AHLFNet: Adaptive High–Low Frequency Collaborative Auxiliary Feature Alignment Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a novel frequency-centric design paradigm. Motivated by the complementary roles of frequency components in images—where low frequencies govern semantic consistency and high frequencies dictate boundary precision—we introduce a principled Adaptive High–Low Frequency Collaborative framework. This framework is specifically designed to address the root causes of intra-class conflict and edge drift in dense prediction tasks, ensuring both strong semantic discriminability and fine boundary precision.
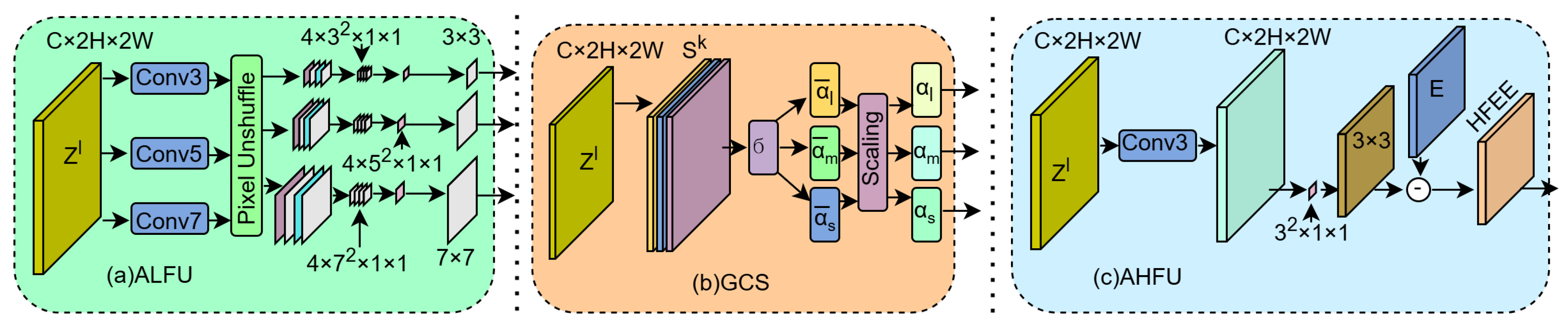
- Under this paradigm, we instantiate the AHLFNet which integrates three key components: (1) an Adaptive Low-frequency Unit (ALFU), which smooths object interiors to suppress high-frequency interference and reduce intra-class conflict; (2) a Gate-Controlled Selector (GCS), which adaptively determines the kernel size for smoothing through similarity analysis to ensure feature consistency; and (3) an Adaptive High-frequency Unit (AHFU), which compensates for boundary details lost during downsampling to improve edge localization accuracy.
- Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method yields significant performance improvements in object detection, instance segmentation, and semantic segmentation. Consistent gains are achieved across benchmark datasets including COCO, ADE20K, and Cityscapes, validating the effectiveness and robustness of our approach.
2. Related Work
2.1. Feature Fusion and Upsampling Methods
2.2. Intra-Class Conflict and Boundary Issues
2.3. Applications of Frequency-Domain Methods in Visual Tasks
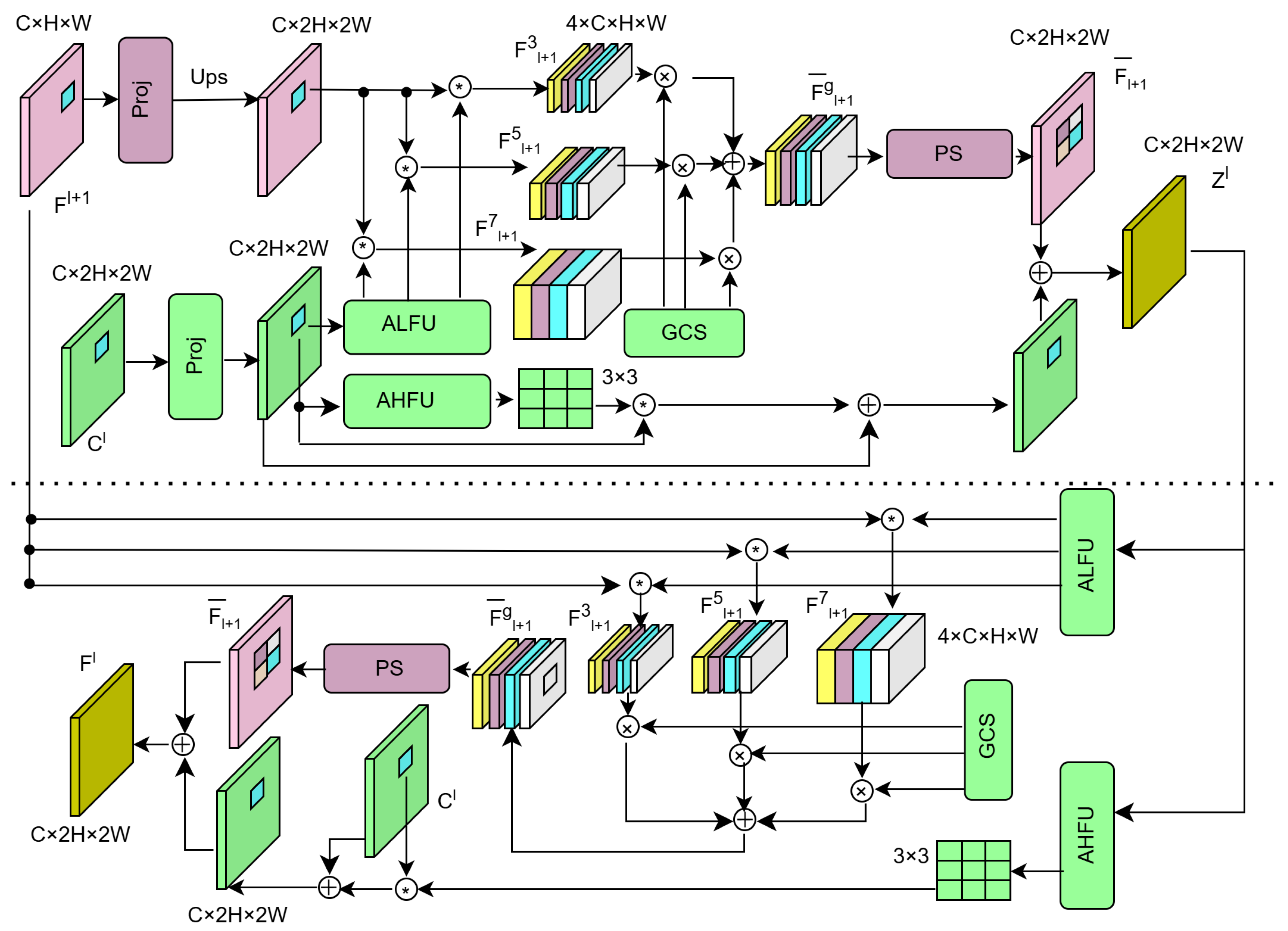
3. Method
3.1. Overall Improvement Through Feature Fusion
3.2. AHLFNet
4. Experiment
4.1. Semantic Segmentation
4.2. Object Detection
4.3. Instance Segmentation
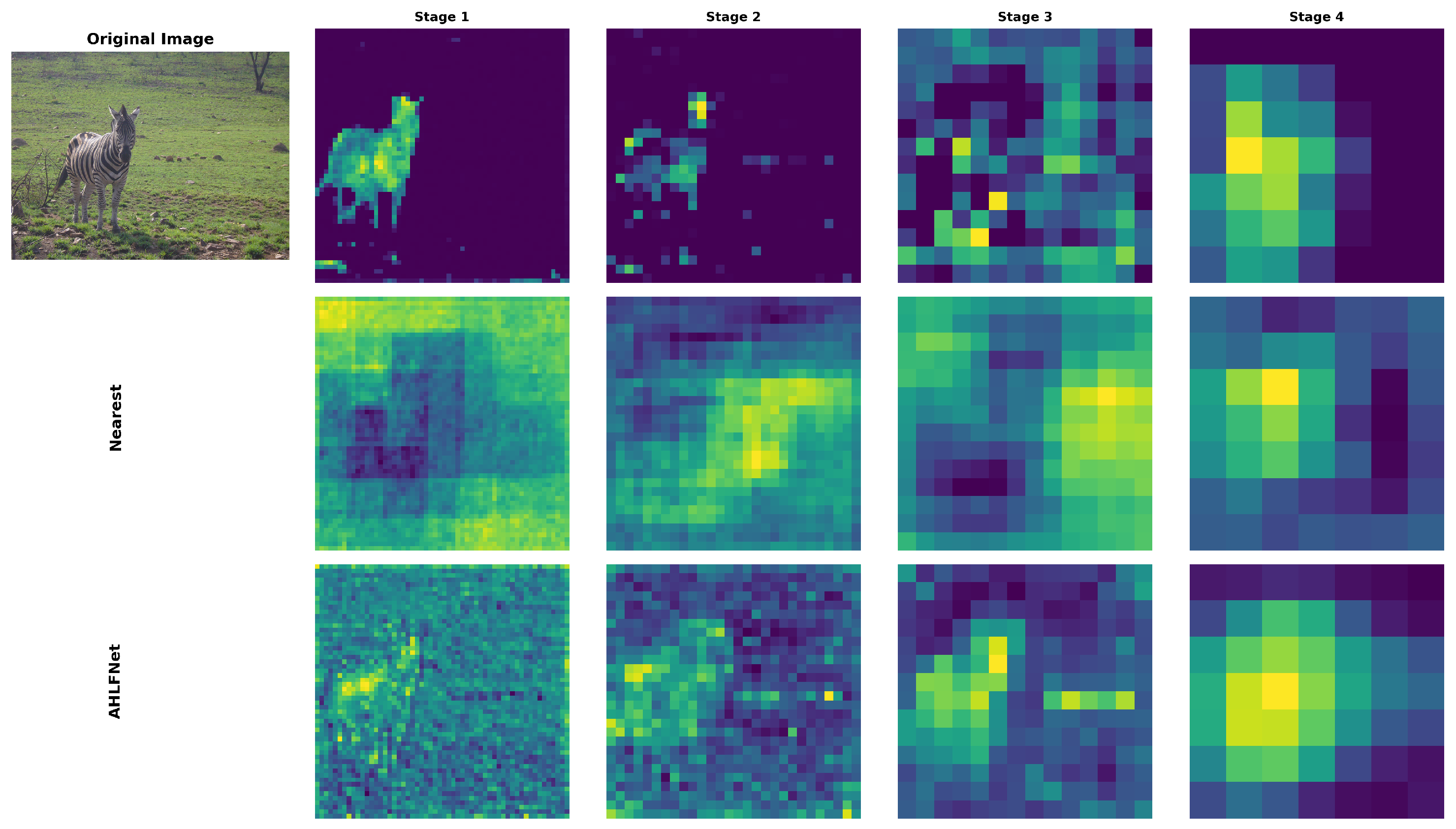
4.4. Ablation Studies
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, W.; Jung, H.; Nam, G.; Lee, D.I.; Park, H.; Yoon, S.H.; Joo, J.; Kim, S. Insightful Instance Features for 3D Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 14057–14067. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Chen, G.; Chen, Y. Enhanced boundary perception and streamlined instance segmentation. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bär, A.; Houlsby, N.; Dehghani, M.; Kumar, M. Frozen feature augmentation for few-shot image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 16046–16057. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, B.A.; Singhania, S.; Patel, A.; Kumar, R.; Fryling, H.; Li, S.; Sun, H.; He, P.; Li, Z. Logarithmic lenses: Exploring log rgb data for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 17470–17479. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Ni, Y.; Du, J.; Xue, Y.; Torr, P.; Koniusz, P.; van den Hengel, A. Open-World Objectness Modeling Unifies Novel Object Detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 30332–30342. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Li, C.; Lyu, J.; Pei, H.; Zhang, B.; Jin, T.; Ji, R. DAMamba: Vision State Space Model with Dynamic Adaptive Scan. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Liu, W.; Ye, Z.; Fu, H.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Z. SAPA: Similarity-aware point affiliation for feature upsampling. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 20889–20901. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Liu, W.; Fu, H.; Cao, Z. FADE: Fusing the assets of decoder and encoder for task-agnostic upsampling. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 231–247. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.; Lin, Q.; Xie, W.; Wu, B.; Xie, J.; Shen, L. Frequency-driven imperceptible adversarial attack on semantic similarity. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 15315–15324. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Gu, L.; Fu, Y. When semantic segmentation meets frequency aliasing. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.09065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masum, M.H.R. Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Caballero, J.; Huszár, F.; Totz, J.; Aitken, A.P.; Bishop, R.; Rueckert, D.; Wang, Z. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1874–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; He, T.; Shen, C.; Yan, Y. Decoders matter for semantic segmentation: Data-dependent decoding enables flexible feature aggregation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3126–3135. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q. Learnable Heterogeneous Convolution: Learning both topology and strength. Neural Netw. 2021, 141, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Guo, Z.; Li, A.; Yu, C.; Sang, N.; Gao, C. Semantic segmentation via pixel-to-center similarity calculation. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2024, 9, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, K.; Xu, R.; Liu, Z.; Loy, C.C.; Lin, D. Carafe++: Unified content-aware reassembly of features. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 4674–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzini, D. Guided upsampling network for real-time semantic segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.07466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, T.S.; Shi, H. Alignseg: Feature-aligned segmentation networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Lu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.04159. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.; Wang, P.; Luo, H.; Wang, F.; Shou, M.Z. Revisiting vision transformer from the view of path ensemble. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 19889–19899. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. Learning a discriminative feature network for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1857–1866. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Peng, C.; Xue, X.; Sun, J. Exfuse: Enhancing feature fusion for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 269–284. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, A.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Panoptic feature pyramid networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 6399–6408. [Google Scholar]
- Pitas, I. Digital Image Processing Algorithms and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, D.; Gontijo Lopes, R.; Shlens, J.; Cubuk, E.D.; Gilmer, J. A fourier perspective on model robustness in computer vision. In Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2019), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 13276–13286. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Huang, Z.; Xing, E.P. High-frequency component helps explain the generalization of convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 8684–8694. [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman, N.; Baratin, A.; Arpit, D.; Draxler, F.; Lin, M.; Hamprecht, F.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. On the spectral bias of neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; PMLR: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 5301–5310. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.J.; Zhou, H. Deep frequency principle towards understanding why deeper learning is faster. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtually, 19–21 May 2021; Volume 35, pp. 10541–10550. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.; Xiao, F.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Lee, Y.J. Delving deeper into anti-aliasing in convnets. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2023, 131, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabinski, J.; Jung, S.; Keuper, J.; Keuper, M. Frequencylowcut pooling-plug and play against catastrophic overfitting. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 36–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Fu, Y.; Wei, K.; Zheng, D.; Heide, F. Instance segmentation in the dark. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2023, 131, 2198–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magid, S.A.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, D.; Jang, W.D.; Lin, Z.; Fu, Y.; Pfister, H. Dynamic high-pass filtering and multi-spectral attention for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 4288–4297. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, F.; Li, X. Fcanet: Frequency channel attention networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 783–792. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lan, C.; Zha, Z.J.; Lu, Y.; Guo, B. Adaptive frequency filters as efficient global token mixers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 6049–6059. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, J. Unified perceptual parsing for scene understanding. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 418–434. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, H.; Puig, X.; Fidler, S.; Barriuso, A.; Torralba, A. Scene parsing through ade20k dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 633–641. [Google Scholar]
- Caesar, H.; Uijlings, J.; Ferrari, V. Coco-stuff: Thing and stuff classes in context. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1209–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Misra, I.; Schwing, A.G.; Kirillov, A.; Girdhar, R. Masked-attention mask transformer for universal image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1290–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.H.; Lu, C.Z.; Hou, Q.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, M.M.; Hu, S.M. Segnext: Rethinking convolutional attention design for semantic segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 1140–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled weight decay regularization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05101. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, K.; Xu, R.; Liu, Z.; Loy, C.C.; Lin, D. Carafe: Content-aware reassembly of features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3007–3016. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Dai, Y.; Shen, C.; Xu, S. Index networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Lu, H.; Shen, C. Learning affinity-aware upsampling for deep image matting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 6841–6850. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Lu, H.; Fu, H.; Cao, Z. Learning to upsample by learning to sample. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 6027–6037. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Borse, S.; Cai, H.; Porikli, F.; Wang, X. Learning implicit feature alignment function for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 487–505. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Lu, Z.; Cheng, R.; He, C. FaPN: Feature-aligned pyramid network for dense image prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 864–873. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Lou, M.; Yu, Y. SegMAN: Omni-scale context modeling with state space models and local attention for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 19077–19087. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. MMDetection: Open mmlab detection toolbox and benchmark. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.07155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Luan, X. FreqSpatNet: Frequency and Spatial Dual-Domain Collaborative Learning for Low-Light Image Enhancement. Electronics 2025, 14, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, E.; Wang, A.; Shiri, B.; Lin, W. VNDHR: Variational single nighttime image Dehazing for enhancing visibility in intelligent transportation systems via hybrid regularization. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 10189–10203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Symbols | Meanings | Symbols | Meanings |
|---|---|---|---|
| UpS | Upsampling | Proj | 1 × 1 Convolution |
| AL | ALFU | AH | AHFU Convolution |
| Conv | Convolution | exp | Exponential Function |
| Sim | Cosine Similarity | cen | center |
| nei | neighbor | Hyperparameter | |
| activation function |
| Methods | Params (M) | mIoU (%) | bIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SegFormer-B1 [38] (BL) | 13.7 | 41.7 | 27.8 |
| Carafe [45] (2019ICCV) | 14.2 | 42.8 | 29.8 |
| IndexNet [46] (2020TPAMI) | 26.3 | 41.5 | 28.3 |
| PixelShuffle [15] (2016CVPR) | 27.9 | 41.5 | 26.6 |
| A2U [47] (2021CVPR) | 13.9 | 41.5 | 27.3 |
| Dysample-S [48] (2023ICCV) | 13.8 | 43.6 | 29.9 |
| Sapa-B [10] (2022NeurlPS) | 13.8 | 43.2 | 31.0 |
| FADE [11] (2022ECCV) | 14.0 | 43.1 | 31.7 |
| AHLFNet (Ours) | 14.2 | 44.6 | 32.7 |
| Methods | Backbone | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|
| IFA [49] (2022ECCV) | ResNet-50 | 78.0 |
| AlignSeg [21] (2021TPAMI) | ResNet-50 | 78.5 |
| FaPN [50] (2021ICCV) | ResNet-50 | 80.0 |
| Mask2Former [42] | ResNet-50 | 79.4 |
| Mask2Former + AHLFNet | ResNet-50 | 80.5 (+1.1) |
| Mask2Former | ResNet-101 | 80.1 |
| Mask2Former + AHLFNet | ResNet-101 | 80.9 (+0.8) |
| Methods | Backbone | Params (M) | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| UPerNet [39] | ResNet-50 | 29.2 | 79.8 (+1.0) |
| UPerNet | DAMamba-T | 55.3 | 80.4 (+0.7) |
| SegFormer [38] | MiT-B1 | 14.1 | 80.2 (+1.7) |
| SegNeXt [43] | MSCAN-T | 4.4 | 80.7 (+0.9) |
| Methods | Params (M) | Cityscapes/mIoU | ADE20K | COCO-Stuff |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SegNeXt-T [43] | 4.3 | 79.8 | 41.1 | 38.7 |
| SegNeXt-T + AHLFNet | 4.6 | 80.7 (+0.9) | 43.4 (+2.3) | 40.8 (+2.1) |
| SegMAN-L [43] | 92.4 | 84.2 | 53.2 | 48.8 |
| SegMAN-L + AHLFNet | 92.6 | 84.6 (+0.4) | 53.5 (+0.3) | 49.1 (+0.3) |
| Methods | Params (M) | (1×) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nearest(BL) | 46.8 | 37.5 | 58.2 | 40.8 |
| PixelShuffle [15] | 56.2 | 37.5 | 58.5 | 40.4 |
| IndexNet [46] | 55.2 | 37.6 | 58.4 | 40.9 |
| Carafe [45] | 47.1 | 38.6 | 59.9 | 42.2 |
| A2U [47] | 46.9 | 37.3 | 58.7 | 40.0 |
| FADE [11] | 47.0 | 38.5 | 59.6 | 41.8 |
| DySample+ [19] | 46.9 | 38.7 | 60.0 | 42.2 |
| AHLFNet (Ours) | 47.2 | 39.4 | 60.9 | 42.8 |
| Methods | (1×) | (1×) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nearest (BL) | 38.3 | 58.7 | 42.0 | 34.7 | 55.8 | 37.2 |
| Carafe [45] | 39.2 | 60.0 | 43.0 | 35.4 | 56.7 | 37.6 |
| IndexNet [46] | 38.4 | 59.2 | 41.7 | 34.7 | 55.9 | 37.1 |
| PixelShufffe [15] | 38.5 | 59.4 | 41.9 | 34.8 | 56.0 | 37.3 |
| FADE [11] | 39.1 | 60.3 | 42.4 | 35.1 | 56.7 | 37.2 |
| A2U [47] | 38.2 | 59.2 | 41.4 | 34.6 | 56.0 | 36.8 |
| DySample+ [19] | 39.6 | 60.4 | 43.5 | 35.7 | 57.3 | 38.2 |
| AHLFNet (Ours) | 40.0 | 61.1 | 43.6 | 35.9 | 57.9 | 38.1 |
| ALFU | GCS | AHFU | Params (M) | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| × | × | × | 4.26 | 41.1 |
| ✓ | × | × | 4.43 | 42.0 (+0.9) |
| × | × | ✓ | 4.28 | 41.7 (+0.6) |
| ✓ | × | ✓ | 4.45 | 42.6 (+1.5) |
| × | ✓ | ✓ | 4.40 | 42.1 (+1.0) |
| ✓ | ✓ | × | 4.55 | 42.7 (+1.6) |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 4.57 | 43.4 (+2.3) |
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 × 3 | 41.2 | 41.6 | 42.0 | 41.7 | 41.6 |
| 5 × 5 | 41.1 | 41.4 | 41.7 | 41.5 | 41.3 |
| 7 × 7 | 41.2 | 41.5 | 41.7 | 41.5 | 41.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, C.; Li, J. AHLFNet: Adaptive High–Low Frequency Collaborative Auxiliary Feature Alignment Network. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111952
Yue C, Li J. AHLFNet: Adaptive High–Low Frequency Collaborative Auxiliary Feature Alignment Network. Symmetry. 2025; 17(11):1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111952
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Chunguang, and Jinbao Li. 2025. "AHLFNet: Adaptive High–Low Frequency Collaborative Auxiliary Feature Alignment Network" Symmetry 17, no. 11: 1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111952
APA StyleYue, C., & Li, J. (2025). AHLFNet: Adaptive High–Low Frequency Collaborative Auxiliary Feature Alignment Network. Symmetry, 17(11), 1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111952






