Irreversibility, Dissipation, and Its Measure: A New Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Goals
- What makes a thermodynamic process irreversible?
- Does irreversibility always bring a thermodynamic system to EQ or can it take it away from it?
- What is dissipation and how does it depend on the temperature (positive and negative) of the system?
- Is dissipation simply dissipated or lost work during a process between two EQ macrostates, which is the most common definition of dissipation as was first proposed by Thomson [47]?
- How to describe dissipation between two arbitrary macrostates?
- Does dissipation occur when only heat is transferred from hot to cold?
- How should dissipation be quantified?
- Do current methods of quantification work for both isolated and interacting systems?
- Is dissipation always directly related to the irreversible entropy generation () as is commonly thought of?
- Is a violation of SL?
- Can dissipation be ever negative?
1.2. Mechanical and Thermodynamic Uniformity
1.3. Layout
2. Fundamental Concepts and Preliminaries
2.1. BCGM Proposal
BCGM Proposal: While microstates of a mechanical Hamiltonian are deterministic so they are oblivious to any sense of stochasticity, thermodynamic description of is obtained by appending probabilities to them to describe a macrostate specified by .
2.2. Thermodynamic Force
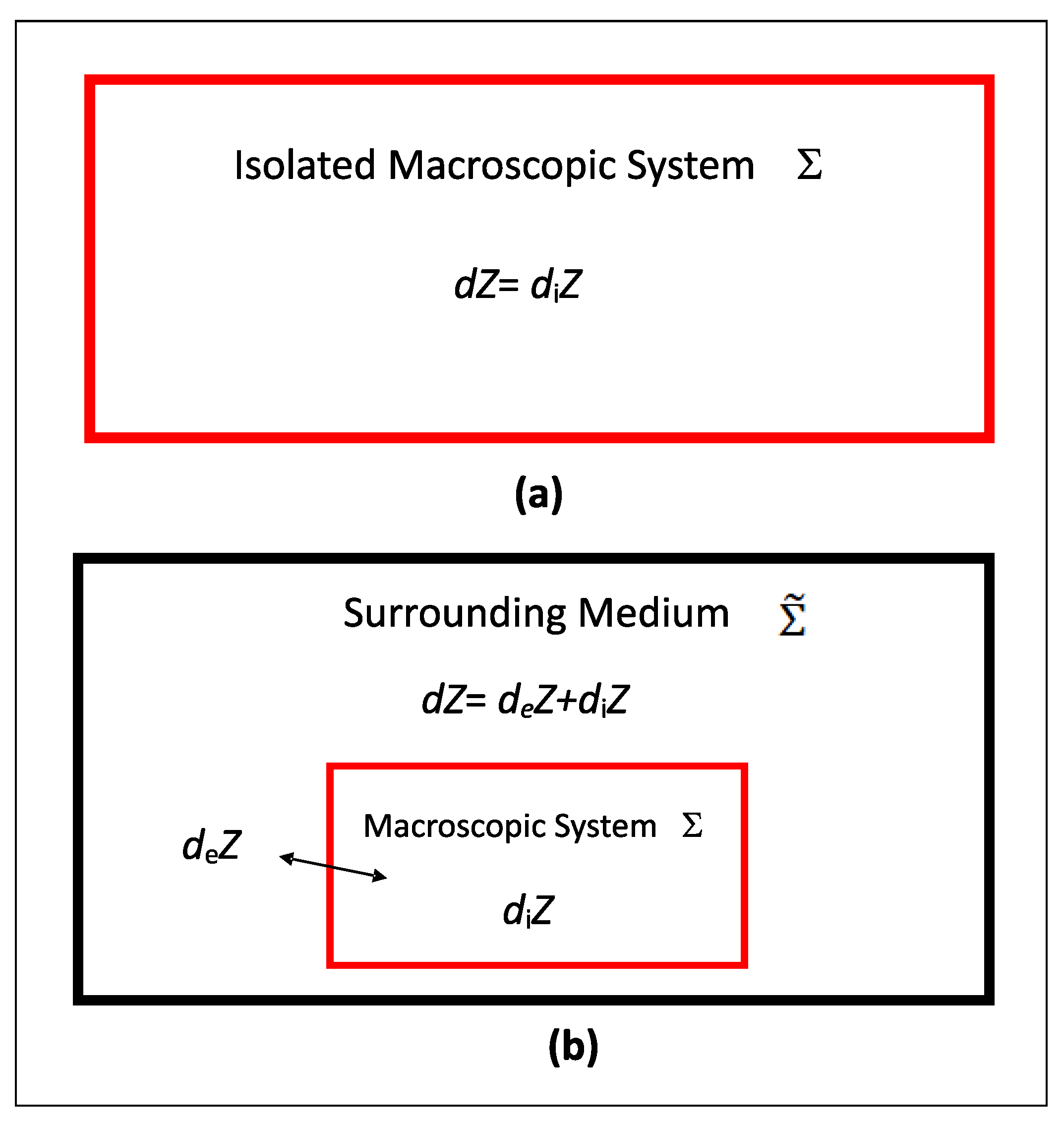
2.3. First Law Formulations & Irreversibility Principle
2.4. Thermodynamic Dissipation
2.5. Kullback-Leibler Distance and Irreversibility
2.6. Detailed Balance
3. The MNEQT: A Brief Review
3.1. A Simple Example
3.2. General Extension
4. NEQ Statistical Mechanics (NEQT)
4.1. Microstate Probability
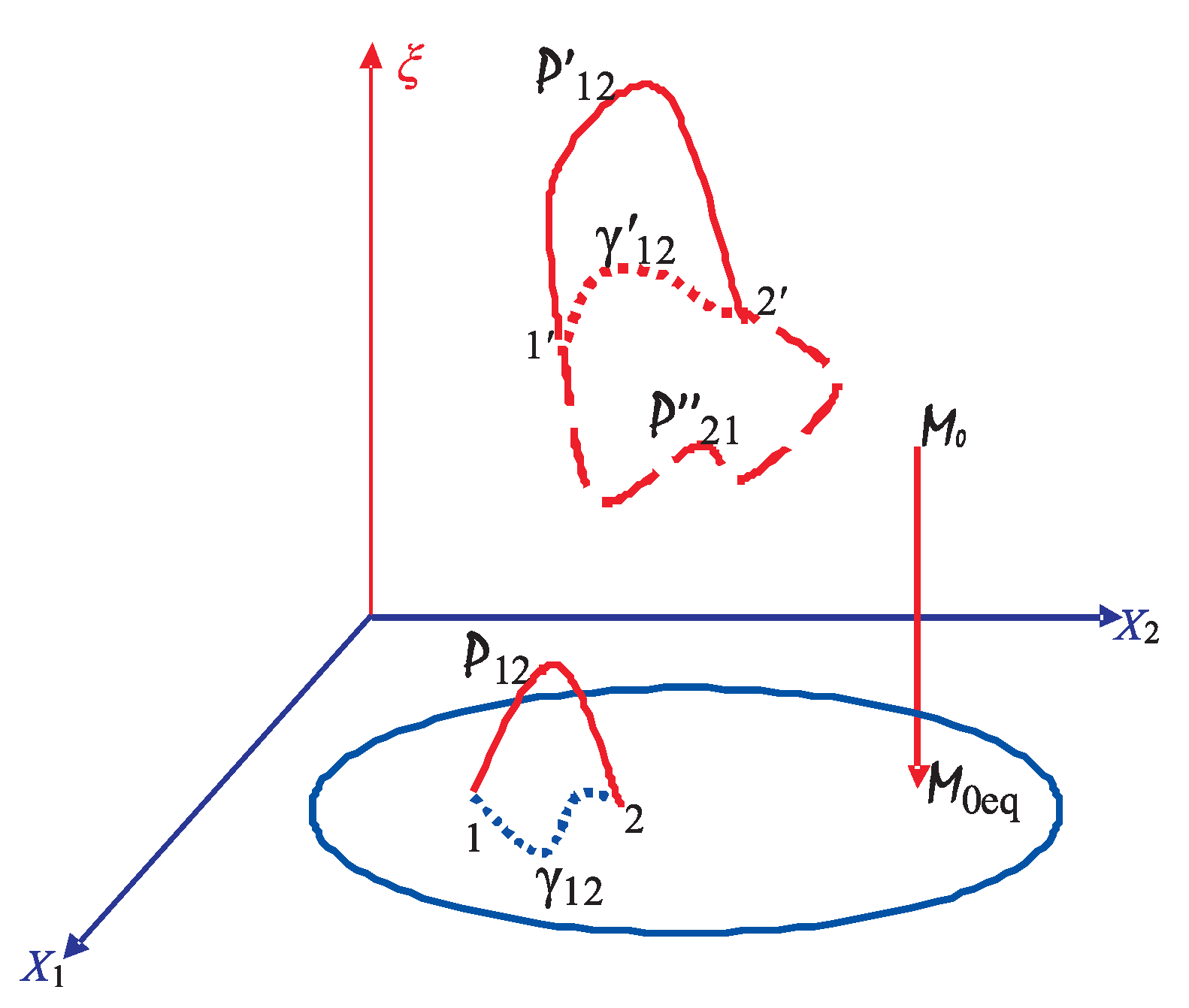
5. Mechanical Foundation of Irreversibility and Dissipation
5.1. Dissipative Dynamics
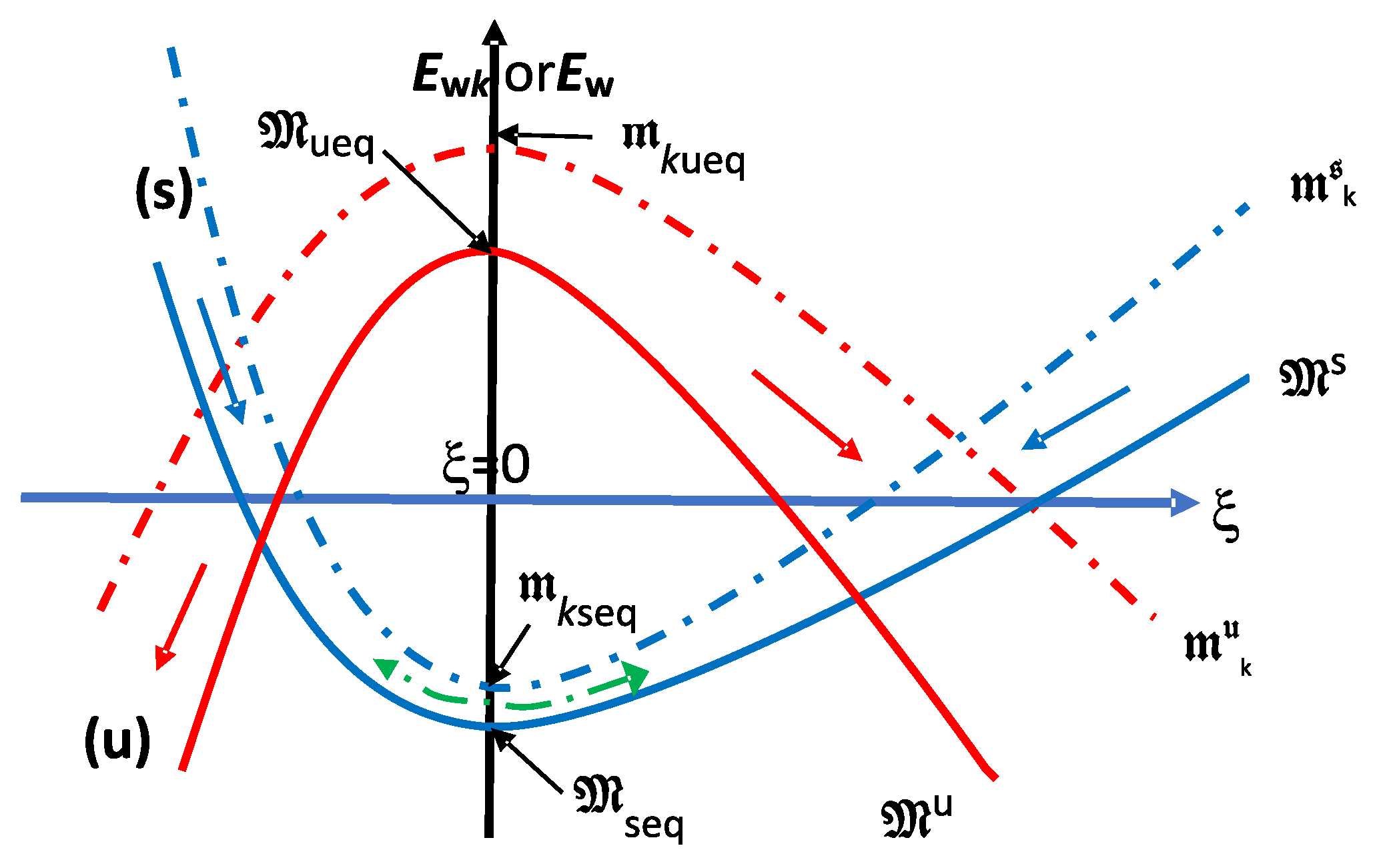
5.2. and
5.3. Mechanical Equilibrium Principle of Energy (Mec-EQ-P) for
5.4. Dissipation
5.5. Principle of Dissipation and D
5.6. Connection with
5.7. Positive and Negative T
5.8. Consequences
6. Relation Between Kullback-Leibler Distance and
7. Determining and
7.1. Fokker-Planck Equation Not Suitable for
7.2. Master Equations
7.3. Transition Matrix and Isolated Systems
7.4. Principle of Detailed Balance
8. Summary and Discussion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clausius, R. Über die Wärmeleitung gasförmiger Körper. Ann. Phys. 1862, 115, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausius, R. The Mechanical Theory of Heat; Macmillan: London, UK, 1879. [Google Scholar]
- De Donder, T.; Rysselberghe, P.V. Thermodynamic Theory of Affinity: A Book of Principles; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1936. [Google Scholar]
- Fermi, E. Thermodynamics; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Tolman, R.C. The Principles of Statistical Mechanics; Oxford University: London, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Reif, F. Fundamentals of Statistical and Thermal Physics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Tisza, L. Generalized Thermodynamics; M.I.T. Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, O.K. Statistical Mechanics, Thermodynamics and Kinetics; W.H. Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Prigogine, I. Introduction to Thermodynamics of Irreversible Processes, 3rd ed.; Interscience Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Woods, L.C. The Thermodynamics of Fluids Systems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Kestin, J. A Course in Thermodynamics; Revised Printing; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volumes 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- de Groot, S.R.; Mazur, P. Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics, 1st ed.; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Callen, H.B. Thermodynamics and an Introduction to Thermostatistics, 2nd ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Waldram, J.R. The Theory of Thermodynamics; Cambridge University: Cambridge, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. Statistical Physics, 3rd ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1986; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Balian, R. From Microphysics to Macrophysics; Springer: Berlin, Gremnay, 1991; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kuiken, G.D.C. Thermodynamics of Irreversible Processes; John Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Jou, D.; Casas-Vázquez, J.; Lebon, G. Extended Irreversible Thermodynamics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kondepudi, D.; Prigogine, I. Modern Thermodynamics; John Wiley and Sons: Bognor Regis, West Sussex, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gallavotti, G. Statistical Mecahanics, A Short Treatise; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Maugin, G.A. The Thermomechanics of Nonlinear Irreversible Behaviors: An Introduction; World Scientific: Singapore, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ottinger, H.C. Beyond Equilibrium Thermodynamics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bejan, A. Applied Engineering Thermodynamics, 3rd ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kjelstrum, S.; Bedeaux, D. Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics of Heterogeneous Systems; World-Scientific: Singapore, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Eu, B.C. Kinetic Theory of Nonequilibrium Ensembles, Irreversible Thermodynamics, and Generalized Hydrodynamics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, T.; Ikeda, T.N.; Kaminish, E.; Ueda, M. Thermalization and prethermalization in isolated quantum systems: A theoretical overview. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2018, 51, 112001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roduner, E.; Krüger, T.P.J. The origin of irreversibility and thermalization in thermodynamic processes. Phys. Rep. 2022, 944, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, T.; Ghosal, P.; Bej, P.; Banerjee, A.; Deb, P. Thermalization of isolated quantum many-body system and the role of entanglement. Phys. Lett. A 2024, 509, 129501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltzman, L. Lectures on Gas Theory; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Boltzmann, L. über die Beziehung zwischen dem Zweiten Hauptsatze der mechanischen Wärmetheorie und der Wahrscheinlichkeitsrechnung resp. den Sätzen über das Wärmegleichgewicht. Wien Ber. 1877, 76, 373–435. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, J.W. Elementary Principles in Statistical Mechanics; Scribner’s Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1902. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. Mechanics, 3rd ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Gujrati, P.D. Loss of Temporal Homogeneity and Symmetry in Statistical Systems: Deterministic Versus Stochastic Dynamics. Symmetry 2010, 2, 1201–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujrati, P.D. Mechanical Foundations of the Generalized Second Law and the Irreversity Principle. Foundations 2024, 4, 560–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujrati, P.D. A Review of the System-Intrinsic Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics in Extended Space (MNEQT) with Applications. Entropy 2021, 23, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujrati, P.D. Foundations of Nonequilibrium Statistical Mechanics in Extended State Space. Foundations 2023, 3, 419–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, E.; Pound, R. A Nuclear Spin System at Negative Temperature. Phys. Rev. 1951, 81, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, N.F. Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics at Negative Absolute Temperatures. Phys. Rev. 1956, 103, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, E.; Penrose, O. Physics of negative absolute temperatures. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 012125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szilard, L. über die Entropieverminderung in einem thermodynamischen System bei Eingriffen intelligenter Wesen. Z. Phys. 1929, 53, 840–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leff, H.S.; Rex, A.F. (Eds.) Maxwell’s Demon 2: Entropy, Classical and Quantum Information, Computing; CRT Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gujrati, P.D. Overlooked Work and Heat of Intervention and the Fate of Information Principles of Szilard and Landauer. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.02373v2. [Google Scholar]
- Lerner, V.S. Information Path from Randomness and Uncertainty to Information, Thermodynamics, and Intelligence of Observer. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1401.7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H. Overview of Information Theory, Computer Science Theory, and Stochastic Thermodynamics for Thermodynamics of Computation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1901.00386. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, U. Stochastic thermodynamics: Principles and perspectives. Eur. Phys. J. B 2008, 64, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekimoto, K. Stochastic Energetics; Lecture Notes in Physics 799; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- William Thomson, (Lord Kelvin). On a Universal Tendency in Nature to the Dissipation of Mechanical Energy (Google Books) (URL), Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh for April 19, 1852, Also Philosophical Magazine, Oct. 1852, Also Mathematical and Physical Papers, Vol. i, art. 59, pp. 511. Available online: https://zapatopi.net/kelvin/papers/on_a_universal_tendency.html (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Gujrati, P.D. Non-equilibrium Thermodynamics: Structural Relaxation, Fictive temperature and Tool-Narayanaswamy phenomenology in Glasses. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 051130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujrati, P.D. First-principles nonequilibrium deterministic equation of motion of a Brownian particle and microscopic viscous drag. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 012140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, J.C. Theory of Heat; Longmans, Green, and Co.: London, UK, 1902; p. 338. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfest, P.; Ehrenfest, T. The Conceptual Foundations of the Statistical Approach in Mechanics; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Schottky, W.H. Thermodynamik; Julius Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1929. [Google Scholar]
- Muschik, W. Discrete systems in thermal physics and engineering: A glance from non-equilibrium thermodynamics. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 2021, 33, 2411–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, B.D. Thermodynamics with Internal State Variables. J. Chem. Phys. 1967, 47, 597–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujrati, P.D. Hierarchy of Relaxation Times and Residual Entropy: A Nonequilibrium Approach. Entropy 2018, 20, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujrati, P.D. Nonequilibrium Work and its Hamiltonian Connection for a Microstate in Nonequilibrium Statistical Thermodynamics: A Case of Mistaken Identity. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.00455. [Google Scholar]
- Gujrati, P.D. Correcting the Mistaken Identification of Nonequilibrium Microscopic Work. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.09725. [Google Scholar]
- Gujrati, P.D. Nonequilibrium thermodynamics. II. Application to inhomogeneous systems. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 041128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujrati, P.D.; Aung, P.P. Nonequilibrium thermodynamics. III. Generalization of Maxwell, Clausius-Clapeyron, and response-function relations, and the Prigogine-Defay ratio for systems in internal equilibrium. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 041129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieb, E.; Yngvason, J. The Mathematics of the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Phys. Rep. 1999, 310, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keizer, J. On the kinetic meaning of the second law of thermodynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 1976, 64, 4466–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujrati, P.D. On Equivalence of Nonequilibrium Thermodynamic and Statistical Entropies. Entropy 2015, 17, 710–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyling, J.B. An axiomatic approach to classical thermodynamics. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1972, 329, 35–70. [Google Scholar]
- Lucia, U. The Gouy-Stodola Theorem in Bioenergetic Analysis of Living Systems (Irreversibility in Bioenergetics of Living Systems). Energies 2014, 7, 5717–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vágner, P.; Pavelka, M.; Maršik, F. Pitfalls of Exergy Analysis. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 2017, 42, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. Chemical exergy of ideal and non-ideal gas mixtures and liquid solutions with applications. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Educ. 2017, 45, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reini, M.; Casisi, M. The Gouy-Stodola Theorem and the derivation of exergy revised. Energy 2020, 210, 118486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzynski, C. Nonequilibrium equality for free energy differences. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, G.E. Entropy production fluctuation theorem and the nonequilibrium work relation for free energy differences. Phys. Rev. E 1999, 60, 2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.G.D.; Mauzerall, D. A note on the Jarzynski equality. J. Stat. Mech. 2004, 2004, P07006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.G.D.; Mauzerall, D. The Jarzynski equality and the Boltzmann factor. Mol. Phys. 2005, 103, 2923–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, R.; Parrondo, J.M.R.; Van den Broeck, C. Dissipation: The Phase-Space Perspective. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 080602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujrati, P.D. Jensen inequality and the second law. Phys. Lett. A 2020, 384, 126460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, D.S.P. Quantum relative entropy uncertainty relation. Phys. Rev. E 2024, 109, L012103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, J.S. Logical Relations among the Principles of Statistical Mechanics and Thermodynamics. Phys. Rev. 1953, 91, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsager, L. Reciprocal Relations in Irreversible Processes. I. Phys. Rev. 1931, 37, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsager, L. Reciprocal Relations in Irreversible Processes. II. Phys. Rev. 1931, 38, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.J.; Meijer, P.H.E. Principle of Minimum Entropy Production. Phys. Rev. 1954, 97, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.J. Principle of Detailed Balance. Phys. Rev. 1955, 96, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevick, E.M.; Prabhakar, R.; Williams, S.R.; Searl, D.J. Fluctuation theorems. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2008, 59, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, U. Stochastic thermodynamics, fluctuation theorems and molecular machines. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 126001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinney, R.; Ford, I. Nonequilibrium Statistical Physics of Small Systems: Fluctuation Relations and Beyond; Klages, R., Just, W., Jarzynski, C., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gujrati, P.D. Generalized Non-equilibrium Heat and Work and the Fate of the Clausius Inequality. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1105.5549. [Google Scholar]
- Gujrati, P.D. Nonequilibrium Entropy. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1304.3768. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. Quantum Mechanics, 3rd ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, A.I. Mathematical Methods of Classical Mechanics, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Chetaev, N.G. Theoretical Mechanics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kubo, R. The fluctuation-dissipation theorem. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1966, 29, 255–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.A.B.P.; Gelbwaser-Klimovsky, D. Quantum work: Reconciling quantum mechanics and thermodynamics. Phys. Rev. Res. 2024, 6, L022036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, D.; Rubi, J.M.; Vilar, J.M.G. The Mesoscopic Dynamics of Thermodynamic Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 21502–21515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risken, H. The Fokker-Planck Equation: Methods of Solution and Applications, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Tomé, T.; de Oliveira, M.J. Entropy production in irreversible systems described by a Fokker-Planck equation. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 021120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordsieck, A.; Lamb, W.E.; Uhlenbeck, G.E. On the theory of cosmic-ray showers I. The furry model and the fluctuation problem, Physica 1940, 7, 344–360. [Google Scholar]
- Kac, M. Foundations of kinetic theory. In Procedeeings of the Third Berkely Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, 1954–1955; University of California Press: Berkerly, CA, USA, 1956; Volume III, pp. 171–197. [Google Scholar]
- Gujrati, P.D. A No-Go Theorem of Analytical Mechanics for the Second Law Violation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.17007. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gujrati, P.D. Irreversibility, Dissipation, and Its Measure: A New Perspective. Symmetry 2025, 17, 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17020232
Gujrati PD. Irreversibility, Dissipation, and Its Measure: A New Perspective. Symmetry. 2025; 17(2):232. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17020232
Chicago/Turabian StyleGujrati, Purushottam Das. 2025. "Irreversibility, Dissipation, and Its Measure: A New Perspective" Symmetry 17, no. 2: 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17020232
APA StyleGujrati, P. D. (2025). Irreversibility, Dissipation, and Its Measure: A New Perspective. Symmetry, 17(2), 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17020232






