The 2+1-Dimensional Special Relativity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Lorentz Transformation Emerging from the Conformal Velocity Space
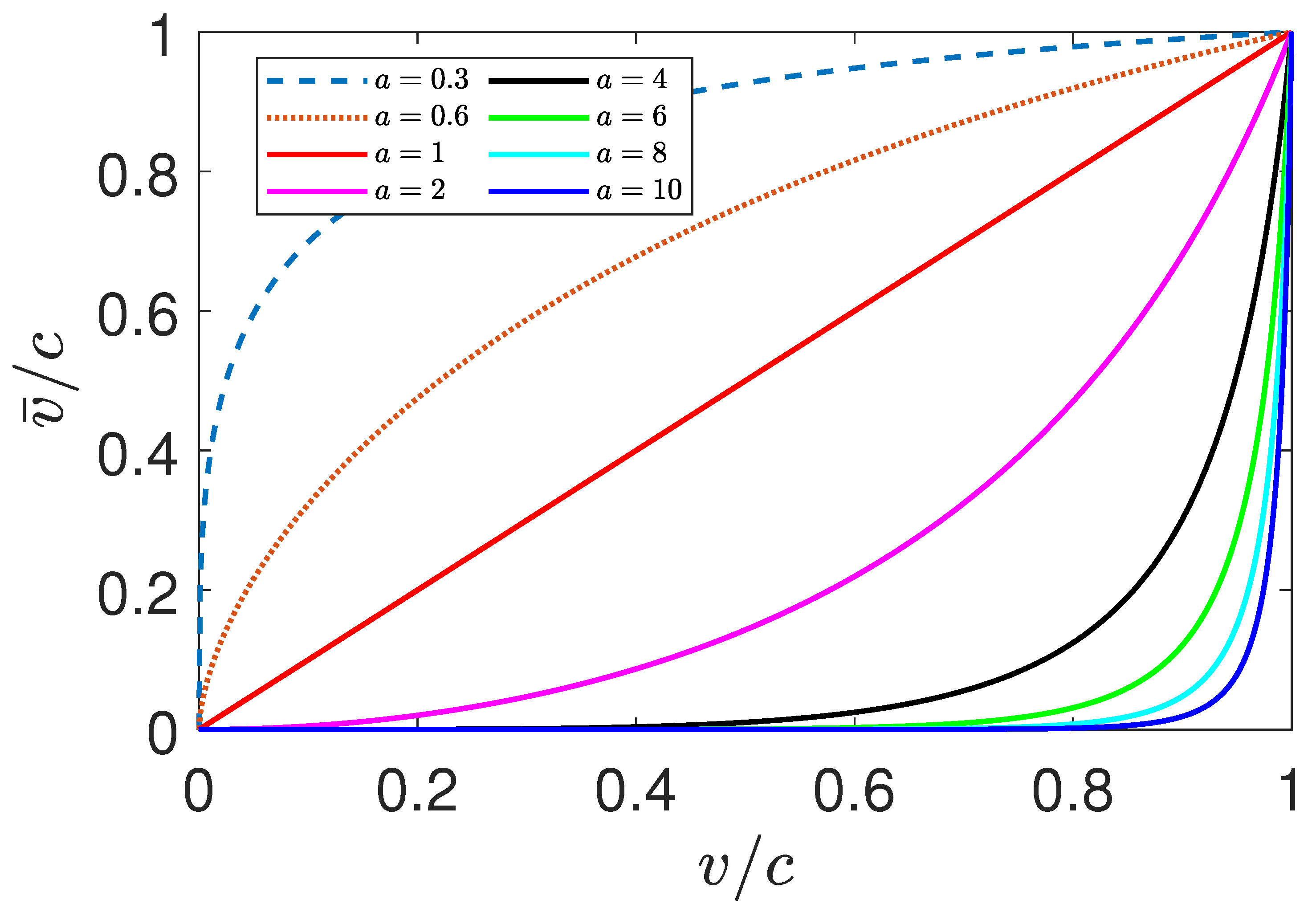
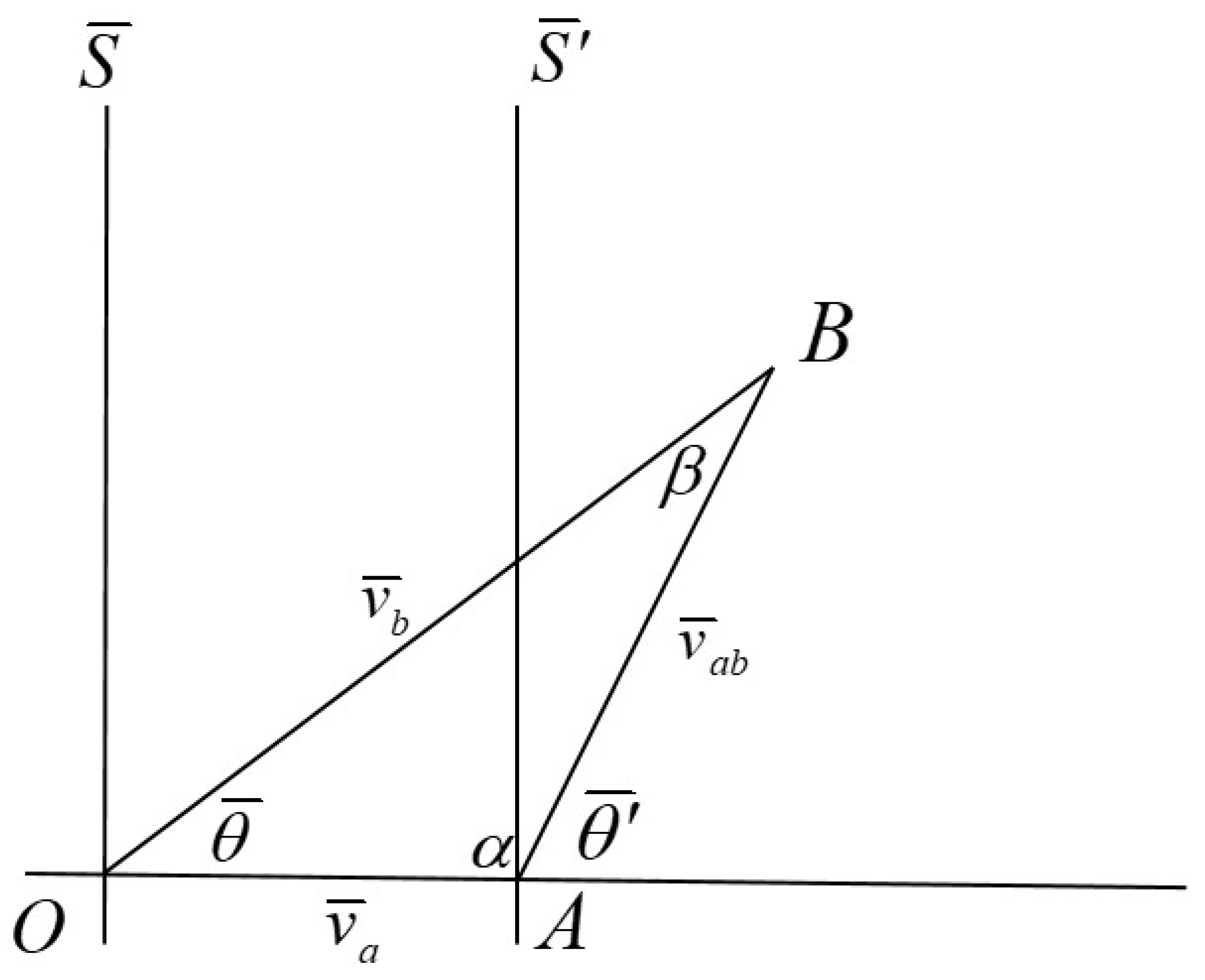
2.1. The Expression of Relative Velocity
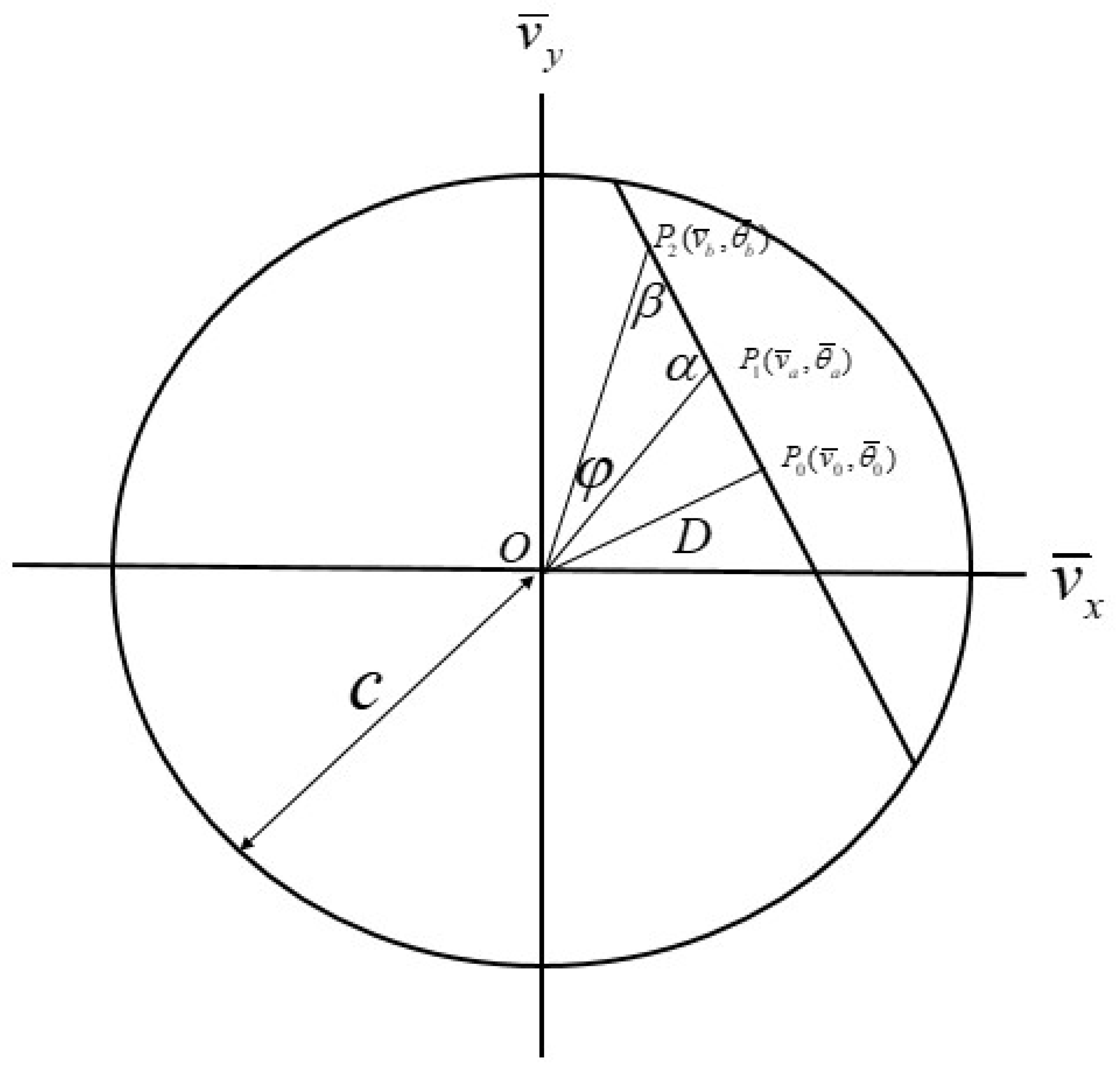
2.2. The Measurement of the Intersecting Angle between Two Geodesics on the Conformal Klein Model
3. Equation of Motion, Momentum, and Energy
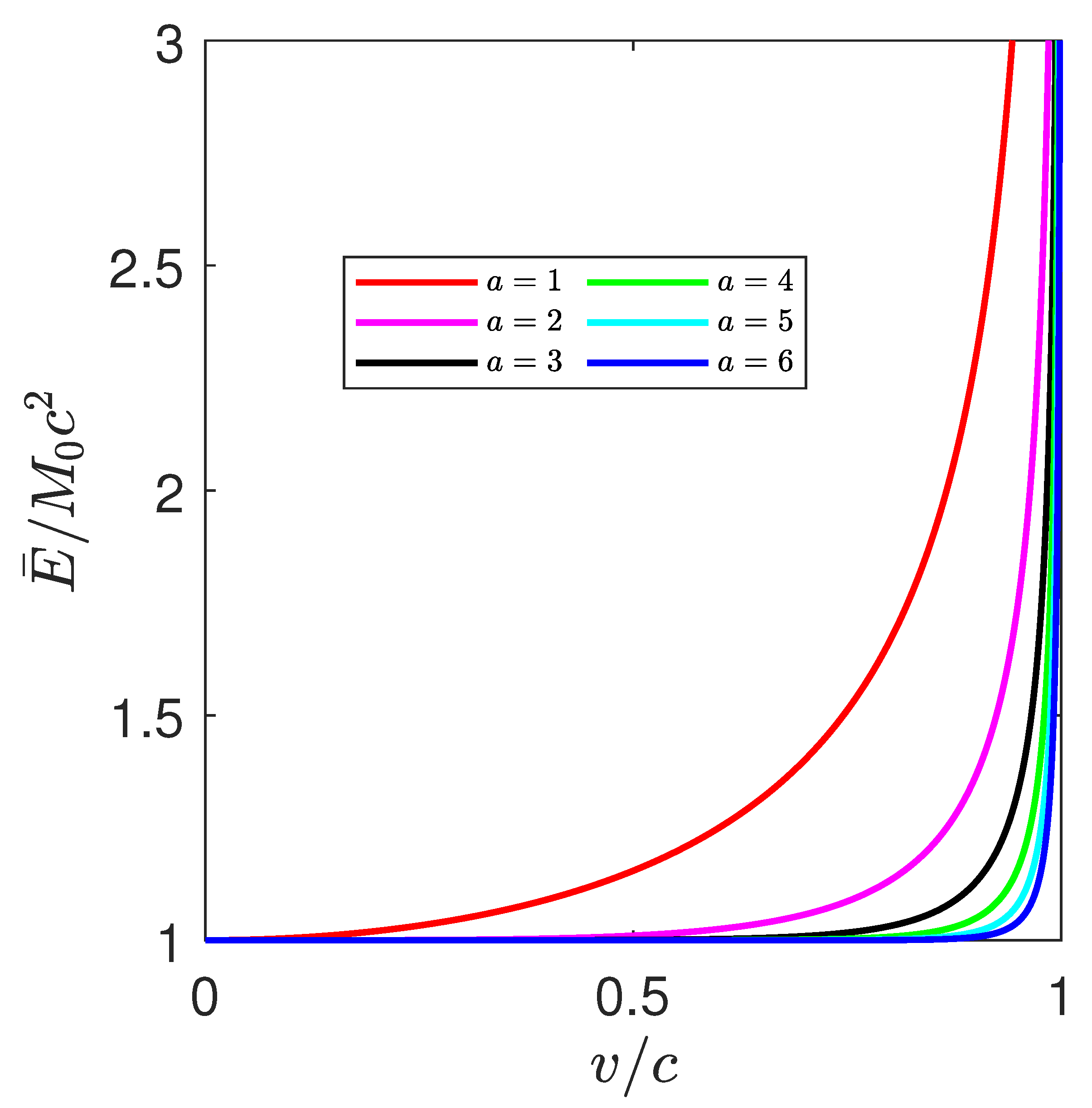
3.1. Energy–Momentum Vector and Its Transformation
3.2. The Relativistic Doppler Effect
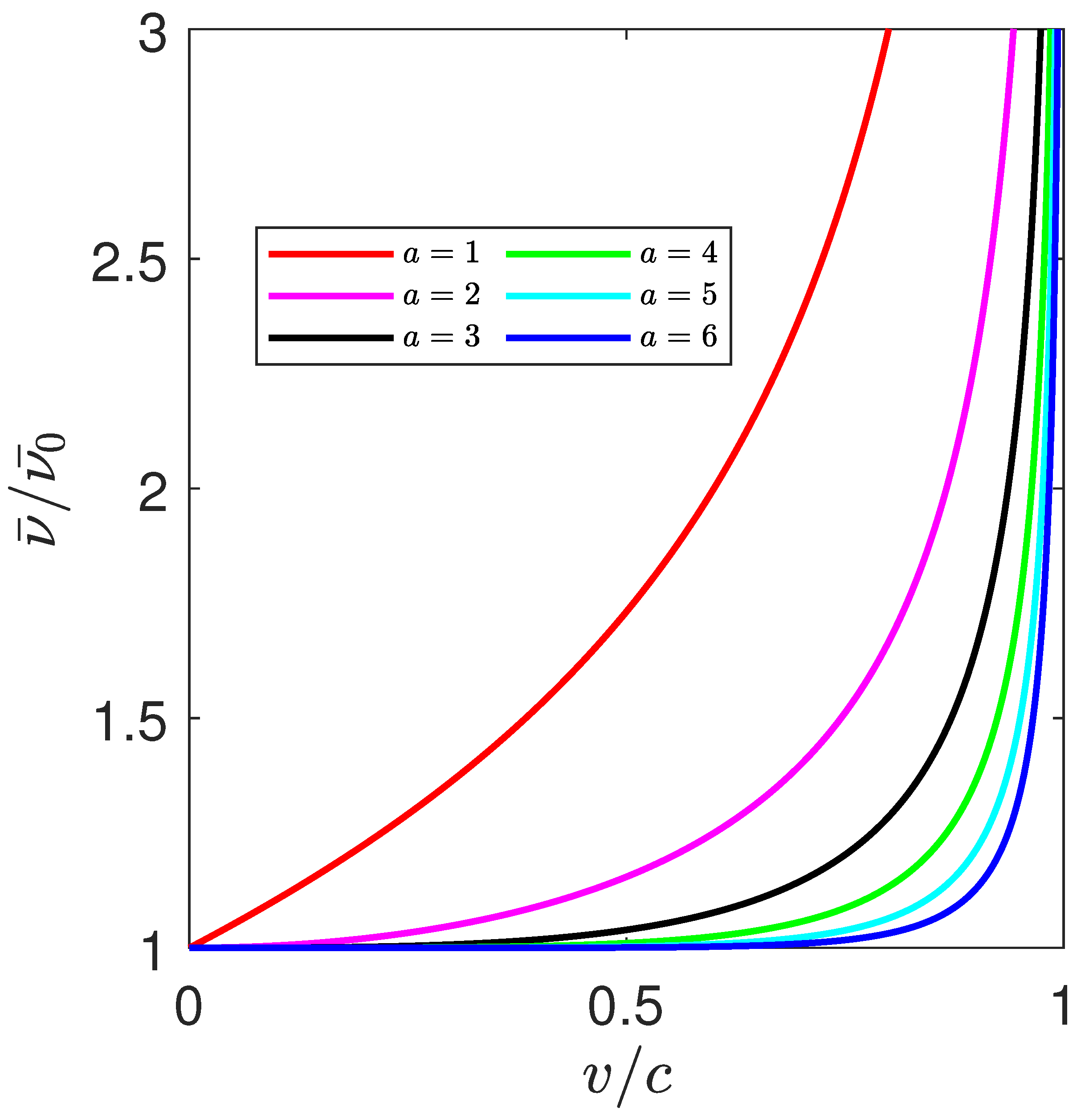
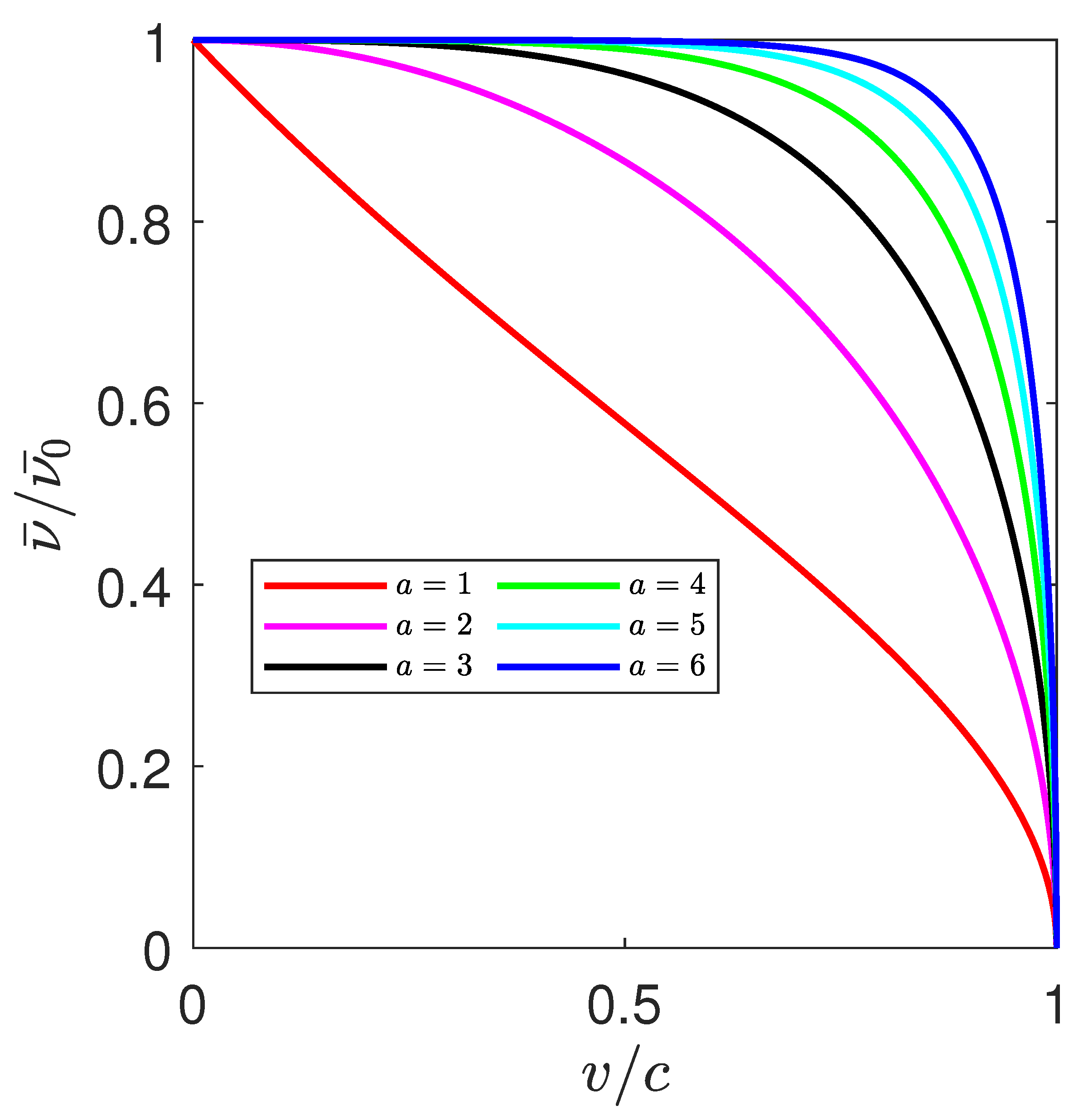
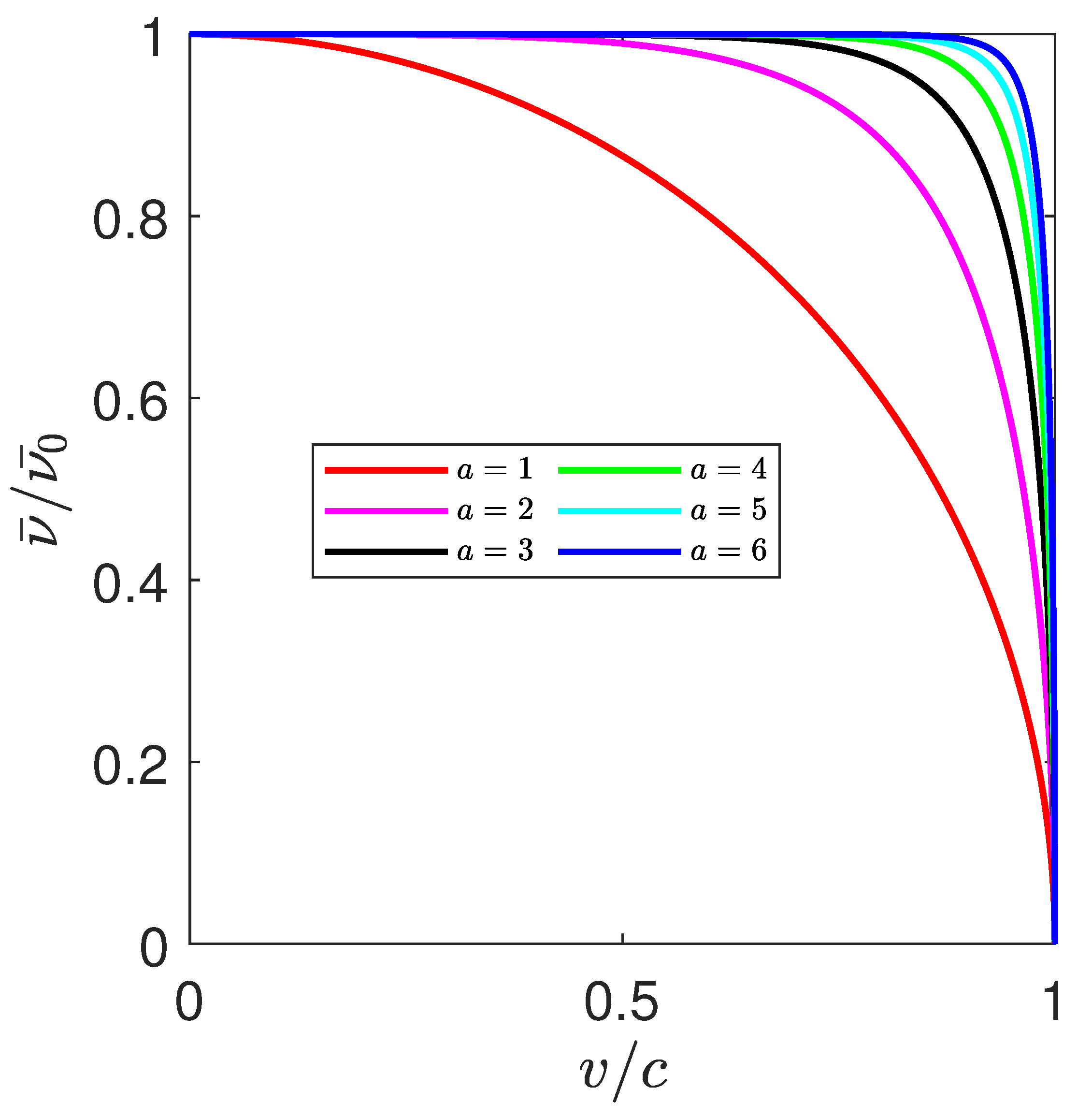
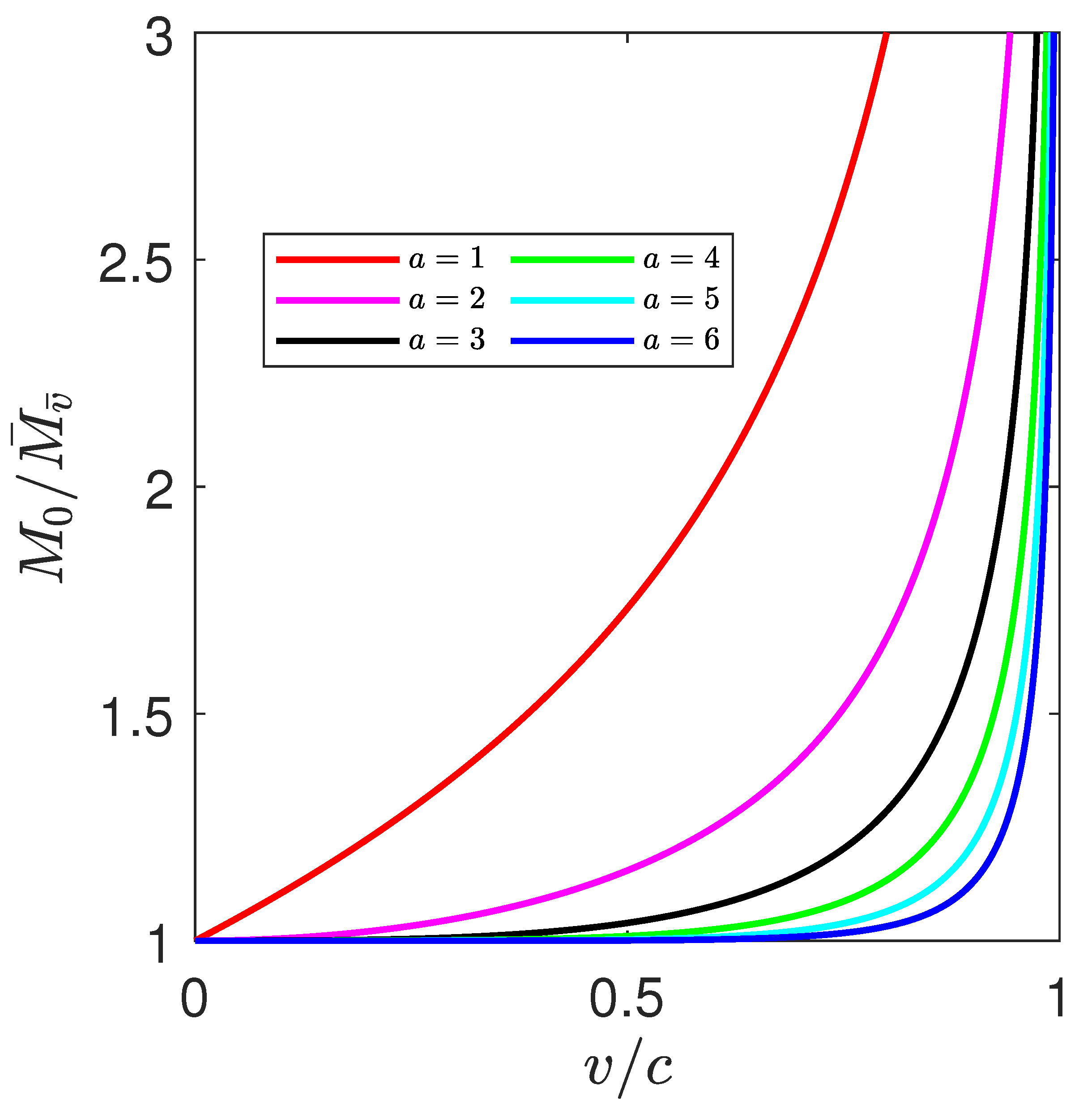
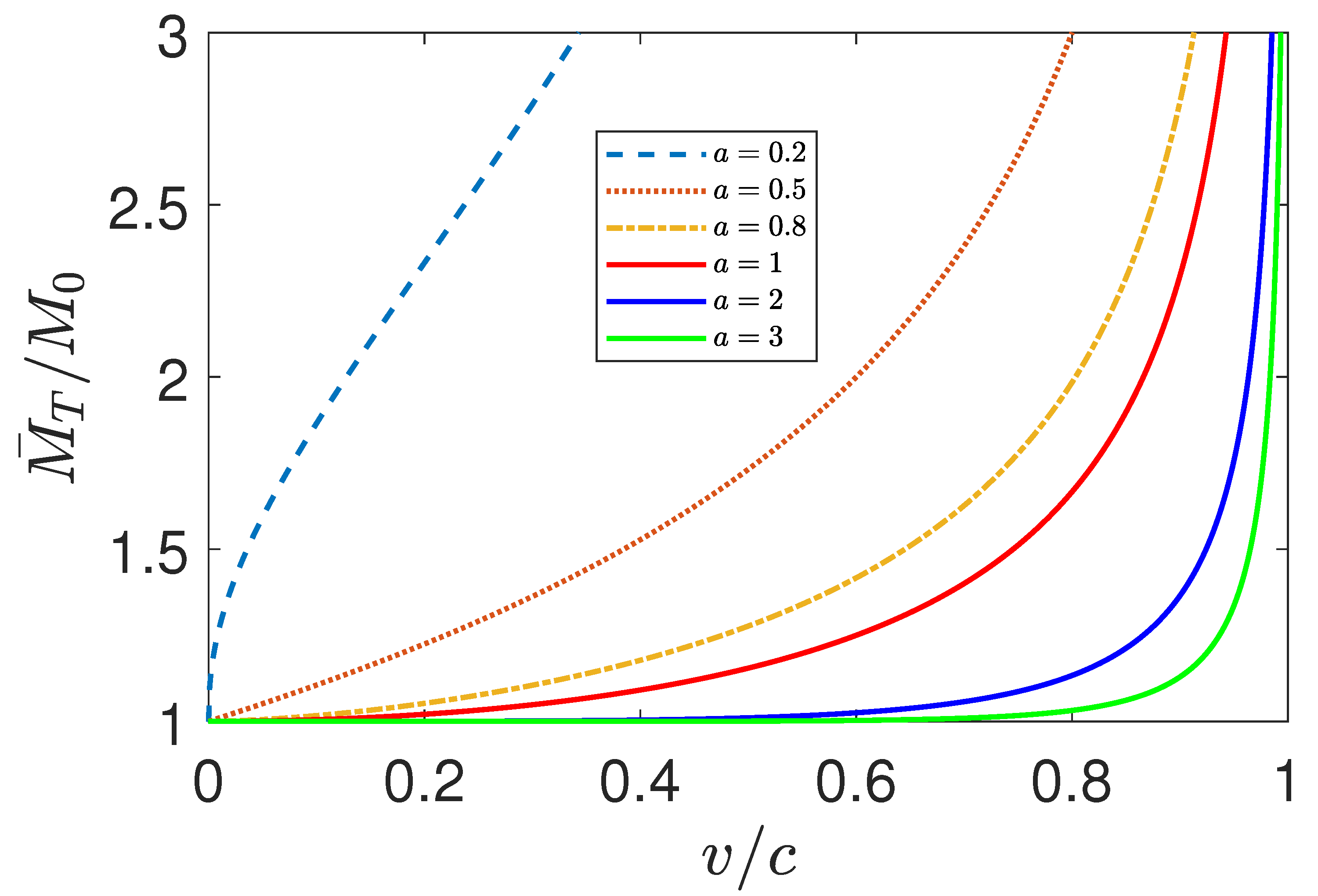
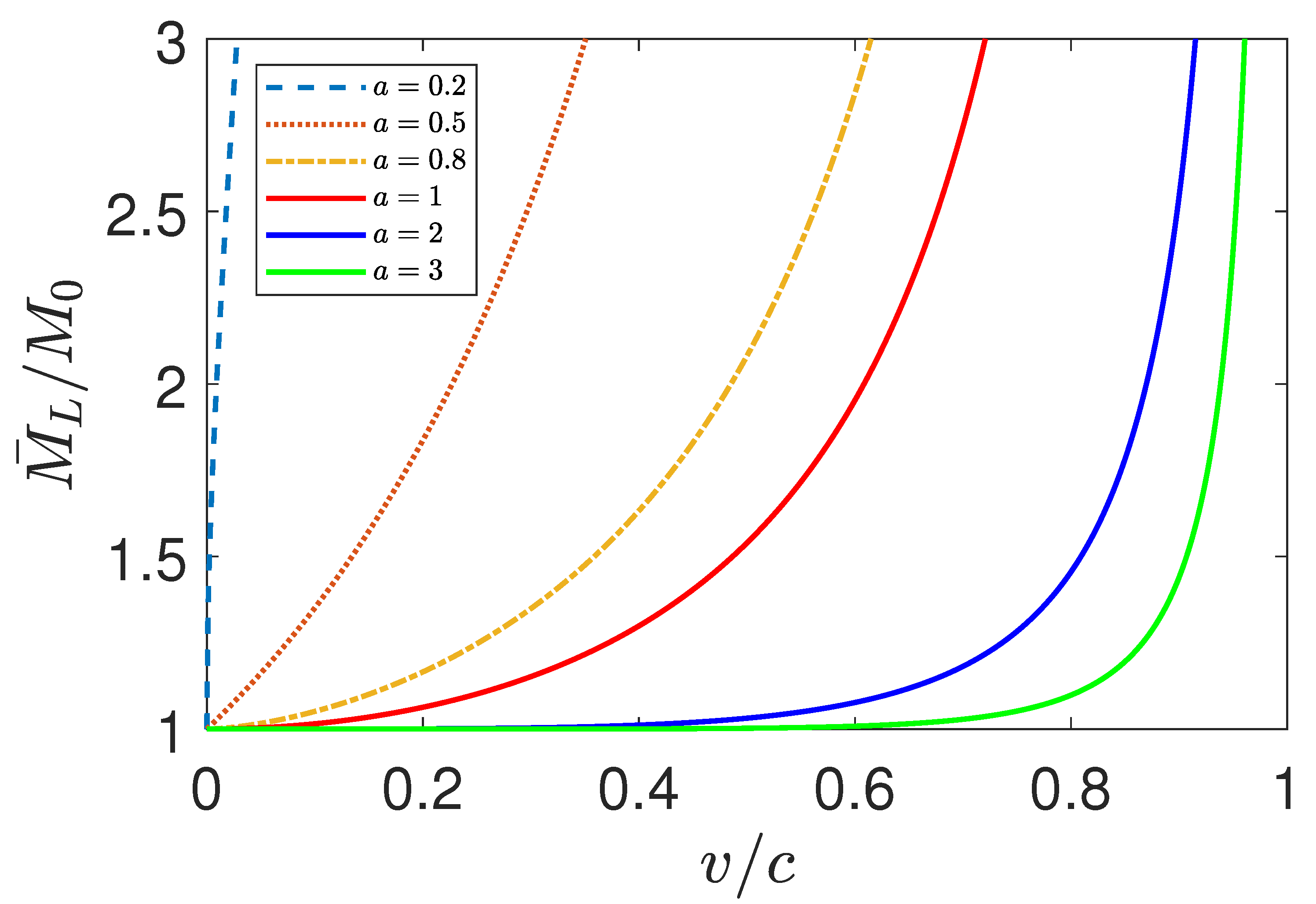
3.3. The Relativistic Rocket Equation
4. Thomas Precession in the Conformal Velocity Space
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Relativistic Velocity Space with Conformal Degrees of Freedom
References
- Zhang, Y.Z. Special Relativity and Its Experimental Foundation; World Scientific: Singapore, 1997; Available online: https://www.worldscientific.com/doi/pdf/10.1142/3180 (accessed on 27 September 2022).
- Mattingly, D. Modern Tests of Lorentz Invariance. Living Rev. Relativ. 2005, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelino-Camelia, G. Special treatment. Nature 2002, 418, 34–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelino-Camelia, G. Doubly-special relativity: Facts, myths and some key open issues. Symmetry 2010, 2, 230–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. The Classical Theory of Fields; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Fock, B.A. The Theory of Space Time and Gravitation, 2nd ed.; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Ungar, A.A. Thomas precession: It underlying gyrogroup axioms and their use in hyperbolic geometry and relativistic physics. Found. Phys. 1997, 27, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, J.A.; Semon, M.D. Relativistic velocity space, Wigner rotation and Thomas precession. Am. J. Phys. 2004, 72, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, A.A. Thomas precession: A kinematic effect of the algebra of Einstein’s velocity addition law. Eur. J. Phys. 2006, 27, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, B.-J.; Huang, W.-H. Hyperbolic geometry property of relativistic velocity space and general expression of Thomas precession. Coll. Phys. 2010, 29, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, B.-J.; Li, Z.-G. Relativistic velocity and hyperbolic geometry. Phys. Essays 1997, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, A.A. Einstein’s special relativity: Unleashing the power of its hyperbolic geometry. Comput. Math. Appl. 2005, 49, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, B.-J. Relativity and Non-Euclidean Geometry; Beiging Press: Beiging, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Leonhardt, U. The Optical conformal mapping. Science 2006, 312, 1777–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendry, J.B.; Schurig, D.; Smith, D.R. Controlling electromagnetic fields. Science 2006, 312, 1780–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.-H. The magnetic Hooke-Newton transmutation in momentum space. Symmetry 2021, 13, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.-H. Quantum states emerging from charged transformation-wave in a uniform magnetic field. Eur. Phys. J. D 2016, 70, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondi, H.; Van der Burg, M.G.J.; Metzner, A. Gravitational waves in general relativity: VII. Waves from axi-symmetric isolated systems. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1962, 269, 21–52. [Google Scholar]
- Sachs, R. Asymptotic symmetries in gravitational theory. Phys. Rev. 1962, 128, 2851–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strominger, A. Lectures on the Infrared Structure of Gravity and Gauge Theory. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.05448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, W. Theory of Relativity; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Ackeret, J. Zur theorie der racketen. Helv. Phys. Acta 1946, 19, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, L.H. The motion of the spinning electron. Nature 1926, 117, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, C. The Theory of Relativity; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Gradshteyn, I.S.; Ryzhik, I.M. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products, 5th ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.-H. Conformal deformation, monopoles, and their application to control the measurement, Berry phase’s path, and resonant frequency of a spin. Symmetry 2022, 14, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M. Quantal phase factors accompanying adiabatic changes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1984, 392, 45–57. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, D.-H. The 2+1-Dimensional Special Relativity. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14112403
Lin D-H. The 2+1-Dimensional Special Relativity. Symmetry. 2022; 14(11):2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14112403
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, De-Hone. 2022. "The 2+1-Dimensional Special Relativity" Symmetry 14, no. 11: 2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14112403
APA StyleLin, D.-H. (2022). The 2+1-Dimensional Special Relativity. Symmetry, 14(11), 2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14112403




