Abstract
In real-life mixed-model assembly lines, multiple problems collectively affect the final production’s performance. In this study, mixed-model assembly lines integrated with balancing and sequencing problems are considered simultaneously solved. A comprehensive mathematical model is formulated to evaluate the current multi-objective problem. An intelligent hybrid genetic algorithm (IHGA) is proposed to solve the integrated mixed-model assembly line balancing and sequencing problem. The performance of the proposed algorithm is triggered by integrating heuristic rules through a generation gap mechanism which helps in reducing search space without succumbing to local optima. Additionally, parametric tuning of the algorithm is performed using Q-learning, enabling adaptive optimization through reinforcement learning. This helps to enhance computational efficiency and achieve robust performance of the proposed algorithm. The performance of the IHGA algorithm is rigorously compared with existing approaches, including a non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm, multi-objective artificial bee colony, multi-objective particle swarm optimization, multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on Decomposition, and multi-objective grey wolf optimizer. Results demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed algorithm across various metrics, showcasing its efficacy in optimizing mixed-model assembly lines, where symmetry in task allocation and sequencing can significantly enhance operational efficiency in contemporary industrial settings. Additionally, a real-life case study is solved to validate the empirical applicability of the proposed IHGA. The extensive experimental analysis notably shows that the proposed IHGA outperforms the existing methods.
1. Introduction
Optimizing assembly line efficiency in modern manufacturing is pivotal to meeting the growing demands for product diversity, quality, and cost-effectiveness. Mixed-model assembly lines (MMALs) have emerged as a prominent solution to accommodate diverse product variants while maintaining high efficiency. In MMAL, different job models are intermixed to be produced on the same line with the same or different batch sizes. Moreover, the MMALs allow for the simultaneous production of multiple product models on the same line, enabling manufacturers to achieve greater flexibility and responsiveness to fluctuating market demands. Despite their advantages, MMALs present unique challenges in line balancing, sequencing, and resource allocation, directly impacting overall efficiency. Traditional optimization methods, such as mathematical programming and heuristic algorithms, have been extensively utilized to address these challenges [1]. Addressing MMAL problems to evaluate key performance measures such as cycle and flow times presents several challenges. Managers struggle to gather accurate and comprehensive data on cycle times and product mix, navigate the inherent complexity of MMAL environments, and adapt evaluation strategies to dynamic operational conditions. Due to this, the day-to-day decision-making processes pose additional hurdles. Symmetrical task and model distribution helps achieve workload uniformity, reduce idle times, and enhance overall line stability. This perspective supports multi-objective optimization and improves the robustness of mixed-model assembly systems.
1.1. Related Literature
In contemporary manufacturing environments, the optimization of MMAL has become increasingly vital to efficiently meet the demands of dynamic markets and varied product lines. The mixed-model assembly line balancing (MMALB) problem has garnered significant attention from researchers seeking to enhance productivity and operational efficiency in industrial settings [2]. Central to this endeavor is developing and applying optimization methodologies that effectively address the complexities inherent in MMALB, focusing on minimizing cycle time, improving the smoothness index, and enhancing overall balance efficiency. Moreover, the MMALB problem and the model sequencing (MS) problem have garnered significant attention from researchers seeking to improve productivity and operational efficiency in industrial settings [3]. The ALB problem concerns allocating tasks to assembly stations to optimize critical performance metrics such as cycle time, smoothness index, and balance efficiency. Conversely, MSP focuses on determining the optimal sequence in which product variety should be assembled, aiming to minimize or optimize metrics. These challenges necessitate consideration and strategic decision-making with multi-objective problems to enhance the overall efficiency and effectiveness of MMALB and MS problems. These multi-objective challenges underscore the complexity of MMAL optimization when solving simultaneously, making the problem NP-hard [4]. However, as assembly line complexity increases, conventional approaches often struggle to deliver satisfactory results within acceptable time frames.
The prevalence of MMAL within industries has spurred considerable research attention toward the associated optimization challenges, particularly in line balancing and sequencing problems. Investigations have explored various facets of MMAL, including formulating objective functions tailored to specific optimization goals. Bai, Zhao, and Zhu [5] devised a mathematical framework targeting multi-objective MMAL for balancing problems to minimize the number of workstations while maximizing the assembly line’s efficiency. Simaria and Vilarinho [6] extended this research paradigm by incorporating three objectives in MMAL problem analysis, primarily focusing on cycle time minimization, supplemented by workload balancing and adherence to zoning constraints. Subsequent Mamun, Khaled [7] and Özcan, Çerçioğlu [8] further studied the MMAL problem for workstation minimization strategies to balance the assembly line. Moreover, the researchers pursued a dual objective of minimizing workstations while maximizing balance efficiency in their MMALBP investigation. Chica, Cordón [9] introduced robustness functions tailored for the time and space-based line balancing to reduce the number of workstations and station areas while ensuring a fixed cycle time, employing genetic algorithm (GA) optimization techniques. Through an analysis of the literature, it becomes evident that cycle time is a pivotal performance metric in MMALBP studies.
Moreover, in MMALs, effective model sequencing is critical to minimizing bottlenecks and maintaining smoothness in production flow [10]. Poor sequencing can lead to increased workstation starvation, inventory imbalances, and higher costs [11]. Effective model sequencing also enhances flexibility, allowing manufacturers to meet diverse customer demands while maintaining efficiency and reducing utility work, such as part feeding and line reconfigurations [12]. As modern manufacturing trends toward high-mix, low-volume production, advanced sequencing strategies become even more crucial for maintaining competitiveness, reducing lead times, and ensuring smooth, cost-effective assembly line operations [10]. Therefore, optimization of model sequencing in the MMAL problem is extensively studied to address challenges such as minimizing the cycle time, flow time, workload smoothing, utility work, and reducing line stoppages.
In recent years, evolutionary algorithms, mainly GA, have gained prominence as powerful optimization techniques for MMALs [13]. It has emerged as a popular approach for MMALB optimization due to its ability to mimic evolutionary processes and iteratively refine assembly line configurations. The traditional GA often entails high computational costs from exhaustive search processes and the risk of premature convergence [14]. Moreover, GA offers the advantage of efficiently exploring large solution spaces and identifying near-optimal solutions through iterative processes inspired by natural selection and genetics. Nevertheless, the computational overhead associated with traditional GA remains a significant bottleneck, especially when dealing with complex MMAL configurations [15]. Among the literature works in this domain, Noorul Haq, Rengarajan, and Jayaprakash [16] proposed a hybrid GA specifically tailored to address the MMALB type-I problem. The approach introduced a rank positional weight method for population initialization, resulting in superior performance compared to conventional genetic algorithms. Bai, Zhao, and Zhu [5] advanced this inquiry by introducing a hybrid approach that combined simulated annealing (SA) with GA to counter premature convergence in MMALB optimization. Simaria and Vilarinho [6] developed a GA optimized for MMALB scenarios featuring parallel workstations. At the same time, Su and Lu [17] proposed a phased optimization strategy to achieve workload balance across stations. The authors optimized the problem in two phases. In the first phase, the upper limit for the cycle time is set and a feasible solution is obtained. The feasible solution is again fine-tuned in the second phase to obtain the best solution. The existing literature on solving MMAL balancing and sequencing problems encompasses various methodologies and algorithms to improve production efficiency in diverse industrial settings.
Moreover, the existing literature on solving MMAL encompasses various methodologies and algorithms to improve production efficiency in diverse industrial settings. Mamun and Khaled [7] utilized a GA augmented with a local search heuristic to prevent solution convergence, applying it to a local plastic bag manufacturing industry. Sivasankaran and Shahabudeen [18] proposed a GA focusing on minimizing the number of workstations while maximizing balance efficiency. Özcan, Çerçioğlu [8] addressed MMAL balancing and sequencing using a simulated annealing algorithm. Delice, Aydoğan [19] introduced an ant colony optimization algorithm for a two-sided MMALB type-I problem. Yang, Gao, and Sun [13] introduced a multi-objective GA to rebalance the MMALB problem in response to demand changes. Li and Gao [20] developed a branch and bound (B&B) algorithm considering unstable demand, utilizing overtime work to meet demand. As evident from Table 1, researchers commonly augment GA with various heuristic methods to enhance performance. These studies often use different heuristics as initial populations for GA. However, relying on these initial populations can sometimes restrict the search for local solutions within the heuristics. Therefore, this study proposes a novel intelligent hybrid GA (IHGA), distinguished by introducing solutions from heuristics through a generation gap mechanism and parametric tuning using Q-learning, enabling adaptive optimization through reinforcement learning.

Table 1.
Summary of literature on MMALB-MSP using hybrid GAs.
1.2. Research Gap
The contributions of this study can be categorized based on the studied problem, and solution approach.
Mixed-model assembly lines integrated with balancing and sequencing problems are considered simultaneously to identify their combined effect on real-life industrial problems.
A comprehensive MIP mathematical model is formulated to evaluate the current NP-hard multi-objective optimization problem by considering all related constraints to make it feasible for the empirical application.
This study proposes a novel intelligent hybrid GA (IHGA), distinguished by introducing three novel features and enhancing the performance of the proposed approach. The proposed IHGA is further implemented on a multi-objective mixed-model assembly line integrated with line balancing and sequencing problems.
The first embedded feature is the generation gap mechanism approach which helps mitigate the limitation of confining solutions to heuristics and facilitates gradual convergence toward optimal solutions by leveraging exploitation and exploration. The second feature is parametric tuning using Q-learning, enabling adaptive optimization through reinforcement learning. Adaptive parametric tuning using the Q-learning approach activates computational efficiency and achieves robust performance for the proposed algorithm.
1.3. Structure of the Paper
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows: Problem description and mathematical model are present in Section 2. Section 3 outlines the methodology employed in developing the proposed IHGA approach. Section 4 presents the case study problem and implementation of the proposed method. Section 5 discusses the results of the experiments and their implications. Finally, Section 6 offers conclusions and avenues for future research.
2. Problem Description and Mathematical Model
The integration of advanced computational techniques has become essential to optimize manufacturing processes. The MMAL under consideration consists of many sequential stations that produce different models ( in an intermixed order. Each model has its own set of required tasks (, making it more complex. Moreover, the concept of a combined precedence diagram is used to form a single precedence diagram. A few assumptions are considered to decrease and minimize the complexity of the current model. Process time for each known model is deterministic and constant. The precedence diagram for each model is known. Parallel workstations are not allowed. Similar and dissimilar tasks of different models may have different task times. Each task is assigned to only one station at a time.
The first objective in Equation (1) is to minimize the assembly line’s maximum cycle time () among all stations (j). Cycle time is equal to the maximum service time (Tsj) of the jth station.
The second objective is given in Equation (2), which is used to minimize the average flow time. Here, n is the number of models. CTij is the completion time of model (i) at station (j) and ATi1 is the arrival time of model (i) at station one. There are various constraints to consider while solving this multi-objective problem.
The constraint in Equation (3) ensures that one task cannot be assigned to more than one station. is a decision variable with value one if task (t) is assigned to station (i) otherwise zero.
Constraint (4) indicates that the total task time at any station is always less than the cycle time. Tt is time required to perform tth task.
The constraint (5) defines that task v can only be assigned to the same or next station as of its predecessor task (t) and ensures the precedence constraints. Here, is the subset of the set of direct predecessors of the tasks.
Equation (6) ensures that only one model is assigned to one station. Here, Yij is the decision variable with value one if model (i) is assigned to station (j) otherwise zero.
The Equation (7) ensures that the workstation can be idle.
Equation (8) shows that the arrival time of the first model at the first station is zero.
The arrival time of model i at the first station is equal to the completion time of the previous model, as given in Equation (9).
3. Proposed Optimization Approach
This section outlines the proposed intelligent hybrid genetic algorithm (IHGA) and elucidates its significance in solving the MMALB-MSP. The IHGA amalgamates the advantageous features of GAs, non-dominated sorted Pareto solutions, and local search techniques to explore the search space efficiently and converge to optimal or near-optimal solutions. The fundamental challenge in optimization problems is balancing exploring and exploiting search space. Traditional GAs excel in exploration by maintaining a diverse population, while local search techniques focus on exploitation by refining promising solutions. The proposed IHGA introduces a more fit chromosome (MFC) through a generation gap to reduce the search space, which helps achieve a harmonious balance between these two aspects and leverages the strength of both paradigms. By integrating local search operators into the genetic algorithm framework, the IHGA harnesses the power of exploitation to accelerate convergence. Local search techniques enable the algorithm to exploit the local neighborhood of solutions, guiding the search towards promising regions of the solution space. Consequently, the IHGA exhibits faster convergence rates than traditional GAs, reducing computational time and resource utilization.
The proposed IHGA algorithm begins with generating an initial population using a hybrid method termed hybrid-method-generated initial population (HMGIP), which combines random generation with heuristic approaches for efficient exploration. Subsequently, genetic operations, including selection, crossover, and mutation, are applied to the population to maintain diversity and explore the solution space. The algorithm then employs a local search procedure to refine candidate solutions, focusing on promising regions identified through genetic operations. This iterative process continues until a convergence criterion is met, ensuring the algorithm efficiently converges towards optimal or near-optimal solutions. This hybrid nature of the proposed algorithm endows it with robustness and adaptability across various problem domains. Traditional GAs may struggle with complex landscapes characterized by multiple local optima, while local search techniques may get trapped in suboptimal solutions. By combining these methodologies, the IHGA can navigate through intricate solution spaces with agility, ensuring robust performance and adaptability to diverse problem scenarios.
After generating the population, each chromosome’s fitness function value is assessed, and the one with the poorest fitness function value is replaced with an MFC generated through a heuristic method. This dynamic introduction of solutions eliminates the constraint of being limited to the HMGIP and facilitates a gradual convergence towards optimal or suboptimal solutions with each iteration. Following replacement, chromosomes are selected for reproduction in the following population generation. Genetic operations, including mutation and crossover, are then applied to generate a new population. These steps iterate until the termination condition is met. The schematic representation of the proposed IHGA is illustrated in Figure 1.
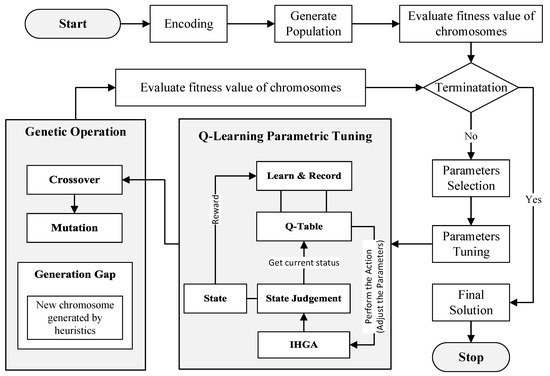
Figure 1.
Framework of proposed intelligent hybrid genetic algorithm (IHGA).
3.1. Reinforcement Learning-Based Parameter Tuning
The proposed IHGA’s performance depends on key parameters like crossover rate () and mutation rate (). Traditional manual tuning is often inefficient. To address this, Q-Learning-based parameter adaptation is integrated to dynamically adjust these parameters and enhance algorithm performance. Q-learning, a reinforcement learning technique, enables the algorithm to learn optimal parameter settings by maximizing a reward signal. In this IHGA, Q-Learning adjusts parameters based on the algorithm’s state (e.g., solution quality) and the resulting reward (e.g., improvement in objective function values). One common challenge in integrating reinforcement learning is the ineffective updating of the Q-table. To address cases where Q-learning fails to update the Q-table (e.g., due to insufficient exploration or weak reward signals), an ε-greedy policy is used to ensure continued exploration. If learning stagnates, a re-initialization of state-action pairs is triggered after a fixed number of stagnant generations. This dynamic adaptation allows the IHGA to explore the parameter space effectively, avoid premature convergence, and improve its ability to solve the integrated MMALB-MSP.
3.1.1. State Definition
A suitable state representation is essential to implement Q-Learning for parameter adaptation in the IHGA. The state is designed to capture the search process’s diversity and fitness. Specifically, the state considers population diversity, average fitness, and maximum fitness. Population diversity is measured by the average distance between individual solutions, calculated using Equations (10) and (11).
where is the Euclidean distance between individuals and , and are the maximum and minimum distances, and N is the population size. Objective values are normalized, and fitness values are calculated accordingly. Average and maximum fitness values are also calculated. The population state () integrates population diversity and fitness values using Equations (12) to (16).
Here, is the fitness of individual at generation , and , , and are the weights for normalized diversity (), normalized fitness (), and maximum fitness (). The values of , , and are 0.34, 0.33, and 0.33, respectively. The state space is divided into 10 states: . If ; if * ∈ [0.1, 0.2), = (2); and if .
3.1.2. Action Definition
To implement Q-Learning, it is necessary to define the learning agent’s actions to adjust the IHGA’s parameters. In this case, the action involves modifying the two key parameters of the HGA: the crossover rate () and mutation rate (). Each action represents a change to one of these parameters. For example, can be adjusted according to the Equation (17).
Here, (t) and represent the values of at generation and , respectively, and constitutes the action space for . The action space for each of the two parameters consists of two possible actions. The values of the action spaces for these parameters are given in Table 2. Based on generation and population state, solutions update via crossover or mutation. Actions are selected randomly from for crossover, and from for mutation.

Table 2.
Action space of reinforcement learning-based parameter tuning.
3.1.3. Reward Function
Q-Learning uses a reward system to evaluate the effectiveness of actions and update the value function. The reward is feedback from the state transition, and it depends on the change in the population state. In this implementation, each action of the parameters and has a corresponding reward: and respectively. This reward is calculated using the following Equation (18). The updated value function of the agent is calculated using the Q-Learning update rule given in Equation (19).
where and are the current and subsequent states, respectively. and are the current and subsequent actions, respectively. is the learning rate. is the discount factor. The Pseudo code for the implementation of IHGA with Q-Learning is given in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1. Intelligent Hybrid Genetic Algorithm with Q-Learning |
| Input: problem_files, mutation set M, crossover set C, episodes E, learning rate α, discount factor β, initial exploration ε, decay εdecay, action magnitudes cc, cr, stagnation threshold Ts Output: , final Pareto fronts, cycle time Z1, avg. flow time Z2  |
4. Empirical Application Proposed Approach
The case study focuses on a real-world application involving a hydraulic pump assembly line to demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed IHGA. This line is utilized to assemble five distinct models of hydraulic pumps, identified as HP-27092 (A), HP-27095 (B), HP-27098 (C), HP-28001 (D), and HP-28015 (E) among others, with each model exhibiting its specific configuration and assembly requirements. The assembly process encompasses various critical tasks, including the attachment of valves to valve chambers, pistons to valve chambers, stud, and strainer assembly to housing intake, response levers, non-returnable valves, cover plates, bush bearings, hex sockets, control valves, safety valves, and camshafts to respective front and rear body components. These tasks must be sequentially assembled following predefined precedence relationships, ensuring operational efficiency and product quality. The assembly process begins with loading the models onto station 1 and progresses through various stations until unloading at station 7, as depicted in Figure 2. This detailed breakdown reflects the complexity and variety of operations required, highlighting the critical need for an effective and efficient line balancing and sequencing approach. Given the complexity of assembling multiple pump variants on a single mixed-model assembly line, the practical application of the proposed optimization methodology is vital for minimizing cycle time and flow time. Comprehensive data from the real assembly operations serve as an essential input to validate the IHGA approach detailed in this paper, providing robust evidence for its practical applicability and superior performance compared to existing methods. This study entails a three-week time and motion analysis to determine the average task duration for various assembly processes across five distinct models. A total of 24 tasks, encompassing similar and dissimilar operations, are identified as essential for assembling these models. The average task durations for each model are outlined in Table 3. Furthermore, the production requirements for models A, B, C, D, and E are specified as 3.38, 3.07, 2.97, 1.87, and 3.32 units per unit of time, respectively.
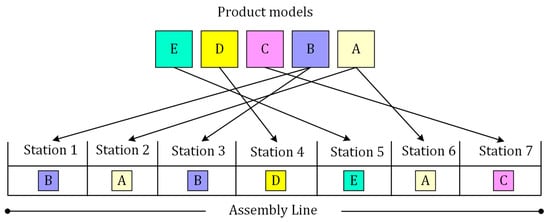
Figure 2.
Mixed-model assembly line.

Table 3.
Tasks time of the considered models.
4.1. Implementation of the Proposed Approach
The first step of the proposed intelligent hybrid genetic algorithm, i.e., IHGA, involves encoding the solutions. One-to-one encoding of solution is proposed, meaning encoding of one solution is represented by one chromosome [6]. Chromosomes are represented by length N. Each task is represented by an element (known as a gene), while the workstation represents the value of each component. The encoding of the solution and decoding of the chromosome is shown in Figure 3. The initial population of 100 chromosomes is generated randomly. Elitism criteria of 10% are used, meaning 10 unchanged chromosomes are used in the next population. Roulette wheel selection criteria are used to select the chromosomes for genetic operations.
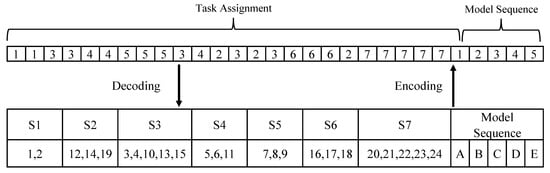
Figure 3.
Encoding and decoding of chromosomes.
In standard GA, two fundamental genetic operations, crossover and mutation, are employed. Crossover operation enables the algorithm to combine genes from different chromosomes, forming new chromosomes, referred to as offspring, for the subsequent population. In this context, uniform crossover is applied, which differs from other techniques by allowing crossover to occur at the gene level rather than the segment level, as depicted in Figure 4. It is widely used in evolutionary algorithms for optimization problems due to its ability to explore the solution space efficiently and maintain genetic diversity. Uniform crossover involves randomly selected genes from two-parent individuals and exchanging them to create offspring. The process typically starts by randomly selecting a crossover mask that determines which genes will be inherited from each parent. Then, for each gene position, a random number is generated to decide whether the gene will be inherited from the first or the second parent according to the mask. This results in offspring that inherit genetic material from both parents, promoting diversity in the population.
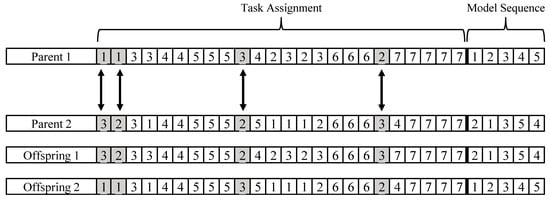
Figure 4.
Generation of offspring by crossover.
In mutation operation, random chromosome gene changes are applied to create offspring, as shown in Figure 5. Mutation is a crucial factor in introducing genetic diversity in a population. It works by randomly altering the genetic material of individuals within the population. In binary encoding, mutation typically involves flipping the bits of a chromosome with a small probability, often called the mutation rate. This small, controlled change allows the algorithm to explore new regions of the solution space that may lead to improved solutions. The mutation prevents premature convergence by continuously introducing novel genetic material, ensuring the algorithm can escape local optima and thoroughly explore the search space. Mutation operation increases the chance of developing chromosomes with better fitness function values. Otherwise, the algorithm could only produce the chromosome with genes from the initial population’s genes.
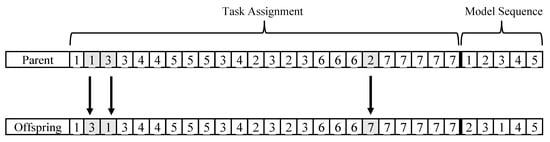
Figure 5.
Generation of offspring by mutation.
The generation gap expands the algorithm’s search space, with its value typically ranging from 0 to 1. A smaller generation gap fosters greater exploitation, facilitating the algorithm’s expedited convergence towards optimal or near-optimal solutions. Accordingly, a generation gap of 1% is recommended, implying that each new generation comprises one additional chromosome, given a population size of 100. This additional chromosome is generated using the MFC heuristic method and replaces the chromosome with the poorest fitness value. It is stipulated that the fitness value of the MFC should surpass that of the replaced chromosome. Notably, adopting the MFC approach following each generation constitutes a novel contribution to the existing literature. Iterations are terminated at 200 s. The chromosome, with the minimum objective value obtained after executing the IHGA, is given in Figure 6.
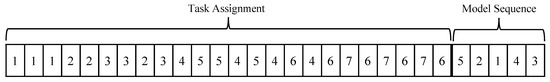
Figure 6.
Chromosome obtained from IHGA.
Decoding translates the encoded representation of solutions, typically in the form of chromosomes, into a format that can be evaluated and understood in the context of the problem domain. This process is essential for assessing the fitness of individuals and guiding the search for optimal solutions. Figure 6 shows the tasks assigned to the stations and model sequence. As can be seen from Figure 6 tasks 1, 2, and 3 are assigned to station 1, while tasks 4, 5, and 8 are assigned to station 2. The solution obtained from the decoding of the chromosome is provided in Table 4. The sequence of models is 5, 2, 1, 4, 3 which translates to .

Table 4.
Solution obtained from the decoding of the chromosome.
4.2. Performance Analysis
The hydraulic pump assembly line problem has been solved through IHGA, NSGA-II [36], MOPSO [37], MOABC [38], MOEAD [39] and MOGWO [40]. Equations (1) and (2) are used to measure the objective values from the solutions provided by the various algorithms. The values of each objective function obtained from various algorithms are given in Table 5. As cycle and flow time are trade-off objectives, utilizing multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) techniques is imperative for evaluating algorithmic performance. Without such decision-making methodologies, determining the superior algorithm solely on performance measures becomes unfeasible. Therefore, applying MCDM techniques becomes necessary to effectively compare and discern the performance of different algorithms across multiple criteria or dimensions. The TOPSIS holds significance as an MCDM approach due to its ability to comprehensively evaluate alternatives across multiple criteria, flexibility to accommodate various types of criteria, effectiveness in handling trade-offs, and robustness in yielding reliable results even in the presence of uncertainties. Therefore, the analysis uses TOPSIS to select the best algorithm based on priorities. In TOPSIS, distances to the positive and negative ideal solutions are calculated simultaneously to measure the ranking order of all alternatives [41]. It can be seen from Table 5 that proposed IHGA is ranked 1st based on TOPSIS analysis.

Table 5.
Performance measures of algorithms.
The progression of objective function values every two seconds is recorded and depicted in Figure 7. Figure 7 provides the convergence insight of different algorithms. As shown in Figure 7, the proposed IHGA algorithm begins to converge after 20 s and achieves the minimum cycle time. In contrast, NSGA-II and MOEAD appear to stagnate in local optima after 25 s, while MOABC, MOPSO, and MOGWO fail to converge even by the end of the termination period. For flow time, IHGA converges faster than other compared algorithms. The reason for superior performance could be implementing HMGIP and Q-learning, which help algorithms converge fast and find better solutions.
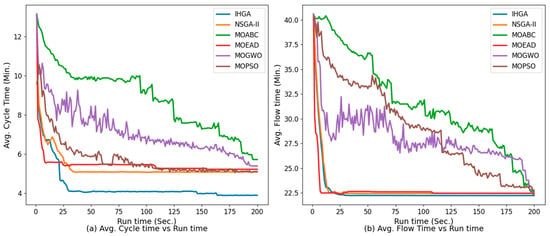
Figure 7.
Convergence comparison of algorithms based on objective functions.
5. Computational Experiments and Analysis
This study adopts three categories of benchmark problem instances developed by Kim, Kim, and Kim [42] to evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm. To evaluate the proposed algorithm: small (20 tasks, 3 models), medium (62 tasks, 4 models), and large (112 tasks, 5 models). Task times were modified using uniform variation, resulting in a total of 30 test instances for performance validation. The performance of the proposed IHGA algorithm is evaluated using various key metrics, i.e., Cycle time (CT), flow time (FT), hypervolume (HV), inverted generational distance (IGD), number of non-dominated Pareto solutions (NP) of the Pareto solutions and TOPSIS. The IGD value assesses the overall effectiveness of the algorithm, where a smaller IGD value indicates better convergence and diversity performance [43]. The hypervolume metric evaluates the quality of a Pareto front approximation by measuring the volume of the objective space dominated by its solutions relative to a reference point, with a higher value indicating better convergence and diversity [44]. Moreover, NP further complements this analysis by evaluating the coverage and dominance quality of the solutions [45].
Therefore, the performance of the proposed IHGA algorithm is compared with the other competitor algorithms, i.e., GA, MOPSO, MOABC, MOEAD, and MOGWO. The test problem instances are categorized into small, medium, and large size problems with (n, k) = (3, 20), (4, 62), and (5, 112), respectively. To ensure a reliable average of the optimal results, each instance was independently executed 10 times for all algorithms, with a uniform termination criterion of 200 s. Table 6 contains the mean values of all performance indicators, i.e., cycle time, flow time, HV, IGD, NP, and TOPSIS values obtained by the algorithms. The numerical results across BM1, BM2, and BM3 clearly demonstrate that IHGA consistently delivers superior performance in terms of solution quality, convergence, and diversity. It achieves the highest hypervolume and lowest IGD values across all problem sizes, indicating well-distributed and accurately converged Pareto fronts. IHGA also maintains competitive cycle and flow times and secures the highest TOPSIS score (1.00) in each instance, confirming its robustness and overall effectiveness. While NSGA-II performs reasonably well on smaller problems, its performance degrades with scale. Other algorithms like MOABC, MOEAD, and MOPSO show consistently inferior results, especially in HV and IGD, highlighting their limited scalability and reliability compared to IHGA.

Table 6.
Mean values of performance indicators for different algorithms.
The results in Figure 8 compare the performance of six comparison algorithms using two significant performance indicator metrics: HV and IGD for small-size problems (BM1). The results indicate that the proposed IHGA consistently outperformed the compared algorithms, achieving the highest HV value and the lowest IGD value, suggesting superior convergence and diversity of solutions. NSGA-II shows moderate performance with reasonable HV and average IGD, indicating acceptable but suboptimal solutions. MOABC performs poorly, with low HV and high IGD, reflecting scattered and distant solutions. MOEAD achieves better HV than MOABC and NSGA-II, but its high IGD suggests limited convergence accuracy. MOGWO performs weakly on both metrics, with low HV, high IGD, and inconsistent behavior. MOPSO is the least effective, showing the lowest HV, high IGD, and minimal solution diversity. Overall, the proposed IHGA proved to be the most effective algorithm.
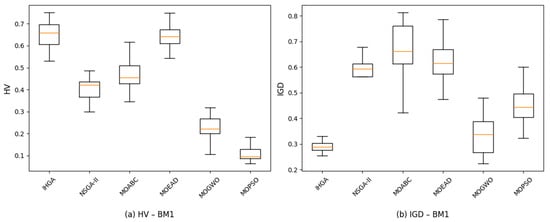
Figure 8.
Robustness of different algorithms based on HV and IGD for small-size problems.
For medium-sized problems (BM2), the performance evaluation using HV and IGD further highlights the superiority of the proposed IHGA as shown in Figure 9. IHGA again outperforms all other methods, achieving the highest HV values with minimal variance, indicating excellent solution diversity and convergence. Its IGD is also the lowest and most consistent, confirming high accuracy and stability. NSGA-II performs well with high HV but slightly elevated and variable IGD, indicating less precise convergence than IHGA. MOABC shows poor performance with low HV and high, inconsistent IGD. MOEAD slightly improves in HV but has the highest IGD, reflecting poor accuracy. MOGWO yields moderate results but lacks consistency. MOPSO outperforms MOABC and MOEAD but remains less reliable due to high variability and suboptimal IGD. These findings reinforce the proposed IHGA’s robustness and efficiency, especially as problem complexity increases.
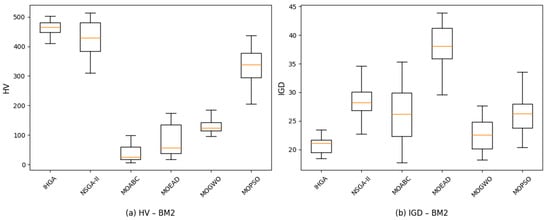
Figure 9.
Robustness of different algorithms based on HV and IGD for medium-size problems.
Similarly, in the case of large-sized problems (BM3), our proposed IHGA algorithm also maintained its leading performance among the four tested algorithms given in Figure 10. IHGA maintains clear superiority with the highest HV and the lowest, most consistent IGD, confirming its robustness and accuracy on large-scale problems. NSGA-II performs second best, with moderate HV and slightly higher IGD than IHGA. Its results show more variability but remain competitive. MOABC delivers limited performance, with low HV and moderately high IGD, suggesting insufficient convergence and poor solution quality. MOEAD shows slight HV improvement over MOABC but still underperforms in IGD, reflecting weak convergence to the true front. MOGWO achieves better consistency than MOABC and MOEAD, but both HV and IGD remain clearly inferior to IHGA and NSGA-II. MOPSO exhibits the worst performance overall. It has moderate HV but the highest and most variable IGD, indicating unstable and inaccurate solutions.
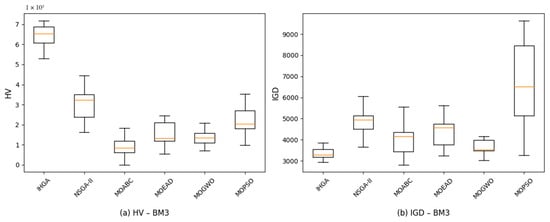
Figure 10.
Robustness of different algorithms based on HV and IGD for large-size problems.
Based on the comparative performance across small, medium, and large problem sizes, it is evident that the proposed IHGA algorithm consistently outperforms the other algorithms in both convergence and diverse metrics. Its superior hypervolume scores indicate a well-distributed set of solutions, while its consistently low IGD values demonstrate effective convergence toward the true Pareto front. NSGA-II shows reasonably competitive performance but lacks consistency, especially as the problem size increases. MOABC and MOEAD generally exhibit poor performance with low HV and high IGD values. MOPSO performs inconsistently and shows the highest variability in IGD, particularly in larger instances. Overall, IHGA demonstrates robust and superior performance across all benchmark sizes. Therefore, it can be concluded that the proposed IHGA outperforms the comparison algorithms.
6. Conclusions
This study investigates the efficiency of integrated mixed-model assembly lines (MMAL) by addressing balancing and sequencing problems. To solve this complex combinatorial optimization problem, a novel multi-objective intelligent hybrid genetic algorithm (IHGA) is proposed. The performance of the IHGA approach is triggered by integrating two significant features, i.e., generation gap mechanism for reducing search space without succumbing to local optima while optimizing performance effectively and Q-learning for parametric tuning enabling adaptive optimization through reinforcement learning. A comprehensive mathematical model is proposed to evaluate the current multi-objective mixed-model assembly line problem. It incorporates cycle and flow time as objectives and their related constraints for line balancing and model sequencing. Afterward, the proposed algorithm is applied to an empirical case problem containing a mixed-model assembly line process to validate the practical applicability. The performance of the proposed IHGA algorithm is further compared against existing methods using significant performance indicators, i.e., IGD, HV, NP, and TOPSIS for robustness and diversity of solution quality. Results on benchmark problems demonstrate that IHGA consistently achieves the highest hypervolume, lowest IGD, and best TOPSIS scores, indicating superior convergence, diversity, and stability across varying problem sizes. While some algorithms show competitive behavior in isolated metrics, IHGA maintains top performance across all evaluations, confirming its robustness and effectiveness for real-world MMALBSP applications. Results demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed IHGA algorithm compared to the compared algorithms, indicating its efficacy for the studied problem.
Overall, this research contributes significant insights and practical implications for advancing the efficiency of mixed-model assembly lines, addressing a critical need in contemporary industrial operations. Future research in MMAL could explore several promising directions to enhance efficiency further and address emerging challenges. One limitation of the current IHGA is its focus on static production environments. Its applicability in dynamic settings where product mix and demand fluctuate over time remains untested. Future research could extend the IHGA framework to accommodate such dynamic conditions, enabling adaptive scheduling and real-time decision-making in complex manufacturing systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.R.; Data curation, M.U.; Formal analysis, M.R.; Funding acquisition, M.R. and J.M.; Investigation, J.M.; Methodology, M.R. and J.M.; Project administration, M.U. and J.M.; Resources, K.A.M. and J.M.; Software, R.A.; Supervision, M.U. and J.M.; Validation, M.R. and J.M.; Visualization, R.A.; Writing—original draft, M.R; Writing—review and editing, K.A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been supported by the Basic Scientific Research Project of Wenzhou City (G2023036) and (G20240020).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Boysen, N.; Fliedner, M.; Scholl, A. Sequencing mixed-model assembly lines: Survey, classification and model critique. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 192, 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Lei, M. Optimisation of mixed-model assembly line balancing problem under uncertain demand. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 59, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, P.; Askari, A. A Multi-objective mixed-model assembly line sequencing problem with stochastic operation time. J. Optim. Ind. Eng. 2018, 11, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Manavizadeh, N.; Tavakoli, L.; Rabbani, M.; Jolai, F. A multi-objective mixed-model assembly line sequencing problem in order to minimize total costs in a Make-To-Order environment, considering order priority. J. Manuf. Syst. 2013, 32, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, L. Mixed-model assembly line balancing using the hybrid genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation, Zhangjiajie, China, 11–12 April 2009; pp. 242–245. [Google Scholar]
- Simaria, A.S.; Vilarinho, P.M. A genetic algorithm based approach to the mixed-model assembly line balancing problem of type II. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2004, 47, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, A.A.; Khaled, A.A.; Ali, S.M.; Chowdhury, M.M. A heuristic approach for balancing mixed-model assembly line of type I using genetic algorithm. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2012, 50, 5106–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, U.; Çerçioğlu, H.; Gökçen, H.; Toklu, B. Balancing and sequencing of parallel mixed-model assembly lines. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2010, 48, 5089–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chica, M.; Cordón, Ó.; Damas, S.; Bautista, J. A robustness information and visualization model for time and space assembly line balancing under uncertain demand. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 145, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, J.; Alfaro, R.; Batalla, C. Modeling and solving the mixed-model sequencing problem to improve productivity. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 161, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosadegh, H.; Ghomi, S.F.; Süer, G. Heuristic approaches for mixed-model sequencing problem with stochastic processing times. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 2857–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, J.; Alfaro-Pozo, R.; Batalla-García, C. Consideration of human resources in the Mixed-model Sequencing Problem with Work Overload Minimization: Legal provisions and productivity improvement. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 8896–8910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Gao, J.; Sun, L. A multi-objective genetic algorithm for mixed-model assembly line rebalancing. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2013, 65, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, J.; Zailin, G.; Mirza, J.; Rauf, M.; Sarfraz, S.; Shehab, E. Makespan minimization for flow shop scheduling problems using modified operators in genetic algorithm. In Advances in Manufacturing Technology XXXII; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 435–440. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J. A multi-objective cellular genetic algorithm for energy-oriented balancing and sequencing problem of mixed-model assembly line. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorul Haq, A.; Rengarajan, K.; Jayaprakash, J. A hybrid genetic algorithm approach to mixed-model assembly line balancing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 28, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Lu, Y. Combining genetic algorithm and simulation for the mixed-model assembly line balancing problem. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Natural Computation (ICNC 2007), Haikou, China, 24–27 August 2007; pp. 314–318. [Google Scholar]
- Sivasankaran, P.; Shahabudeen, P.M. Genetic algorithm for concurrent balancing of mixed-model assembly lines with original task times of models. Intell. Inf. Manag. 2013, 5, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delice, Y.; Aydoğan, E.K.; Söylemez, İ.; Özcan, U. An ant colony optimisation algorithm for balancing two-sided U-type assembly lines with sequence-dependent set-up times. Sādhanā 2018, 43, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, J. Balancing manual mixed-model assembly lines using overtime work in a demand variation environment. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2014, 52, 3552–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Floudas, C.A.; Cao, X. Balancing mixed-model assembly lines with sequence-dependent tasks via hybrid genetic algorithm. J. Glob. Optim. 2016, 65, 83–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu Li, B.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Xiao, T. Robust balancing of mixed model assembly line. COMPEL-Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2009, 28, 1489–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.E.; Omar, M.K.; Bakar, N.A. Solving assembly line balancing problem using genetic algorithm with heuristics-treated initial population. In Proceedings of the the World Congress on Engineering, London, UK, 2–4 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.-Q.; Su, P. Combining genetic algorithm and simulation analysis for mixed-model assembly line balancing problem. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2008, 6, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Akpınar, S.; Bayhan, G.M. A hybrid genetic algorithm for mixed model assembly line balancing problem with parallel workstations and zoning constraints. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2011, 24, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AkpıNar, S.; Bayhan, G.M.; Baykasoglu, A. Hybridizing ant colony optimization via genetic algorithm for mixed-model assembly line balancing problem with sequence dependent setup times between tasks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 574–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukkoc, I.; Yaman, R. A new hybrid genetic algorithm to solve more realistic mixed-model assembly line balancing problem. Int. J. Logist. Syst. Manag. 2013, 14, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, S.M.; Ghodsi, R.; Rabbani, M.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. A novel two-stage genetic algorithm for a mixed-model U-line balancing problem with duplicated tasks. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 55, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, M.; Montazeri, M.; Farrokhi-Asl, H.; Rafiei, H. A multi-objective genetic algorithm for a mixed-model assembly U-line balancing type-I problem considering human-related issues, training, and learning. J. Ind. Eng. Int. 2016, 12, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hamzadayi, A.; Yildiz, G. A genetic algorithm based approach for simultaneously balancing and sequencing of mixed-model U-lines with parallel workstations and zoning constraints. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2012, 62, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hao, J. Adaptive and Improved Genetic Algorithm for Mixed-model Assembly Line Balancing Problem. Adv. Inf. Sci. Serv. Sci. 2013, 5, 375. [Google Scholar]
- Rabbani, M.; Siadatian, R.; Farrokhi-Asl, H.; Manavizadeh, N. Multi-objective optimization algorithms for mixed model assembly line balancing problem with parallel workstations. Cogent Eng. 2016, 3, 1158903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekiek, B.; De Lit, P.; Pellichero, F.; L’Eglise, T.; Fouda, P.; Falkenauer, E.; Delchambre, A. A multiple objective grouping genetic algorithm for assembly line design. J. Intell. Manuf. 2001, 12, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gen, M. An efficient multiobjective genetic algorithm for mixed-model assembly line balancing problem considering demand ratio-based cycle time. J. Intell. Manuf. 2011, 22, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, M.; Mousavi, Z.; Farrokhi-Asl, H. Multi-objective metaheuristics for solving a type II robotic mixed-model assembly line balancing problem. J. Ind. Prod. Eng. 2016, 33, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabani, M.; Yazdanbakhsh, M.; Farrokhi-Asl, H. Solving a multi-objective mixed-model assembly line balancing and sequencing problem. J. Ind. Syst. Eng. 2017, 10, 155–170. [Google Scholar]
- Ab Rashid, M.F.F.; Tiwari, A.; Hutabarat, W. Integrated optimization of mixed-model assembly sequence planning and line balancing using Multi-objective Discrete Particle Swarm Optimization. Artif. Intell. Eng. Des. Anal. Manuf. 2019, 33, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, U.; Guan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, B.; Mirza, J. Multi-objective artificial bee colony algorithm for order oriented simultaneous sequencing and balancing of multi-mixed model assembly line. J. Intell. Manuf. 2019, 30, 1195–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Rauf, M.; Wang, C. Differential Evolution Algorithm to Solve the Parallel Batch Processing Machine Scheduling Problem with Multiple Jobs. Eng. Proc. 2023, 45, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Paprocka, I.; Krenczyk, D. On Energy Consumption and Productivity in a Mixed-Model Assembly Line Sequencing Problem. Energies 2023, 16, 7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, M.; Guan, Z.; Sarfraz, S.; Mumtaz, J.; Shehab, E.; Jahanzaib, M.; Hanif, M. A smart algorithm for multi-criteria optimization of model sequencing problem in assembly lines. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2020, 61, 101844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, Y. An endosymbiotic evolutionary algorithm for the integration of balancing and sequencing in mixed-model U-lines. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2006, 168, 838–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Luo, D.; Mudassar, R.; Yue, L.; Meng, L. A novel deep self-learning method for flexible job-shop scheduling problems with multiplicity: Deep reinforcement learning assisted the fluid master-apprentice evolutionary algorithm. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2025, 94, 101907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Du, J.; Mumtaz, J.; Zhong, J.; Rauf, M. An efficient Q-learning integrated multi-objective hyper-heuristic approach for hybrid flow shop scheduling problems with lot streaming. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 262, 125616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Wang, G.; Rauf, M. Optimization of Multi-Operator Human–Robot Collaborative Disassembly Line Balancing Problem Using Hybrid Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm. Eng. Proc. 2024, 75, 16. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).