A New Asymmetric H-6 Structured Multilevel Inverter with Reduced Power Components
Abstract
1. Introduction
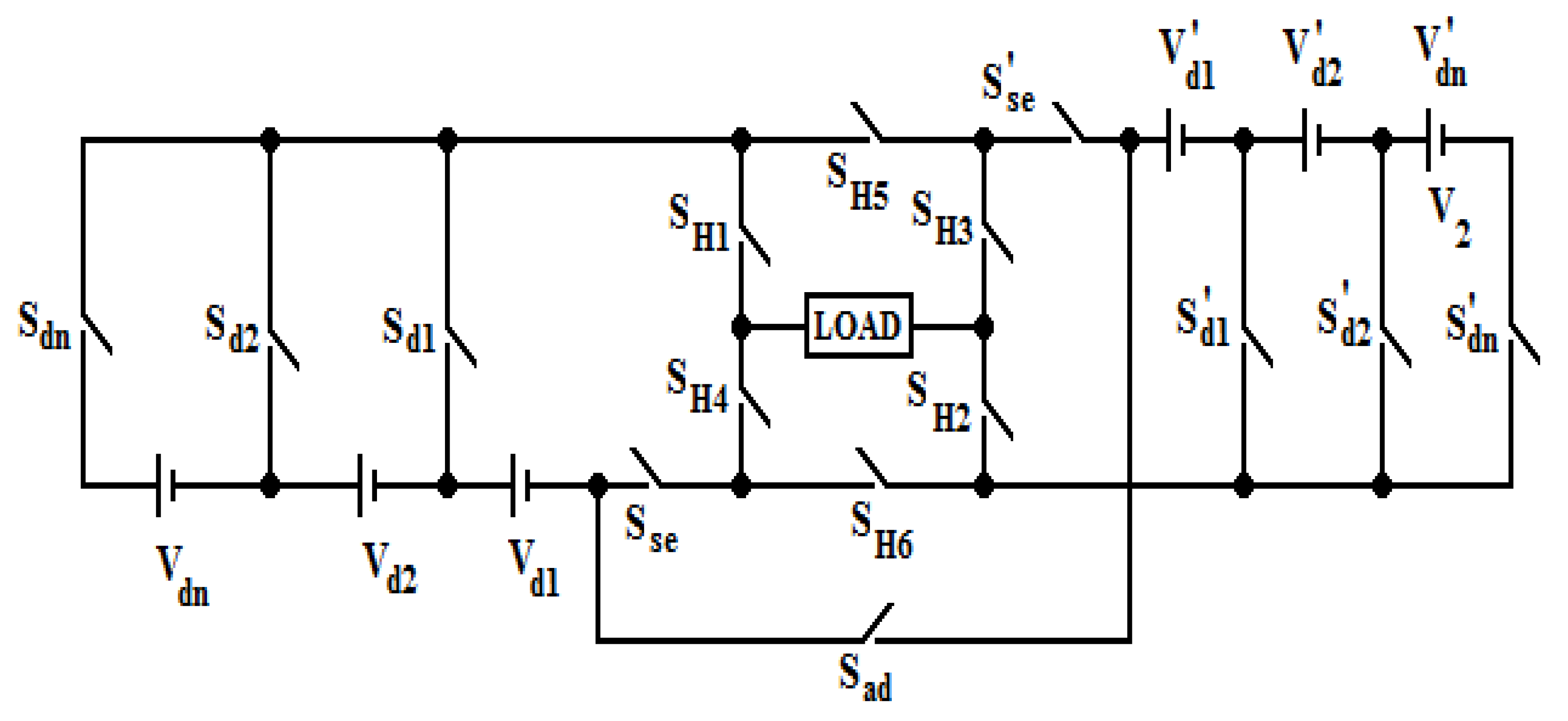
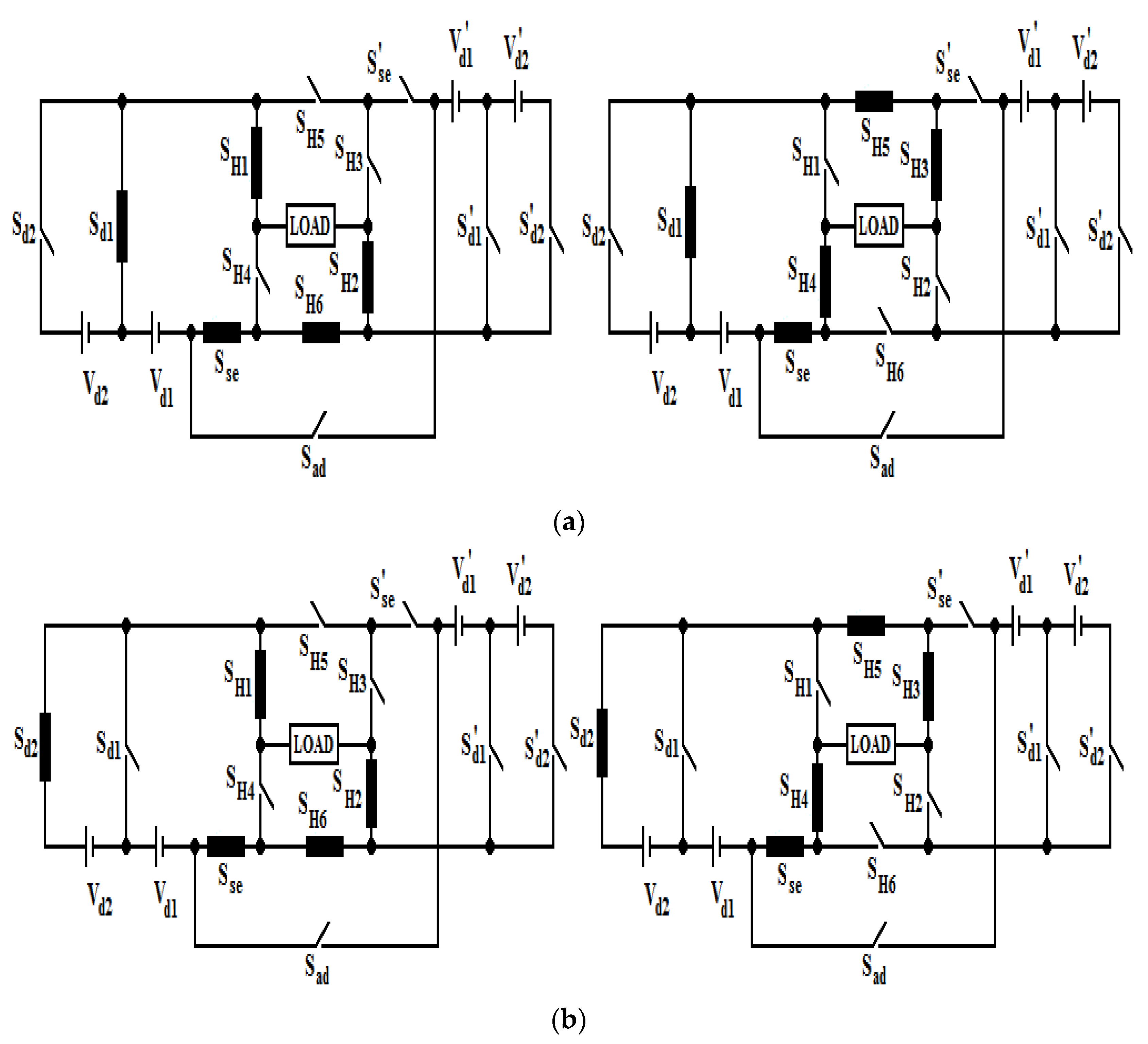
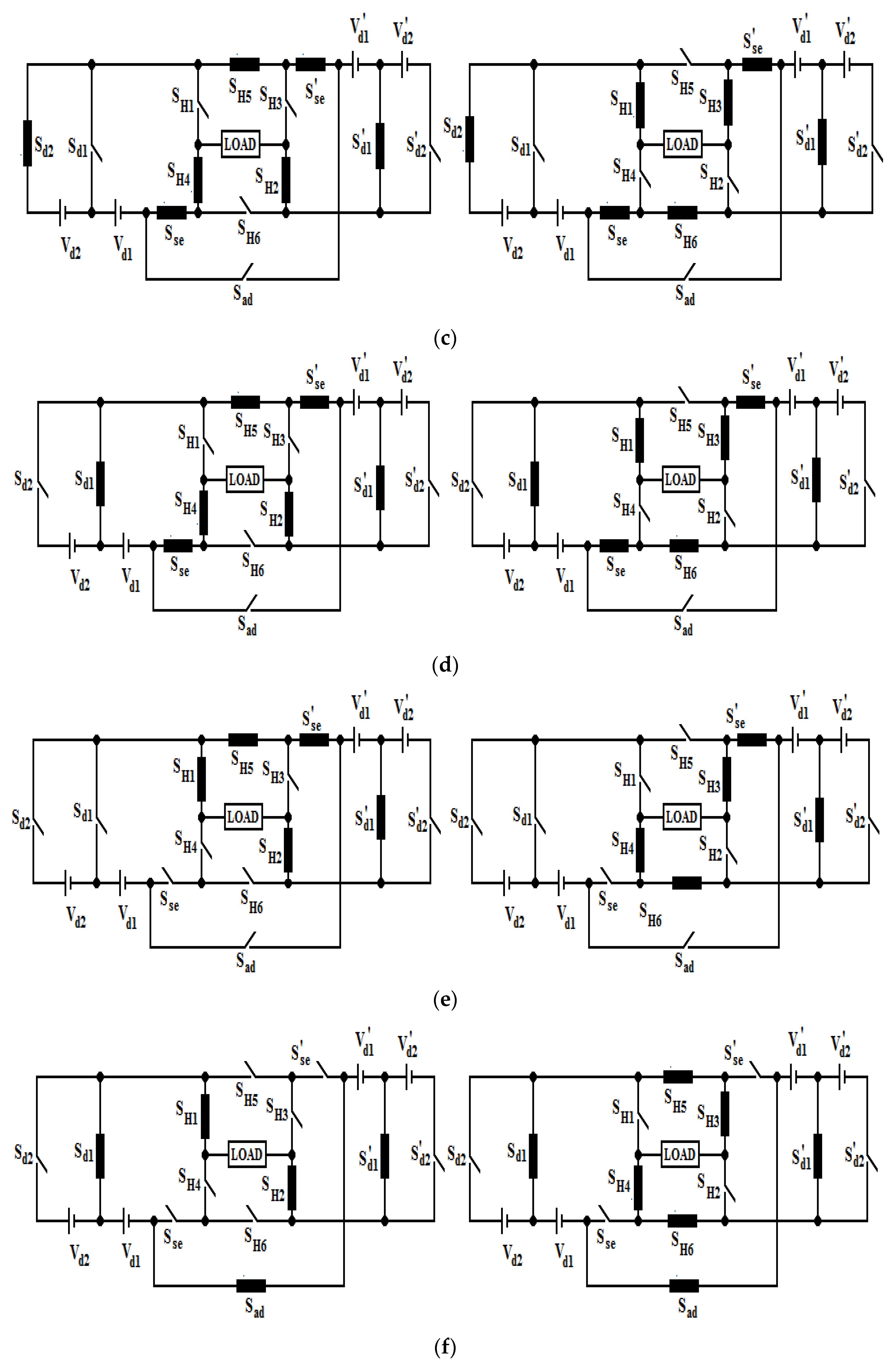
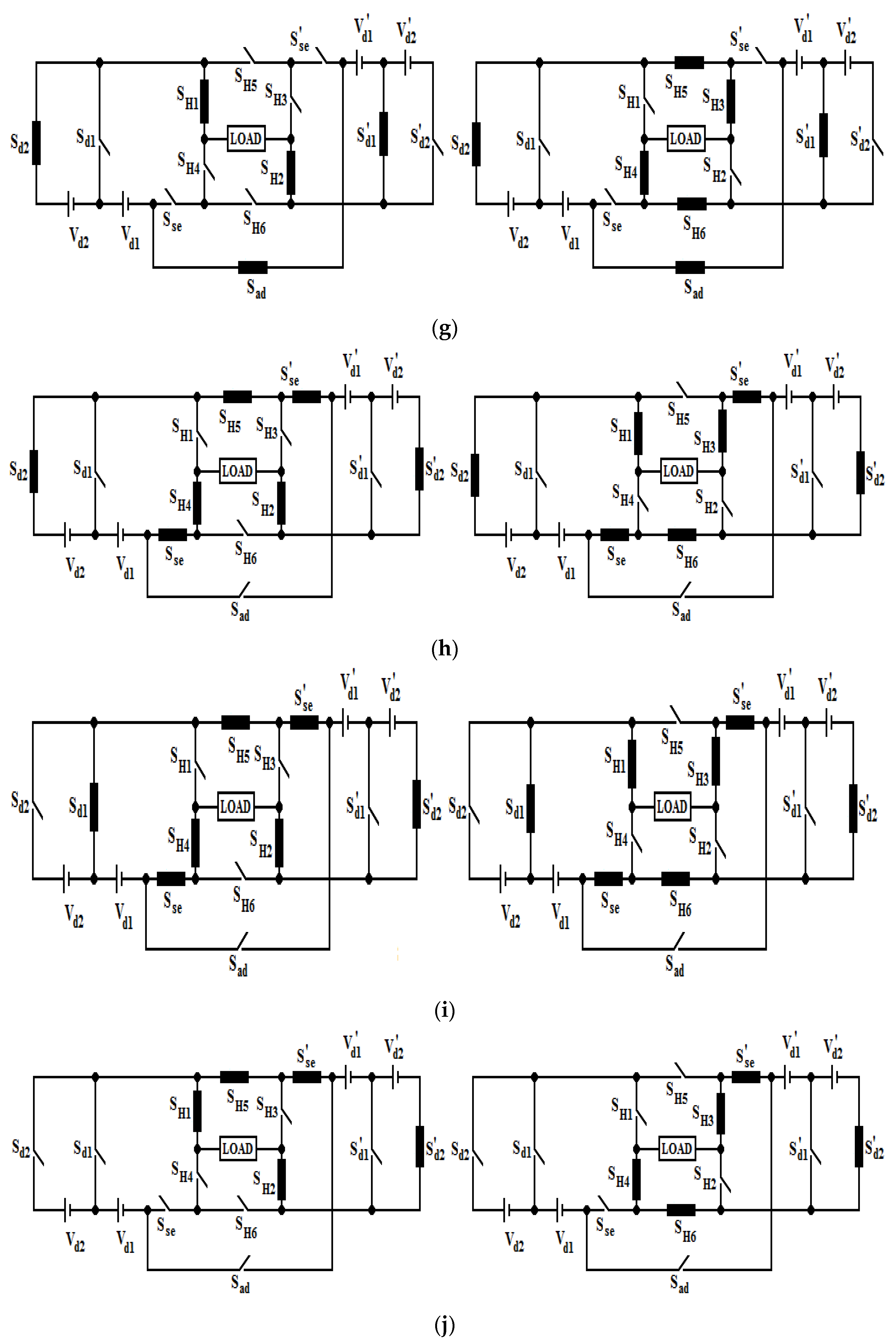
2. Proposed Topology
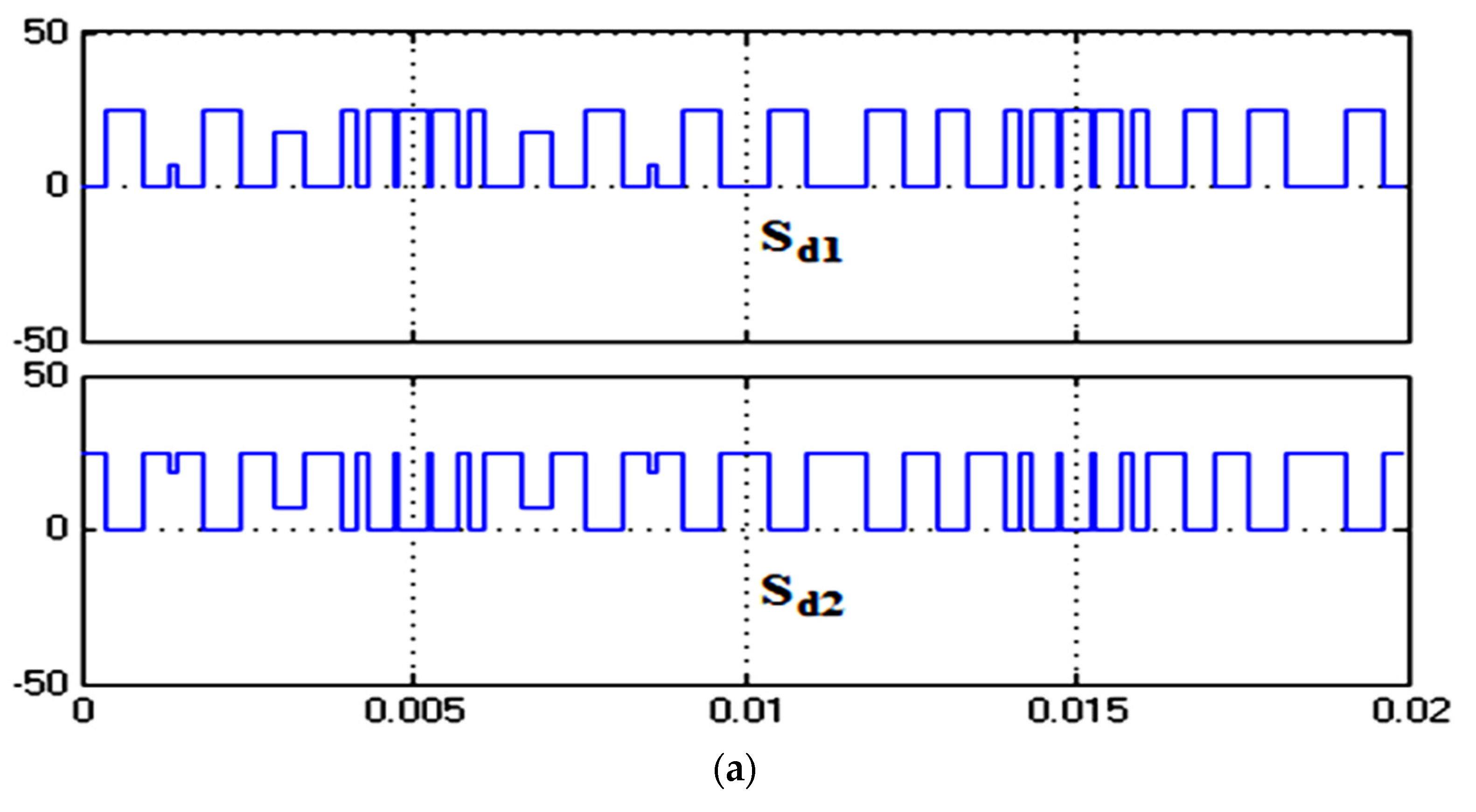
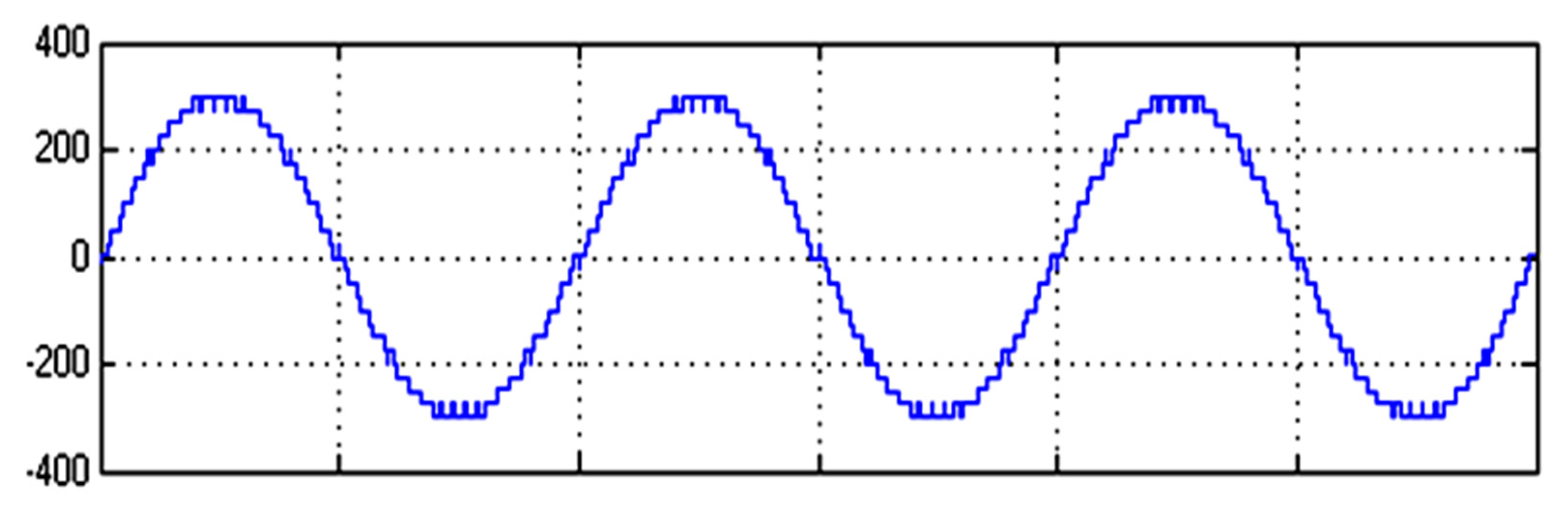
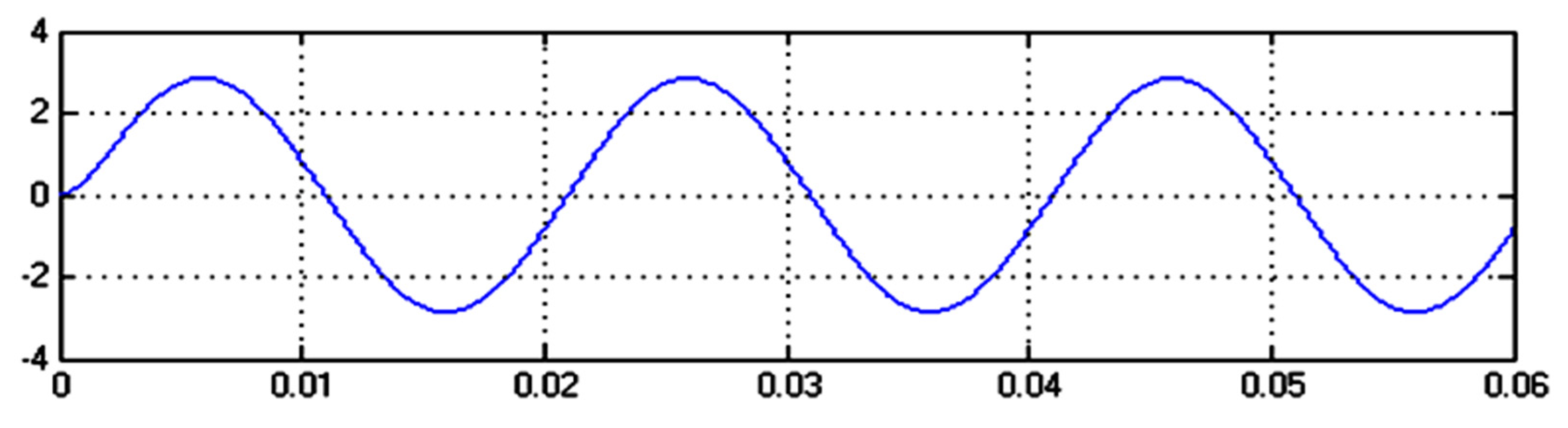
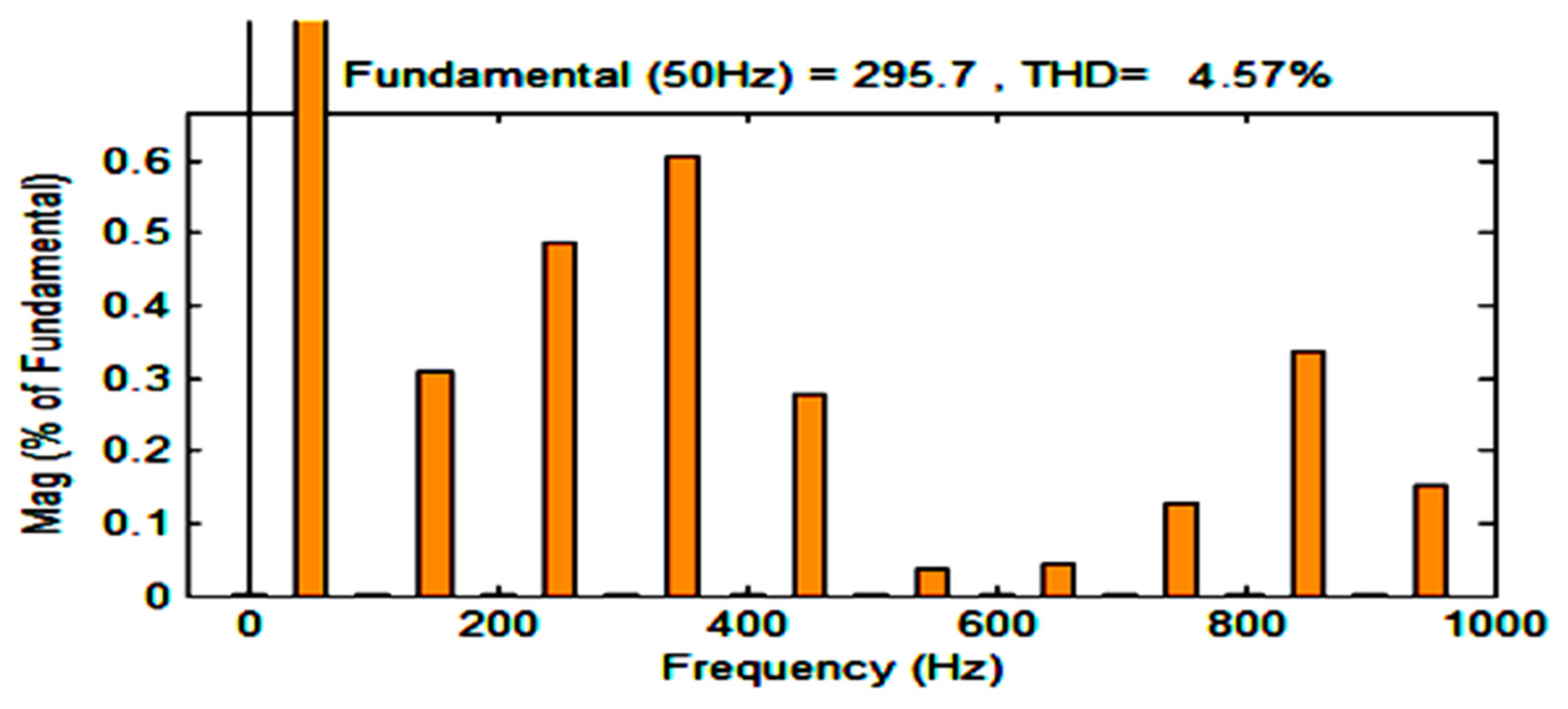
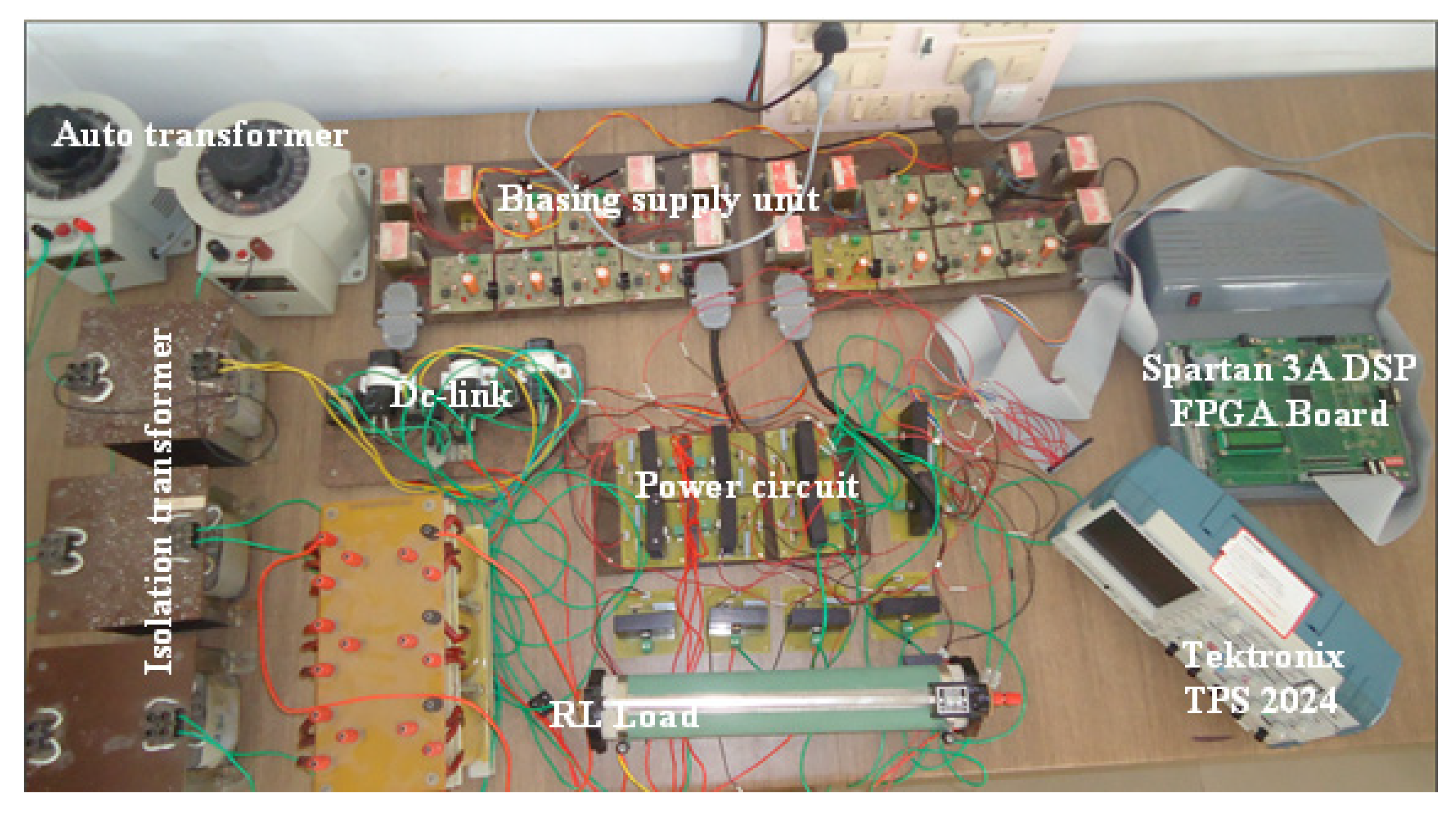
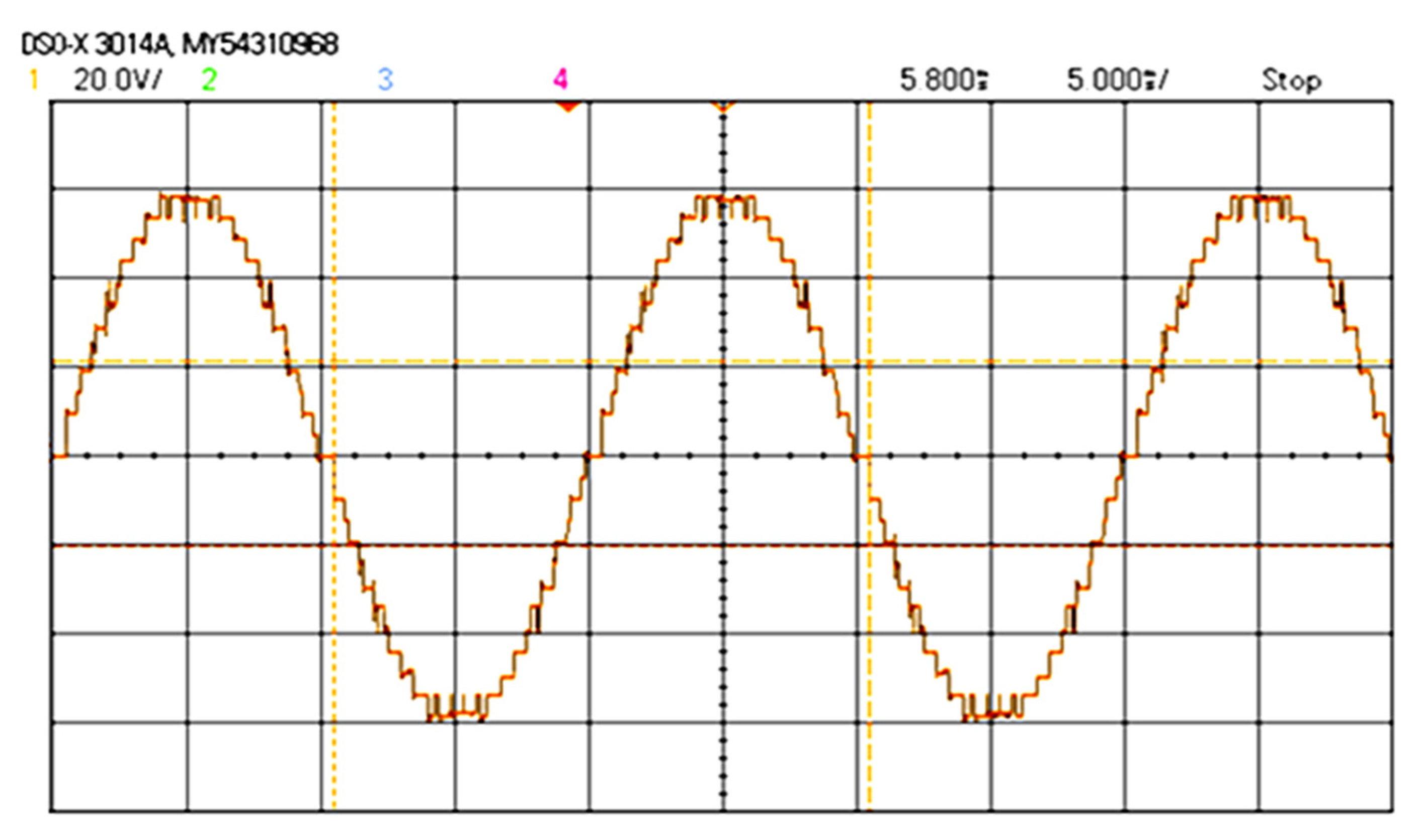
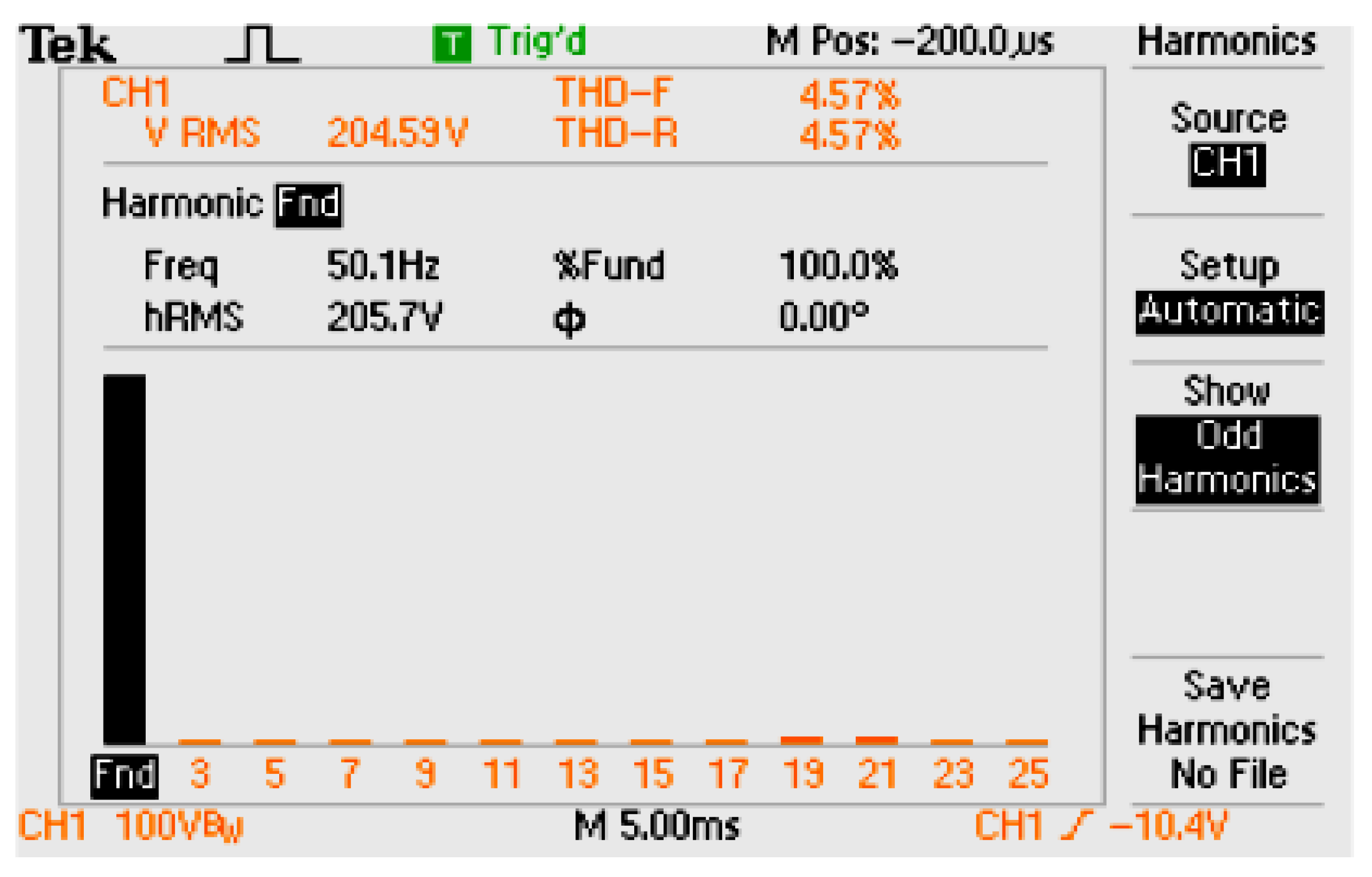
3. Simulation and Experimental Investigation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruiz-Gonzalez, A.; Heredia-Larrubia, J.-R.; Meco-Gutierrez, M.J.; Perez-Hidalgo, F.-M. Pulse-Width Modulation Technique with Harmonic Injection in the Modulating Wave and Discontinuous Frequency Modulation for the Carrier Wave for Multilevel Inverters: An Application to the Reduction of Acoustic Noise in Induction Motors. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 40579–40590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Biswas, S.P.; Islam, R.; Muyeen, S.M. A Five-Level Switched-Capacitor Based Transformerless Inverter with Boosting Capability for Grid-Tied PV Applications. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 12426–12443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Tayyab, M.; Sarwar, A.; Khalid, M. A Low Switch Count 13-Level Switched-Capacitor Inverter with Hexad Voltage-Boosting for Renewable Energy Integration. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 36300–36308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Seshadrinath, J. A Single-Phase Seven-Level Triple Boost Inverter for Grid-Connected Transformerless PV Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 9004–9015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondol, H.; Rahman, A.; Biswas, S.P.; Islam, R.; Kibria, F.; Muttaqi, K.M. A New Integrated Multilevel Inverter Topology for Renewable Energy Transformation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 3031–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Gong, C. An Optimized Reactive Power Compensation Strategy to Extend the Working Range of CHB Multilevel Grid-Tied Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 5500–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.A.; Sarebanzadeh, M.; Kennel, R.; Babaei, E.; Rivera, M. New Generalized Circuits for Single-Phase Multisource Multilevel Power Inverter Topologies. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 6823–6830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, N.; Chattopadhyay, S.K.; Chakraborty, C. Single-Sourced Double-Stage Multilevel Inverter for Grid-Connected Solar PV Systems. IEEE Open J. Ind. Electron. Soc. 2022, 3, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, S.C.S.; Jacobina, C.B.; Fabricio, E.L.L.; Felinto, A.S. Asymmetric 49-Levels Cascaded MPUC Multilevel Inverter Fed by a Single DC Source. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 7539–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraj, S.T.; Rahman, M.S.A.; Yahaya, N.Z.; Ker, P.J.; Hossain, T.M.; Lipu, M.S.H.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Hannan, M.A. A Pencil Shaped 9-Level Multilevel Inverter with Voltage Boosting Ability: Configuration and Experimental Investigation. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 111310–111321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Ebrahimi, J.; Jafarian, Y.; Bakhshai, A. A Multilevel Inverter Topology with an Improved Reliability and a Reduced Number of Components. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondol, H.; Biswas, S.P.; Rahman, A.; Islam, R.; Mahfuz-Ur-Rahman, A.M.; Muttaqi, K.M. A New Hybrid Multilevel Inverter Topology with Level Shifted Multicarrier PWM Technique for Harvesting Renewable Energy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 2574–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamar, A.E.T.; Kermadi, M.; Helaimi, M.; Taleb, R.; Mekhilef, S. An Improved Single-Phase Asymmetrical Multilevel Inverter Structure with Reduced Number of Switches and Higher Power Quality. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 68, 2092–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakar, S.; Ayob, S.B.M.; Iqbal, A.; Nordin, N.M.; Bin Arif, M.S.; Gore, S. New Asymmetrical Modular Multilevel Inverter Topology with Reduced Number of Switches. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 27627–27637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanbakhsh, R.; Ibanez, F.M.; Koohi, P.; Martin, F. A New Asymmetric Cascaded Multilevel Converter Topology with Reduced Voltage Stress and Number of Switches. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 92276–92287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanamjayulu, C.; Prasad, D.; Padmanaban, S.; Maroti, P.K.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B.; Blaabjerg, F. Design and Implementation of Seventeen Level Inverter with Reduced Components. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 16746–16760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isazadeh, A.; Adabi, J.; Rezanejad, M.; Adabi, M.E. Operation and Control of a Grid-Connected Asymmetrical Cascaded Multilevel Inverter. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoun-Jahan, H. University of tabriz switched capacitor based cascaded half-bridge multilevel inverter with voltage boosting feature. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2021, 6, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, E.; Laali, S.; Bayat, Z. A Single-Phase Cascaded Multilevel Inverter Based on a New Basic Unit with Reduced Number of Power Switches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Wang, Y.; Raghuram, M.; Pilli, N.K.; Singh, S.K.; Pan, X.; Xiong, X. A Generalized Switched Inductor Cell Modular Multilevel Inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.N. National institute of technology karnataka development of cascaded multilevel inverter based active power filter with reduced transformers. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2020, 5, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, R.; Chattopadhyay, S.K.; Chakraborty, C. Asymmetric Cascaded H-Bridge Multilevel Inverter with Single DC Source per Phase. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 5398–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, A.; Afjei, E.S.; Torkaman, H. Novel Symmetric Modular Hybrid Multilevel Inverter with Reduced Number of Semiconductors and Low-Voltage Stress Across Switches. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 4297–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, P.; Sivaraman, P.; Almakhles, D.J.; Padmanaban, S.; Leonowicz, Z.; Alagu, M.; Ali, J.S.M. A New Multilevel Inverter Topology with Reduced Power Components for Domestic Solar PV Applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 187483–187497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, T.; Sadhu, P.K.; Dasgupta, A. Cross-Switched Multilevel Inverter Using Novel Switched Capacitor Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 8521–8532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamiri, E.; Moradzadeh, M.; Barzegarkhoo, R.; Hamkari, S.; Sabahi, M. Cascaded Multilevel Inverters Using Proposed Series Sub-multilevel Basic Blocks with Reduced Switching Devices. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2017, 45, 1691–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittathuru, D.; Padmanaban, S.; Prasad, R. Design and Implementation of Asymmetric Cascaded Multilevel Inverter with Optimal Components. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2021, 49, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamani, P.L.; Mulla, M.A. A Home-type (H-type) Cascaded Multilevel Inverter with Reduced Device Count: Analysis and Implementation. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2019, 47, 1691–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.D.; Rawa, M.; Mekhilef, S.; Shah, N.M. A new cascaded asymmetrical multilevel inverter based on switched dc voltage sources. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 128, 106730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Raj, R.A.; Nema, R.K.; Nema, S. A Novel Higher Level Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Multilevel Inverter for Solar Energy Environment. IETE J. Res. 2022, 68, 3670–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

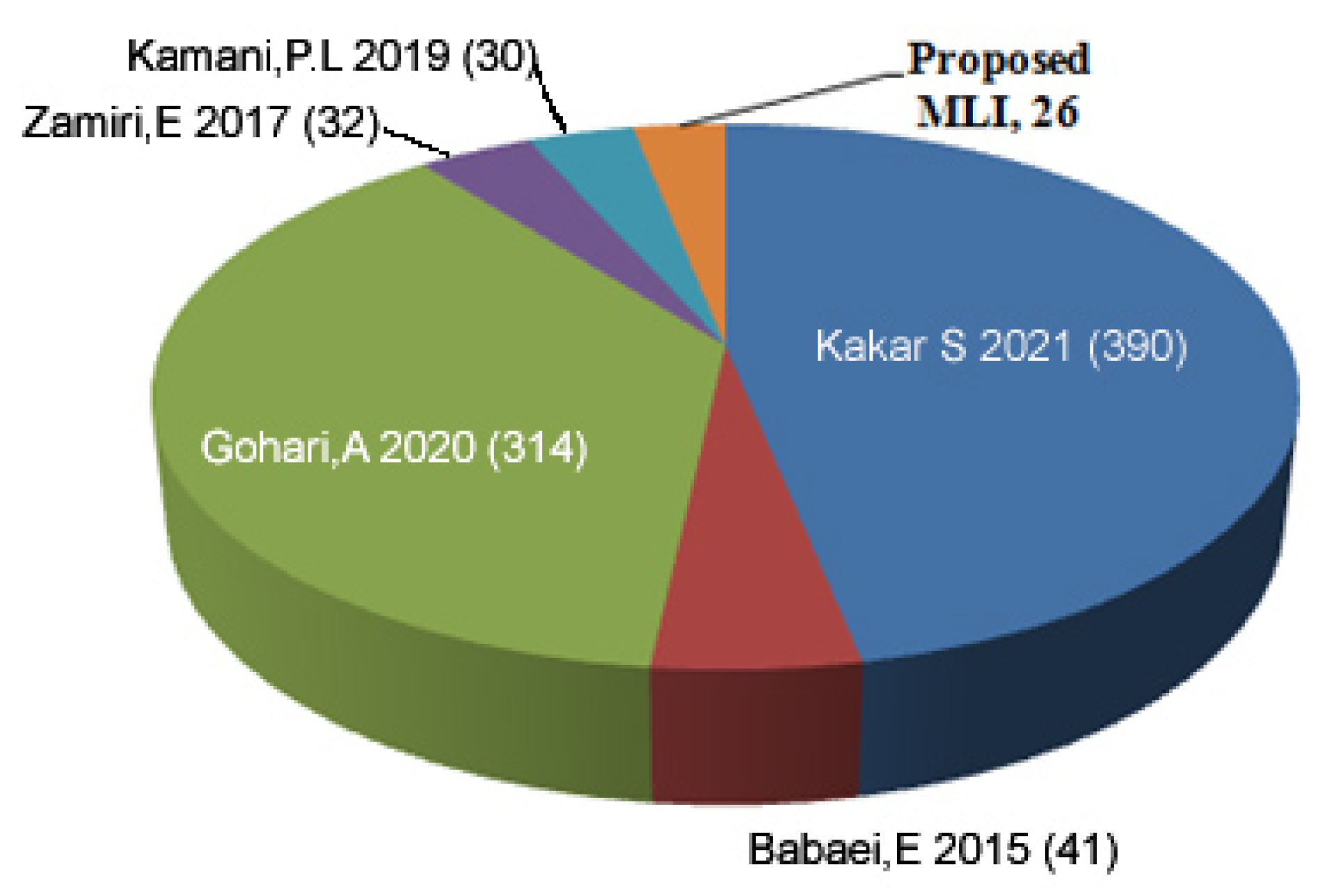
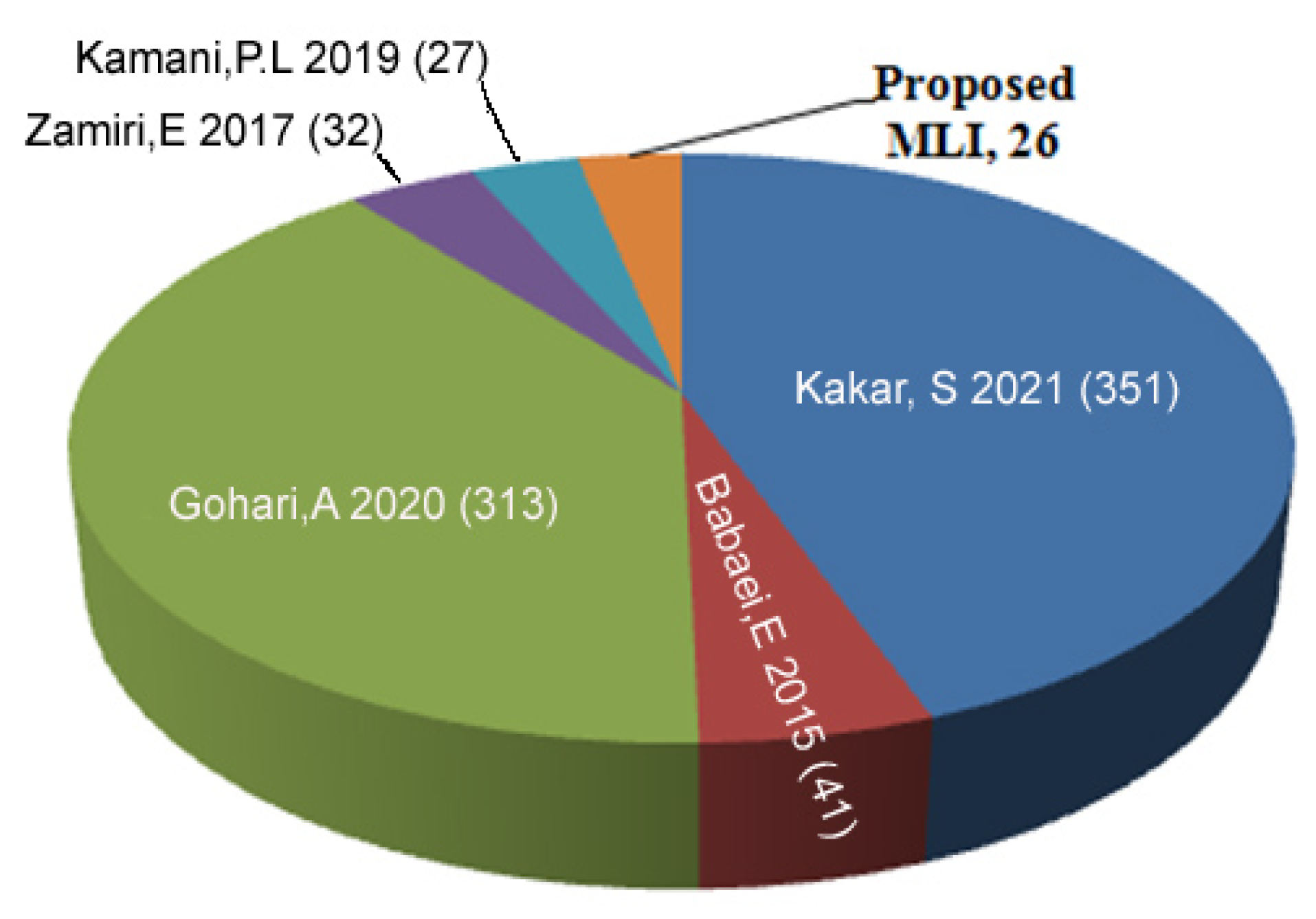
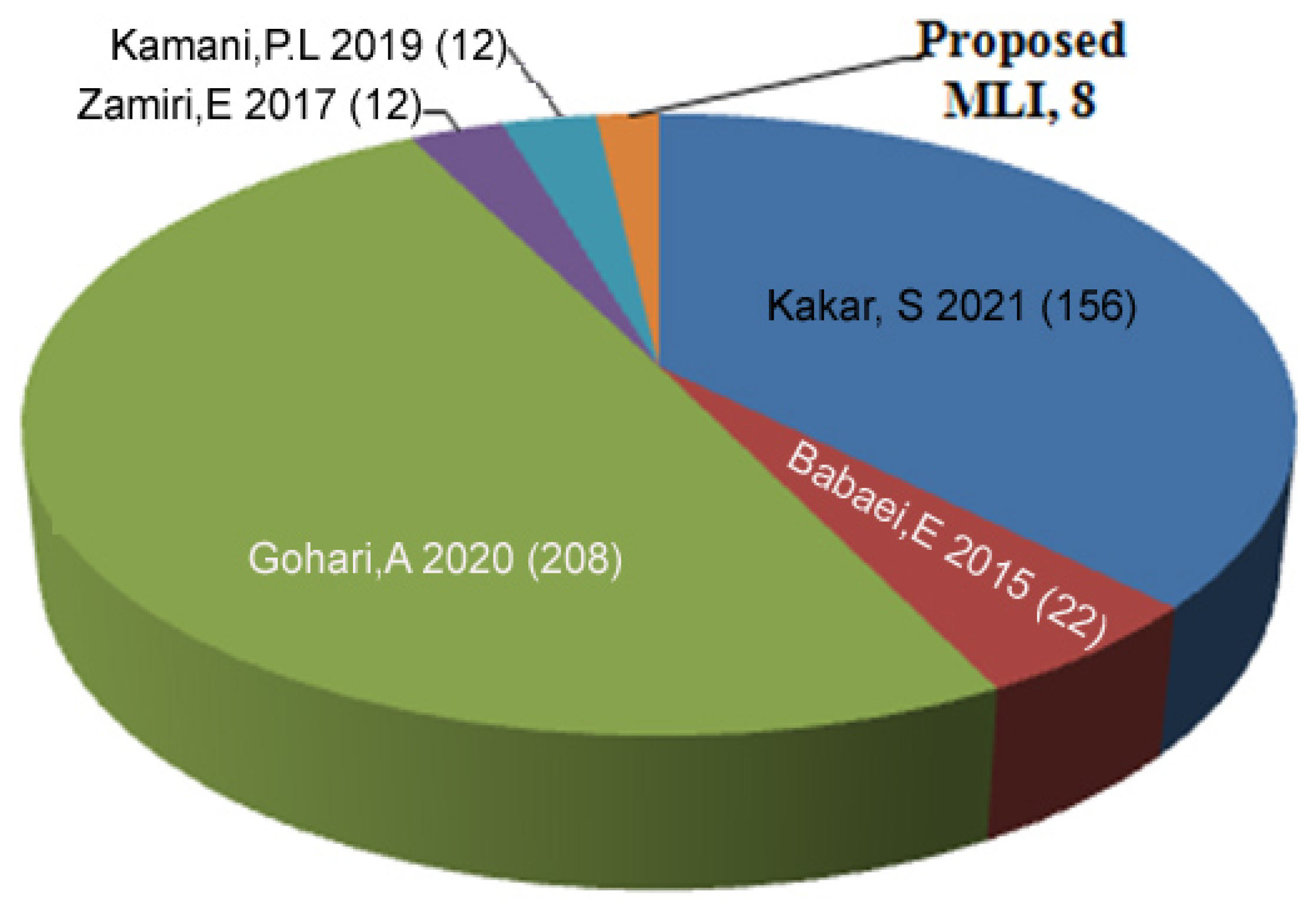
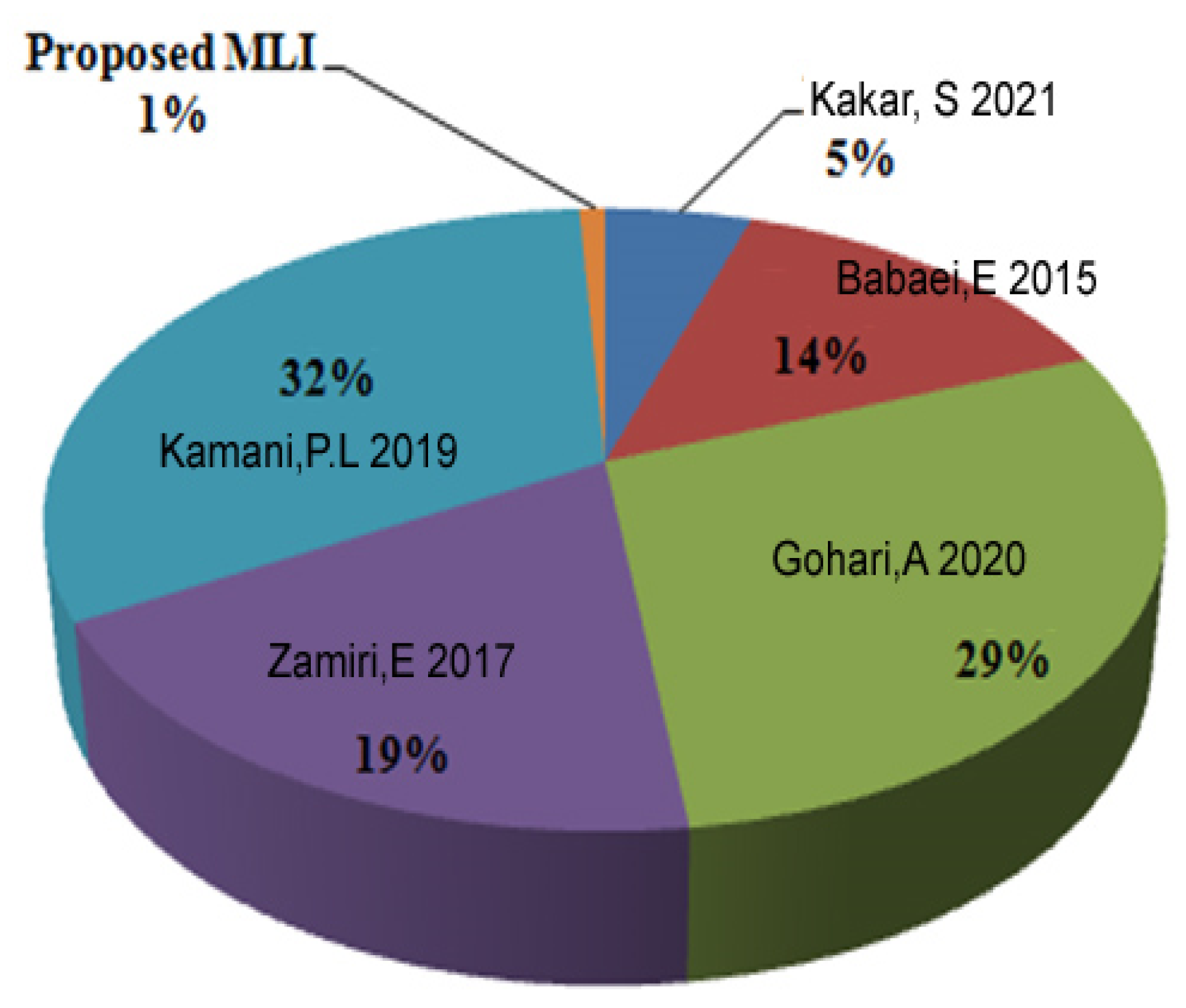


| Algorithm | Voltage Sources Values and Max. Output Voltage | No. of Voltage Levels | Blocking Voltage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed Algorithm 1 | (8 × n) + 1 | 27nVdc | |
| Proposed Algorithm 2 | (12 × n) + 1 | 44nVdc | |
| Proposed Algorithm 3 | 44Vdc; n = 1 [44 + (5 × 2n) + (17 × 2n − 1)] × Vdc; n > 1 | ||
| Proposed Algorithm 4 | 27Vdc; n = 1 27 × [1 + 3n − 1] × Vdc; n > 1 | ||
| Proposed Algorithm 5 | 27Vdc; n = 1 [27 + (22 × 2n] × Vdc; n > 1 | ||
| Proposed Algorithm 6 | 27Vdc; n = 1 [27 + (44 × 3n − 1] × Vdc; n > 1 | ||
| Proposed Algorithm 7 | 34Vdc; n = 1 27 × [1 + 4n − 1] × Vdc; n > 1 | ||
| Proposed Algorithm 8 | [44 × 5n − 1] × Vdc | ||
| Proposed Algorithm 9 | [44 × 7n − 1] × Vdc | ||
| Proposed Algorithm 10 | [95 × 25n − 1] × Vdc |
| Stages | PA3 | PA4 | PA5 | PA6 | PA7 | PA8 | PA9 | PA10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (S = 13) | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = 2Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = 2Vdc | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = Vdc | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = Vdc | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = Vdc | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = Vdc | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = 2Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = 2Vdc | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = 2Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = 2Vdc | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = 5Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = 5Vdc |
| III (S = 39) | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = 2Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = 2Vdc Vd(1,2) = 2Vdc Vd(2,2) = 2Vdc Vd(1,2)’ = 4Vdc Vd(2,2)’ = 4Vdc Vd(1,3) = 4Vdc Vd(2,3) = 4Vdc Vd(1,3)’ = 8Vdc Vd(2,3)’ = 8Vdc | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = 3Vdc Vd(1,2) = 3Vdc Vd(2,2) = 3Vdc Vd(1,2)’ = 3Vdc Vd(2,2)’ = 3Vdc Vd(1,3) = 9Vdc Vd(2,3) = 9Vdc Vd(1,3)’ = 9Vdc Vd(2,3)’ = 9Vdc | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = Vdc Vd(1,2) = 2Vdc Vd(2,2) = 2Vdc Vd(1,2)’ = 4Vdc Vd(2,2)’ = 4Vdc Vd(1,3) = 4Vdc Vd(2,3) = 4Vdc Vd(1,3)’ = 8Vdc Vd(2,3)’ = 8Vdc | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = Vdc Vd(1,2) = 3Vdc Vd(2,2) = 3Vdc Vd(1,2)’ = 6Vdc Vd(2,2)’ = 6Vdc Vd(1,3) = 9Vdc Vd(2,3) = 9Vdc Vd(1,3)’ = 18Vdc Vd(2,3)’ = 18Vdc | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = Vdc Vd(1,2) = 4Vdc Vd(2,2) = 4Vdc Vd(1,2)’ = 4Vdc Vd(2,2)’ = 4Vdc Vd(1,3) = 16Vdc Vd(2,3) = 16Vdc Vd(1,3)’ = 16Vdc Vd(2,3)’ = 16Vdc | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = 2Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = 2Vdc Vd(1,2) = 5Vdc Vd(2,2) = 5Vdc Vd(1,2)’ = 10Vdc Vd(2,2)’ = 10Vdc Vd(1,3) = 25Vdc Vd(2,3) = 25Vdc Vd(1,3)’ = 50Vdc Vd(2,3)’ = 50Vdc | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = 2Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = 2Vdc Vd(1,2) = 7Vdc Vd(2,2) = 7Vdc Vd(1,2)’ = 14Vdc Vd(2,2)’ = 14Vdc Vd(1,3) = 49Vdc Vd(2,3) = 49Vdc Vd(1,3)’ = 98Vdc Vd(2,3)’ = 98Vdc | Vd(1,1) = Vdc Vd(2,1) = Vdc Vd(1,1)’ = 5Vdc Vd(2,1)’ = 5Vdc Vd(1,2) = 25Vdc Vd(2,2) = 25Vdc Vd(1,2)’ = 125Vdc Vd(2,2)’ = 125Vdc Vd(1,3) = 625Vdc Vd(2,3) = 625Vdc Vd(1,3)’ = 3125Vdc Vd(2,3)’ = 3125Vdc |
| Ref. | IGBTs | Gate Drivers | DC Sources | TBV | Levels |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 10n | 9n | 4n | 33n | 16n + 1 |
| 19 | 5n + 6 | 5n + 6 | 3n + 1 | 7(2(n + 2)) − 22 | (2(n + 3)) − 5 |
| 23 | 6n + 8 | 6n + 7 | 4n + 1 | 144n + 12.5 | 12n + 13 |
| 26 | 8n | 8n | 3n | 2(7n − 1) | 7n |
| 28 | 10n | 9n | 4n | 17(15n − 1)/7 | 15n |
| Proposed MLI (PA10) | 13n | 13n | 4n | 95(25(n − 1)) | 25n |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radhakrishnan, A.; Arasan, E.S.; Ramalingam, B.C.; Chandrasekaran, K. A New Asymmetric H-6 Structured Multilevel Inverter with Reduced Power Components. Symmetry 2024, 16, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16010072
Radhakrishnan A, Arasan ES, Ramalingam BC, Chandrasekaran K. A New Asymmetric H-6 Structured Multilevel Inverter with Reduced Power Components. Symmetry. 2024; 16(1):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16010072
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadhakrishnan, Annadurai, Elankurisil S. Arasan, Balamurugan C. Ramalingam, and Kannan Chandrasekaran. 2024. "A New Asymmetric H-6 Structured Multilevel Inverter with Reduced Power Components" Symmetry 16, no. 1: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16010072
APA StyleRadhakrishnan, A., Arasan, E. S., Ramalingam, B. C., & Chandrasekaran, K. (2024). A New Asymmetric H-6 Structured Multilevel Inverter with Reduced Power Components. Symmetry, 16(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16010072







