Nonlinear Adaptive Fuzzy Control Design for Wheeled Mobile Robots with Using the Skew Symmetrical Property
Abstract
1. Introduction
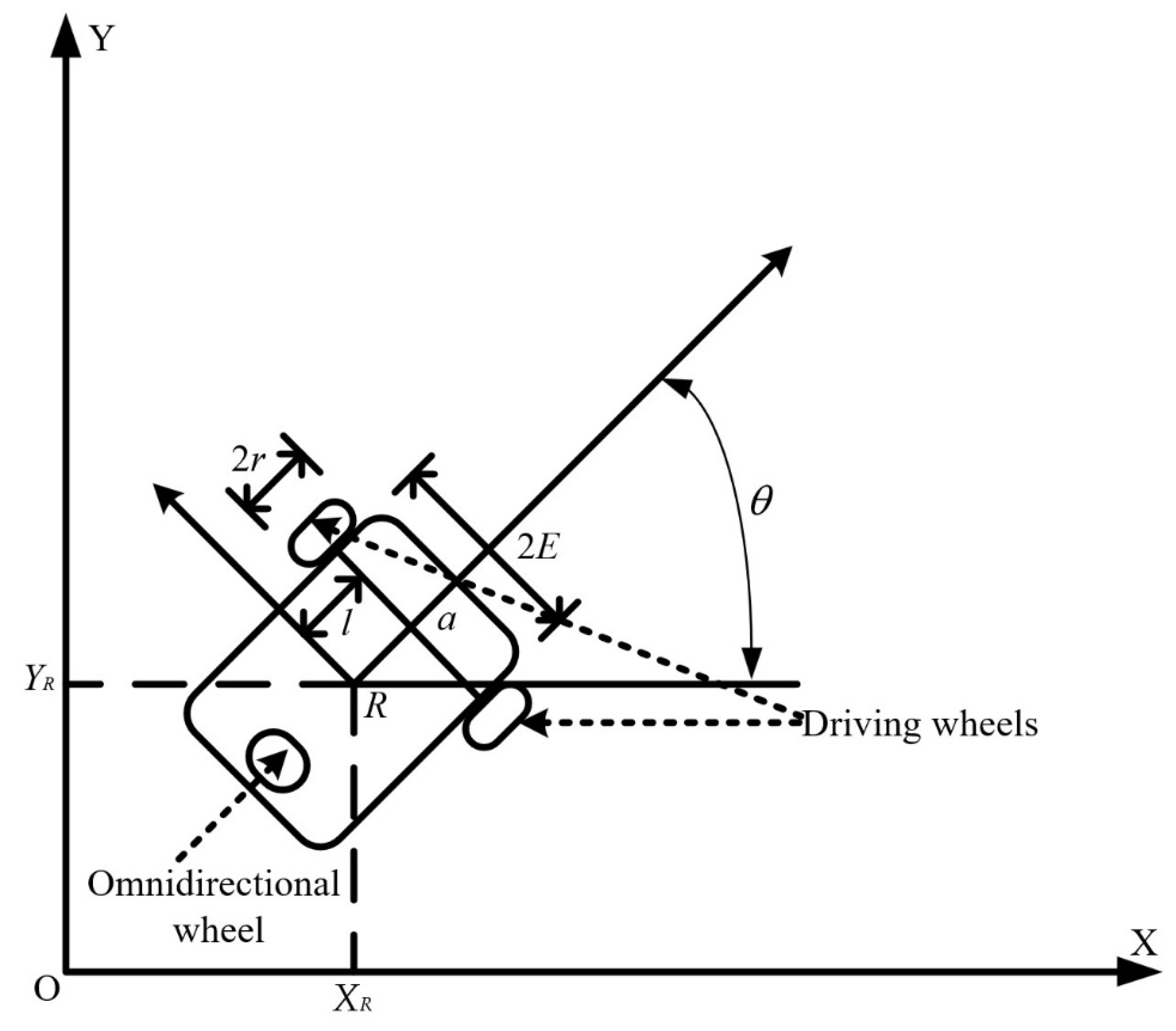
2. Wheeled Mobile Robot Dynamics
2.1. Wheeled Mobile Robot Dynamics
2.2. The Mathematical Model of Trajectory Tracking Error Dynamics
3. Adaptive Fuzzy with H2 Control Design
3.1. Adaptive Fuzzy with H2 Trajectory Tracking Problem for WMR
3.2. Analytical Solution of Adaptive Fuzzy with H2 Trajectory Tracking Problem
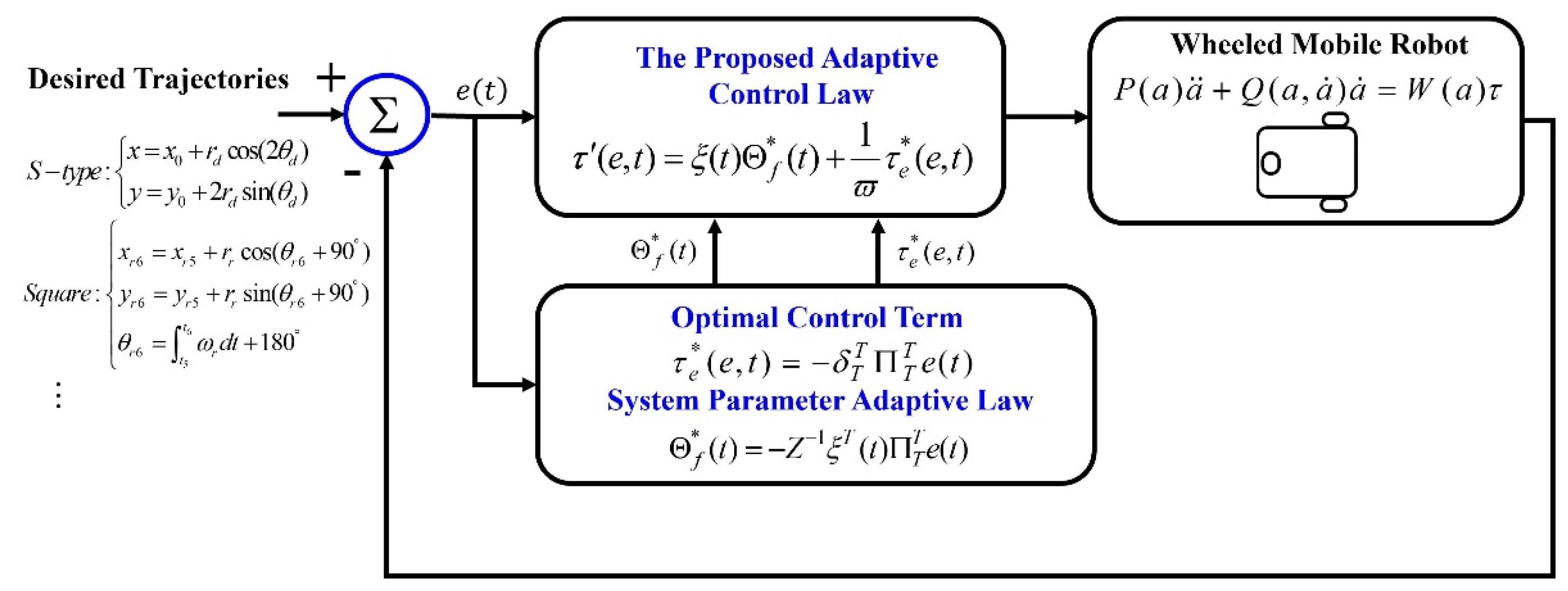
3.3. Closed-Loop Control Diagram of This Proposed Method
4. Verification Results
4.1. Verification Environment Configuration
4.2. The Fuzzy Logic System Definition
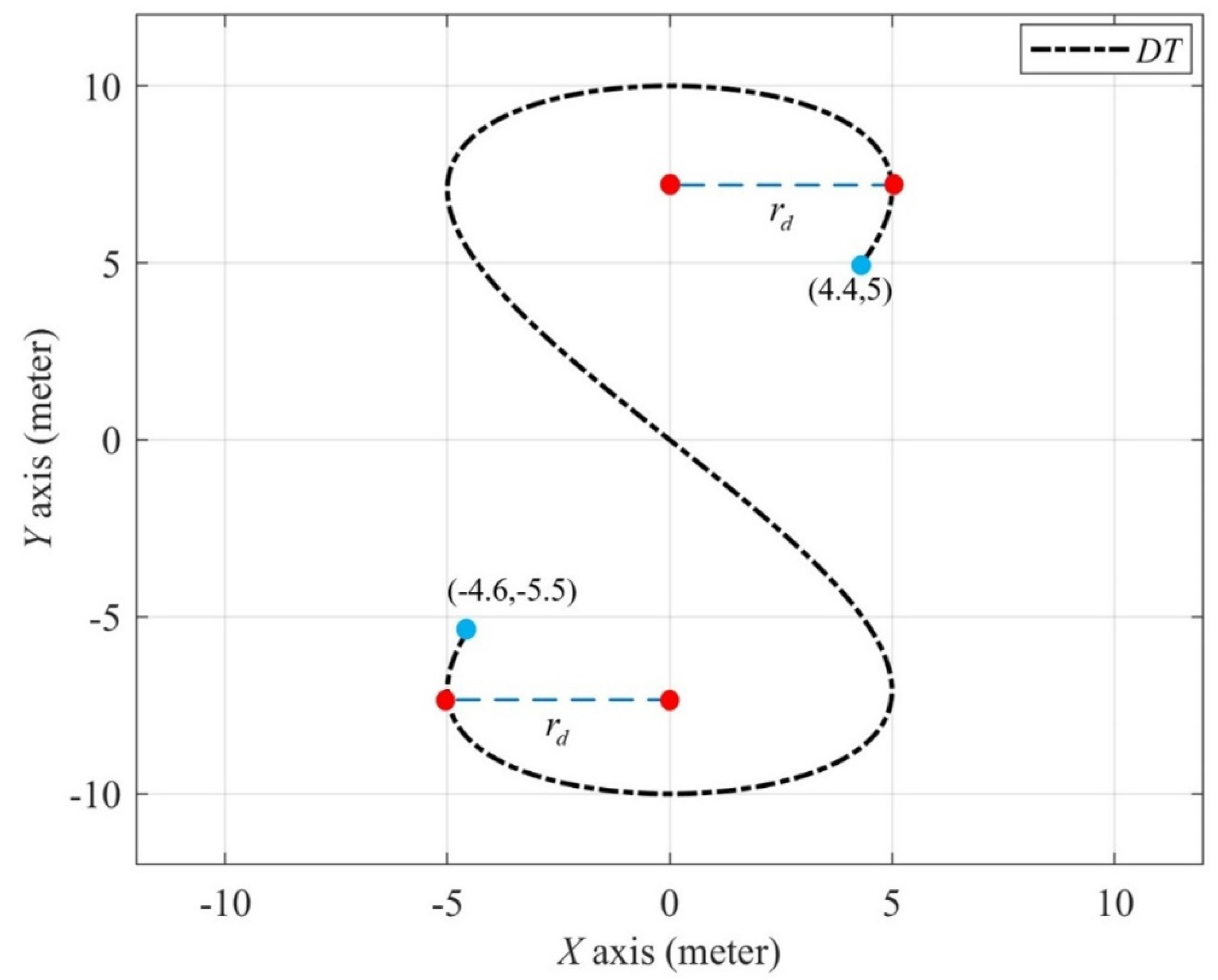
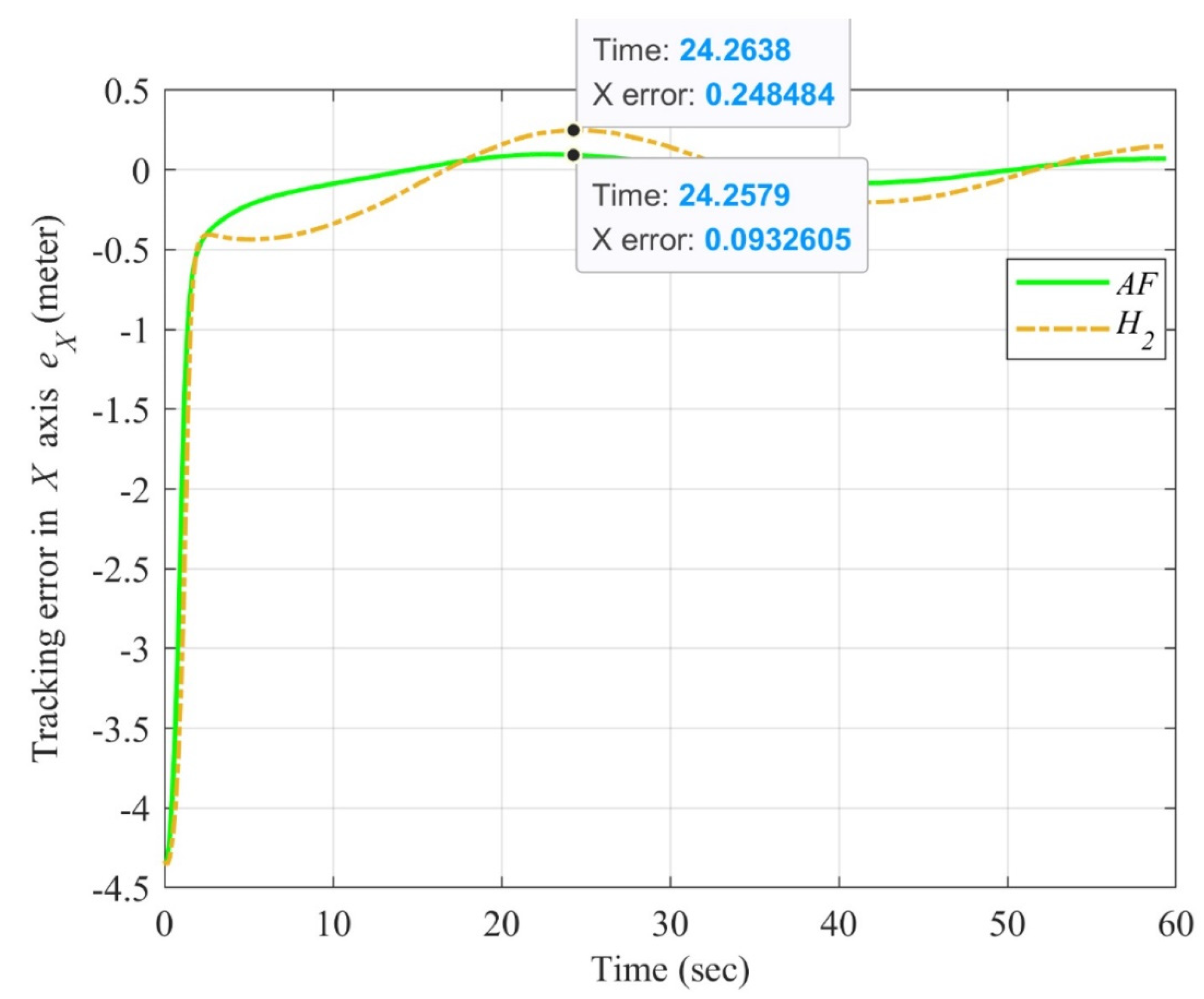
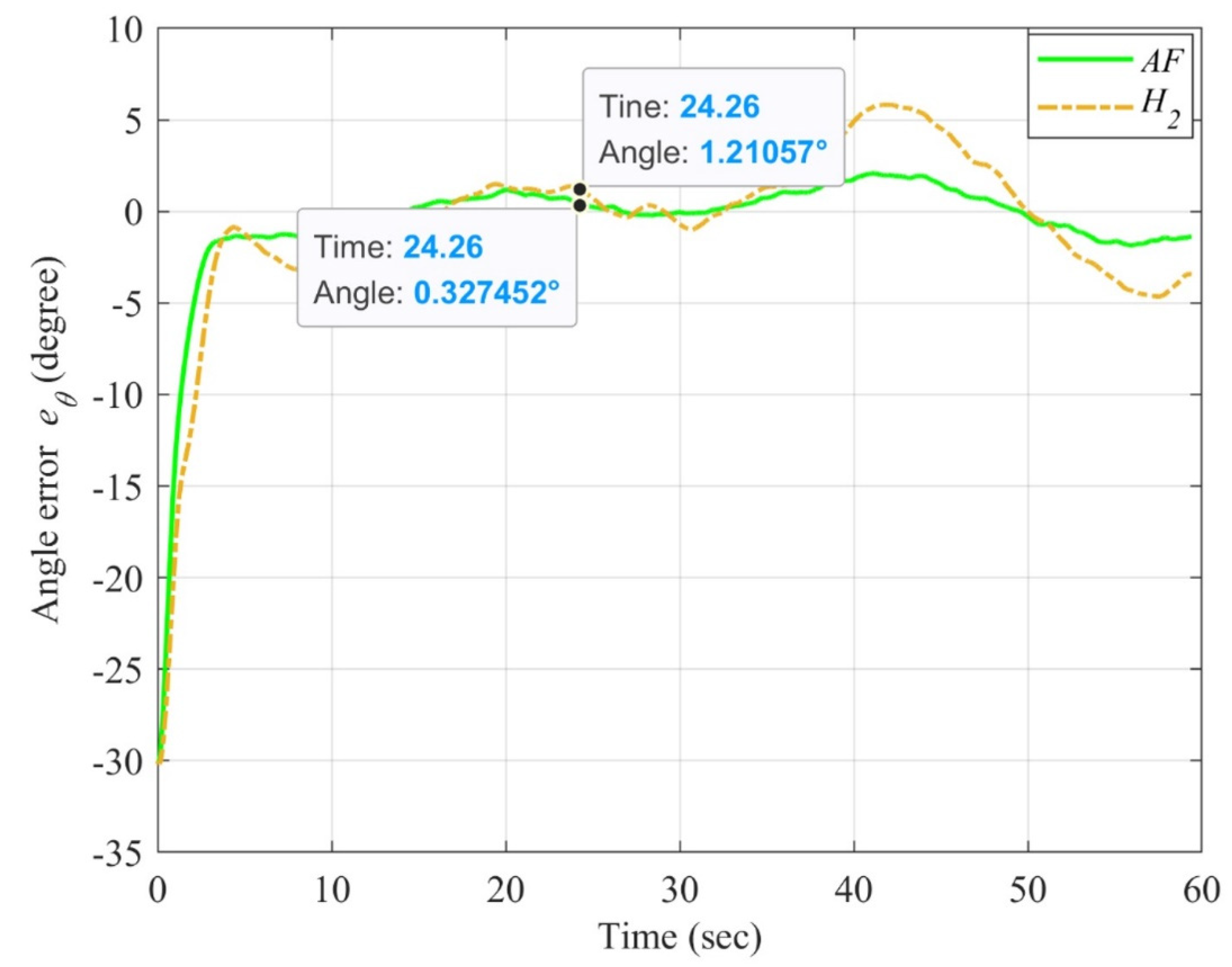
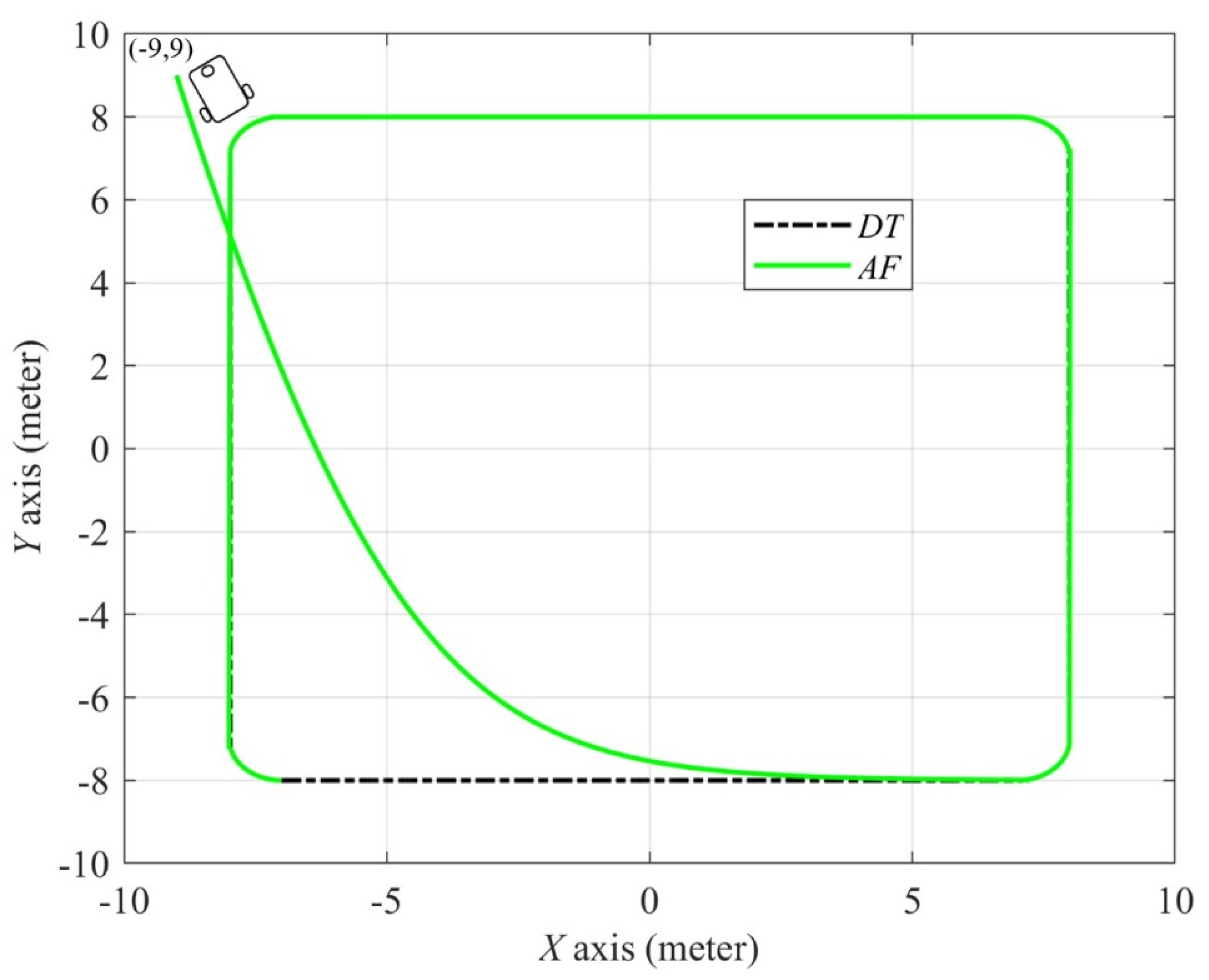
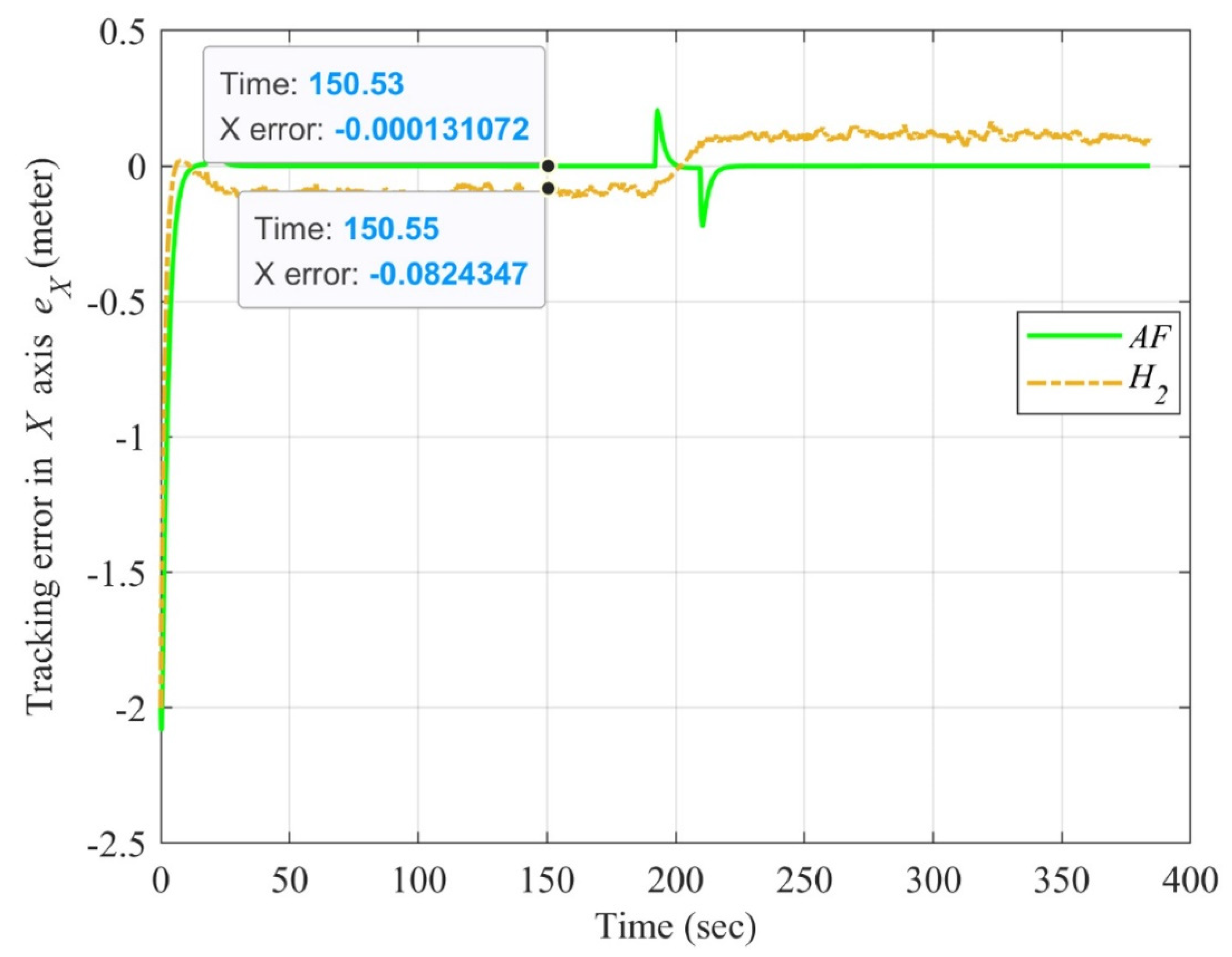
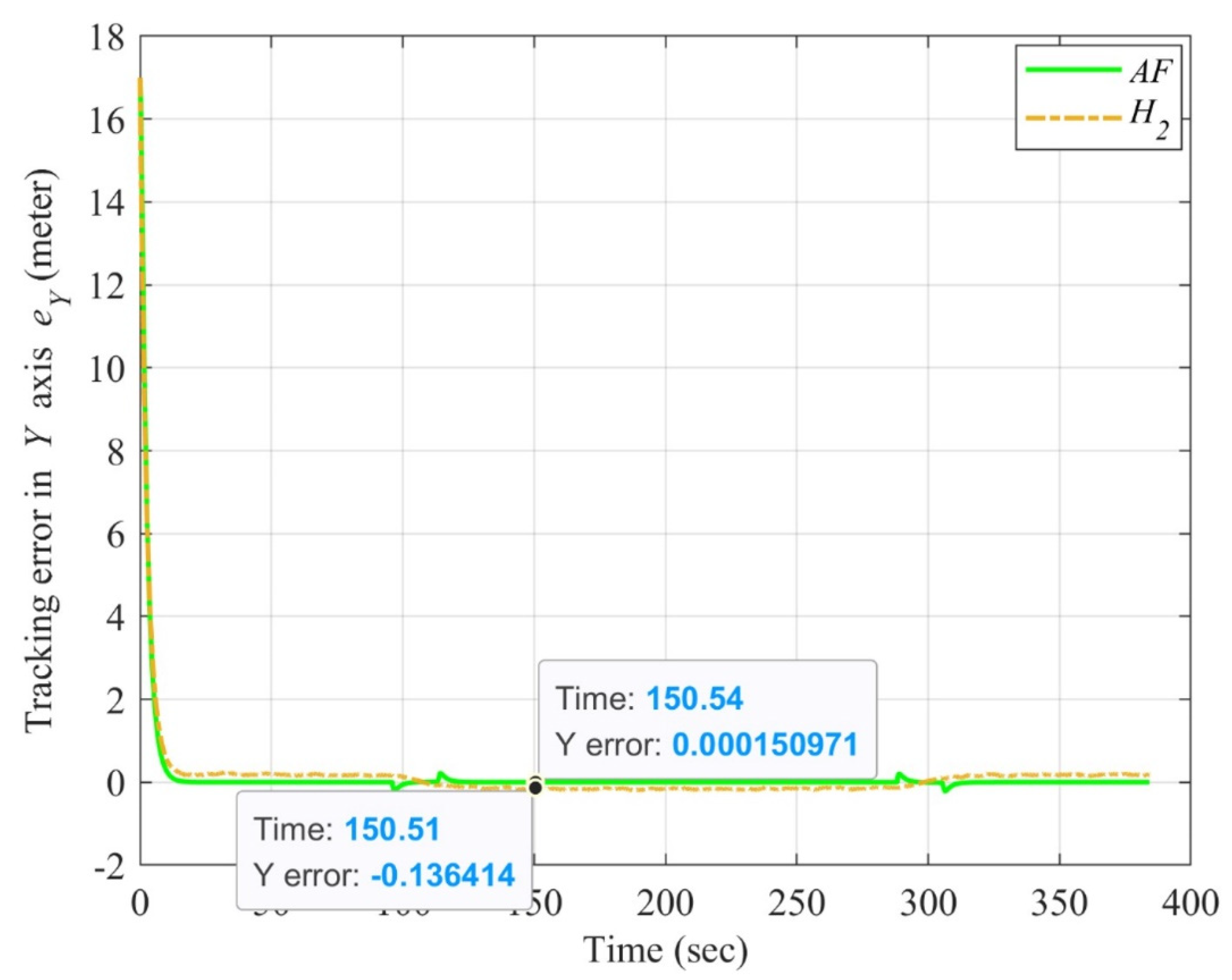
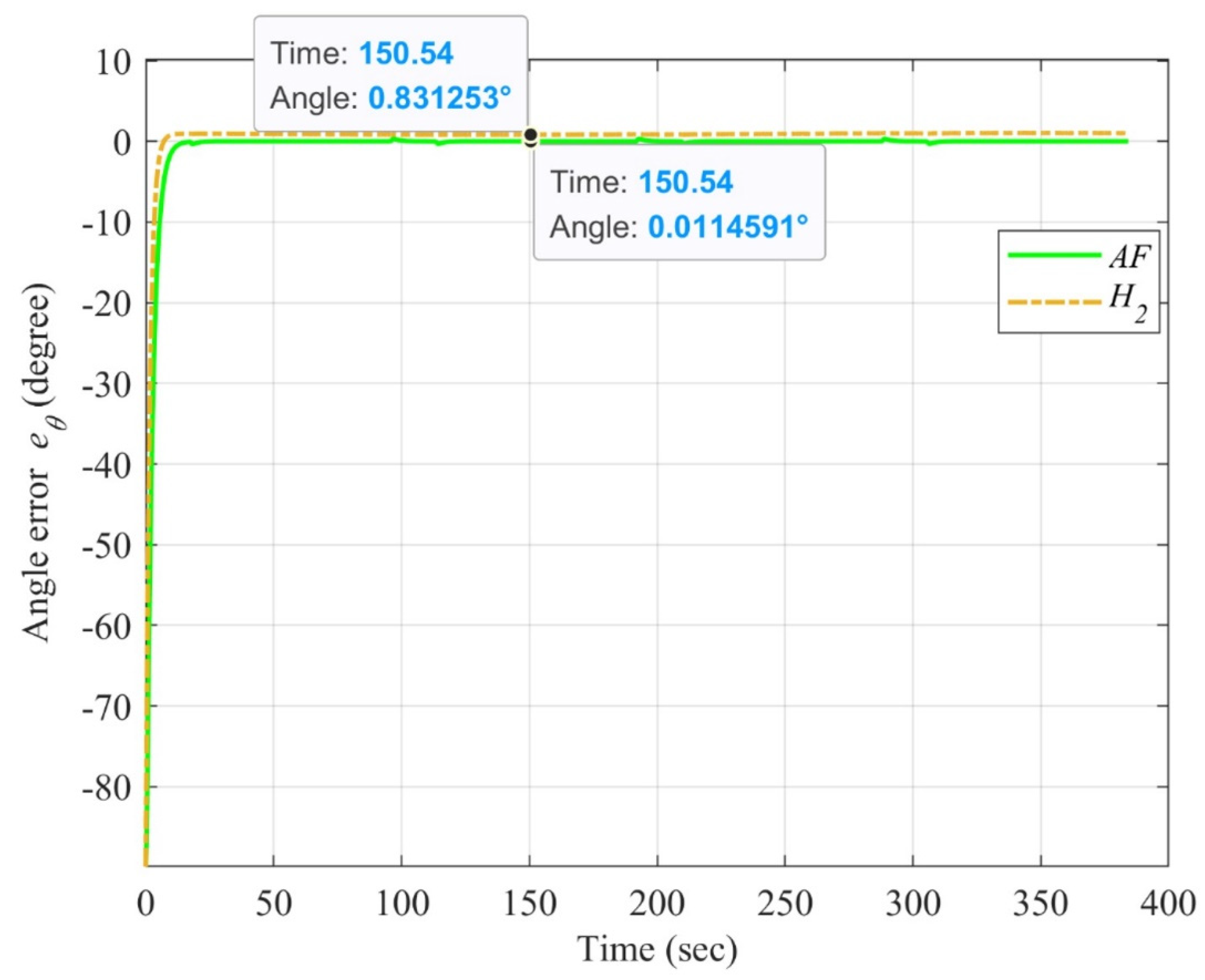
4.3. Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Hu, F.; Jiang, A.; Yang, C. Trajectory Tracking of an Omni-Directional Wheeled Mobile Robot Using a Model Predictive Control Strategy. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Xu, Z.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, L. A Robust Localization, Slip Estimation, and Compensation System for WMR in the Indoor Environments. Symmetry 2018, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, S.; Zhao, L.; Yan, X.; Shi, Y. Topological Design Methods for Mecanum Wheel Configurations of an Omnidirectional Mobile Robot. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosoftei, C.; Popovici, A.; Sacaleanu, P.; Gherghel, P.; Budaciu, C. Hardware in the Loop Topology for an Omnidirectional Mobile Robot Using Matlab in a Robot Operating System Environment. Symmetry 2021, 13, 969. [Google Scholar]
- Eyad, A.; Mustafa, K. Modeling and Trajectory Planning Optimization for the Symmetrical Multi- Wheeled Omnidirectional Mobile Robot. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1033. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chao, C.H.; Cheng, C.F.; Huang, C.J. A Fuzzy Control Design for the Trajectory Tracking of Autonomous Mobile Robot. Adv. Rob. Mech. Eng. 2020, 2, 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.; Wang, Y.; Miao, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhong, H.; Lin, J. Adaptive Fuzzy Control of Mobile Robots with Full-State Constraints and Unknown Longitudinal Slipping. Non. Dyn. 2021, 106, 3315–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, O.; Sha, L.; Shi, W.; Sun, L. Adaptive Fuzzy Path Tracking Control for Mobile Robots with Unknown Control Direction. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2021, 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahim, M.; Hicham, A.; Mohammed, D. Fuzzy Adaptive Sliding Mode Controller for Electrically Driven Wheeled Mobile Robot for Trajectory Tracking Task. J. Con. Dec. 2022, 9, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Amani, A.; Abderrazak, C. Indirect Neural Adaptive Control for Wheeled Mobile Robot. Int. J. Inn. Tech. Exp. Eng. 2019, 9, 2138–2145. [Google Scholar]
- Chiraz, B.; Hassene, S. Design of a PID Optimized Neural Networks and PD Fuzzy Logic Controllers for a Two-Wheeled Mobile Robot. Asian J. Con. 2021, 23, 23–41. [Google Scholar]
- Mateusz, S.; Marcin, S. Neural Tracking Control of a Four-Wheeled Mobile Robot with Mecanum Wheels. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5322. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, J.Y.; Song, Z.B. Adaptive Sliding Mode Trajectory Tracking Control for Wheeled Mobile Robots. Int. J. Con. 2019, 92, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishanu, N.; Asifa, Y.; Anirban, N.; Manas, K.B. Event-Triggered Sliding-Mode Control of Two Wheeled Mobile Robot: An Experimental Validation. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Elec. 2021, 2, 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, X.; Meng, W.; Zheng, S.; Jiang, L.; Meng, J.; Wang, S. Coupled Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Control and Obstacle Avoidance of a Four-Wheeled Steerable Mobile Robot. ISA Tran. 2021, 108, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahim, M.; Hicham, A.; Mohammed, D. Extended State Observer-Based Finite-Time Adaptive Sliding Mode Control for Wheeled Mobile Robot. J. Con. Dec. 2022, 9, 465–476. [Google Scholar]
- Ibari, B.; Benchikh, L. Backstepping Approach for Autonomous Mobile Robot Trajectory Tracking. J. Elect. Eng. Comp. Sci. 2016, 2, 478–485. [Google Scholar]
- Nasim, E.; Alireza, A.; Hossein, K. Balancing and Trajectory Tracking of Two-Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Backstepping Sliding Mode Control: Design and Experiments. J. Int. Rob. Sys. 2017, 87, 601–613. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, J.R.; Attaullah, Y.M. Trajectory Tracking and Stabilization of Nonholonomic Wheeled Mobile Robot Using Recursive Integral Backstepping Control. Electronics 2021, 10, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, T.; Sugeno, M. Trajectory Tracking Controls for Non-Holonomic Systems Using Dynamic Feedback Linearization Based on Piecewise Multi-Linear Models. J. Appl. Math. 2017, 47, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Korayem, M.H.; Yousefzadeh, M.; Manteghi, S. Dynamics and Input–Output Feedback Linearization Control of a Wheeled Mobile Cable-Driven Parallel Robot. Mult. Sys. Dyn. 2017, 40, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welid, B.; Rabah, M.; Mohammed, S.B. The Impact of the Dynamic Model in Feedback Linearization Trajectory Tracking of a Mobile Robot. Period. Pol. Elec. Eng. Comp. Sci. 2021, 65, 329–343. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.H.; Li, T.H.S.; Chen, Y.Y. A Novel Nonlinear Control Law with Trajectory Tracking Capability for Mobile Robots: Closed-Form Solution Design. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 2013, 7, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lou, S.J.; Huang, C.J. Energy Saving Control Approach for Trajectory Tracking of Autonomous Mobile Robots. Intel. Auto. Soft Comp. 2021, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Lou, S.J. Control Design of a Swarm of Intelligent Robots: A Closed-Form H2 Nonlinear Control Approach. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chen, Y.Y. Trajectory Tracking Design for a Swarm of Autonomous Mobile Robots: A Nonlinear Adaptive Optimal Approach. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasra, E.; Farzaneh, A.; Heidar, A.T. Adaptive Control of Uncertain Nonaffine Nonlinear Systems with Input Saturation Using Neural Networks. IEEE Tran. Neu. Net. Lear. Sys. 2015, 26, 2311–2322. [Google Scholar]
- Aguiar, A.P.; Hespanha, J.P. Trajectory-Tracking and Path-Following of Underactuated Autonomous Vehicles with Parametric Modeling Uncertainty. IEEE Tran. Auto. Cont. 2007, 52, 1362–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Wu, X.; Park, J.H.; Yi, Y.; Sun, Y. Iterative Learning Control of Constrained Systems with Varying Trial Lengths Under Alignment Condition. IEEE Tran. Neu. Net. Lear. Syst. 2021, 1–7. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9664474 (accessed on 21 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Wang, X.; Park, J.H.; Yi, Y.; Che, W.W. Extended Disturbance-Observer-Based Data-Driven Control of Networked Nonlinear Systems with Event-Triggered Output. IEEE Tran. Sys. Man Cyb. 2022, 1–12. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9966320 (accessed on 21 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Kar, I.N.; Chaudhury, S. Simple Neuron-Based Adaptive Controller for a Nonholonomic Mobile Robot Including Actuator Dynamics. Neurocomputing 2006, 69, 2140–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukens, M.; Boukabou, A. Design of an Intelligent Optimal Neural Network-Based Tracking Controller for Nonholonomic Mobile Robot Systems. Neurocomputing 2017, 226, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Chang, Y.C. Nonlinear Mixed H2/H ∞ Control for Robust Tracking Design of Robotic Systems. Int. J. Cont. 1997, 67, 837–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Description | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| WMR wheel radius | 6.5 (cm) | |
| WMR width | 35.6 (cm) | |
| Distance from to C | 14 (cm) | |
| WMR mass | 10 (kg) | |
| WMR inertia | 10 (kg-m2) |
| Tracking Trajectory | , | |
|---|---|---|
| S Type Trajectory | (0,3.8) | |
| Square Trajectory | (−9,9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y. Nonlinear Adaptive Fuzzy Control Design for Wheeled Mobile Robots with Using the Skew Symmetrical Property. Symmetry 2023, 15, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15010221
Chen Y-H, Chen Y-Y. Nonlinear Adaptive Fuzzy Control Design for Wheeled Mobile Robots with Using the Skew Symmetrical Property. Symmetry. 2023; 15(1):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15010221
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yung-Hsiang, and Yung-Yue Chen. 2023. "Nonlinear Adaptive Fuzzy Control Design for Wheeled Mobile Robots with Using the Skew Symmetrical Property" Symmetry 15, no. 1: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15010221
APA StyleChen, Y.-H., & Chen, Y.-Y. (2023). Nonlinear Adaptive Fuzzy Control Design for Wheeled Mobile Robots with Using the Skew Symmetrical Property. Symmetry, 15(1), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15010221










