Flexible Concentration Gradient Droplet Generation via Partitioning–Recombination in a Shear Flow-Driven Multilayer Microfluidic Chip
Abstract
1. Introduction
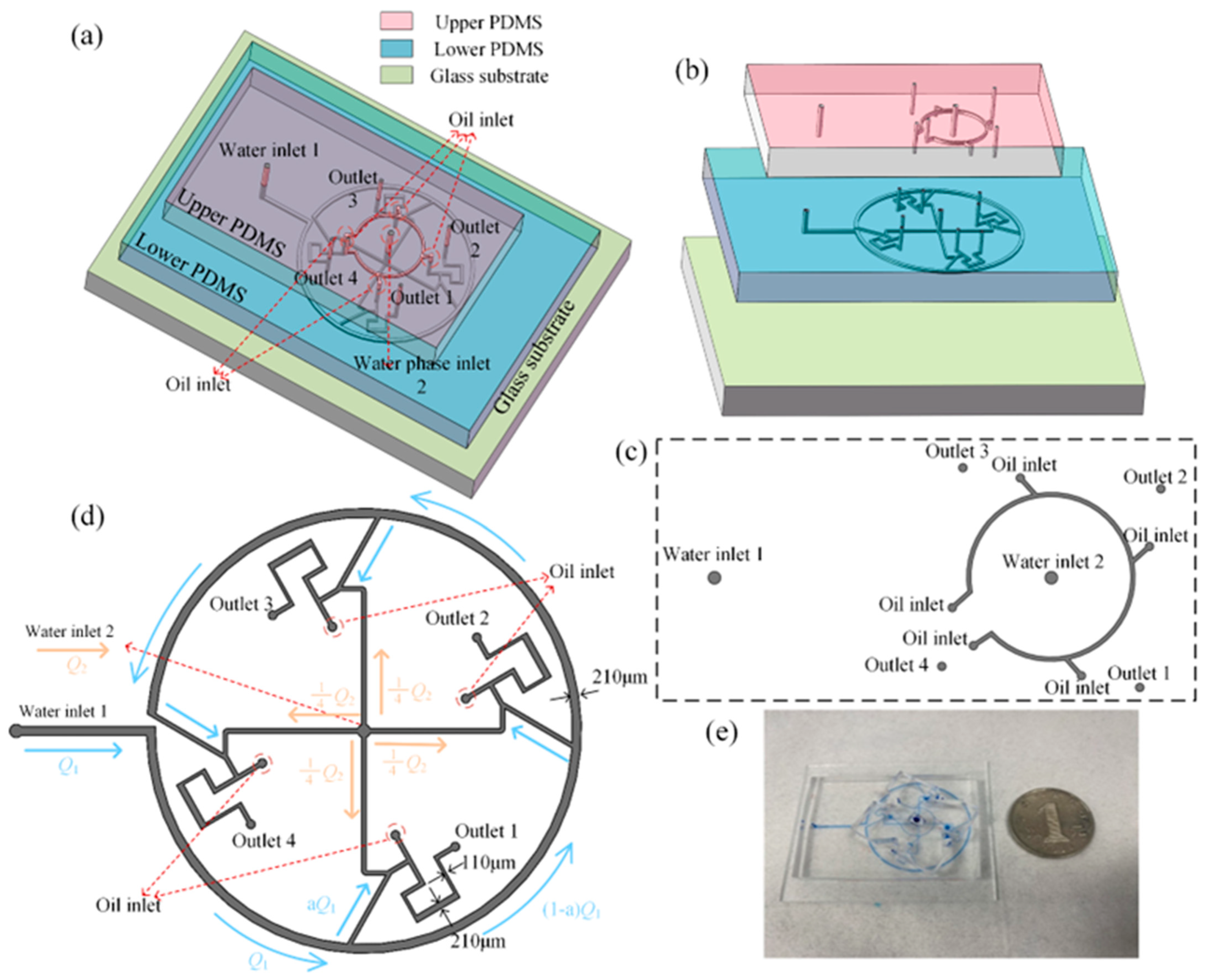
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
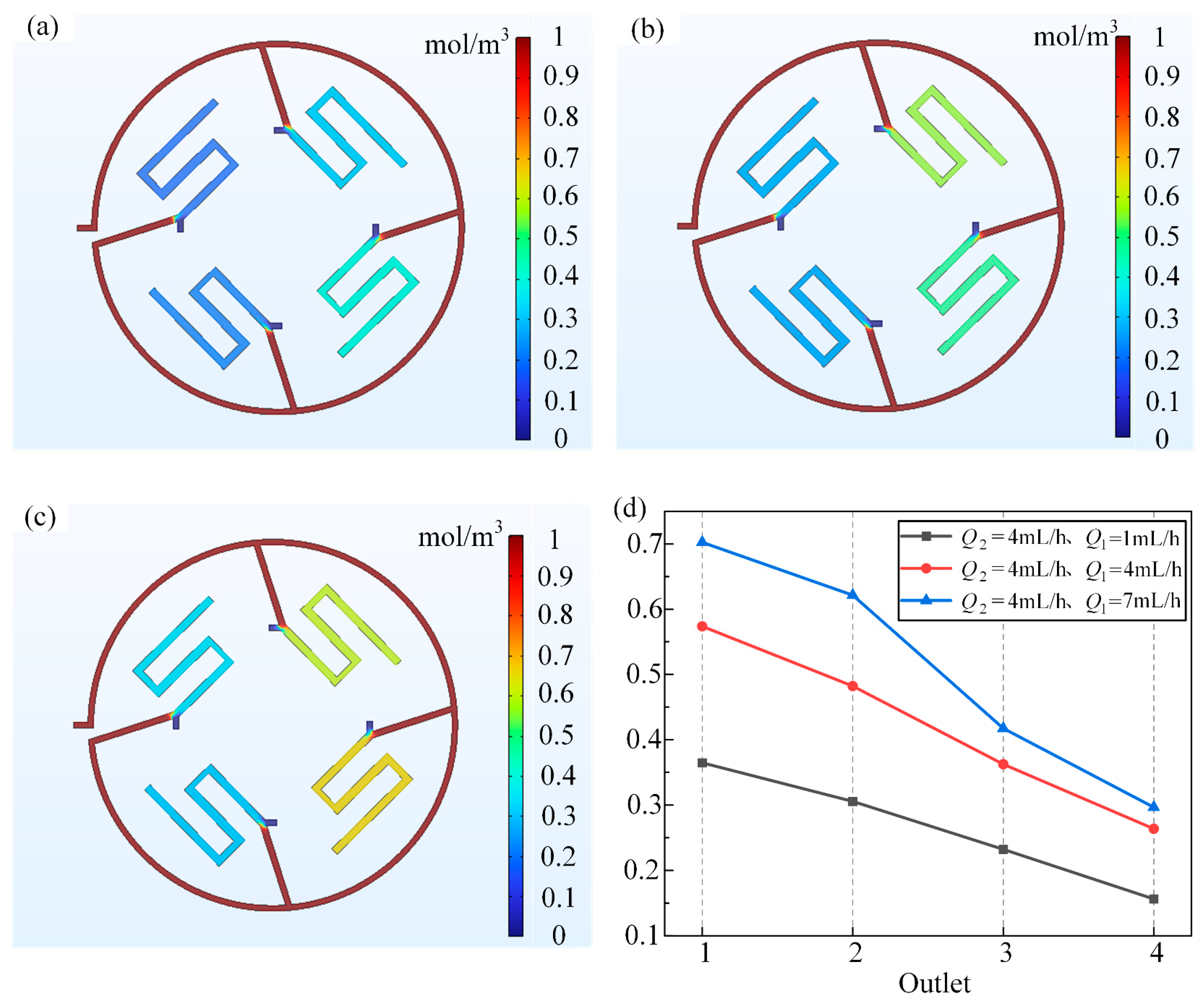
3.1. Analysis of Simulation Results
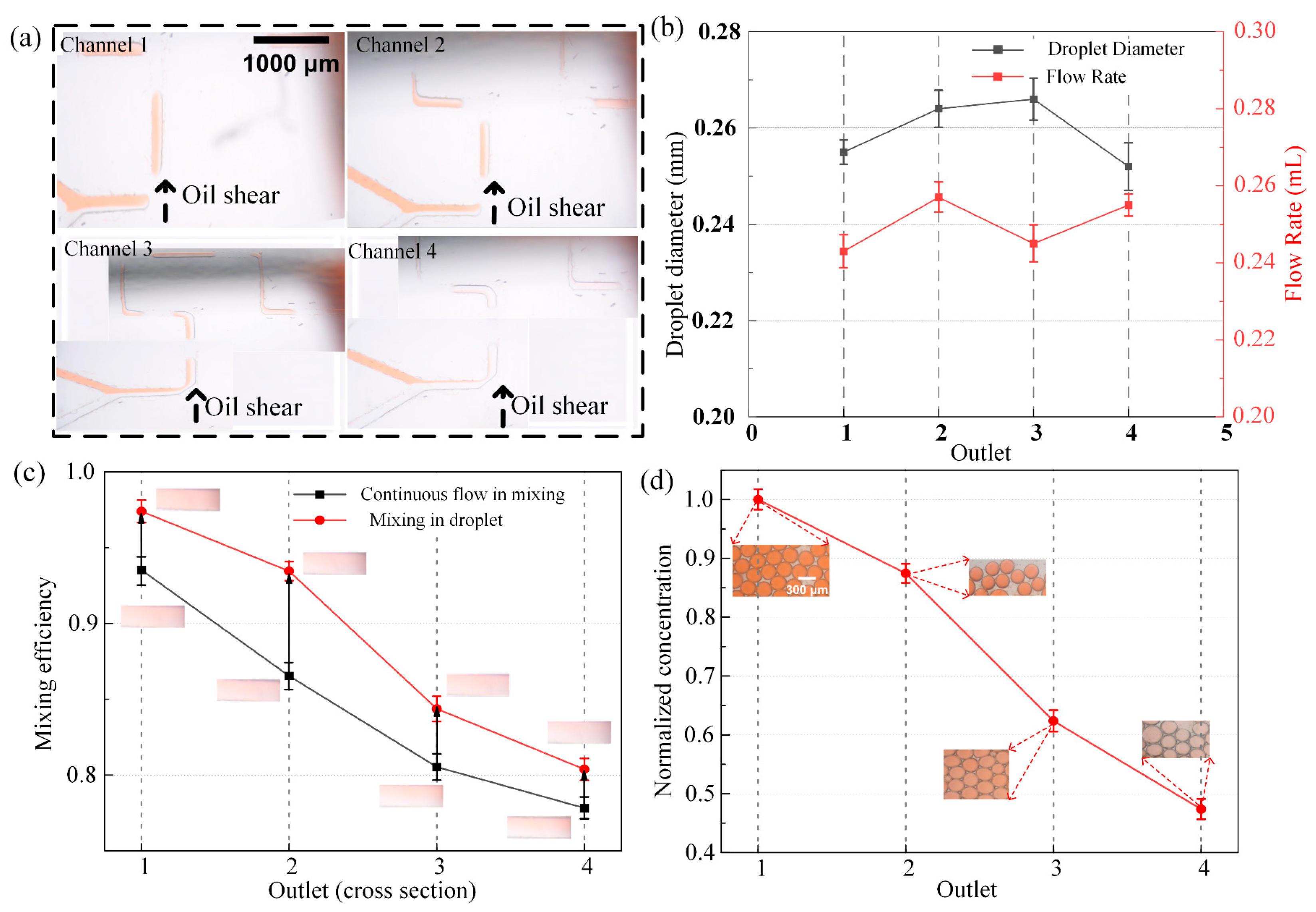
3.2. Experimental Study on the Partitioning–Recombination of Two Fluids Under Continuous Flow Conditions
3.3. Flexible Generation and Analysis of Concentration Gradient Droplets
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bacchin, P.; Leng, J.; Salmon, J.-B. Microfluidic Evaporation, Pervaporation, and Osmosis: From Passive Pumping to Solute Concentration. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 6938–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, D.; Xiong, R.; Braeckmans, K.; Scheid, B.; Huang, C.; Sauvage, F.; De Smedt, S.C. Concentration Gradients in Material Sciences: Methods to Design and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Hu, X.; Gao, X.; Dai, F.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, Y. An Optofluidic System for the Concentration Gradient Screening of Oocyte Protection Drugs. Talanta 2024, 278, 126472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shourabi, A.Y.; Kashaninejad, N.; Saidi, M.S. An Integrated Microfluidic Concentration Gradient Generator for Mechanical Stimulation and Drug Delivery. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2021, 6, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, B.D.; Castanheira, E.M.S.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Cardoso, V.F. Recent Advances on Cell Culture Platforms for in Vitro Drug Screening and Cell Therapies: From Conventional to Microfluidic Strategies. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2202936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Toprakcioglu, Z.; Jayaram, A.K.; Guo, G.; Wang, X.; Knowles, T.P.J. Formation of Protein Nanoparticles in Microdroplet Flow Reactors. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 11335–11344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yang, D.; Yu, Z.; He, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J. Deep Learning-Aided High-Throughput Screening of Time-Resolved Protein Crystallization on Programmable Microliter-Droplet Systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K.; Sreedhara, A.; Colandene, J.D.; Chou, D.K.; Filipe, V.; Grapentin, C.; Searles, J.; Christian, T.R.; Narhi, L.O.; Jiskoot, W. Stress Factors in Protein Drug Product Manufacturing and Their Impact on Product Quality. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 868–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Tian, F.; Dai, B.; Sun, J. One-Step Thermophoretic AND Gate Operation on Extracellular Vesicles Improves Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2022, 61, e202207037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Li, Y.; Yan, H.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Friedman, L.; Zeng, Y. Advances in Microfluidic Extracellular Vesicle Analysis for Cancer Diagnostics. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3219–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; McElroy, W.; Pawliszyn, J.; Heger, C.D. Imaged Capillary Isoelectric Focusing: Applications in the Pharmaceutical Industry and Recent Innovations of the Technology. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 150, 116567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, A.; Perego, C.; Salvalaglio, M.; Parrinello, M.; Yazaydin, O. Concentration Gradient Driven Molecular Dynamics: A New Method for Simulations of Membrane Permeation and Separation. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 3858–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinnrock, A.; Martens, M.; Enders, F.; Boldt, K.; Cölfen, H. Controlled Preparation of Nanoparticle Gradient Materials by Diffusion. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthier, E.; Beebe, D.J. Gradient Generation Platforms: New Directions for an Established Microfluidic Technology. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3241–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, R.; Peng, X.; Su, Y.-C.; Sun, D. 3D Printed Microfluidic Chip for Multiple Anticancer Drug Combinations. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 276, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.-Y.; Hu, S.-W.; Qian, G.-S.; Xu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. A Novel Microfluidic Platform with Stable Concentration Gradient for on Chip Cell Culture and Screening Assays. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 3714–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Pang, Y. Concentration Gradient Generation Methods Based on Microfluidic Systems. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 29966–29984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Nie, F. Microfluidic Platforms for Gradient Generation and Its Applications. Biochem. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 06, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Huang, X.; Chu, Q.; Ning, X.; Wang, Y.; Kong, S.-K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Ho, H.-P. A Linear Concentration Gradient Generator Based on Multi-Layered Centrifugal Microfluidics and Its Application in Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.; Hu, G. Generation of Multiple Concentration Gradients Using a TwoDimensional Pyramid Array. Anal. Chem. 2023, 96, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Xue, P.; Wu, Y.; Bao, J.; Chuah, Y.J.; Kang, Y. A Concentration Gradient Generator on a Paper-Based Microfluidic Chip Coupled with Cell Culture Microarray for High-Throughput Drug Screening. Biomed. Microdevices 2016, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Wu, Y.; Feng, Q.; Qiu, X.; Sun, L.; Yang, H. Rapid In-Droplet Tri-Fluid Micromixing and Concentration Gradient Generation for Nanoparticle Synthesis. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 708, 135983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, M.; Moshksayan, K.; Kashaninejad, N.; Saidi, M.S.; Nguyen, N.-T. A Tool for Designing Tree-like Concentration Gradient Generators for Lab-on-a-Chip Applications. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 212, 115339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rismanian, M.; Saidi, M.S.; Kashaninejad, N. A New Non-Dimensional Parameter to Obtain the Minimum Mixing Length in Tree-like Concentration Gradient Generators. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 195, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, X. Simulation and Experimental Investigation on Tree Concentration Gradient Generator with U-Shape Microchannel. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Minerick, A.R. Reaction-Free Concentration Gradient Generation in Spatially Nonuniform AC Electric Fields. Langmuir 2022, 38, 5977–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, B.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Generation of Droplets with Adjustable Chemical Concentrations Based on Fixed Potential Induced-Charge Electro-Osmosis. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, Y.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Sung, H.J.; Jeon, J.S. Antibiotic Susceptibility Test under a Linear Concentration Gradient Using Travelling Surface Acoustic Waves. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 3449–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destgeer, G.; Im, S.; Ha, B.H.; Jung, J.H.; Ansari, M.A.; Sung, H.J. Adjustable, Rapidly Switching Microfluidic Gradient Generation Using Focused Travelling Surface Acoustic Waves. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 023506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.C.R.; Salin, E.D. Pneumatically pumping fluids radially inward on centrifugal microfluidic platforms in motion. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8039–8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, J.F.; Zehnle, S.; Juelg, P.; Hutzenlaub, T.; Zengerle, R.; Paust, N. Review on pneumatic operations in centrifugal microfluidics. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 3745–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skafte-Pedersen, P.; Sabourin, D.; Dufva, M.; Snakenborg, D. Multi-channel peristaltic pump for microfluidic applications featuring monolithic PDMS inlay. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 3003–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.B.; Chien, C.C.; You, H.L.; Kuo, F.C.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, G.B. An integrated microfluidic system for antimicrobial susceptibility testing with antibiotic combination. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2699–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, H.; Xu, H.; Dai, W.; Xu, L.; Du, H.; Zhang, D. A Review on the Development and Application of Microfluidic Concentration Gradient Generators. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 072014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ren, Y.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, T.; Jiang, H. Three-Fluid Sequential Micromixing-Assisted Nanoparticle Synthesis Utilizing Alternating Current Electrothermal Flow. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 12514–12524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Ren, Y.; Sun, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, K.; Jia, Y.; Hou, L.; Xiao, M.; Jiang, H. Effect of Vortex on Mass Transport and Mixing in Microcapillary Channels. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaleiro, J.M. Flowrate Independent 3D Printed Microfluidic Concentration Gradient Generator. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, H. An Effective Splitting-and-Recombination Micromixer with Self-Rotated Contact Surface for Wide Reynolds Number Range Applications. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 54121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjigeorgiou, A.G.; Boudouvis, A.G.; Kokkoris, G. Thorough Computational Analysis of the Staggered Herringbone Micromixer Reveals Transport Mechanisms and Enables Mixing Efficiency-Based Improved Design. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 128775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhu, M.; Chen, T.; Sun, L. Analysis of Sequential Micromixing Driven by Sinusoidally Shaped Induced-Charge Electroosmotic Flow. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ren, Y.; Hou, L.; Tao, Y.; Liu, W.; Jiang, T.; Jiang, H. Continuous Microfluidic Mixing and the Highly Controlled Nanoparticle Synthesis Using Direct Current-Induced Thermal Buoyancy Convection. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2020, 24, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Jiang, B.; Peng, T.; Zhou, M.; Drummer, D. Investigation of Efficient Mixing Enhancement in Planar Micromixers with Short Mixing Length. Chem. Eng. Process. 2022, 171, 108747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; Feng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Sun, H.; Yang, H.; Sun, L. Flexible Concentration Gradient Droplet Generation via Partitioning–Recombination in a Shear Flow-Driven Multilayer Microfluidic Chip. Symmetry 2025, 17, 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060826
Yu L, Feng Q, Chen Y, Wu Y, Sun H, Yang H, Sun L. Flexible Concentration Gradient Droplet Generation via Partitioning–Recombination in a Shear Flow-Driven Multilayer Microfluidic Chip. Symmetry. 2025; 17(6):826. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060826
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Linkai, Qingyang Feng, Yifan Chen, Yongji Wu, Haizhen Sun, Hao Yang, and Lining Sun. 2025. "Flexible Concentration Gradient Droplet Generation via Partitioning–Recombination in a Shear Flow-Driven Multilayer Microfluidic Chip" Symmetry 17, no. 6: 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060826
APA StyleYu, L., Feng, Q., Chen, Y., Wu, Y., Sun, H., Yang, H., & Sun, L. (2025). Flexible Concentration Gradient Droplet Generation via Partitioning–Recombination in a Shear Flow-Driven Multilayer Microfluidic Chip. Symmetry, 17(6), 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060826








