Abstract
In social networking analysis, there exists a fundamental problem called maximal cliques enumeration(MCE), which has been extensively investigated in many fields, including social networks, biological science, etc. As a matter of fact, the formation principle of maximal cliques that can help us to speed up the detection of maximal cliques from social networks is often ignored by most existing research works. Aiming to exploit the formation of maximal cliques in social networks, this paper pioneers a creative research issue on the detection of bases of maximal cliques in social networks. We propose a formal concept analysis-based approach for detecting the bases of maximal cliques and detection theorem. It is believed that our work can provide a new research solution and direction for future topological structure analysis in various complex networking systems.
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
Recent years witnessed the booming development of graph data modeling and its widely used applications. In practice, many applications can be represented with graph data modeling, such as social networks, web networks, and protein interactive networks. Therefore, analyzing and mining the useful knowledge from graphs is significantly meaningful. In particular, maximal cliques enumeration (MCE) is an important research issue in graphs. In graphs, a clique refers to a complete sub-graph where any two vertices are connected to each other. Meanwhile, a maximal clique is a clique such that there is no clique with more vertices. At present, the detection of maximal cliques or MCE is mainly to identify all maximal cliques because these cliques or maximal cliques contain more valued knowledge and information. Thus, MCE is widely used in community detection, topological analysis of web networks, and so forth.
1.2. Related Work
MCE is a fundamental problem in graph theory, and has been extensively investigated by many researchers [1,2]. They mainly focus on devising an approximate algorithm (since MCE is an NP-hard problem) for extracting all maximal cliques. The existence of an algorithm for addressing MCE is categorized as: (1) sequential in-memory algorithms [3,4]; (2) sequential I/O efficient algorithms [5,6] which concentrate on reducing the high cost of random disk I/Os for processing graphs that cannot fit in main memory [2]; (3) aiming to reduce the running time—the third type approach is parallel, and distributed algorithms [7,8] are proposed. However, these existing studies usually ignore the formation principle of maximal cliques. As a matter of fact, the formation principle of maximal cliques is a kind of useful information for better MCE process. That is to say, if we can obtain the partial topological structures which can further form the maximal clique, then this issue can be addressed efficiently.
Formally, problems in graph theory have also been analyzed by formal concept analysis; for example, K-clique of dynamic social networks are mined from formal concept lattice [9,10]. From the formal concept analysis point of view, if a graph is converted into a formal context, then notions of formal concept analysis can be used to express problems in graph theory, if fact, social networks graphs are converted into a special formal context [9,10], in which are vertices of the graphs and I means the edges between two vertices; accordingly, the K-cliques problem of the social networks is expressed by K-formal concepts of the special formal context . Theoretically, many interesting notions and mining methods have been proposed in formal concept analysis, such as frequent itemsets, closed frequent itemsets, maximal frequent itemsets, expressive generalized itemsets, and disjunctive closed itemsets [11,12,13,14]. A priori-inspired algorithms and frequent pattern-growth-inspired algorithms [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22] have been provided to fast mine many kinds of itemsets. In [23], Pei et al. proposed a method based on a topology for attributes of a formal context to generate the formal concept lattice, and the topology for attributes was induced by a reflexive and transitive relation on the set of attributes; by defining an equivalent relation on the topology for attributes, it has been proved that the formal concept lattice and the quotient topology for attributes decided by the equivalent relation is isomorphic.
1.3. Contributions
Motivated by our earlier works [9,10,23], this paper pioneers the study of the bases of maximal cliques in social networks. We firstly present the concept of base of maximal clique, then we point out that the maximal clique can be formed based on the detected bases. Therefore, the main contributions of this work are twofold: (1) formalize an interesting problem about the detection of bases of maximal cliques in social networks; (2) exploit the formation procedure of maximal cliques and then present an efficient approach for obtaining the bases of maximal cliques.
1.4. Paper Organization
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 provides the problem statement. Then, a formal concept analysis-based detection approach for the bases of maximal clique in social networks is presented in Section 3. A case study is conducted in Section 4. Finally, Section 5 concludes this paper.
2. Problem Statement
To study the problem of the detection of bases of maximal cliques in social networks, the graph model and basic concept of maximal cliques are firstly presented, and the problem statement is then formalized.
2.1. Graph Model and Maximal Clique
This work focuses on undirected graph and managing the maximal cliques on it; hence, graph model is here defined with an undirected graph model , where V is the set of vertices and E is the set of edges of G. Particularly, a set of vertices is a clique if each vertex in C are connected each other. If there is no any other set of vertices such that is a clique in G, then C is a maximal clique.
2.2. Problem Descriptions
According to our previous work [9], we know that the k-clique community can be formed with skeleton sub-graphs. Similarly, finding the bases of maximal cliques could help us to detect maximal cliques quickly. Note that the base of maximal clique refers to the common sub-graph (can be line, or other sub-graph) among maximal cliques.
Problem 1.
Problem Definition: Given a social network , this paper proposes a novel topic and the corresponding approach for finding the bases of maximal cliques from G, denoted as B ((G)).
To better understand the above problem statement, an illustrative example is shown as follows.
Figure 1a shows an input of the problem (i.e., social network G, composed of seven vertices). We can easily get the maximal cliques from G using the existing algorithm. However, we found that the common edges between maximal cliques 2,3,5 and 2,5,6 as shown in Figure 1b. Actually, the edge is a base of maximal cliques and , since they can be formed by simply adding vertex 3 or 6.
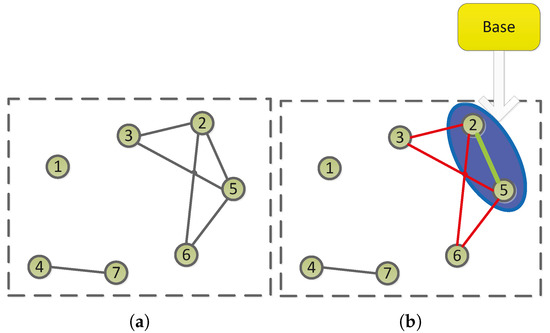
Figure 1.
An illustrative example on bases of maximal cliques. (a) Social Network G; (b) Base of Maximal Cliques.
3. Detecting Bases of Maximal Cliques Based on Formal Concept Analysis
To address the above problem, this section is devoted to presenting our proposed approach for detecting the bases of maximal cliques by using formal concept analysis. In Section 3.1, we firstly analyze the reason for bases of maximal clique for interpreting how maximal cliques can be formed via their bases. Then, a new formal context and its concept lattice are generated by aggregating the attributes which have common objects. Finally, we extract the extents from the maximal cliques associated concepts and from the new formal concept lattice and then make the intersection. After that, topological structure analysis of a social graph is formally provided in Section 3.2. Based on the proposed detection approach and the corresponding topological structure analysis, a newly proposed detection theorem is presented in Section 3.3.
3.1. Detection Approach
Suppose G is a social network, denoted as . We firstly construct the formal context using the approach presented in [9]. Obviously, is a special formal context; i.e., its objects and attributes are the same as vertices of the graph , and I is decided by edge if it exists between two vertices. Due to the speciality of , we can granulate vertices when they are as attributes; the granulation of vertices is achieved by an equivalence relation R on V which is induced by I; i.e., the granulation of vertices is formalized as follows: For any , we have
where means there exists an edge between vertices i and j. Based on Equation (1), the equivalence relation R on V is induced by
it is easily proved that R on V is symmetrical, reflexive and transitive; i.e., R on V decided by Equation (2) is an equivalence relation, and R can be used to granulate vertices as for any ,
Let ; this makes us obtain a new formal context from . That is, , where , it is obvious that has the same objects with but the different attributes from the original formal context . For example, in Figure 1a, as our the input is the social network G, then the converted formal context and its induced formal context are constructed as shown in Table 1 and Table 2.

Table 1.
The formal context of .

Table 2.
The induced formal context of .
The corresponding concept lattices are generated by the existing concept lattice generation algorithm. The relationship between the concept lattices of the original formal context K (i.e., ) and induced formal context (i.e, ) is shown in Figure 2. According to the findings about the equivalence between equiconcept and clique [9,10], it is clear that the maximal cliques in G include . Interestingly, these maximal cliques are aggregated then represented as the relevant concepts in Figure 2. For example, the common attribute of maximal cliques and is ; that is to say, is the formation base for maximal cliques and .
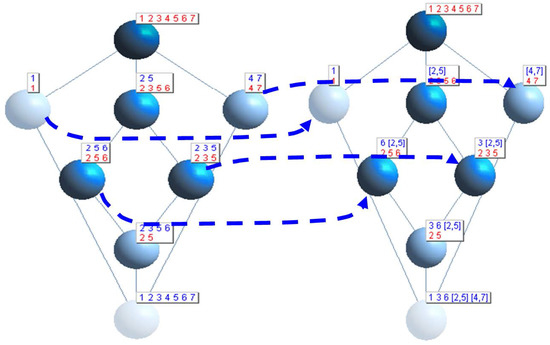
Figure 2.
The relationship between and .
3.2. Topological Structure Analysis of a Social Graph
Based on the reflexive and transitive relation R on V of a social graph , this section focuses on constructing a topological space of vertices set V. Formally, a reflexive and transitive relation on a set can be used to induce covering approximation space [24,25,26]. In our previous work [23], the reflexive and transitive relation on a set has been used to construct an approximation space and a topology for attributes of a formal context, respectively, and a base for the topology can be adopted to generate intensions of all formal concepts of the formal context and construct the formal concept lattice. Inspired by our previous work, a topological space of vertices set V is constructed by using the reflexive and transitive relation R that are used to represent relationships and the hierarchical structures of a social graph , and provide several interesting results to show topological analysis of a social graph.
Property 1.
In the formal context of an undirected graph , for any , is a -clique in .
Definition 1.
In the formal context of a social graph , for any subgraph , lower vertices approximations of is
According to , can also be rewritten by
Theorem 1.
[23] For any formal context of undirected graph ,
- 1.
- is a topology for V, and is a topological space for V;
- 2.
- is a base for the topology .
Theorem 1 means that any social graph can be represented by its topology , which is induced by the binary relation R decided by Equation (2); it is more important that the topology for V can be generated by the base , which is obtained from every vertex of V according to Equation (1).
Corollary 1.
[27] For any , if and , then .
Because is a -clique in by Property 1, Corollary 1 means that i and j generate the same k-clique in ; i.e.,
Corollary 2.
[27] If i and j are in a k-clique in , then and they are the k-clique in .
According to Theorem 1 and Corollary 2, we have the following corollary.
Corollary 3.
[27] Any social network can be generated by its all k-clique in , where .
3.3. Detection Theorem
Therefore, the following detection theorem is derived with the above detection approach.
Theorem 2.
Given a social network , the formal context of G is K, the concept lattice of K is denoted as , the bases of maximal cliques can be obtained from maximal cliques associated formal concepts in concept lattice , where is an induced formal context from K based on equivalence relation R over attributes.
3.4. Practical Applicability
Based on the above detection theorem, our work can bring more opportunities for: (1) future topological structure analysis in various complex networking systems; (2) finding the trust/sentiment dominators by identifying the base of maximal cliques since the dominators are playing the skeleton role in trust/sentiment management and propagation in social networks [28,29,30,31] as well as the large data clustering in Internet of Things [32]; (3) providing a new solution for recommender systems incorporating the maximal cliques. We may detect the maximal cliques by virtue of base of it, then adopt the conventional approaches, such as collaborative filtering or matrix factorization for items recommendation [33]; (4) in addition, our work is also beneficial to the protein complex identification from protein–protein interaction networks [34].
4. Case Study
This section manages a case study on a real-life scientist collaboration network. Aiming to validate the feasibility and performance of the proposed approach, the largest maximal cliques (i.e, the maximal cliques including the largest number of vertices) will be detected based on our approach.
4.1. Dataset
The dataset of the case study is a network of collaborations between scientists working on “Networks” [35]. The statistics of this dataset are as follows: this collaboration social network contains 1589 scientists (vertices in the graph), and 2742 collaborations (edges in the graph).
4.2. Results
To detect the largest maximal cliques from the above network, we firstly find the base of the largest maximal cliques and exploit their formation principle. The experiments detect only one largest maximal clique formed by 20 scientists from the testing dataset. Importantly, the bases of these maximal clique , , are identified as well.
In other words, the largest maximal clique can be gradually formed based on the base of it. This evolution phenomenon is quite important and promising for later complex topological structures mining and analysis. For example, for a company who wants to promote their new product, we may suggest this company plant their ads and provide the incentives to the base of the maximal cliques (i.e, targeted seed customers). From the application point of view, the achievements of this research can be applicable to various social networking services, like social marketing, social advertising, and social recommendation.
5. Conclusions
Aiming to exploit the formation of maximal cliques in social networks, this paper formalizes a novel problem on detection of bases of maximal cliques from social networks. In order to address this problem, this paper proposed a formal concept analysis-based approach for detecting the bases of maximal cliques in social networks. We mathematically present a detection theorem according to our proposed approach. Hence, this detection theorem is ubiquitous and can be applied to various complex networks. The proposed detection approach reveals the formation principle of maximal cliques by investigating the relationship between original concept lattice and aggregated concept lattice. We believe that this work can pave the way for future topological structure analysis of social networks and other complex networking systems.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (No. NRF-2017R1A2B1008421) and the MSIP(Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning), Korea, under the ITRC (Information Technology Research Center) support program (IITP-2017-2014-0-00720) supervised by the IITP (Institute for Information & communications Technology Promotion) and was also supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (GK201703059). Z. Pei’s work was partially supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61372187).
Author Contributions
Fei Hao proposed the topic and initial idea, performed the case study and wrote the paper; Doo-Soon Park improved the idea and presentation of the paper; Zheng Pei extended and improved the Section 1 and also wrote the Section 3.2.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Conte, A.; De Virgilio, R.; Maccioni, A.; Patrignani, M.; Torlone, R. Finding All Maximal Cliques in Very Large Social Networks. In Proceedings of the Extending Database Technology (EDBT), Bordeaux, France, 15–18 March 2016; pp. 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Fu, A.W.C. Distributed Maximal Clique Computation and Management. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2016, 9, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modani, N.; Dey, K. Large Maximal Cliques Enumeration in Large Sparse Graphs. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM conference on Information and knowledge management, Napa Valley, CA, USA, 26–30 October 2008; pp. 1377–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Eppstein, D.; Loffler, M.; Strash, D. Listing All Maximal Cliques in Sparse Graphs in Near-Optimal Time. In Proceedings of the 21st International Symposium on Algorithms and Computation, Jeju Island, Korea, 15–17 December 2010; pp. 403–414. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Zhu, L.; Ke, Y.; Chu, S. Fast Algorithms for Maximal Clique Enumeration with Limited Memory. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Beijing, China, 12–16 August 2012; pp. 1240–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich, M.T.; Pszona, P. External-Memory Network Analysis Algorithms for Naturally Sparse Graphs. In Proceedings of the 19th Europe Conference on Algorithms, Saarbrücken, Germany, 5–9 September 2011; pp. 664–676. [Google Scholar]
- Du, N.; Wu, B.; Xu, L.; Wang, B.; Xin, P. Parallel Algorithm for Enumerating Maximal Cliques in Complex Network. In Mining Complex Data; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 207–221. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.C.; Samatova, N.F.; Thomas, K.; Park, B.H. A scalable, parallel algorithm for maximal clique enumeration. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2009, 69, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Min, G.; Pei, Z.; Park, D.S.; Yang, L.T. K-clique Communities Detection in Social Networks based on Formal Concept Analysis. IEEE Syst. J. 2017, 11, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Park, D.S.; Min, G.; Jeong, Y.S.; Park, J.H. K-clique Mining in Dynamic Social Networks based on Triadic Formal Concept Analysis. Neurocomputing 2016, 209, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baralis, E.; Cagliero, L.; Cerquitelli, T.; D’Elia, V.; Garza, P. Expressive generalized itemsets. Inform. Sci. 2014, 278, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagliero, L.; Cerquitelli, T.; Garza, P.; Grimaudo, L. Misleading generalized itemset discovery. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 1400–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calders, T.; Dexters, N.; Gillis, J.J.M.; Goethals, B. Mining frequent itemsets in a stream. Inform. Syst. 2014, 39, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrouni, T.; Ben Yahia, S.; Mephu Nguifo, E. Sweeping the disjunctive search space towards mining new exact concise representations of frequent itemsets. Data Knowledge Eng. 2009, 68, 1091–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.; Imielinski, T.; Swami, A. Mining association rules between sets of items in large databases. In Proceedings of the 1993 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Washington, DC, USA, 25–28 May 1993; pp. 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Cheng, H.; Xin, D.; Yan, X. Frequent pattern mining: Current status and future directions. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2007, 15, 55–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib, T.F. An efficient algorithm for mining frequent maximal and closed itemsets. Int. J. Hybrid Intell. Syst. 2009, 6, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grahne, G.; Zhu, J.F. Fast Algorithms for Frequent Itemset Mining Using FP-Trees. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2005, 17, 1347–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, M.J.; Hsiao, C.J. Efficient algorithms for mining closed itemsets and their lattice structure. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2005, 17, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.; Hong, T.P.; Le, B. A lattice-based approach for mining most generalization association rules. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2013, 45, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.; Coenen, F.; Le, B. A new method for mining Frequent Weighted Itemsets based on WIT-trees. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, V.S.; Shie, B.E.; Wu, C.W.; Yu, P.S. Efficient Algorithms for Mining High Utility Itemsets from Transactional Databases. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2013, 25, 1772–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Ruan, D.; Meng, D.; Liu, Z. Formal concept analysis based on the topology for attributes of a formal context. Inform. Sci. 2013, 236, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syau, Y.-R.; Lin, E.-B. Neighborhood systems and covering approximation spaces. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2014, 66, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Gao, Y.; Pei, Z. On covering rough sets. In Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology, Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence; Yao, J.T., Lingras, P., Wu, W.Z., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 4481, pp. 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W. Relationship between generalized rough sets based on binary relation and covering. Inform. Sci. 2009, 179, 210–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Pei, Z.; Park, D.S.; Yang, L.T.; Jeong, Y.S.; Park, J.H. Iceberg Clique Queries in Large Graphs. Neurocomputing 2017, 256, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meo, P.D.; Musial-Gabrys, K.; Rosaci, D.; Sarne, G.M.; Aroyo, L. Using Centrality Measures to Predict Helpfulness-Based Reputation in Trust Networks. ACM Trans. Int. Technol. 2017, 17, 8:1–8:20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbeck, J.; Parsia, B.; Hendler, J. Trust networks on the semantic web. In Cooperative Information Agents VII; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 238–249. [Google Scholar]
- Jamali, M.; Abolhassani, H. Different aspects of social network analysis. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence (WI 2006), Hong Kong, China, 18–22 December 2006; pp. 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A.; Mahdian, M.; Reeves, D.M.; Pennock, D.M.; Fugger, R. Mechanism Design on Trust Networks. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Web and Internet Economics, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–14 December 2007; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 257–268. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, C.; Yang, L.T.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, L.; Li, P. An Incremental CFS Algorithm for Clustering Large Data in Industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; He, Y. Collaborative Filtering Recommendation Algorithm Based on Users of Maximum Similar Clique. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Information Science and Cloud Computing Companion, Guangzhou, China, 7–8 December 2013; pp. 852–857. [Google Scholar]
- He, T.; Chan, K.C.C. Evolutionary Graph Clustering for Protein Complex Identification. IEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2016, PP, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Dataset of Collaborations between Scientists. Available online: http://www-personal.umich.edu/~mejn/netdata/ (accessed on 17 June 2017).
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).