A Review of Pavement Performance Deterioration Modeling: Influencing Factors and Techniques
Abstract
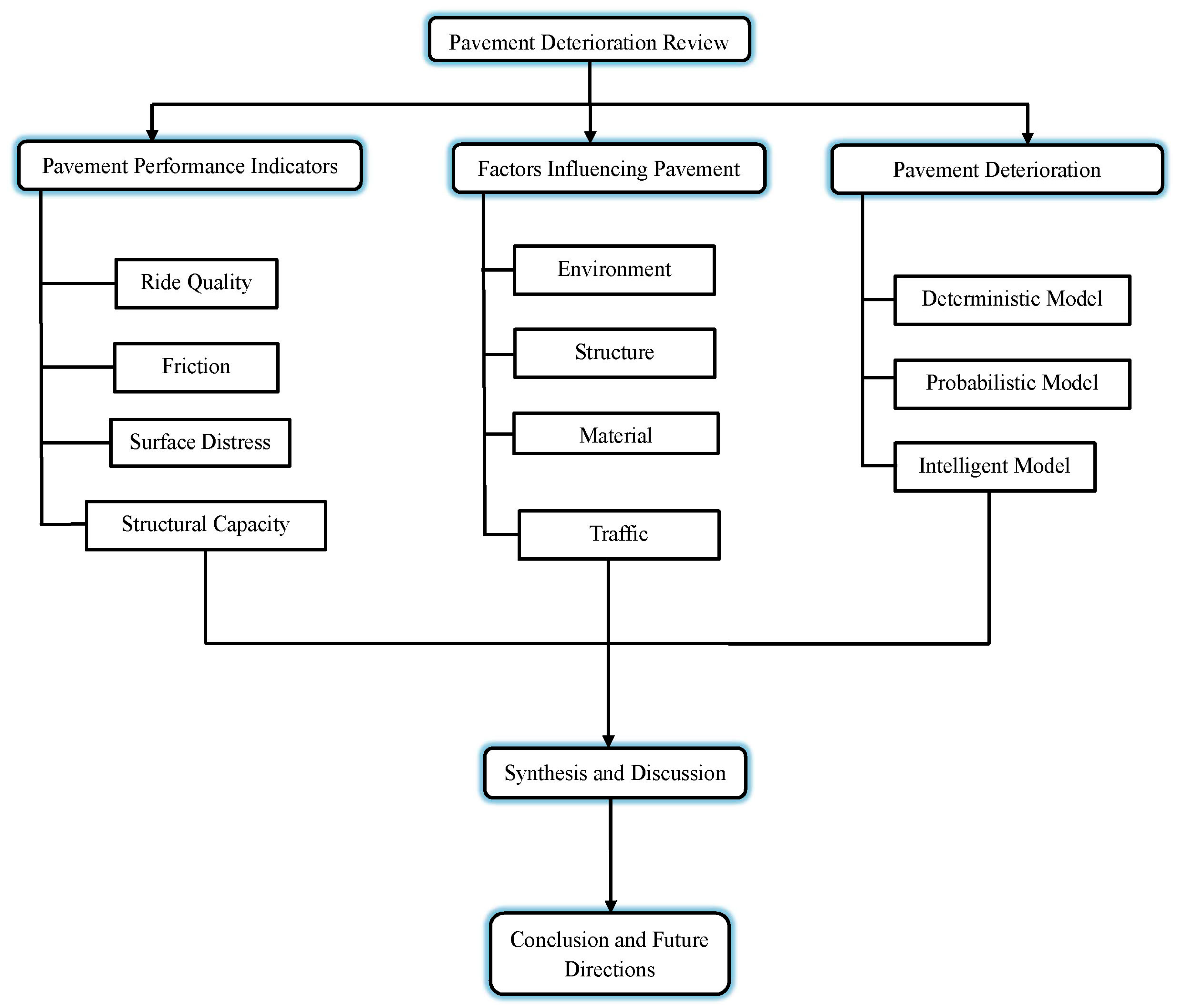
1. Introduction
- Examines key factors influencing pavement deterioration, including traffic load, material characteristics, and environmental conditions;
- Evaluates major pavement performance indicators used in condition assessment and management systems;
- Compares and analyzes modeling frameworks, from deterministic, probabilistic, and machine learning-based techniques, to identify research trends and methodological gaps.
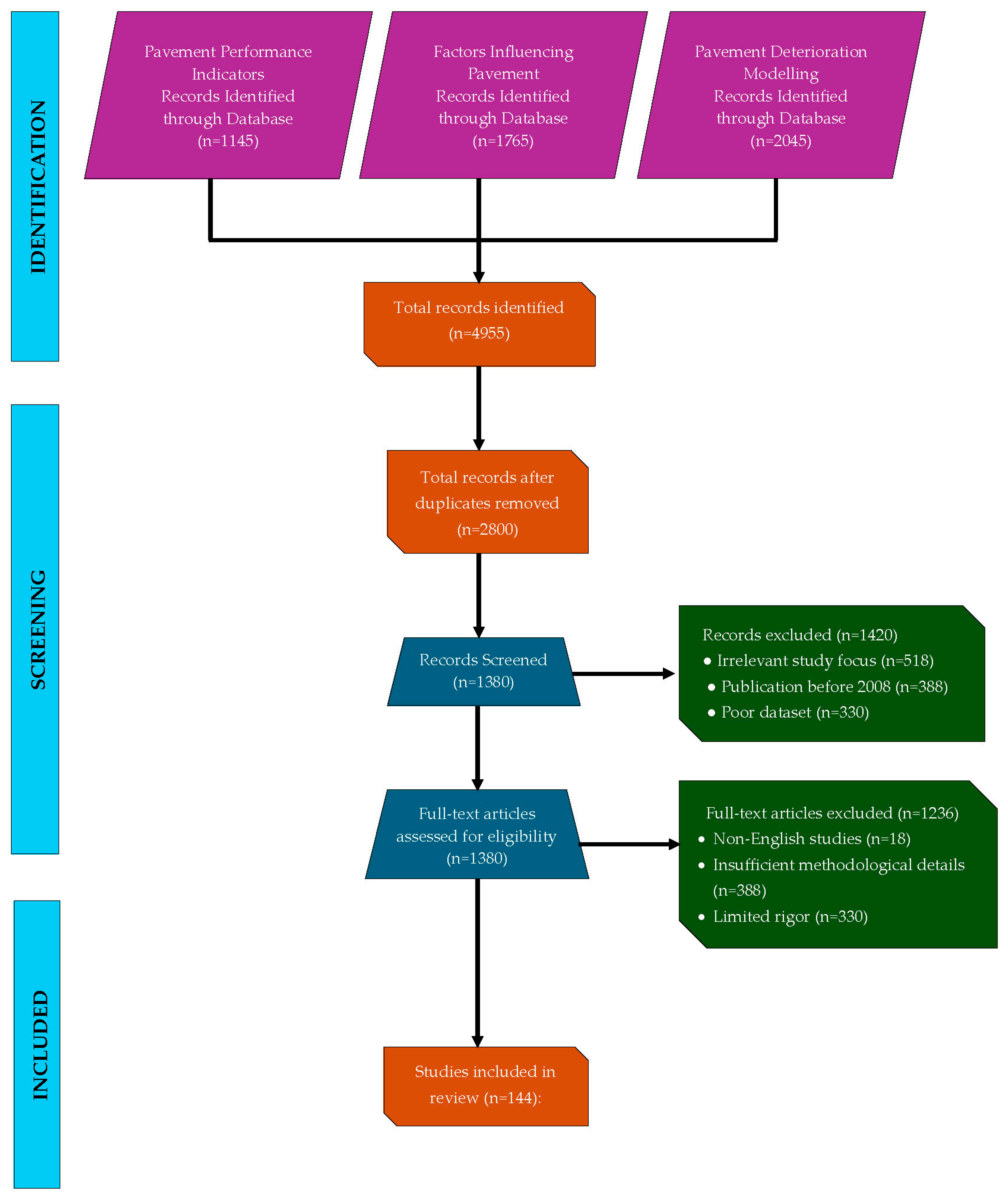
2. Review Methodology
3. Pavement Performance Indicators
3.1. Ride Quality
International Roughness Index (IRI)
3.2. Friction
Skid Number (SN)
3.3. Surface Distress Indicator
3.3.1. Pavement Condition Index (PCI)
3.3.2. PASER (Pavement Surface Evaluation and Rating)
3.4. Structural Capacity
Structural Number (SN)
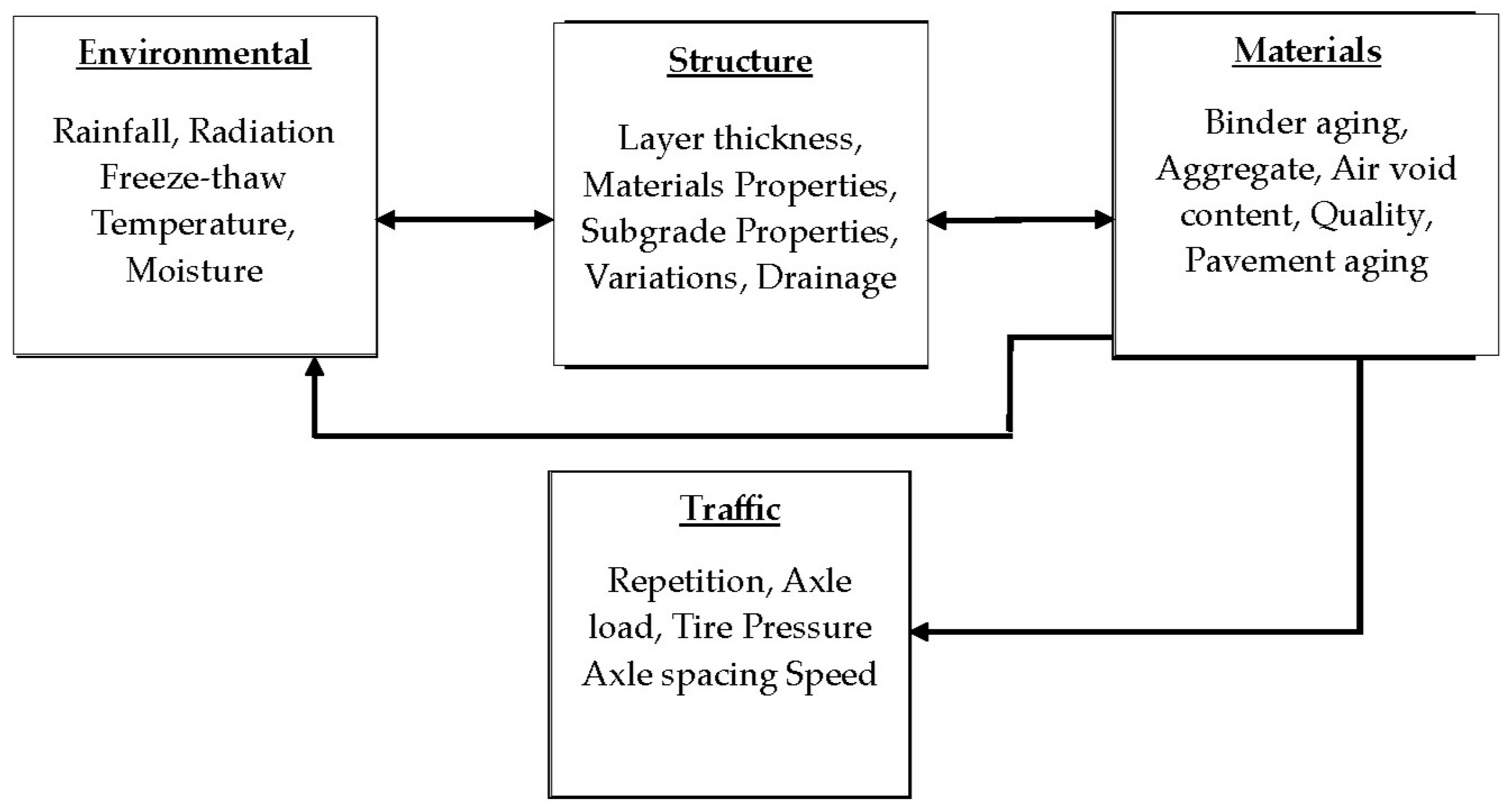
4. Factors Influencing Pavement Deterioration
4.1. Environmental Factors
4.1.1. Temperature Effects
4.1.2. Precipitation and Flooding
4.2. Structure Factors
4.3. Pavement Age and Material Properties
4.4. Traffic Load and Fatigue in Pavement Deterioration
5. Approaches to Pavement Deterioration Modeling
5.1. Traditional Modeling Methods
5.1.1. Deterministic Approach
Deterministic Approaches in Pavement Performance Prediction
Strengths of Deterministic Models
Limitations of Deterministic Models
Applications of Deterministic Models in Pavement Management
5.1.2. Probabilistic Approach
Probabilistic Approaches in Pavement Performance Prediction
Strengths of Probabilistic Models
Limitations of Probabilistic Models
Applications of Probabilistic Models in Pavement Management Systems
5.2. Intelligent Models for Pavement Performance Prediction
5.2.1. Machine Learning Model (ML)
5.2.2. Deep Learning Models (DL)
5.2.3. Hybrid Models
6. Discussion
6.1. Pavement Performance Indicators
6.2. Influencing Factors in Pavement Deterioration
6.3. Comparison of Modeling Approaches
6.3.1. Deterministic Models
6.3.2. Probabilistic Models
6.3.3. Intelligent Models
6.4. Real-World Adoption and Limitations
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
- Influence of Performance Indicators and Data Sources: Most existing models rely heavily on surface condition indicators such as the International Roughness Index (IRI) and Pavement Condition Index (PCI). While these measures are valuable for assessing ride quality and surface distress, they often overlook the structural capacity of pavement layers and safety-related attributes. Moreover, many prediction frameworks have been developed using datasets from the Long-Term Pavement Performance (LTPP) database, which provides extensive historical data for calibration and validation. However, the absence of integrated frameworks that combine surface, structural, and safety performance remains a limitation for transportation agencies seeking holistic and data-driven maintenance strategies.
- Evolution of Modeling Techniques: Modeling has evolved from traditional deterministic and probabilistic frameworks toward intelligent, data-driven approaches. Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) methods have demonstrated superior capability in capturing nonlinear relationships among influencing factors such as traffic loading, pavement age, environmental variations, and treatment history. Despite their accuracy, many intelligent models operate as “black boxes,” offering limited interpretability of variable contributions. This limitation highlights the need for hybrid and explainable models that integrate the transparency of statistical approaches with the predictive power of AI-based techniques.
- Comparative Strengths and Limitations: Each modeling technique exhibits unique strengths and drawbacks. Deterministic models remain straightforward and computationally efficient but lack flexibility in representing stochastic variability. Probabilistic models address uncertainty and reliability assessment but require large, high-quality datasets and significant computational resources. Intelligent models excel at handling multi-dimensional data and complex variable interactions; however, they depend heavily on data availability, model calibration, and standardized validation protocols to ensure generalizability.
- Integration of Multisource Indicators: Develop unified models that combine surface, structural, and safety metrics—such as IRI, rutting depth, skid resistance, and remaining service life—to enable comprehensive performance evaluation.
- Data Quality and Automation: Enhance the completeness and consistency of pavement databases through automated sensing, LiDAR, and real-time monitoring to reduce subjectivity and improve model reliability.
- Climate and Regional Calibration: Incorporate climate-sensitive parameters and localized calibration procedures to improve model adaptability across diverse geographic and environmental contexts.
- Hybrid and Explainable Modeling: Advance interpretable hybrid frameworks that merge the strengths of deterministic, probabilistic, and machine learning techniques while maintaining transparency in decision-making.
- Standardization and Implementation: Establish common performance metrics, validation criteria, and data-sharing protocols across agencies to promote interoperability, benchmarking, and practical adoption.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PMS | Pavement Management System |
| PCI | Pavement Condition Index |
| PASER | Pavement Surface Evaluation and Rating |
| IRI | International Roughness Index |
| AADT | Annual Average Daily Traffic |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| LTPP | Long-Term Pavement Performance |
| DOT | Department of Transportation |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
References
- Aina, J.; Haghi, N.; Famewo, B.; Lambert, T.; Owolabi, D.; Efe, S. Real-Time Road Damage Detection Using YOLOv8. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Transportation and Development 2025, Glendale, AZ, USA, 8–11 June 2025; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2025; pp. 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Shu, X.; Huang, B. Sustainability innovations in transportation infrastructure: An overview of the special volume on sustainable road paving. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llopis-Castelló, D.; García-Segura, T.; Montalbán-Domingo, L.; Sanz-Benlloch, A.; Pellicer, E. Influence of Pavement Structure, Traffic, and Weather on Urban Flexible Pavement Deterioration. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaqbi, A.J.; Zeiada, W.; Al-Khateeb, G.G.; Hamad, K.; Barakat, S. Creating Rutting Prediction Models through Machine Learning Techniques Utilizing the Long-Term Pavement Performance Database. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkins, G.E.; Ostrom, B. Long-Term Pavement Performance Information Management System User Guide; United States Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2021.
- Dong, J.; Meng, W.; Liu, Y.; Ti, J. A framework of pavement management system based on IoT and big data. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 47, 101226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.B.; Park, J.; Hill, S.H. Use of Pavement Management System Data to Monitor Performance of Pavements under Warranty. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2005, 1940, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, K.S.; Shrestha, J.K.; Shrestha, R.N. Pavement performance model for road maintenance and repair planning: A review of predictive techniques. Digit. Transp. Saf. 2023, 2, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.-L.; Lin, J.-D.; Huang, W.-H.; Kuo, C.-H.; Chiou, Y.-S.; Huang, M.-Y. Developing Pavement Maintenance Strategies and Implementing Management Systems. Infrastructures 2024, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaty, A.; Jeong, H.D.; Smadi, O. Barriers to Implementing Data-Driven Pavement Treatment Performance Evaluation Process. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2018, 144, 04017022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Wang, H. Predicting Asphalt Pavement Deterioration Under Climate Change Uncertainty Using Bayesian Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transport. Syst. 2025, 26, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, S.; Huang, K.; Shi, X.; Lytton, R.L. Determination of flexible pavement deterioration conditions using Long-Term Pavement Performance database and artificial intelligence-based finite element model updating. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2021, 28, e2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onayev, A.; Swei, O. IRI deterioration model for asphalt concrete pavements: Capturing performance improvements over time. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 271, 121768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, N.; Li, Y. Enhancing pavement maintenance: A deep learning model for accurate prediction and early detection of pavement structural damage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 133970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yin, G.; Wang, X.; Yan, W. Automated decision making in highway pavement preventive maintenance based on deep learning. Autom. Constr. 2022, 135, 104111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Ortiz, S.; Pascual-Muñoz, P.; Castro-Fresno, D. Machine learning algorithms for monitoring pavement performance. Autom. Constr. 2022, 139, 104309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Alas, M. Applications of Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Pavement Crack Detection and Characterisation: A Comparative Approach. In 16th International Conference on Applications of Fuzzy Systems, Soft Computing and Artificial Intelligence Tools—ICAFS-2023; Aliev, R.A., Kacprzyk, J., Pedrycz, W., Jamshidi, M., Babanli, M.B., Sadikoglu, F.M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 1141, pp. 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Fawzy, M.M.; Shrakawy, A.S.E.; Hassan, A.A.; Khalifa, Y.A. Enhancing sustainability for pavement maintenance decision-making through image processing-based distress detection. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2024, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Hao, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, C. A Review on Automated Detection and Identification Algorithms for Highway Pavement Distress. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adwan, I.; Milad, A.; Memon, Z.A.; Widyatmoko, I.; Ahmat Zanuri, N.; Memon, N.A.; Yusoff, N.I.M. Asphalt Pavement Temperature Prediction Models: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justo-Silva, R.; Ferreira, A.; Flintsch, G. Review on Machine Learning Techniques for Developing Pavement Performance Prediction Models. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adarkwa, O.; Attoh-Okine, N. Pavement Condition Surveys; Delaware Center for Transportation: Newark, DE, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bryce, J.; Boadi, R.; Groeger, J. Relating Pavement Condition Index and Present Serviceability Rating for Asphalt-Surfaced Pavements. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2019, 2673, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrette, T.P. Comparison of PASER and PCI Pavement Distress Indices; Master of Science in Civil Engineering, Michigan Technological University: Houghton, MI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Majidifard, H.; Adu-Gyamfi, Y.; Buttlar, W.G. Deep machine learning approach to develop a new asphalt pavement condition index. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 247, 118513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dela Cruz, O.G.; Mendoza, C.A.; Lopez, K.D. International Roughness Index as Road Performance Indicator: A Literature Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 822, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloop, M.R.; El-Badawy, S.M.; Ahn, J.; Sim, H.-B.; Hu, J.W.; Abd El-Hakim, R.T. A hybrid wavelet-optimally-pruned extreme learning machine model for the estimation of international roughness index of rigid pavements. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, D.; Teng, L.; Zhu, J. Development of a Relationship between Pavement Condition Index and Riding Quality Index on Rural Roads: A Case Study in China. Mathematics 2024, 12, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, L.N.O.; Attoh-Okine, N.O.; McNeil, S. Developing Pavement Performance Models for Delaware. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2012, 2304, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.K.; Oppermann, M.C.; Wu, S.-S. North Carolina’s Experience in Development of Pavement Performance Prediction and Modeling. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 1997, 1592, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Nguyen, T. Priority-based optimisation model for developing CIP using PASER for city roads: A case study. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 2703–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyala, M.; Odoki, J.; Baker, C. Hierarchical asphalt pavement deterioration model for climate impact studies. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2014, 15, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Han, C.; Xiao, Y.; Han, Z.; Wu, S.; Cheng, M. Prediction modelling of rutting depth index for asphalt pavement using de-noising method. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X. Predicting Rutting Development Using Machine Learning Methods Based on RIOCHTrack Data. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, Z.F.B.M. Computational Modeling and Simulations of Condition Deterioration to Enhance Asphalt Highway Pavement Design and Asset Management. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Mississippi, Oxford, MS, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ram, P.V.; Thompson, P.D.; Smith, K.; Zimmerman, K.; Allen, B.W. Next-Generation Pavement Performance Measures TechBrief; U.S. Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Arce, O.D.G.; Zhang, Z. Skid resistance deterioration model at the network level using Markov chains. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Dong, N.; Yu, H. Investigating the Deterioration of Pavement Skid Resistance Using an Accelerated Pavement Test. Materials 2023, 16, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Masad, E.; Chowdhury, A.; Harris, P. Predicting Asphalt Mixture Skid Resistance by Aggregate Characteristics and Gradation. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2009, 2104, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatkowski, W.; Hosking, J. The Effect of Traffic and Aggregate on the Skidding Restistance of Bituminous Surfacing; Transport and Road Research Laboratory: Wokingham, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Correia, A.G.; Branco, F.E.F. Bearing capacity of roads, railways and airfields. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Bearing Capacity of Roads and Airfields, Lisbon, Portugal, 24–26 June 2002; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sidess, A.; Ravina, A.; Oged, E. A model for predicting the deterioration of the pavement condition index. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 1625–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosada, A.; Arliansyah, J.; Buchari, E. Evaluation Pavement Deteriorating Condition on Surface Distress Index (SDI) Data Using Radial Basis Function Neural Networks (RBFNN). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1198, 032008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, A.; Mazari, M.; Saghafi, M.; Hosseini, A.; Kumar, S. Parametric Study of Pavement Deterioration Using Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the International Airfield and Highway Pavements Conference 2019, Chicago, IL, USA, 21–24 July 2019; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2019; pp. 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Cavalline, T.; Ogunro, V.; Thompson, D. Development and Validation of Pavement Deterioration Models and Analysis Weight Factors for the NCDOT Pavement Management System; Rep. No. FHWA/NC/2011-01; Federal Highway Administration (FHWA): Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Golroo, A.; Tighe, S.L. Alternative modeling framework for pervious concrete pavement condition analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 4043–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.V. Pavement surface condition assessment: A-state-of-the-art research review and future perspective. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2024, 9, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, A.; Rahman, M.; Thom, N.; Hargreaves, D.; Li, L.; Airey, G. Predicting pavement performance using distress deterioration curves. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2024, 25, 1174–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador-Jiménez, L.E.; Mrawira, D. Reliability-based initial pavement performance deterioration modelling. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2011, 12, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryce, J.; Flintsch, G.; Katicha, S.; Diefenderfer, B. Developing a Network-Level Structural Capacity Index for Asphalt Pavements. J. Transp. Eng. 2013, 139, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Manuel, L.; Damnjanovic, I.; Li, Z. Development of a New Methodology for Characterizing Pavement Structural Condition for Network-Level Applications; Texas Department of Transportation: Austin, TX, USA, 2003.
- Haas, R.; Hudson, W.R.; Zaniewski, J.P. Modern Pavement Management; Krieger Publishing Company: Melbourne, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hays, J. Comparison of New Technology for Measuring Ride Quality. Master’s Thesis, Auburn University, Auburn, AL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Katicha, S.W.; Flintsch, G.W.; Valeri, S.M. Ride Quality Assessment Using Probe Vehicle Acceleration Measurements; Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fortunatus, M.; Onyango, L.; Fomunung, I.; Owino, J. Use of a smart phone based application to measure roughness of polyurethane stabilized concrete pavement. Civ. Eng. Res. J. 2018, 4, 555645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Tallam, T.; Kumar, C.N. Assessment of Ride Quality and Road Roughness by Measuring the Response from a Vehicle Mounted Android Smartphone. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Chennai, India, 18–19 April 2022; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2022; Volume 982, p. 012062. [Google Scholar]
- Pawar, P.R.; Mathew, A.T.; Saraf, M.R. IRI (International Roughness Index): An Indicator Of Vehicle Response. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 11738–11750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, M.W.; Gillespie, T.D.; Paterson, W.D.O. Guidelines for Conducting and Calibrating Road Roughness Measurements; World Bank Technical Paper; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelaziz, N.; Abd El-Hakim, R.T.; El-Badawy, S.M.; Afify, H.A. International Roughness Index prediction model for flexible pavements. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-P.; Siao, G.-J.; Chen, A.-C.; Lee, C.-C. Algorithm for Estimating International Roughness Index by Response-Based Measuring Device. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2020, 146, 04020031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, P.O.; Junior, E.F.N.; Arantes, A.E. Effects of international roughness index on vehicle emissions. Int. J. Veh. Syst. Model. Test. 2021, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujon, M.A. Weigh-in-Motion Data-Driven Pavement Performance Prediction Models. Ph.D. Thesis, West Virginia University Libraries, Morgantown, WV, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tamagusko, T.; Ferreira, A. Machine Learning for Prediction of the International Roughness Index on Flexible Pavements: A Review, Challenges, and Future Directions. Infrastructures 2023, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Sun, Y.; Shu, X.; Huang, B. Use of random forests regression for predicting IRI of asphalt pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 189, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaqbi, A.J.; Zeiada, W.; Al-Khateeb, G.; Abttan, A.; Abuzwidah, M. Predictive models for flexible pavement fatigue cracking based on machine learning. Transp. Eng. 2024, 16, 100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sachdeva, S.N.; Aggarwal, P. Predicting IRI Using Machine Learning Techniques. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2023, 16, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopisetti, L.S.P. International Roughness Index Prediction of Flexible and Rigid Pavements Using Climate and Traffic Data. Master’s Thesis, Bradley University, Peoria, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sandra, A.K.; Sarkar, A.K. Development of a model for estimating International Roughness Index from pavement distresses. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2013, 14, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, L.E.A. Quantifying Uncertainties in Performance Deterioration Modeling with Practical Considerations in Transportation Asset Management; University of New Brunswick: Saint John, NB, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fwa, T. Skid resistance determination for pavement management and wet-weather road safety. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 6, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, R.; Flintsch, G.; de León Izeppi, E. Impact of skid resistance on dry and wet weather crashes. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2021, 147, 04021029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flintsch, G.W.; De León, E.; McGhee, K.K.; AI-Qadi, I.L. Pavement surface macrotexture measurement and applications. Transp. Res. Rec. 2003, 1860, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunford, A. Friction and the Texture of Aggregate Particles Used in the Road Surface Course. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, C.; Peterson, T. Using Pavement Texture to Screen and Target Annual Skid Number Assessment; Parametrix: Seattle, WA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Q.; Yang, H. Temperature Correction and Analysis of Pavement Skid Resistance Performance Based on RIOHTrack Full-Scale Track. Coatings 2020, 10, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plati, C.; Pomoni, M.; Georgouli, K. Quantification of skid resistance seasonal variation in asphalt pavements. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. Engl. Ed. 2020, 7, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, P.; Izeppi, E.; Flintsch, G.; Katicha, S.; McCarthy, R. Pavement Friction for Road Safety: Primer on Friction Measurement and Management Methods. 2023. Available online: https://highways.dot.gov/sites/fhwa.dot.gov/files/2023-06/FHWA%20Pavement%20Friction%20for%20Road%20Safety%20Primer.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Loutzenheiser, D. Background and development of the federal highway administration’s skid-accident reduction program. Transp. Res. Rec. 1974, 523, 20–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer, R.; Fernando, E. Evaluation of Skid Measurements Used by Txdot: Technical Report; Texas A&M Transportation Institute College Station, Texas 77843-3135: College Station, TX, USA, 2013; FHWA/TX-13/0-6619-1; Available online: http://tti.tamu.edu/documents/0-6619-1.pdf (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Salma, S.; Hakan, Y.; Rulian, B.; Jacob, N. Incorporating Maintenance and Rehabilitation History into Pavement Performance Modeling for Jointed Plain Concrete Pavement. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Transportation and Development 2022, Seattle, WA, USA, 31 May–3 June 2022; pp. 24–35. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W. Characterizing Pavement Skid Resistance for Roadway Crash Prediction in Oklahoma. Master’s Thesis, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater, OK, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, F.; Chen, C.; Heitzman, M.; Potter, R.; Powell, B. Evaluation of locked-wheel skid trailer and SCRIM friction measurements at NCAT test track. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2023, 24, 2124249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E303-22; Test Method for Measuring Surface Frictional Properties Using the British Pendulum Tester. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, A. Review of factors controlling skid resistance at tire-pavement interface. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 2733054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Luo, Z.; Lin, X.; Nie, Z.; Deng, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, T. Pavement preventive maintenance decision-making for high antiwear and optimized skid resistance performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asi, I.M. Evaluating skid resistance of different asphalt concrete mixes. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, C.M.; Rusch, P.F.; Noyce, D.A. State Practices to Reduce Wet Weather Skidding Crashes; United States Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Rith, M.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, S.W. Characterization of long-term skid resistance in exposed aggregate concrete pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 256, 119423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titus-Glover, L.; Tayabji, S.D. Assessment of LTPP Friction Data; Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center: McLean, VA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Noyce, D.A.; Bahia, H.; Yambo, J.; Chapman, J.; Bill, A. Incorporating road safety into pavement management: Maximizing surface friction for road safety improvements. Work 2007, 5, 241. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Fortes, A.P.; Giudici, H. A recent overview of the effect of road surface properties on road safety, environment, and how to monitor them. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 65993–66009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, Y.U.; Jain, S.; Tiwari, D.; Jain, M. Development of overall pavement condition index for urban road network. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 104, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, A.; Samaneh, H.; Ghanim, M. Predicting pavement condition index using artificial neural networks approach. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dong, Q.; Zhu, H.; Huang, B. Development of distress condition index of asphalt pavements using LTPP data through structural equation modeling. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2016, 68, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E17 Committee. Practice for Roads and Parking Lots Pavement Condition Index Surveys; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietersen, R.; Beauregard, M.; Einstein, H. Automated method for airfield pavement condition index evaluations. Autom. Constr. 2022, 141, 104408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholevar, N.; Golroo, A.; Esfahani, S.R. Machine learning techniques for pavement condition evaluation. Autom. Constr. 2022, 136, 104190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranyal, E.; Sadhu, A.; Jain, K. Road Condition Monitoring Using Smart Sensing and Artificial Intelligence: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelino, P.; De Lurdes Antunes, M.; Fortunato, E.; Gomes, M.C. Machine learning approach for pavement performance prediction. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, K. Deep Learning in Data-Driven Pavement Image Analysis and Automated Distress Detection: A Review. Data 2018, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnazari, H.; Tutunchian, M.A.; Mashayekhi, M.; Amini, A.A. Application of Soft Computing for Prediction of Pavement Condition Index. J. Transp. Eng. 2012, 138, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, M.; Floris, I.; Quadrifoglio, L. Computer-Aided Prediction of Pavement Condition Index (Pci) Using Ann. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computers and Industrial Engineering, Lisbon, Portugal, 11–13 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, F.M.A.; Rubasi, K.A.H.; Saleh, A.A. The Road Pavement Condition Index (PCI) Evaluation and Maintenance: A Case Study of Yemen. Organ. Technol. Manag. Constr. Int. J. 2016, 8, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of the Army, United States. Pavement Maintenance Management (PAVER 1982). In Technical Manual TM 5-623; Department of the Army: Washington, DC, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Elhadidy, A.A.; El-Badawy, S.M.; Elbeltagi, E.E. A simplified pavement condition index regression model for pavement evaluation. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo E Silva, F.; Van Dam, T.J.; Bulleit, W.M.; Ylitalo, R. Proposed Pavement Performance Models for Local Government Agencies in Michigan. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2000, 1699, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, W.S.; Power, D.; Ullah, I.; Mulry, B.; Feighan, K.; McKeever, S.; O’Sullivan, D. Deep learning framework for intelligent pavement condition rating: A direct classification approach for regional and local roads. Autom. Constr. 2023, 153, 104945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, S.R.; Haddock, J.E. Accuracy of Statewide Pavement Surface Evaluations and Ratings Performed by Local Agencies. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2019, 2673, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angela, W.; Schattler, K.; Kathryn, Z.; Rietgraf, A. Implementing Pavement Management Systems for Local Agencies; Illinois Center for Transportation: Urbana, IL, USA, 2011; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/2142/45815 (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Fakhri, M.; Shahni Dezfoulian, R. Pavement structural evaluation based on roughness and surface distress survey using neural network model. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 204, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegaran, J.; Shahni Dezfoulian, R.; Fakhri, M. Estimation of IRI from PASER using ANN based on k-means and fuzzy c-means clustering techniques: A case study. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 5153–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, T.; Shekharan, R.A.; Diefenderfer, B.K. Implementation of network-level falling weight deflectometer survey. Transp. Res. Rec. 2012, 2304, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flora, W.F. Development of a Structural Index for Pavement Management: An Exploratory Analysis; Purdue University: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zaghloul, S.; He, Z.; Vitillo, N.; Brian Kerr, J. Project scoping using falling weight deflectometer testing: New Jersey experience. Transp. Res. Rec. 1998, 1643, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, E.; Hefer, A.; Maina, J. Determination of pavement number for flexible pavements using FWD deflection bowl information. In Proceedings of the Southern African Transport Conference, Pretoria, South Africa, 6–9 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials; AASHTO Joint Task Force on Pavements (Eds.) Pavement Management Guide, 2nd ed.; American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Raof, H.S.; Abd El-Hakim, R.T.; El-Badawy, S.M.; Afify, H.A. Structural number prediction for flexible pavements using the long term pavement performance data. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 841–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, B.; Murphy, M.; Zhang, Z.; Arellano, M. Improved structural condition index for pavement evaluation at network level. In Proceedings of the Airfield and Highway Pavement 2013: Sustainable and Efficient Pavements, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 June 2013; pp. 781–790. [Google Scholar]
- Pandya, H.I.; Ali, A.A.; Mehta, Y.A. Enhancing falling weight deflectometer (FWD) testing: Comprehensive review and development of robust procedure in the United States. J. Test. Eval. 2024, 52, 2039–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, G.; Jooste, F.; Sadzik, E.; Henning, T. The Calibration and Use of Hdm-Iv Performance Models in a Pavement Management System. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Managing Pavements, Durban, South Africa, 17–21 May 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kavussi, A.; Abbasghorbani, M.; Moghadas Nejad, F.; Bamdad Ziksari, A. A new method to determine maintenance and repair activities at network-level pavement management using falling weight deflectometer. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2017, 23, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Murphy, M.R. Improved method for evaluating the pavement structural number with falling weight deflectometer deflections. Transp. Res. Rec. 2013, 2366, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-P.; Guo, Y.-X.; Wu, M.-Y.; Xiang, K.; Sun, S.-R. Review on structural damage rehabilitation and performance assessment of asphalt pavements. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2021, 60, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, M.K. Analysis of Pavement Deterioration. Ph.D. Thesis, National Institute of Technology Rourkela, Rourkela, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Buhari, R.; Md Rohani, M.; Puteh, S. Pavement Life Variation with Material Characteristics, Road Profiles and Environmental Effects. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2018, 8, 2386–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.W.; Buch, N.; Chatti, K. Effect of Traffic Load Characterization (ESAL versus Axle load Spectra) on Rigid Pavement Performance. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Concrete Pavements, ICCP 2025, Toronto, ON, Canada, 21–23 July 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.; Wang, Y. Resilient pavement design with consideration of flooding effect caused by climate change. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2020, 16, 1136–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortney, E.M.; Schuldt, S.J.; Brown, S.L.; Allen, J.P.; Delorit, J.D. A Statistical Principal Component Regression-Based Approach to Modeling the Degradative Effects of Local Climate and Traffic on Airfield Pavement Performance. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2022, 148, 04022018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, C.E.; Andrei, D.; Witczak, M.W.; Houston, W.N. Incorporation of Environmental Effects in Pavement Design. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2007, 8, 667–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Mills, L.; McNeil, S. The Implications of Climate Change on Pavement Performance and Design; University Transportation Center, University of Delaware: Newark, DE, USA, 2011. Available online: https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/24360 (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Bernier, A.T. The Impact of Historical Climate Change Induced Heat Waves on the Predicted Performance of Canadian Flexible Pavements. Master’s Thesis, Carleton University, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Tan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Zhou, X. Resilience assessment of asphalt pavement rutting under climate change. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 109, 103395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, S.; Chen, G. Regional variations of climate change impacts on asphalt pavement rutting distress. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2024, 126, 103968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauß, M.; Pinnau, S. Determining the impact of climate change on road infrastructure in Germany. In Eleventh International Conference on the Bearing Capacity of Roads, Railways and Airfields, Volume 2; CRC Press: London, UK, 2022; pp. 168–177. [Google Scholar]
- Si, W.; Ma, B.; Li, N.; Ren, J.; Wang, H. Reliability-based assessment of deteriorating performance to asphalt pavement under freeze–thaw cycles in cold regions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 68, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assogba, O.C.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Anato, J.N. Numerical investigation of the mechanical response of semi-rigid base asphalt pavement under traffic load and nonlinear temperature gradient effect. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 235, 117406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Flintsch, G.W.; Dawson, A.R.; Parry, T. Examining Effects of Climatic Factors on Flexible Pavement Performance and Service Life. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2013, 2349, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration. Mechanistic Empirical Pavement Design Guide; U.S. Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Gao, L.; Hong, F.; Ren, Y.-H. Impacts of Seasonal and Annual Weather Variations on Network-Level Pavement Performance. Infrastructures 2019, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallès-Vallès, D.; Torres-Machi, C. Deterioration of Flexible Pavements Induced by Flooding: Case Study Using Stochastic Monte Carlo Simulations in Discrete-Time Markov Chains. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2023, 29, 05022009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbi, P.S.R.; Tavassoti, P.; Tighe, S. Enhanced Pavement Design and Analysis Framework to Improve the Resiliency of Flexible Airfield Pavements. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2023, 2677, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darshan, N.; Kataware, A.V. Review on Porous Asphalt Pavements: A Comprehensive Resolution for Stormwater Management and Applications in Current Built Environment. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marath, A.; Revelli, V.; Huang, C.; Swarna, S.T.; Goli, A.K.; Mehta, Y. Impact of Climate Data Sources on Pavement Mechanistic-Empirical Design Pavement Distress Predictions. In Proceedings of the Airfield and Highway Pavements 2023, Austin, TX, USA, 14–17 June 2023; American Society of Civil Engineers: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; pp. 162–172. [Google Scholar]
- Wayessa, S.G.; Abuye, D. The major causes of flexible pavement deterioration and propose its remedial measures: A case study Bako to Gedo Road, Oromia Region, Ethiopia. Am. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2019, 4, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumrawi, M.M. Survey and evaluation of flexible pavement failures. Int. J. Sci. Res 2015, 4, 1602–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Feyissa, B.A. Analysis and modeling of rutting for long life asphalt concrete pavement. In Functional Pavement Design; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 563–571. [Google Scholar]
- Bilodeau, J.P.; Doré, G.; Drolet, F.P.; Chaumont, D. Correction of air freezing index for pavement frost protection design to consider future climate changes. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 43, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakye, S.Y.; Abbey, S.J.; Booth, C.A. Road pavement defect investigation using treated and untreated expansive road subgrade materials with varying plasticity index. Transp. Eng. 2022, 9, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, R.W. Pavement deterioration: Case study. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 1995, 9, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, H.A.; Mostafa, S.A. Minimum Acceptable Cross Slopes of Asphalt Roads for Drainage Consideration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Civil and Architecture Engineering, Yantai, China, 25–27 May 2012; Military Technical College: Cairo, Egypt, 2012; Volume 9, pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.; Si, W. Reliability risk modelling of asphalt pavement structure performance under the impact of freeze-thaw cycles. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galinmoghadam, J.; Zhang, X. Performance of Wicking Geotextile (H2Ri) to Mitigate Pavement Pumping–Phase 2; Department of Transportation, Construction and Materials Division: Jefferson City, MO, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaidēs, A.; Manthos, E.; International Conference Bituminous Mixtures and Pavements (Eds.) Bituminous Mixtures and Pavements VIII; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, M. Long-Term Mechanical Deterioration Trends and Mechanisms of SBS-Modified Asphalt Mixtures. Coatings 2024, 14, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remišová, E.; Briliak, D. Investigation of the environmental degradation of asphalt pavement mixtures. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Road and Rail Infrastructure, Cavtat, Croatia, 15–17 May 2024; pp. 571–577. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shen, S.; Wu, S.; Mohammad, L.N.; She, X. Effects of Field Aging on Material Properties and Rutting Performance of Asphalt Pavement. Materials 2022, 16, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shen, S.; Wu, S.; Ma, T.; Zhou, X.; Mohammad, L.N.; Fu, Y. Effect of aged material properties on transverse crack performance with two-round field observations. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2024, 25, 1037–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.; Luo, X.; Wang, F. Understanding the effects of structural factors and traffic loading on flexible pavement performance. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 12, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tari, Y.H.; Shamsabadi, S.S.; Birken, R.; Wang, M. Deterioration Modeling for Condition Assessment of Flexible Pavements Considering Extreme Weather Events. In Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures and Materials + Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–12 March 2015; Shull, P.J., Ed.; SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; p. 943721. [Google Scholar]
- Grande, G.; Wood, S.; Ominski, A.; Regehr, J.D. Evaluating Annual Average Daily Traffic Calculation Methods with Continuous Truck Traffic Data. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2017, 2644, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Acebo, H.; Linares-Unamunzaga, A.; Rojí, E.; Gonzalo-Orden, H. IRI Performance Models for Flexible Pavements in Two-Lane Roads until First Maintenance and/or Rehabilitation Work. Coatings 2020, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaswadko, N.; Hassan, R. Rutting progression models for light duty pavements. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2018, 19, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlinge, S.; Gupta, A.K. Pavement Deterioration and its Causes. Int. J. Innov. Res. Dev. 2013, 2, 437–450. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, A.; Moreira, J.J.M.; Silva, J.P.; Viteri, C.G.V. Impact of traffic loads on flexible pavements considering Ecuador’s traffic and pavement condition. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.A. Data-Driven Framework for Modeling Deterioration of Pavements in the State of Iowa. Ph.D. Thesis, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 2020. Available online: http://proxy-ms.researchport.umd.edu/login?url=https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/data-driven-framework-modeling-deterioration/docview/2425779518/se-2?accountid=12557 (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Gupta, A.; Kumar, P.; Rastogi, R. Pavement Deterioration and Maintenance Model for Low Volume Roads. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2011, 4, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Taheri, A.; Sobanjo, J. Ensemble Learning Approach for Developing Performance Models of Flexible Pavement. Infrastructures 2024, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Shan, F.; Han, Y.; Zhong, G. Improved model for pavement performance prediction based on recurrent neural network using LTPP database. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2025, 19, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deneko, E.; Filaj, E.; Gheibi, M.; Moezzi, R. Predicting pavement surface conditions through artificial neural networks. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Munic. Eng. 2024, 177, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Pavement performance deterioration model based on deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Transportation and City Engineering (STCE 2023), Chongqing, China, 16–18 December 2023; Mikusova, M., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2024; p. 80. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.A.; Milad, A.; Hussein, A.; Md Yusoff, N.I.; Heneash, U. Predicting pavement condition index based on the utilization of machine learning techniques: A case study. J. Road Eng. 2023, 3, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.; Rahman, M.; Mathavan, S. A multi-input deterioration-prediction model for asphalt road networks. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. —Transp. 2019, 172, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, H. Machine learning based pavement performance prediction for data-driven decision of asphalt pavement overlay. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2025, 21, 940–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samahi, S.; Zeiada, W.; Al-Khateeb, G.G.; Hamad, K.; Alnaqbi, A. A Comparative Study of Pavement Roughness Prediction Models under Different Climatic Conditions. Infrastructures 2024, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabureddy, A.; Kumar, R.P.; Abhilash, P.; Ramadasu, T.L.; Ray, S.K.; Baba, A.N.S. AI-Enhanced Prediction of Pavement Crack Propagation: A Study Using Traffic Load, Environmental and Material Data. South East. Eur. J. Public Health 2024, XXV S1 2024, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fwa, T.F. The Handbook of Highway Engineering; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.M.; Ramirez-Flores, R.A. Development of Probability-Based Pavement Performance Curves for Pavement Management Systems. In Proceedings of the TRB 94th Annual Meeting Compendium of Papers, Washington, DC, USA, 11–15 January 2015; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Acebo, H.; Gonzalo-Orden, H.; Findley, D.J.; Rojí, E. A skid resistance prediction model for an entire road network. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Do, M. Development of the Road Pavement Deterioration Model Based on the Deep Learning Method. Electronics 2019, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, L.; Camargo, R.; Arellana, J.; Velosa, C.; Martinez, G. Modelling pavement serviceability of urban roads using deterministic and probabilistic approaches. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.S.R. The Pavement Performance Modeling: Deterministic vs. Stochastic Approaches. In Numerical Methods for Reliability and Safety Assessment; Kadry, S., El Hami, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 179–196. [Google Scholar]
- Khraibani, H.; Lorino, T.; Lepert, P.; Marion, J.-M. Nonlinear Mixed-Effects Model for the Evaluation and Prediction of Pavement Deterioration. J. Transp. Eng. 2012, 138, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Su, E.; Du, X.; Teng, L. Linear mixed effect model for airport pavement performance prediction. J. Tongji Univ. Natl. Sci 2014, 42, 707–713. [Google Scholar]
- Khattak, M.J.; Landry, C.; Veazey, J.; Zhang, Z. Rigid and composite pavement index-based performance models for network pavement management system in the state of Louisiana. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2013, 14, 612–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Lird, A.; Chamorro, A.; González, Á. Analysis of roughness performance of chloride-stabilised rural roads. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 1720–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Amador-Jimenez, L.; Elsaid, F. Simplified Pavement Performance Modeling with Only Two-Time Series Observations: A Case Study of Montreal Island. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2019, 145, 05019004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, A.; Fiegel, G.; Calkins, R.; Lim, D.S.; Holland, J. Performance Prediction Models for Cracked, Seated, and Overlaid Concrete Pavements in California. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2013, 2368, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekheet, W.; Helali, K.; Li, Y.; Cheetham, A.; Stanciu, D. Comparison between probabilistic and deterministic pavement management analysis: A case study for Arisona DOT. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Managing Pavement Assets, Calgary, AB, Canada, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Uddin, M.M.; Gassman, S.L. Pavement performance evaluation models for South Carolina. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2017, 21, 2695–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Kim, N. Development of performance prediction models in flexible pavement using regression analysis method. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2006, 10, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Bai, L.; Sun, Z. Pavement Deterioration Modeling and Prediction for Kentucky Interstate and Highways. In Proceedings of the IISE Annual Conference 2014, Montreal, QC, Canada, 31 May–3 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fani, A.; Golroo, A.; Fahmani, M.; Naseri, H.; Moghadas Nejad, F. Analysis of the pavement deterioration uncertainty scenarios on pavement maintenance and rehabilitation planning optimization. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2025, 21, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Ksaibati, K.; Atadero, R. Developing Pavement Distress Deterioration Models for Pavement Management System Using Markovian Probabilistic Process. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2017, 2017, 8292056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakody, N.; Robert, D.; Navaratnarajah, S.; Tran, H.; Nasvi, M.; Gunarathna, P.; Kurukulasuriya, C.; Giustozzi, F.; Gunasekara, C.; Setunge, S. Road maintenance optimization using a probabilistic approach calibrated with 15-year monitoring data. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasiq, S.; Golroo, A. Probabilistic pavement performance modeling using hybrid Markov Chain: A case study in Afghanistan. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Shi, B.; Gao, J.; Chen, H.; Yang, D. Enhanced probabilistic prediction of pavement deterioration using Bayesian neural networks and cuckoo search optimization. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Huang, B.; Richards, S.H. Calibration and Application of Treatment Performance Models in a Pavement Management System in Tennessee. J. Transp. Eng. 2015, 141, 04014076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Haas, R.; Xie, W.C. Development of a new asphalt pavement performance prediction model. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 1997, 24, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Donev, V. Probabilistic modeling of flexible pavement performance and LCC based service lives with failure distributions. In Life-Cycle of Structural Systems; CRC Press: London, UK, 2014; pp. 1981–1988. [Google Scholar]
- Abaza, K.A.; Ashur, S.A.; Al-Khatib, I.A. Integrated Pavement Management System with a Markovian Prediction Model. J. Transp. Eng. 2004, 130, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, O.; Sobanjo, J. Comparison of Markov Chain and Semi-Markov Models for Crack Deterioration on Flexible Pavements. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2013, 19, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Katicha, S.; Flintsch, G.W.; Diefenderfer., K. Pavement deterioration modeling and network-level pavement management using continuous deflection measurements. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2021, 27, 04021022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaza, K.A. Simplified staged-homogenous Markov model for flexible pavement performance prediction. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2016, 17, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaza, K.A. Optimal novel approach for estimating the pavement transition probabilities used in Markovian prediction models. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 2809–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamany, M.; Abraham, D. Hybrid Approach to Incorporate Preventive Maintenance Effectiveness into Probabilistic Pavement Performance Models. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2020, 147, 04020077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.P.; Wang, S.S. Stochastic Modeling of Pavement Performance. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2003, 4, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishalani, R.G.; Madanat, S.M. Computation of Infrastructure Transition Probabilities Using Stochastic Duration Models. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2002, 8, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Prozzi, J.A. Estimation of Pavement Performance Deterioration Using Bayesian Approach. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2006, 12, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Kuna, K.K. Reliability-Based Pavement Roughness Progression Modeling Using Bayesian Approach. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2024, 2678, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.C.P.; Li, Q. Pavement Smoothness Prediction Based on Fuzzy and Gray Theories. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2011, 26, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, S.; Sargın, Ş.; Saltan, M. Pavement Performance Prediction through Fuzzy Logic Using Marine Corps Air Station Cherry Point, North Carolina Measurements. In Proceedings of the Airfield and Highway Pavement 2013, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 June 2013; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2013; pp. 650–661. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.; Kim, H. Prediction of Flexible Pavement Deterioration in Relation to Climate Change Using Fuzzy Logic. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2017, 23, 04017008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soncim, S.P.; De Oliveira, I.C.S.; Santos, F.B. Development of fuzzy models for asphalt pavement performance. Acta Sci. Technol. 2019, 41, 35626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehia, A.; Swei, O. Probabilistic infrastructure performance models: An iterative-methods approach. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 111, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamany, M.; Abraham, D.; Labi, S. Comparative Analysis of Markovian Methodologies for Modeling Infrastructure System Performance. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2021, 27, 04021003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaee, N.; Ziyadi, M. Bayesian Approach to Updating Markov-Based Models for Predicting Pavement Performance. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2013, 2366, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Kaito, K.; Kobayashi, K. Application of Bayesian estimation method with Markov hazard model to improve deterioration forecasts for infrastructure asset management. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2014, 18, 2107–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshaghani, A. Application of the Bayesian statistical approach to develop a Stone Mastic Asphalt (SMA) pavement performance model. J. Archit. Environ. Struct. Eng. Res. 2020, 2, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heba, A.; Assaf, G.J. Road Performance Prediction Model for the Libyan Road Network Depending on Experts’ Knowledge and Current Road Condition Using Bayes Linear Regression. In Recent Developments in Railway Track and Transportation Engineering; Pombo, J., Jing, G., Eds.; Sustainable Civil Infrastructures; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 153–167. [Google Scholar]
- Yamany, M.S. Stochastic Performance and Maintenance Optimization Models for Pavement Infrastructure Management. Ph.D. Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yamany, M.S.; Abraham, D.M. Prediction of pavement performance using non-homogeneous Markov models: Incorporating the impact of preventive maintenance. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Board 99th Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 12–16 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Asadi, B.; Hajj, R.; Al-Qadi, I.L. Asphalt concrete dynamic modulus prediction: Bayesian neural network approach. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2023, 24, 2270569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.V.; Tinoco, J.; Oliveira, J.R.; Santos, A. An application of Markov chains to predict the evolution of performance indicators based on pavement historical data. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2018, 19, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, S.B.; Ortiz-Garcia, J.J.; Snaith, M.S. Analytical tool for calculating transition probabilities for pavement performance prediction. Road Transp. Res. A J. Aust. New Zealand Res. Pract. 2016, 25, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Xie, W.-C.; Haas, R. Reliability-based processing of Markov chains for modeling pavement network deterioration. Transp. Res. Rec. 1996, 1524, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Yang, S.; Ma, Y. Establishment of probabilistic prediction models for pavement deterioration based on Bayesian neural network. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2023, 24, 2076854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madanat, S.; Prozzi, J.A.; Han, M. Effect of Performance Model Accuracy on Optimal Pavement Design. Comput. Aided Civ. Eng. 2002, 17, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.L.; Tran, V.Q. Data-driven approach for investigating and predicting rutting depth of asphalt concrete containing reclaimed asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 377, 131116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez Flores, R.A. A Stochastic Approach for Pavement Condition Projections and Budget Needs for the Mtc Pavement Management System; The University of Texas at El Paso: El Paso, TX, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dussadee, S.; Pannapa, H. Exploring Predictive Strengths of Stochastic Pavement Deterioration Models: A Case Study of Thailand’s Highway Network. Asia-Pac. J. Rural. Dev. 2007, 17, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyirandayisabye, R.; Li, H.; Dong, Q.; Hakuzweyezu, T.; Nkinahamira, F. Automatic pavement damage predictions using various machine learning algorithms: Evaluation and comparison. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinero-Perez, N.; García-Segura, T.; Montalban-Domingo, L.; Sanz-Benlloch, A.; Mansanet, J.; Pellicer, E. Artificial Intelligent Techniques to Improve Pavement Maintenance Management. In Proceedings of the Construction Research Congress 2024, Des Moines, IA, USA, 20–23 March 2024; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2024; pp. 1097–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Shi, X. Short-Term Predictions of Asphalt Pavement Rutting Using Deep-Learning Models. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2024, 150, 04024004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Han, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; You, Z. Research and comparison of pavement performance prediction based on neural networks and fusion transformer architecture. Electron. Res. Arch. 2024, 32, 1239–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, B.; Xu, Z.; AlJassmi, H.; Zhang, Q.; Ali, L. ASENN: Attention-based selective embedding neural networks for road distress prediction. J. Big Data 2023, 10, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Meng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, J.; Philip, B.; AlJassmi, H.; Yang, Z. AGA-RFNN: Adaptive Genetic Algorithm-based Random Forest Neural Network for Pavement Deterioration Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Real-time Computing and Robotics (RCAR), Datong, China, 17–20 July 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 731–736. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, R.; Ding, P.; Peng, R.; Qiao, J. Prediction of asphalt pavement performance based on DEPSO-BP neural network. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2023, 50, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.A.; Alhasan, A.; Smadi, O. Use of Deep Learning to Study Modeling Deterioration of Pavements a Case Study in Iowa. Infrastructures 2020, 5, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.; Anuraj, U.; Mathavan, S.; Rahman, M. A unified artificial neural network model for asphalt pavement condition prediction. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Transp. 2023, 176, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Gong, H.; Jia, X.; Xiao, R.; Jiang, X.; Ma, Y.; Huang, B. Analysis of critical factors to asphalt overlay performance using gradient boosted models. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeh Piryonesi, S.; El-Diraby, T.E. Using Machine Learning to Examine Impact of Type of Performance Indicator on Flexible Pavement Deterioration Modeling. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2021, 27, 04021005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. From ensemble learning to deep ensemble learning: A case study on multi-indicator prediction of pavement performance. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 166, 112188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, A.; Abdelkader, E.M.; Faris, N.; Zayed, T. Using Machine Learning for Road Performance Modelling and Influential Factors Investigation. Int. J. Struct. Civil Eng. Res. 2023, 12, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Gao, L.; Hong, F.; Sun, J. Evaluating Pavement Deterioration Rates Due to Flooding Events Using Explainable AI. Buildings 2025, 15, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Fu, D.; Sollazzo, G. An ensemble learning model for asphalt pavement performance prediction based on gradient boosting decision tree. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 3633–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaqbi, A.; Zeiada, W.; Al-Khateeb, G.G. Machine learning modeling of pavement performance and IRI prediction in flexible pavement. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2024, 9, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlotjes, M.R.; Burrow, M.P.N.; Evdorides, H.T.; Henning, T.F.P. Using support vector machines to predict the probability of pavement failure. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Transp. 2015, 168, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabipour, N.; Karballaeezadeh, N.; Dineva, A.; Mosavi, A.; Mohammadzadeh, S.D.; Shamshirband, S. Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Models for Prediction of Remaining Service Life of Flexible Pavement. Mathematics 2019, 7, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaee, N.; Ziyadi, M.; Shafahi, Y. Two-Stage Support Vector Classifier and Recurrent Neural Network Predictor for Pavement Performance Modeling. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2013, 19, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Highway Administration. AASHTO Joint Technical Committee on Pavements. Federal Highway Administration, Pavement Management Quarterly Webinars. 2018. Available online: https://www.fhwa.dot.gov/pavement/mana.cfm (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Panthi, K. A Methodological Framework for Modeling Pavement Maintenance Costs for Projects with Performance-Based Contracts. Ph.D. Thesis, Florida International University, Miami, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, R.K.; Mahoney, J.P.; Jackson, N.C. The WSDOT Pavement Management System: A 1993 Update; Washington State Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 1993.
- Tsai, J.Y.; Wang, Z.; Gardner, L.; Salameh, R.; Jiao, Y. Data-Driven Pavement Maintenance and Rehabilitation Strategies for GDOT’s New State Route Prioritization Policy; Georgia Department of Transporation, Office of Performance-Based Management and Research: Forest Park, GA, USA, 2019.
- Tsai, J.Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.R. Georgia Concrete Pavement Performance and Longevity; Georgia Department of Transportation, Office of Performance-Based Management and Research: Forest Park, GA, USA, 2012.
- Ong, G.P.R.; Nantung, T.; Sinha, K. Indiana Pavement Preservation Program; Joint Transportation Research Program: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.; Picado-Santos, L.D.; Wu, Z.; Flintsch, G. Selection of pavement performance models for use in the Portuguese PMS. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2011, 12, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timm, D.; Birgisson, B.; Newcomb, D. Development of Mechanistic-Empirical Pavement Design in Minnesota. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 1998, 1629, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakol, M.; Felber, B.T.; DeStefano, D. New Jersey Turnpike Authority Approach to Pavement Management System. In Proceedings of the Geotechnical Frontiers 2025, Louisville, KY, USA, 2–5 March 2025; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2025; pp. 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, P. Modeling Pavement Performance and Preservation. Ph.D. Thesis, North Dakota State University, Fargo, ND, USA, 2011. Available online: http://proxy-ms.researchport.umd.edu/login?url=https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/modeling-pavement-performance-preservation/docview/912376585/se-2?accountid=12557 (accessed on 15 August 2025).

| Considered Factors | Pavement Performance Indicator | References |
|---|---|---|
| Ride Quality | International Roughness Index (IRI), Ride Quality Index, Overall Performance Condition (OPC), Pavement Condition Rating (PCR), Rutting Depth (RD) Rutting Depth Index (RDI), Future Pavement Surface Condition (FPSC). Next-Generation Pavement Performance Measures (NGPPM) | [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37] |
| Friction | Skid number (SN), Skidding Index, International Friction Index, Skidding Resistance Index (SRI) | [38,39,40,41] |
| Surface Distress | Pavement Condition Index (PCI), PASER, Crack Index (CI), Surface Distress Index, Alligator Deterioration Index (ADI), Distress Rating (DR), Pervious Concrete Distress Index (PCDI), Pavement Distress Condition Index (PDCI), Future Pavement Surface Condition (FPSC), Rutting Depth Index (RDI) | [32,42,43,44,45,46,47,48] |
| Structural Capacity | Structural Number (SN), Pavement Structural Strength Index (PSSI), Surface Curvature Index (SCI), Structural Capacity Index, Structural Strength Index (StSI), Structural Adequacy Index (SAI) | [3,49,50,51,52,53] |
| Studies | Factors Considered | Dataset |
|---|---|---|
| Hosseini et al. [166] | Pavement age, reconstruction history, traffic levels, automated distress data, and ride quality metrics | 20 years of PMS data (1998–2018, Iowa) |
| Marcelino et al. [100] | Structural, climatic, and traffic variables with IRI as performance indicator | 5–10 years Long-Term Pavement Performance (LTPP) data covering 7 sections |
| Sidess et al. [43] | PCI-based deterioration influenced by pavement age, load, and condition | Localized PCI records |
| Gupta et al. [167] | Pavement age, subgrade CBR, thickness, traffic loading, deflection, and roughness | 18 low-volume road sections (2 years, India) |
| Taheri et al. [168] | Structural/material characteristics, compaction density, air voids, traffic loading, precipitation, and freeze–thaw cycles | 367 sections from LTPP |
| Chen et al. [169] | Surface condition, structure, climate, traffic volume, and maintenance actions | LTPP dataset (2464 PCI and 3238 IRI samples) |
| Deneko et al. [170] | Traffic volume, land use, number of lanes, width, alignment, pavement age, and weather | Pavement survey dataset |
| Li et al. [171] | Service time, traffic load, rutting, and cracking | Interstate Highway System, Pennsylvania |
| Ali et al. [172] | Multiple pavement distress types (rutting, fatigue, block, longitudinal, transverse cracking, potholes, patching, delamination) | Field data (2018–2021), 19 roads (37 sections), Newfoundland, Canada |
| Mahmood et al. [173] | Pavement age, cracking extent, cumulative loading, functional class, climate, and maintenance | In-service pavement test sections, USA |
| Zhao et al. [174] | Climate and traffic factors for overlay decision-making | LTPP |
| Al-Samahi et al. [175] | Pavement age, thickness, precipitation, temperature, and Average Annual Daily Truck Traffic (AADTT) | UAE Ministry of Energy dataset + LTPP |
| Mabureddy et al. [176] | Traffic loading, environmental conditions, and material properties | - |
| Studies | Country | Model/Method | Modeling Method | Uniqueness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [239] | USA (IOWA) | Deterministic ML | LSTM and Regression model |
|
| [100] | - | Probabilistic ML | Random forests algorithm |
|
| [167] | India | Probabilistic ML | Statistical analysis tools and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) |
|
| [168] | USA (Florida) | Probabilistic ML | Random forest, Extremely Randomized Trees (ETR), and Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) |
|
| [170] | China | Probabilistic ML | Fully Connected Neural Network (FCNN), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), and LSTM-Attention model |
|
| [171] | China | Probabilistic ML | Artificial Neural Network (ANN) |
|
| [172] | Canada | Probabilistic ML | Coefficient of determination, Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), and Mean Absolute Error (MAE) |
|
| [240] | USA | Probabilistic ML | Artificial Neural Network (ANN) |
|
| [174] | USA (New Jersey) | Probabilistic ML | Support Vector Regression, Ensemble machine learning methods |
|
| Modeling Approach | Category | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Modeling | Deterministic Models |
|
| Probabilistic Models |
| |
| Intelligent Modeling | AI/ML Based Models |
|
| Studies | Model Type | Main Features | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [171,174,176,239] | Neural Networks (ANN, LSTM, RNN, DNN, BNN) | Adaptable to large datasets with multiple indicators, learn nonlinear patterns and can process sequential data. | Capture complex interactions between pavement age, traffic, climate, and material variables. Effective for time-series prediction of deterioration rates. | Require large, high-quality datasets; prone to overfitting if data is limited. It is difficult to interpret the influence of individual factors on predictions. |
| [175,229] | Decision Trees | Splits data into decision nodes for classification or regression tasks. | Easy to implement and interpret; suitable for identifying key variables in small datasets. | Lower predictive accuracy on larger or more complex datasets; sensitive to noisy data. |
| [11,168] | Ensemble Models (Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, XGBoost) | Combine multiple weak learners to improve overall prediction performance and reduce overfitting. | More robust and generalizable than single decision trees; perform well with heterogeneous pavement and environmental data. | Computationally intensive; model complexity can make it harder to interpret results in practice. |
| [248,249,250] | Support Vector Machines (SVM, SVR) | Create hyperplanes to separate data classes or predict continuous variables. | Perform well with smaller datasets and can handle high-dimensional variables. | Sensitive to parameter tuning and kernel selection; less effective with large, noisy datasets. |
| [28,206,236,238] | Hybrid Models (e.g., LSTM-Attention, Bayesian Neural Networks, DEPSO-BP) | Integrate multiple modeling techniques to capture uncertainty, spatial variability, and temporal patterns. | Achieve higher accuracy and robustness by leveraging strengths of each method; capable of quantifying uncertainty for risk-based pavement management. | Require advanced expertise, significant computational resources, and extensive datasets to achieve optimal performance. |
| Year Implemented | Agencies | Models Used |
|---|---|---|
| 2018 | USA: Alaska Department of Transport (DOT) [251] | Regression Analysis |
| 2012 | Delaware DOT [30] | Regression Analysis |
| 2009 | Florida DOT [252] | Markov Chain Process |
| 1993 | Washington DOT [253] | Regression Analysis |
| 2019, 2012 | Georgia DOT [254,255] | Survival analysis |
| 2011 | Indiana DOT [256] | Regression Analysis |
| 2020 | Iowa DOT (At project level) [166] | Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) |
| 2013 | Louisiana Department of Transportation and Development (LADOTD) [185] | Regression Analysis |
| 2011 | Nevada DOT [257] | Regression Analysis |
| 1998 | Minnesota DOT [258] | Regression Analysis |
| 2025 | New Jersey DOT [259] | Regression Analysis |
| 2014 | North Carolina DOT [46] | Regression Analysis |
| 2011 | North Dakota DOT [260] | Regression Analysis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Famewo, B.G.; Shokouhian, M. A Review of Pavement Performance Deterioration Modeling: Influencing Factors and Techniques. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111992
Famewo BG, Shokouhian M. A Review of Pavement Performance Deterioration Modeling: Influencing Factors and Techniques. Symmetry. 2025; 17(11):1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111992
Chicago/Turabian StyleFamewo, Benjamin G., and Mehdi Shokouhian. 2025. "A Review of Pavement Performance Deterioration Modeling: Influencing Factors and Techniques" Symmetry 17, no. 11: 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111992
APA StyleFamewo, B. G., & Shokouhian, M. (2025). A Review of Pavement Performance Deterioration Modeling: Influencing Factors and Techniques. Symmetry, 17(11), 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111992








