High-Precision Digital Time-Interval Measurement in Dual-Comb Systems via Adaptive Signal Processing and Centroid Localization
Abstract
1. Introduction
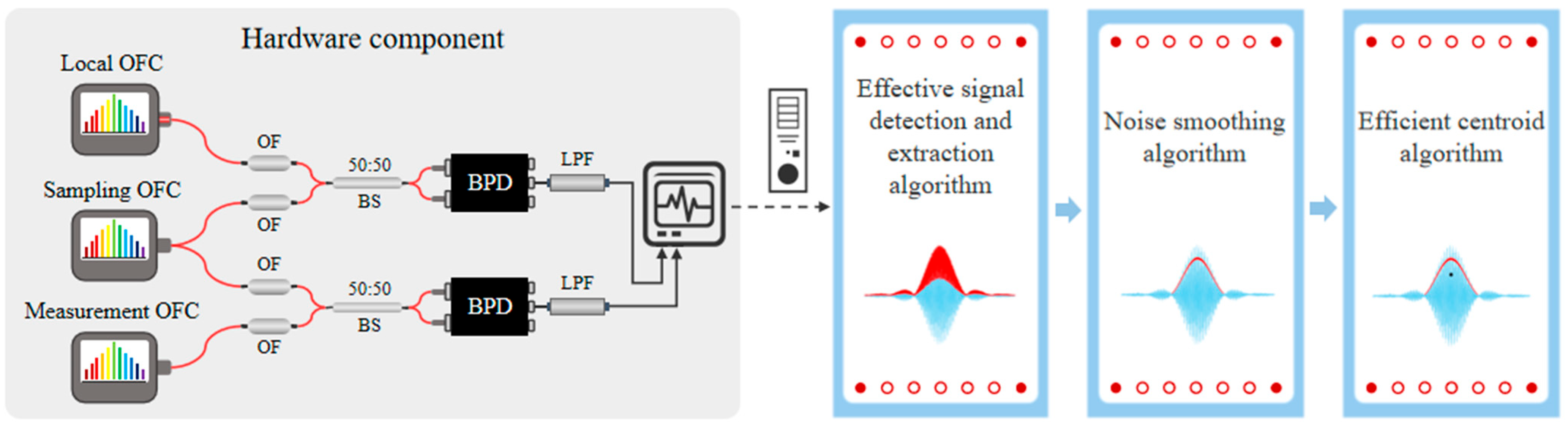
2. Materials and Methods
- Effective signal detection and extraction algorithm: The effective signal detection and extraction algorithm searches for the peak position of the signal as the starting point, takes the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the main pulse of the dual comb interference pulse signal as the extraction unit to discard the ineffective energy that does not contribute to the time estimation results during the entire acquisition process, allowing for the extraction of the effective signal necessary for accurate time estimation;
- Noise smoothing algorithm: The noise smoothing algorithm uses sliding average filtering on the envelope of the effective signal to reduce the impact of amplitude noise on the signal envelope waveform. Additionally, it utilizes feature points of the envelope signal that are less sensitive to noise, thereby minimizing the additional impact of amplitude noise on the centroid position;
- Efficient centroid algorithm: The efficient centroid algorithm calculates the centroid of the effective signal envelope to locate the time information in the dual comb interference pulse signal, and obtains the time difference necessary for dual comb time synchronization by calculating the time interval between the centroids of the two interference pulses in the time domain.
2.1. Effective Signal Detection and Extraction Algorithm
2.2. Noise Smoothing Algorithm
2.3. Efficient Centroid Algorithm
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, B.; Guo, H. Time-Frequency Transfer over Optical Fiber. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2025, 12, nwaf236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Mazuelas, S.; Win, M.Z. Network Navigation: Theory and Interpretation. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2012, 30, 1823–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, J.; Cosart, L.; Zampetti, G. Precise Timing for Vehicle Navigation in the Smart City: An Overview. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2020, 58, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tu, R.; Lu, X.; Gao, Y.; Lihong, F. Performance of global positioning system precise time and frequency transfer with integer ambiguity resolution. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, I.; Swann, W.C.; Nenadovic, L.; Newbury, N.R. Rapid and precise absolute distance measurements at long range. Nat. Photonics 2009, 6, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajima, M.; Minoshima, K. Optical zooming interferometer for subnanometer positioning using an optical frequency comb. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 5844–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, Y.; Jeon, C.G.; Ahn, C.; Hyun, M.; Kwon, D.; Shin, J.; Kim, J. Ultrafast, subnanometre-precision and multifunctional time-of-flight detection. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, E.D.; Sinclair, L.C.; Newbury, N.R.; Deschenes, J.-D. The time-programmable frequency comb andits use in quantum-limited ranging. Nature 2022, 610, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkley, N.; Sherman, J.A.; Phillips, N.B.; Schioppo, M.; Lemke, N.D.; Beloy, K.; Pizzocaro, M.; Oates, C.W.; Ludlow, A.D. An Atomic Clock with 10-18 Instability. Science 2013, 341, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgetta, F.R.; Swann, W.C.; Sinclair, L.C.; Baumann, E.; Coddington, I.; Newbury, N.R. Optical two-way time and frequency transfer over free space. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschênes, J.D.; Sinclair, L.C.; Giorgetta, F.R.; Swann, W.C.; Baumann, E.; Bergeron, H.; Cermak, M.; Coddington, I.; Newbury, N.R. Synchronization of Distant Optical Clocks at the Femtosecond Level. Physics 2015, 16, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, H.; Sinclair, L.C.; Swann, W.C.; Nelson, C.W.; Deschênes, J.-D.; Baumann, E.; Giorgetta, F.R.; Coddington, I.; Newbury, N.R. Tight real-time synchronization of a microwave clock to an optical clock across a turbulent air path. Optica 2016, 3, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, L.C.; Swann, W.C.; Bergeron, H.; Baumann, E.; Cermak, M.; Coddington, I.; Deschênes, J.-D.; Giorgetta, F.R.; Juarez, J.C.; Khader, I.; et al. Synchronization of clocks through 12 km of strongly turbulent air over a city. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, L.C.; Bergeron, H.; Swann, W.C.; Khader, I.; Cossel, K.C.; Cermak, M.; Newbury, N.R.; Deschênes, J.-D. Femtosecond optical two-way time-frequency transfer in the presence of motion. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 99, 023844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, H.; Sinclair, L.C.; Swann, W.C.; Khader, I.; Cossel, K.C.; Cermak, M.; Deschênes, J.-D.; Newbury, N.R. Femtosecond time synchronization of optical clocks off of a flying quadcopter. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodine, M.I.; Ellis, J.L.; Swann, W.C.; Stevenson, S.A.; Deschênes, J.-D.; Hannah, E.D.; Manurkar, P.; Newbury, N.R.; Sinclair, L.C. Optical time-frequency transfer across a free-space, three-node network. APL Photonics 2020, 5, 076113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Shen, Q.; Guan, J.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Liao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, C. Sensitive linear optical sampling system with femtosecond precision. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 91, 035113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Chen, Z.; Yang, X.; Xu, Y.; Jin, Z.; Ma, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, S.; Luo, B.; Guo, H. Time interval measurement with linear optical sampling at the femtosecond level. Photonics Res. 2023, 11, 2222–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, I.; Swann, W.C.; Newbury, N.R. Coherent linear optical sampling at 15 bits of resolution. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Ni, K.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, G. Digital correction method for realizing a phase-stable dual-comb interferometer. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 16813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yu, D.; Niu, J.; Chen, X.; Guo, H. Hundred-femtosecond-level concise optical time delay measurement system based on linear optical sampling. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2023, 94, 085105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Yu, S.; Luo, B.; Guo, H. Microwave frequency transfer over 3000-km fiber based on optical frequency combs and active noise cancellation. Phys. Rev. Res. 2024, 6, 023005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorrer, C.; Kilper, D.C.; Stuart, H.R.; Raybon, G.; Raymer, M.G. Linear optical sampling. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2003, 15, 1746–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, D.; Lu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, S.; Luo, B.; Guo, H. Dual-comb-enhanced microwave clock synchronization over commercial fiber. Optica 2024, 11, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, G.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Chen, S.; Xiao, L.; Chen, Z.; Luo, B.; et al. High-Precision Digital Time-Interval Measurement in Dual-Comb Systems via Adaptive Signal Processing and Centroid Localization. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101769
Lu G, Yu D, Zhang Z, Xie Y, Zhang Y, Fu Z, Chen S, Xiao L, Chen Z, Luo B, et al. High-Precision Digital Time-Interval Measurement in Dual-Comb Systems via Adaptive Signal Processing and Centroid Localization. Symmetry. 2025; 17(10):1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101769
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Ganbin, Dongrui Yu, Ziyue Zhang, Yang Xie, Yufei Zhang, Zhongyuan Fu, Sifei Chen, Lin Xiao, Ziyang Chen, Bin Luo, and et al. 2025. "High-Precision Digital Time-Interval Measurement in Dual-Comb Systems via Adaptive Signal Processing and Centroid Localization" Symmetry 17, no. 10: 1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101769
APA StyleLu, G., Yu, D., Zhang, Z., Xie, Y., Zhang, Y., Fu, Z., Chen, S., Xiao, L., Chen, Z., Luo, B., & Guo, H. (2025). High-Precision Digital Time-Interval Measurement in Dual-Comb Systems via Adaptive Signal Processing and Centroid Localization. Symmetry, 17(10), 1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101769





