Abstract
The Dombi operations of T-norm and T-conorm introduced by Dombi can have the advantage of good flexibility with the operational parameter. In existing studies, however, the Dombi operations have so far not yet been used for neutrosophic sets. To propose new aggregation operators for neutrosophic sets by the extension of the Dombi operations, this paper firstly presents the Dombi operations of single-valued neutrosophic numbers (SVNNs) based on the operations of the Dombi T-norm and T-conorm, and then proposes the single-valued neutrosophic Dombi weighted arithmetic average (SVNDWAA) operator and the single-valued neutrosophic Dombi weighted geometric average (SVNDWGA) operator to deal with the aggregation of SVNNs and investigates their properties. Because the SVNDWAA and SVNDWGA operators have the advantage of good flexibility with the operational parameter, we develop a multiple attribute decision-making (MADM) method based on the SVNWAA or SVNWGA operator under a SVNN environment. Finally, an illustrative example about the selection problem of investment alternatives is given to demonstrate the application and feasibility of the developed approach.
1. Introduction
In 1965, Zadeh [1] introduced a membership function between 0 and 1 instead of traditional crisp value of 0 and 1 and defined the fuzzy set (FS). Fuzzy theory is an important and interesting research topic in decision-making theory and science. However, FS is characterized only by its membership function between 0 and 1, but not a non-membership function. To overcome the insufficient of FS, Atanassov [2] introduced the concept of an intuitionistic fuzzy set (IFS), which is characterized by its membership function and non-membership function between 0 and 1. As a further generalization of an IFS, Atanassov and Gargov [3] further introduced the concept of an interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy set (IVIFS), which is characterized by its interval membership function and interval non-membership function in the unit interval [0, 1]. Because IFSs and IVIFSs cannot represent indeterminate and inconsistent information, Smarandache [4] introduced a neutrosophic set (NS) from a philosophical point of view to express indeterminate and inconsistent information. In a NS A, its truth, falsity, and indeterminacy membership functions TA(x), IA(x) and FA(x) are represented independently, which lie in real standard or nonstandard subsets of ]−0, 1+[, i.e., TA(x): X → ]−0, 1+[, IA(x): X → ]−0, 1+[, and FA(x): X → ]−0, 1+[. Thus, the nonstandard interval ]−0, 1+[ may result in the difficulty of actual applications. Based on the real standard interval [0, 1], therefore, the concepts of a single-valued neutrosophic set (SVNS) [5] and an interval neutrosophic set (INS) [6] was presented as subclasses of NS to be easily used for actual applications, and then Ye [7] introduced a simplified neutrosophic set (SNS), including the concepts of SVNS and INS, which are the extension of IFS and IVIFS. Obviously, SNS is a subclass of NS, while SVNS and INS are subclasses of SNS. As mentioned in the literature [4,5,6,7], NS is the generalization of FS, IFS, and IVIFS. Thereby, Figure 1 shows the flow chart extended from FS to NS (SNS, SVNS, INS).
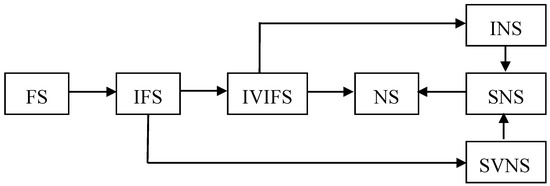
Figure 1.
Flow chart extended from fuzzy set (FS) to neutrosophic set (NS) (simplified neutrosophic set (SNS), single-valued neutrosophic set (SVNS), interval neutrosophic set (INS)). IFS: intuitionistic fuzzy set; IVIFS: interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy set.
On the other hand, some researchers also introduced other fuzzy extensions, such as fuzzy soft sets, hesitant FSs, and hesitant fuzzy soft sets (see [8,9] for detail).
However, SNS (SVNS and INS) is very suitable for the expression of incomplete, indeterminate, and inconsistent information in actual applications. Recently, SNSs (INSs, and SVNSs) have been widely applied in many areas [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28], such as decision-making, image processing, medical diagnosis, fault diagnosis, and clustering analysis. Especially, many researchers [7,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36] have developed various aggregation operators, like simplified neutrosophic weighted aggregation operators, simplified neutrosophic prioritized aggregation operators, single-valued neutrosophic normalized weighted Bonferroni mean operators, generalized neutrosophic Hamacher aggregation operators, generalized weighted aggregation operators, interval neutrosophic prioritized ordered weighted average operators, interval neutrosophic Choquet integral operators, interval neutrosophic exponential weighted aggregation operators, and so on, and applied them to decision-making problems with SNS/SVNS/INS information. Obviously, the aggregation operators give us powerful tools to deal with the aggregation of simplified (single-valued and interval) neutrosophic information in the decision making process.
In 1982, Dombi [37] developed the operations of the Dombi T-norm and T-conorm, which show the advantage of good flexibility with the operational parameter. Hence, Liu et al. [38] extended the Dombi operations to IFSs and proposed some intuitionistic fuzzy Dombi Bonferroni mean operators and applied them to multiple attribute group decision-making (MAGDM) problems with intuitionistic fuzzy information. From the existing studies, we can see that the Dombi operations are not extended to neutrosophic sets so far. To develop new aggregation operators for NSs based on the extension of the Dombi operations, the main purposes of this study are (1) to present some Dombi operations of single-valued neutrosophic numbers (SVNNs) (basic elements in SVNS), (2) to propose a single-valued neutrosophic Dombi weighted arithmetic average (SVNDWAA) operator and a single-valued neutrosophic Dombi weighted geometric average (SVNDWGA) operator for the aggregation of SVNN information and to investigate their properties, and (3) to develop a decision-making approach based on the SVNDWAA and SVNDWGA operators for solving multiple attribute decision-making (MADM) problems with SVNN information.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 briefly describes some concepts of SVNSs to be used for the study. Section 3 presents some new Dombi operations of SVNNs. In Section 4, we propose the SVNDWAA and SVNDWGA operators and investigate their properties. Section 5 develops a MADM approach based on the SVNDWAA and SVNDWGA operators. An illustrative example is presented in Section 6. Section 7 gives conclusions and future research directions.
2. Some Concepts of SVNSs
As the extension of IFSs, Wang et al. [5] introduced the definition of a SVNS as a subclass of NS proposed by Smarandache [4] to easily apply in real scientific and engineering areas.
Definition 1.
[5] Let X be a universal set. A SVNS N in X is described by a truth-membership function tN(x), an indeterminacy-membership function uN(x), and a falsity-membership function vN(x). Then, a SVNS N can be denoted as the following form:
where the functions tN(x), uN(x), vN(x) [0, 1] satisfy the condition 0 ≤ tN(x) + uN(x) + vN(x) ≤ 3 for x X.
For convenient expression, a basic element <x, tN(x), uN(x), vN(x)> in N is denoted by s = <t, u, v>, which is called a SVNN.
For any SVNN s = <t, u, v>, its score and accuracy functions [29] can be introduced, respectively, as follows:
According to the two functions E(s) and H(s), the comparison and ranking of two SVNNs are introduced by the following definition [29].
Definition 2.
[29] Let s1 = <t1, u1, v1> and s2 = <t2, u2, v2> be two SVNNs. Then the ranking method for s1 and s2 is defined as follows:
- (1)
- If E(s1) > E(s2), then s1 s2,
- (2)
- If E(s1) = E(s2) and H(s1) > H(s2), then s1 s2,
- (3)
- If E(s1) = E(s2) and H(s1) = H(s2), then s1 = s2.
3. Some Single-Valued Neutrosophic Dombi Operations
Definition 3.
[37]. Let p and q be any two real numbers. Then, the Dombi T-norm and T-conorm between p and q are defined as follows:
where ρ ≥ 1 and (p, q) [0, 1] × [0, 1].
According to the Dombi T-norm and T-conorm, we define the Dombi operations of SVNNs.
Definition 4.
Let s1 = <t1, u1, v1> and s2 = <t2, u2, v2> be two SVNNs, ρ ≥ 1, and λ > 0. Then, the Dombi T-norm and T-conorm operations of SVNNs are defined below:
4. Dombi Weighted Aggregation Operators of SVNNs
Based on the Dombi operations of SVNNs in Definition 4, we propose the two Dombi weighted aggregation operators: the SVNDWAA and SVNDWGA operators, and then investigate their properties.
Definition 5.
Let sj = <tj, uj, vj> (j = 1, 2, …, n) be a collection of SVNNs and w = (w1, w2, …, wn) be the weight vector for sj with wj [0, 1] and . Then, the SVNDWAA and SVNDWGA operators are defined, respectively, as follows:
Theorem 1.
Let sj = <tj, uj, vj> (j = 1, 2, …, n) be a collection of SVNNs and w = (w1, w2, …, wn) be the weight vector for sj with wj [0, 1] and . Then, the aggregated value of the SVNDWAA operator is still a SVNN, which is calculated by the following formula:
By the mathematical induction, we can prove Theorem 1.
Proof.
If n = 2, based on the Dombi operations of SVNNs in Definition 4 we can obtain the following result:
If n = k, based on Equation (7), we have the following equation:
If n = k + 1, there is the following result:
Hence, Theorem 1 is true for n = k + 1. Thus, Equation (7) holds for all n. □
Then, the SVNDWAA operator contains the following properties:
- (1)
- Reducibility: When w = (1/n, 1/n, …, 1/n), it is obvious that there exists
- (2)
- Idempotency: Let all the SVNNs be sj = <tj, uj, vj> = s (j = 1, 2, …, n). Then, SVNDWAA(s1, s2, …, sn) = s.
- (3)
- Commutativity: Let the SVNS (s1’, s2’, …, sn’) be any permutation of (s1, s2, …, sn). Then, there is SVNDWAA(s1’, s2’, …, sn’) = SVNDWAA(s1, s2, …, sn).
- (4)
- Boundedness: Let smin = min(s1, s2, …, sn) and smax = max(s1, s2, …, sn). Then, smin ≤ SVNDWAA(s1, s2, …, sn) ≤ smax.
Proof.
(1) Based on Equation (7), the property is obvious.
(2) Since sj = <tj, uj, vj> = s (j = 1, 2, …, n). Then, by using Equation (7) we can obtain the following result:
Hence, SVNDWAA(s1, s2, …, sn) = s holds.
(3) The property is obvious.
(4) Let smin = min(s1, s2, …, sn) = <t−, u−, v−> and smax = max(s1, s2, …, sn) = <t+, u+, v+>. Then, we have , , , , , and . Thus, there are the following inequalities:
Hence, smin ≤ SVNDWAA(s1, s2, …, sn) ≤ smax holds. □
Theorem 2.
Let sj = <tj, uj, vj> (j = 1, 2, …, n) be a collection of SVNNs and w = (w1, w2, …, wn) be the weight vector for sj with wj [0, 1] and . Then, the aggregated value of the SVNDWGA operator is still a SVNN, which is calculated by the following formula:
The proof of Theorem 2 is the same as that of Theorem 1. Thus, it is omitted here.
Obviously, the SVNDWGA operator also contains the following properties:
- (1)
- Reducibility: When the weight vector is w = (1/n, 1/n, …, 1/n), it is obvious that there exists the following result:
- (2)
- Idempotency: Let all the SVNNs be sj = <tj, uj, vj> = s (j = 1, 2, …, n). Then, SVNDWGA(s1, s2, …, sn) = s.
- (3)
- Commutativity: Let the SVNS (s1’, s2’, …, sn’) be any permutation of (s1, s2, …, sn). Then, there is SVNDWGA(s1’, s2’, …, sn’) = SVNDWGA(s1, s2, …, sn).
- (4)
- Boundedness: Let smin = min(s1, s2, …, sn) and smax = max(s1, s2, …, sn). Then, smin ≤ SVNDWGA(s1, s2, …, sn) ≤ smax.
The proof processes of these properties are the same as the ones of the properties for the SVNDWAA operator. Hence, they are not repeated here.
5. MADM Method Using the SVNDWAA Operator or the SVNDWGA Operator
In this section, we propose a MADM method by using the SVNDWAA operator or the SVNDWGA operator to handle MADM problems with SVNN information.
For a MADM problem with SVNN information, let S = {S1, S2, …, Sm} be a discrete set of alternatives and G = {G1, G2, …, Gn} be a discrete set of attributes. Assume that the weight vector of the attributes is given as w = (w1, w2, …, wn) such that wj [0, 1] and . If the decision makers are required to provide their suitability evaluation about the alternative Si (i = 1, 2, …, m) under the attribute Gj (j = 1, 2, …, n) by the SVNN sij = <tij, uij, vij> (i = 1, 2, …, m; j = 1, 2, …, n), then, we can elicit a SVNN decision matrix D = (sij)m×n.
Thus, we utilize the SVNDWAA operator or the SVNDWGA operator to develop a handling approach for MADM problems with SVNN information, which can be described by the following decision steps:
Step 1. Derive the collective SVNN si (i = 1, 2, …, m) for the alternative Si (i = 1, 2, …, m) by using the SVNDWAA operator:
or by using the SVNDWGA operator:
where w = (w1, w2, …, wn) is the weight vector such that wj [0, 1] and .
Step 2. Calculate the score values of E(si) (the accuracy degrees of H(si) if necessary) of the collective SVNN si (i = 1, 2, …, m) by using Equations (1) and (2).
Step 3. Rank the alternatives and select the best one(s).
Step 4. End.
6. Illustrative Example
An illustrative example about investment alternatives for a MADM problem adapted from Ye [10] is used for the applications of the proposed decision-making method under a SVNN environment. An investment company wants to invest a sum of money in the best option. To invest the money, a panel provides four possible alternatives: (1) S1 is a car company; (2) S2 is a food company; (3) S3 is a computer company; (4) S4 is an arms company. The investment company must take a decision corresponding to the requirements of the three attributes: (1) G1 is the risk; (2) G2 is the growth; (3) G3 is the environmental impact. The suitability evaluations of the alternative Si (i = 1, 2, 3, 4) corresponding to the three attributes of Gj (j = 1, 2, 3) are given by some decision makers or experts and expressed by the form of SVNNs. Thus, when the four possible alternatives corresponding to the above three attributes are evaluated by the decision makers, we can give the single-valued neutrosophic decision matrix D(sij)m×n, where sij = <tij, uij, vij> (i = 1, 2, 3, 4; j = 1, 2, 3) is SVNN, as follows:
The weight vector of the three attributes is given as w = (0.35, 0.25, 0.4).
Then, we utilize the SVNDWAA operator or the SVNDWGA operator to handle the MADM problem with SVNN information.
In this decision-making problem, the MADM steps based on the SVNDWAA operator can be described as follows:
Step 1. Derive the collective SVNNs of si for the alternative Si (i = 1, 2, 3, 4) by using Equation (9) for ρ = 1 as follows:
s1 = <0.6667, 0.2000, 0.3571>, s2 = <0.5652, 0.1250, 0.2857>, s3 = <0.4444, 0.2308, 0.4000>, and s4 = <0.6418, 0, 0.1905>.
Step 2. Calculate the score values of E(si) of the collective SVNN si (i = 1, 2, 3, 4) for the alternatives Si (i = 1, 2, 3, 4) by using Equation (1) as the following results:
E(s1) = 0.7032, E(s2) = 0.7182, E(s3) = 0.6046, and E(s4) = 0.8171.
Step 3. Based on the obtained score values, the ranking order of the alternatives is S4 S2 S1 S3 and the best one is S4.
Or we use the SVNDWGA operator for the MADM problem, which can be described as the following steps:
Step 1’. Derive the collective SVNNs of si for the alternative Si (i = 1, 2, 3, 4) by using Equation (10) for ρ = 1 as follows:
s1 = <0.5000, 0.2000, 0.3966>, s2 = <0.5556, 0.1429, 0.6364>, s3 = <0.4054, 0.2432, 0.6500>, and s4 = <0.6316, 0.1661, 0.6298>.
Step 2’. Calculate the score values of E(si) of the collective SVNN si (i = 1, 2, 3, 4) for the alternatives Si (i = 1, 2, 3, 4) by using Equation (1) as the following results:
E(s1) = 0.6345, E(s2) = 0.5921, E(s3) = 0.5041, and E(s4) = 0.6119.
Step 3’. Based on the obtained score values, the ranking order of the alternatives is S1 S4 S2 S3 and the best one is S1.
In order to ascertain the effects on the ranking alternatives by changing parameters of ρ [1, 10] in the SVNDWAA and SVNDWGA operators, all the results are depicted in Table 1 and Table 2.

Table 1.
Ranking results for different operational parameters of the single-valued neutrosophic Dombi weighted arithmetic average (SVNDWAA) operator.

Table 2.
Ranking results for different operational parameters of the single-valued neutrosophic Dombi weighted geometric average (SVNDWGA) operator.
From Table 1 and Table 2, we see that the ranking orders based on the SVNDWAA and SVNDWGA operators indicate their obvious difference due to using different aggregation operators. Then, the different operational parameters of ρ can change the ranking orders corresponding to the SVNDWGA operator, which is more sensitive to ρ in this decision-making problem; while the different operation parameters of ρ show the same ranking orders corresponding to the SVNDWAA operator, which is not sensitive to ρ in this decision-making problem.
Compared with existing related method [38], the decision-making method developed in this paper can deal with single-valued neutrosophic or intuitionistic fuzzy MADM problems, while existing method [38] cannot handle single-valued neutrosophic MADM problems.
However, this MADM method based on the SVNDWAA and SVNDWGA operators indicates the advantage of its flexibility in actual applications. Therefore, the developed MADM method provides a new effective way for decision makers to handle single-valued neutrosophic MADM problems.
7. Conclusions
This paper presented some Dombi operations of SVNNs based on the Dombi T-norm and T-conorm operations, and then proposed the SVNDWAA and SVNDWGA operators and investigated their properties. Further, we developed to a MADM method by using the SVNDWAA operator or the SVNDWGA operator to deal with MADM problems under a SVNN environment, in which attribute values with respect to alternatives are evaluated by the form of SVNNs and the attribute weights are known information. We utilized the SVNDWAA operator or the SVNDWGA operator and the score (accuracy) function to rank the alternatives and to determine the best one(s) according to the score (accuracy) values in the different operational parameters. Finally, an illustrative example about the decision-making problem of investment alternatives was provided to demonstrate the application and feasibility of the developed approach. The decision-making results of the illustrative example demonstrated the main highlights of the proposed MADM method: (1) different operational parameters of ρ in the SVNDWGA and SVNDWAA operators can affect the ranking orders; (2) the decision-making process is more flexible corresponding to some operational parameter ρ specified by decision makers’ preference and/or actual requirements; (3) the SVNDWGA and SVNDWAA operators provide new aggregation methods of SVNNs to solve MADM problems under an SVNN environment.
In the future work, we shall further develop new Dombi aggregation operators for simplified neutrosophic sets (including SVNSs and INSs) and apply them to solve practical applications in these areas like group decision-making in [39,40], expert system, information fusion system, fault diagnosis, medical diagnosis, and so on.
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 71471172).
Author Contributions
J. Ye proposed the single-valued neutrosophic Dombi weighted arithmetic average (SVNDWAA) and single-valued neutrosophic Dombi weighted geometric average (SVNDWGA) operators, and their decision-making method; J. Chen performed the calculation and analysis of the illustrative example; J. Chen and J. Ye wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy Sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassov, K. Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1986, 20, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassov, K.; Gargov, G. Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1989, 31, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smarandache, F. Neutrosophy: Neutrosophic Probability, Set, and Logic: Analytic Synthesis & Synthetic Analysis; American Research Press: Rehoboth, DE, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Smarandache, F.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Sunderraman, R. Single valued neutrosophic sets. Multisp. Multistruct. 2010, 4, 410–413. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Smarandache, F.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Sunderraman, R. Interval Neutrosophic Sets and Logic: Theory and Applications in Computing; Hexis: Phoenix, AZ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J. A multicriteria decision-making method using aggregation operators for simplified neutrosophic sets. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 26, 2459–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustince, H.; Barrenechea, E.; Fernandez, J.; Pagola, M.; Montero, J. The origin of fuzzy extensions. In Springer Handbook of Computational Intelligence; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 89–112. [Google Scholar]
- Alcantud, J.C.R. Some formal relationships among soft sets, fuzzy sets, and their extensions. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2016, 68, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Multicriteria decision-making method using the correlation coefficient under single-value neutrosophic environment. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2013, 42, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, P.; Samant, S.K. On similarity and entropy of neutrosophic sets. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 26, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.J.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, X.H. An outranking approach for multi-criteria decision-making problems with simplified neutrosophic sets. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 25, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Similarity measures between interval neutrosophic sets and their applications in multicriteria decision making. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 26, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Single valued neutrosophic cross-entropy for multicriteria decision making problems. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sengur, A.; Ye, J. A novel image thresholding algorithm based on neutrosophic similarity score. Measurement 2014, 58, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Multiple attribute decision-making method based on the possibility degree ranking method and ordered weighted aggregation operators of interval neutrosophic numbers. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 28, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Improved cosine similarity measures of simplified neutrosophic sets for medical diagnoses. Artif. Intell. Med. 2015, 63, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, R.; Kucuk, A. Subsethood measure for single valued neutrosophic sets. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 29, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Ji, P.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.H. An improved weighted correlation coefficient based on integrated weight for interval neutrosophic sets and its application in multi-criteria decision-making problems. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2015, 8, 1027–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Interval neutrosophic multiple attribute decision-making method with credibility information. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 18, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Fu, J. Multi-period medical diagnosis method using a single valued neutrosophic similarity measure based on tangent function. Comput. Methods Program Biomed. 2015, 123, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, P.; Pramanik, S.; Giri, B.C. TOPSIS method for multi-attribute group decision-making under single-valued neutrosophic environment. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Chen, X.H. An outranking approach for multi-criteria decision-making problems with interval-valued neutrosophic sets. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.J.; Wang, J.Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, X.H. Simplified neutrosophic sets and their applications in multi-criteria group decision-making problems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2016, 47, 2342–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.P.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.Q.; Chen, X.H. Multi-criteria decision-making method based on a cross-entropy with interval neutrosophic sets. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2016, 47, 3598–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Projection and bidirectional projection measures of single valued neutrosophic sets and their decision-making method for mechanical design schemes. J. Exp. Theor. Artif. Intell. 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Single-valued neutrosophic clustering algorithms based on similarity measures. J. Classif. 2017, 34, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Single valued neutrosophic similarity measures based on cotangent function and their application in the fault diagnosis of steam turbine. Soft Comput. 2017, 21, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Chen, X.H. Interval neutrosophic sets and their application in multicriteria decision making problems. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 645953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.D.; Wang, Y.M. Multiple attribute decision making method based on single-valued neutrosophic normalized weighted Bonferroni mean. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 25, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.D.; Chu, Y.C.; Li, Y.W.; Chen, Y.B. Some generalized neutrosophic number Hamacher aggregation operators and their application to group decision making. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 16, 242–255. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, A.W.; Du, J.G.; Guan, H.J. Interval valued neutrosophic sets and multi-attribute decision-making based on generalized weighted aggregation operator. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 29, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.X.; Yang, H.X.; Wu, J.Z.; Yao, O.Y. Interval neutrosophic numbers Choquet integral operator for multi-criteria decision making. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 28, 2443–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.D.; Wang, Y.M. Interval neutrosophic prioritized OWA operator and its application to multiple attribute decision making. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2016, 29, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.H.; Wang, J.Q.; Peng, J.J.; Chen, X.H. Cross-entropy and prioritized aggregation operator with simplified neutrosophic sets and their application in multi-criteria decision-making problems. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 18, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Exponential operations and aggregation operators of interval neutrosophic sets and their decision making methods. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dombi, J. A general class of fuzzy operators, the demorgan class of fuzzy operators and fuzziness measures induced by fuzzy operators. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1982, 8, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.D.; Liu, J.L.; Chen, S.M. Some intuitionistic fuzzy Dombi Bonferroni mean operators and their application to multi-attribute group decision making. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2017, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio, C.D.; Fenza, G.; Loia, V.; Orciuoli, F.; Herrera-Viedma, E. A framework for context-aware heterogeneous group decision making in business processes. Knowl-Based Syst. 2016, 102, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio, C.D.; Fenza, G.; Loia, V.; Orciuoli, F.; Herrera-Viedma, E. A context-aware fuzzy linguistic consensus model supporting innovation processes. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 1685–1692. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).