Tuning the Ellipticity of High-Order Harmonics from Helium in Orthogonal Two-Color Laser Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
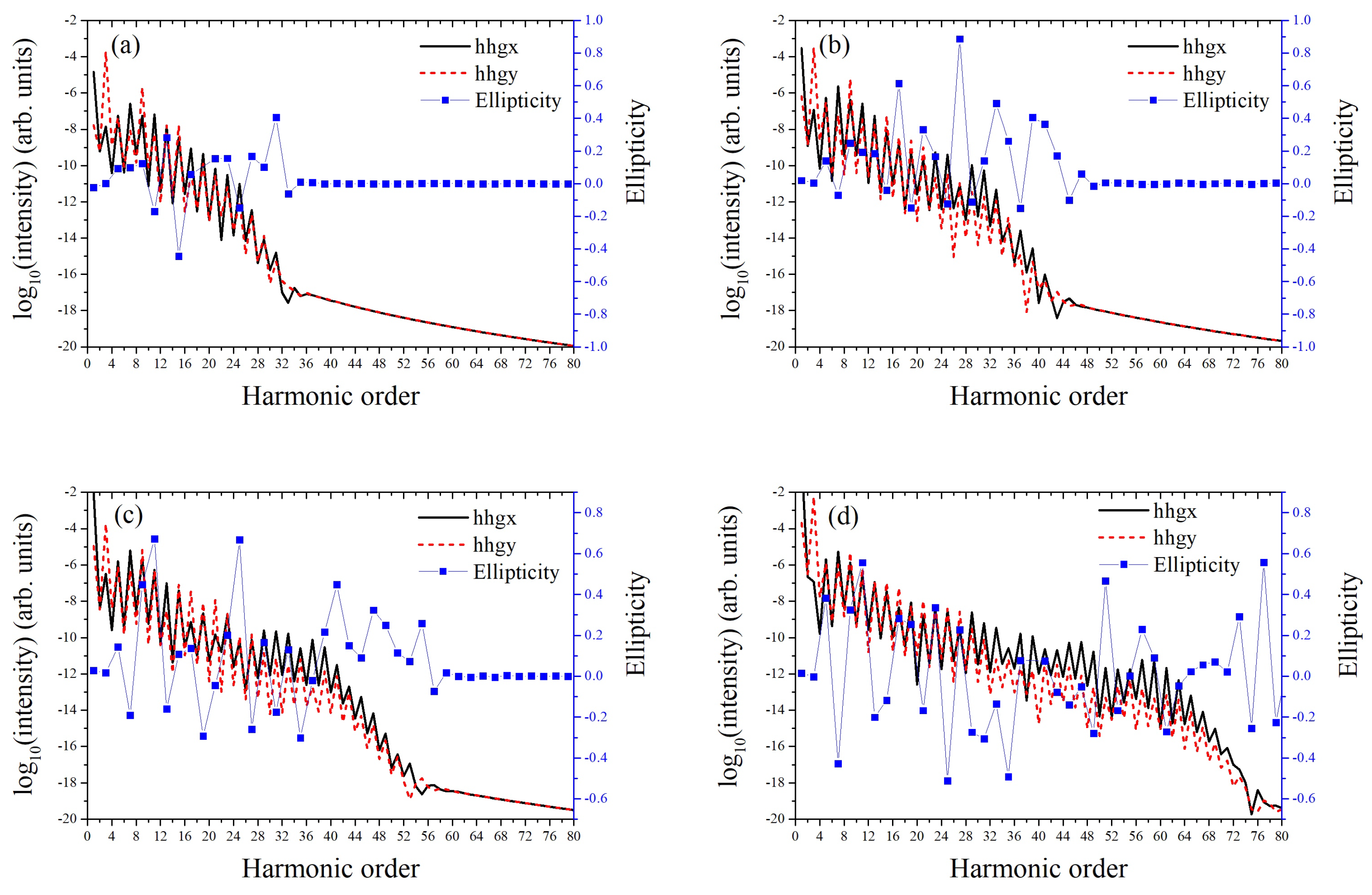
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, K.J.; Bandrauk, A.D. Symmetry in circularly polarized molecular high-order harmonic generation with intense bicircular laser pulses. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 023408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, G.; Benedetti, E.; Calegari, F.; Vozzi, C.; Avaldi, L.; Flammini, R.; Poletto, L.; Villoresi, P.; Altucci, C.; Velotta, R.; et al. Isolated Single-Cycle Attosecond Pulses. Science 2006, 314, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, R.A.; Paul, A.; Green, H.; Kapteyn, H.C.; Murnane, M.M.; Backus, S.; Christov, I.P.; Liu, Y.; Attwood, D.; Jacobsen, C. Generation of Spatially Coherent Light at Extreme Ultraviolet Wavelengths. Science 2002, 297, 376–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferray, M.; L’Huillier, A.; Li, X.F.; Lompre, L.A.; Mainfray, G.; Manus, C. Multiple-harmonic conversion of 1064 nm radiation in rare gases. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 1988, 21, L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, D.; Álvaro, J.G.; Lukas, M.; Misha, I. Control of the helicity of high-order harmonic radiation using bichromatic circularly polarized laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 053402. [Google Scholar]
- Ayuso, D.; Jiménez-Galán, A.; Morales, F.; Ivanov, M.; Smirnova, O. Attosecond control of spin polarization in electron–ion recollision driven by intense tailored fields. New J. Phys. 2017, 19, 073007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xie, M.F.; Wang, H.; Jia, L.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Cai, J.; Hong, X.; Shi, X.; Lv, Y.; et al. Observation of Laser-Assisted Dynamic Interference by Attosecond Controlled Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2024, 133, 253201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Zhou, S.S.; Wang, Y. Regulation of helium atom higher harmonic emission and attosecond pulse angle in inhomogeneous fields. Results Phys. 2025, 72, 108190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Dang, T.N.; Charron, E.; Keller, A.; Atabek, O. Laser-induced electron diffraction: A tool for molecular orbital imaging. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 85, 053417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozzi, C.; Negro, M.; Calegari, F.; Sansone, G.; Nisoli, M.; Silvestri, S.D.; Stagira, S. Generalized molecular orbital tomography. Nat. Phys. 2011, 7, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niikura, H.; Dudovich, N.; Villeneuve, D.M.; Corkum, P.B. Mapping Molecular Orbital Symmetry on High-Order Harmonic Generation Spectrum Using Two-Color Laser Fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 053003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itatani, J.; Levesque, J.; Zeidler, D.; Hiromichi, N.; Pépin, H.; Kieffer, J.C.; Corkum, P.B.; Villeneuve, D.M. Tomographic imaging of molecular orbitals. Nature 2004, 432, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corkum, P.; Krausz, F. Attosecond science. Nat. Phys. 2007, 3, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausz, F.; Ivanov., M. Attosecond physics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 163–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallmann, L.; Cirelli, C.; Keller, U. Attosecond Science: Recent Highlights and Future Trends. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2012, 63, 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthumpally-Joseph, R.; Viau-Trudel, J.; Peters, M.; Nguyen-Dang, T.T.; Atabek, O.; Charron, E. Inversion of strong-field photoelectron spectra for molecular orbital imaging. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 023421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krečinić, F.; Wopperer, P.; Frusteri, B.; Brauße, F.; Brisset, J.G.; De Giovannini, U.; Rubio, A.; Rouzée, A.; Vrakking, M.J.J. Multiple-orbital effects in laser-induced electron diffraction of aligned molecules. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 041401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurell, H.; Luo, S.; Weissenbilder, R. Measuring the quantum state of photoelectrons. Nat. Photonics 2025, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Weissenbilder, R.; Laurell, H.; Bello, R.Y.; Marante, C.; Ammitzböll, M.; Neoričić, L.; Ljungdahl, A.; Squibb, R.J.; Feifel, R.; et al. Influence of final state interactions in attosecond photoelectron interferometry. Phys. Rev. Res. 2024, 6, 043271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, S. The Role of Multi-Electron and Multi-Orbital Effects in High-Order Harmonic Generation of Benzonitrile Molecules. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2025, 42, 043201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, H.; Hu, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, X. Review of the Generation, Regulation, and Applications of High-Order Harmonic Generation in Gases Studied Using Time-Dependent Density Functional Theory. Symmetry 2025, 17, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, W.; Guo, F.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y. Modulation of harmonics from solids by laser pulses with a small chirp. Phys. Rev. A 2025, 111, 013501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Liu, A.; He, L.; Zhao, X. Non vertical ionization-dissociation model for strong IR induced dissociation dynamics of D2O2+. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corkum, P.B. Plasma Perspective on Strong-Field Multiphoton Ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 71, 1994–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böwering, N.; Lischke, T.; Schmidtke, B.; Müller, N.; Khalil, T.; Heinzmann, U. Asymmetry in Photoelectron Emission from Chiral Molecules Induced by Circularly Polarized Light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergenhahn, U.; Rennie, E.E.; Kugeler, O.; Marburger, S.; Lischke, T.; Powis, I.; Garcia, G. Photoelectron circular dichroism in core level ionization of randomly oriented pure enantiomers of the chiral molecule camphor. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120, 4553–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, B.; Antoine, C.; Baptiste, F.; Dominique, D.; Amélie, F.; Gustavo, G.; Romain, G.; Francois, L.; Laurent, N.; Stéphane, P.; et al. Probing ultrafast dynamics of chiral molecules using time-resolved photoelectron circular dichroism. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 194, 325–348. [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld, O.; Cohen, O. Optical Chirality in Nonlinear Optics: Application to High Harmonic Generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 133206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M. Drive round the twist. Nat. Phys. 2015, 11, 621–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.M.; Kirschner, J. Spin- and angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy from solid surfaces with circularly polarized light. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 1995, 20, 179–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isabella, G.; Matti, L.; Hartmut, H.; Christian, R.A.; Klaus, K. Graphene sublattice symmetry and isospin determined by circular dichroism in angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3900–3904. [Google Scholar]
- Ferré, A.; Handschin, C.; Dumergue, M. A table-top ultrashort light source in the extreme ultraviolet for circular dichroism experiments. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, I.; Vahaplar, K.; Stamm, C.; Kachel, T.; Pontius, N.; Dürr, H.A.; Ostler, T.A.; Barker, J.; Evans, R.F.L.; Chantrell, R.W.; et al. Transient ferromagnetic-like state mediating ultrafast reversal of antiferromagnetically coupled spins. Nature 2011, 472, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandrauk, A.D.; Jing, G.; Kai-Jun, Y. Circularly polarized attosecond pulse generation and applications to ultrafast magnetism. J. Opt. 2017, 19, 124016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.J.; Bandrauk, A.D. Attosecond-magnetic-field-pulse generation by coherent circular molecular electron wave packets. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 91, 042509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.J.; Guo, J.; Bandrauk, A.D. Generation of ultrafast magnetic fields from molecular coherent electron currents. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 043410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, M.; Cheng, Y.; Khan, S.D.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, K.; Chini, M.; Paulus, G.G.; Chang, Z. Dependence of high-order-harmonic-generation yield on driving-laser ellipticity. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 86, 011401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihe, F.A.; Dutta, S.K.; Korn, G.; Du, D.; Bucksbaum, P.H.; Shkolnikov, P.L. Polarization of high-intensity high-harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. A 1995, 51, R3433–R3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heslar, J.; Telnov, D.A.; Chu, S.I. Generation of circularly polarized XUV and soft-x-ray high-order harmonics by homonuclear and heteronuclear diatomic molecules subject to bichromatic counter-rotating circularly polarized intense laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 063404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Jiang, T.; Liu, J.; Luo, S.; Ren, D.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Lang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; et al. Strong Field Ionization Dynamics Resolved by Two-Color Elliptical Phase-of-Phase Spectroscopy. Ultrafast Sci. 2024, 4, 0066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, S.; Yang, Y. Modulation of High-Order Harmonic Generation from a Monolayer ZnO by Co-rotating Two-Color Circularly Polarized Laser Fields. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2024, 41, 14205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Becker, W.; McIver, J.K. Model calculations of polarization-dependent two-color high-harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. A 1995, 52, 2262–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichmann, H.; Egbert, A.; Nolte, S.; Momma, C.; Wellegehausen, B.; Becker, W.; Long, S.; McIver, J.K. Polarization-dependent high-order two-color mixing. Phys. Rev. A 1995, 51, R3414–R3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, A.; Kfir, O.; Diskin, T.; Sidorenko, P.; Cohen, O. Spin angular momentum and tunable polarization in high-harmonic generation. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Kondo, K.; Nabekawa, Y.; Sagisaka, A.; Kobayashi, Y. Two-Color Phase Control in Tunneling Ionization and Harmonic Generation by a Strong Laser Field and Its Third Harmonic. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 73, 2692–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milošević, D.B.; Becker, W. X-ray harmonic generation by orthogonally polarized two-color fields: Spectral shape and polarization. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 031401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.-L.; Miao, X.-Y. Generation of Linear Isolated Sub-60 Attosecond Pulses by Combining a Circularly Polarized Pulse with an Elliptically Polarized Pulse. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2015, 32, 043202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.-L.; Miao, X.-Y. Broadband-Isolated Attosecond Pulse Generation by Two-Color Elliptically Polarized Laser Pulses. Spectrosc. Lett. 2015, 48, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.X.; Xing, Y.H.; Qi, T.; Sun, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.S. Elliptical high-order harmonic generation from driven by orthogonally polarized two-color laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 103, 053116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, J.G.; Wang, J.; Guo, F.M.; Yang, Y.J. High-order harmonic generation from H2+ irradiated by a co-rotating two-color circularly polarized laser field. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 063428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Shao, R.; Lan, P.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Njoroge, S.M.; He, L.; Lu, P. Ellipticity control of high-order harmonic generation with nearly orthogonal two-color laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 2020, 101, 053407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Z.; Xu, Y.; Jia, G.R.; Bian, X.B. Controlling polarization of high-order harmonic generation by molecular alignment in a bicircular laser field. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 033410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Lan, P.; Lu, P. Ellipticity-tunable attosecond XUV pulse generation with a rotating bichromatic circularly polarized laser field. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odžak, S.; Milošević, D.B. Bicircular-laser-field-assisted electron-ion radiative recombination. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 92, 053416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
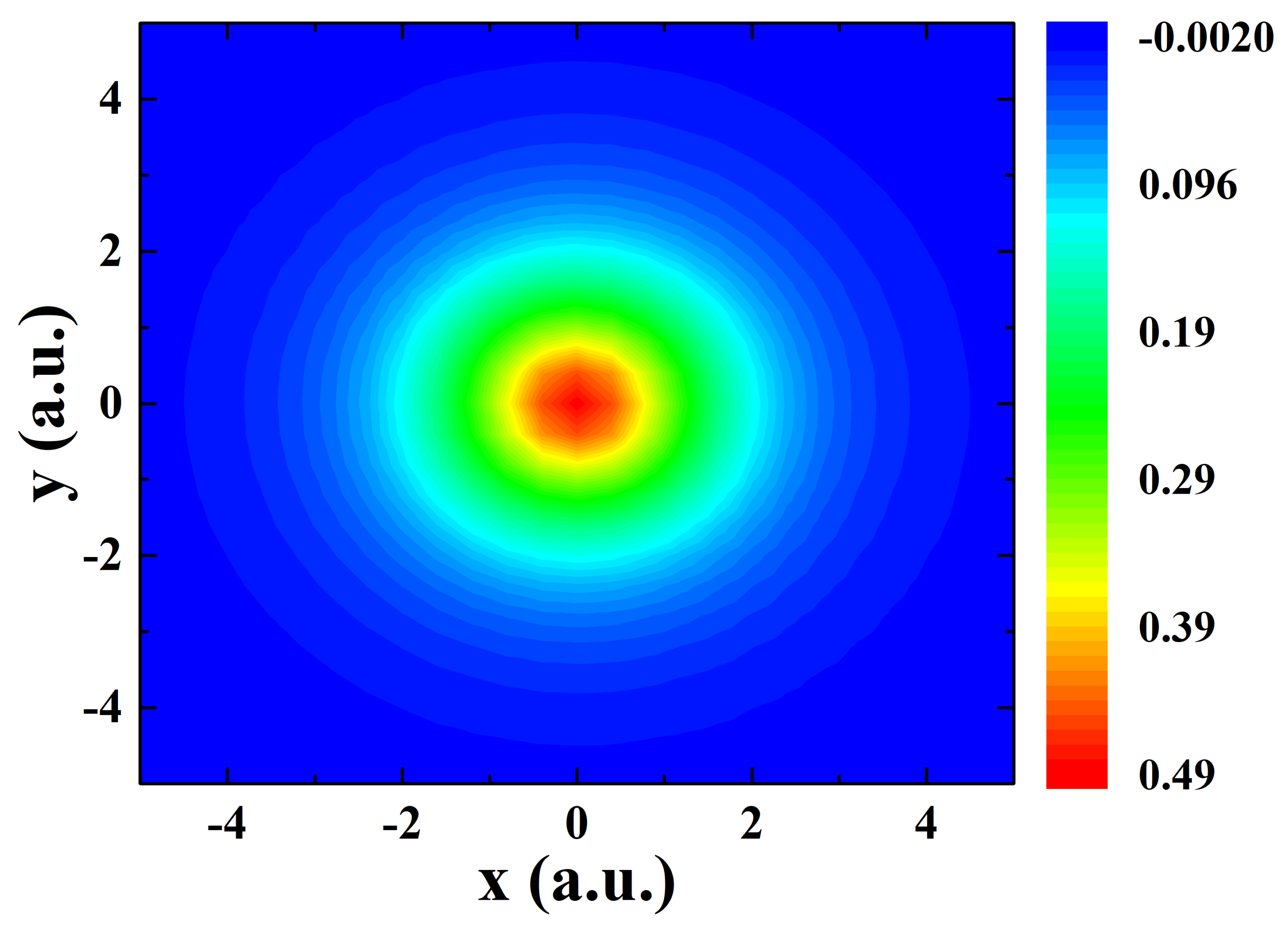
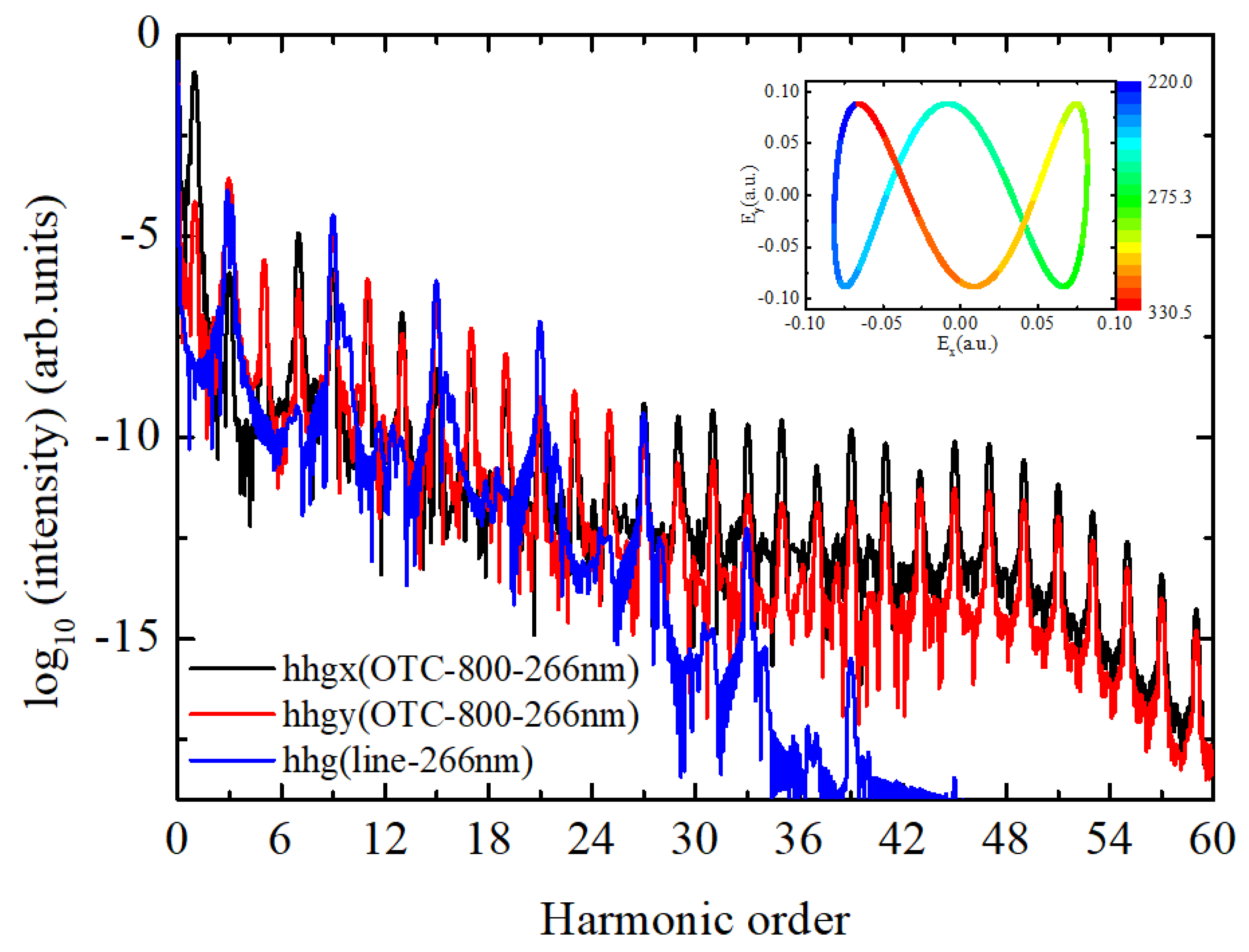
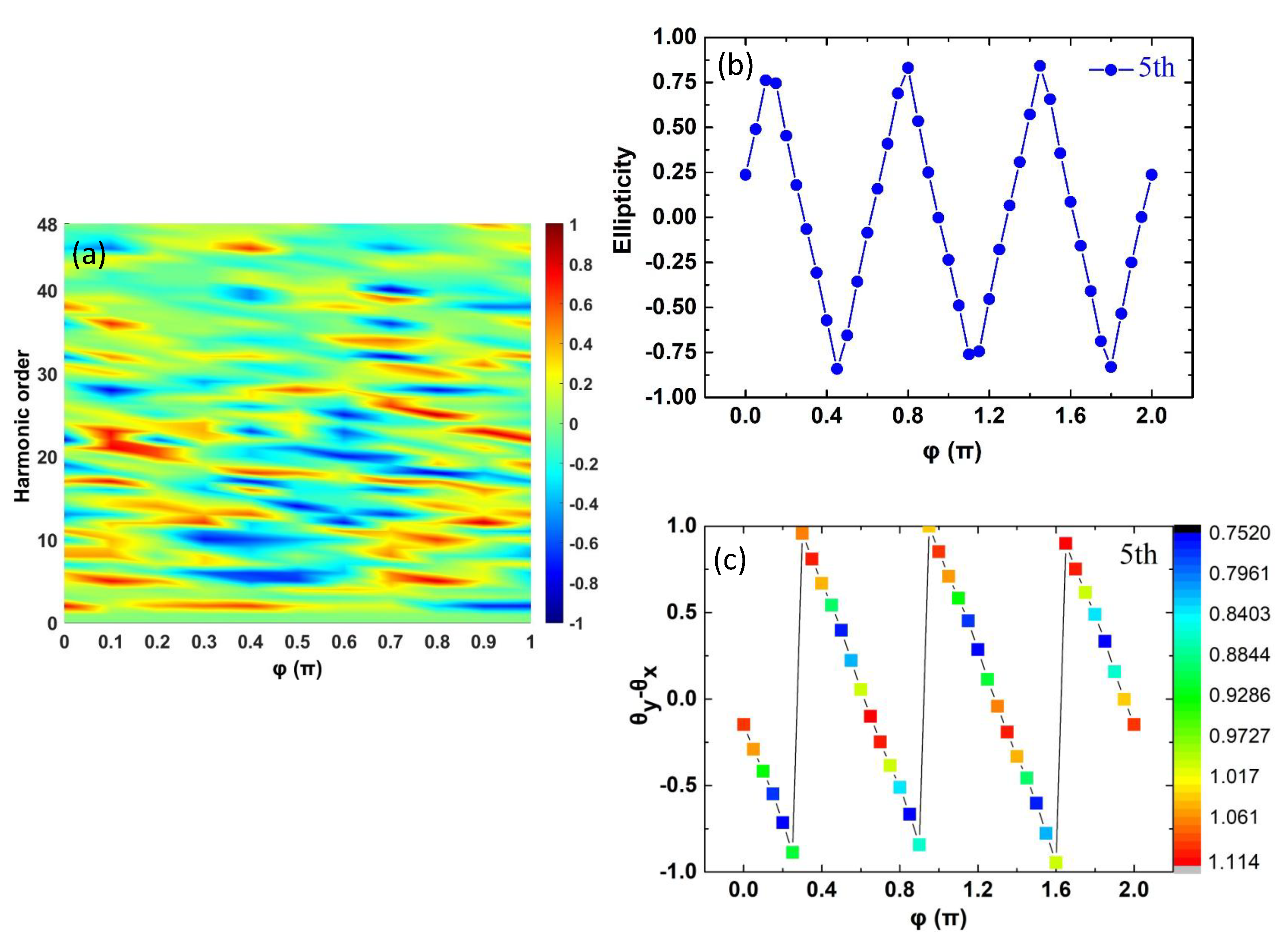

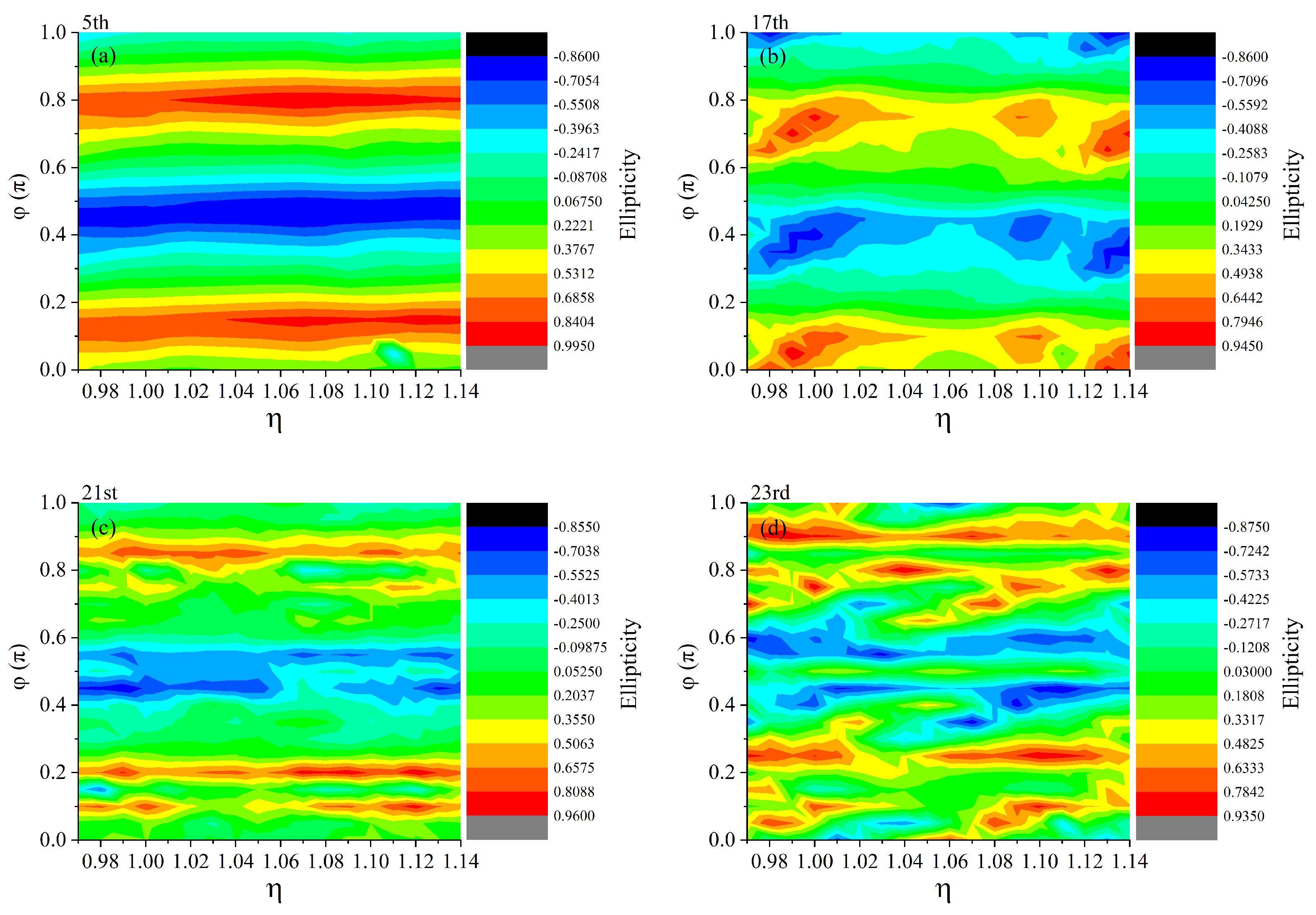
| Parameter | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Spatial grid size | 409.6 a.u. (radius) with 0.2 a.u. spacing |
| Absorbing boundary | 51.2 a.u. thick cosine mask starting at 358.4 a.u. |
| Pulse duration | 8 optical cycles (≈21.1 fs at 800 nm), trapezoidal envelope |
| Time step | 0.1 a.u. (≈2.4 attoseconds) |
| Laser wavelength | Fundamental: 800 nm; third harmonic: 266 nm |
| Intensity | W/cm2 for both fields ( = 0.085 a.u.) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, S.; Wang, H.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, N.; Guo, F.; Yang, Y.; Hu, M. Tuning the Ellipticity of High-Order Harmonics from Helium in Orthogonal Two-Color Laser Fields. Symmetry 2025, 17, 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060967
Zhou S, Wang H, Qiao Y, Xu N, Guo F, Yang Y, Hu M. Tuning the Ellipticity of High-Order Harmonics from Helium in Orthogonal Two-Color Laser Fields. Symmetry. 2025; 17(6):967. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060967
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Shushan, Hao Wang, Yue Qiao, Nan Xu, Fuming Guo, Yujun Yang, and Muhong Hu. 2025. "Tuning the Ellipticity of High-Order Harmonics from Helium in Orthogonal Two-Color Laser Fields" Symmetry 17, no. 6: 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060967
APA StyleZhou, S., Wang, H., Qiao, Y., Xu, N., Guo, F., Yang, Y., & Hu, M. (2025). Tuning the Ellipticity of High-Order Harmonics from Helium in Orthogonal Two-Color Laser Fields. Symmetry, 17(6), 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060967






