A Symmetric Deep Learning Approach for Dynamic Reserve Evaluation of Tight Sandstone Gas Wells
Abstract
1. Introduction
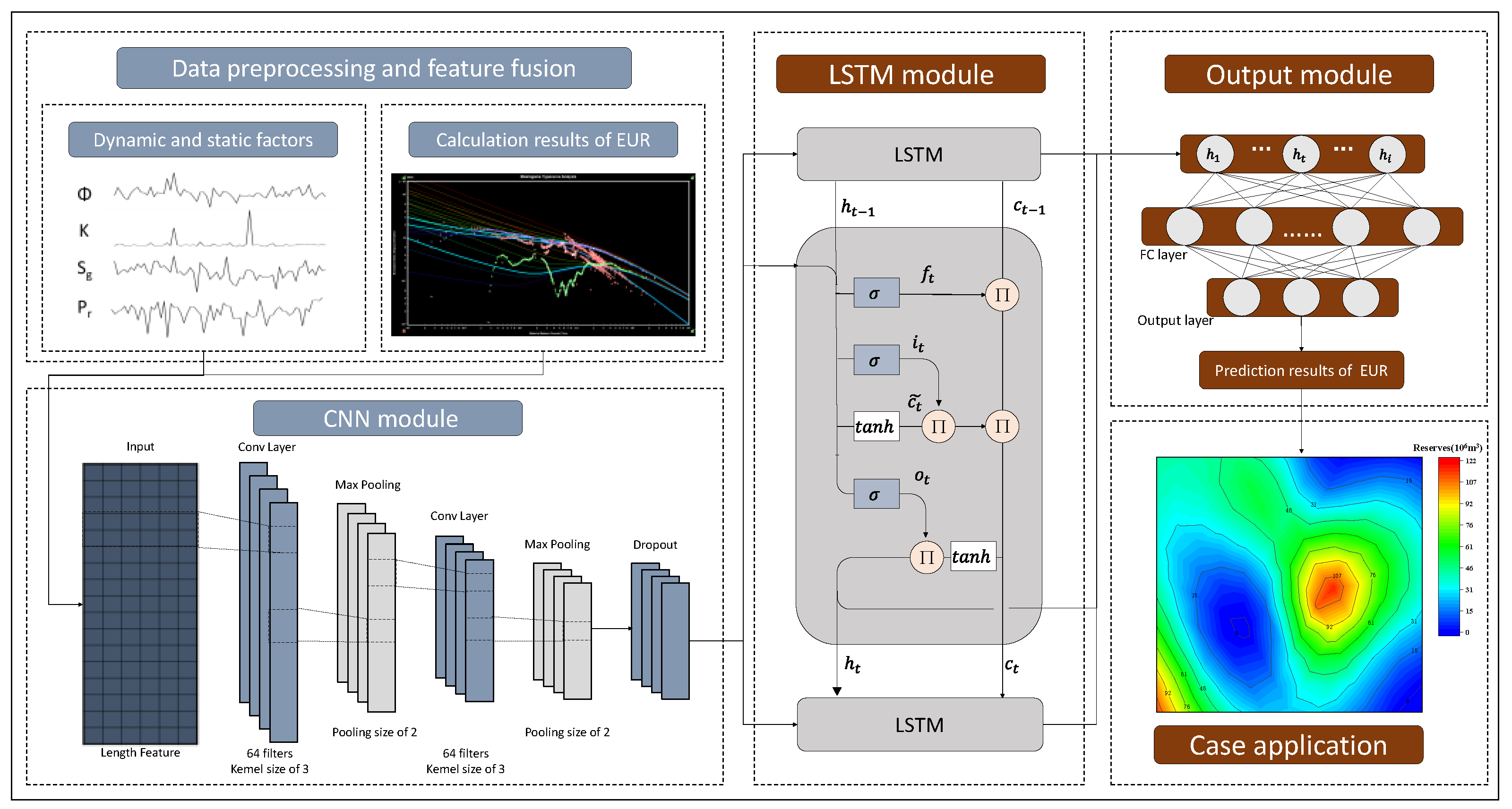
2. Dynamic Reserve Prediction Model
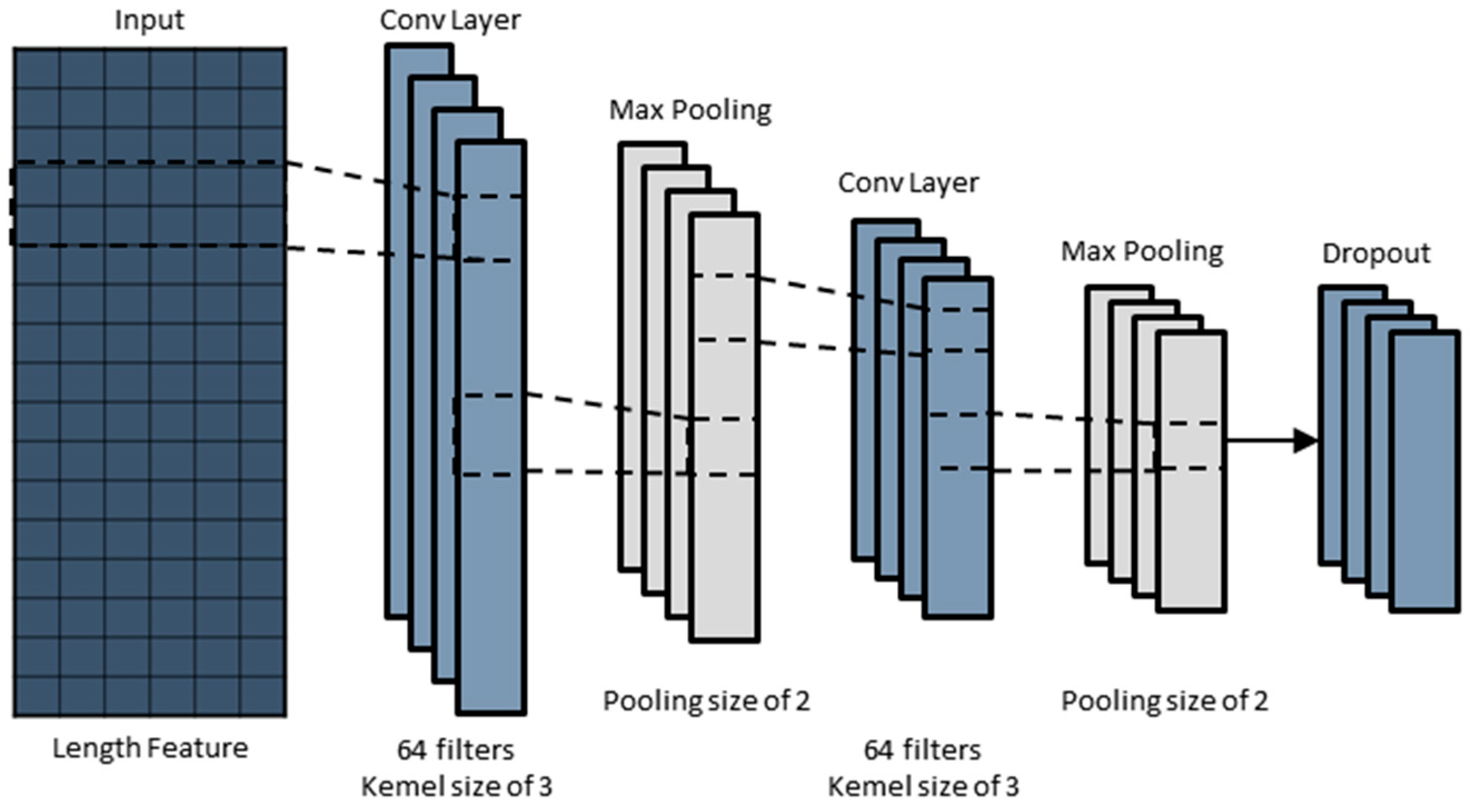
2.1. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
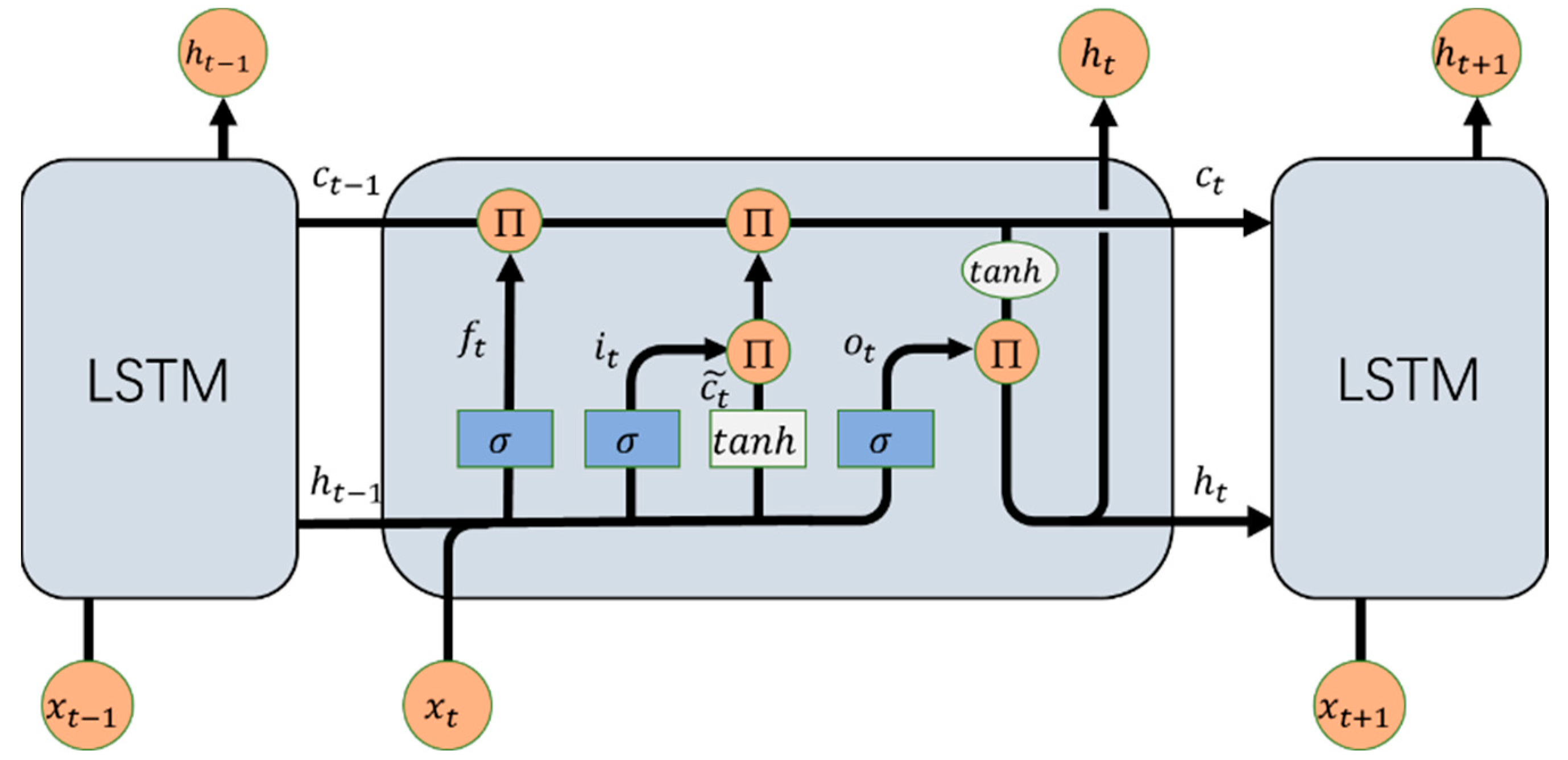
2.2. Long Short-Term Memory Neural (LSTM) Network
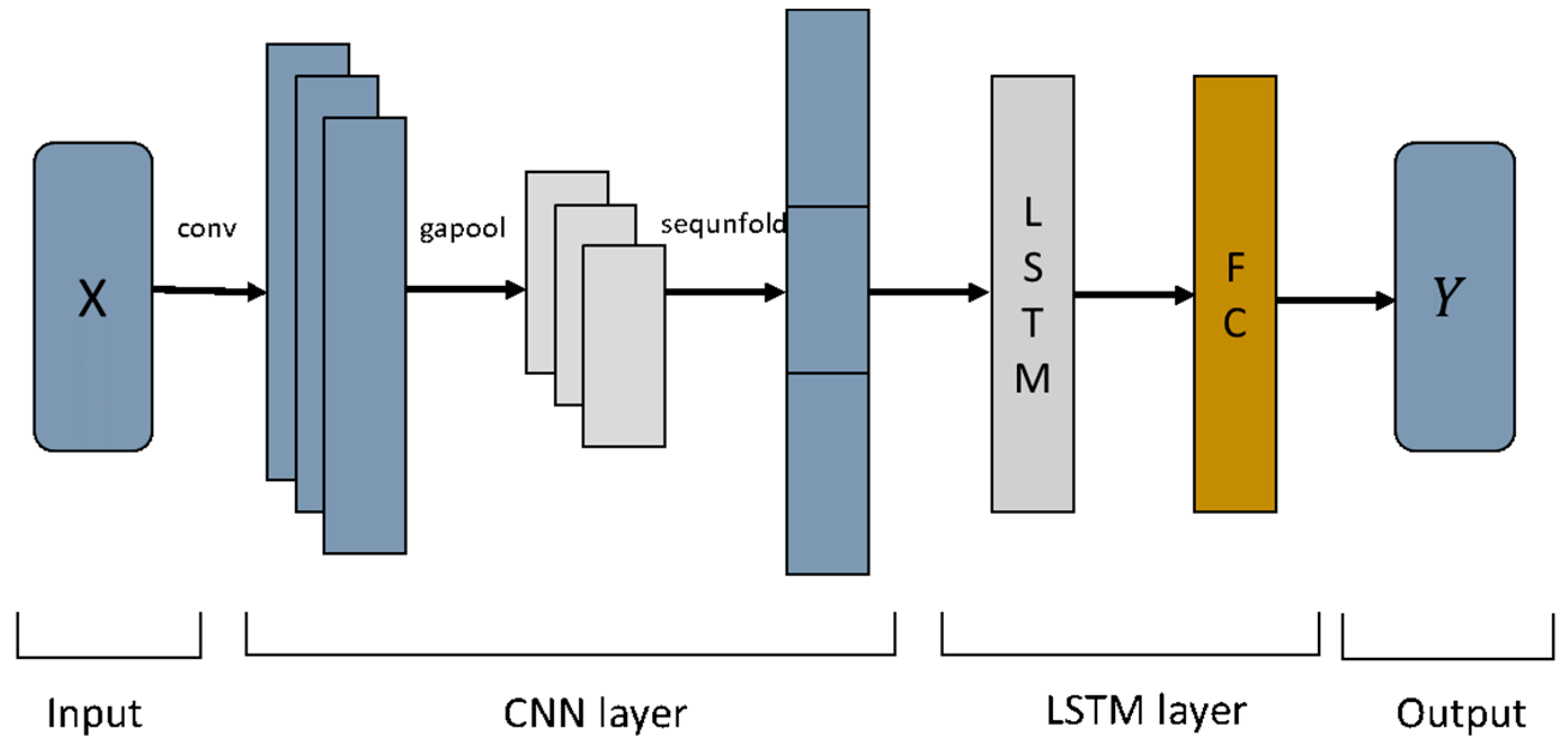
2.3. CNN-LSTM Model
3. Data Collection and Experimental Setup
3.1. Information on the Research Area
3.2. Data Acquisition and Processing
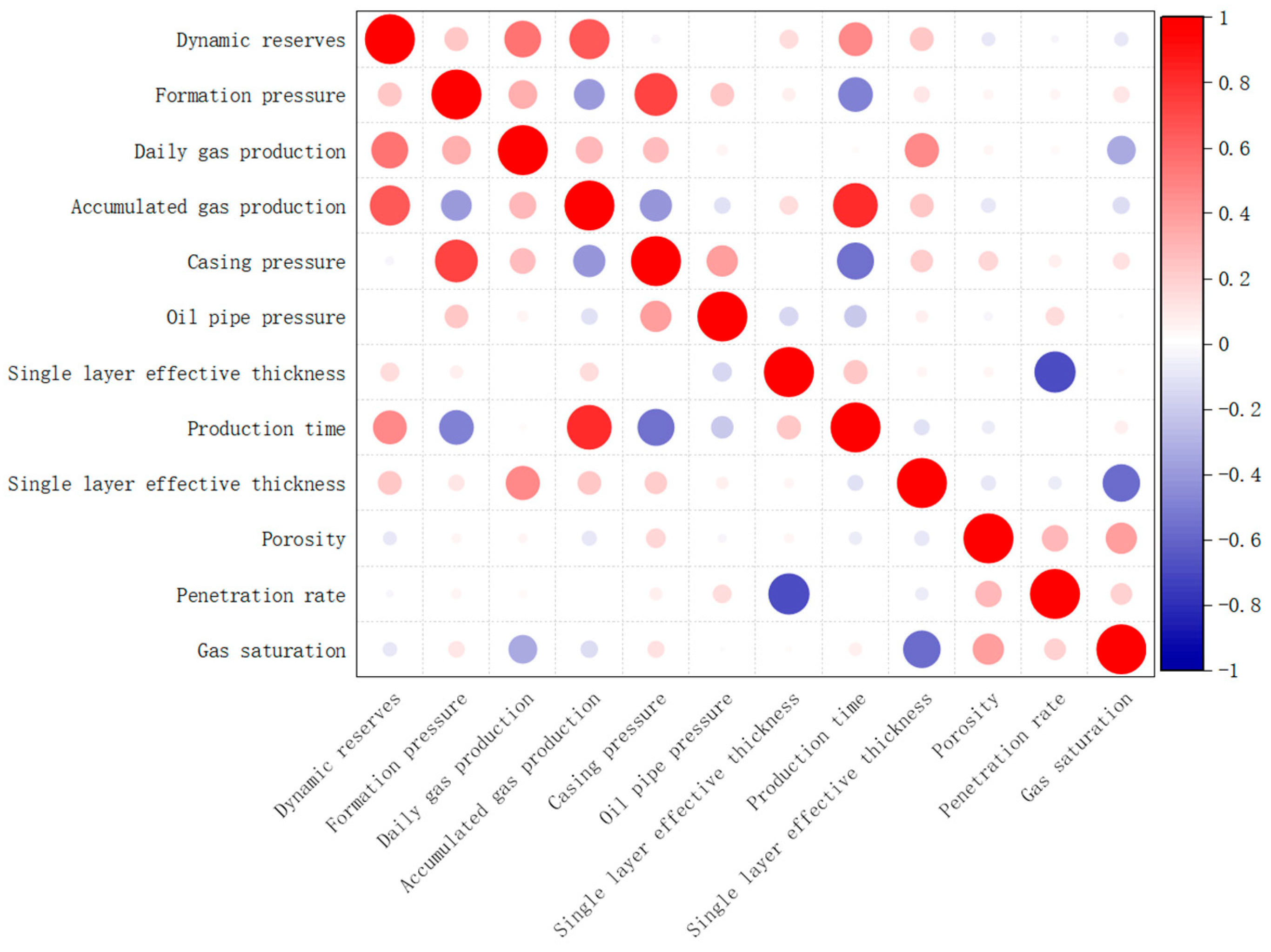
3.3. Correlation Analysis
3.4. Construction of Deep Learning Prediction Models
4. Example Application
4.1. Model Parameter Settings
4.2. Analysis of Model Prediction Results
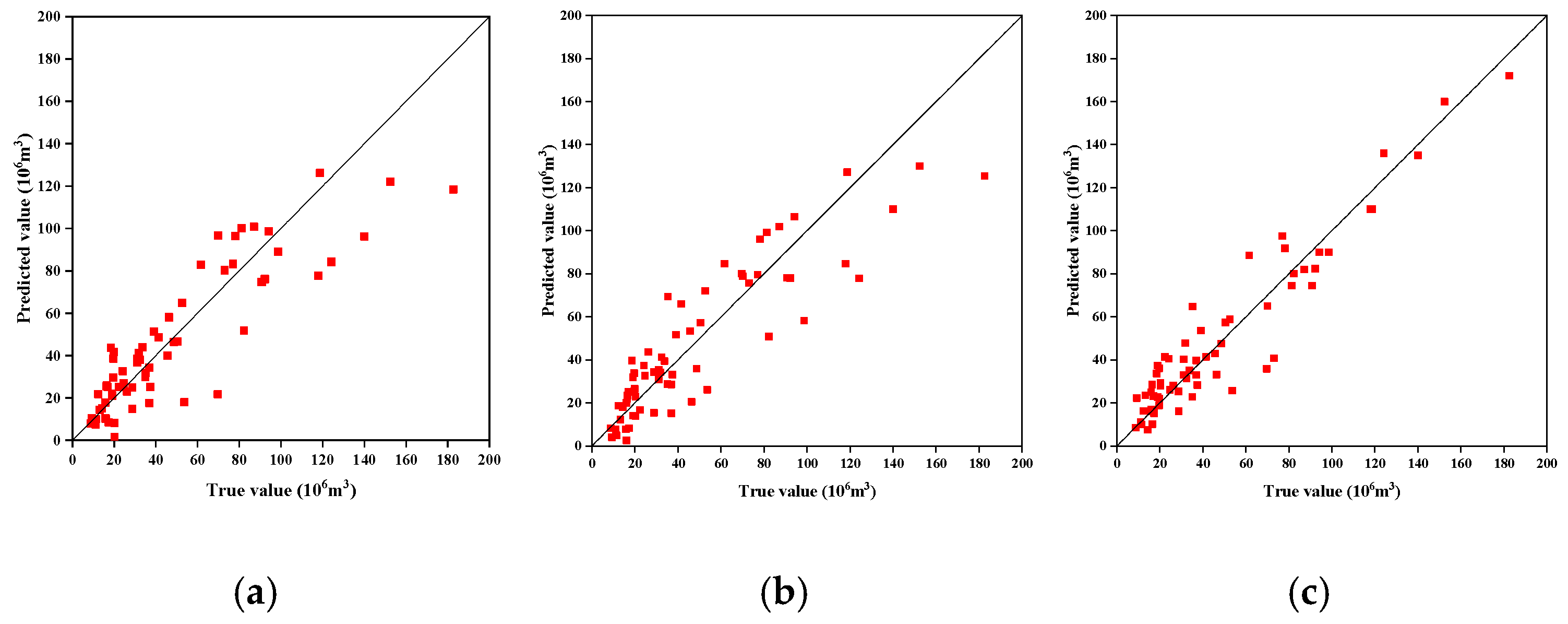
4.3. Comparative Experiment
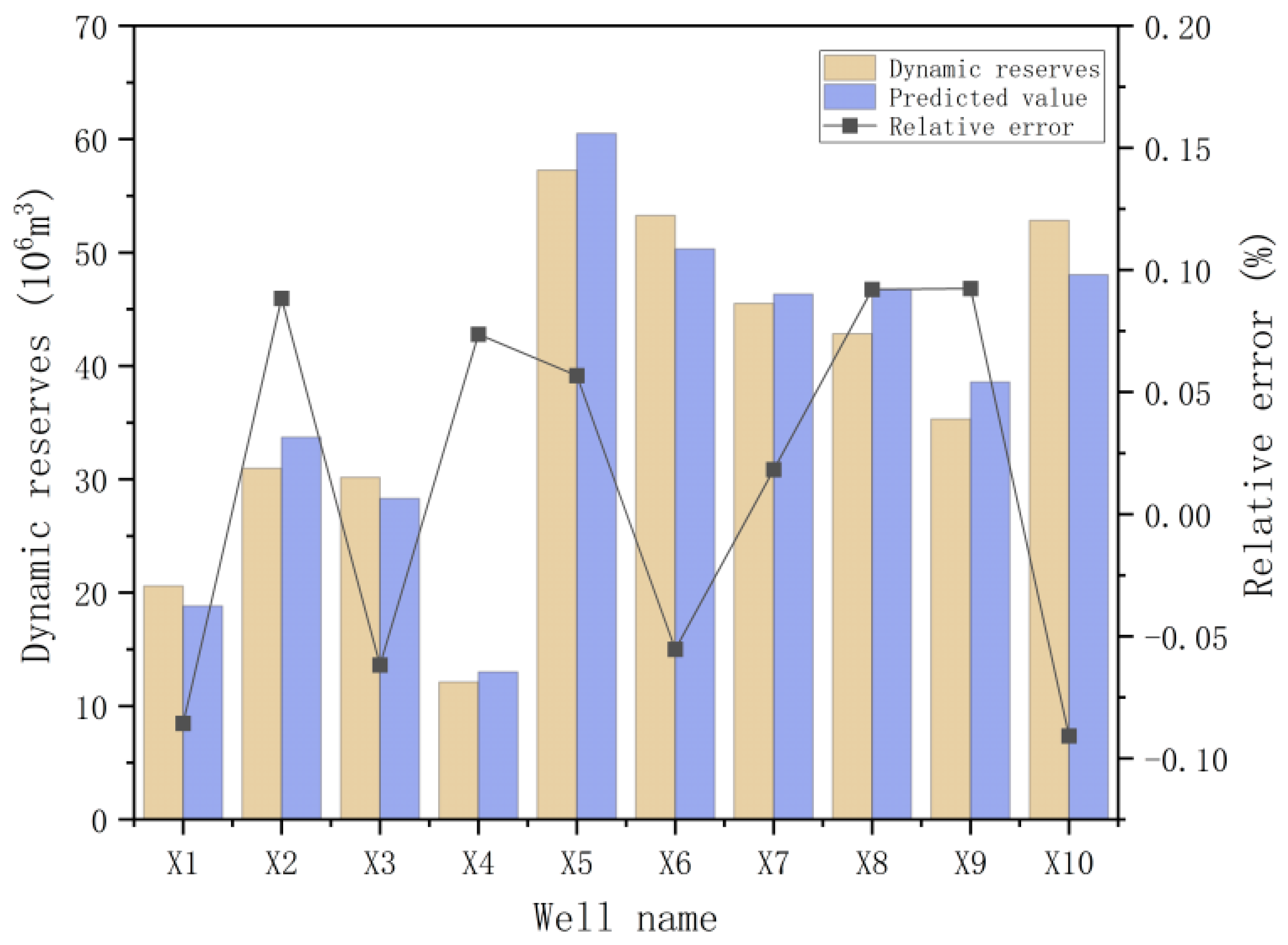
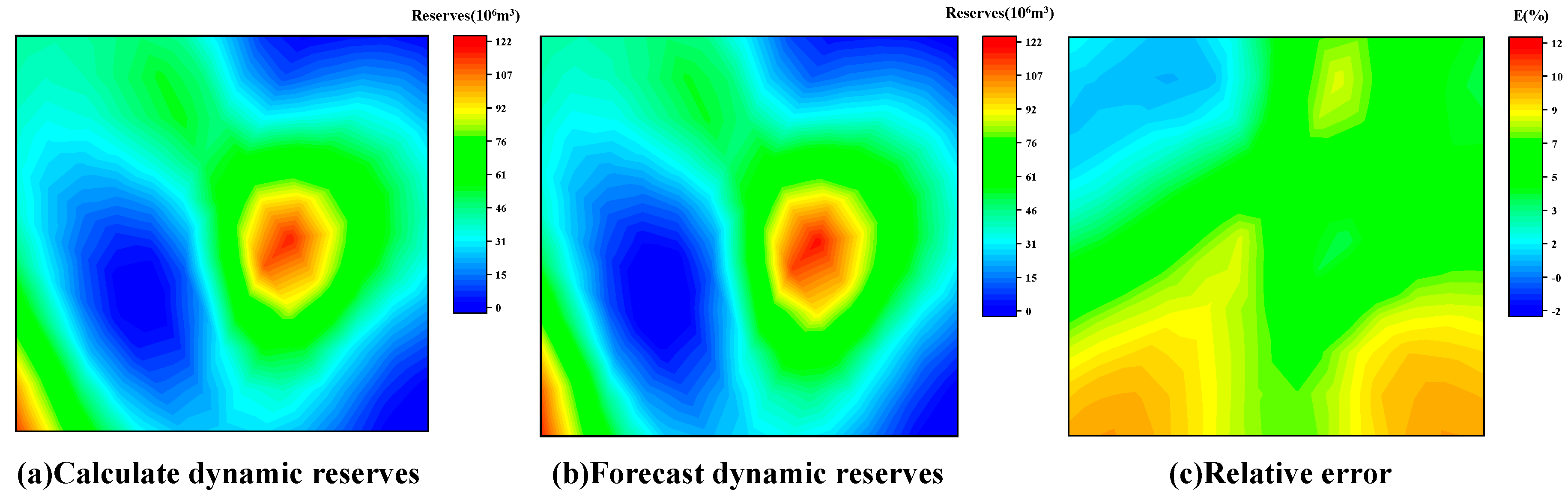
4.4. Practical Applications
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- To address the industry bottleneck in dynamic reserve assessment of low-permeability tight gas wells, an innovative deep learning technology approach combining CNN and LSTM was adopted. By leveraging on-site dynamic and static data, this model offers a solution for the fast and precise estimation of gas well dynamic reserves, providing a new technique for tight gas reservoir evaluation.
- (2)
- The results of the instance test show that the R2 predicted by the CNN-LSTM model reaches 0.959. This accuracy is markedly higher than that achieved by traditional machine learning models such as the individual CNN and LSTM architectures.
- (3)
- The application results show that the relative error of the single-well dynamic reserves prediction test is less than 10%, and it shows good stability and high accuracy in the dynamic reserves prediction test of adjacent multi-well groups in a small range, and the calculation results meet the engineering requirements.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, C.; Lin, M.; Ma, F.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Y.; Guan, C.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Progress, challenges and countermeasures of China’s natural gas industry under the goal of carbon neutrality. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oil and Gas Department of National Energy Administration; Resource and Environmental Policy Research Institute of the Development Research Center of the State Council; Oil and Gas Resources Strategic Research Center of the Ministry of Natural Resources. Natural Gas Development Report of China; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Lei, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhao, M. Technical strategy for beneficial development of tight sand gas in Sulige Gas Field. Pet. Reserv. Eval. Dev. 2024, 14, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, B.; Hu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hu, A. Development of China’s natural gas: Review 2023 and outlook 2024. Nat. Gas Ind. 2024, 44, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Qiang, K.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Wei, Q.; Wang, R. Research on Intelligent Production Optimization of Low-Permeability Tight Gas Wells. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, C.; Niu, G.; Liang, H.; Bu, L.; Gu, J. Dynamic Reserves Evaluation of Fractured-Cavity Reservoirs with Closed Water: A Case from Halahatang Oilfield, Tarim Basin. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2020, 41, 321–325. Available online: https://www.zgxjpg.com/CN/Y2020/V41/I3/321 (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Wang, C.; Jia, A.; Wei, Y.; Guo, J. Comparisons and application of single well and reservoir dynamic reserves evaluation methods: Case study of a small fault block gas reservoir. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2024, 35, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Wei, Q.; Lu, H.; Zhu, P.; Wang, R.; Yan, Y. A Model for apparent permeability of organic slit nanopores in shale gas based on GCMC molecular simulation. Fuel 2025, 381, 133236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Jia, A.; Xu, Y.; Fang, J. Progress on different reserve calculation methods in the whole life cycle of gas reservoir development. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2020, 31, 1749–1756. Available online: http://www.nggs.ac.cn/CN/10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2020.07.005 (accessed on 15 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- SY/T 6098-2010; The People’s Republic of China Petroleum and Natural Gas Industry Standard, Natural Gas Recoverable Reserves Calculation Method. Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Yue, S.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zheng, C.; Jing, Z.; Zhang, T. A new method for calculating dynamic reserves and water influx of water-invaded gas reservoirs. Lithol. Reserv. 2023, 35, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chen, L.; Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, Z. A new technique of reserve estimation in water-production tight gas wells. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2022, 22, 6482–6487. Available online: http://www.stae.com.cn/jsygc/article/abstract/2107253?st=article_issue (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Huang, F. SEC estimation by DCA on shale gas fields: A case study of Pingqiao South Block of Nanchuan Gas Field. Pet. Reserv. Eval. Dev. 2021, 11, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Peng, X.; Yu, P.; Li, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, B.; Mao, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, Y. New method of flowing material balance in ultra deep carbonate gas reservoirs. Fract. Block Oil Gas Fields 2023, 30, 656–664. Available online: https://www.dkyqt.com/#/digest?ArticleID=4977 (accessed on 25 December 2024).
- Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Zhu, S. A dynamic reserve evaluation method for deep high-pressure gas reservoirs without considering the compression factor. Nat. Gas Ind. 2023, 43, 78. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3ruWTMGvziWyIlzhmYT-xrrZwabIAvHkUQFq659gqVmL4QEr9kvsEEqsLzRYn_Myfxn1vY8WubHDQT0-k1rtrVZ5eCDAU5KGcgVC4pDLgCYJst1IIYkbyCURr_-rcmhlf39djkGuta6Rd2wazZHjpLFPH6vxzxJVp0hDeOkYC9ACoFBIYPffQw==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 25 December 2024).
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, H.; Zhu, P.; Wang, R. Status quo and development trends of research on shale gas adsorption and seepage in shale gas reservoirs. Oil Gas Geol. 2024, 45, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guofa, J. Research progress and development tendency of transient well testing technology. Spec. Oil Gas Reserv. 2024, 31, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.; Wang, B.; Yang, L.; Zhang, M.; Wen, S.; Gao, S. Application of rate-transient analysis in Yuanba Gas Field. Pet. Reserv. Eval. Dev. 2021, 11, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Jiang, J. Correction of errors in modern production decreasing analysis Blasingame plate making. Nat. Gas Ind. 2015, 35, 71–77. Available online: https://trqgy.paperonce.org/#/digest?ArticleID=1436 (accessed on 25 December 2024).
- Wei, M.; Duan, Y.; Chen, W.; Fang, Q.; Li, Z.; Guo, X. Blasingame production decline type curves for analysing a multi-fractured horizontal well in tight gas reservoirs. J. Cent. South Univ. 2017, 24, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X. Question and comment for Fetkovich’s typical curve. Pet. Reserv. Eval. Dev. 2024, 14, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, W.; Liu, Y.; Wan, W.; Luo, R.; Li, D.; Yang, S.; Xu, Y. Forecasting monthly gas field production based on the CNN-LSTM model. Energy 2022, 260, 124889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargalla, M.A.M.; Yan, W.; Deng, J.; Wu, T.; Kiyingi, W.; Li, G.; Zhang, W. TimeNet: Time2Vec attention-based CNN-BiGRU neural network for predicting production in shale and sandstone gas reservoirs. Energy 2022, 290, 130184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Jia, H. Production performance forecasting method based on multivariate time series and vector autoregressive machine learning model for waterflooding reservoirs. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 175–184. Available online: https://www.cpedm.com/CN/10.11698/PED.2021.01.16 (accessed on 25 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tian, L.; Liu, S.; Li, N.; Zhang, J.; Ping, X.; Ma, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, N. Prediction model of tight gas well productivity based on composite machine algorithm: Taking Block SM of Ordos Basin as an example. Pet. Geol. Oilfield Dev. Daqing 2024, 43, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, N.; Qiao, X.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Xu, W.; Xie, X. Application of artificial intelligence method to calculate recoverable reserves in tight gas reservoirs—An example of BP neural network. Daqing Pet. Geol. Dev. 2024, 44, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Yang, C.; Sun, H.; Yao, J.; Zhang, L.; Fu, S.; Luo, F. Shale gas well production forecasting based on time sequence similarity and ma chine learning methods. J. China Univ. Pet. 2024, 48, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Ma, X.-H.; Zhang, X.-W.; Guo, W.; Kang, L.-X.; Yu, R.-Z.; Sun, Y.-P. A deep-learning-based prediction method of the estimated ultimate recovery (EUR) of shale gas wells. Pet. Sci. 2021, 18, 1450–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hou, M.; Quan, H.; Yu, J. A production prediction method for tight gas wells based on knowledge graph and random forest algorithm. Spec. Oil Gas Reserv. 2024, 31, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Bai, H.; Jiao, X.; Tan, C. Study and application of a data-driven prediction model for gas well liquid loading and production. Nat. Gas Oil 2025, 43, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Wang, W.; Fan, D.; Yao, J.; Luo, F.; Yang, C. Production prediction of atmospheric shale gas Wells based on production decline coupled with LSTM. Reserv. Eval. Dev. 2023, 13, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hang, X. Prediction method of horizontal well fracture pressure based on neural network model. J. Cent. South Univ. 2024, 55, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter Name | Minimum Values | Maximum Values |
|---|---|---|
| Porosity/(%) | 4.22 | 13.36 |
| Penetration rate/(10−3 μm2) | 0.14 | 7.08 |
| Gas saturation/(%) | 28.63 | 69.00 |
| Single-layer effective thickness/(m) | 1.90 | 8.20 |
| Formation pressure/(MPa) | 5.21 | 29.71 |
| Pre-production set pressure/(MPa) | 22.00 | 28.00 |
| Daily gas production/(104 m3/d) | 0.19 | 5.97 |
| Accumulated gas production/(104 m3) | 281.96 | 6984.73 |
| Casing pressure/(MPa) | 1.08 | 22.53 |
| Oil pipe pressure/(MPa) | 0.55 | 5.94 |
| Production time (a) | 1 | 12 |
| Model | R2 | MAE | RMSE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 0.686 | 13.043 | 18.315 | 0.314 |
| LSTM | 0.731 | 13.227 | 17.472 | 0.332 |
| CNN-LSTM | 0.959 | 5.311 | 7.627 | 0.139 |
| Model | R2 | MAE | RMSE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| decision tree | 0.736 | 12.856 | 16.932 | 0.295 |
| Support Vector Machine | 0.686 | 14.213 | 19.047 | 0.324 |
| linear regression | 0.785 | 11.328 | 15.641 | 0.274 |
| BP neural network | 0.825 | 10.574 | 14.283 | 0.263 |
| CNN-LSTM model | 0.959 | 5.311 | 7.627 | 0.139 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, B.; Zeng, H.; Bai, J.; Tian, X.; Liu, P.; Wu, J.; Feng, C. A Symmetric Deep Learning Approach for Dynamic Reserve Evaluation of Tight Sandstone Gas Wells. Symmetry 2025, 17, 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122033
Zhang Y, Zhang B, Liu B, Zeng H, Bai J, Tian X, Liu P, Wu J, Feng C. A Symmetric Deep Learning Approach for Dynamic Reserve Evaluation of Tight Sandstone Gas Wells. Symmetry. 2025; 17(12):2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122033
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yi, Bin Zhang, Banghua Liu, Haikun Zeng, Junhui Bai, Xijun Tian, Peng Liu, Jiahui Wu, and Chaoqiang Feng. 2025. "A Symmetric Deep Learning Approach for Dynamic Reserve Evaluation of Tight Sandstone Gas Wells" Symmetry 17, no. 12: 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122033
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhang, B., Liu, B., Zeng, H., Bai, J., Tian, X., Liu, P., Wu, J., & Feng, C. (2025). A Symmetric Deep Learning Approach for Dynamic Reserve Evaluation of Tight Sandstone Gas Wells. Symmetry, 17(12), 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122033





