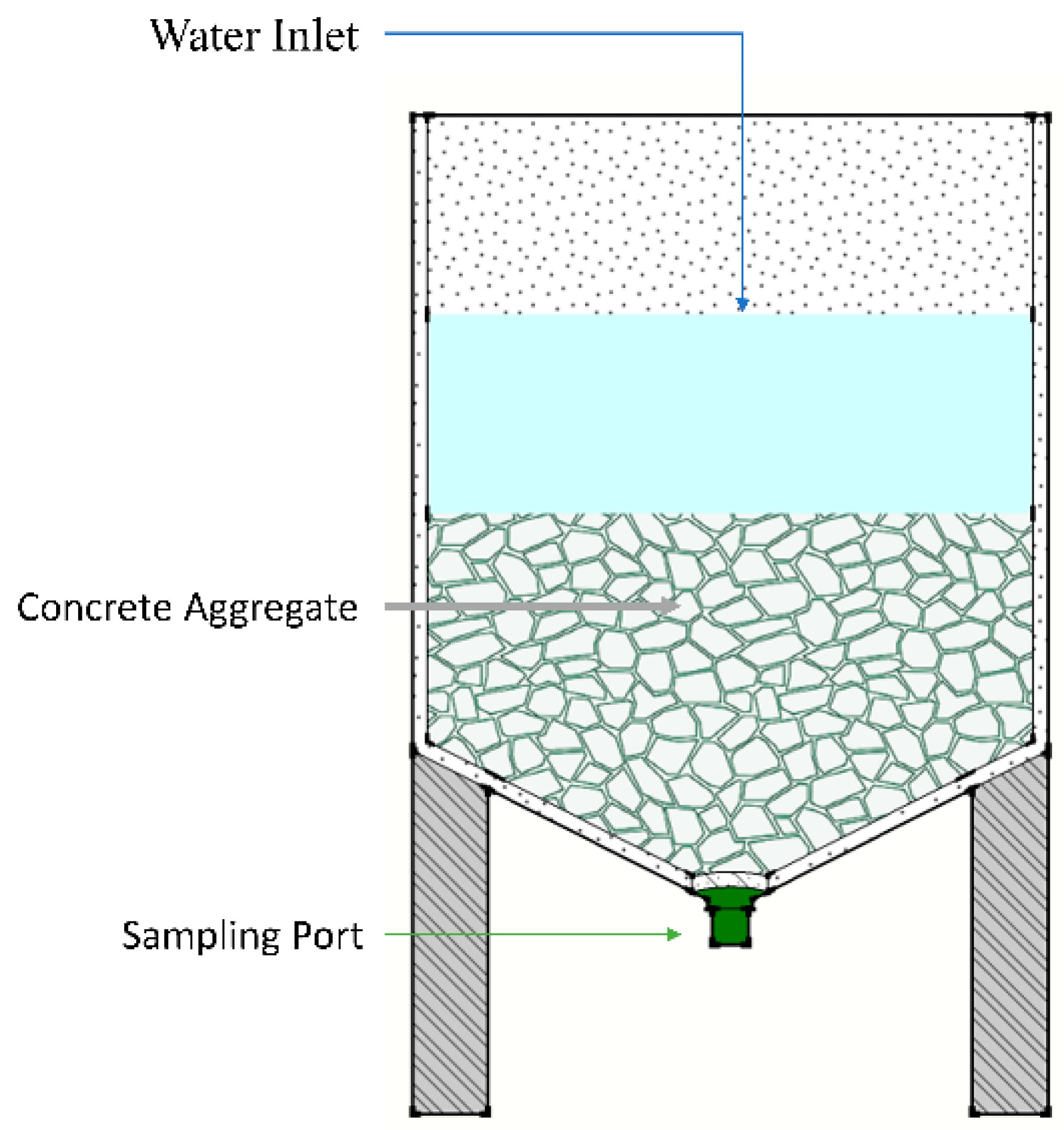
2.4. Jar Test Using Different Alkaline-Generating Materials
2.5. Batch Test Using Various Particle Sizes
2.6. Geochemical Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Whole Rock Chemistry
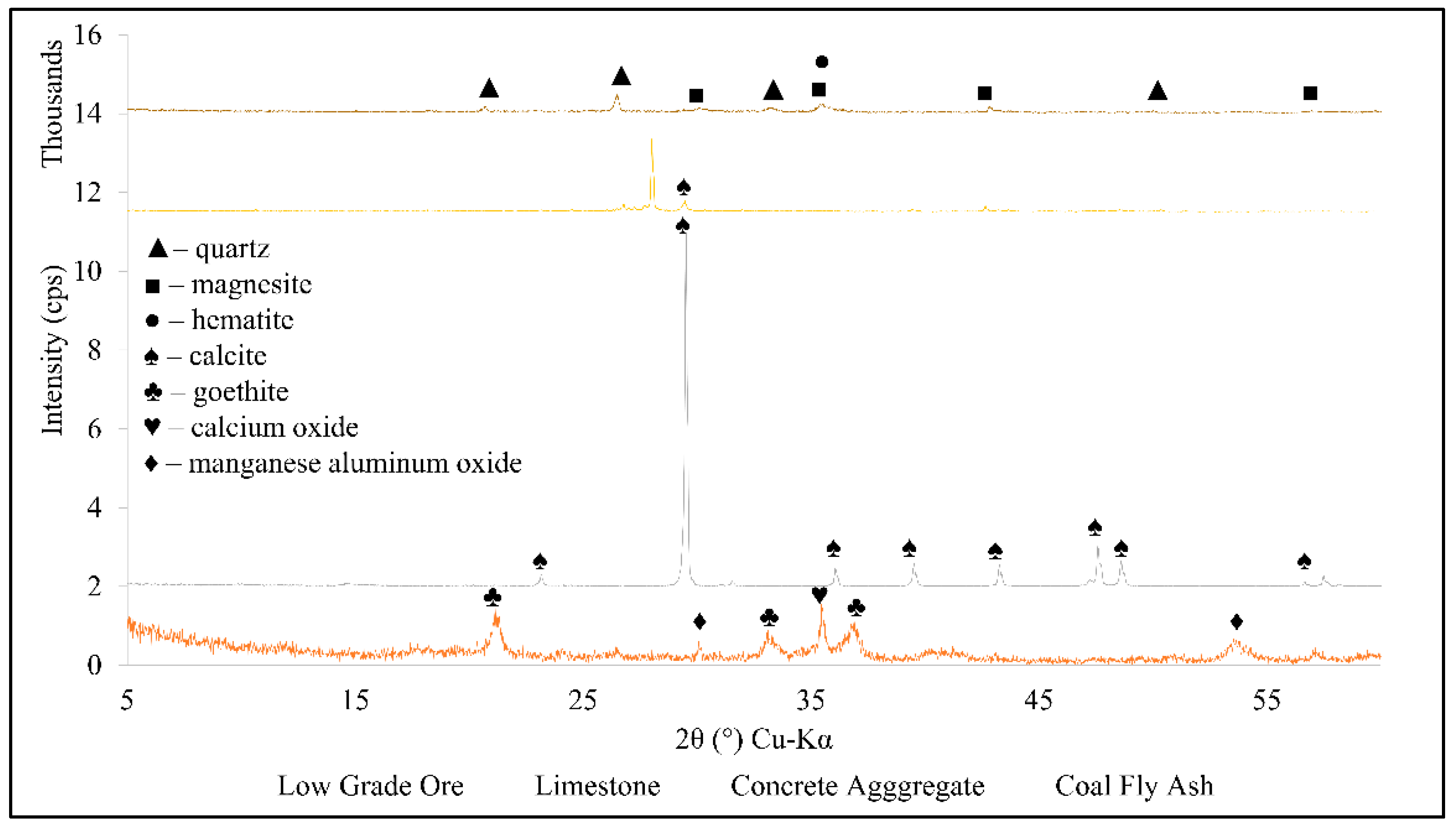
3.2. Mineralogy
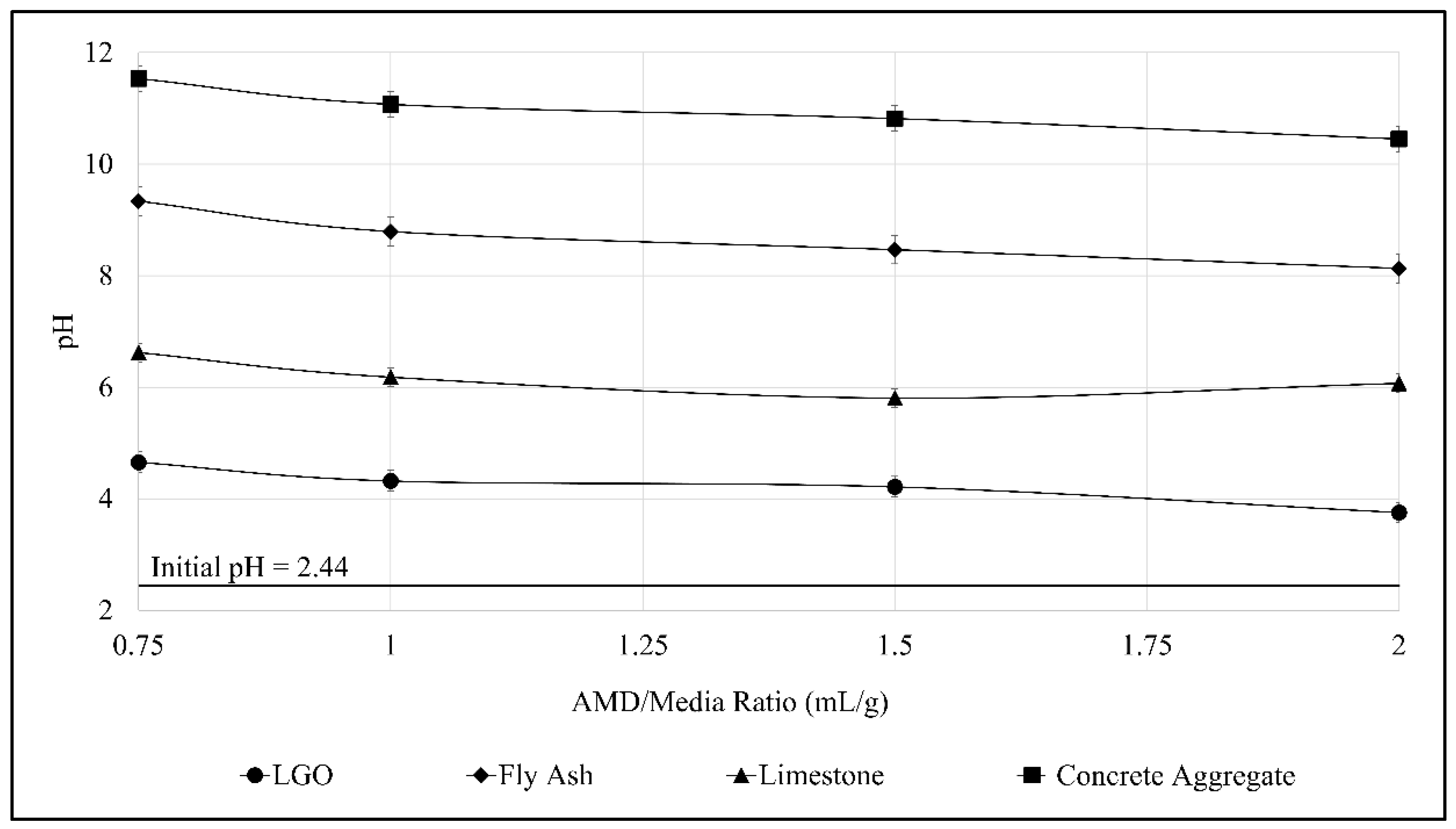
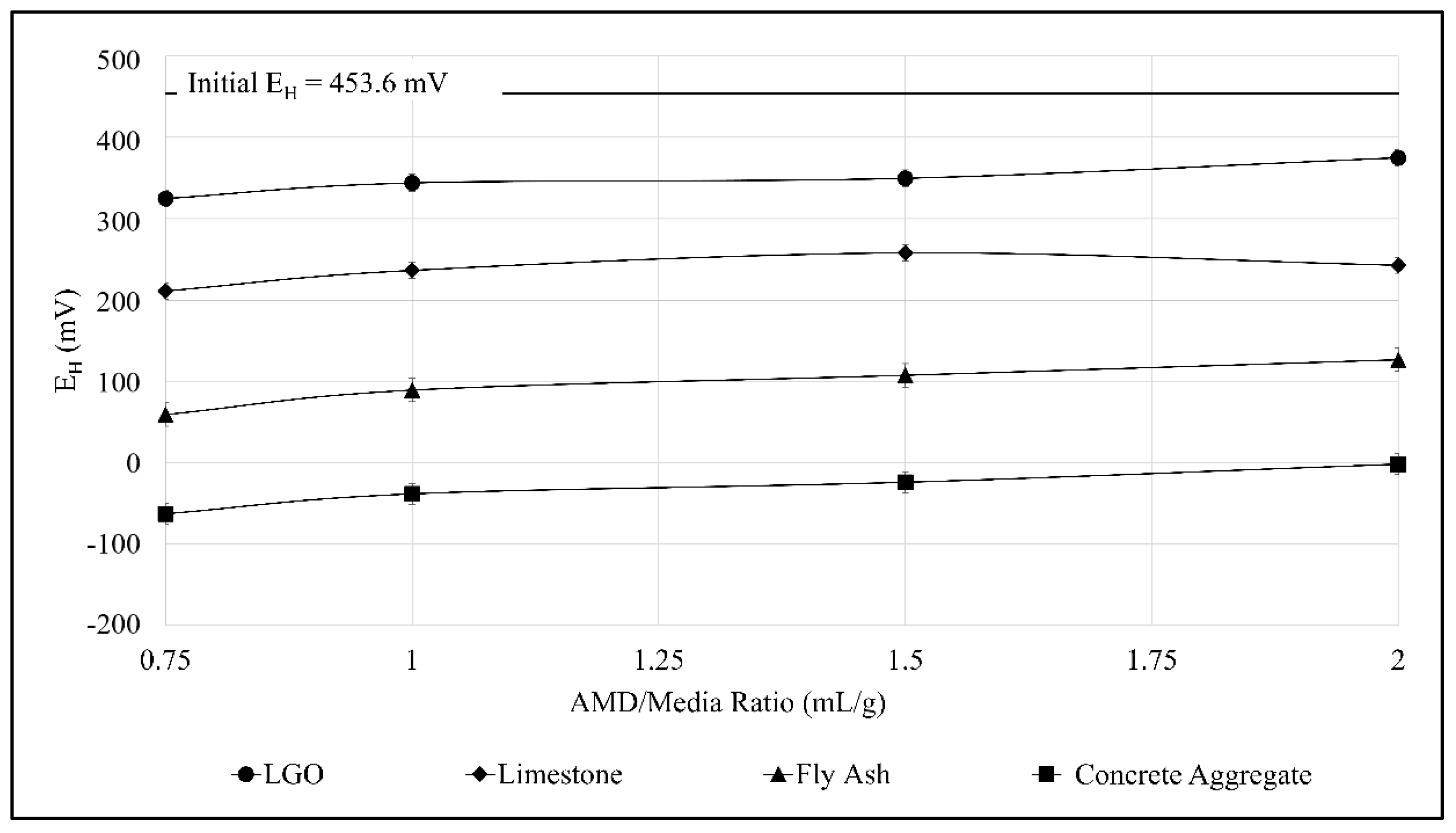
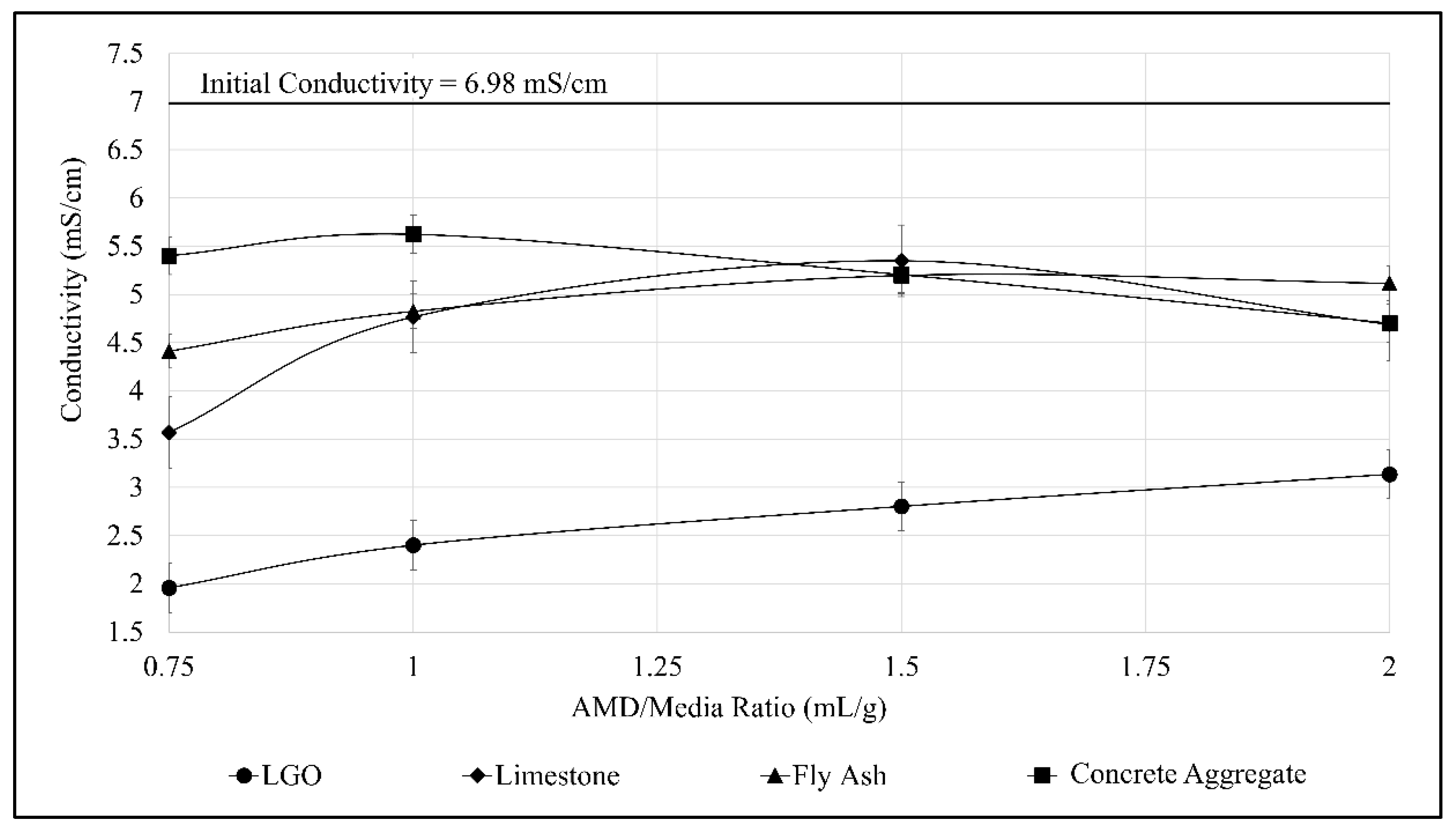
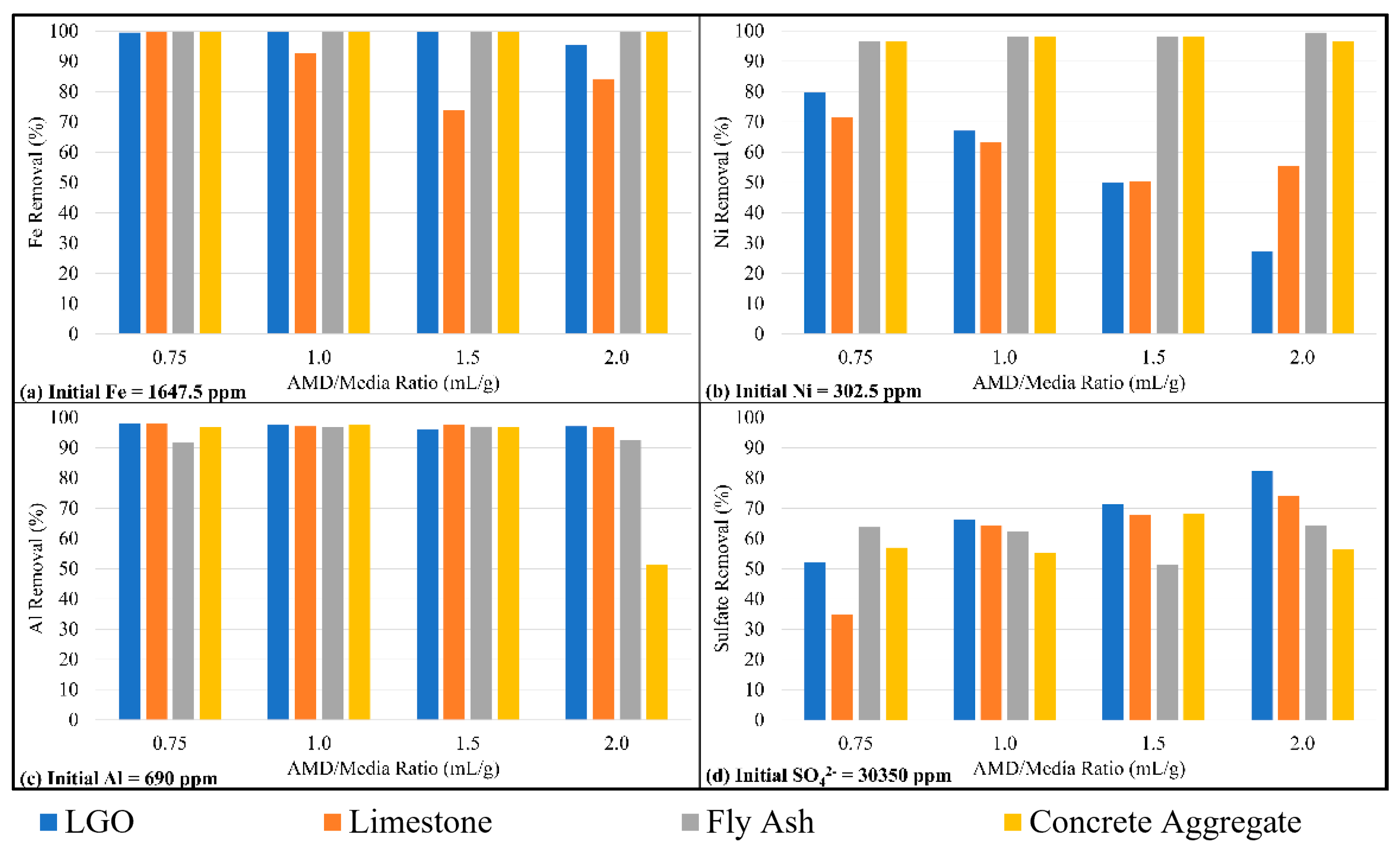
3.3. Jar Test Using Various Neutralizing Agents
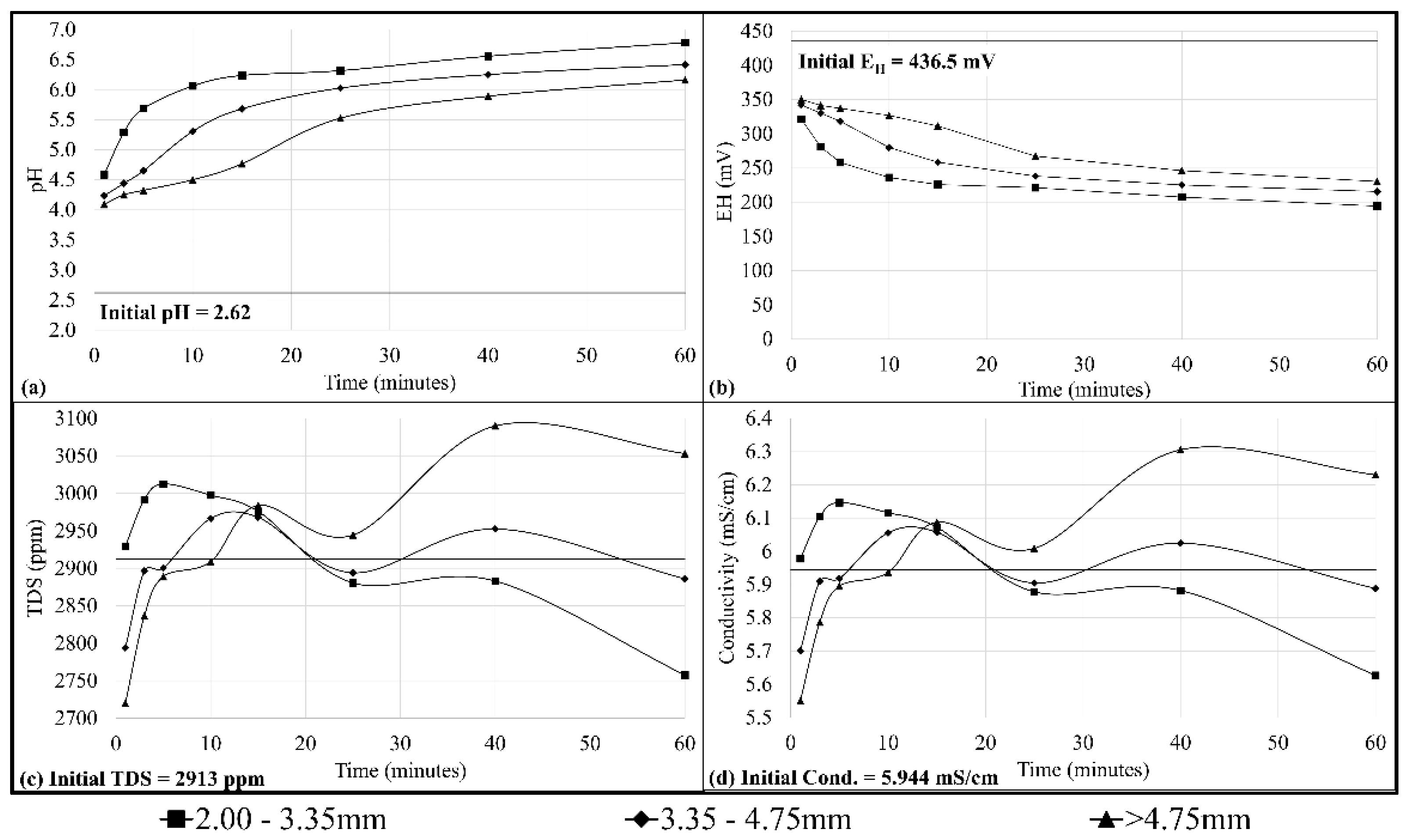
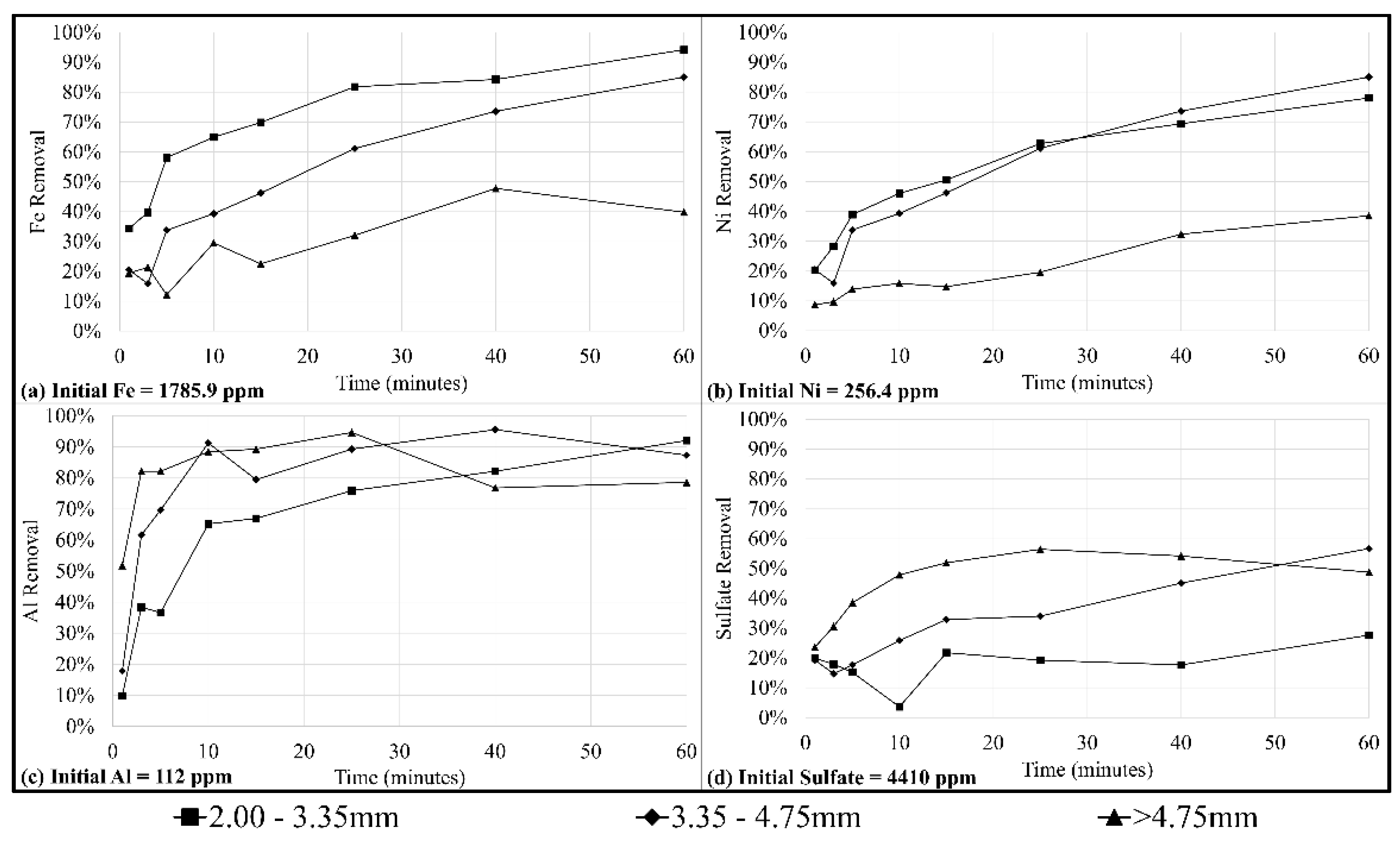
3.4. Effect of Particle Size on AMD Treatment
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of the Treatment Efficiencies of Various Neutralizing Agents
4.2. Effect of Particle Size on Acid Mine Drainage Treatment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Igarashi, T.; Herrera, P.; Uchiyama, H.; Miyamae, H.; Iyatomi, N.; Hashimoto, K.; Tabelin, C. The two-step neutralization ferrite-formation process for sustainable acid mine drainage treatment: Removal of copper, zinc and arsenic, and the influence of coexisting ions on ferritization. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skousen, J.; Ziemkiewicz, P.; Mcdonald, L. Acid mine drainage formation, control and treatment: Approaches and strategies. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2019, 6, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabelin, C.; Igarashi, T.; Villacorte-Tabelin, M.; Park, I.; Opiso, E.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N. Arsenic, selenium, boron, lead, cadmium, copper, and zinc in naturally contaminated rocks: A review of their sources, modes of enrichment, mechanisms of release, and mitigation strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1522–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simate, G.S.; Ndlovu, S. Acid mine drainage: Challenges and opportunities. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1785–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, B.; Pemmasani, N.; Phagura, S. Acid Mine Drainage Treatment Public Policy Report. 2015. Available online: https://www.cmu.edu/epp/people/faculty/course-reports/NTCReport2015-AcidMineDrainage.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Park, I.; Tabelin, C.; Jeon, S.; Li, X.; Seno, K.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N. A review of recent strategies for acid mine drainage prevention and mine tailings recycling. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintans, J. Mining industry in the Philippines. The Manila Times. 2017. Available online: https://www.manilatimes.net/2017/09/04/supplements/mining-industry-philippines/348610/#:~:text=THE%20Philippines%20is%20the%20fifth,mineral%20wealth%2C%20as%20of%202012 (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Mines & Geosciences Bureau. Mining Industry Statistics. 2020. Available online: https://mgb.gov.ph/images/Mineral_Statistics/MIS_Q12020_May292020.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Kefeni, K.; Msagati, T.; Mamba, B. Acid mine drainage: Prevention, treatment options, and resource recovery: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyen, D.; Tabelin, C.; Thuan, H.; Dang, D.; Truong, P.; Vonghuthone, B.; Kobayashi, M.; Igarashi, T. The solid-phase partitioning of arsenic in unconsolidated sediments of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam and its modes of release under various conditions. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcil, A.; Koldas, S. Acid mine drainage (AMD): Causes, treatment and case studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, M.; Hiroyoshi, N.; Tabelin, C.; Taketsugu, T.; Ito, M. Suppression of pyrite oxidation by ferric-catecholate complexes: An electrochemical study. Miner. Eng. 2019, 138, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre Louis, A.; Yu, H.; Shumlas, S.; Van Aken, B.; Schoonen, M.; Strongin, D. Effect of Phospholipid on Pyrite Oxidation and Microbial Communities under Simulated Acid Mine Drainage (AMD) Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7701–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, P.; Crundwell, F. The kinetics of the oxidation of pyrite by ferric ions and dissolved oxygen: An electrochemical study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lu, G.; Guo, C.; Yang, C.; Wu, J.; Huang, W.; Yee, N.; Dang, Z. Sulfate migration in a river affected by acid mine drainage from the Dabaoshan mining area, South China. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skousen, J.G.; Sexstone, A.; Ziemkiewicz, P. Acid mine drainage control and treatment. Reclam. Drastically Disturb. Lands 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, J.C.; Santomartino, S. Acid rock drainage treatment technologies: Identifying appropriate solutions. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Acid Rock Drainage, Cairns, QLD, Australia, 14–17 July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Skousen, J.; Ziemkiewicz, P. Performance of 116 passive treatment systems for acid mine drainage. In Proceedings of the 2005 National Meeting of the American Society of Mining and Reclamation, Breckenridge, CO, USA, 19–23 June 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morallo, A. DENR to Close 21 Mining Firms. The Philippine Star. 2017. Available online: https://www.philstar.com/business/2017/02/02/1668370/denr-close-21-mining-firms (accessed on 31 May 2020).
- Masindi, V.; Akinwekomi, V. Comparison of mine water neutralisation efficiencies of different alkaline generating agents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3903–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potgieter-Vermaak, S.S.; Potgieter, J.H. Comparison of limestone, dolomite and fly ash as pre-treatment agents for acid mine drainage. Miner. Eng. 2005, 19, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemkiewicz, P.F.; Skousen, J.G.; Lovett, R. Open limestone channels for treating acid mine drainage: A new look at an old idea. Green Lands 1994, 24, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Cravotta, C.A., III; Trahan, M.K. Limestone drains to increase pH and remove dissolved metals from acidic mine drainage. Appl. Geochem. 1999, 14, 581–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.E. Diversion wells—A low-cost approach to treatment of acid mine drainage. In Proceedings of the Twelfth West Virginia Surface Mine Drainage Task Force Symposium, Morgantown, WV, USA, 3–4 April 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Hedin, R.; Narin, R.; Kleinmann, R. The Passive Treatment of Coal Mine Drainage; Bureau of Mines IC 9389; U.S. Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Muliwa, A.; Leswifi, T. Performance evaluation of eggshell waste material for remediation of acid mine drainage drom coal dump leachate. Miner. Eng. 2018, 122, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heviánková, S.; Bestová, I. The application of wood ash as a reagent in acid mine drainage treatment. Miner. Eng. 2014, 56, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouakibi, O.; Hakkou, R. Phosphate carbonated wastes used as drains for acidic mine drainage passive treatment. Procedia Eng. 2014, 83, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, N.M.; Sulaiman, S.K. Bench-Scale study of acid mine drainage treatment using local neutralisation agents. Malays. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2014, 10, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, C.E.; Zachara, J.M.; Resch, C.T. Cadmium adsorption on iron oxides in the presence of alkaline-earth elements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. 2017. Carbonate Mineral. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/carbonate-mineral (accessed on 23 June 2020).
- Bernier, L.R. The potential use of serpentinite in the passive treatment of acid mine drainage: Batch experiments. Environ. Geol. 2005, 47, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turingan, C.; Singson, G.; Melchor, B.; Alorro, R.; Beltran, A.; Orbecido, A. A comparison of acid mine drainage (AMD) neutralization potential of low grade nickel laterite and other alkaline-generating materials. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, M.M.; Leckie, J.O. Multiple-Site adsorption of Cd, Cu, Zn, and Pb on amorphous iron oxyhydroxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1981, 79, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balistrieri, L.S.; Chao, T. Adsorption of selenium by amorphous iron oxyhydroxide and manganese dioxide. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachara, J.M.; Girvin, D.C.; Schmidt, R.L.; Resch, C.T. Chromate adsorption on amorphous iron oxyhydroxide in the presence of major groundwater ions. Environm. Sci. Technol. 1987, 21, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcim, G.T.Z. Reuse and Recycling of Construction and Demolition Waste. 2007. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/5963/263e9892bc081f55928f45fe9ff09eaa51bb.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Kalaw, M.; Culaba, A.; Hinode, H.; Kurniawan, W.; Gallardo, S.; Promentilla, M. Optimizing and Characterizing Geopolymers from Ternary Blend of Philippine Coal Fly Ash, Coal Bottom Ash and Rice Hull Ash. Materials 2016, 9, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. Description and Input and Examples for PHREEQC Version 3—A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations. In USGS Techniques and Methods 6-A43; USGS: Denver, CO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.; Cetin, B. Evaluation of waste materials for acid mine drainage remediation. Fuel 2017, 188, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisatto, M.; Dalconi, M.; Valentini, L.; Artioli, G.; Rack, A.; Tucoulou, R.; Cruciani, G.; Ferrari, G. Examining microstructural evolution of Portland cements by in-situ synchrotron micro-tomography. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 50, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb, G.; Mahmud, H. Study on Properties of Rice Husk Ash and Its Use as Cement Replacement Material. Mater. Res. 2010, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henmi, T.; Wells, N. Poorly-Ordered iron-rich precipitates from springs and streams on andesitic volcanoes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1980, 44, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambor, J.L.; Dutrizac, J.E. Occurrence and constitution of natural and synthetic ferrihydrite, a widespread iron oxyhydroxide. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 2549–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koeppenkastrop, D.; De Carlo, E.H. Sorption of rare-earth elements from seawater onto synthetic mineral particles: An experimental approach. Chem. Geol. 1992, 95, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, J.M.; Boi, M. The passivation of calcite by acid mine water: Column experiments with ferric sulfate and ferric chloride solutions at pH 2. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3579–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offeddu, F.; Cama, J. Processes affecting the efficiency of limestone in passive treatments for AMD: Column experiments. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, Z.; Zhou, L. High efficiency of heavy metal removal in mine water by limestone. Chin. J. Geochem. 2009, 28, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. Hydroxide. Britannica. 2017. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/hydroxide (accessed on 31 May 2020).
- Liu, H.; Chen, T. An overview of the role of goethite surfaces in the environment. Chemosphere 2014, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietra, R.P.; Hiemstra, T. Sulfate adsorption on goethite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 218, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrence and Uses; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; Volume 2, p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Gao, H.; Sun, Y.; Huang, M. The adsorption and desorption of Ni(II) on Al substituted goethite. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 201, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Cadorin, L.; Rubio, J. Sulphate ions removal from an aqueous solution: I. Co-precipitation with hydrolysed aluminum-bearing salts. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skousen, J.; Politan, K. Acid mine drainage treatment systems: Chemicals and costs. Green Lands 1990, 20, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A.; Figueroa, L.; Wildeman, T. Zinc and nickel removal in simulated limestone treatment of mining influenced water. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadapalli, V.; Klink, M.; Etchebers, O.; Petrik, L.; Gitari, W.; White, R.; Key, D.; Iwuoha, E. Neutralization of Acid Mine Drainage using Fly Ash and Strength Development of the Resulting Solid Residues. South Afr. J. Sci. 2008, 104, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Golab, A.; Peterson, M.; Indraratna, B. Selection of potential reactive materials for a permeable reactive barrier for remediating acidic groundwater in acid sulphate soil terrains. Fac. Eng. Pap. 2006, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reagents | Mass (g) |
|---|---|
| FeSO4∙7H2O | 65.46 |
| Al2(SO4)3∙18H2O | 17.28 |
| NiSO4∙6H2O | 9.39 |
| CuSO4∙5H2O | 1.4 |
| MnSO4∙H2O | 1.4 |
| MgSO4∙7H2O | 1.4 |
| 1.5 M H2SO4 | 60 mL |
| Parameter | Measurement |
|---|---|
| pH | 2.44 |
| Oxidation-Reduction Potential (EH) | 453.6 mV |
| Conductivity | 6.98 mS/cm |
| Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) | 3420.5 ppm |
| Fe | 1647.48 ppm |
| Ni | 302.49 ppm |
| Al | 690 ppm |
| Sulfates | 30,350 ppm |
| Element | Material | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LGO | Limestone | Fly Ash | Concrete Aggregate [40,41,42] | |
| Al2O3 | 4.19 | 0.93 | 8.55 | 4.71 ± 1.50 |
| CaO | 4.56 | 85.66 | 16.04 | 58.57 ± 11.68 |
| Fe2O3 | 54.07 | 7.59 | 44.63 | 4.11 ± 1.88 |
| MgO | 7.96 | 0.02 | n/a | 1.38 ± 1.01 |
| SiO2 | 23.87 | 1.78 | 24.65 | 26.63 ± 9.75 |
| NiO | 2.13 | 0.76 | n/a | n/a |
| Others | 3.22 | 3.26 | 6.13 | 4.03 ± 1.87 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turingan, C.O.A.; Singson, G.B.; Melchor, B.T.; Alorro, R.D.; Beltran, A.B.; Orbecido, A.H. Evaluation of Efficiencies of Locally Available Neutralizing Agents for Passive Treatment of Acid Mine Drainage. Minerals 2020, 10, 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100845
Turingan COA, Singson GB, Melchor BT, Alorro RD, Beltran AB, Orbecido AH. Evaluation of Efficiencies of Locally Available Neutralizing Agents for Passive Treatment of Acid Mine Drainage. Minerals. 2020; 10(10):845. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100845
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuringan, Casey Oliver A., Giulio B. Singson, Bernadette T. Melchor, Richard D. Alorro, Arnel B. Beltran, and Aileen H. Orbecido. 2020. "Evaluation of Efficiencies of Locally Available Neutralizing Agents for Passive Treatment of Acid Mine Drainage" Minerals 10, no. 10: 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100845
APA StyleTuringan, C. O. A., Singson, G. B., Melchor, B. T., Alorro, R. D., Beltran, A. B., & Orbecido, A. H. (2020). Evaluation of Efficiencies of Locally Available Neutralizing Agents for Passive Treatment of Acid Mine Drainage. Minerals, 10(10), 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100845






