Riverine Sediment Geochemistry as Provenance Fingerprints along the Eastern Coast of China: Constraint, Approach, and Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Sediment Geochemistry of the Major Rivers along the Eastern Coast of China
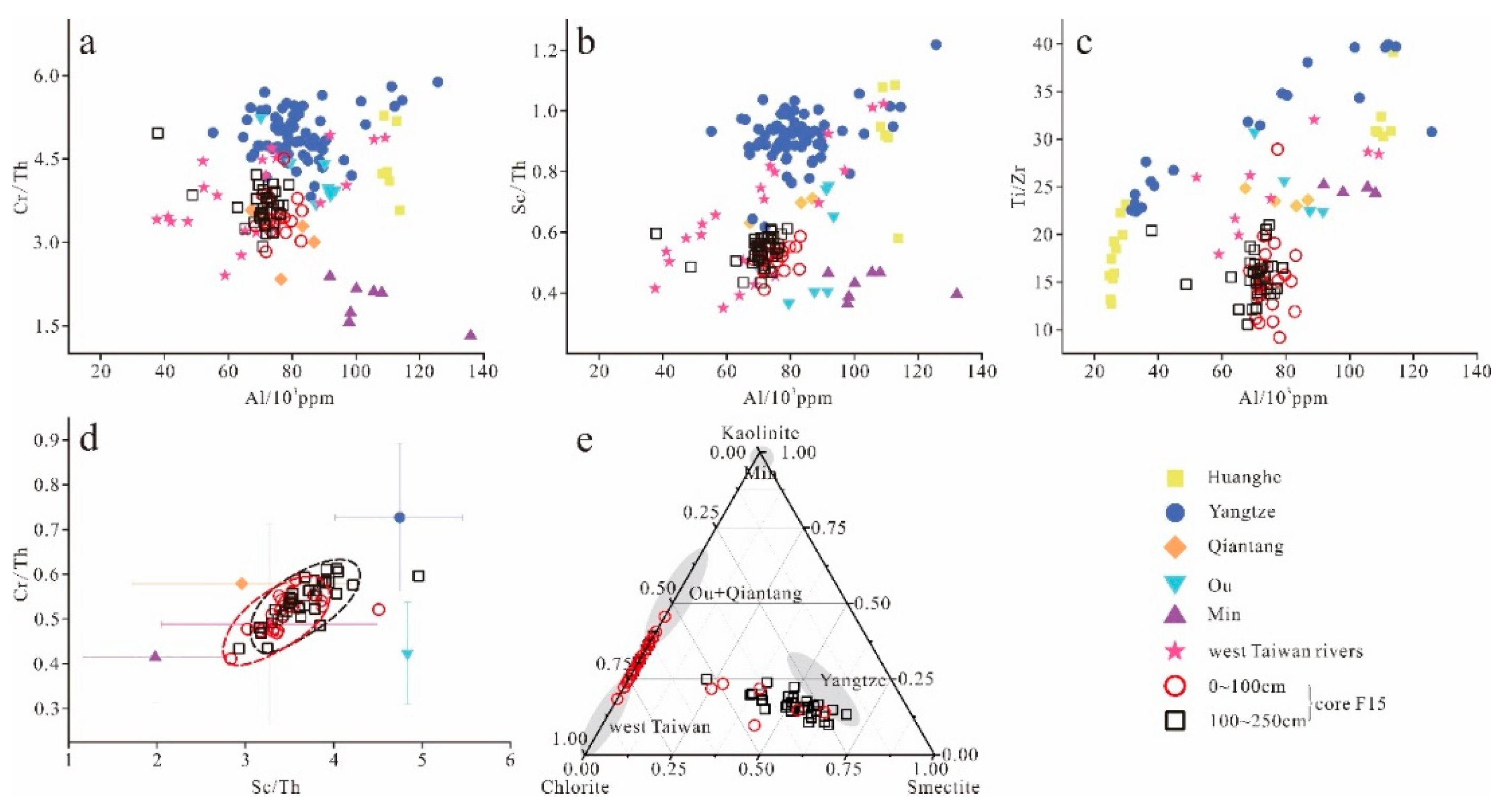
4.1.1. Geochemical Characteristics Related to Chemical Partition
4.1.2. Geochemical Characteristics Related to Sediment Grain Size
4.1.3. Geochemical Differences of Riverine Sediments along the Eastern Coast of China
4.2. Geochemical Characteristics of Core F15 Sediments in the Southernmost Inner-Shelf Mud Wedge
5. Discussion
5.1. Geochemical Provenance Fingerprint Constrained by Chemical Partition and Sediment Grain Size
5.2. Geochemical Disparity of Riverine Sediments along the Eastern Coast of China and the Approach Proposed for Provenance Determination
5.3. Provenance Discrimination of Core F15: An Application of the Geochemical Approach
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, S.; Collins, M.B. Holocene sedimentary systems on continental shelves. Mar. Geol. 2014, 352, 268–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, W.; Han, Z.; Yu, Q.; Li, G. Holocene sedimentary systems on a broad continental shelf with abundant river input: Process—Product relationships. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2016, 429, 223–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Shen, H.; Yang, Z.; Mead, R.H. Transport and deposition of river sediment in the Changjiang estuary and adjacent continental shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 1985, 4, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wei, G.; Shao, L.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Jian, Z.; Sun, M.; Wang, P. Geochemical and Nd isotopic variations in sediments of the South China Sea: A response to Cenozoic tectonism in SE Asia. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 211, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Jung, H.S.; Li, C. Two unique weathering regimes in the Changjiang and Huanghe drainage basins: Geochemical evidence from river sediments. Sediment. Geol. 2004, 164, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yim, W.W.S.; Huang, G. Geochemical composition of inner shelf Quaternary sediments in the northern South China Sea with implications for provenance discrimination and paleoenvironmental reconstruction. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 60, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnoli, F.; Dinelli, E.; Giordano, P.; Marcaccio, M.; Zaffagnini, F.; Frascari, F. Sedimentological, biogeochemical and mineralogical facies of Northern and Central Western Adriatic Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 139, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, S.E. The mineralogy and geochemistry of near-shore sediments. Chem. Oceanogr. 1976, 6, 187–280. [Google Scholar]
- Spagnoli, F.; Dell’Anno, A.; De Marco, A.; Dinelli, E.; Fabiano, M.; Gadaleta, M.V.; Ianni, C.; Loiacono, F.; Manini, E.; Marini, M.; et al. Biogeochemistry, grain size and mineralogy of the central and southern Adriatic Sea sediments: A review. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 26, 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The continental crust: Its composition and evolution. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1985, 42, 196–197. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y. Advances in provenance studies of Changjiang Riverine sediments. Adv. Earth Sci. 2012, 27, 515–528. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, D.; Jung, H.; Xu, Z.; Jeong, K.; Li, T. Elemental and Sr-Nd isotopic compositional disparity of riverine sediments around the Yellow Sea: Constraints from grain-size and chemical partitioning. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 63, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wei, G.; Shi, X. Geochemical approaches of tracing source-to-sink sediment processes and environmental changes at the East Asian continental margin. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2015, 34, 902–910. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, L.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dou, Y.; Li, C.; Zheng, H. Provenance study of the Holocene sediments in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) estuary and inner shelf of the East China sea. Quat. Int. 2017, 441, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wan, S.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, D.; Liu, X.; Li, A.; Li, T. Geochemical records of Taiwan-sourced sediments in the South China Sea linked to Holocene climate changes. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2016, 441, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Lo, C.; Lee, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Y.; Chung, S. Provenance of cored sediments from active margin off southwestern Taiwan deduced from geochemical constraints. Acta Geol. Sin. 2014, 88, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.; Xu, Z.; Choi, J.; Li, T.; Kim, S. Holocene changes in detrital sediment supply to the eastern part of the central Yellow Sea and their forcing mechanisms. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 105, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, A.; Dong, J.; Lu, J.; Huang, J.; Wan, S. Provenance discrimination of sediments in the Zhejiang-Fujian mud belt, East China Sea: Implications for the development of the mud depocenter. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 151, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, A.; Li, T.; Chen, S.; Cao, Y.; Dong, C.; Qiu, L. Provenance of mud sediments in the inner shelf of East China Sea since mid-HoIocene. J. China Univ. Pet. Ed. Nat. Sci. 2011, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Li, A.; Liu, J.P.; Milliman, J.D.; Yang, Z.; Liu, C.S.; Kao, S.J.; Wan, S.; Xu, F. Provenance, structure, and formation of the mud wedge along inner continental shelf of the East China Sea: A synthesis of the Yangtze dispersal system. Mar. Geol. 2012, 291, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Bi, L.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Dou, Y. Major sinks of the Changjiang (Yangtze River)-derived sediments in the East China Sea during the late Quaternary. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2016, 429, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Jung, H.S.; Lim, D.I.; Li, C. A review on the provenance discrimination of sediments in the Yellow Sea. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2003, 63, 93–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.T.; Yin, P. Geochemistry of river-borne clays entering the East China Sea indicates two contrasting types of weathering and sediment transport processes. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2015, 16, 3034–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzanti, E.; Resentini, A. Provenance control on chemical indices of weathering (Taiwan river sands). Sediment. Geol. 2016, 336, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shi, X.; Kao, S.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, H.; Zou, J.; Liu, S.; Qiao, S. Rare earth elements in fine-grained sediments of major rivers from the high-standing island of Taiwan. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, C. Characteristic element compositions of the Yangtze and the Yellow River sediments and their geological background. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 1999, 19, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Shu, J. Heterogeneity of geochemical compositions of the Changjiang River sediments and provenance indication. Quat. Sci. 2013, 33, 645–655. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchez, J.; Lupker, M.; Gaillardet, J.; France Lanord, C.; Maurice, L. How important is it to integrate riverine suspended sediment chemical composition with depth? Clues from Amazon River depth-profiles. Geochim. Cosmochimi. Acta 2011, 75, 6955–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, S.; Su, N.; Yin, P.; Wang, Z. Rare earth element geochemistry of the sediments from small rivers draining southeast China. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2018, 38, 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y. Elemental Geochemistry of the Fluvial Sediments in Zhejiang and Fujian Provinces: Controls of Provenance and Chemical Weathering; Tongji University: Shanghai, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, C.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, X. Elemental composition of suspended sediments from the Changjiang river and its environmental implication. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2012, 32, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L. Geology of the East China Sea; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1987; p. 290. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, China Academy of Sciences. Geology Map of China; Sinomap Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- China Water Resources Bulletin 2017; Ministry of Water Resources of China, China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Kao, S.J.; Milliman, J.D. Water and sediment discharge from small mountainous rivers, Taiwan: The roles of lithology, episodic events, and human activities. J. Geol. 2008, 116, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Meade, R.H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans. J. Geol. 1983, 91, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Milliman, J.D.; Li, P.; Xu, K. 50,000 dams later: Erosion of the Yangtze River and its delta. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2011, 75, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, K.; Li, A.; Milliman, J.D.; Velozzi, D.M.; Xiao, S.; Yang, Z. Flux and fate of Yangtze River sediment delivered to the East China Sea. Geomorphology 2007, 85, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, J. A unique Yellow River-derived distal subaqueous delta in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Geol. 2007, 240, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, C.S.; Huh, C.A. Magnetic properties as tracers for source-to-sink dispersal of sediments: A case study in the Taiwan Strait. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 309, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, C.A.; Chen, W.; Hsu, F.H.; Su, C.C.; Chiu, J.K.; Lin, S.; Liu, C.S.; Huang, B.J. Modern (<100 years) sedimentation in the Taiwan Strait: Rates and source-to-sink pathways elucidated from radionuclides and particle size distribution. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Milliman, J.D.; Li, A.; Liu, J.P.; Kao, S.J.; Wan, S. Yangtze-and Taiwan-derived sediments on the inner shelf of East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 2240–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadson, S.J.; Hovius, N.; Chen, H.; Dade, W.B.; Hsieh, M.L.; Willett, S.D.; Hu, J.C.; Horng, M.J.; Chen, M.C.; Stark, C.P. Links between erosion, runoff variability and seismicity in the Taiwan orogen. Nature 2003, 426, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.J.; Lee, T.Y.; Milliman, J.D. Calculating highly fluctuated suspended sediment fluxes from mountainous rivers in Taiwan. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2005, 16, 653–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ma, J.; Xu, K.; Liu, Y.; Cao, W.; Wei, T.; Zhao, B.; Chen, Z. Provenance discrimination of the clay sediment in the western Taiwan Strait and its implication for coastal current variability during the late-Holocene. Holocene 2017, 27, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Chen, J.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Chen, Z. China’s Yangtze delta: Geochemical fingerprints reflecting river connection to the sea. Geomorphology 2014, 227, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.S.; Lim, D.; Jeong, D.H.; Xu, Z.; Li, T. Discrimination of sediment provenance in the Yellow Sea: Secondary grain-size effect and REE proxy. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 123, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.I.; Jung, H.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Yang, S.; Ahn, K.S. Geochemical compositions of river and shelf sediments in the Yellow Sea: Grain-size normalization and sediment provenance. Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 26, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Yang, Z.; Mao, D.; Guo, Z. Clay minerals and geochemistry of the sediments from the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2001, 21, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, X.; Wang, H.; Li, R.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z. Major elements composition and provenance analysis in the sediments of the South Yellow Sea. Earth Sci. Front. 2007, 14, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Saito, Y.; Kong, X.; Wang, H.; Xiang, L.; Wen, C.; Nakashima, R. Sedimentary record of environmental evolution off the Yangtze River estuary, East China Sea, during the last ~13,000 years, with special reference to the influence of the Yellow River on the Yangtze River delta during the last 600 years. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2010, 29, 2424–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wei, Z.; Wei, T.; Wei, W. Diagnostic heavy minerals in Plio–Pleistocene sediments of the Yangtze Coast, China with special reference to the Yangtze River connection into the sea. Geomorphology 2009, 113, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Letolle, R.; Jusserand, C. Major element chemistry of the Huanghe (Yellow River), China-weathering processes and chemical fluxes. J. Hydrol. 1995, 168, 173–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gu, S.; Yan, W.; Liu, F. Contained in surface sediments at south Nansha trough and adjacent sea area and its affecting factors. Mar. Sci. 2002, 26, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Chu, T.; Zhang, J. Element Geochemistry; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Fralick, P.W.; Kronberg, B.I. Geochemical discrimination of elastic sedimentary rock sources. Sediment. Geol. 1997, 113, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzanti, E.; Andò, S.; Vezzoli, G. Grain-size dependence of sediment composition and environmental bias in provenance studies. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 277, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.G.; Lee, C.B.; Choi, M.S. Geochemistry of surface sediments off the southern and western coasts of Korea. Mar. Geol. 1999, 159, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzanti, E.; Andó, S.; France Lanord, C.; Censi, P.; Vignola, P.; Galy, V.; Lupker, M. Mineralogical and chemical variability of fluvial sediments 2. Suspended-load silt (Ganga–Brahmaputra, Bangladesh). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 302, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.S.; Lim, D.; Xu, Z.; Kang, J.H. Quantitative compensation of grain-size effects in elemental concentration: A Korean coastal sediments case study. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 151, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.X.; Yang, S.L.; Zhang, J. The impact of the Three Gorges Dam on the downstream distribution and texture of sediments along the middle and lower Yangtze River (Changjiang) and its estuary, and subsequent sediment dispersal in the East China Sea. Geomorphology 2012, 179, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Su, N.; Bi, L.; Chang, Y.P.; Chang, S.C. Detrital zircon geochronology of river sands from Taiwan: Implications for sedimentary provenance of Taiwan and its source link with the east China mainland. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 164, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.Y.; Lee, C.S.; Shen, J.J.S.; Lu, C.Y.; Mertzman, S.A.; Wu, T.W. Nd-Sr isotopic composition and geochemistry of sediments from Taiwan and their implications. West. Pac. Earth Sci. 2002, 2, 205–222. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, S.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Xiang, R.; Shi, X.; Fan, D.; Saito, Y. Records of late-Holocene East Asian winter monsoon in the East China Sea: Key grain-size component of quartz versus bulk sediments. Quat. Int. 2011, 230, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Li, A.; Chen, M.; Liu, J.; Jiang, F.; Li, T.; Xie, Q.; Xiang, R.; Chen, Z. Recent 8 ka mud records of the East Asian Winter Monsoon from the inner shelf of the East China Sea. Earth Sci. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2005, 30, 573–581. [Google Scholar]
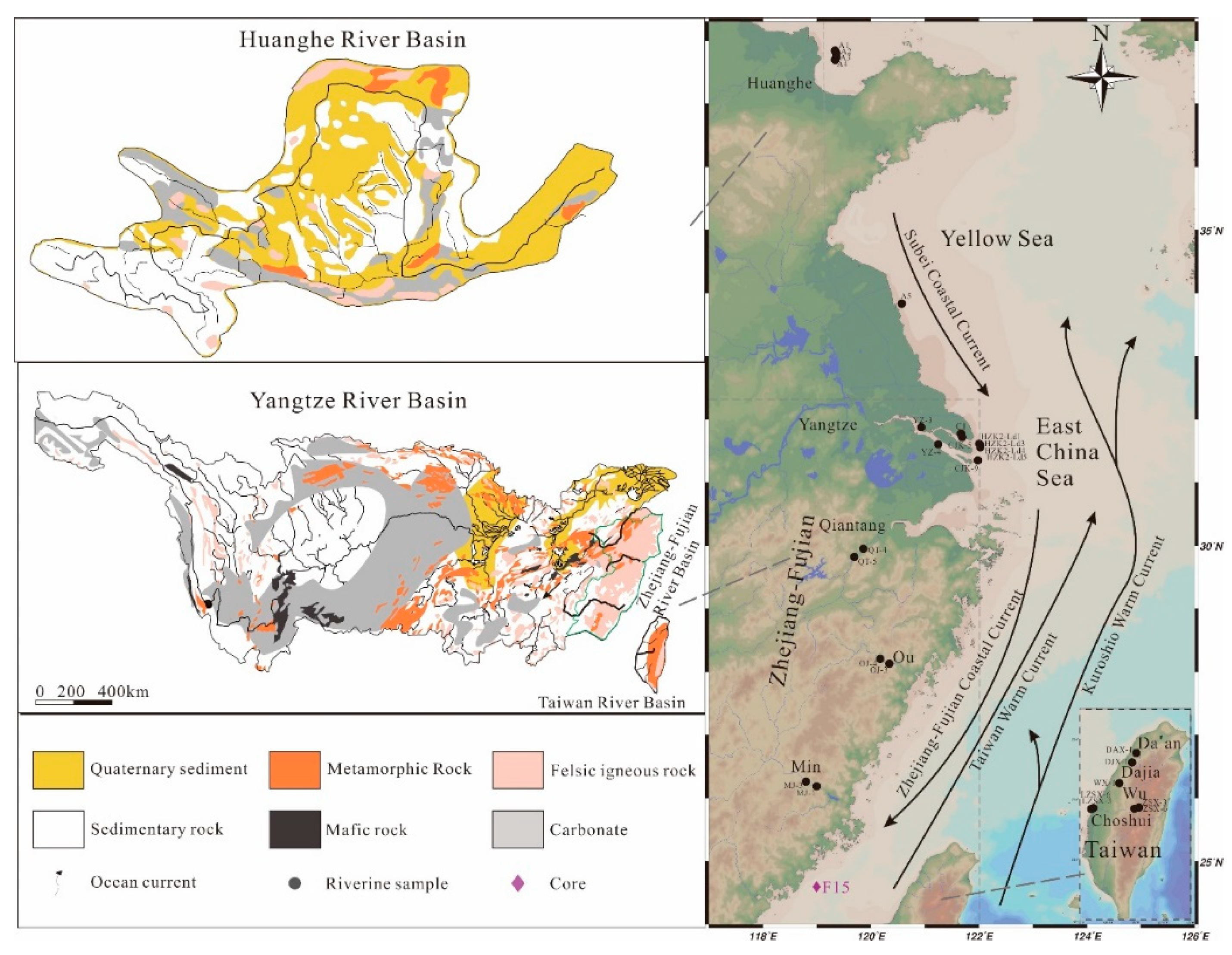
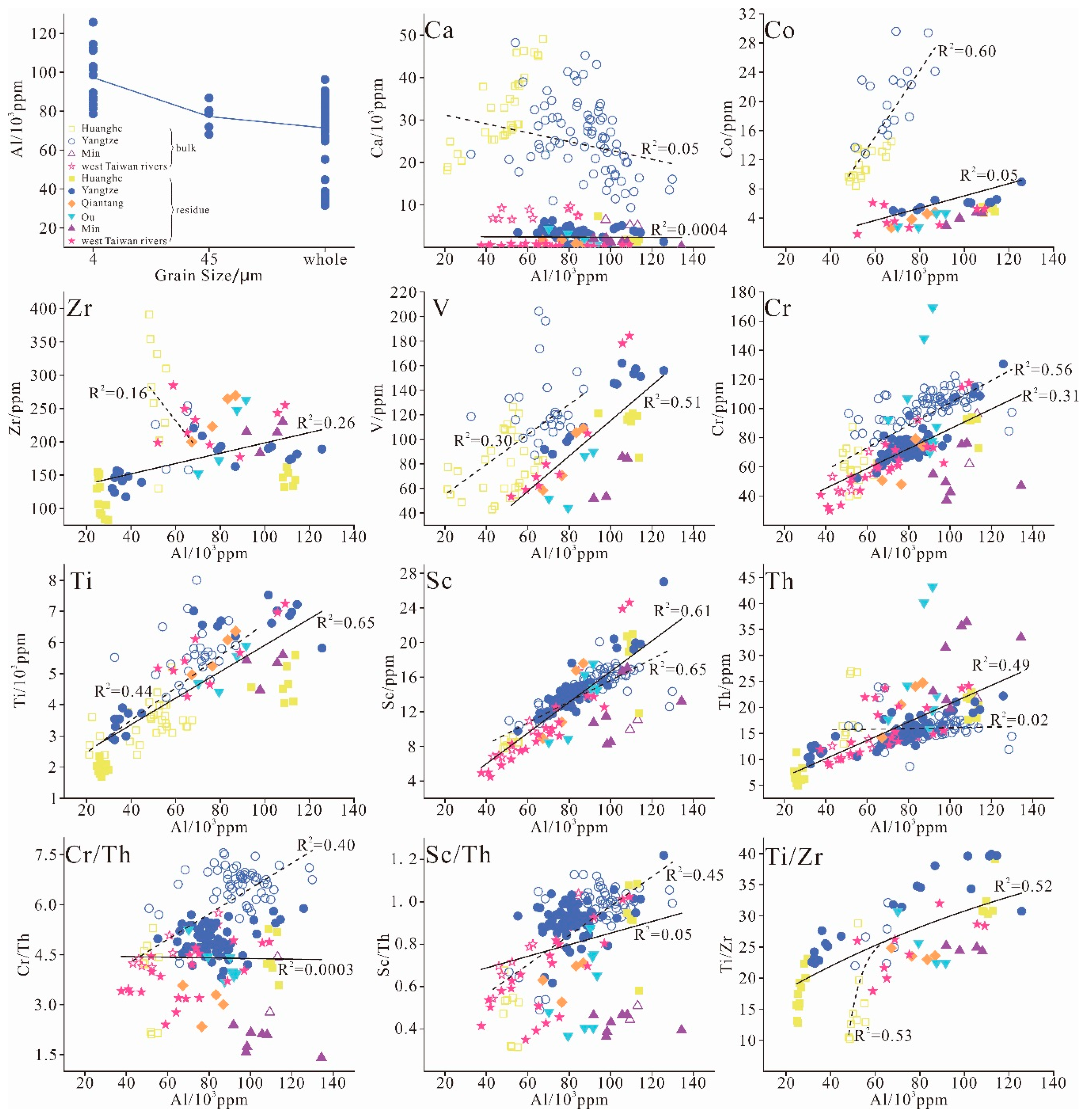
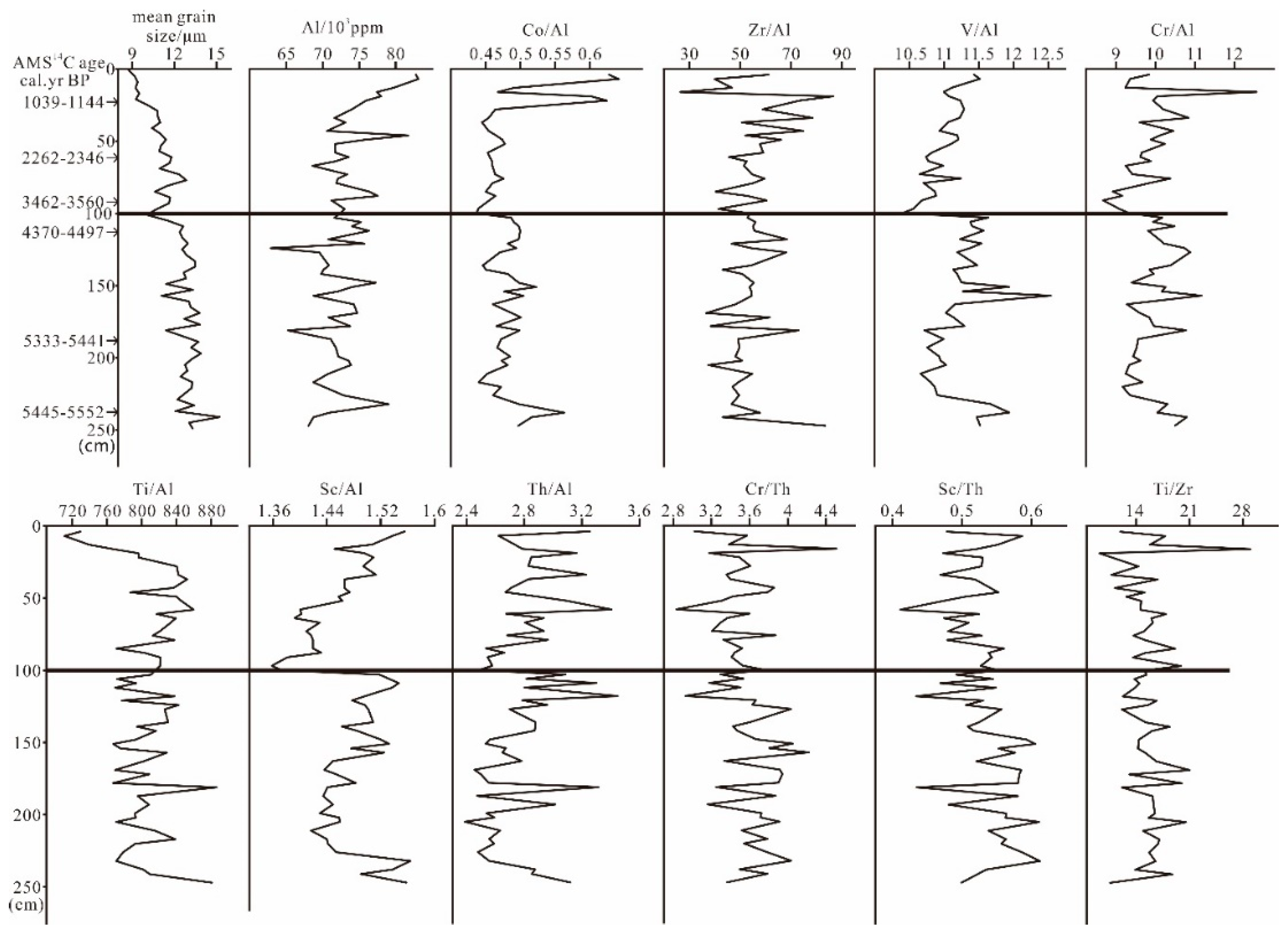
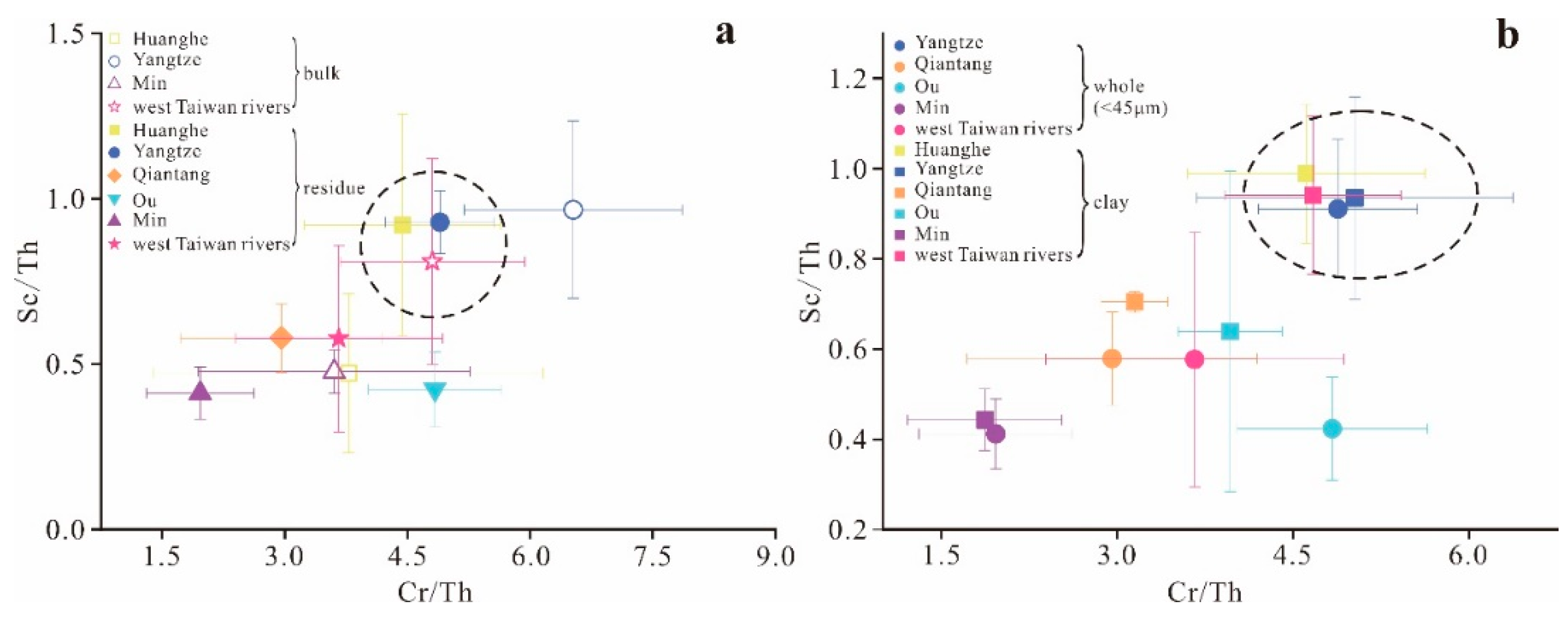
| River | Length (km) | Area (103 km2) | Water Discharge (108 m3/Year) | Sediment Load (104 t/Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huanghe [34] | 5464 | 682 | 336 | 97,800 |
| Yangtze1 [34] | 6380 | 1800 | 8931 | 36,800 |
| Qiantang [34] | 688 | 24 | 291 | 670 |
| Oujiang [34] | 388 | 18 | 221 | 289 |
| Minjiang [34] | 577 | 56 | 573 | 599 |
| Choshui [35] | 186 | 3.2 | 61 | 6387 |
| Dajiaxi [35] | 140 | 1.2 | 26 | 403 |
| Daanxi [35] | 98 | 0.8 | 12 | 497 |
| Wuxi [35] | 117 | 2.0 | 37.3 | 679 |
| River | Huanghe | Yangtze | Zhejiang–Fujian | Western Taiwan | All | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | ||||||
| Ca | - | −0.224 | −0.538 * | −0.195 | −0.020 | |
| Co | - | 0.237 | 0.656 * | 0.292 | 0.229 | |
| Zr | 0.509 * | 0.696 ** | 0.298 | 0.055 | 0.511 ** | |
| V | - | 0.950 ** | 0.321 | 0.963 ** | 0.712 ** | |
| Cr | - | 0.848 ** | −0.209 | 0.893 ** | 0.556 ** | |
| Ti | 0.965 ** | 0.719 ** | 0.264 | 0.787 * | 0.806 ** | |
| Sc | - | 0.900 ** | 0.284 | 0.914 ** | 0.781 ** | |
| Th | 0.960 ** | 0.823 ** | 0.492 * | 0.649 ** | 0.697 ** | |
| Cr/Th | - | 0.219 | −0.655 ** | 0.554 ** | −0.016 | |
| Sc/Th | - | 0.358 ** | −0.287 | 0.758 ** | 0.227 * | |
| Ti/Zr | 0.924 ** | 0.896 ** | −0.344 | 0.669 * | 0.722 ** | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Liu, P.; Sun, D.; Zhang, D.; Miao, B.; Chen, J. Riverine Sediment Geochemistry as Provenance Fingerprints along the Eastern Coast of China: Constraint, Approach, and Application. Minerals 2020, 10, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10010029
Chen J, Liu P, Sun D, Zhang D, Miao B, Chen J. Riverine Sediment Geochemistry as Provenance Fingerprints along the Eastern Coast of China: Constraint, Approach, and Application. Minerals. 2020; 10(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10010029
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jie, Ping Liu, Dandan Sun, Dan Zhang, Bingdi Miao, and Jing Chen. 2020. "Riverine Sediment Geochemistry as Provenance Fingerprints along the Eastern Coast of China: Constraint, Approach, and Application" Minerals 10, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10010029
APA StyleChen, J., Liu, P., Sun, D., Zhang, D., Miao, B., & Chen, J. (2020). Riverine Sediment Geochemistry as Provenance Fingerprints along the Eastern Coast of China: Constraint, Approach, and Application. Minerals, 10(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10010029




