Two-Dimensional C-V Heat Conduction Investigation of an FG-Finite Axisymmetric Hollow Cylinder
Abstract
1. Introduction
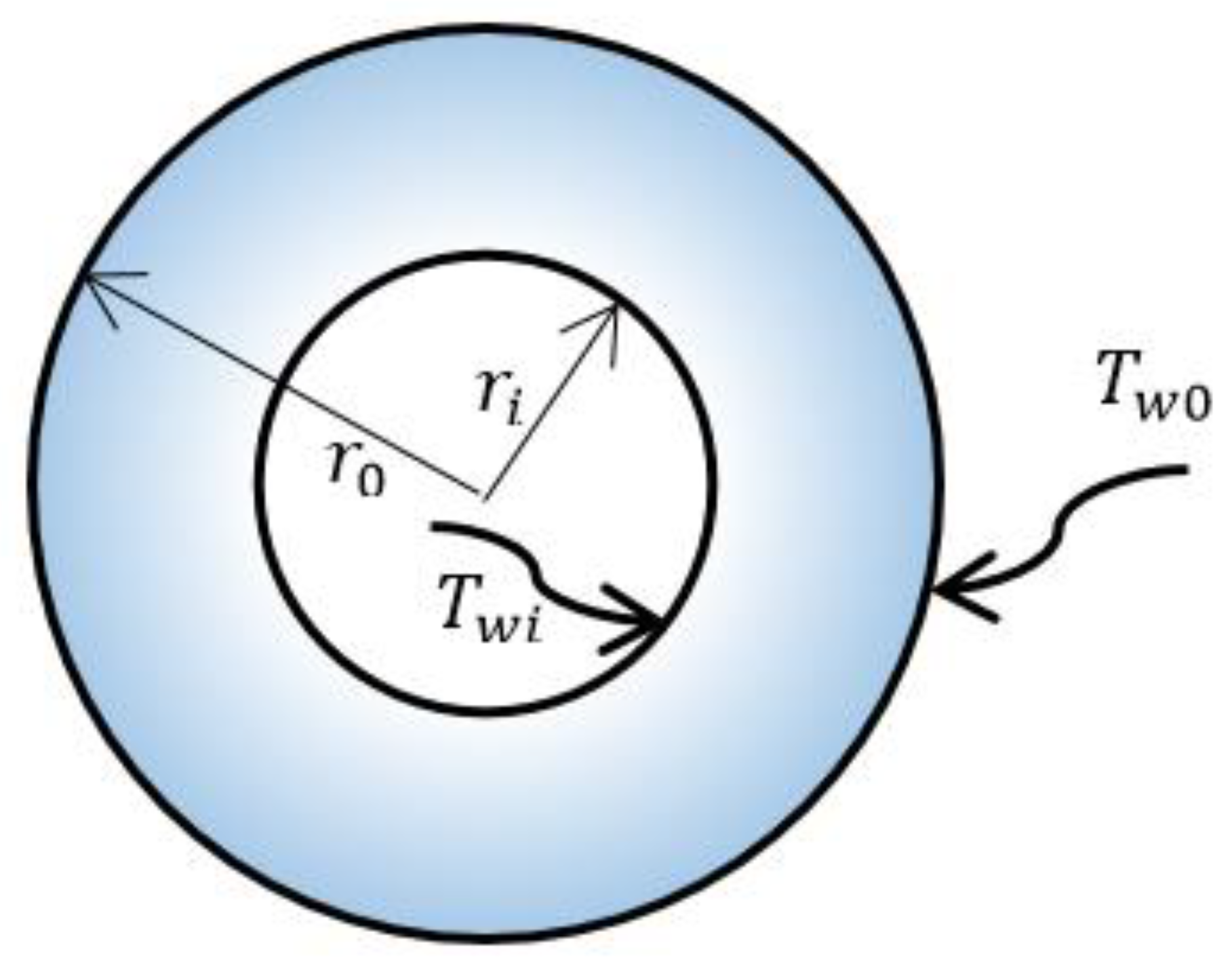
2. Mathematical and Material Models
2.1. FGM Material Distribution
2.2. Numerical Scheme
3. Numerical Results and Discussions
3.1. Example 1: Verification
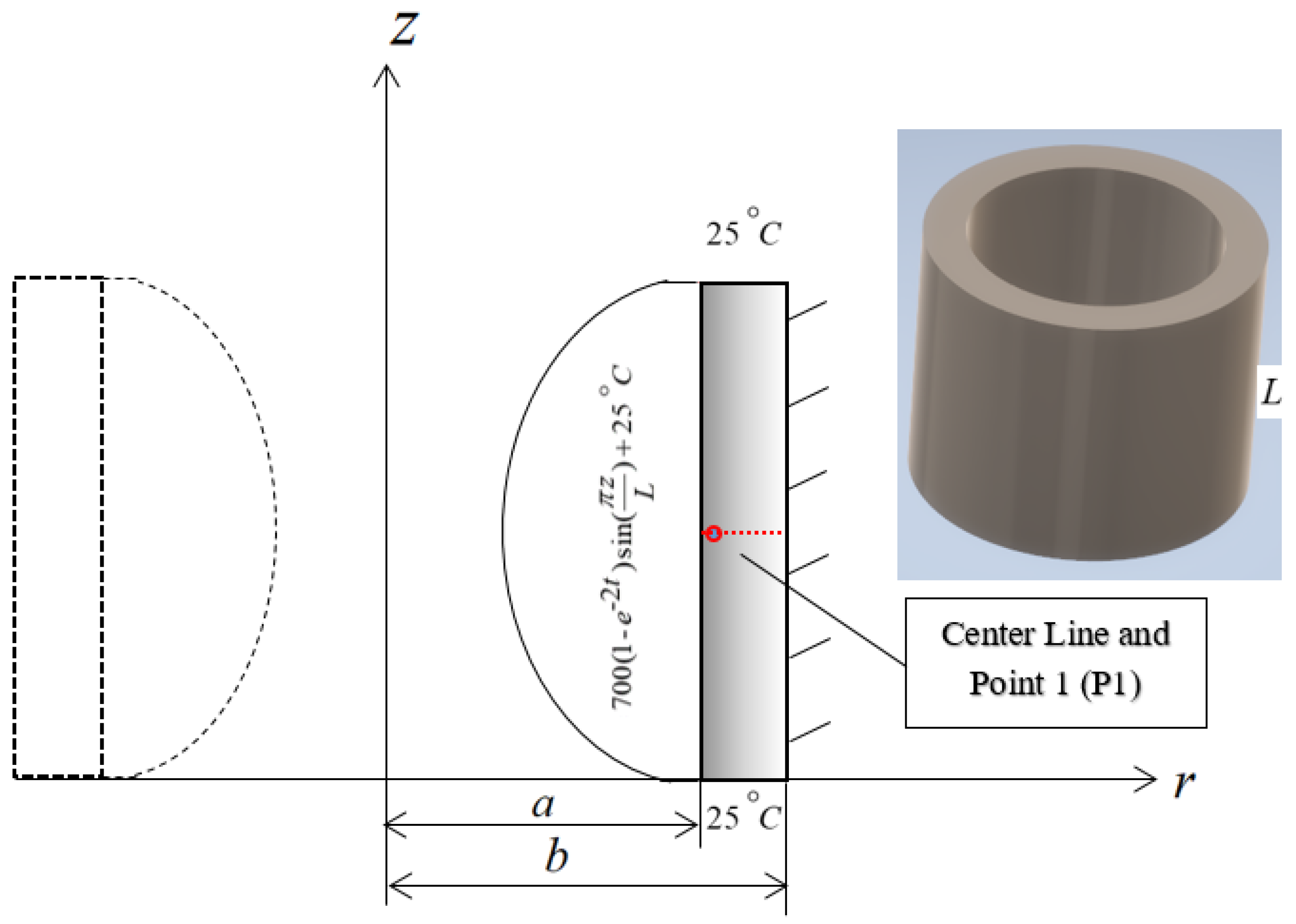
3.2. Example 2: Graded Finite Element Analysis of FG Axisymmetric Cylinder
4. Conclusions
- 1-
- The effective material thermal properties’ gradation, including the thermal relation time, is distributed along the radial direction by the simple rules of the mixture and power-law volume fractions.
- 2-
- Faster temperature wave velocity is related to the homogeneous cylinder wall made of SUS304 in contrast with the ceramic-rich cylinder wall, which is demonstrated to be the slowest one.
- 3-
- For n = 2 and n = 5, there is no difference in the temperature distributions along the radial direction for all Ve numbers.
- 4-
- By increasing the Ve numbers, the temperature waves move slower for all material distributions.
- 5-
- The tuning of the material distribution and, consequently, thermal relaxation time can lead to desirable results for the temperature distribution.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature and Abbreviations
| 1D | One-Dimensional |
| B.C. | Boundary Condition |
| BDF | Backward Difference Formula |
| C-V | Cattaneo–Vernotte |
| DQM | Differential Quadrature Method |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
| FGM | Functionally Graded Material |
| Fo | Fourier Number |
| I.C. | Initial Condition |
| LT | Laplace Transformation |
| SOV | Separation of Variables |
| Ve | Vernotte |
| Degree of Kelvin and Centigrade | |
| Heat Flux | |
| Relaxation Time | |
| Coefficient of Thermal Conductivity | |
| Temperature, and Pulse Peak Temperature | |
| Time | |
| Density | |
| Specific Heat Capacity | |
| Power Exponent | |
| Inner Radius, Outer Radius, and Length of the Cylinder | |
| r and z-direction | |
| Ceramic and Metal Volume Fraction | |
| Effective Material Properties | |
| Second-Sound (temperature) Wave Velocity | |
| Matrix of Quadratic Interpolation Functions | |
| Nodal Temperature | |
| Boundary Flux | |
| Volume | |
| Non-Dimensional Temperature |
References
- Fu, J.; Hu, K.; Qian, L.; Chen, Z. Non-Fourier Heat Conduction of a Functionally Graded Cylinder Containing a Cylindrical Crack. Adv. Math. Phys. 2020, 2020, 8121295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Kaysser, W.A.; Rabin, B.H.; Kawasaki, A.; Ford, R.G. Functionally Graded Materials: Design, Processing and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Mahamood, R.M.; Akinlabi, E.T. Introduction to functionally graded materials. In Functionally Graded Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Han, J. Thermal shock resistance and thermal fracture of a thermopiezoelectric cylinder based on hyperbolic heat conduction. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2020, 230, 107003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, Z. Investigation of the thermal-elastic problem in cracked semi-infinite FGM under thermal shock using hyperbolic heat conduction theory. J. Therm. Stress. 2019, 42, 993–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaeefard, M.H.; Najibi, A. Nonlinear Transient Heat Conduction Analysis for a Thick Hollow 2D-FGM Cylinder with Finite Length. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 9001–9014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaeefard, M.H.; Najibi, A. Nonlinear transient heat conduction analysis of hollow thick temperature-dependent 2D-FGM cylinders with finite length using numerical method. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2014, 28, 3825–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Ma, G. Thermo-mechanical stresses in functionally graded circular hollow cylinder with linearly increasing boundary temperature. Compos. Struct. 2008, 83, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Cui, X.; Li, G.; Feng, H.; Xu, F. Thermo-mechanical analysis of functionally graded cylindrical vessels using edge-based smoothed finite element method. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2013, 111–112, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najibi, A.; Talebitooti, R. Nonlinear transient thermo-elastic analysis of a 2D-FGM thick hollow finite length cylinder. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 111, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najibi, A.; Alizadeh, P.; Ghazifard, P. Transient thermal stress analysis for a short thick hollow FGM cylinder with nonlinear temperature-dependent material properties. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 146, 1971–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-L.; Chang, W.-J.; Sun, S.-H.; Yang, Y.-C. Estimation of temperature distributions and thermal stresses in a functionally graded hollow cylinder simultaneously subjected to inner-and-outer boundary heat fluxes. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosaie, A. A nonlinear analysis of thermal stresses in an incompressible functionally graded hollow cylinder with temperature-dependent material properties. Eur. J. Mech.-A/Solids 2016, 55, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, B. Thermal shock fracture of a cylinder with a penny-shaped crack based on hyperbolic heat conduction. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 91, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, M.H.; Chen, Z. Transient Hyperbolic Heat Conduction in a Functionally Graded Hollow Cylinder. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 2010, 24, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, C. A form of heat-conduction equations which eliminates the paradox of instantaneous propagation. Comptes Rendus 1958, 247, 431. [Google Scholar]
- Vernotee, P. Les Paradoxes de la Theorie Continue de L’equation de la Chaleur. Comput Rendus 1958, 246, 3154. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-L.; Chou, H.-M.; Salazar, J.L.L. Inverse hyperbolic thermoelastic analysis of a functionally graded hollow circular cylinder in estimating surface heat flux and thermal stresses. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 60, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-Y. Direct and inverse solutions of the two-dimensional hyperbolic heat conduction problems. Appl. Math. Model. 2009, 33, 2907–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, M.; Saedodin, S. Analytical and numerical solutions of hyperbolic heat conduction in cylindrical coordinates. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 2011, 25, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbasi, R.; Alaeddin, S.M.; Akbari, M.; Afrand, M. Analytical Solution of Heat Conduction in a Symmetrical Cylinder Using the Solution Structure Theorem and Superposition Technique. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Araki, N. Non-fourier heat conduction in a finite medium under periodic surface thermal disturbance. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1996, 39, 1585–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Alshomrani, A.S.; Muhammad, T.; Anwar, M.S. Entropy analysis in mixed convective flow of hybrid nanofluid subject to melting heat and chemical reactions. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 34, 101972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puneeth, V.; Ali, F.; Khan, M.R.; Anwar, M.S.; Ahammad, N.A. Theoretical analysis of the thermal characteristics of Ree–Eyring nanofluid flowing past a stretching sheet due to bioconvection. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puneeth, V.; Sarpabhushana, M.; Anwar, M.S.; Aly, E.H.; Gireesha, B.J. Impact of bioconvection on the free stream flow of a pseudoplastic nanofluid past a rotating cone. Heat Transf. 2022, 51, 4544–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamood, R.M.; Akinlabi, E.T. Types of functionally graded materials and their areas of application. In Functionally Graded Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Chen, Z.; Qian, L. Coupled thermoelastic analysis of a multi-layered hollow cylinder based on the C–T theory and its application on functionally graded materials. Compos. Struct. 2015, 131, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekzadeh, P.; Haghighi, M.R.G.; Heydarpour, Y. Heat transfer analysis of functionally graded hollow cylinders subjected to an axisymmetric moving boundary heat flux. Numer. Heat Transfer Part A Appl. 2012, 61, 614–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, K.P.; Maiti, D.K. Thermoelastic wave propagation due to local thermal shock on the functionally graded media. J. Therm. Stress. 2022, 45, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Dahab, S.M.; Abouelregal, A.E.; Marin, M. Generalized Thermoelastic Functionally Graded on a Thin Slim Strip Non-Gaussian Laser Beam. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Jain, P.K.; Uddin, R. Analytical solution to transient heat conduction in polar coordinates with multiple layers in radial direction. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2008, 47, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabani, I.; Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Vaidya, H.; Ismail, A. Numerical analysis of magnetic hybrid Nano-fluid natural convective flow in an adjusted porous trapezoidal enclosure. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 564, 170142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, J.; Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Lund, L.A. The flow of magnetised convective Casson liquid via a porous channel with shrinking and stationary walls. Pramana 2022, 96, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Laouira, H.; Hussein, A.K.; Omri, M.; Abderrahmane, A.; Kolsi, L.; Biswal, U. Mixed convection inside a duct with an open trapezoidal cavity equipped with two discrete heat sources and moving walls. Mathematics 2022, 10, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosaie, A. Non-Fourier heat conduction in a finite medium subjected to arbitrary non-periodic surface disturbance. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2008, 35, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.C.; Sahai, H. Analyses of non-Fourier heat conduction in 1-D cylindrical and spherical geometry—An application of the lattice Boltzmann method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 7015–7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nimr, M.A.; Naji, M. The Hyperbolic Heat Conduction Equation in an Anisotropic Material. Int. J. Thermophys. 2000, 21, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.Q.; Hu, C. Thermal waves scattering by a subsurface sphere in a semi-infinite exponentially graded material using non-Fourier’s model. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 453, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, A.H.; Chen, Z.T. Transient Heat Conduction in a Functionally Graded Cylindrical Panel Based on the Dual Phase Lag Theory. Int. J. Thermophys. 2012, 33, 1100–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, R.; Pekel, H. Transient Heat Conduction in Functionally Graded Material Hollow Cylinders by Numerical Method. In Proceedings of the ICOVP-2013—11th International Conference on Vibration Problems, Lisbon, Portugal, 9–12 September 2013; pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Babaei, M.H.; Chen, Z.T. Hyperbolic Heat Conduction in a Functionally Graded Hollow Sphere. Int. J. Thermophys. 2008, 29, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, I.; Conker, C. Transient hyperbolic heat conduction in thick-walled FGM cylinders and spheres with exponentially-varying properties. Eur. J. Mech.-A/Solids 2011, 30, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutradhar, A.; Paulino, G.H.; Gray, L. Transient heat conduction in homogeneous and non-homogeneous materials by the Laplace transform Galerkin boundary element method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2002, 26, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F. Solution and analysis of hyperbolic heat propagation in hollow spherical objects. Heat Mass Transf. 2006, 42, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshjou, K.; Bakhtiari, M.; Parsania, H.; Fakoor, M. Non-Fourier heat conduction analysis of infinite 2D orthotropic FG hollow cylinders subjected to time-dependent heat source. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 98, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Jain, P.K.; Uddin, R. Finite integral transform method to solve asymmetric heat conduction in a multilayer annulus with time-dependent boundary conditions. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2011, 241, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Akhlaghi, M.; Shakeri, M. Transient heat conduction in functionally graded thick hollow cylinders by analytical method. Heat Mass Transf. 2006, 43, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaee, M.R.; Atefi, G. Non-Fourier heat conduction in a finite hollow cylinder with periodic surface heat flux. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2011, 81, 1793–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.H.; Hoseinzadeh, S.; Heyns, P.S.; Wilke, D. Numerical analysis of non-fourier heat transfer in a solid cylinder with dual-phase-lag phenomenon. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2020, 122, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.-T.; Chu, Y.-H. An inverse non-Fourier heat conduction problem approach for estimating the boundary condition in electronic device. Appl. Math. Model. 2004, 28, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, A.; Zanchini, E. Hyperbolic heat conduction and thermal resonances in a cylindrical solid carrying a steady-periodic electric field. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1996, 39, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roetzel, W.; Putra, N.; Das, S.K. Experiment and analysis for non-Fourier conduction in materials with non-homogeneous inner structure. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2003, 42, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, W. Hyperbolic heat conduction equation for materials with a nonhomogeneous inner structure. J. Heat Transf. 1990, 112, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, K.; Kumar, S.; Vedevarz, A.; Moallemi, M.K. Experimental evidence of hyperbolic heat conduction in processed meat. J. Heat Transf. 1995, 117, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graßmann, A.; Peters, F. Experimental investigation of heat conduction in wet sand. Heat Mass Transf. 1999, 35, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwig, H.; Beckert, K. Experimental evidence about the controversy concerning Fourier or non-Fourier heat conduction in materials with a nonhomogeneous inner structure. Heat Mass Transf. 2000, 36, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, D. A review of the models using the Cattaneo and Vernotte hyperbolic heat equation and their experimental validation. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 139, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auriault, J.-L. The paradox of fourier heat equation: A theoretical refutation. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2017, 118, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najibi, A.; Shojaeefard, M.H. Fourier and time-phase-lag heat conduction analysis of the functionally graded porosity media. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 136, 106183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, J.N.; Chin, C.D. Thermomechanical analysis of functionally graded cylinders and plates. J. Therm. Stress. 1998, 21, 593–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.-S. Functionally Graded Materials: Nonlinear Analysis of Plates and Shells; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Wei, X. Heat Conduction: Mathematical Models and Analytical Solutions; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Najibi, A.; Shojaeefard, M.H. Stress wave propagation analysis of 2D-FGM axisymmetric finite hollow thick cylinder. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 2023, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santare, M.H.; Thamburaj, P.; Gazonas, G.A. The use of graded finite elements in the study of elastic wave propagation in continuously nonhomogeneous materials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2003, 40, 5621–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, M.; Hobiny, A.; Abbas, I. Finite Element Analysis of Nonlinear Bioheat Model in Skin Tissue Due to External Thermal Sources. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L.; Taylor, R.L. The Finite Element Method: Solid Mechanics; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2000; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Torabi, M.; Yaghoobi, H.; Boubaker, K. Thermal Analysis of Non-linear Convective–Radiative Hyperbolic Lumped Systems with Simultaneous Variation of Temperature-Dependent Specific Heat and Surface Emissivity by MsDTM and BPES. Int. J. Thermophys. 2013, 34, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Materials/Thermal Properties | |||
| 1.71 | 491 | 5670 | |
| SUS304 | 14.91 | 483 | 7790 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Najibi, A.; Wang, G.-H. Two-Dimensional C-V Heat Conduction Investigation of an FG-Finite Axisymmetric Hollow Cylinder. Symmetry 2023, 15, 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15051009
Najibi A, Wang G-H. Two-Dimensional C-V Heat Conduction Investigation of an FG-Finite Axisymmetric Hollow Cylinder. Symmetry. 2023; 15(5):1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15051009
Chicago/Turabian StyleNajibi, Amir, and Guang-Hui Wang. 2023. "Two-Dimensional C-V Heat Conduction Investigation of an FG-Finite Axisymmetric Hollow Cylinder" Symmetry 15, no. 5: 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15051009
APA StyleNajibi, A., & Wang, G.-H. (2023). Two-Dimensional C-V Heat Conduction Investigation of an FG-Finite Axisymmetric Hollow Cylinder. Symmetry, 15(5), 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15051009






