An Adaptive Learning Algorithm Based on Spiking Neural Network for Global Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Spiking Neural Network Model and Its Model Simplification
2.1. Spiking Neural Network Model
2.2. Model Simplification
3. Adaptive Learning Algorithm for Spiking Neural Networks
3.1. Adaptive Adjustment for Synaptic Connection Weights
| Algorithm 1 d-dimensional Gibbs sampling algorithm for the learning factor |
| Step 1 Random initialization |
| Step 2 Sampled cyclically with |
| 1. |
| 2. |
| 3. … |
| 4. |
| 5. … |
| 6. |
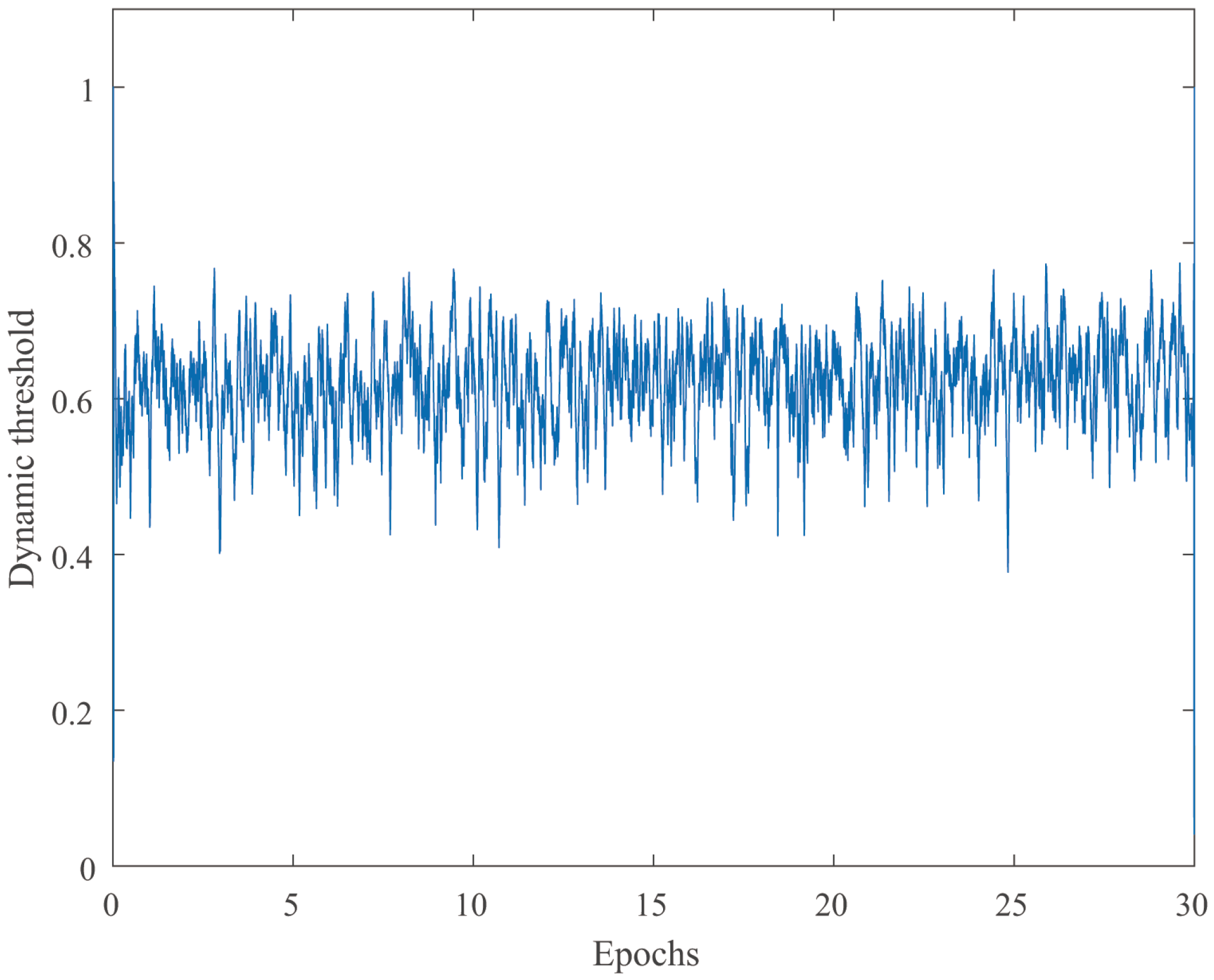
3.2. The Self-Organized Learning Method of SNN Dynamic Threshold
- The rate of convergence to an optimal result is not ideal.
- It is easy to cause local extreme values or over-optimization phenomena.
4. Simulation and Discussion
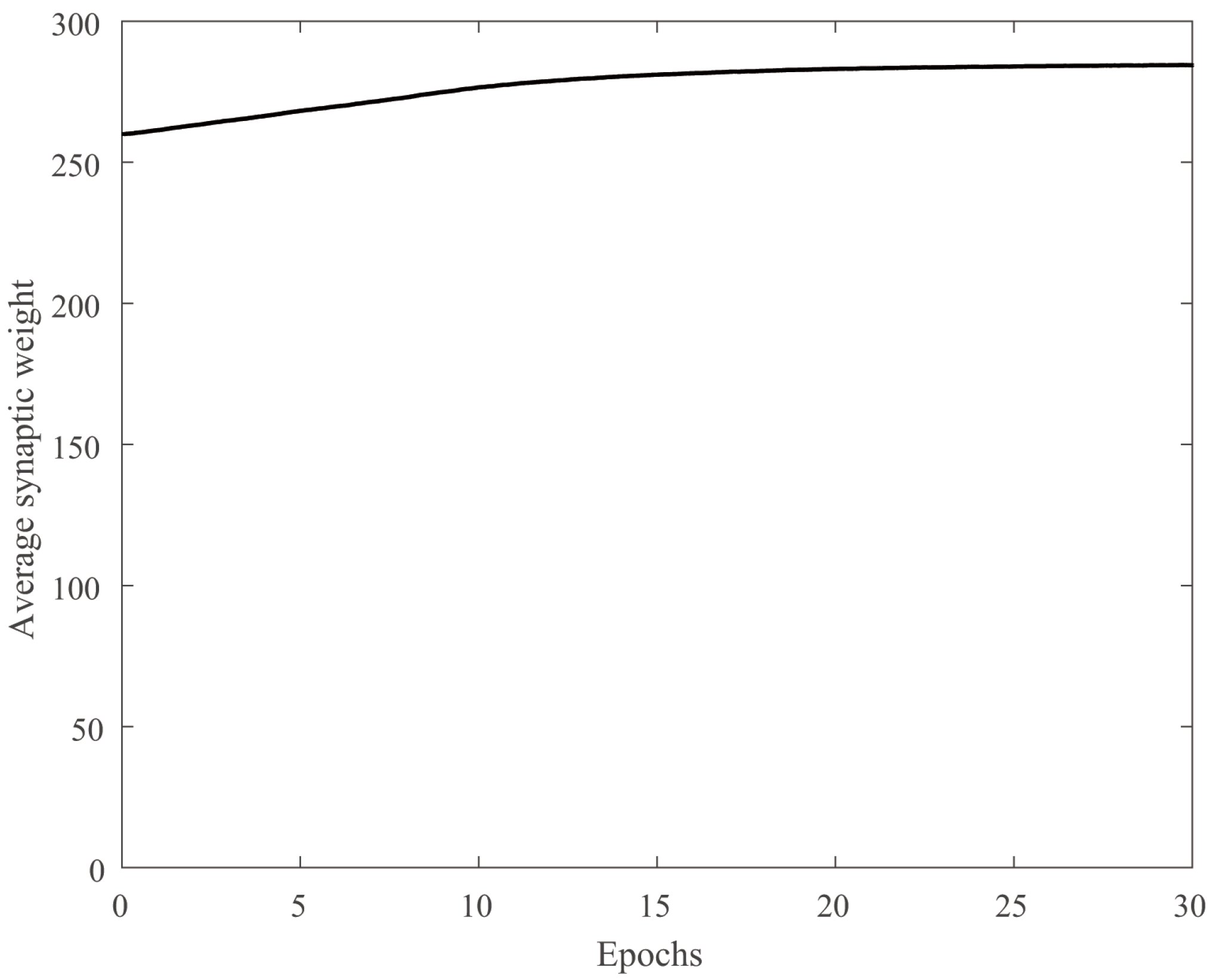
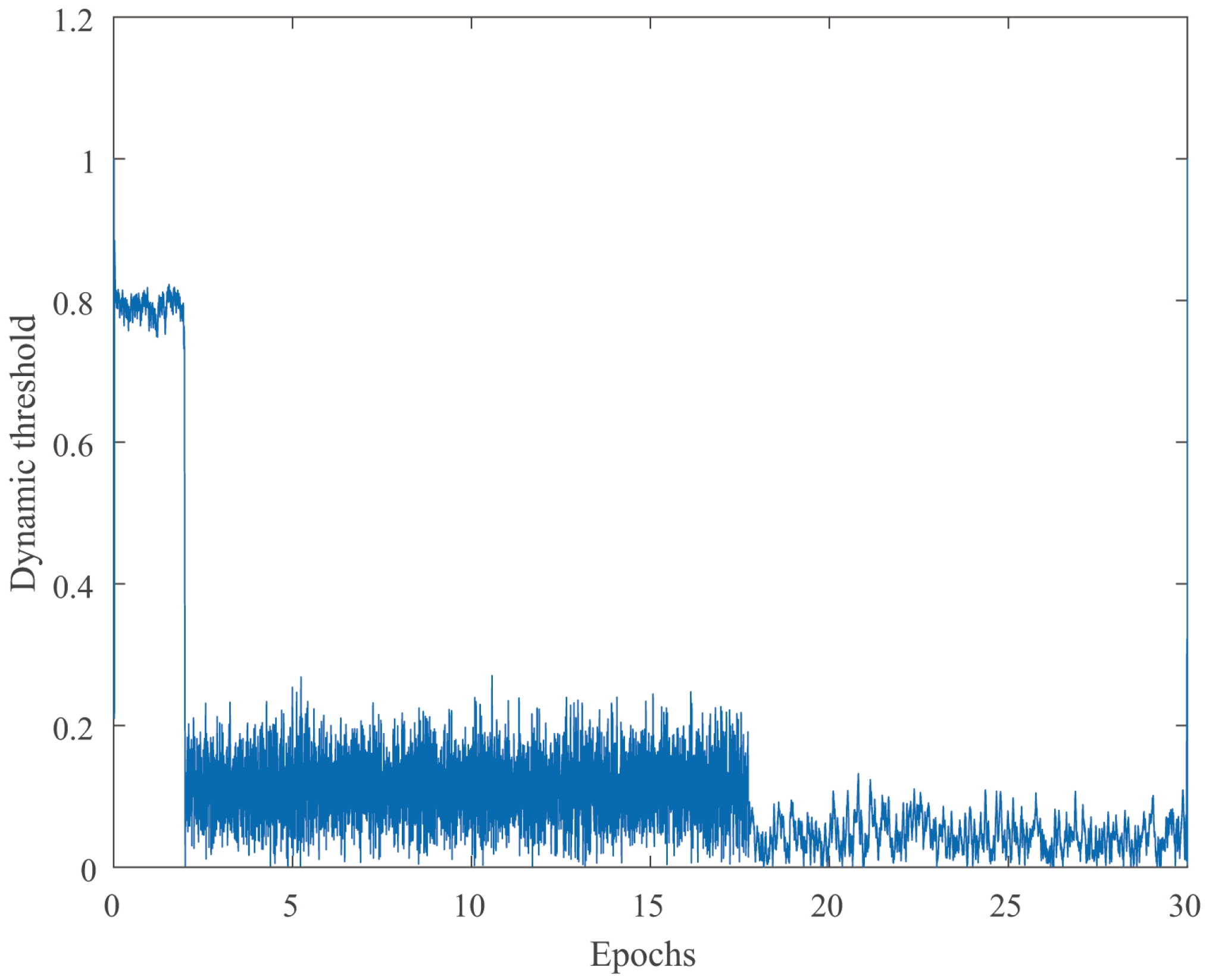
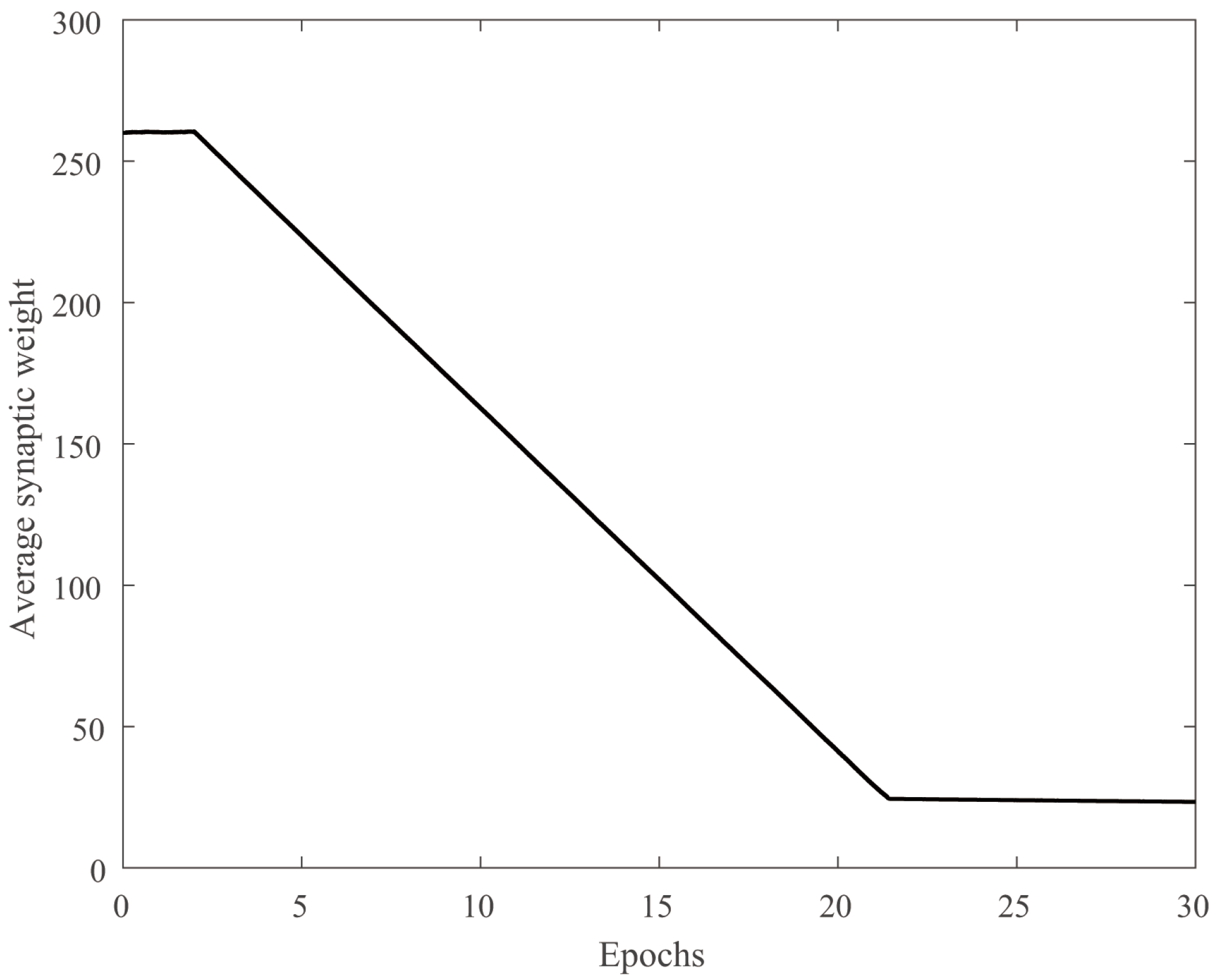
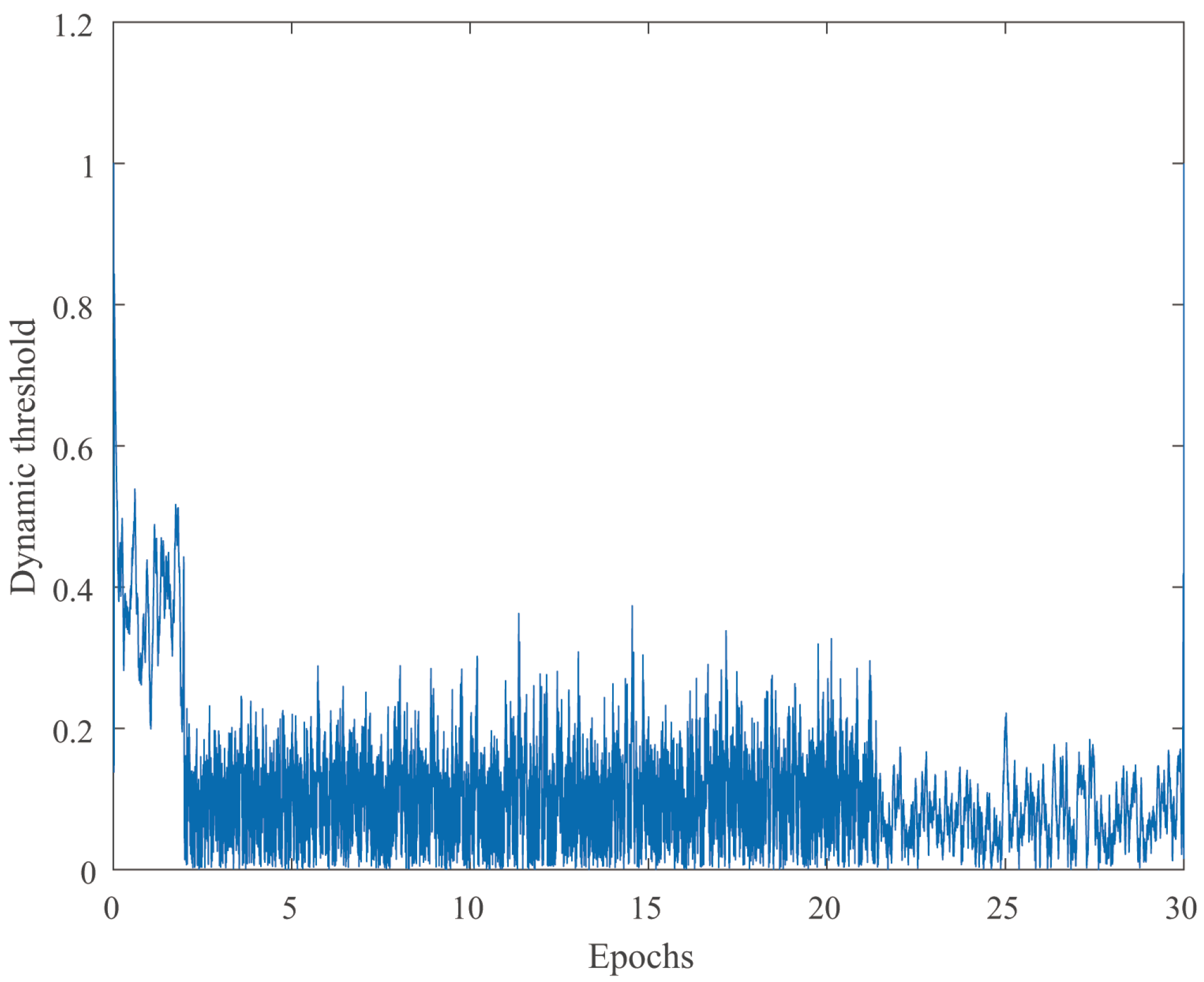
4.1. Stability and Robustness Verification
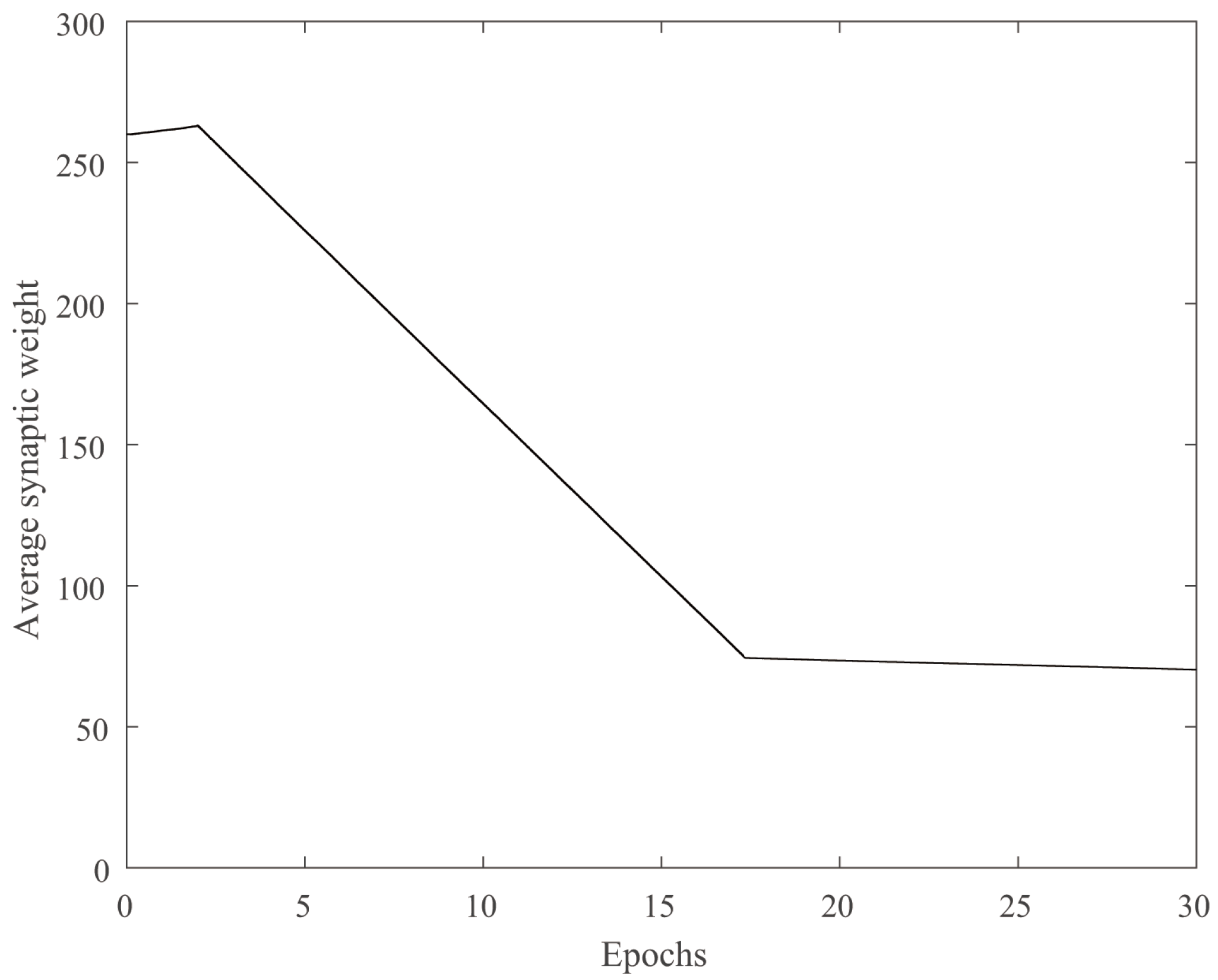
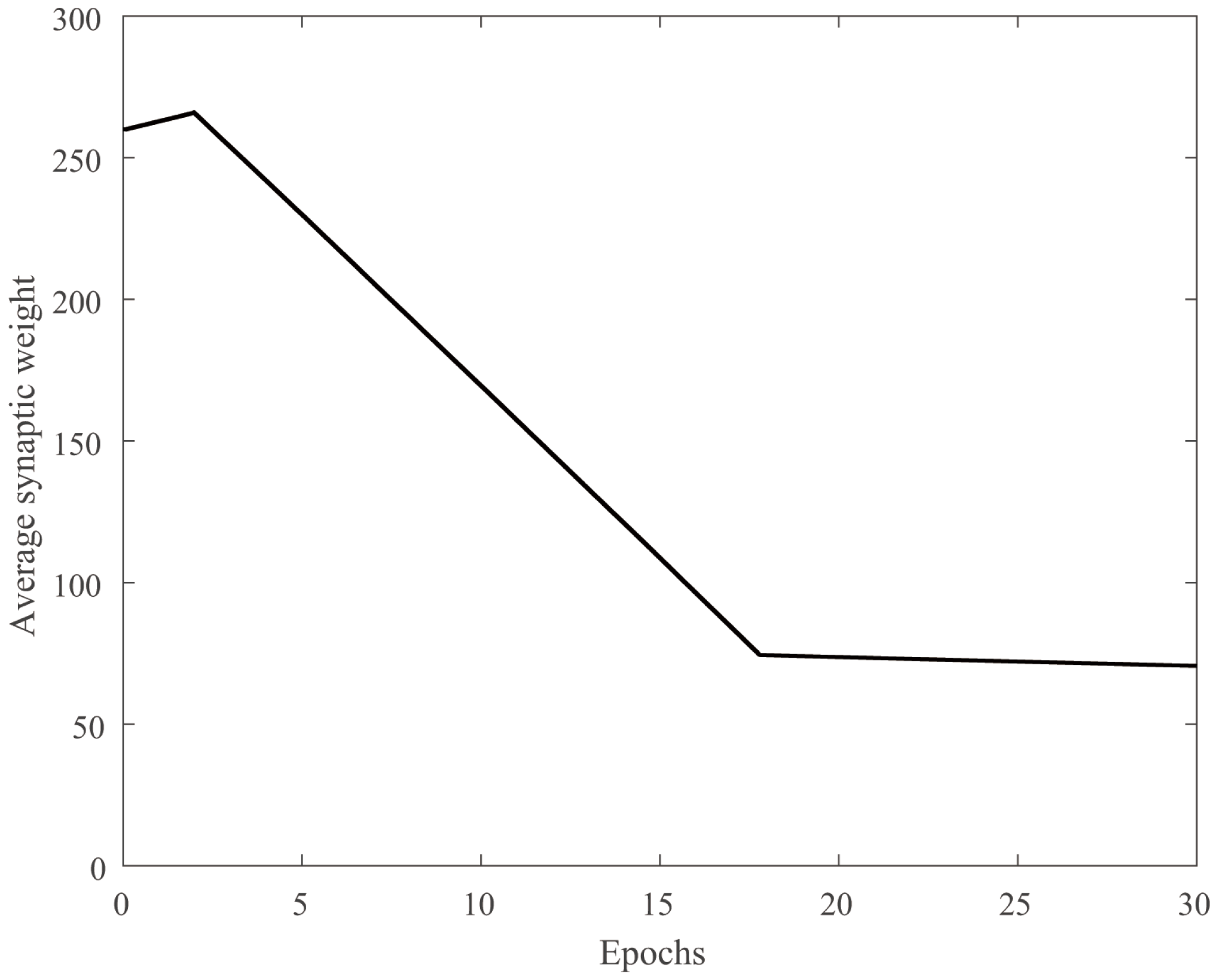
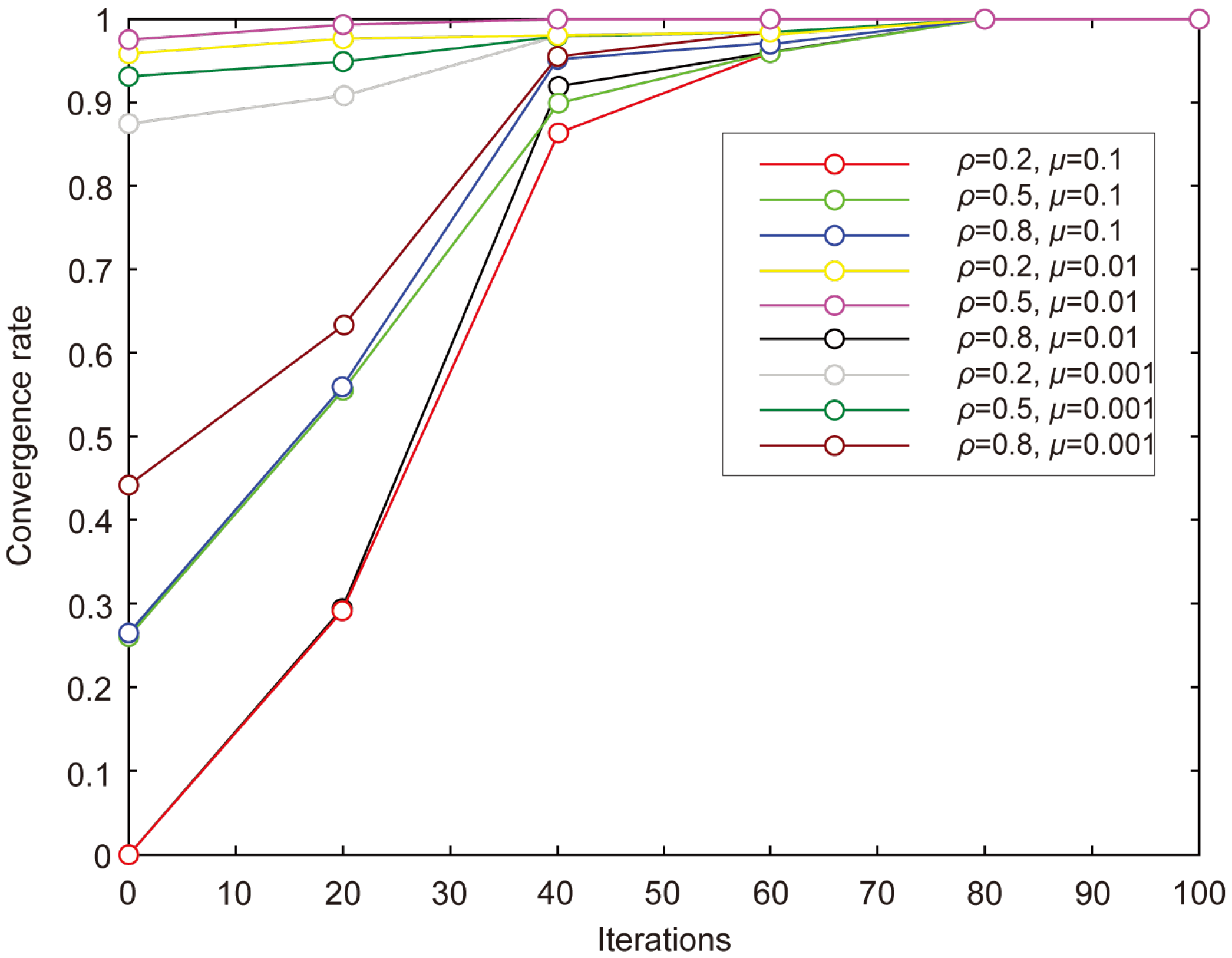
4.2. Traveling Salesman Problem
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, M.; Yang, Q.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G.; Gou, X.; Rong, H.; Paul, P.; Neri, F. An adaptive optimization spiking neural P system for binary problems. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2021, 31, 2050054. [Google Scholar]
- Woodward, A.; Froese, T.; Ikegami, T. Neural coordination can be enhanced by occasional interruption of normal firing patterns: A self-optimizing spiking neural network model. Neural Netw. 2015, 62, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.W.; Kukreja, S.L.; Thakor, N.V. CONE: Convex-optimized-synaptic efficacies for temporally precise spike map. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2016, 28, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C. A spiking neural network with probability information transmission. Neurocomputing 2020, 408, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, W. Noisy spiking neurons with temporal coding have more computational power than sigmoidal neurons. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1997, 9, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes-Vallés, F.; Scheper, K.Y.; De Croon, G.C. Unsupervised learning of a hierarchical spiking neural network for optical flow estimation: From events to global motion perception. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 42, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, S.; Faez, K.; Janahmadi, M. A new approach to detect the coding rule of the cortical spiking model in the information transmission. Neural Netw. 2018, 99, 68–78. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Fouda, M.E.; Yantir, H.E.; Eltawil, A.M.; Salama, K.N. Unsupervised adaptive weight pruning for energy-efficient neuromorphic systems. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 598876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Qu, H.; Belatreche, A.; Chen, Y.; Yi, Z. A highly effective and robust membrane potential-driven supervised learning method for spiking neurons. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 30, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Yantır, H.E.; Fouda, M.E.; Eltawil, A.M.; Salama, K.N. Towards efficient neuromorphic hardware: Unsupervised adaptive neuron pruning. Electronics 2020, 9, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, H.; Xie, X.; Han, J. Neural-network-based learning algorithms for cooperative games of discrete-time multi-player systems with control constraints via adaptive dynamic programming. Neurocomputing 2019, 344, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richert, D.; Masaud, K.; Macnab, C.J.B. Discrete-time weight updates in neural-adaptive control. Soft Comput. 2013, 17, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.B.; Song, Q. Robust spike-train learning in spike-event based weight update. Neural Netw. 2017, 96, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Bae, J.H.; Eum, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, C.H.; Kwon, D.; Park, B.G.; Lee, J.H. Adaptive learning rule for hardware-based deep neural networks using electronic synapse devices. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 8101–8116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelyanov, A.V.; Nikiruy, K.E.; Serenko, A.V.; Sitnikov, A.V.; Presnyakov, M.Y.; Rybka, R.B.; Sboev, A.G.; Rylkov, V.V.; Kashkarov, P.K.; Kovalchuk, M.V.; et al. Self-adaptive STDP-based learning of a spiking neuron with nanocomposite memristive weights. Nanotechnology 2019, 31, 045201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilly, P.K.; Grossberg, S. Spiking neurons in a hierarchical self-organizing map model can learn to develop spatial and temporal properties of entorhinal grid cells and hippocampal place cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.B.; Song, Q. Adaptive learning rate of SpikeProp based on weight convergence analysis. Neural Netw. 2015, 63, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodyanskiy, Y.; Dolotov, A.; Vynokurova, O. Evolving spiking wavelet-neuro-fuzzy self-learning system. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 14, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RamachandranPillai, R.; Arock, M. An adaptive spiking neural P system for solving vehicle routing problems. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 2513–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.; Bull, L.; de Lacy Costello, B. Evolving unipolar memristor spiking neural networks. Connect. Sci. 2015, 27, 397–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt, L.; Howard, D.; Indiveri, G.; Sandamirskaya, Y. Parameter optimization and learning in a spiking neural network for UAV obstacle avoidance targeting neuromorphic processors. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 31, 3305–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Belatreche, A.; Maguire, L.P.; McGinnity, T.M. Spiketemp: An enhanced rank-order-based learning approach for spiking neural networks with adaptive structure. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 28, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maass, W. Networks of spiking neurons: The third generation of neural network models. Neural Netw. 1997, 10, 1659–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Varas, R.; Vazquez, R.A. Evaluating spiking neural models in the classification of motor imagery EEG signals using short calibration sessions. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 67, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, X.; Dang, X. Supervised learning in spiking neural networks: A review of algorithms and evaluations. Neural Netw. 2020, 125, 258–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohmer, B.; Stagsted, R.K.; Manoonpong, P.; Larsen, L.B. Integrating non-spiking interneurons in spiking neural networks. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 633945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q. Spike-event-driven deep spiking neural network with temporal encoding. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 28, 484–488. [Google Scholar]
- Markov, S.; Kyurkchiev, N.; Iliev, A.; Rahnev, A. On the approximation of the generalized cut functions of degree p + 1 by smooth hyper-log-logistic function. Dyn. Syst. Appl. 2018, 27, 715–728. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y. Random neural network methods and deep learning. Probab. Eng. Informational Sci. 2021, 35, 6–36. [Google Scholar]
- Basanisi, R.; Brovelli, A.; Cartoni, E.; Baldassarre, G. A generative spiking neural-network model of goal-directed behaviour and one-step planning. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Huh, S.; Lee, J.; Choi, K. Deep neural networks with weighted spikes. Neurocomputing 2018, 311, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.; Allred, J.M.; Ramanathan, S.; Roy, K. Asp: Learning to forget with adaptive synaptic plasticity in spiking neural networks. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2017, 8, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.; Aketi, S.A.; Roy, K. Toward scalable, efficient, and accurate deep spiking neural networks with backward residual connections, stochastic softmax, and hybridization. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 535502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Hu, G.; Wu, S.; Rasch, M.J. Different propagation speeds of recalled sequences in plastic spiking neural networks. New J. Phys. 2015, 17, 035006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobov, S.A.; Mikhaylov, A.N.; Shamshin, M.; Makarov, V.A.; Kazantsev, V.B. Spatial properties of STDP in a self-learning spiking neural network enable controlling a mobile robot. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 491341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buesing, L.; Bill, J.; Nessler, B.; Maass, W. Neural dynamics as sampling: A model for stochastic computation in recurrent networks of spiking neurons. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krunglevicius, D. Competitive STDP learning of overlapping spatial patterns. Neural Comput. 2015, 27, 1673–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wu, J.; Zou, L.; Feng, Y.; Tu, Z. A generalization of the cauchy-schwarz inequality and its application to stability analysis of nonlinear impulsive control systems. Complexity 2019, 2019, 6048909. [Google Scholar]
- Demin, V.A.; Nekhaev, D.V.; Surazhevsky, I.A.; Nikiruy, K.E.; Emelyanov, A.V.; Nikolaev, S.N.; Rylkov, V.V.; Kovalchuk, M.V. Necessary conditions for STDP-based pattern recognition learning in a memristive spiking neural network. Neural Netw. 2021, 134, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Huang, X.; Dong, M.; Xu, B. A biologically plausible supervised learning method for spiking neural networks using the symmetric STDP rule. Neural Netw. 2020, 121, 387–395. [Google Scholar]
- Rathi, N.; Panda, P.; Roy, K. STDP-based pruning of connections and weight quantization in spiking neural networks for energy-efficient recognition. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2018, 38, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strain, T.J.; McDaid, L.J.; McGinnity, T.M.; Maguire, L.P.; Sayers, H.M. An STDP training algorithm for a spiking neural network with dynamic threshold neurons. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2010, 20, 463–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, H.; Cessac, B. Parameter estimation for spatio-temporal maximum entropy distributions: Application to neural spike trains. Entropy 2014, 16, 2244–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Davis, E.J. Calculating Rényi entropies with neural autoregressive quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 2020, 102, 062413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashkirov, A.G.E. Renyi entropy as a statistical entropy for complex systems. Theor. Math. Phys. 2006, 149, 1559–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, D.R. Model averages sharpened into Occam’s razors: Deep learning enhanced by Rényi entropy. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 2022, 51, 8283–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah Eddine, M.; El Joumani, S.; Zennouhi, R.; Masmoudi, L. Multi-objective optimization for worldview image segmentation funded on the entropies of tsallis and rényi. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 30637–30652. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsaldin, A.S.; Rashid, T.A.; Al-Rashid Agha, R.A.; Al-Salihi, N.K.; Mohammadi, M. Donkey and smuggler optimization algorithm: A collaborative working approach to path finding. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2019, 6, 562–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


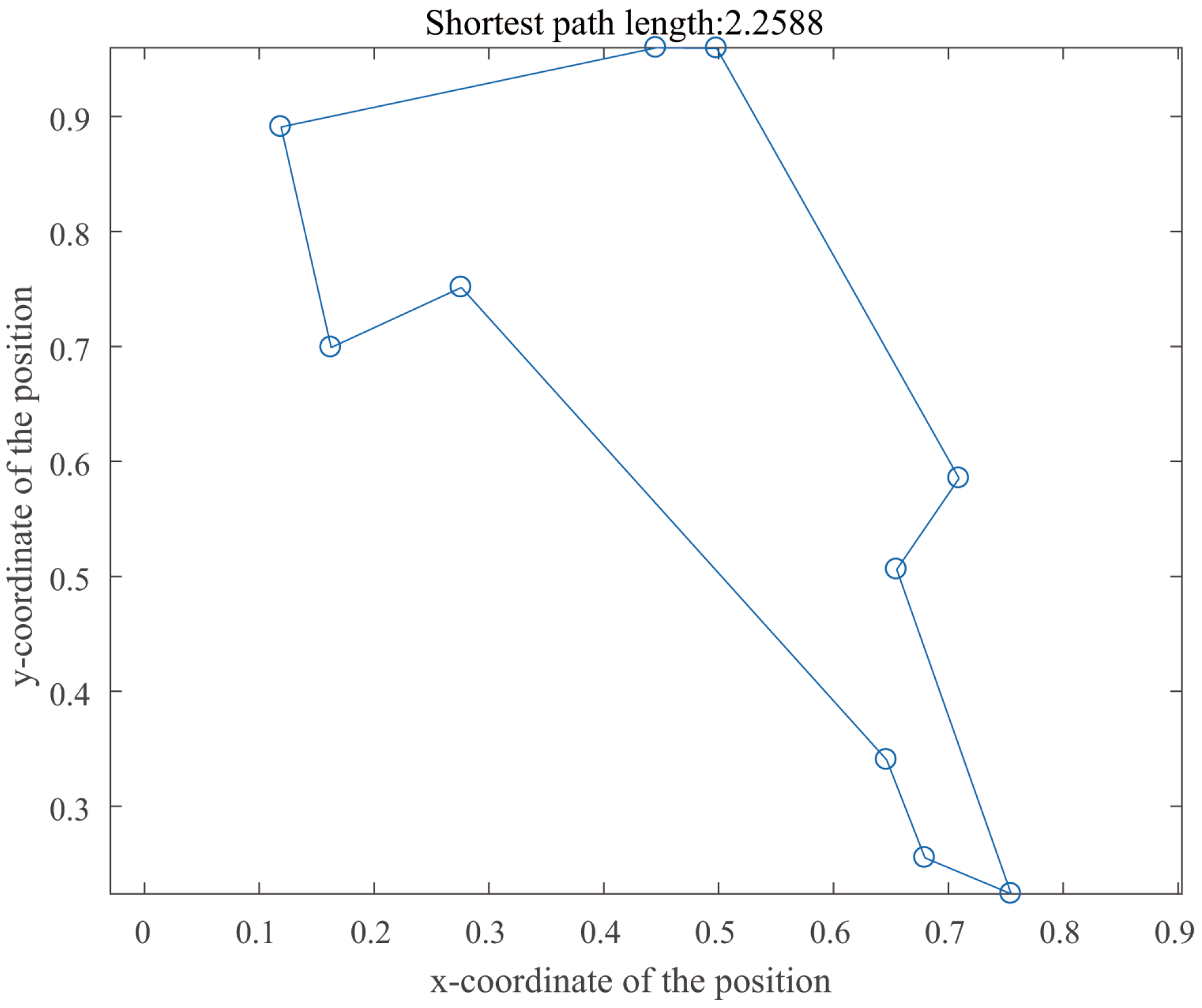
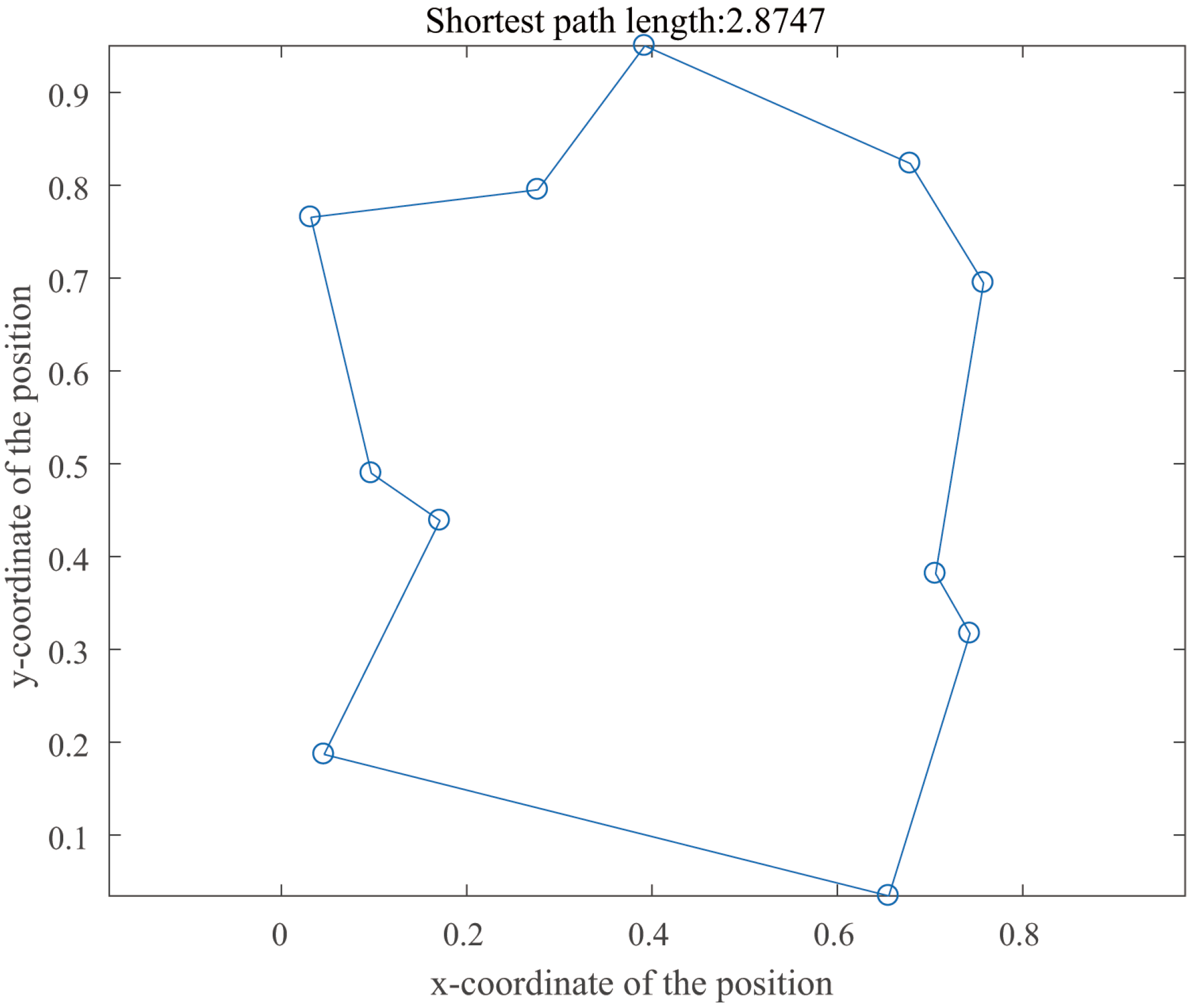
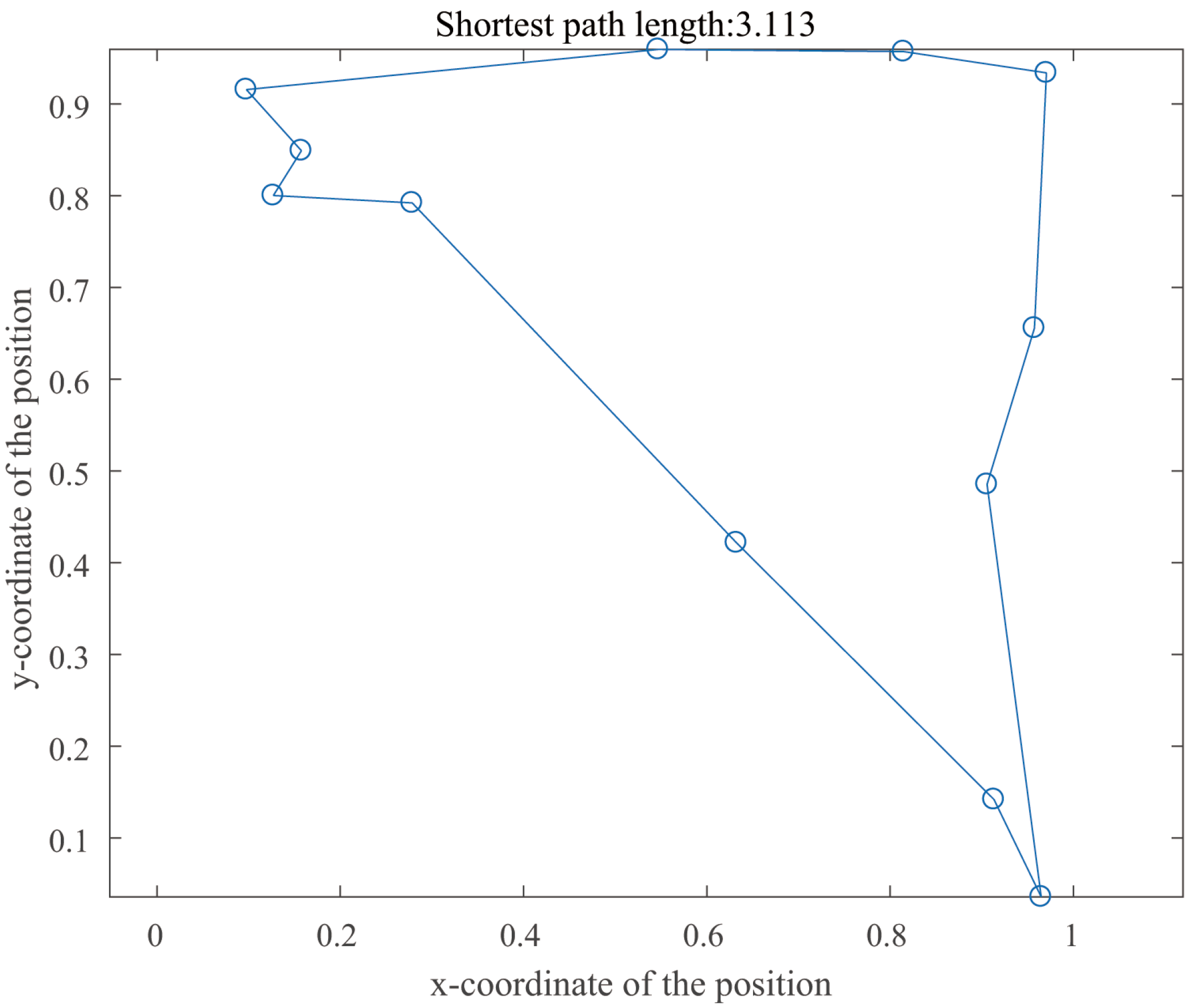
| Shortest Path | Operation Time/s | Minimum Cost | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cities | SNN(A) | SNN(O) | SNN(A) | SNN(O) | SNN(A) | SNN(O) |
| 13 | 3.6189 | 3.9345 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 52 | 57 |
| 14 | 3.8432 | 4.6348 | 0.55 | 0.24 | 55 | 59 |
| 15 | 4.0837 | 4.9123 | 0.74 | 0.42 | 58 | 61 |
| 16 | 4.1324 | 5.1619 | 0.89 | 0.65 | 62 | 69 |
| 17 | 4.8756 | 5.6537 | 1.15 | 0.77 | 65 | 73 |
| 18 | 5.0019 | 5.9871 | 2.68 | 0.81 | 68 | 78 |
| 19 | 5.3126 | 6.1566 | 3.15 | 0.89 | 71 | 85 |
| 20 | 5.8427 | 7.0234 | 3.22 | 1.08 | 72 | 89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.-X.; Chen, Y.-X. An Adaptive Learning Algorithm Based on Spiking Neural Network for Global Optimization. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111814
Wang R-X, Chen Y-X. An Adaptive Learning Algorithm Based on Spiking Neural Network for Global Optimization. Symmetry. 2025; 17(11):1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111814
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Rui-Xuan, and Yu-Xuan Chen. 2025. "An Adaptive Learning Algorithm Based on Spiking Neural Network for Global Optimization" Symmetry 17, no. 11: 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111814
APA StyleWang, R.-X., & Chen, Y.-X. (2025). An Adaptive Learning Algorithm Based on Spiking Neural Network for Global Optimization. Symmetry, 17(11), 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111814




