Social Content Recommendation Based on Spatial-Temporal Aware Diffusion Modeling in Social Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background and Related Literature Review
3. Social Content Recommendations Based on Spatial-Temporal Aware Diffusion in Social Networks
3.1. Multicriteria-Based Social Ties Relationship (Influence) Modeling
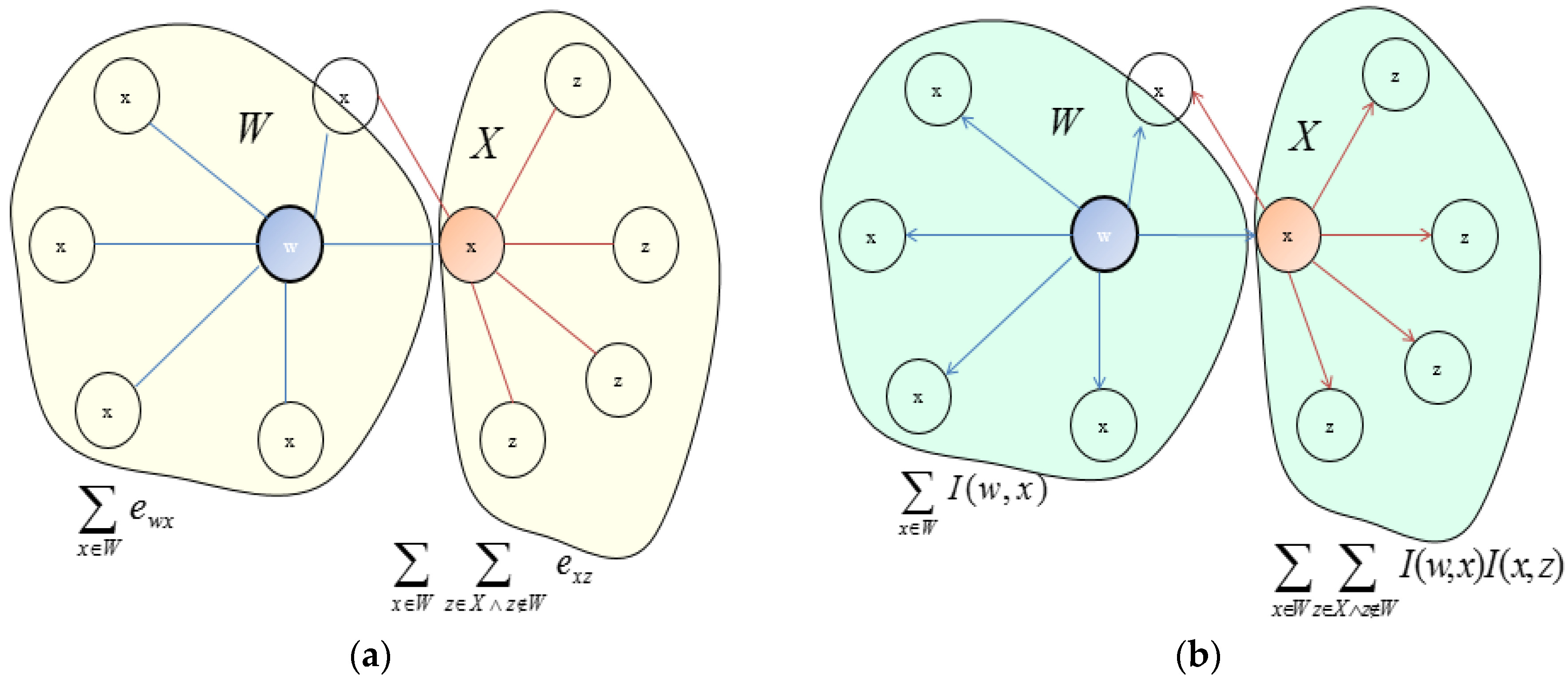
3.2. Ranking Algorithm for the Selection of the Most Influential Nodes to Initialize the Diffusion Process in an OSN
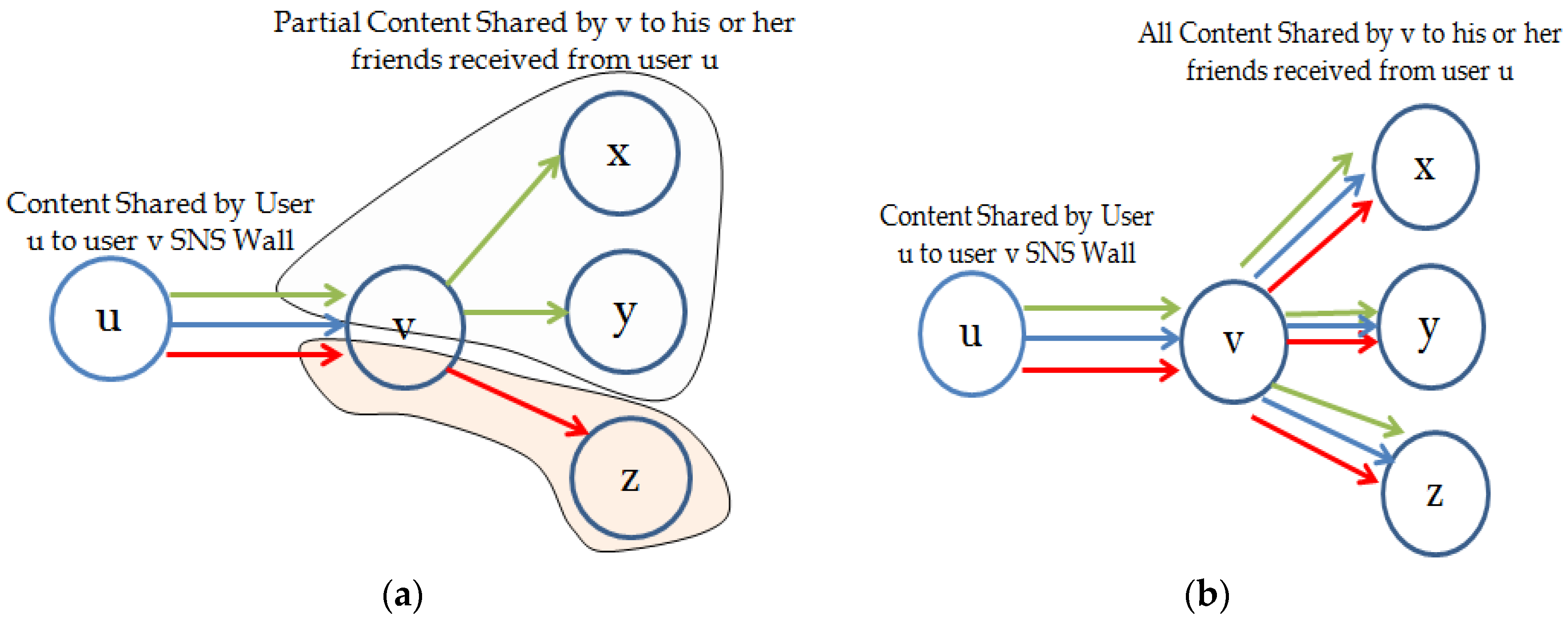
3.3. Temporal Aware Probabilistic Diffusion-Based Social Content Recommendations in OSNs
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
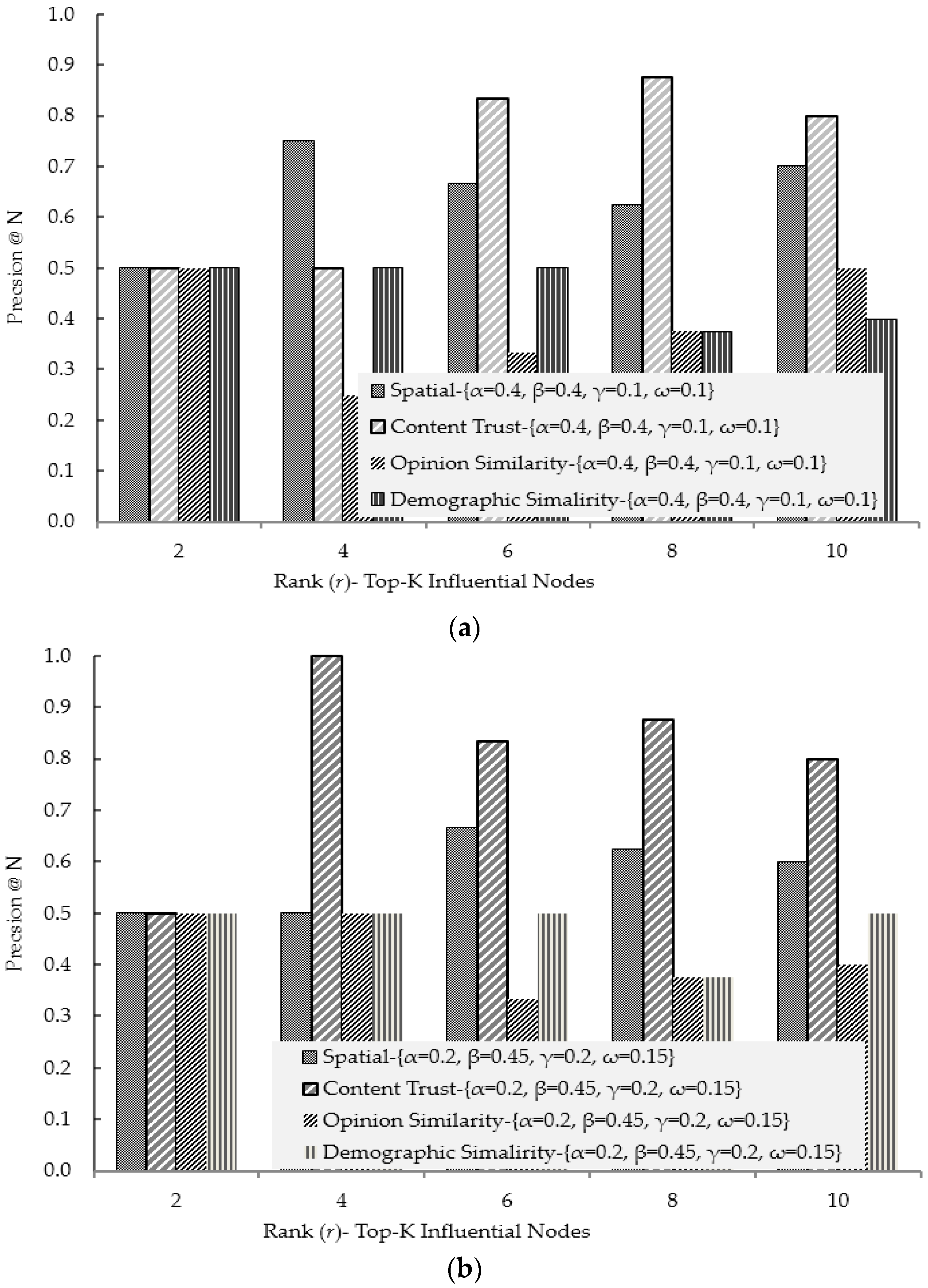
4.1. Experimental Results for Social Ties Relationship (Influence) Factors
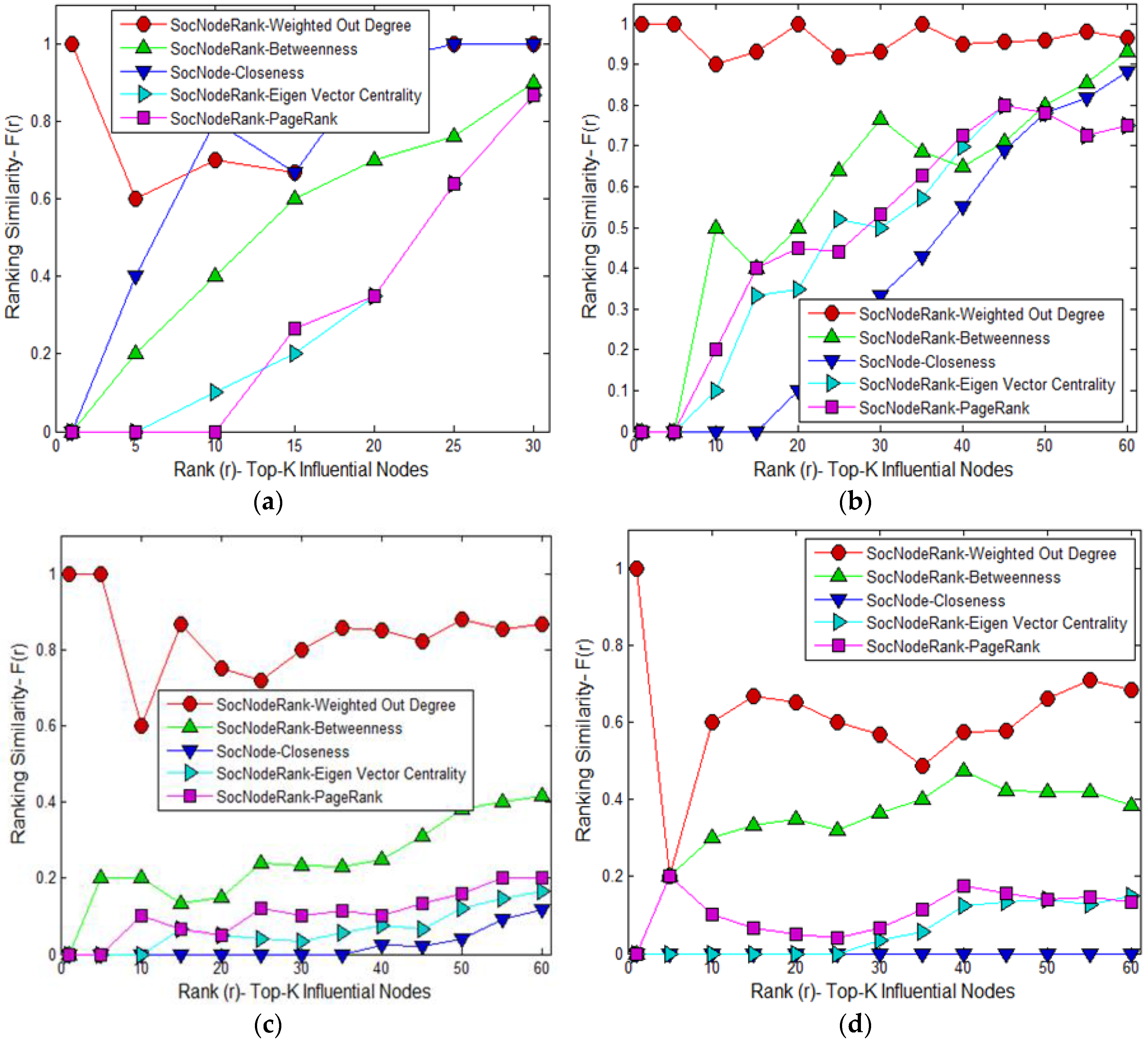
4.2. Results of Proposed Social Node Ranking Algorithm (Selection of Highest Influential Nodes)
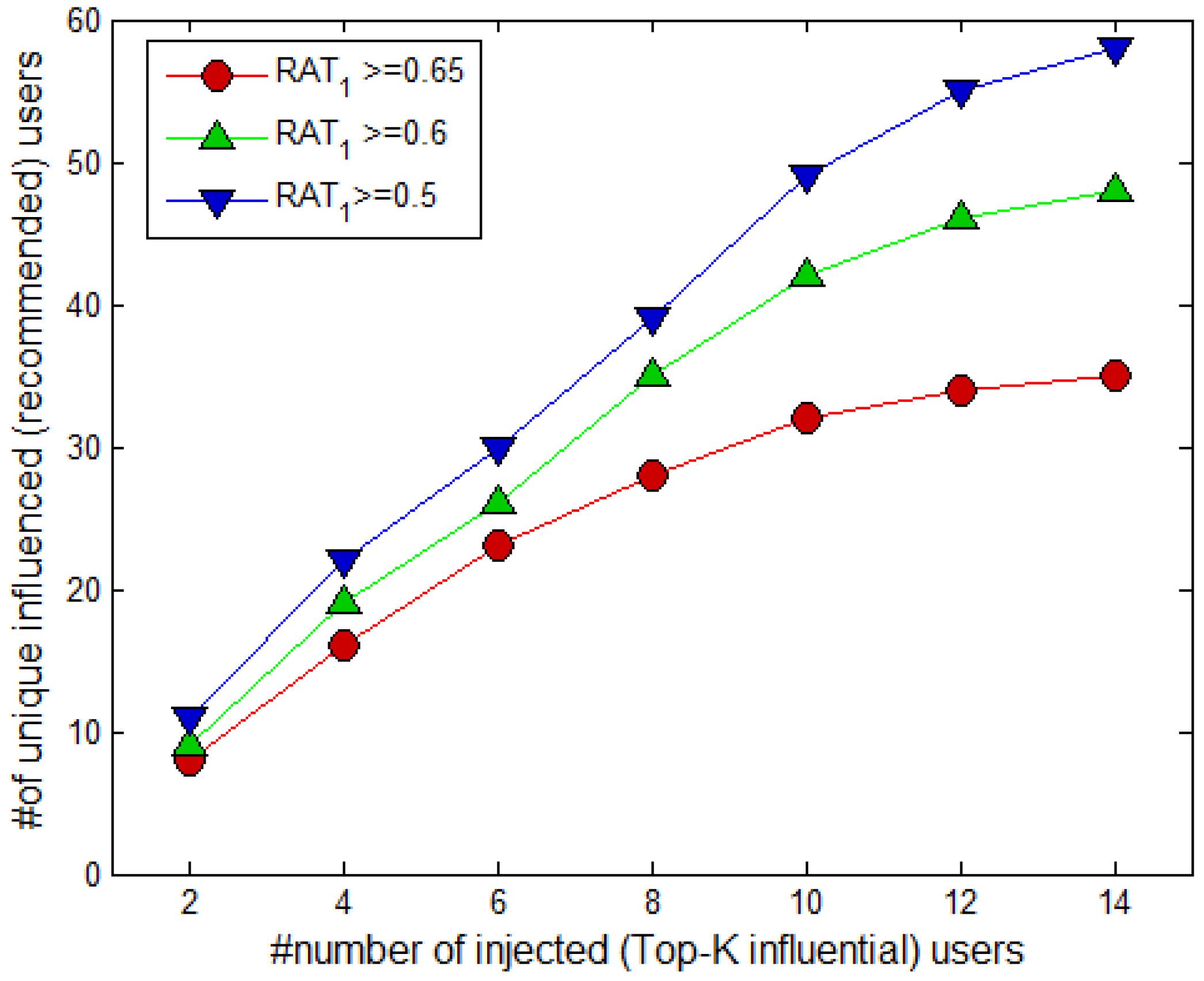
4.3. Results of the Temporal Aware Probabilistic Diffusion-Based Social Content Recommendations in OSNs
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ricci, F.; Rokach, L.; Shapira, B. Introduction to Recommender Systems Handbook; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, F.; Sarwar, G.; Lee, S. N-screen aware multicriteria hybrid recommender system using weight based subspace clustering. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 679849. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.; Yu, Z. Cross-domain community detection in heterogeneous social networks. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2014, 18, 369–383. [Google Scholar]
- Adamic, L.A.; Glance, N. The political blogosphere and the 2004 US election: Divided they blog. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Link Discovery, Chicago, IL, USA, 21–24 August 2005; pp. 36–43.
- Doo, M. Spatial and Social Diffusion of Information and Influence: Models and Algorithms; Georgia Institute of Technology: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cowan, R.; Jonard, N. Network structure and the diffusion of knowledge. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2004, 28, 1557–1575. [Google Scholar]
- Dolde, W.; Tirtiroglu, D. Temporal and spatial information diffusion in real estate price changes and variances. Real Estate Econ. 1997, 25, 539–565. [Google Scholar]
- Ugander, J.; Karrer, B.; Backstrom, L.; Marlow, C. The anatomy of the Facebook Social Graph. 2011. arXiv:1111.4503. arXiv Preprint. Available online: http://arxiv.org/pdf/1111.4503v1.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2016).
- Koroleva, K.; Krasnova, H.; Günther, O. ‘STOP SPAMMING ME!’—Exploring Information Overload on Facebook. In Proceedings of the 16th Americas Conference on Information Systems, Lima, Peru, 12–15 August 2010; p. 447.
- Goldenberg, J.; Libai, B.; Muller, E. Talk of the network: A complex systems look at the underlying process of word-of-mouth. Mark. Lett. 2001, 12, 211–223. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, B.J.; Zhang, M.; Sobel, K.; Chowdury, A. Twitter power: Tweets as electronic word of mouth. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 2169–2188. [Google Scholar]
- Oxford dictionaries. Available online: http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english (accessed on 8 June 2016).
- Travers, J.; Milgram, S. An experimental study of the small world problem. Sociometry 1969, 32, 425–443. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, A. Six Degrees of Separation, Twitter Style. 1969, Volume 5. Available online: http://www.sysomos.com/insidetwitter/sixdegrees/ (accessed on 8 June 2016).
- Guille, A.; Hacid, H.; Favre, C.; Zighed, D.A. Information diffusion in online social networks: A survey. ACM SIGMOD Rec. 2013, 42, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Teo, T.S. Demographic and motivation variables associated with Internet usage activities. Internet Res. 2001, 11, 125–137. [Google Scholar]
- Broecheler, M.; Shakarian, P.; Subrahmanian, V.S. A scalable framework for modeling competitive diffusion in social networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Second International Conference on Social Computing (SocialCom), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 20–22 August 2010; pp. 295–302.
- Simmel, G. The Metropolis and Mental Life, 1903. Available online: https://books.google.com/books?hl=zh-CN&lr=&id=-mk5rOctXtEC&oi=fnd&pg=PA1999-IA2&dq=The+Metropolis+and+Mental+Life&ots=J_cSXCMc01&sig=qeTE6ihpClC6jjhu5ZkHswrlZ5s#v=onepage&q=The%20Metropolis%20and%20Mental%20Life&f=false (accessed on 8 June 2016).
- Moreno, J.L. Who Shall Survive; ASGPP: Washington, DC, USA, 1934; Volume 58. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, J.A. Class and committees in a Norwegian island parish. Hum. Relat. 1954, 7, 39–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, N.B. Social network sites: Definition, history, and scholarship. J. Comput. Med. Commun. 2007, 13, 210–230. [Google Scholar]
- Garrido, A. Symmetry in complex networks. Symmetry 2011, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, K.S.K.; Piraveenan, M.; Hossain, L. Topology of online social networks. In Encyclopedia of Social Network Analysis and Mining; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 2191–2202. [Google Scholar]
- Haythornthwaite, C. Social networks and Internet connectivity effects. Inf. Community Soc. 2005, 8, 125–147. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, P.T.; Shneiderman, B.; Fleischmann, K.R.; Preece, J.; Qu, Y.; Wu, P.F. Community response grids: E-government, social networks, and effective emergency management. Telecommun. Policy 2007, 31, 592–604. [Google Scholar]
- Zappen, J.P.; Harrison, T.M.; Watson, D. A new paradigm for designing e-government: Web 2.0 and experience design. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Government Research, Montreal, QC, Canada, 18–21 May 2008.
- Ho, J.Y.; Dempsey, M. Viral marketing: Motivations to forward online content. J. Bus. Res. 2010, 63, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, M.; Domingos, P. Mining knowledge-sharing sites for viral marketing. In Proceedings of the Eighth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 23–25 July 2002; pp. 61–70.
- Pan, Y.; Cong, F.; Chen, K.; Yu, Y. Diffusion-aware personalized social update recommendation. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Hong Kong, China, 12–16 October 2013; pp. 69–76.
- Coleman, J.S.; Katz, E.; Menzel, H. Medical Innovation: A Diffusion Study; Bobbs-Merrill Co.: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Saulwick, A.; Trentelman, K. Towards a formal semantics of social influence. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2014, 71, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kasthurirathna, D.; Harre, M.; Piraveenan, M. Influence modelling using bounded rationality in social networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining, Paris, France, 25–28 August 2015; pp. 33–40.
- Katona, Z.; Zubcsek, P.P.; Sarvary, M. Network effects and personal influences: The diffusion of an online social network. J. Mark. Res. 2011, 48, 425–443. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z. Social influence analysis in large-scale networks. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data mining, Paris, France, 28 June–1 July 2009; pp. 807–816.
- Bonacich, P.; Lloyd, P. Eigenvector-like measures of centrality for asymmetric relations. Soc. Netw. 2001, 23, 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, L.C. A set of measures of centrality based on betweenness. Sociometry 1977, 40, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Piraveenan, M.; Prokopenko, M.; Hossain, L. Percolation Centrality: Quantifying Graph-Theoretic Impact of Nodes during Percolation in Networks. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, L.; Brin, S.; Motwani, R.; Winograd, T. The PageRank Citation Ranking: Bringing Order to the Web. Available online: http://ilpubs.stanford.edu:8090/422/1/1999-66.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2016).
- Brin, S.; Page, L. Reprint of: The anatomy of a large-scale hypertextual web search engine. Comput. Netw. 2012, 56, 3825–3833. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Wang, B.; Wu, B.; Zhu, C. Maximizing the spread of influence ranking in social networks. Inf. Sci. 2014, 278, 535–544. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, B.; Liu, Q.; Chen, E.; Xiong, H.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y. PageRank with Priors: An Influence Propagation Perspective. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Third International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Beijing, China, 3–9 August 2013.
- Luarn, P.; Yang, J.C.; Chiu, Y.P. The network effect on information dissemination on social network sites. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Danchin, É.; Giraldeau, L.A.; Valone, T.J.; Wagner, R.H. Public information: From nosy neighbors to cultural evolution. Science 2004, 305, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delre, S.A.; Jager, W.; Bijmolt, T.H.; Janssen, M.A. Will it spread or not? The effects of social influences and network topology on innovation diffusion. J. Product Innov. Manag. 2010, 27, 267–282. [Google Scholar]
- Kempe, D.; Kleinberg, J.; Tardos, É. Maximizing the spread of influence through a social network. In Proceedings of the Ninth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Washington, DC, USA, 24–27 August 2003; pp. 137–146.
- Kempe, D.; Kleinberg, J.; Tardos, É. Maximizing the spread of influence through a social network. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 105–147. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, A.; Lu, W.; Lakshmanan, L.V. Simpath: An efficient algorithm for influence maximization under the linear threshold model. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 11th International Conference on Data Mining, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 11–14 December 2011; pp. 211–220.
- Chen, W.; Collins, A.; Cummings, R.; Ke, T.; Liu, Z.; Rincon, D.; Yuan, Y. Influence Maximization in Social Networks When Negative Opinions May Emerge and Propagate. In Proceedings of the SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (SDM ’2011), Mesa, AZ, USA, 28–30 April 2011; Volume 11, pp. 379–390.
- Bakshy, E.; Rosenn, I.; Marlow, C.; Adamic, L. The role of social networks in information diffusion. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on World Wide Web, Lyon, France, 16—20 April 2012; pp. 519–528.
- Kim, M.; Newth, D.; Christen, P. Modeling dynamics of diffusion across heterogeneous social networks: News diffusion in social media. Entropy 2013, 15, 4215–4242. [Google Scholar]
- Kasthurirathna, D.; Piraveenan, M.; Harré, M. Influence of topology in the evolution of coordination in complex networks under information diffusion constraints. Eur. Phys. J. B 2014, 87, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, F.; Sarwar, G.; Lee, S.C.; Park, Y.K.; Moon, K.D.; Kim, J.T. Hybrid recommender system with temporal information. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications, Fukuoka, Japan, 26–29 March 2012; pp. 421–425.
- Nicosia, V.; Tang, J.; Mascolo, C.; Musolesi, M.; Russo, G.; Latora, V. Graph metrics for temporal networks. In Temporal Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 15–40. [Google Scholar]
- Holme, P.; Saramäki, J. Temporal networks. Phys. Rep. 2012, 519, 97–125. [Google Scholar]
- Barthélemy, M. Spatial networks. Phys. Rep. 2011, 499, 1–101. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Meng, X. A Location-Based Business Information Recommendation Algorithm. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 345480. [Google Scholar]
- Sinnott, R.W. Virtues of the Haversine. Sky Telesc. 1984, 68, 158. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, M.C. Calculation of distance traveled by fishing vessels using GPS positional data: A theoretical evaluation of the sources of error. Fish. Res. 2008, 89, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Borgatti, S.P. Centrality and network flow. Soc. Netw. 2005, 27, 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Nocera, A.; Ursino, D. PHIS: A system for scouting potential hubs and for favoring their “growth” in a Social Internetworking Scenario. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2012, 36, 288–299. [Google Scholar]
- Doo, M.; Liu, L. Probabilistic Diffusion of Social Influence with Incentives. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2014, 7, 387–400. [Google Scholar]
- Kurant, M.; Gjoka, M.; Wang, Y.; Almquist, Z.W.; Butts, C.T.; Markopoulou, A. Coarse-grained topology estimation via graph sampling. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM Workshop on Workshop on Online Social Networks, Helsinki, Finland, 13–17 August 2012; pp. 25–30.
- Rossi, R.; Ahmed, N. The Network Data Repository with Interactive Graph Analytics and Visualization. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-15), Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015; Volume 15, pp. 4292–4293.
- GroupLens Dataset (ml-100k). Available online: http://grouplens.org/datasets/movielens/ (accessed on 8 June 2016).
- Zachary, W.W. An information flow model for conflict and fission in small groups. J. Anthropol. Res. 1977, 33, 452–473. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, M.E. Who is the best connected scientist? A study of scientific coauthorship networks. In Complex Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 337–370. [Google Scholar]
- Knuth, D.E. The Stanford GraphBase: A Platform for Combinatorial Computing; Addison-Wesley: Reading, PA, USA, 1993; Volume 37. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M.; Saito, K. Tractable models for information diffusion in social networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Principles of Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, Berlin, Germany, 18–22 September 2006; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 259–271. [Google Scholar]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Proceedings of the Third International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; Volume 8, pp. 361–362.




| Dataset Attributes | Description/Values of Attributes |
|---|---|
| Number of users | 133 |
| Number of edges | 450 |
| Trust value between users | {0.6, 0.8, 1.0} |
| User demographics | Sex, Age |
| Minimum times same content evaluated by friends | 10 |
| Spatial Similarity | Content Trust | Opinion Similarity | Demographics Similarity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70 | 70 | 70 | 70 | 70 | 70 |
| 29 | 113 | 50 | 109 | 58 | 58 |
| 58 | 114 | 71 | 58 | 114 | 64 |
| 27 | 58 | 114 | 85 | 113 | 27 |
| 64 | 64 | 6 | 114 | 64 | 114 |
| 102 | 71 | 4 | 61 | 27 | 113 |
| 78 | 27 | 48 | 32 | 71 | 29 |
| 32 | 32 | 102 | 55 | 29 | 71 |
| 4 | 127 | 89 | 1 | 109 | 32 |
| 99 | 1 | 113 | 127 | 32 | 4 |
| Rank | Weighted Out Degree | Closeness | Betweenness | PageRank | Eign Vector Centrality | Propose SocNodeRank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 517 | 1027 | 78 | 33 | 645 | 517 |
| 2 | 151 | 492 | 150 | 78 | 1429 | 54 |
| 3 | 97 | 866 | 301 | 30 | 1430 | 516 |
| 4 | 516 | 867 | 516 | 46 | 1431 | 151 |
| 5 | 309 | 986 | 281 | 62 | 1432 | 34 |
| 6 | 34 | 450 | 46 | 216 | 1433 | 132 |
| 7 | 54 | 1182 | 151 | 294 | 33 | 1087 |
| 8 | 744 | 640 | 307 | 150 | 1434 | 133 |
| 9 | 377 | 1026 | 216 | 34 | 30 | 744 |
| 10 | 655 | 499 | 71 | 69 | 1435 | 309 |
| Rank | Weighted Out Degree | Closeness | Betweenness | PageRank | Eign Vector Centrality | Propose SocNodeRank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 855 | 1490 | 855 | 155 | 55 | 855 |
| 2 | 454 | 1405 | 55 | 963 | 155 | 1047 |
| 3 | 512 | 1397 | 1051 | 855 | 641 | 1000 |
| 4 | 387 | 1247 | 155 | 55 | 729 | 980 |
| 5 | 880 | 230 | 454 | 641 | 1051 | 524 |
| 6 | 363 | 216 | 387 | 1051 | 642 | 880 |
| 7 | 1101 | 1340 | 1479 | 1153 | 756 | 387 |
| 8 | 1000 | 1279 | 1101 | 1245 | 535 | 1384 |
| 9 | 524 | 926 | 1041 | 729 | 323 | 615 |
| 10 | 144 | 833 | 729 | 798 | 1245 | 1101 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, F.; Lee, S. Social Content Recommendation Based on Spatial-Temporal Aware Diffusion Modeling in Social Networks. Symmetry 2016, 8, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym8090089
Ullah F, Lee S. Social Content Recommendation Based on Spatial-Temporal Aware Diffusion Modeling in Social Networks. Symmetry. 2016; 8(9):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym8090089
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Farman, and Sungchang Lee. 2016. "Social Content Recommendation Based on Spatial-Temporal Aware Diffusion Modeling in Social Networks" Symmetry 8, no. 9: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym8090089
APA StyleUllah, F., & Lee, S. (2016). Social Content Recommendation Based on Spatial-Temporal Aware Diffusion Modeling in Social Networks. Symmetry, 8(9), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym8090089





