MS-CANet: Multi-Scale Subtraction Network with Coordinate Attention for Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a new multi-scale subtraction network for fundus retinal image segmentation. By deploying multi-scale subtraction units, complementary information from low-order to high-order among layers can be selectively obtained, thereby comprehensively enhancing the perception of vessels regions.
- We add a residual coordinate attention module in the down-sampling stage of the network to improve the ability of the network to extract features. It reduces the loss of feature information due to pooling layers and captures long-range dependencies along one spatial direction while preserving precise location information along another spatial direction.
- We also design a parallel channel attention module and add it to the up-sample output part. It can activate and restore vessels in retinal images, effectively highlighting the boundary information of vessel ends and small vessels.
2. Methods
2.1. The Network Structure of MS-CANet
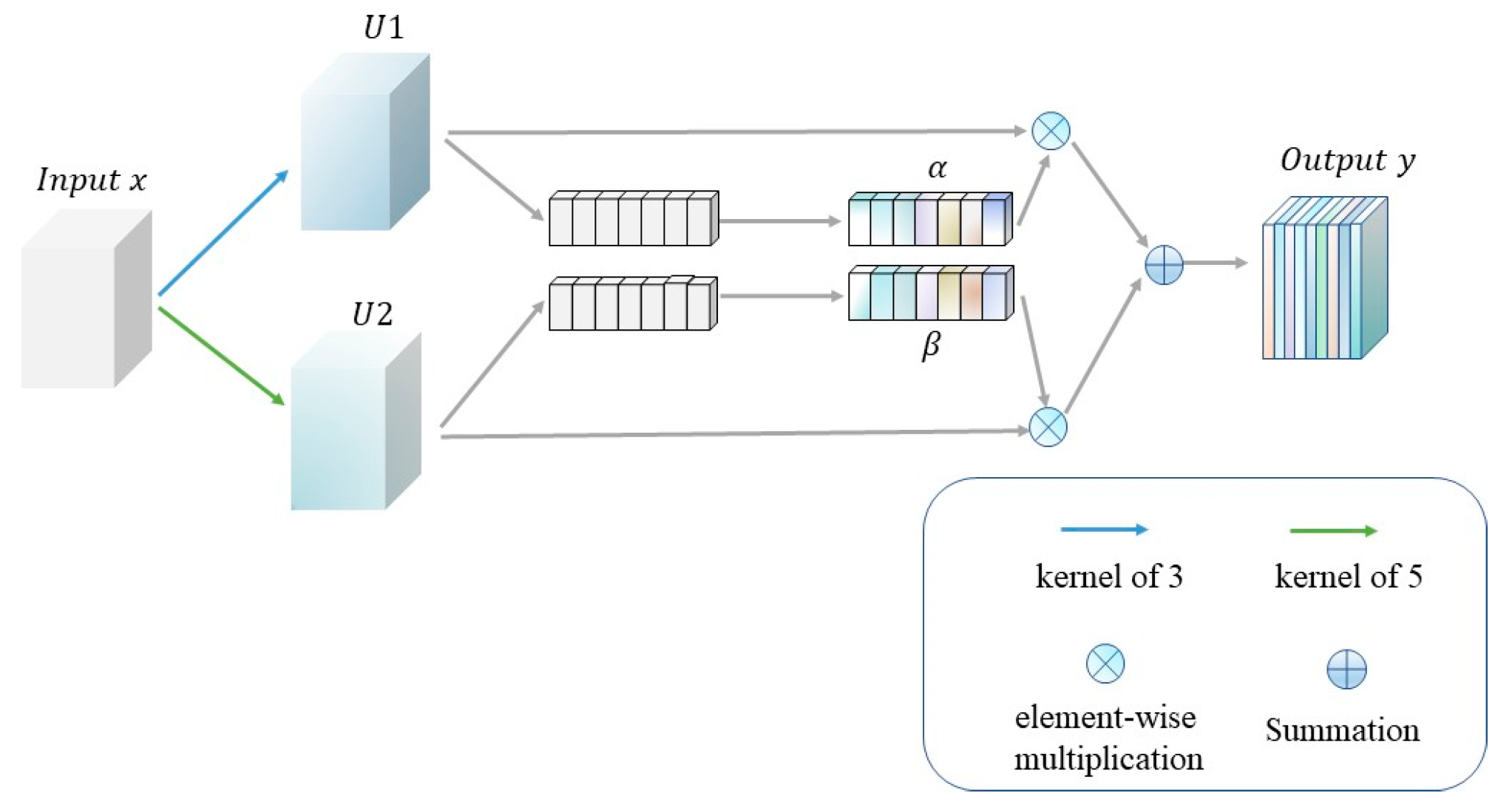
2.2. Residual Coordinate Attention Module
2.3. Multi-Scale Subtraction Units
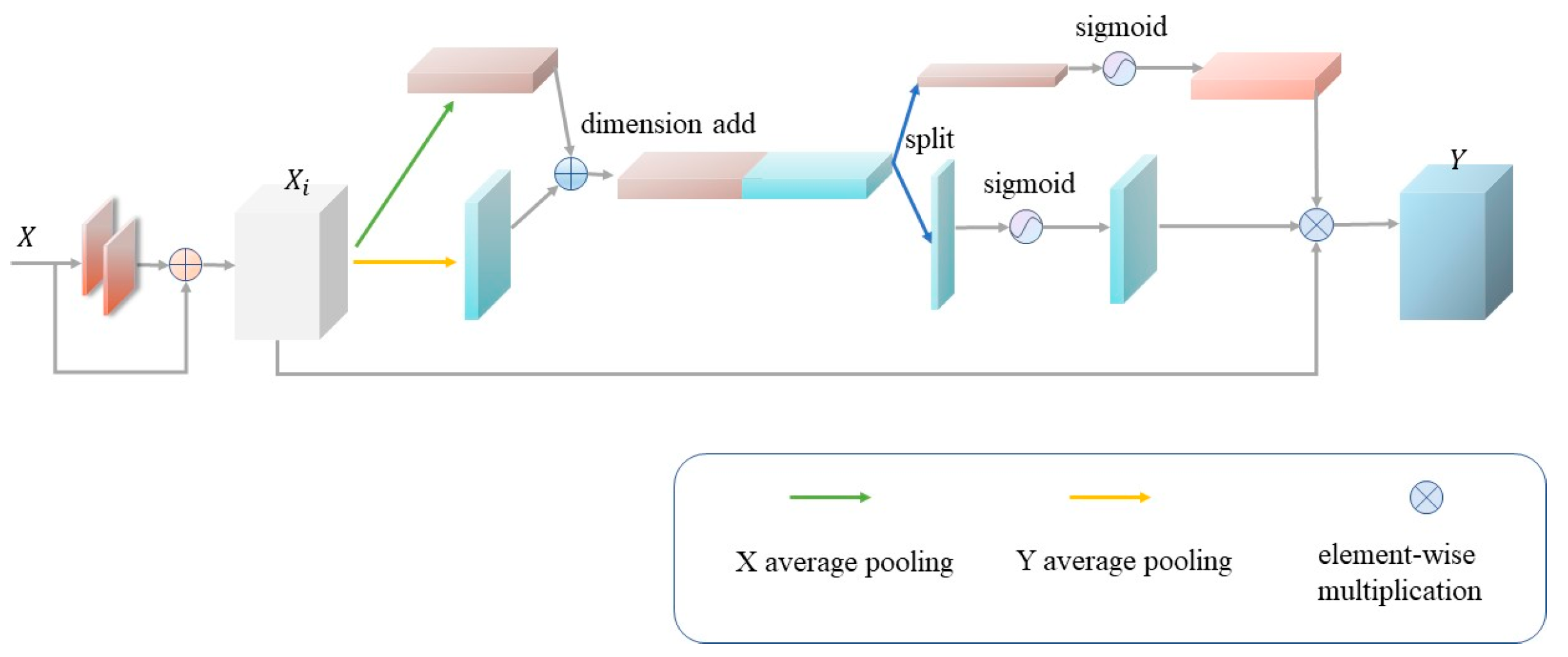
2.4. Parallel Channel Attention Module
3. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
3.1. Datasets
3.2. Implementation Details
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
4. Experiment and Result Analysis
4.1. Structure Ablation
4.2. Attention Module Ablation
4.3. Model Parameter Quantity and Computation Time Analysis
4.4. Comparisons with Other Methods
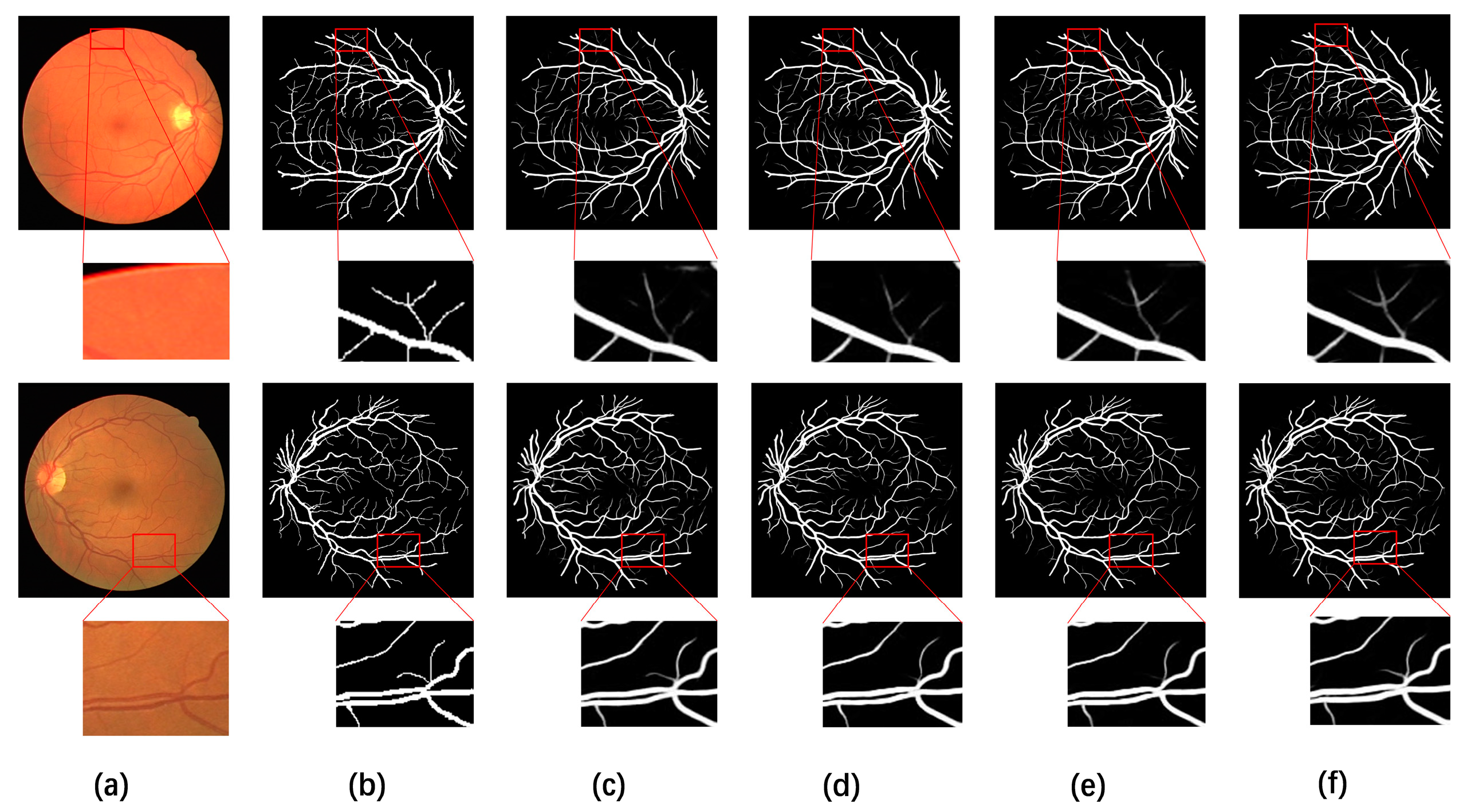
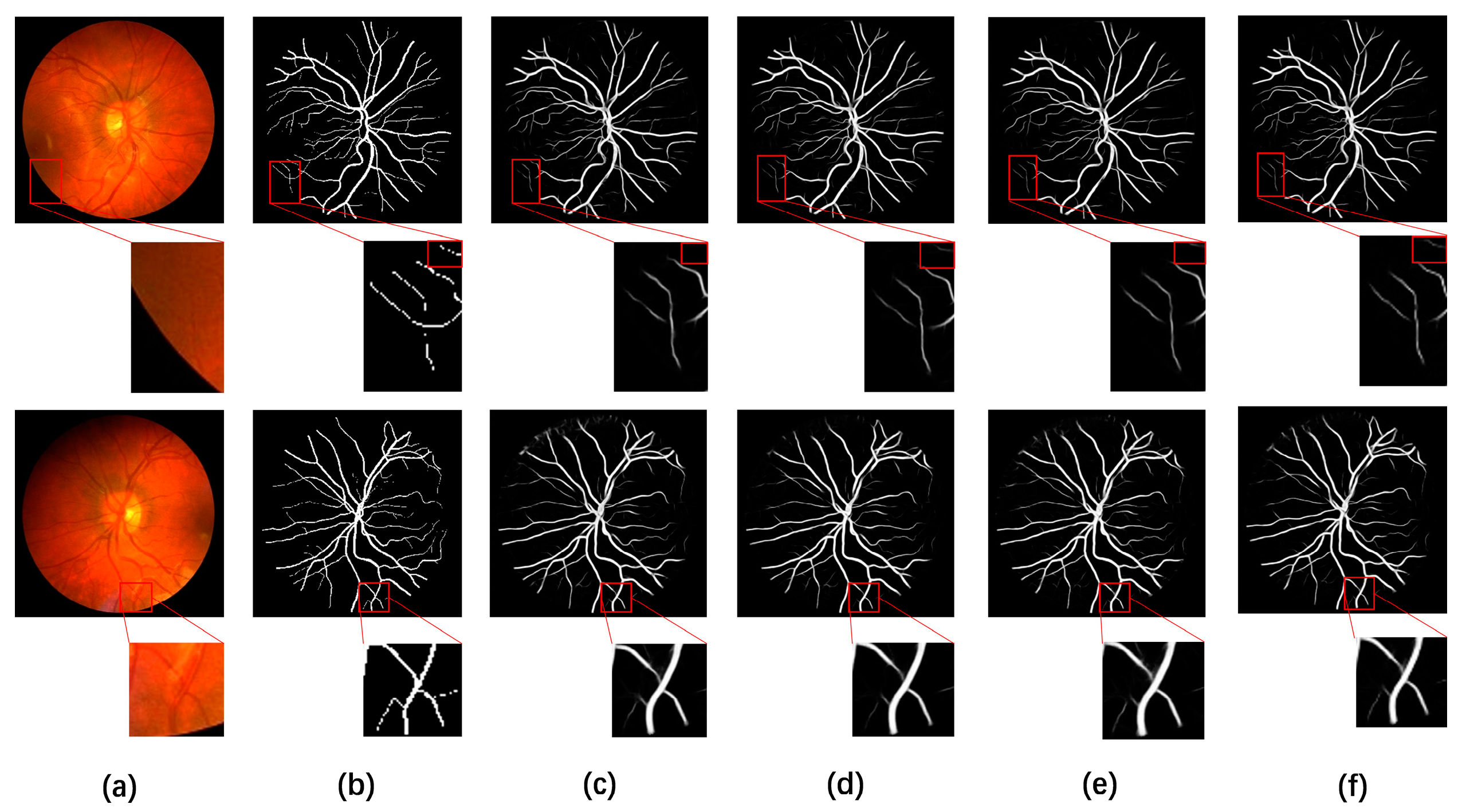
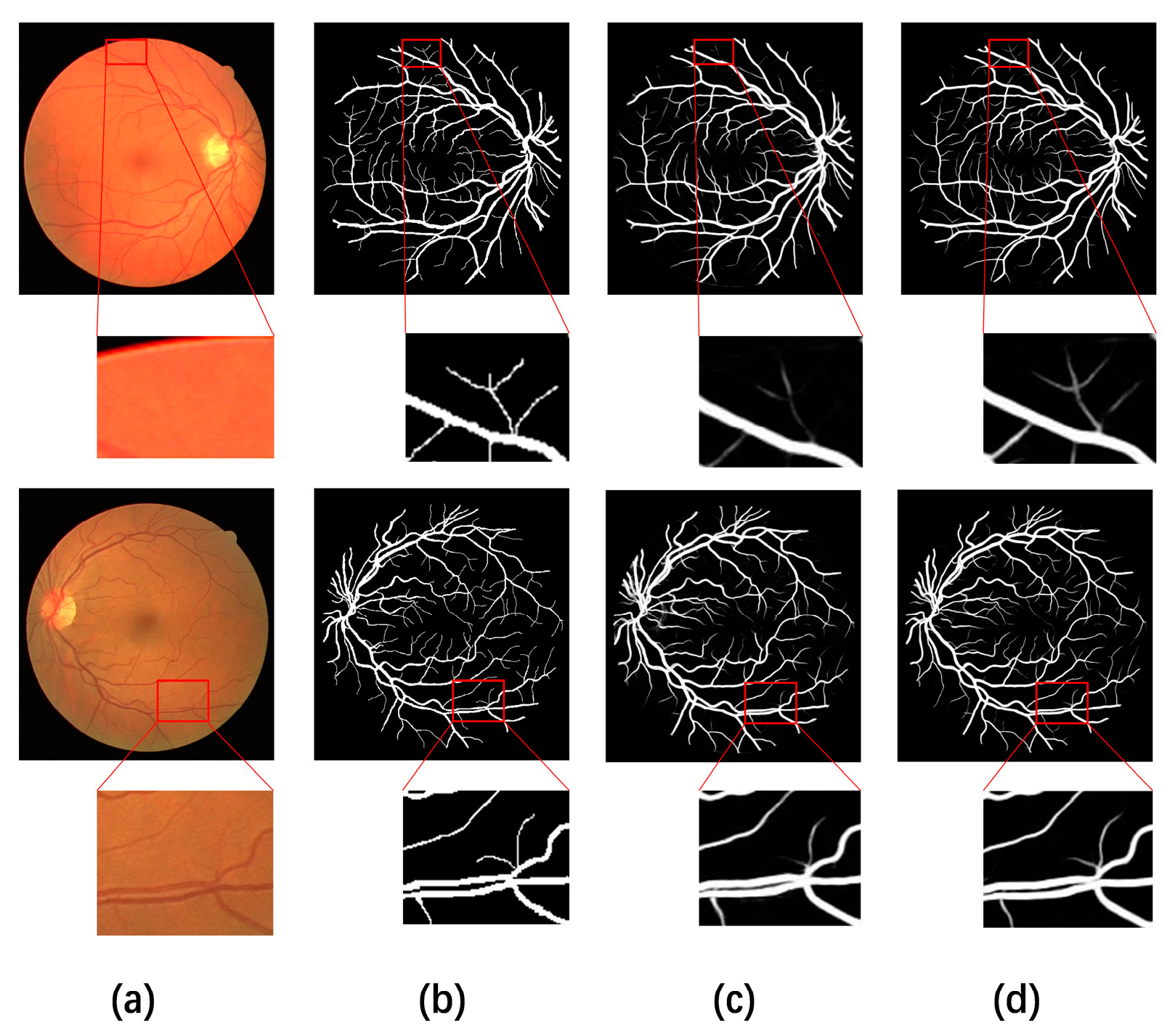
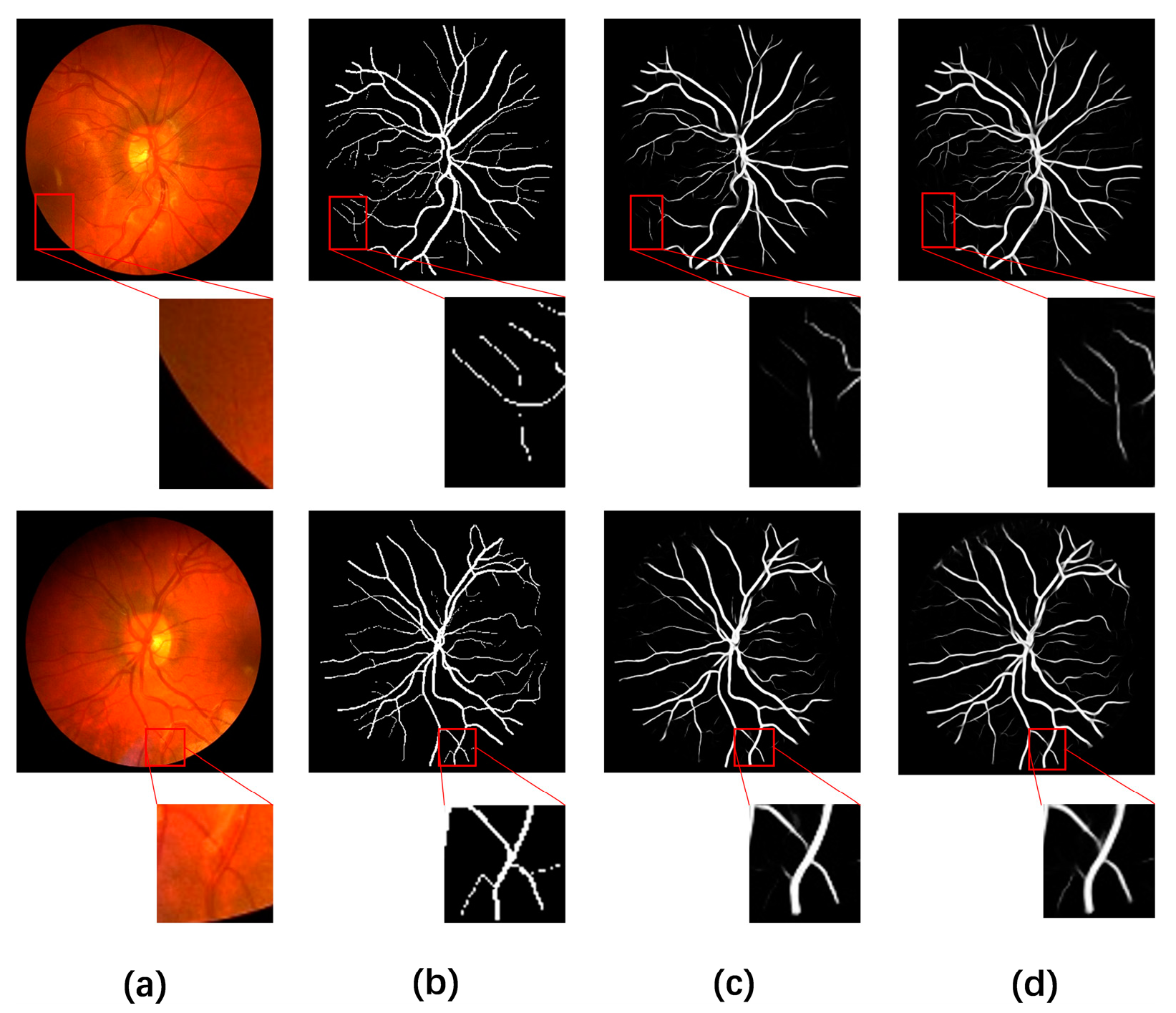
4.5. Visual Comparison with Different Methods
4.6. Robustness Testing
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fong, D.S.; Aiello, L.; Gardner, T.W.; King, G.L.; Blankenship, G.; Cavallerano, J.D.; Ferris, F.L., III; Klein, R. Retinopathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27 (Suppl. S1), s84–s87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, T.J.; Richards, C.J.; Bhatnagar, R.; Pavesio, C.; Agrawal, R.; Jones, P.H. A study of red blood cell deformability in diabetic retinopathy using optical tweezers. Optical trapping and optical micromanipulation XII. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics 2015, 9548, 954825. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Wu, T.; Li, L.; Zhu, C. SUD-GAN: Deep convolution generative adversarial network combined with short connection and dense block for retinal vessel segmentation. Digit. Imaging 2020, 33, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankhead, P.; Scholfield, C.N.; McGeown, J.G.; Curtis, T.M. Fast retinal vessel detection and measurement using wavelets and edge location refinement. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, E.; Perfetti, R. Retinal blood vessel segmentation using line operators and support vector classification. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2007, 26, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Karray, F. Retinal vessel extraction by matched filter with first-order derivative of gaussian. Comput. Biol. Med. 2010, 40, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.H.; Li, X.L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.M. A fuzzy clustering image segmentation algorithm based on hidden Markov random field models and Voronoi tessellation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2017, 85, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filali, H.; Kalti, K. Image segmentation using MRF model optimized by a hybrid ACO-ICM algorithm. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 10181–10204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Muñoz, J.E.; Chowdhury, A.S.; Alexandre, E.B.; Galvão, F.L.; Miranda PA, V.; Falcão, A.X. An iterative spanning forest framework for superpixel segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 3477–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotakis, C.; Papadakis, H.; Grinias, E.; Komodakis, N.; Fragopoulou, P.; Tziritas, G. Interactive image segmentation based on synthetic graph coordinates. Pattern Recognit. 2013, 46, 2940–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucybała, I.; Tabor, Z.; Ciuk, S.; Chrzan, R.; Urbanik, A.; Wojciechowski, W. A fast graph-based algorithm for automated segmentation of subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue in 3D abdominal computed tomography images. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 40, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombini, M.; Solarna, D.; Moser, G.; Dellepiane, S. A goal-driven unsupervised image segmentation method combining graph-based processing and Markov random fields. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 134, 109082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chung, A.C.S. Deep supervision with additional labels for retinal vessel segmentation task. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2018, Granada, Spain, 16–20 September 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Zou, B.; Zhu, C.; Liu, X.; Fu, H.; Wang, L. Multi-Label Classification Scheme Based on Local Regression for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP) 2018, Athens, Greece, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 2765–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W. Multiscale Network Followed Network Model for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, Q.; Chen, F. CTF-Net: Retinal Vessel Segmentation via Deep Coarse-To-Fine Supervision Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Iowa City, IA, USA, 3–7 April 2020; pp. 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, D.; Zhang, C.; Cai, W. Vessel-Net: Retinal Vessel Segmentation Under Multi-path Supervision. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Zhuo, Z.; Pan, D.; Tian, Q. CcNet: A Cross-connected Convolutional Network for Segmenting Retinal Vessels Using Multi-scale Features. Neurocomputing 2019, 392, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, R.; Menaka, R.; Hariharan, M.; Won, D. Ischemic lesion segmentation using ensemble of multi-scale region aligned CNN. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 200, 105831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Pi, D.; Xie, L.; Luo, Y. Multiscale Attentional Residual Neural Network Framework for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Bearings. Measurement 2021, 177, 109310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, J.; Tang, E.; Zheng, S.; Xu, L. Multi-scale attention network for image super-resolution. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2021, 80, 103300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, M.K.; Neog, D.R.; Nath, M.K. Retinal Vessel Segmentation Using Multi-Scale Residual Convolutional Neural Network (MSR-Net) Combined with Generative Adversarial Networks. Circuits Syst. Signal. Process. 2023, 42, 1206–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Automatic Polyp Segmentation via Multi-scale Subtraction Network. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2021; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staal, J.; Abràmoff, M.D.; Niemeijer, M.; Viergever, M.A.; Ginneken, B. Ridge-based vessel segmentation in color images of theretina. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2004, 23, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, C.G.; Rudnicka, A.R.; Mullen, R.; Barman, S.A.; Monekosso, D.; Whincup, P.H.; Ng, J.; Paterson, C. Measuring retinal vessel tortuosity in 10-year-old children: Validation of the computer-assisted image analysis of the retina (CAIAR) program. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 2004–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, A.D.; Kouznetsova, V.; Goldbaum, M. Locating blood vessels in retinal images by piecewise threshold probing of a matched filter response. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2000, 19, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. ECCV 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multi-scale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 39, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alom, M.Z.; Hasan, M.; Yakopcic, C.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Recurrent residual convolutional neural network based on u-net(r2u-net) for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.06955. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Cheng, J.; Gu, Z.; Hao, H.; Qi, H.; Zheng, Y.; Frangi, A.; Liu, J. CS-Net: Channel and spatial attention network for curvilinear structure segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 721–730. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Tan, N.; Peng, T.; Zhang, H. Retinal vessels segmentation based on dilated multi-scale convolutional neural network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 76342–76352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Ma, H.; Li, J.; Liu, S. Attention Guided U-Net With Atrous Convolution for Accurate Retinal Vessels Segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 32826–32839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.M.; Alhussein, M.; Aurangzeb, K.; Arsalan, M.; Naqvi, S.S.; Nawaz, S.J. Residual Connection-Based Encoder Decoder Network (RCED-Net) for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 131257–131272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yao, H.; Wu, C.; Liu, W. A Multi-Scale Residual Attention Network for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. Symmetry 2020, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, G.; Yao, H.X.; Liu, W.H. MFI-Net: A multi-resolution fusion input network for retinal vessel segmentation. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalan, M.; Haider, A.; Lee, Y.W.; Park, K.R. Detecting retinal vasculature as a key biomarker for deep Learning-based intelligent screening and analysis of diabetic and hypertensive retinopathy. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 200, 117009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Meng, Z.; Pham, T.D.; Chen, Q.; Wei, L.; Su, R. DUNet: A deformable network for retinal vessel segmentation. Knowl-Edge-Based Syst. 2019, 178, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laibacher, T.; Weyde, T.; Jalali, S. M2u-net: Effective and efficient retinal vessel segmentation for real world applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Virtual Conference, 19–25 June 2019. [Google Scholar]

| Method | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | F-Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BackBone | 0.9701 | 0.8184 | 0.9874 | 0.8288 |
| BackBone/RCA | 0.9706 | 0.8479 | 0.9846 | 0.8352 |
| BackBone/PCA | 0.9710 | 0.8365 | 0.9864 | 0.8355 |
| BackBone/RCA/PCA | 0.9709 | 0.8432 | 0.9832 | 0.8389 |
| Method | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | F-Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BackBone | 0.9768 | 0.8003 | 0.9877 | 0.8015 |
| BackBone/RCA | 0.9772 | 0.8148 | 0.9885 | 0.8132 |
| BackBone/PCA | 0.9769 | 0.8163 | 0.9888 | 0.8128 |
| BackBone/RCA/PCA | 0.9782 | 0.8306 | 0.9866 | 0.8171 |
| Method | DRIVE | CHASE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROC | PR | ROC | PR | |
| BackBone | 0.9886 | 0.9373 | 0.9874 | 0.8892 |
| BackBone/RCA | 0.9885 | 0.9383 | 0.9880 | 0.8927 |
| BackBone/PCA | 0.9891 | 0.9405 | 0.9876 | 0.8895 |
| BackBone/RCA/PCA | 0.9903 | 0.9441 | 0.9897 | 0.8977 |
| Method | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | F-Measure | ROC | PR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline/ECA | 0.9697 | 0.8613 | 0.9821 | 0.8335 | 0.9883 | 0.9367 |
| Baseline/CBAM | 0.9690 | 0.7912 | 0.9892 | 0.8194 | 0.9881 | 0.9347 |
| Baseline/SE | 0.9713 | 0.8303 | 0.9873 | 0.8356 | 0.9895 | 0.9418 |
| Baseline/PCA | 0.9709 | 0.8432 | 0.9832 | 0.8389 | 0.9903 | 0.9441 |
| Method | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | F-Measure | ROC | PR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline/ECA | 0.9749 | 0.7718 | 0.9886 | 0.7953 | 0.9886 | 0.8726 |
| Baseline/CBAM | 0.9712 | 0.6076 | 0.9957 | 0.7272 | 0.9885 | 0.8209 |
| Baseline/SE | 0.9751 | 0.8096 | 0.9862 | 0.8038 | 0.9886 | 0.8819 |
| Baseline/PCA | 0.9782 | 0.8306 | 0.9866 | 0.8171 | 0.9897 | 0.8977 |
| Method | Year | F-Measure | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNet++ [32] | 2018 | 0.8302 | 0.9701 | 0.8120 | 0.9861 |
| R2U-Net [33] | 2018 | 0.8171 | 0.9556 | 0.7792 | 0.9813 |
| CSNet [34] | 2019 | - | 0.9632 | 0.8170 | 0.9854 |
| Vessel-Net [18] | 2019 | - | 0.9578 | 0.8038 | 0.9802 |
| D-Net [35] | 2019 | 0.8246 | 0.9709 | 0.7839 | 0.9890 |
| CTF-Net [17] | 2020 | 0.8241 | 0.9567 | 0.7849 | 0.9813 |
| AA-UNet [36] | 2020 | 0.8216 | 0.9558 | - | - |
| RCED-Net [37] | 2021 | - | 0.9649 | 0.8252 | 0.9787 |
| MRA-UNet [38] | 2021 | 0.8293 | 0.9698 | 0.8353 | 0.9828 |
| MFI-Net [39] | 2021 | 0.8318 | 0.9708 | 0.8325 | 0.9838 |
| PLRS-Net [40] | 2022 | - | 0.9682 | 0.8269 | 0.9817 |
| Ours | 2022 | 0.8389 | 0.9709 | 0.8432 | 0.9832 |
| Method | Year | F-Measure | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNet++ [32] | 2018 | 0.8139 | 0.9760 | 0.8184 | 0.9810 |
| R2U-Net [33] | 2018 | 0.7928 | 0.9634 | 0.7756 | 0.9820 |
| Vessel-Net [18] | 2019 | - | 0.9661 | 0.8132 | 0.9814 |
| D-Net [35] | 2019 | 0.8062 | 0.9721 | 0.7839 | 0.9894 |
| D-UNet [41] | 2019 | 0.7883 | 0.9610 | - | - |
| M2UNet [42] | 2019 | - | 0.9703 | - | - |
| AA-UNet [36] | 2020 | 0.7892 | 0.9608 | - | - |
| RCED-Net [37] | 2021 | - | 0.9772 | 0.8440 | 0.8440 |
| MRA-UNet [38] | 2021 | 0.8127 | 0.9758 | 0.8324 | 0.9854 |
| MFI-Net [39] | 2021 | 0.8150 | 0.9762 | 0.8309 | 0.9860 |
| PLRS-Net [40] | 2022 | - | 0.9731 | 0.8301 | 0.9893 |
| Ours | 2022 | 0.8171 | 0.9782 | 0.8306 | 0.9866 |
| Method | Year | F-Measure | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNet++ [32] | 2018 | 0.8393 | 0.9753 | 0.8646 | 0.9843 |
| R2U-Net [33] | 2018 | 0.8475 | 0.9712 | 0.8298 | 0.9862 |
| CSNet [34] | 2019 | - | 0.9752 | 0.8816 | 0.9840 |
| D-UNet [41] | 2019 | 0.8143 | 0.9641 | - | - |
| AA-UNet [36] | 2020 | 0.8142 | 0.9640 | - | - |
| RCED-Net [37] | 2021 | - | 0.9659 | 0.8397 | 0.9792 |
| MRA-UNet [38] | 2021 | 0.8422 | 0.9763 | 0.8422 | 0.9873 |
| MFI-Net [39] | 2021 | 0.8483 | 0.9766 | 0.8619 | 0.9859 |
| PLRS-Net [40] | 2022 | - | 0.9715 | 0.8635 | 0.9803 |
| Ours | 2022 | 0.8500 | 0.9772 | 0.8645 | 0.9863 |
| Image | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | F-Measure | ROC | PR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.9771 | 0.8234 | 0.9881 | 0.8278 | 0.9883 | 0.9096 |
| 2 | 0.9799 | 0.8793 | 0.9863 | 0.8401 | 0.9939 | 0.9320 |
| 3 | 0.9803 | 0.8754 | 0.9870 | 0.8422 | 0.9935 | 0.9308 |
| 4 | 0.9651 | 0.8169 | 0.9798 | 0.8088 | 0.9869 | 0.8965 |
| 5 | 0.9745 | 0.9012 | 0.9800 | 0.8315 | 0.9929 | 0.9273 |
| 6 | 0.9790 | 0.9064 | 0.9854 | 0.8741 | 0.9947 | 0.9483 |
| 7 | 0.9791 | 0.8452 | 0.9899 | 0.8581 | 0.9935 | 0.9404 |
| 8 | 0.9843 | 0.8968 | 0.9918 | 0.9001 | 0.9970 | 0.9695 |
| 9 | 0.9765 | 0.8407 | 0.9884 | 0.8521 | 0.9931 | 0.9365 |
| 10 | 0.9806 | 0.8761 | 0.9886 | 0.8657 | 0.9951 | 0.9467 |
| 11 | 0.9816 | 0.9425 | 0.9849 | 0.8882 | 0.9967 | 0.9645 |
| 12 | 0.9796 | 0.8976 | 0.9876 | 0.8869 | 0.9955 | 0.9607 |
| 13 | 0.9790 | 0.8948 | 0.9874 | 0.8855 | 0.9950 | 0.9600 |
| 14 | 0.9776 | 0.8717 | 0.9876 | 0.8707 | 0.9938 | 0.9459 |
| 15 | 0.9650 | 0.8404 | 0.9791 | 0.8307 | 0.9859 | 0.9136 |
| 16 | 0.9761 | 0.8701 | 0.9865 | 0.8671 | 0.9934 | 0.9466 |
| 17 | 0.9850 | 0.8623 | 0.9915 | 0.8537 | 0.9930 | 0.9311 |
| 18 | 0.9838 | 0.8087 | 0.9917 | 0.8119 | 0.9925 | 0.8990 |
| 19 | 0.9701 | 0.8129 | 0.9813 | 0.7843 | 0.9875 | 0.8651 |
| 20 | 0.9713 | 0.8284 | 0.9837 | 0.8219 | 0.9891 | 0.9078 |
| Average | 0.9772 | 0.8645 | 0.9863 | 0.8500 | 0.9925 | 0.9315 |
| F-Measure | Accuracy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRIVE | CHASE | STARE | DRIVE | CHASE | STARE | |
| DRIVE | 0.8389 | 0.5482 | 0.7826 | 0.9709 | 0.9541 | 0.9673 |
| CHASE | 0.6849 | 0.8171 | 0.7952 | 0.9648 | 0.9782 | 0.9716 |
| STARE | 0.8035 | 0.6521 | 0.8500 | 0.9701 | 0.9648 | 0.9772 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Yan, W.; Chen, J.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M. MS-CANet: Multi-Scale Subtraction Network with Coordinate Attention for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. Symmetry 2023, 15, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15040835
Jiang Y, Yan W, Chen J, Qiao H, Zhang Z, Wang M. MS-CANet: Multi-Scale Subtraction Network with Coordinate Attention for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. Symmetry. 2023; 15(4):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15040835
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yun, Wei Yan, Jie Chen, Hao Qiao, Zequn Zhang, and Meiqi Wang. 2023. "MS-CANet: Multi-Scale Subtraction Network with Coordinate Attention for Retinal Vessel Segmentation" Symmetry 15, no. 4: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15040835
APA StyleJiang, Y., Yan, W., Chen, J., Qiao, H., Zhang, Z., & Wang, M. (2023). MS-CANet: Multi-Scale Subtraction Network with Coordinate Attention for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. Symmetry, 15(4), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15040835






