Increasing the Accuracy of Soil Nutrient Prediction by Improving Genetic Algorithm Backpropagation Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Data Sources
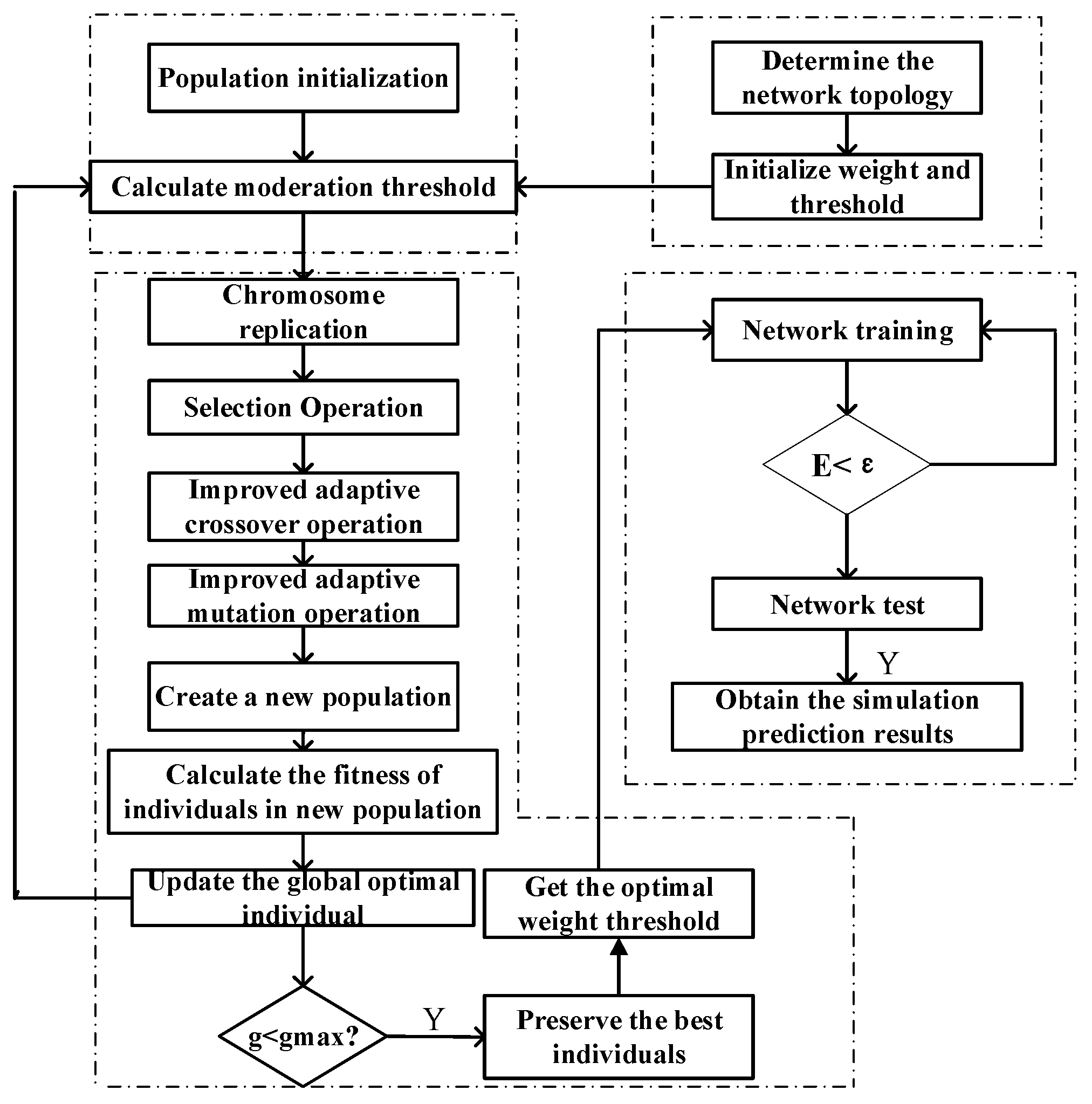
2.2. IGA–BP Neural Network Prediction Model of Soil Nutrient
2.2.1. Determination of Number of Neurons
2.2.2. Encoding Scheme
2.2.3. Adaptation Function
2.2.4. Crossover and Variation Operators
| Algorithm 1 The improved GA |
| Input: : Training set : Validation set : Maximum number of generations Initialize: G = 1; : the initial population randomly in accordance with the structure of the BP neural network; : Set of chromosomes with the largest fitness value in each generation; and : Fitness value of each generation’s best chromosome on training set and validation set. Begin 1. 2. , where denotes the n′-th chromosome of P, and 3. . Repeat for i = 1 to N do 4. Select and in accordance with the roulette wheel strategy. 5. Implement the selective and mutation operations proposed in this study. 6. Calculate if , then 7. Implement the replacement operation end if end for 8. Repeat 2. 9. Repeat 3. g = g + 1 Until g > G End Output: The best chromosome BC[], where = FV. |
2.3. Soil Nutrient Time Series Prediction Process
- (1)
- Soil composition data related to the predicted soil nutrients were obtained and preprocessed. Soil samples were divided into training and validation sets.
- (2)
- A BP neural network model was constructed.
- (3)
- The IGA algorithm was used to determine the weights and thresholds of the BP neural network.
- (4)
- The BP neural network was trained in accordance with the optimal weights and thresholds, and the IGA–BP neural network model was used.
- (5)
- Soil composition data were inputted into the IGA–BP neural network model. After that, soil nutrients were predicted.
3. Results
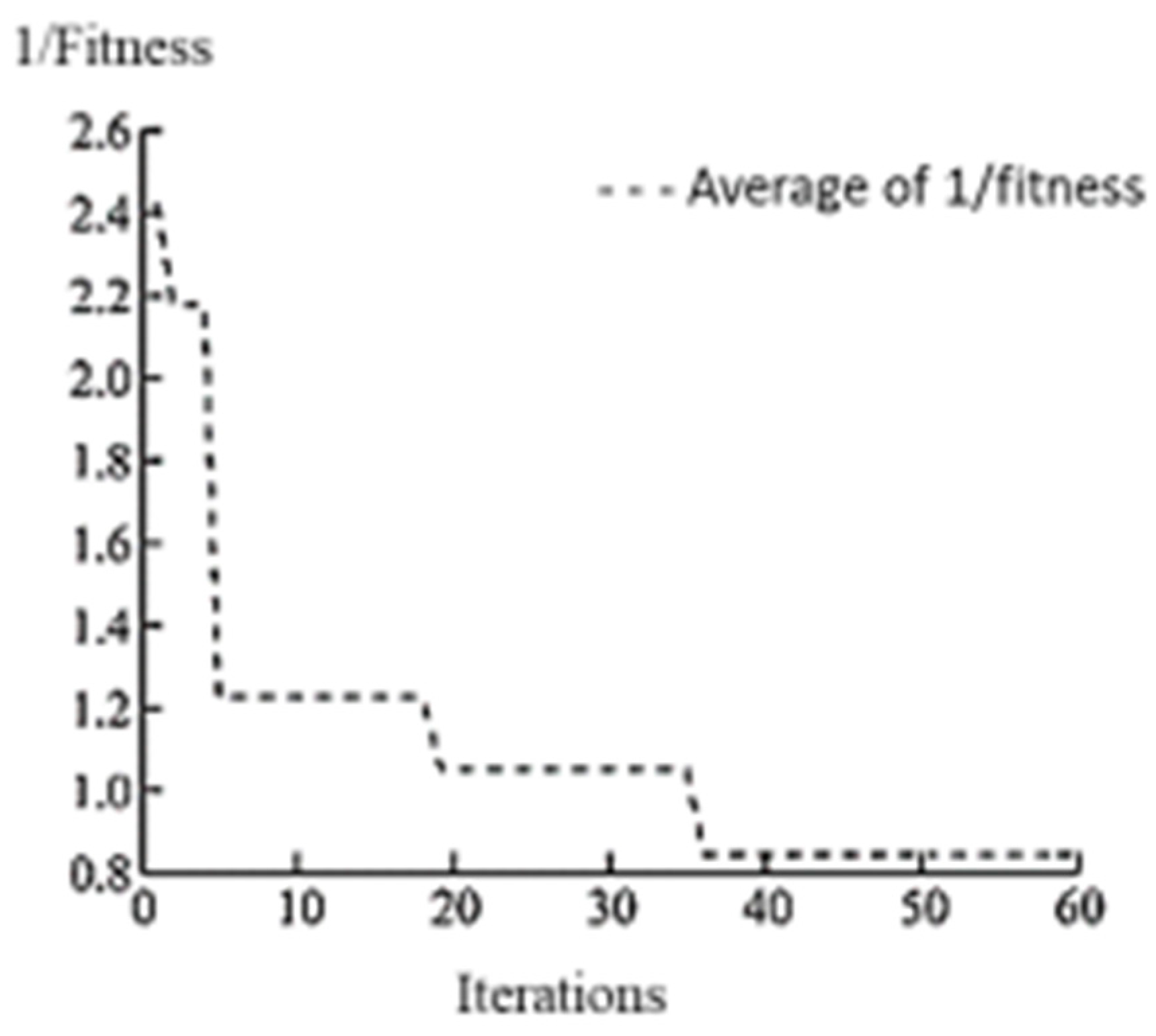
3.1. Weights and Thresholds of IGA Initialization BP Neural Network
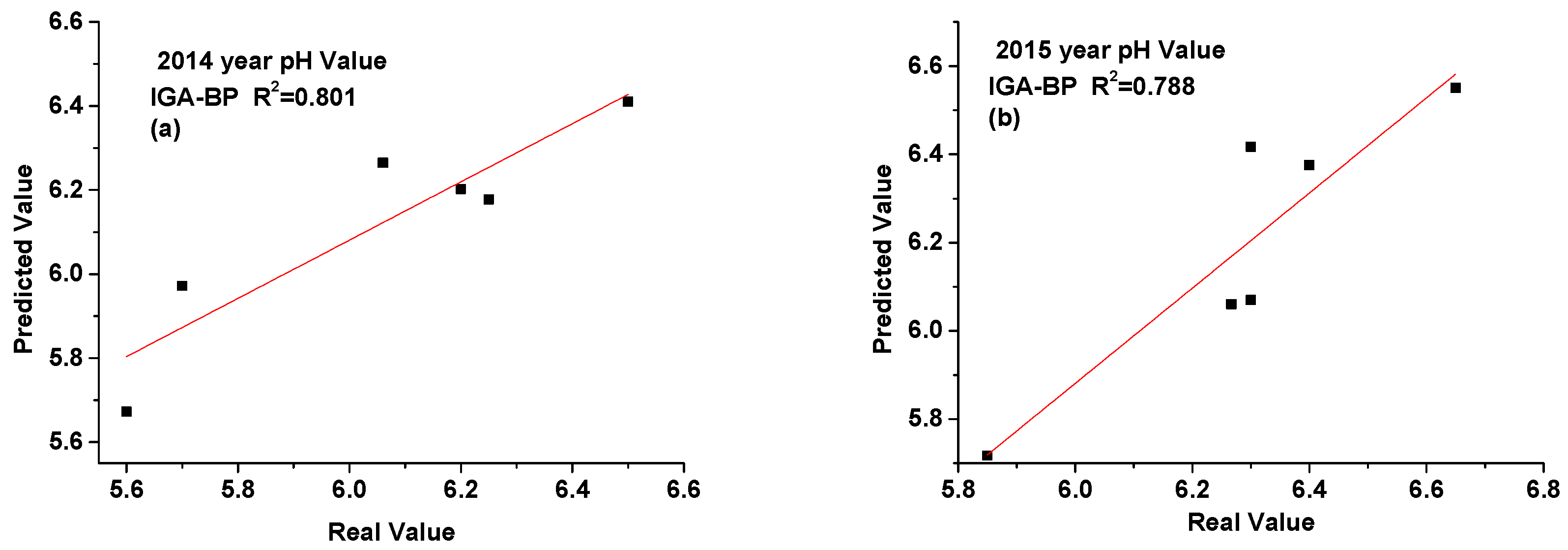
3.2. Time Series Prediction of pH Value in Soil
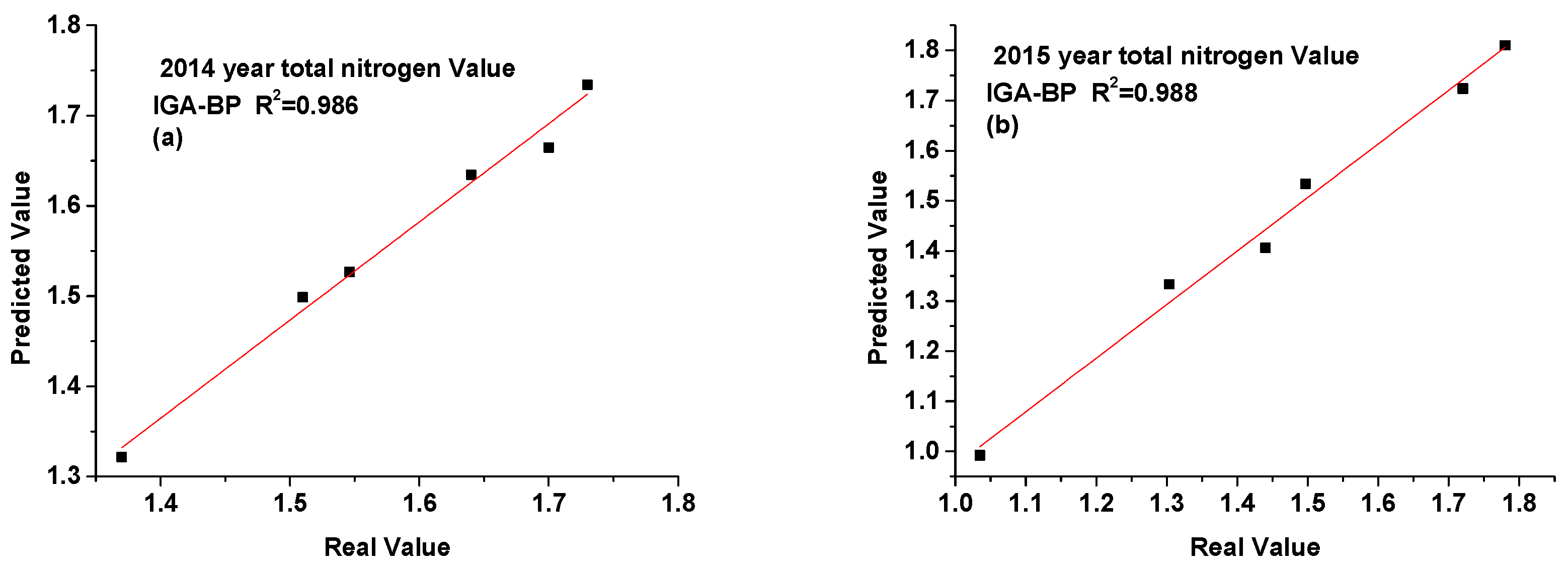
3.3. Time Series Prediction of Total Nitrogen Value in Soil
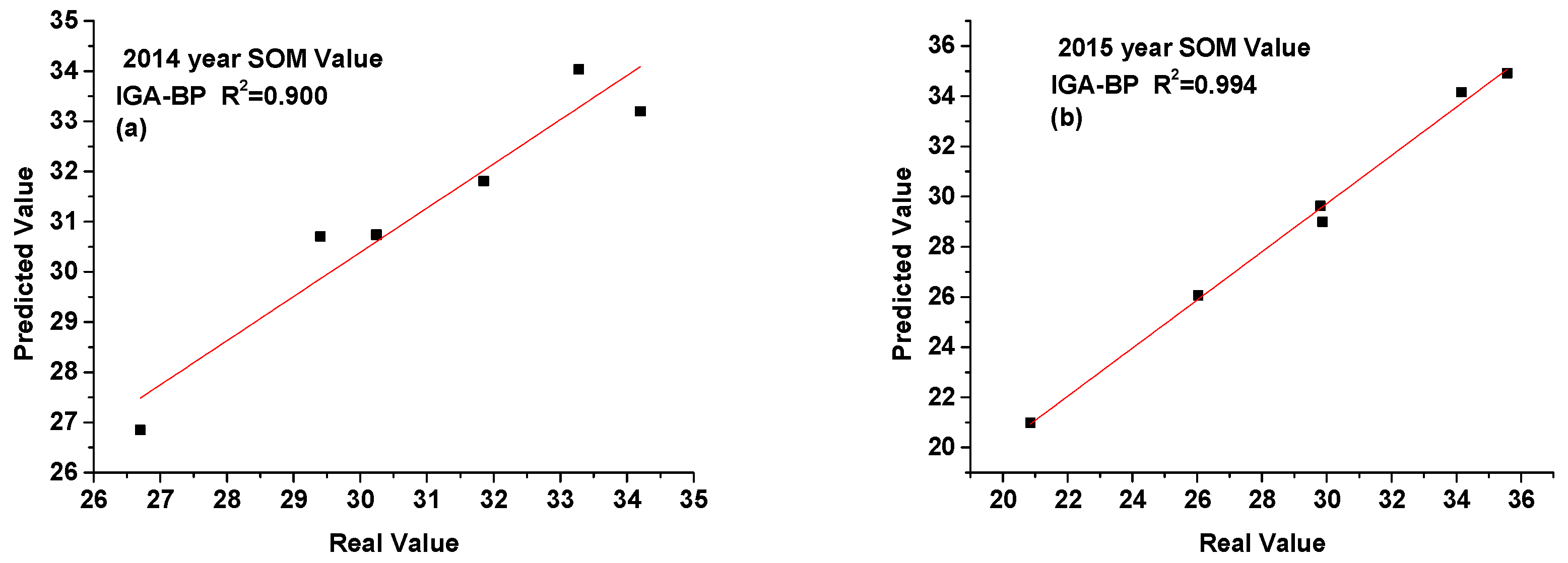
3.4. Time Series Prediction of Organic Matter Value in Soil
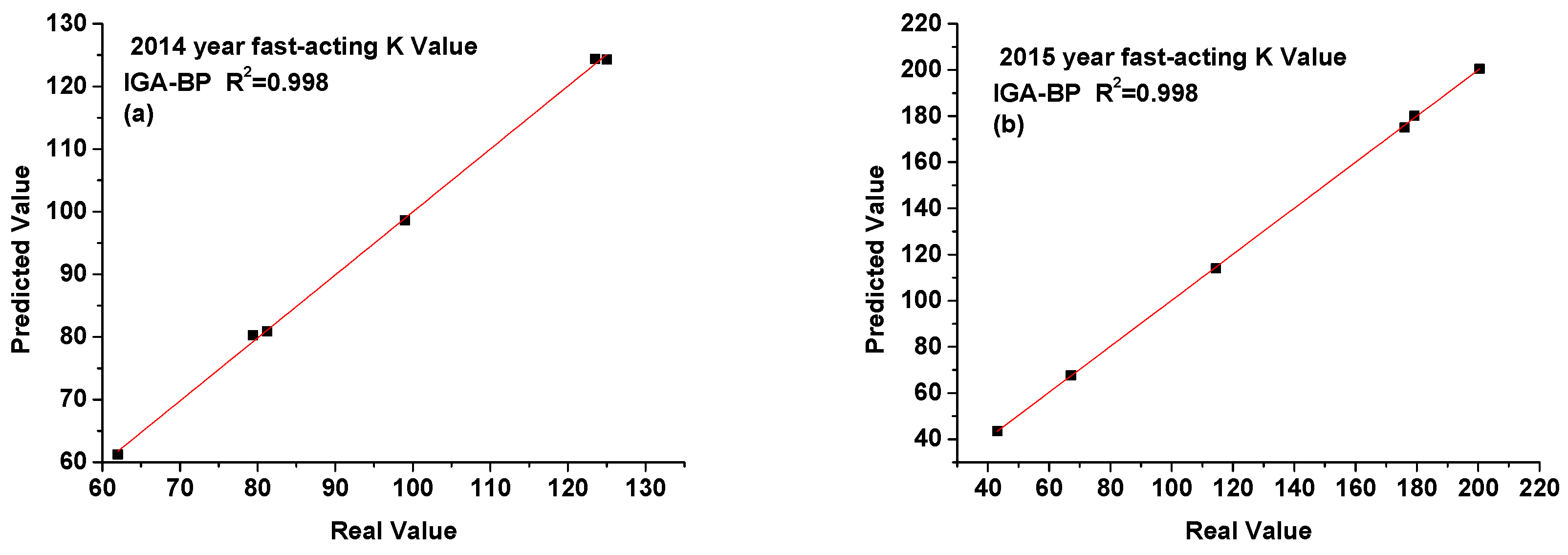
3.5. Time Series Prediction of Fast-Acting Potassium Value in Soil
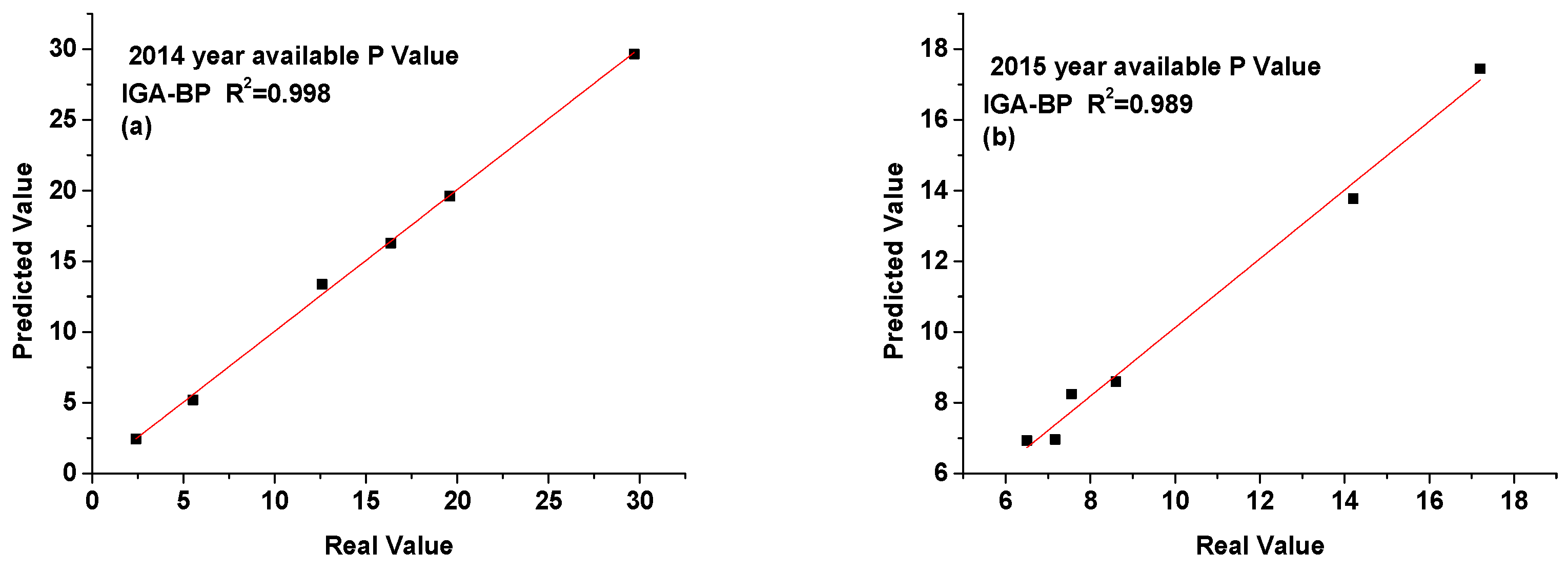
3.6. Time Series Prediction of Available Phosphorus Value in Soil
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, S.; Zhang, D. Improving soil fertility and building sustainable agriculture. Tu Rang Fei Liao 2016, 5, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Li, J. Precision agriculture: Development benefits, international experience and China’s practice. Agric. Econ. 2018, 11, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Jahn, B.R.; Linker, R.; Upadhyaya, S.K.; Shaviv, A.; Slaughter, D.C.; Shmulevich, I. Mid-infrared spectroscopic determination of soil nitrate content. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 94, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, G.; An, Y. Design of soil nutrient content prediction model based on big data statistics. Mod. Electron. Tech. 2020, 43, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Chlingaryan, A.; Sukkarieh, S.; Whelan, B. Machine learning approaches for crop yield prediction and nitrogen status estimation in precision agriculture: A review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 151, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakos, K.; Busato, P.; Moshou, D.; Pearson, S.; Bochtis, D. Machine learning in agriculture: A review. Sensors 2018, 18, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, B.; Yuan, Z.; Sun, Q. Rice nitrogen nutrition estimation with RGB images and machine learning methods. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 180, 105860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, H.; Miao, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, W.; Feng, Z.; Kusnierek, K. Improving unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing-based rice nitrogen nutrition index prediction with machine learning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengl, T.; Leenaars, J.G.B.; Shepherd, K.D.; Walsh, M.G.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Mamo, T.; Tilahun, H.; Berkhout, E.; Cooper, M.; Fegraus, E. Soil nutrient maps of sub-saharan africa: Assessment of soil nutrient content at 250 m spatial resolution using machine learning. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2017, 109, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, E.; Hossain, M.S.; Kong, Y. Feed-forward back-propagation neural networks in side-channel information characterization. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2019, 28, 1950003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriyanov, N. Methods for preventing visual attacks in convolutional neural networks based on data discard and dimensionality reduction. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, K.; Dey, N.; Ashour, A.S.; Wang, D.; Balas, V.E.; McCauley, P.; Shi, F. Rule-based back propagation neural networks for various precision rough set presented KANSEI knowledge prediction: A case study on shoe product form features extraction. Neural Comput. Appl. 2017, 28, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Choi, B.; Wang, L. Multifactor-influenced energy consumption forecasting using enhanced back-propagation neural network. Energy 2017, 127, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Gilley, J.E. Artificial neural network estimation of soil erosion and nutrient concentrations in runoff from land application areas. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 64, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, M.; Eller, A.; Qadi, A. Estimating terrain parameters for a rigid wheeled rover using neural networks. J. Terrach 2013, 50, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.; Grove, I.; Peets, S.; Domun, Y.; Norton, T. Dynamic neural network modelling of soil moisture content for predictive irrigation scheduling. Sensors 2018, 18, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Lin, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.Y. Research on soil moisture forecast model based on BP neural network-a case study at feidong county. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 48, 292–297. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Liang, G.; Zhou, W.; Wang, X.; Xia, W. Fuzzy comprehensive fertility evaluation based on BP artificial network. J. Chin. Soil Fertil. 2011, 5, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Jing, Z.; Pei, D.; Zhao, Y.; Bo, P. An SA–GA–BP neural network-based color correction algorithm for TCM tongue images. Neuro Comput. 2014, 134, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Shcn, Y.; Ceng, W.; Ou, M.; Kuang, Y. Forecast of amount of farmland irrigation based on BP neutral network. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2015, 37, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Beyki, M.; Yaghoobi, M. Chaotic logic gate: A new approach in set and design by genetic algorithm. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2015, 77, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zeng, L.; Lu, Y.; Kai, G.; Fu, S. Fault diagnosis research for servo valve based on GA-BP neural network. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2015, 12, 2846–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Qi, Z.; Fuxing, Y.; Deng, Z. Research of adaptive genetic neural network algorithm in soil moisture prediction. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2018, 54, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Tang, D.; Song, W. Study on soil available zinc with GA-RBF neural network based spatial interpolation method. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2010, 47, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.; Long, X.; Gai, H.; Dang, Z.L.; Wang, S.; Xu, P. Identification of the shear parameters for lunar regolith based on a GA-BP neural network. J. Terramechanics 2020, 89, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, M. Water quality prediction method based on IGA-BP. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Sun, L.; Zhan, W. Binocular camera calibration using improved genetic algorithm to optimize neural network. China Mech. Eng. 2021, 32, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, G.; Yin, G.; Huang, P.; Guo, J.; Chen, L. An improved back propagation neural network prediction model for subsurface drip irrigation system. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2017, 60, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
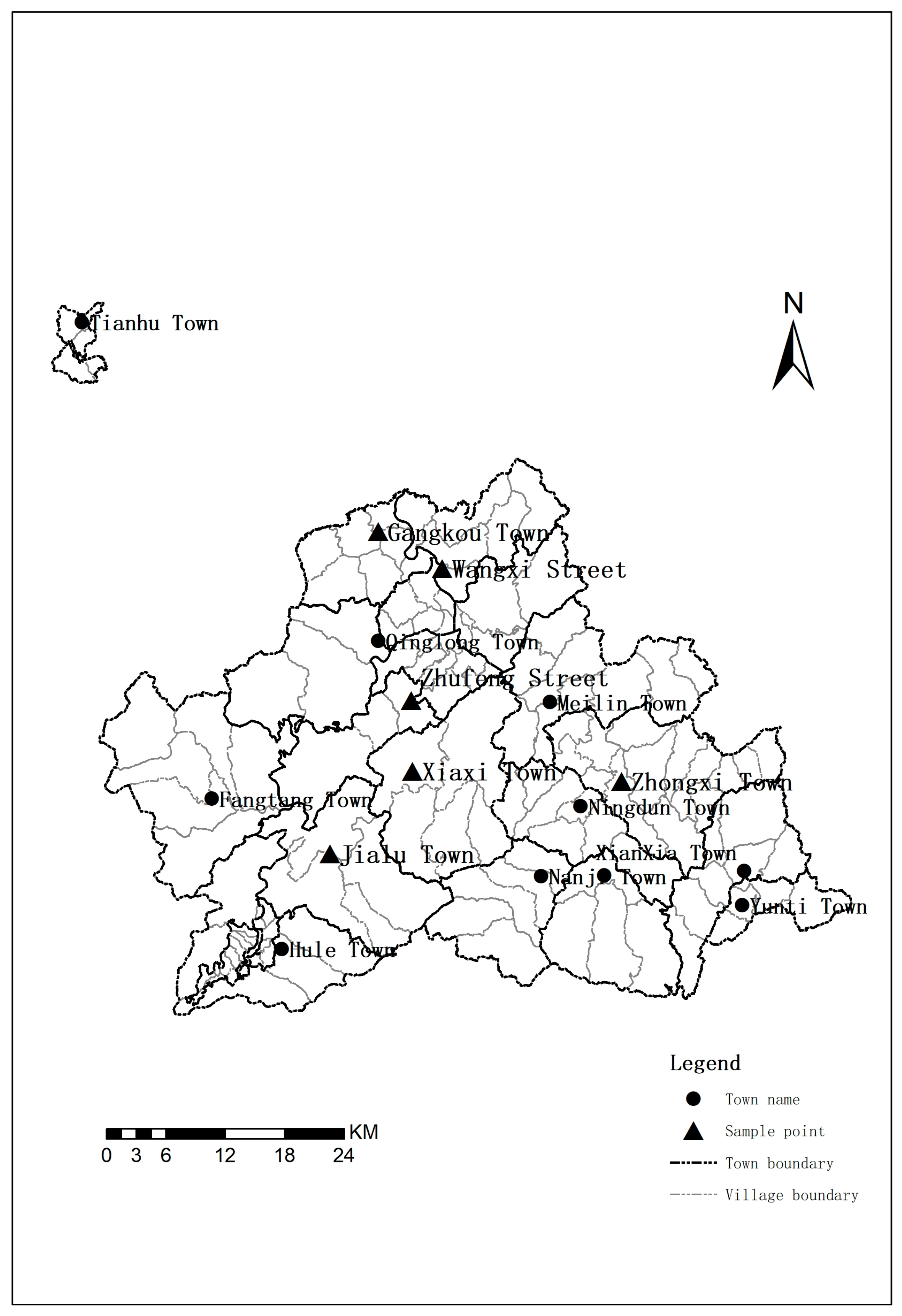

| Township Name | Zhufeng Street | Gangkou Town | Jialu Town | Wangxi Street | Xiaxi Town | Zhongxi Town |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude (°) | 30.5651 | 30.6902 | 30.4329 | 30.6902 | 30.5064 | 30.4942 |
| Longitude (°) | 118.9462 | 118.9896 | 118.8619 | 118.9896 | 118.9501 | 119.1702 |
| Soil Nutrients | Township Name | Year 2014 | Year 2015 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual Value | IGA–BP | GA–BP | BP | Actual Value | IGA–BP | GA–BP | BP | ||
| pH value | Zhufeng Street | 6.50 | 6.41 | 6.26 | 6.73 | 6.30 | 6.42 | 5.82 | 5.87 |
| Gangkou Town | 6.25 | 6.18 | 5.86 | 5.81 | 6.65 | 6.55 | 6.59 | 6.31 | |
| Jialu Town | 5.60 | 5.67 | 5.27 | 5.85 | 5.85 | 5.72 | 5.78 | 5.73 | |
| Wangxi Street | 5.70 | 5.97 | 5.70 | 5.31 | 6.30 | 6.07 | 5.87 | 6.22 | |
| Xiaxi Town | 6.20 | 6.22 | 6.12 | 5.77 | 6.40 | 6.38 | 6.34 | 6.01 | |
| Zhongxi Town | 6.06 | 6.26 | 5.92 | 5.75 | 6.27 | 6.06 | 6.00 | 5.99 | |
| MSE | 0.022 | 0.056 | 0.123 | MSE | 0.023 | 0.084 | 0.092 | ||
| RMSE | 0.150 | 0.237 | 0.351 | RMSE | 0.151 | 0.290 | 0.303 | ||
| Soil Nutrients | Township Name | Year 2014 | Year 2015 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual Value | IGA–BP | GA–BP | BP | Actual Value | IGA–BP | GA–BP | BP | ||
| Total nitrogen (%) | Zhufeng Street | 1.730 | 1.734 | 1.825 | 1.739 | 1.720 | 1.724 | 1.768 | 1.658 |
| Gangkou Town | 1.700 | 1.665 | 1.751 | 1.832 | 1.780 | 1.810 | 1.768 | 1.757 | |
| Jialu Town | 1.640 | 1.634 | 1.618 | 1.639 | 1.035 | 0.992 | 1.067 | 1.342 | |
| Wangxi Street | 1.510 | 1.499 | 1.504 | 1.626 | 1.440 | 1.406 | 1.474 | 1.489 | |
| Xiaxi Town | 1.370 | 1.322 | 1.443 | 1.471 | 1.497 | 1.534 | 1.584 | 1.483 | |
| Zhongxi Town | 1.546 | 1.527 | 1.633 | 1.582 | 1.303 | 1.333 | 1.366 | 1.342 | |
| MSE | 0.0007 | 0.0042 | 0.0071 | MSE | 0.0010 | 0.0027 | 0.0171 | ||
| RMSE | 0.0263 | 0.0646 | 0.0841 | RMSE | 0.0321 | 0.0519 | 0.1306 | ||
| Soil Nutrients | Township Name | Year 2014 | Year 2015 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual Value | IGA–BP | GA–BP | BP | Actual Value | IGA–BP | GA–BP | BP | ||
| Organic matter (g/kg) | Zhufeng Street | 34.20 | 33.20 | 34.44 | 34.04 | 34.16 | 33.16 | 34.98 | 33.83 |
| Gangkou Town | 33.28 | 34.04 | 34.47 | 31.30 | 35.57 | 34.92 | 36.31 | 33.44 | |
| Jialu Town | 31.85 | 31.81 | 32.71 | 29.91 | 20.86 | 21.00 | 20.29 | 19.20 | |
| Wangxi Street | 29.40 | 30.70 | 28.92 | 26.93 | 29.80 | 29.62 | 28.82 | 27.27 | |
| Xiaxi Town | 26.70 | 26.85 | 27.94 | 24.91 | 29.87 | 29.00 | 29.17 | 27.78 | |
| Zhongxi Town | 30.24 | 30.74 | 31.56 | 30.21 | 26.04 | 27.07 | 27.62 | 25.87 | |
| MSE | 0.592 | 0.956 | 1.393 | MSE | 0.549 | 0.915 | 1.485 | ||
| RMSE | 0.769 | 0.978 | 1.180 | RMSE | 0.741 | 0.956 | 1.218 | ||
| Soil Nutrients | Township Name | Year 2014 | Year 2015 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual Value | IGA–BP | GA–BP | BP | Actual Value | IGA–BP | GA–BP | BP | ||
| Fast-acting potassium (mg/kg) | Zhufeng Street | 99.00 | 98.61 | 97.63 | 94.63 | 175.94 | 175.02 | 176.08 | 179.96 |
| Gangkou Town | 81.25 | 80.91 | 80.46 | 77.47 | 114.36 | 114.00 | 113.88 | 116.86 | |
| Jialu Town | 123.50 | 124.38 | 125.39 | 127.94 | 179.20 | 180.17 | 180.69 | 178.44 | |
| Wangxi Street | 62.00 | 61.26 | 63.65 | 62.86 | 43.10 | 43.50 | 44.73 | 45.82 | |
| Xiaxi Town | 125.00 | 124.30 | 124.77 | 123.12 | 200.48 | 200.57 | 199.55 | 196.80 | |
| Zhongxi Town | 79.40 | 80.27 | 77.61 | 82.55 | 67.11 | 67.71 | 66.76 | 63.02 | |
| MSE | 0.474 | 1.999 | 11.229 | MSE | 0.409 | 1.017 | 10.110 | ||
| RMSE | 0.688 | 1.414 | 3.351 | RMSE | 0.640 | 1.008 | 3.179 | ||
| Soil Nutrients | Township Name | Year 2014 | Year 2015 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual Value | IGA–BP | GA–BP | BP | Actual Value | IGA–BP | GA–BP | BP | ||
| Available phosphorus (mg/kg) | Zhufeng Street | 12.60 | 13.38 | 12.64 | 13.46 | 17.20 | 17.45 | 17.57 | 16.99 |
| Gangkou Town | 5.53 | 5.20 | 6.28 | 5.85 | 7.55 | 8.24 | 8.00 | 8.25 | |
| Jialu Town | 2.40 | 2.43 | 2.41 | 3.27 | 6.50 | 6.93 | 6.22 | 7.29 | |
| Wangxi Street | 19.60 | 19.61 | 19.21 | 19.76 | 14.20 | 13.78 | 13.65 | 15.15 | |
| Xiaxi Town | 29.70 | 29.65 | 30.52 | 30.48 | 8.60 | 8.60 | 9.17 | 9.45 | |
| Zhongxi Town | 16.36 | 16.28 | 17.13 | 14.79 | 7.17 | 6.96 | 6.57 | 7.82 | |
| MSE | 0.122 | 0.331 | 0.783 | MSE | 0.159 | 0.233 | 0.536 | ||
| RMSE | 0.349 | 0.576 | 0.885 | RMSE | 0.398 | 0.483 | 0.732 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Lu, C.; Wang, Z.; Che, W. Increasing the Accuracy of Soil Nutrient Prediction by Improving Genetic Algorithm Backpropagation Neural Networks. Symmetry 2023, 15, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15010151
Liu Y, Jiang C, Lu C, Wang Z, Che W. Increasing the Accuracy of Soil Nutrient Prediction by Improving Genetic Algorithm Backpropagation Neural Networks. Symmetry. 2023; 15(1):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15010151
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yanqing, Cuiqing Jiang, Cuiping Lu, Zhao Wang, and Wanliu Che. 2023. "Increasing the Accuracy of Soil Nutrient Prediction by Improving Genetic Algorithm Backpropagation Neural Networks" Symmetry 15, no. 1: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15010151
APA StyleLiu, Y., Jiang, C., Lu, C., Wang, Z., & Che, W. (2023). Increasing the Accuracy of Soil Nutrient Prediction by Improving Genetic Algorithm Backpropagation Neural Networks. Symmetry, 15(1), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15010151





