Kernel Adaptive Swin Transformer for Image Restoration
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We have proposed a multi-degrade super-resolution model called KAST by introducing degradation feature estimation, which has effectively encoded the image degradation by capturing degraded contextual information from different regions of the LR image to achieve better reconstruction performance.
- Benefiting from the local self-attention mechanism and degradation estimation, we have introduced a new perspective to incorporate image degradation features into the SR model.
- Extensive experiments on both paired training data and unpaired real-world data have demonstrated the effectiveness of KAST in image super-resolution.
- We have introduced a log-space continuous position bias (Log-CPB) that has provided smoother and more fine-grained positional representations, enhancing the model’s ability to capture pixel relationships.
2. Related Works
2.1. Single Degrade Super-Resolution
2.2. Blind Super-Resolution
2.3. Vision Transformer
2.4. Comparison with Existing Methods and Related Restoration Tasks
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Motivation
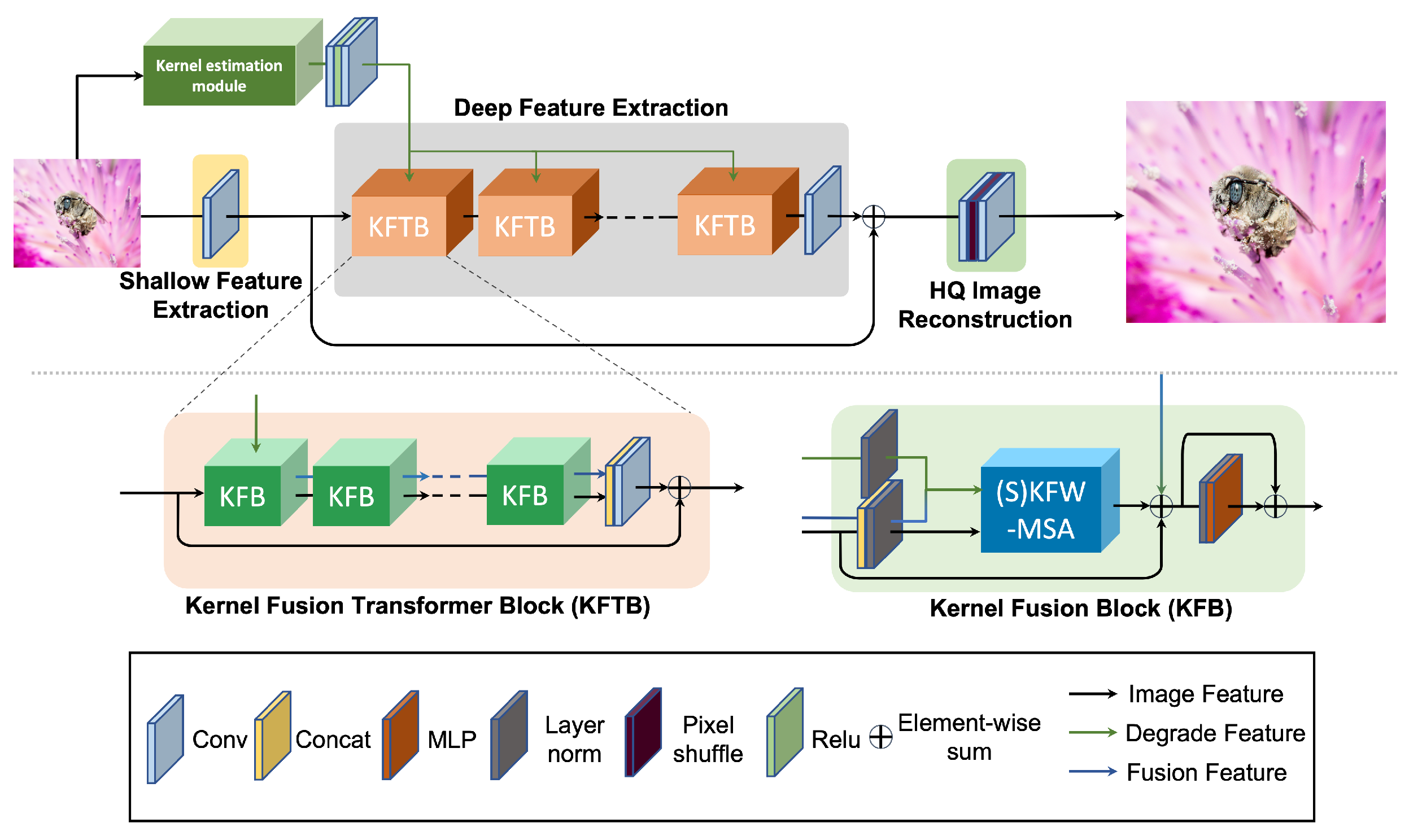
3.2. Overall Pipeline
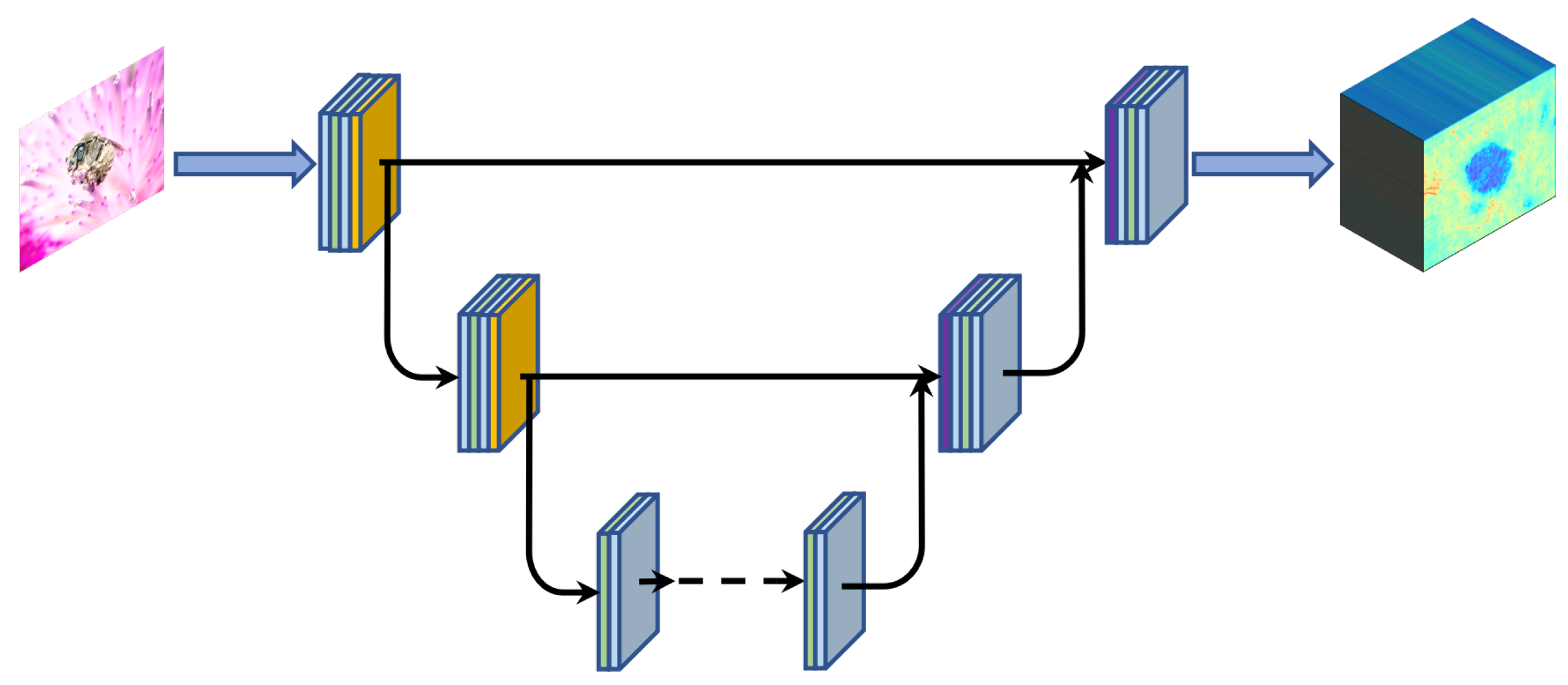
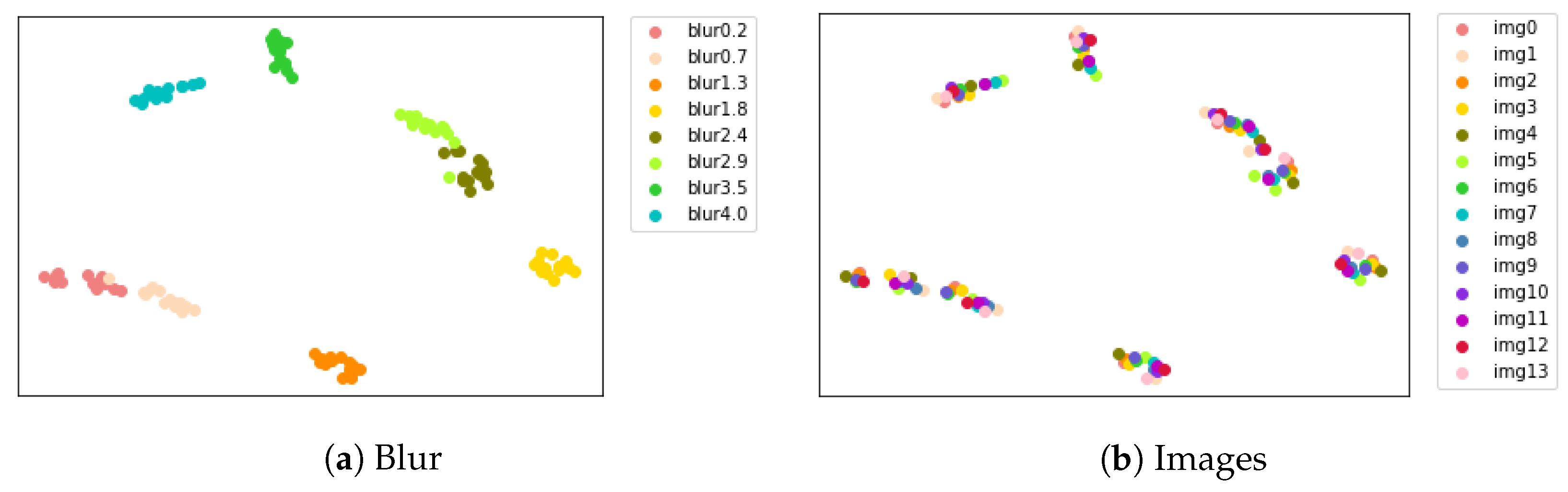
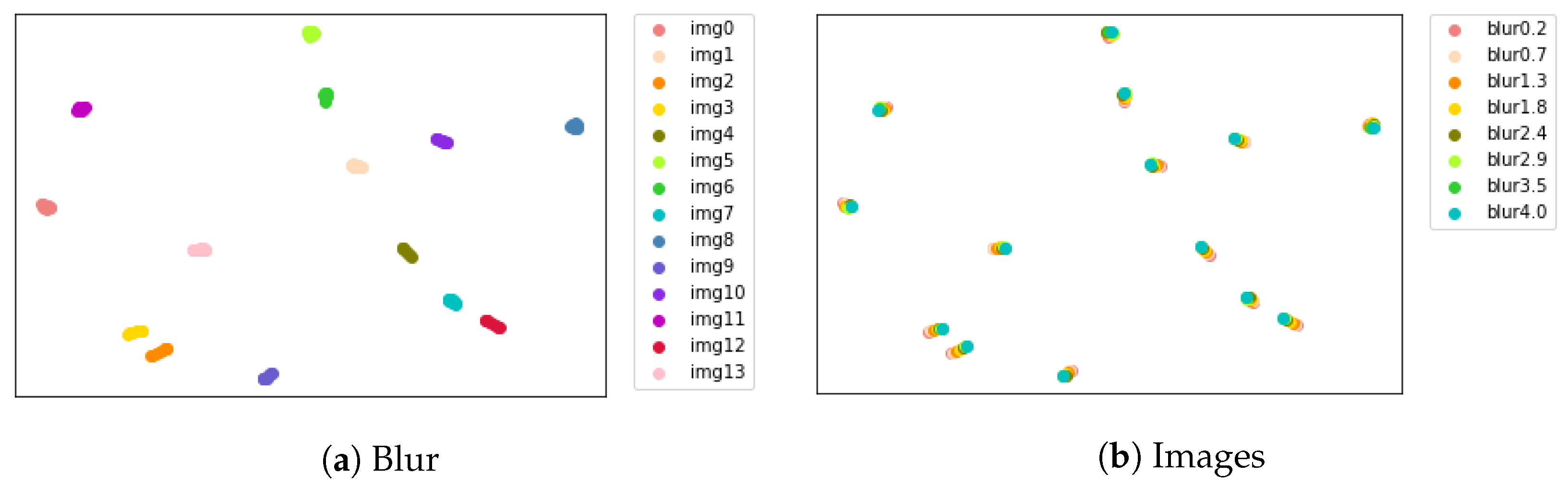
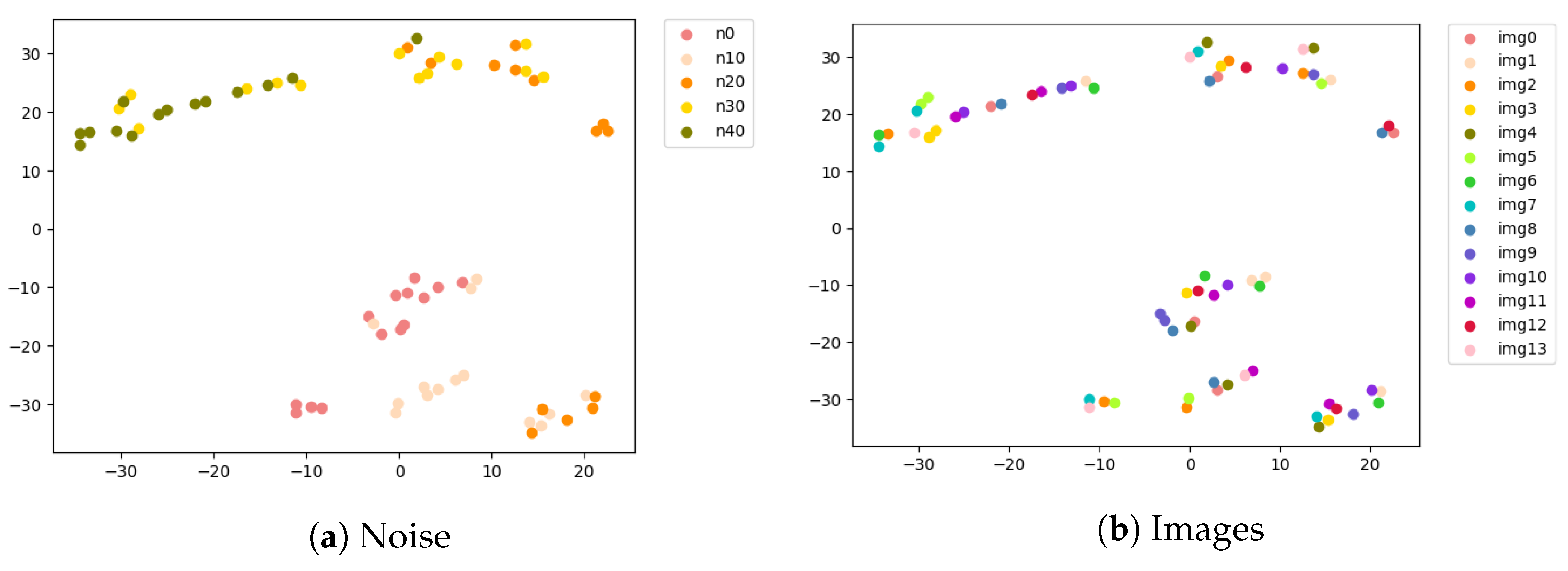
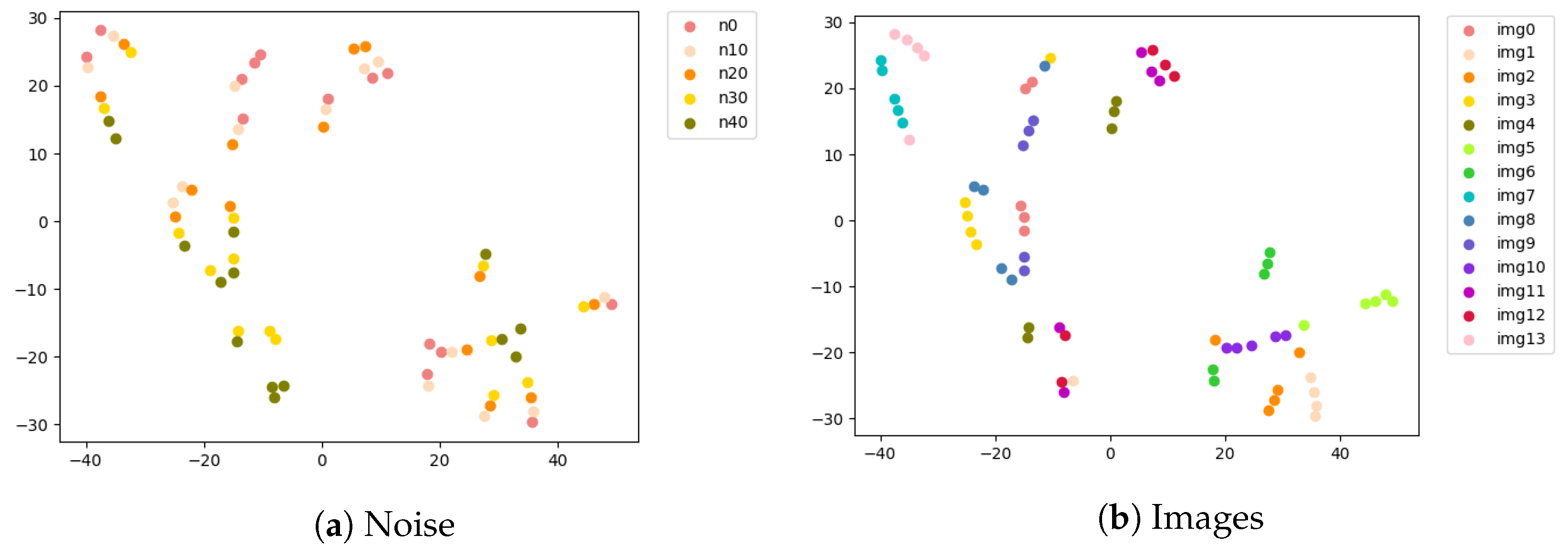
3.3. Degradation Estimation
| Algorithm 1 Training Degradation Estimation |
|
3.4. Theoretical Rationale for U-Net-Based Estimator
3.5. Kernel Fusion Transformer Block
| Algorithm 2 Training-Blind Super-Resolution Model |
|
3.6. Parallel Attention Fusion
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Implementation Details
4.1.2. PSNR and SSIM Definitions
4.2. Ablation Study and Discussion
4.2.1. Effectiveness of Log-CPB
4.2.2. Effectiveness of Pre-Trained Degradation Estimation Model
4.2.3. Effectiveness of Kernel Fusion Blocks
4.3. Comparison with Other Methods
4.3.1. Quantitative Results with Baseline Methods
4.3.2. Quantitative Results with Other Methods
4.3.3. Visual Results with Real-World Images
4.3.4. Limitations and Failure Cases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, B.; Son, S.; Kim, H.; Nah, S.; Mu Lee, K. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, K.M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1646–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Zhong, B.; Fu, Y. Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 286–301. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Liang, J.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. Designing a practical degradation model for deep blind image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 4791–4800. [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Kligler, S.; Shocher, A.; Irani, M. Blind super-resolution kernel estimation using an internal-gan. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 284–293. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Unfolding the alternating optimization for blind super resolution. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 5632–5643. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Sim, H.; Kim, M. Koalanet: Blind super-resolution using kernel-oriented adaptive local adjustment. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 10606–10615. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Wang, T.; Cai, Y.; Fan, H.; Li, Z. StainGAN: Learning a structural preserving translation for white blood cell images. J. Biophotonics 2023, 16, e202300196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L. Learning a single convolutional super-resolution network for multiple degradations. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3262–3271. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Huang, H.; Yu, L.; Li, Y.; Fan, H.; Liu, S. Deep constrained least squares for blind image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–22 June 2022; pp. 17642–17652. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Gao, X. Learning the non-differentiable optimization for blind super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 2093–2102. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, W.; Peng, S. Kernel-aware raw burst blind super-resolution. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.07315. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, L. Efficient and degradation-adaptive network for real-world image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 574–591. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Cao, J.; Sun, G.; Zhang, K.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. Swinir: Image restoration using swin transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 1833–1844. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, S.; Sang, N.; Ma, F. Fast image super resolution via local regression. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR2012), Tsukuba, Japan, 11–15 November 2012; pp. 3128–3131. [Google Scholar]
- Michaeli, T.; Irani, M. Nonparametric blind super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 945–952. [Google Scholar]
- Timofte, R.; De Smet, V.; Van Gool, L. Anchored neighborhood regression for fast example-based super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 1920–1927. [Google Scholar]
- Riegler, G.; Schulter, S.; Ruther, M.; Bischof, H. Conditioned regression models for non-blind single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 522–530. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Wang, X.; Dong, C.; Qi, Z.; Shan, Y. Finding discriminative filters for specific degradations in blind super-resolution. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, K.; Gu, S.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. Flow-based kernel prior with application to blind super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10601–10610. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Caballero, J.; Huszár, F.; Totz, J.; Aitken, A.P.; Bishop, R. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1874–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Zhao, H.; Qiao, Y.; Dong, C. Classsr: A general framework to accelerate super-resolution networks by data characteristic. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 12016–12025. [Google Scholar]
- Muqeet, A.; Iqbal, M.T.B.; Bae, S.H. HRAN: Hybrid residual attention network for single image super-resolution. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 137020–137029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, M.; Volino, M.; Hilton, A. Attention-based multi-reference learning for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 14697–14706. [Google Scholar]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszár, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Shi, W. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4681–4690. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.; Alahi, A.; Li, F.-F. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 694–711. [Google Scholar]
- Mechrez, R.; Talmi, I.; Shama, F.; Zelnik-Manor, L. Maintaining natural image statistics with the contextual loss. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1803.04626. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Wu, S.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C. Esrgan: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2019; pp. 63–79. [Google Scholar]
- Efrat, N.; Glasner, D.; Apartsin, A.; Nadler, B.; Levin, A. Accurate blur models vs. image priors in single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 2832–2839. [Google Scholar]
- Shocher, A.; Cohen, N.; Irani, M. “zero-shot” super-resolution using deep internal learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3118–3126. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, X.; Cao, Y.; Tai, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Huang, F. Real-world super-resolution via kernel estimation and noise injection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 466–467. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Lu, H.; Zuo, W.; Dong, C. Blind super-resolution with iterative kernel correction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 1604–1613. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Lu, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, X.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Feng, J.; Xiang, T.; Torr, P.H.S.; et al. Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 6877–6886. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Chen, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L. Beyond a gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep cnn for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3142–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Weng, J.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Qian, J.; Li, J.; Yang, J. Driving-video dehazing with non-aligned regularization for safety assistance. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–24 June 2024; pp. 26109–26119. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, E.; Wang, A.; Shiri, B.; Lin, W. VNDHR: Variational single nighttime image Dehazing for enhancing visibility in intelligent transportation systems via hybrid regularization. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 10189–10203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Shen, L.; Wan, S.; Ren, W. Wavelet-based physically guided normalization network for real-time traffic dehazing. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 2025, 112451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wang, K.; Yan, Z.; Chen, X.; Gao, S.; Li, J.; Yang, J. Depth-centric dehazing and depth-estimation from real-world hazy driving video. Aaai Conf. Artif. Intell. 2025, 39, 2852–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Tan, J.; Li, Y. Multi-purpose oriented single nighttime image haze removal based on unified variational retinex model. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 33, 1643–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, X.; Qian, J.; Li, J.; Yang, J. Non-aligned supervision for real image dehazing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025, 35, 10705–10715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Ren, W.; Zhao, L.; Fan, E.; Huang, F. Exploring Fuzzy Priors From Multi-Mapping GAN for Robust Image Dehazing. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2025, 33, 3946–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y. Image super-resolution with non-local sparse attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 3516–3525. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; De Brab, ere, B.; Tuytelaars, T.; Gool, L.V. Dynamic filter networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, A.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, W.; Qiao, Y.; Dong, C. Discovering “Semantics” in Super-Resolution Networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.00406. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 568–576. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, H.; Lin, Y.; Yao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wei, Y.; Ning, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, L.; et al. Swin transformer v2: Scaling up capacity and resolutionIn. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–22 June 2022; pp. 12009–12019. [Google Scholar]
- Timofte, R.; Agustsson, E.; Van Gool, L.; Yang, M.H.; Zhang, L. Ntire 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: Methods and results. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPRW), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1110–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Lugmayr, A.; Danelljan, M.; Timofte, R. Ntire 2020 challenge on real-world image super-resolution: Methods and results. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 2058–2076. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Dong, C. Interpreting super-resolution networks with local attribution maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 9199–9208. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, G.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Wu, X.M. A closer look at blind super-resolution:Degradation models, baselines, and performance upper bounds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–22 June 2022; pp. 527–536. [Google Scholar]
- Haris, M.; Shakhnarovich, G.; Ukita, N. Deep back-projection networks for super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 1664–1673. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, S.A.; Tirer, T.; Giryes, R. Correction filter for single image super-resolution: Robustifying off-the-shelf deep super-resolvers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1428–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, S.; Lugmayr, A.; Danelljan, M.; Fritsche, M.; Lamour, J.; Timofte, R. Div8k: Diverse 8k resolution image dataset. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 3512–3516. [Google Scholar]
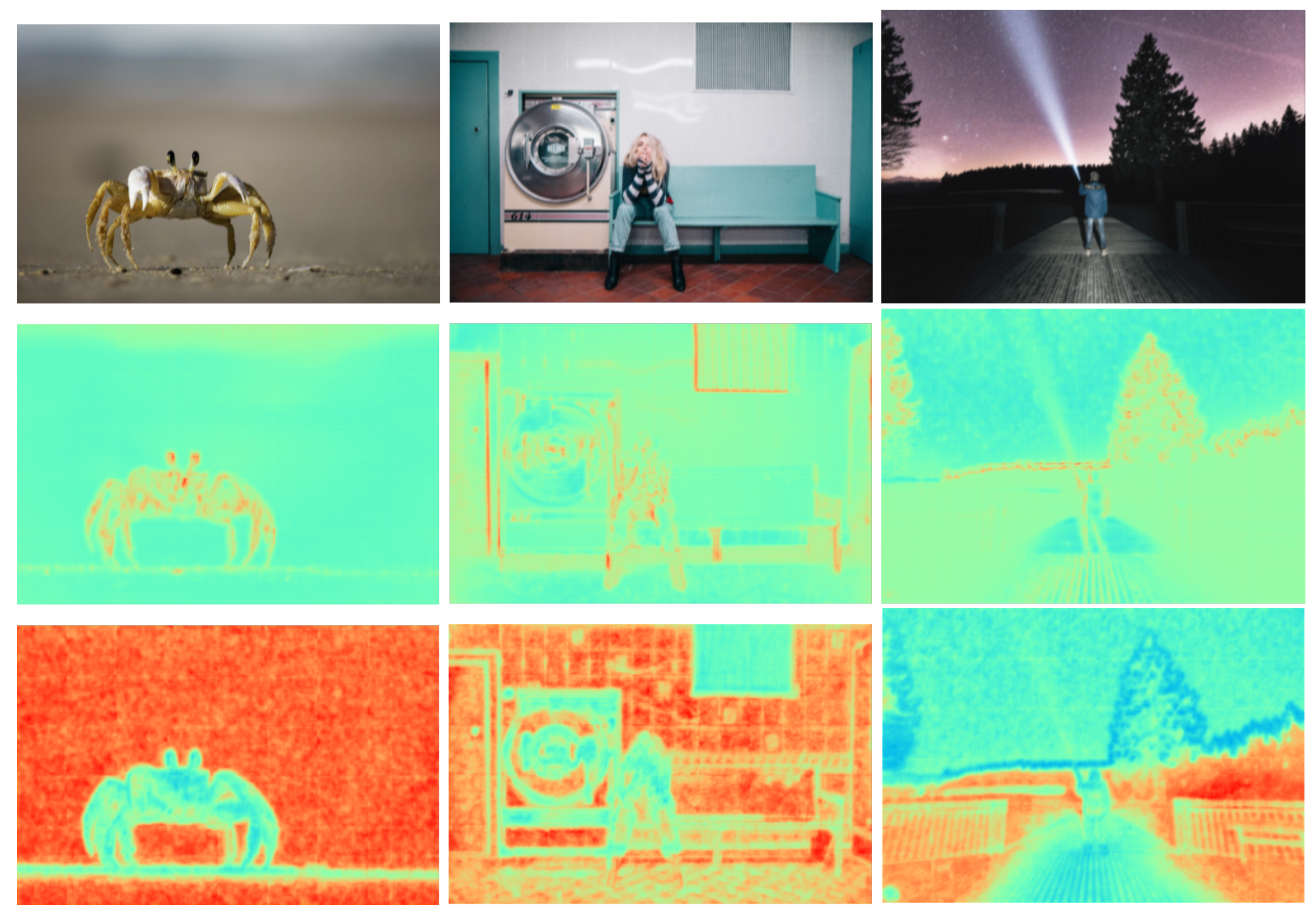





| Method | Degradation Modeling | Fusion Strategy | Attention Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| SRMD [10] | Global | Concatenation | CNN |
| KOALAnet [8] | Local (kernel-oriented) | Adaptive adjustment | CNN |
| SwinIR [16] | Non-degradation-aware | None | Swin Transformer |
| KAST (Ours) | Local degradation-aware | Parallel attention fusion | Swin Transformer + Log-CPB |
| Dataset | w/o Log-CPB | w/ Log-CPB | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | |
| Set5 | 35.95 | 0.944 | 36.05 | 0.945 |
| Set14 | 31.84 | 0.897 | 31.91 | 0.898 |
| Dataset | Method | Degradation Types | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b1 | b2 | b1j60 | b2j60 | b1n20 | b2n20 | b1n20j60 | b2n20j60 | b2n40j60 | ||
| Set5 | SwinIR | 37.63 | 36.77 | 36.35 | 35.68 | 34.69 | 33.87 | 33.96 | 33.34 | 31.03 |
| KAST | 37.82 | 36.95 | 36.49 | 35.80 | 34.80 | 33.93 | 34.11 | 33.57 | 31.24 | |
| Set14 | SwinIR | 33.47 | 33.25 | 32.84 | 32.73 | 31.48 | 31.18 | 30.89 | 30.82 | 28.95 |
| KAST | 33.60 | 33.48 | 32.98 | 32.96 | 31.56 | 31.35 | 31.01 | 31.03 | 29.12 | |
| Urban100 | SwinIR | 31.58 | 30.71 | 31.04 | 30.33 | 30.14 | 29.44 | 29.72 | 29.12 | 27.15 |
| KAST | 31.58 | 30.84 | 31.01 | 30.41 | 30.17 | 29.61 | 29.74 | 29.23 | 27.36 | |
| BSD100 | SwinIR | 32.25 | 32.40 | 31.74 | 31.84 | 30.35 | 30.40 | 30.01 | 30.03 | 28.18 |
| KAST | 32.22 | 32.34 | 31.73 | 31.79 | 30.33 | 30.37 | 29.99 | 30.07 | 28.16 | |
| Manga109 | SwinIR | 38.26 | 36.09 | 36.47 | 35.88 | 34.62 | 34.28 | 34.00 | 33.86 | 30.69 |
| KAST | 38.33 | 36.24 | 36.56 | 36.09 | 34.71 | 34.46 | 34.12 | 33.97 | 30.83 | |
| Dataset | Method | Degradation Types | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b3 | b4 | b3j60 | b4j60 | b3n20 | b4n20 | b3n20j60 | b4n20j60 | b4n40j60 | ||
| Set5 | SwinIR | 31.49 | 29.54 | 31.36 | 29.39 | 30.80 | 28.64 | 30.54 | 28.73 | 27.43 |
| KAST | 31.71 | 29.90 | 31.51 | 29.73 | 31.00 | 28.95 | 30.74 | 28.89 | 27.81 | |
| Set14 | SwinIR | 28.67 | 28.05 | 28.50 | 27.95 | 28.13 | 27.56 | 27.99 | 27.54 | 26.61 |
| KAST | 28.85 | 28.23 | 28.70 | 28.19 | 28.32 | 27.74 | 28.18 | 27.76 | 26.88 | |
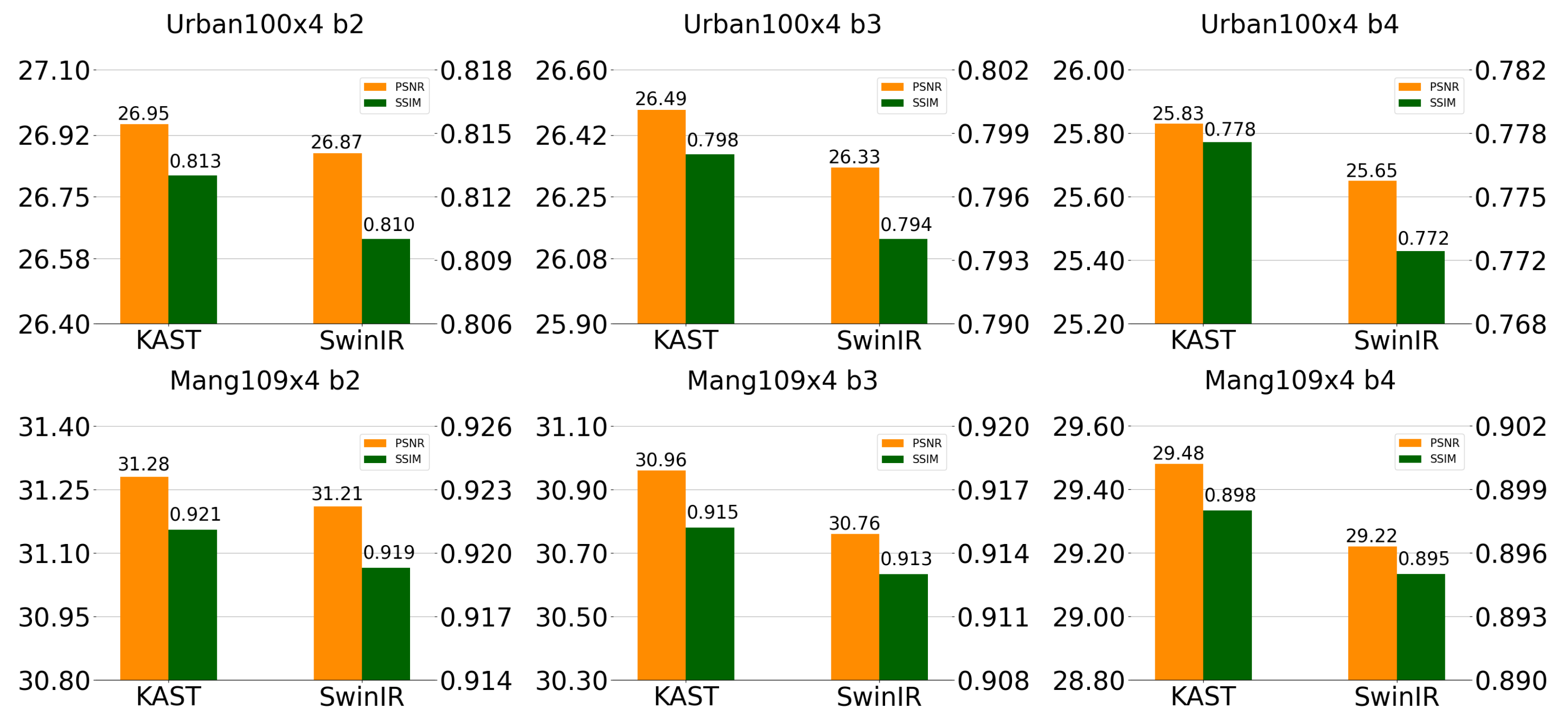
| Urban100 | SwinIR | 26.33 | 25.65 | 26.06 | 25.52 | 25.98 | 25.23 | 25.79 | 25.29 | 24.75 |
| KAST | 26.49 | 25.83 | 26.19 | 25.66 | 26.09 | 25.48 | 25.87 | 25.40 | 24.85 | |
| BSD100 | SwinIR | 27.87 | 27.75 | 27.67 | 27.54 | 27.39 | 27.27 | 27.22 | 27.14 | 26.42 |
| KAST | 27.86 | 27.68 | 27.66 | 27.51 | 27.38 | 27.26 | 27.23 | 27.12 | 26.46 | |
| Manga109 | SwinIR | 30.76 | 29.22 | 30.43 | 29.08 | 30.03 | 28.64 | 29.82 | 28.53 | 27.42 |
| KAST | 30.96 | 29.48 | 30.66 | 29.32 | 30.27 | 28.91 | 30.03 | 28.83 | 27.71 | |
| Dataset | w/o Pre-Train | w/ Pre-Train | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | |
| Set5 | 32.31 | 0.904 | 32.65 | 0.909 |
| Set14 | 29.55 | 0.839 | 29.90 | 0.846 |
| Dataset | Methods | Degradation Types | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bic | b2 | n20 | j60 | b2n20 | b2j60 | n20j60 | b2n20j60 | Average | ||
| BSD100 | Bicubic | 24.63 | 25.40 | 21.56 | 24.06 | 21.90 | 24.65 | 21.22 | 21.72 | 23.14 |
| RCAN [4] | 25.65 | 26.77 | 24.63 | 25.16 | 24.39 | 25.36 | 24.36 | 24.15 | 25.06 | |
| SRResNet-FAIG [53] | 25.58 | 26.72 | 24.53 | 25.11 | 24.26 | 25.29 | 24.32 | 24.07 | 24.99 | |
| RRDBNet [55] | 25.62 | 26.76 | 24.58 | 25.13 | 24.33 | 25.32 | 24.34 | 24.11 | 25.02 | |
| SwinIR [16] | 25.84 | 27.05 | 24.77 | 25.27 | 24.48 | 25.44 | 24.44 | 24.18 | 25.18 | |
| RRDBNet-GD [55] | 26.25 | 27.31 | 25.31 | 25.23 | 24.95 | 25.32 | 24.38 | 24.07 | 25.35 | |
| SwinIR-GD [16] | 26.61 | 27.58 | 25.64 | 25.30 | 25.30 | 25.39 | 24.44 | 24.14 | 25.55 | |
| KAST (Ours) | 26.68 | 27.82 | 25.44 | 25.24 | 25.35 | 25.45 | 24.64 | 24.48 | 25.61 | |
| Urban100 | Bicubic | 21.89 | 22.54 | 20.00 | 21.50 | 20.36 | 22.02 | 19.74 | 20.20 | 21.03 |
| RCAN [4] | 23.65 | 24.67 | 22.93 | 23.35 | 22.59 | 23.36 | 22.77 | 22.35 | 23.21 | |
| SRResNet-FAIG [53] | 23.54 | 24.42 | 22.88 | 23.26 | 22.42 | 23.16 | 22.73 | 22.19 | 23.08 | |
| RRDBNet [55] | 23.53 | 24.46 | 22.89 | 23.28 | 22.48 | 23.17 | 22.75 | 22.24 | 23.10 | |
| SwinIR [16] | 24.16 | 25.10 | 23.34 | 23.73 | 22.86 | 23.62 | 23.09 | 22.53 | 23.55 | |
| RRDBNet-GD [55] | 24.51 | 25.39 | 23.57 | 23.67 | 23.05 | 23.18 | 22.92 | 22.13 | 23.55 | |
| SwinIR-GD [16] | 25.55 | 26.12 | 24.40 | 24.11 | 23.83 | 23.56 | 23.26 | 22.42 | 24.16 | |
| KAST (Ours) | 25.85 | 26.96 | 24.41 | 24.16 | 24.01 | 23.76 | 23.56 | 22.89 | 24.44 | |
| Method | DIV2KRKx2 | |
|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | |
| Bicubic | 28.73 | 0.8040 |
| Bicubic+ZSSR [32] | 29.10 | 0.8215 |
| EDSR [2] | 29.17 | 0.8216 |
| RCAN [4] | 29.20 | 0.8233 |
| DBPN | 29.13 | 0.8190 |
| DBPN+Correction | 30.38 | 0.8717 |
| KernelGAN [6]+SRMD [10] | 29.57 | 0.8564 |
| KernelGAN [6]+ZSSR [32] | 30.36 | 0.8669 |
| KOALAnet [8] | 31.89 | 0.8852 |
| KAST | 32.21 | 0.8957 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, Z.; Wang, J.; Bhattacharjya, A.; Yan, L. Kernel Adaptive Swin Transformer for Image Restoration. Symmetry 2025, 17, 2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122161
Ni Z, Wang J, Bhattacharjya A, Yan L. Kernel Adaptive Swin Transformer for Image Restoration. Symmetry. 2025; 17(12):2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122161
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Zhen, Jingyu Wang, Aniruddha Bhattacharjya, and Le Yan. 2025. "Kernel Adaptive Swin Transformer for Image Restoration" Symmetry 17, no. 12: 2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122161
APA StyleNi, Z., Wang, J., Bhattacharjya, A., & Yan, L. (2025). Kernel Adaptive Swin Transformer for Image Restoration. Symmetry, 17(12), 2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122161






