A Bonferroni Mean Operator for p,q-Rung Triangular Orthopair Fuzzy Environments and Its Application in COPRAS Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Preliminaries
4. The p,q-Rung Triangular Orthopair Fuzzy Number
- 1.
- If , then ,
- 2.
- If , then
- (1)
- If , then ,
- (2)
- If , then .
4.1. Operational Method of p,q-RTOFNs
4.2. Distance Measure
- : As , it implies , and . The equality means . Moreover, as and , they imply and .
- Similarly, it can be deduced that and . Then is proven. is easy to prove.
- As , , and , they imply .
- As , and , they imply . □
4.3. Weight Power Bonferroni Mean Operator of p,q-RTOFNs
- (1)
- ;
- (2)
- ;
- (3)
- If , then .
4.4. Calculation of Entropy Weights Under p,q-RTOF Environment
- The formula to calculate the characteristic weight of an element in set is
- The entropy value of set is
- The entropy weight of set is
- : Consider the following function:Calculate the partial derivatives of with respect to and , respectively:
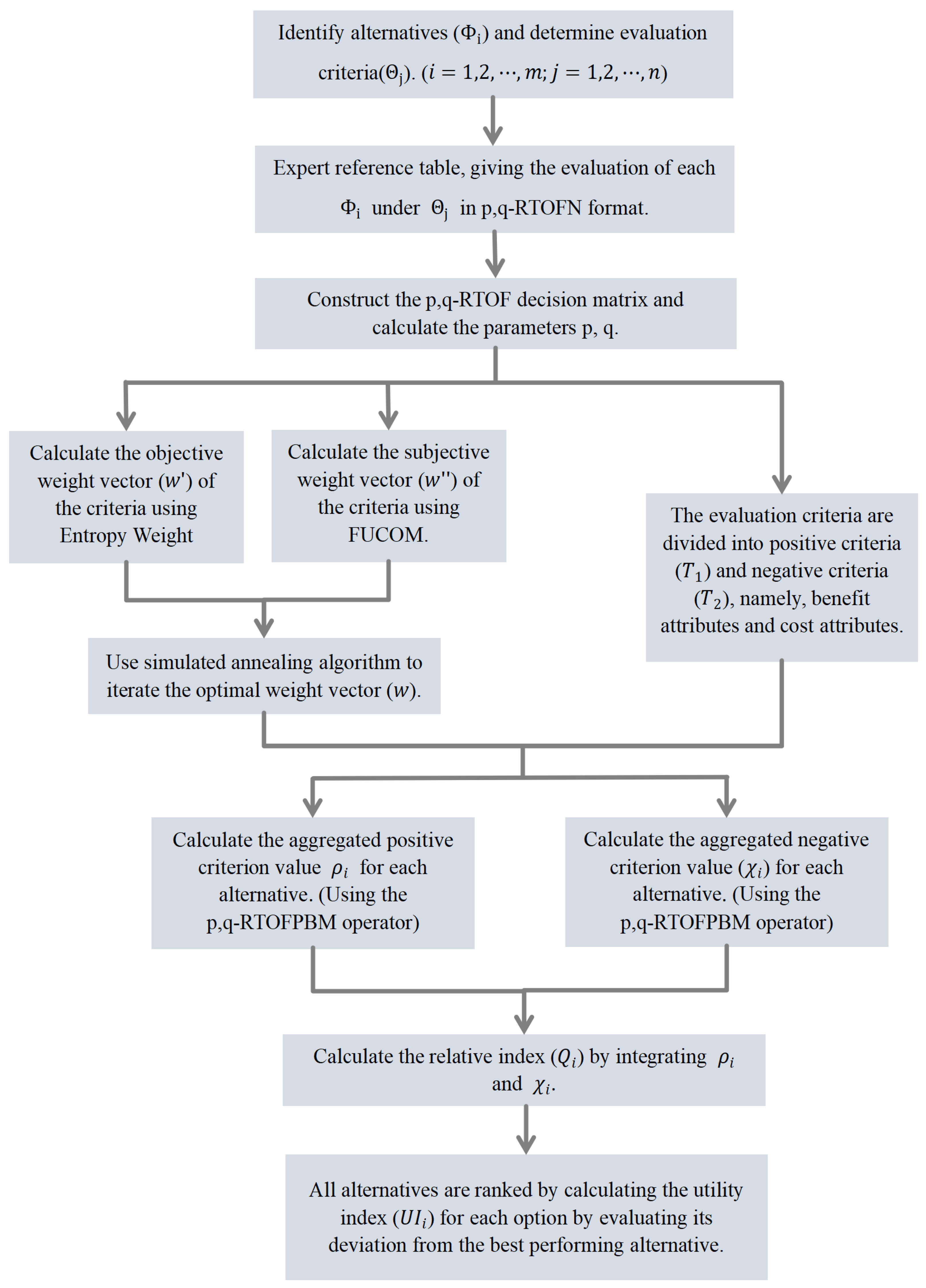
5. The p,q-RTOF-PBM-COPRAS Method
| Algorithm 1 Iterate optimal weight vector |
|
6. Case Analysis
6.1. Background
6.2. Experimental Procedures
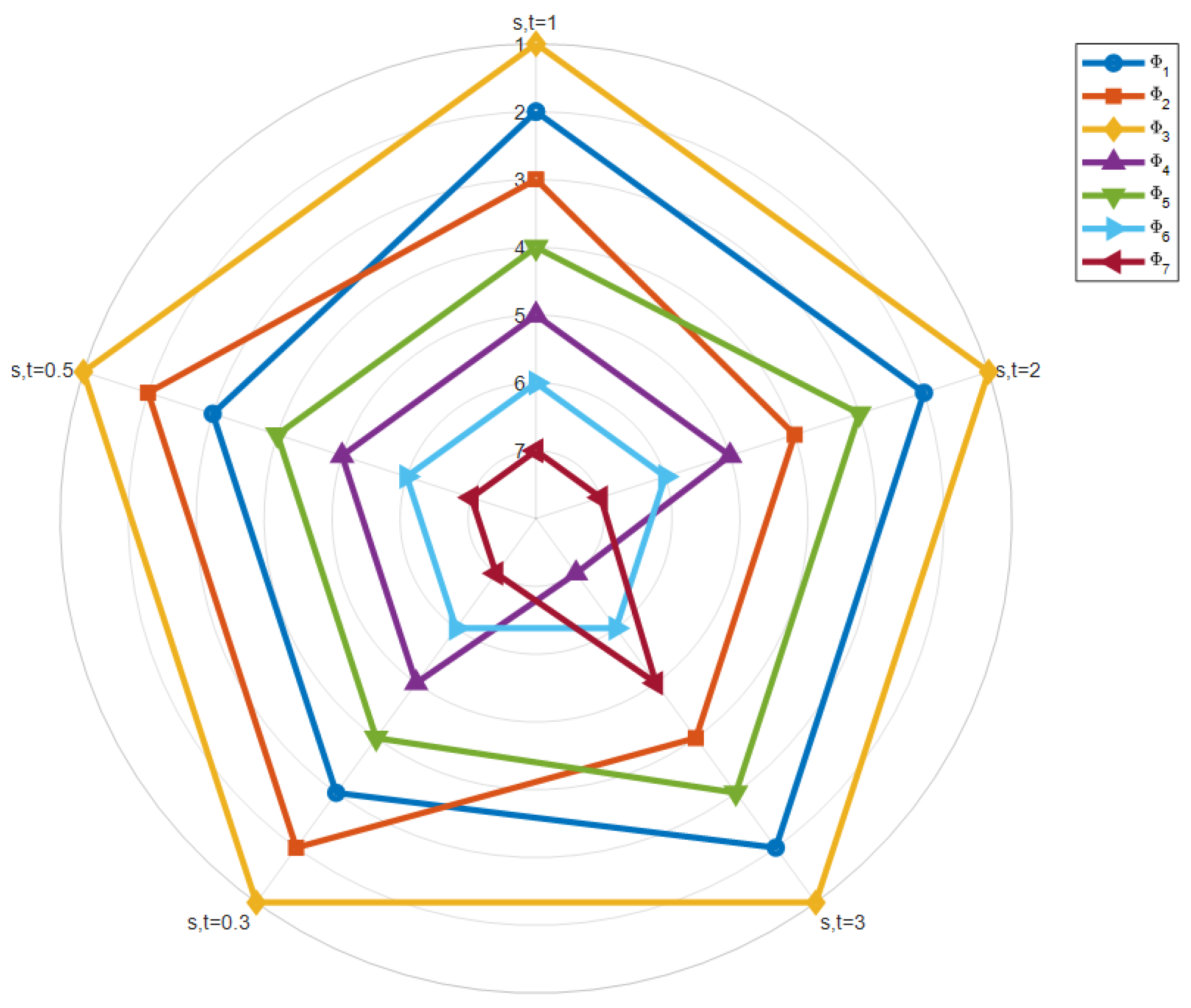
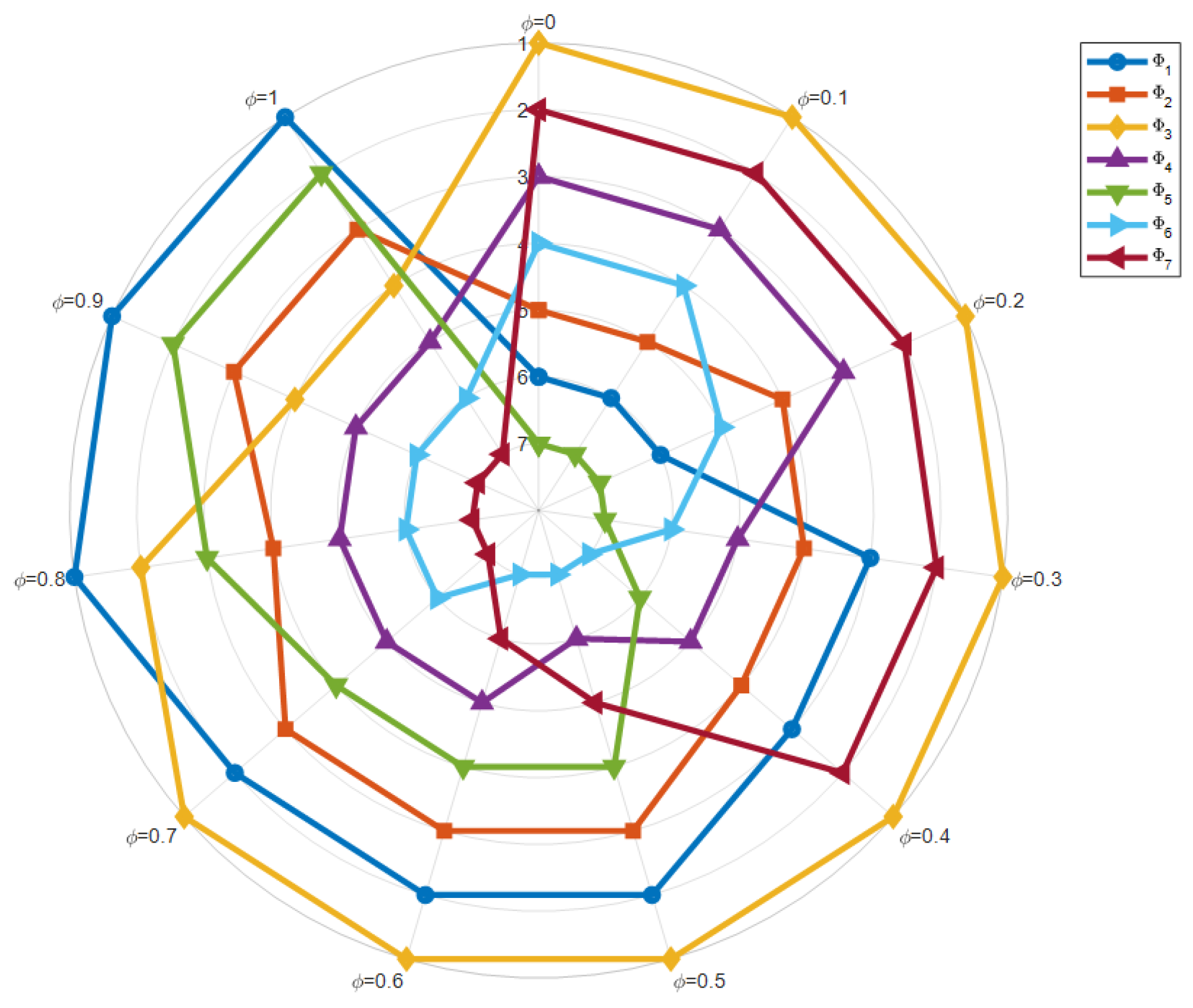
6.3. Parameter Analysis
6.4. Comparative Analysis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Set of all nonzero natural numbers . | |
| Set of all real numbers. | |
| Set of non-negative real numbers. | |
| Membership degree. | |
| Non-membership degree. | |
| IFS | Intuitionistic fuzzy set. |
| q-ROFS | q-rung orthopair fuzzy set. |
| p,q-ROFS | p,q-rung orthopair fuzzy set. |
| TFN | Triangular fuzzy number. |
| p,q-RTOFN | p,q-rung triangular orthopair fuzzy number. |
| Power Bonferroni mean. | |
| p,q-RTOFPBM | p,q-rung triangular orthopair fuzzy power Bonferroni mean. |
| p,q-RTOFWPBM | p,q-rung triangular orthopair fuzzy weight power Bonferroni mean. |
| T-SF | T-spherical fuzzy. |
| PFN | Pythagorean fuzzy number. |
| IVIFS | Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy set. |
| IVHFFS | Interval-valued hesitant fermatean fuzzy set. |
| IVpqr-SFN | Interval-valued (p,q,r)-spherical fuzzy number. |
| IT2TrFS | Interval type-2 trapezoidal fuzzy set. |
| SFS | p,q,r-spherical fuzzy set. |
| TOPSIS | Technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solution. |
| AHP | Analytic hierarchy process. |
| EWM | Entropy weight method. |
| COPRAS | Complex proportional assessment |
| SWARA | Step-wise weight assessment ratio analysis. |
| FUCOM | Full consistency method. |
| MEREC | Method based on the removal effects of criteria |
References
- Alcantud, J.C.R.; Stojanović, N.; Djurović, L.; Laković, M. Decision-Making and Clustering Algorithms Based on the Scored-Energy of Hesitant Fuzzy Soft Sets. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudric-Staniskovski, L.; Djurovic, L.; Stojanovic, N. Energy of a fuzzy soft set and its application in decision-making. Iran. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 21, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, P.B.; Prashanta, K.P.; Diptirekha, S. Fuzzy TOPSIS technique for multi-criteria group decision-making: A study of crude oil price. Results Control Optim. 2025, 19, 100565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehr, H.; Ali, E.T.; Sandra, V.; Grit, W. Leading the green charge: A novel type-2 fuzzy VIKOR method applied to eco-conscious freight transport. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 285, 128082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslihan, S.; Melisa, C.D.; Alev, T. Assessing collaboration performance of NGOs by a decomposed Fuzzy approach utilizing AHP and COPRAS methods: Turkiye case. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2024, 111, 104744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohit, K.; Raj, K.; Kovács, A.; Gusztáv, F.; Tej, S. Thermo-hydraulic characterization and design optimization of delta-shaped obstacles in solar water heating system using CRITIC-COPRAS approach. Energy 2022, 261, 125236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Kiran, Z.; Muhammet, D. Multi-criteria group decision-making for optimal management of water supply with fuzzy ELECTRE-based outranking method. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 143, 110403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, J.; Jeonghwan, G.; Dragan, P.; Luis, M. Hybrid integrated decision-making model for operating system based on complex intuitionistic fuzzy and soft information. Inf. Sci. 2023, 651, 119592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, E.S. Assessment of human factor contribution to risk analysis of chemical cargo shortage incidents by using intuitionistic fuzzy integrated fault tree analysis. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 301, 117559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Cheng, C.; Wang, S. Group decision making with incomplete triangular fuzzy multiplicative preference relations for evaluating third-party reverse logistics providers. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 160, 111688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wan, S.; Chen, S.-M. Fuzzy best-worst method based on triangular fuzzy numbers for multi-criteria decision-making. Inf. Sci. 2021, 547, 1080–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Hu, J. A novel multi-interval-valued fuzzy set model to solve MADM problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 122248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manisha, M.; Gupta, S.K. On basic arithmetic operations for interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets using the Hamming distance with their application in decision making. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 239, 122429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronald, R.Y.; Naif, A. Approximate reasoning with generalized orthopair fuzzy sets. Inf. Fusion 2017, 38, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijanur, R.S.; Utpal, M. Multiple attribute group decision making based on quasirung orthopair fuzzy sets: Application to electric vehicle charging station site selection problem. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 115, 105299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, T.; Yager, R.R. Fermatean fuzzy weighted averaging/geometric operators and its application in multi-criteria decision-making methods. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 85, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonferroni, C. Sulle medie multiple di potenze. Boll. Dell’Unione Mat. Ital. 1950, 5, 267–270. [Google Scholar]
- Yager, R.R. The power average operator. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 2001, 31, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yager, R.R. Some geometric aggregation operators based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2006, 35, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.H.; Yao, J. Triangular fuzzy number intuitionistic fuzzy power averaging operator and its application. Acta Anal. Funct. Appl. 2014, 16, 308–314. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.-M. Some intuitionistic fuzzy Dombi Bonferroni mean operators and their application to multi-attribute group decision making. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2018, 69, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Xu, Z.S. Hesitant fuzzy Bonferroni means for multi-criteria decision making. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2013, 64, 1831–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Kaklauskas, A.; Sarka, V. The new method of multicriteria complex proportional assessment of projects. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 1994, 1, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.H.; Xu, Z.S.; He, Y.; Liao, H.C. Severity assessment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease based on hesitant fuzzy linguistic COPRAS method. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 69, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunodaya, R.M.; Pratibha, R.; Abbas, M.; Kamal, R.P.; Kannan, G.; Melfi, A. Healthcare evaluation in hazardous waste recycling using novel interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy information based on complex proportional assessment method. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 139, 106140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krassimir, T.A. Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1986, 20, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, J.J. Possibilistic linear programming with triangular fuzzy numbers. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1988, 26, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamučar, D.; Stević, Ž.; Sremac, S. A New Model for Determining Weight Coefficients of Criteria in MCDM Models: Full Consistency Method (FUCOM). Symmetry 2018, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-T. An integrated MEREC-taxonomy methodology using T-spherical fuzzy information: An application in smart farming decision analytics. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2024, 62, 102891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforidou, M.; Borghuis, G.; Seijger, C. Food security under water scarcity: A comparative analysis of Egypt and Jordan. Food Sec. 2023, 15, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boursianis, A.D.; Papadopoulou, M.S.; Panagiotis, D.; Liopa-Tsakalidi, A.; Barouchas, P.; Salahas, G.; Wan, S.; Goudos, S.K. Internet of Things (IoT) and Agricultural Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) in smart farming: A comprehensive review. Internet Things 2022, 18, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, D.; Lee, E.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Byun, N. Characteristics of Smart Farms for Architectural Planning and Design. Buildings 2023, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavna, P.; Manoj, K.K. An integrated Pythagorean fuzzy SWARA-COPRAS framework to prioritise the solutions for mitigating Industry 4.0 risks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 254, 124412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunodaya, R.M.; Peide, L.; Pratibha, R. COPRAS method based on interval-valued hesitant Fermatean fuzzy sets and its application in selecting desalination technology. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 119, 108570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, K.; Fatih, K. Interval-valued (p,q,r)-spherical fuzzy sets and their applications in MCGDM and MCDM based on TOPSIS method and aggregation operators. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, X.; Lu, J. Optimal investment decision-making of energy storage technologies on renewable energy generation side based on the Internal Type-2 trapezoidal fuzzy sets-PROMETHEE-II method. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2025, 170, 110861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, Z.A.; Salih, H.F.M.; Alajlan, A.I.; Mohammed, R.A.; Asaad, B.A. Enhanced MCDM Based on the TOPSIS Technique and Aggregation Operators Under the Bipolar pqr-Spherical Fuzzy Environment: An Application in Firm Supplier Selection. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Linguistic Terms | Related p,q-RTOFNs |
|---|---|
| Absolutely High (AH) | |
| Very High (VH) | |
| High (H) | |
| Medium High (MH) | |
| Average (A) | |
| Medium Low (ML) | |
| Low (L) | |
| Very Low (VL) | |
| Absolutely Low (AL) |
| L | H | MH | MH | A | H | AH | |
| H | A | VH | H | AL | A | H | |
| A | VL | L | AL | L | MH | ML | |
| ML | ML | A | A | A | A | A | |
| AL | H | H | AH | MH | AH | VH | |
| L | MH | MH | L | H | VH | L | |
| MH | L | ML | VL | A | L | VL |
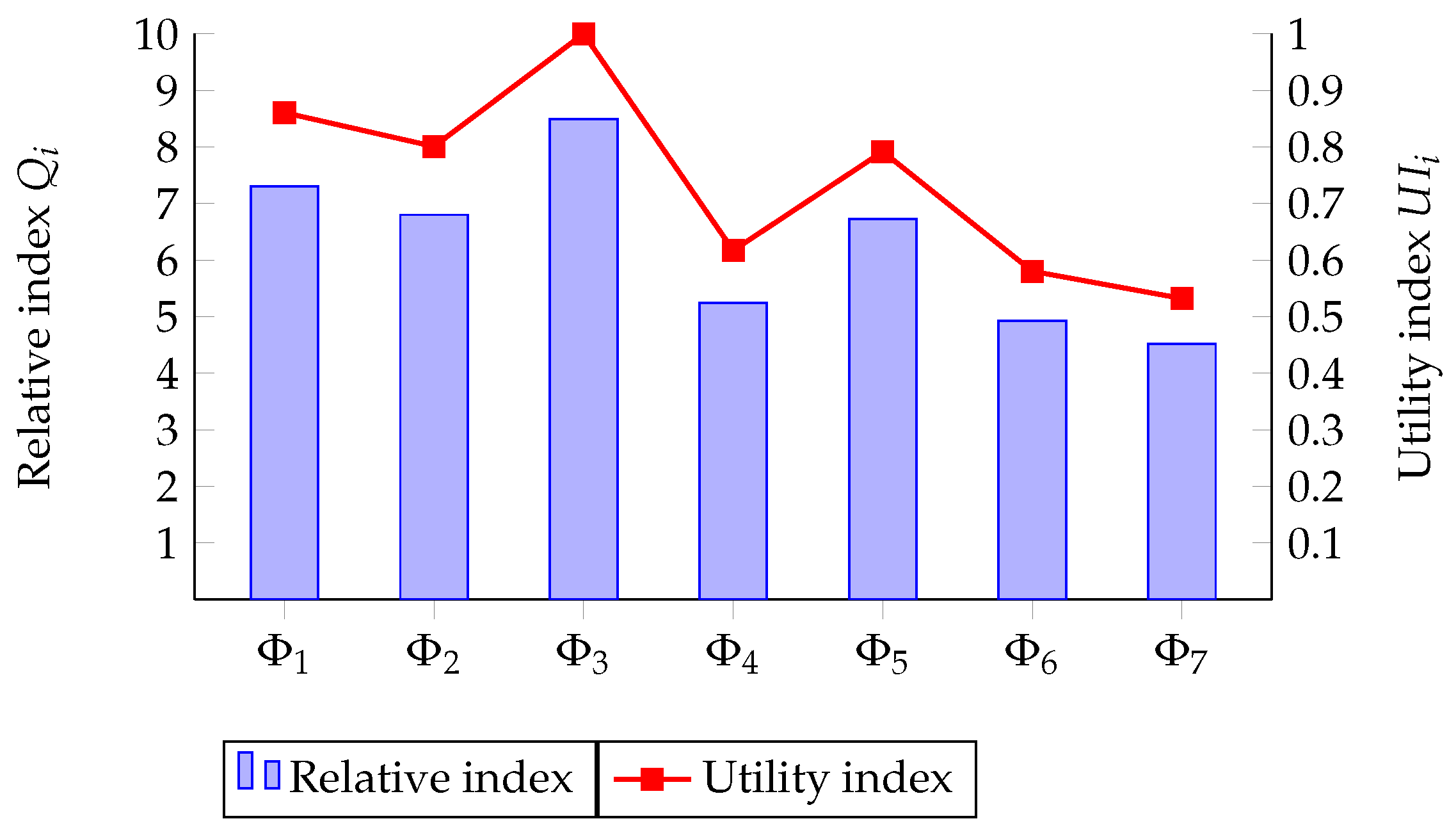
| 7.3066 | 6.7992 | 8.4901 | 5.2383 | 6.723 | 4.9256 | 4.517 | |
| 0.8606 | 0.8008 | 1 | 0.617 | 0.7919 | 0.5802 | 0.532 | |
| Rank | |||||||
| Rank | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8606 | 0.8008 | 1 | 0.617 | 0.7919 | 0.5802 | 0.532 | ||
| 0.8763 | 0.8226 | 1 | 0.6474 | 0.7983 | 0.6083 | 0.5613 | ||
| 0.8703 | 0.831 | 1 | 0.6750 | 0.7782 | 0.6338 | 0.5839 | ||
| 0.86 | 0.8323 | 1 | 0.684 | 0.7562 | 0.6418 | 0.591 | ||
| 0.8454 | 0.8342 | 1 | 0.6862 | 0.7264 | 0.6422 | 0.5948 | ||
| 0.8221 | 0.8327 | 1 | 0.6802 | 0.7056 | 0.6327 | 0.5887 | ||
| 0.8145 | 0.8323 | 1 | 0.6776 | 0.6963 | 0.6281 | 0.5861 |
| Rank | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8606 | 0.8008 | 1 | 0.617 | 0.7919 | 0.5802 | 0.532 | ||
| 0.9076 | 0.8329 | 1 | 0.6808 | 0.8573 | 0.6522 | 0.5896 | ||
| 0.9439 | 0.8595 | 1 | 0.7198 | 0.9008 | 0.6972 | 0.6270 | ||
| 0.9824 | 0.8892 | 1 | 0.7529 | 0.9423 | 0.7335 | 0.6593 | ||
| 0.9946 | 0.8966 | 1 | 0.7612 | 0.9565 | 0.7416 | 0.6664 | ||
| 0.9968 | 0.8956 | 1 | 0.7616 | 0.9607 | 0.7417 | 0.6660 | ||
| 0.9968 | 0.8956 | 1 | 0.7616 | 0.9607 | 0.7417 | 0.6660 |
| Rank | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9619 | 0.9716 | 1 | 0.8943 | 0.9231 | 0.8733 | 0.8498 | ||
| 0.9439 | 0.9503 | 1 | 0.8427 | 0.8936 | 0.8166 | 0.7907 | ||
| 0.8606 | 0.8008 | 1 | 0.6170 | 0.7919 | 0.5802 | 0.5320 | ||
| 0.8433 | 0.7041 | 1 | 0.5445 | 0.8086 | 0.5356 | 0.5296 | ||
| 0.7723 | 0.541 | 1 | 0.3789 | 0.7612 | 0.3918 | 0.3961 |
| Rank | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2213 | 0.2432 | 1 | 0.3168 | 0.1657 | 0.2928 | 0.4887 | ||
| 0.2772 | 0.2920 | 1 | 0.3431 | 0.2205 | 0.3180 | 0.4925 | ||
| 0.3409 | 0.3475 | 1 | 0.3730 | 0.2829 | 0.3466 | 0.4968 | ||
| 0.4140 | 0.4113 | 1 | 0.4073 | 0.3545 | 0.3794 | 0.5017 | ||
| 0.4988 | 0.4853 | 1 | 0.4471 | 0.4375 | 0.4176 | 0.5075 | ||
| 0.5984 | 0.5721 | 1 | 0.4939 | 0.5351 | 0.4623 | 0.5143 | ||
| 0.7170 | 0.6756 | 1 | 0.5496 | 0.6512 | 0.5156 | 0.5223 | ||
| 0.8606 | 0.8008 | 1 | 0.6170 | 0.7919 | 0.5802 | 0.5320 | ||
| 1 | 0.9206 | 0.9633 | 0.6746 | 0.9302 | 0.6357 | 0.5241 | ||
| 1 | 0.9119 | 0.7917 | 0.6381 | 0.9390 | 0.6025 | 0.4428 | ||
| 1 | 0.9044 | 0.6421 | 0.6062 | 0.9466 | 0.5736 | 0.3720 |
| Characteristics | Method Type | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. [30] | Pandey et al. [34] | Mishra et al. [35] | Karaaslan et al. [36] | Li et al. [37] | Ameen et al. [38] | Proposed Method | |
| Decision information | T-SFNs | PFNs | IVHFFSs | IVpqr-SFNs | IT2TrFSs | SFSs | p,q-RTOFNs |
| Methodology framework | Taxonomy | COPRAS | COPRAS | TOPSIS | PROMETHEE | TOPSIS | COPRAS |
| Mathematical measure | Similarity and Closeness | Positive score and Negative loss | Positive score and Negative loss | Distance measure | Preference Measure | Distance measure | p,q-RTOFWPBM operator and Proportional Aggregation |
| Weighting method | MEREC | SWARA | Discrimination weight method | Score weighting method | AHP and EWM | Directly from decision makers | FUCOM and EWM |
| Weigh type | Objective weight | Subjective weight | Objective weight | Subjective weight | Combination weight | Subjective weight | Combination weight |
| Ranking | |||||||
| Best model |
| Characteristics | Fuzzy Numbers | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-SFN | PFN | IVHFFN | IVpqr-SFN | IT2TrFN | SFN | p,q-RTOFN | |
| High-order fuzzy ability | General | None | Strong | General | Strong | Strong | Strong |
| Flexibility and adjustability | Medium | Low | High | High | Low | High | High |
| Resistance to information loss | Medium | Weak | Strong | Strong | Strong | Strong | Strong |
| Expressive ability | General | General | Strong | General | Strong | Strong | Strong |
| Language approximation ability | Medium | Low | High | High | High | Medium | High |
| Structural scalability | Low | Extremely High | Low | High | Low | General | High |
| Computational complexity | Medium | Low | High | High | Extremely High | High | Medium |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, S.; Kong, X. A Bonferroni Mean Operator for p,q-Rung Triangular Orthopair Fuzzy Environments and Its Application in COPRAS Method. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17091422
Qu S, Kong X. A Bonferroni Mean Operator for p,q-Rung Triangular Orthopair Fuzzy Environments and Its Application in COPRAS Method. Symmetry. 2025; 17(9):1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17091422
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Shenjie, and Xiangzhi Kong. 2025. "A Bonferroni Mean Operator for p,q-Rung Triangular Orthopair Fuzzy Environments and Its Application in COPRAS Method" Symmetry 17, no. 9: 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17091422
APA StyleQu, S., & Kong, X. (2025). A Bonferroni Mean Operator for p,q-Rung Triangular Orthopair Fuzzy Environments and Its Application in COPRAS Method. Symmetry, 17(9), 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17091422





