Functional Activation and Connectivity of the Left Inferior Frontal Gyrus during Lexical and Phonological Retrieval
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Stimuli and Task
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Behavioral Data
2.4.2. Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent (BOLD) Activation Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Image Preprocessing
2.4.3. Functional Connectivity fMRI Image Preprocessing
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Data
3.2. Task-Based Activation Results
3.3. Task-Based Functional Connectivity Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bishop, D.V. Cerebral asymmetry and language development: Cause, correlate, or consequence? Science 2013, 340, 1230531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, M.R.; Harris, G.J.; Adrien, K.T.; Ziegler, D.A.; Makris, N.; Kennedy, D.N.; Lange, N.T.; Chabris, C.F.; Bakardjiev, A.; Hodgson, J. Abnormal asymmetry in language association cortex in autism. Ann. Neurol. 2002, 52, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridriksson, J.; Bonilha, L.; Baker, J.M.; Moser, D.; Rorden, C. Activity in preserved left hemisphere regions predicts anomia severity in aphasia. Cereb. Cortex 2010, 20, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woollams, A.M.; Cooper-Pye, E.; Hodges, J.R.; Patterson, K. Anomia: A Doubly typical signature of semantic dementia. Neuropsychologia 2008, 46, 2503–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.S. A review of the tip-of-the-tongue experience. Psychol. Bull. 1991, 109, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strijkers, K.; Costa, A. The cortical dynamics of speaking: Present shortcomings and future avenues. Lang. Cogn. Neurosci. 2016, 31, 484–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indefrey, P. On putative shortcomings and dangerous future avenues: Response to Strijkers & Costa. Lang. Cogn. Neurosci. 2016, 31, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munding, D.; Dubarry, A.-S.; Alario, F.-X. On the cortical dynamics of word production: A review of the MEG evidence. Lang. Cogn. Neurosci. 2016, 31, 441–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhmann, T.; Schiller, N.O.; Goebel, R.; Sack, A.T. Speaking of which: Dissecting the neurocognitive network of language production in picture naming. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indefrey, P.; Levelt, W.J. The spatial and temporal signatures of word production components. Cognition 2004, 92, 101–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.J. The anatomy of language: A review of 100 FMRI studies published in 2009. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1191, 62–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, G.; Magon, S.; Reggiani, F.; Capasso, R.; Monittola, G.; Yang, F.-J.; Miceli, G. Distinguishable neurofunctional effects of task practice and item practice in picture naming: A BOLD FMRI study in healthy subjects. Brain Lang. 2013, 126, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birn, R.M.; Kenworthy, L.; Case, L.; Caravella, R.; Jones, T.B.; Bandettini, P.A.; Martin, A. Neural systems supporting lexical search guided by letter and semantic category cues: A self-paced overt response FMRI study of verbal fluency. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouinard, P.A.; Goodale, M.A. Category-specific neural processing for naming pictures of animals and naming pictures of tools: An ALE meta-analysis. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummine, J.; Szepesvari, E.; Chouinard, B.; Hanif, W.; Georgiou, G.K. A functional investigation of RAN letters, digits, and objects: How similar are they? Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 275, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath, S.; McMahon, K.; Nickels, L.; Angwin, A.; MacDonald, A.; van Hees, S.; Johnson, K.; Copland, D. Priming picture naming with a semantic task: An FMRI investigation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasio, H.; Grabowski, T.J.; Tranel, D.; Hichwa, R.D.; Damasio, A.R. A neural basis for lexical retrieval. Nature 1996, 380, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.F.; Faseyitan, O.; Kim, J.; Coslett, H.B. The dorsal stream contribution to phonological retrieval in object naming. Brain 2012, 135, 3799–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Turennout, M.; Bielamowicz, L.; Martin, A. Modulation of neural activity during object naming: Effects of time and practice. Cereb. Cortex 2003, 13, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagoort, P. Nodes and networks in the neural architecture for language: Broca’s region and beyond. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2014, 28, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heim, S.; Friederici, A.D.; Schiller, N.O.; Rüschemeyer, S.-A.; Amunts, K. The Determiner congruency effect in language production investigated with functional MRI. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 928–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, P.; Lazarova, J.; Hodinott-Hill, I.; Gough, P.; Passingham, R. The inferior frontal gyrus and phonological processing: An investigation using RTMS. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2004, 16, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabb, F.W.; Bilder, R.M.; Chou, M.; Bookheimer, S.Y. Working memory effects on semantic processing: Priming differences in pars orbitalis. Neuroimage 2007, 37, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badre, D.; Poldrack, R.A.; Paré-Blagoev, E.J.; Insler, R.Z.; Wagner, A.D. Dissociable controlled retrieval and generalized selection mechanisms in ventrolateral prefrontal cortex. Neuron 2005, 47, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flinker, A.; Korzeniewska, A.; Shestyuk, A.Y.; Franaszczuk, P.J.; Dronkers, N.F.; Knight, R.T.; Crone, N.E. Redefining the role of Broca’s area in speech. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2871–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.J.; Devlin, J.T.; Moore, C.J.; Morton, C.; Laird, A.R. Meta-analyses of object naming: Effect of baseline. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2005, 25, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganushchak, L.Y.; Christoffels, I.K.; Schiller, N.O. The use of electroencephalography in language production research: A review. Front. Psychol. 2011, 2, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etard, O.; Mellet, E.; Papathanassiou, D.; Benali, K.; Houdé, O.; Mazoyer, B.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. Picture naming without Broca’s and Wernicke’s area. Neuroreport 2000, 11, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtha, S.; Chertkow, H.; Beauregard, M.; Evans, A. The neural substrate of picture naming. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 399–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.J.; Price, C.J. Three distinct ventral occipitotemporal regions for reading and object naming. Neuroimage 1999, 10, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelkowicz, B.J.; Herbster, A.N.; Nebes, R.D.; Mintun, M.A.; Becker, J.T. An Examination of regional cerebral blood flow during object naming tasks. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 1998, 4, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, R.A.; Sommer, W. Does Phonological encoding in speech production always follow the retrieval of semantic knowledge?: Electrophysiological evidence for parallel processing. Cogn. Brain Res. 2003, 16, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Turennout, M.; Hagoort, P.; Brown, C.M. Electrophysiological evidence on the time course of semantic and phonological processes in speech production. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 1997, 23, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Rieth, C.A.; Huber, D.E.; Li, W.; Lee, K.; Tian, J. Neural correlates of top-down letter processing. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Duchon, A.; Perea, M.; Sebastián-Gallés, N.; Martí, A.; Carreiras, M. EsPal: One-stop shopping for Spanish word properties. Behav. Res. Methods 2013, 45, 1246–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durnez, J.; Moerkerke, B.; Nichols, T.E. Post-hoc power estimation for topological inference in FMRI. Neuroimage 2014, 84, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, J.; Friston, K.J. Unified segmentation. Neuroimage 2005, 26, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldjian, J.A.; Laurienti, P.J.; Kraft, R.A.; Burdette, J.H. An Automated method for neuroanatomic and cytoarchitectonic atlas-based interrogation of FMRI data sets. Neuroimage 2003, 19, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, M.; Penny, W.; Kiebel, S. Introduction to random field theory. Hum. Brain Funct. 2003, 2, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roiser, J.P.; Linden, D.E.; Gorno-Tempinin, M.L.; Moran, R.J.; Dickerson, B.C.; Grafton, S.T. Minimum statistical standards for submissions to Neuroimage Clinical. Neuroimage Clin. 2016, 12, 1045–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Nieto-Castanon, A. Conn: A functional connectivity toolbox for correlated and anticorrelated brain networks. Brain Connect. 2012, 2, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, Y.; Restom, K.; Liau, J.; Liu, T.T. A component based noise correction method (CompCor) for BOLD and perfusion based FMRI. Neuroimage 2007, 37, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K.J.; Williams, S.; Howard, R.; Frackowiak, R.S.; Turner, R. Movement-related effects in FMRI time-series. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 35, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, J.D.; Mitra, A.; Laumann, T.O.; Snyder, A.Z.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Petersen, S.E. Methods to detect, characterize, and remove motion artifact in resting state FMRI. Neuroimage 2014, 84, 320–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirer, W.R.; Jiang, H.; Price, C.M.; Ng, B.; Greicius, M.D. Optimization of Rs-FMRI pre-processing for enhanced signal-noise separation, test-retest reliability, and group discrimination. Neuroimage 2015, 117, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchel, C.; Price, C.; Friston, K. A multimodal language region in the ventral visual pathway. Nature 1998, 394, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Loeches, M.; Hinojosa, J.A.; Fernández-Frías, C.; Rubia, F.J. Functional differences in the semantic processing of concrete and abstract words. Neuropsychologia 2001, 39, 1086–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, S.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Ischebeck, A.K.; Friederici, A.D.; Stephan, K.E.; Amunts, K. Effective connectivity of the left BA 44, BA 45, and inferior temporal gyrus during lexical and phonological decisions identified with DCM. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.-D.; Fonteijn, H.M.; Norris, D.G.; Hagoort, P. Topographical functional connectivity pattern in the perisylvian language networks. Cereb. Cortex 2010, 20, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marí-Beffa, P.; Fuentes, L.J.; Catena, A.; Houghton, G. Semantic priming in the prime task effect: Evidence of automatic semantic processing of distractors. Mem. Cogn. 2000, 28, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, T.; Brennen, T.; Brédart, S. On the Importance of Being Ernest: The Cognitive Psychology of Proper Names; Routledge: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Levelt, W.J. Spoken word production: A theory of lexical access. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13464–13471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, B.M.; Münte, T.F.; Kutas, M. Electrophysiological estimates of the time course of semantic and phonological encoding during implicit picture naming. Psychophysiology 2000, 37, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone-Bertolotti, M.; Pichat, C.; Le Bas, J.F.; Baciu, A.; Baciu, M. Functional MRI evidence for modulation of cerebral activity by grapheme-to-phoneme conversion in French, and by the variable of gender. J. Neurolinguist. 2011, 24, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Feature | N | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Word frequency (per million) | 30 | 30.76 | 46.13 |
| Number of letters | 30 | 6.13 | 1.96 |
| Number of substitution neighbors | 30 | 5.97 | 7.25 |
| Number of phonemes | 30 | 5.97 | 1.85 |
| Number of syllables | 30 | 2.67 | 0.76 |
| Number of phonological neighbors | 30 | 14.30 | 14.87 |
| Familiarity * | 26 | 5.91 | 0.75 |
| Imageability * | 26 | 6.17 | 0.30 |
| Concreteness * | 26 | 5.95 | 0.52 |
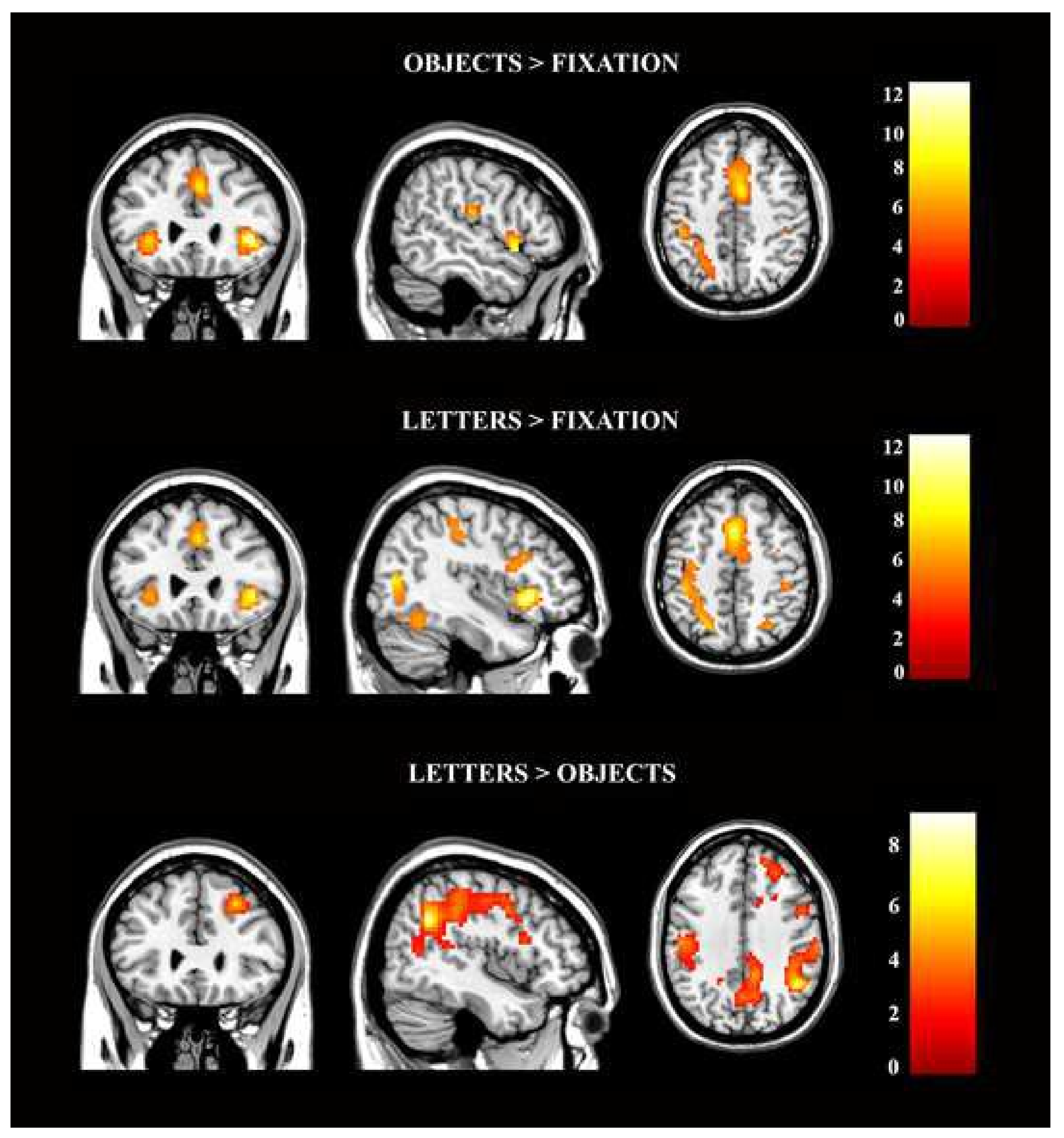
| Brain Region | Cluster Size | L/R | MNI Coordinates (x,y,z) | t-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OBJECTS > FIXATION | ||||||
| Insula | 231 | R | 42 | 26 | −1 | 12.88 |
| Inferior Frontal Gyrus (triangular part) | R | 39 | 29 | 2 | 12.35 | |
| Inferior Frontal Gyrus (orbital part) | R | 33 | 29 | −10 | 8.33 | |
| Calcarine Sulcus | 1421 | L/R | −9/15 | −91/−88 | 8/5 | 11.50/8.25 |
| Fusiform Gyrus | L/R | −24/30 | −52/−58 | −16/−13 | 9.64/11.08 | |
| Middle Occipital Gyrus | L/R | −30/30 | −82/−85 | 2/14 | 8.43/10.83 | |
| Cerebellum | L/R | −18/27 | −64/−61 | −16/−19 | 8.60/10.31 | |
| Cerebellum Vermis | R | 3 | −67 | −13 | 9.98 | |
| Inferior Occipital Gyrus | R | 36 | −79 | −1 | 9.37 | |
| Lingual Gyrus | R | 12 | −76 | −13 | 9.04 | |
| Rolandic Operculum | 30 | R | 51 | −19 | 20 | 10.43 |
| Mid Cingulate Cortex | 550 | R | 6 | 23 | 38 | 10.40 |
| Supplementary Motor Area | R | 3 | 5 | 47 | 9.75 | |
| Thalamus | 114 | L/R | −12/15 | −16/−13 | 5/8 | 6.44/9.85 |
| Globus Pallidus | R | 18 | 5 | 2 | 8.22 | |
| Putamen | R | 18 | 14 | 2 | 7.67 | |
| Insula | 233 | L | −33 | 17 | −1 | 9.54 |
| Inferior Frontal Gyrus (orbital part) | L | −45 | 17 | −7 | 9.52 | |
| Superior Occipital Gyrus | 278 | L | −24 | −76 | 32 | 9.30 |
| Inferior Parietal Lobule | L | −48 | −25 | 44 | 8.69 | |
| Superior Parietal Lobule | L | −27 | −58 | 50 | 8.67 | |
| Postcentral Gyrus | L | −45 | −28 | 47 | 8.28 | |
| Precuneus | L | −6 | −73 | 38 | 6.42 | |
| Precentral Gyrus | 131 | L | −45 | 8 | 35 | 8.89 |
| Inferior Frontal Gyrus (opercular part) | L | −45 | 11 | 29 | 8.72 | |
| Inferior Frontal Gyrus (triangular part) | L | −42 | 20 | 17 | 6.28 | |
| Rolandic Operculum | 31 | L | −48 | −25 | 23 | 8.64 |
| Globus Pallidus | 18 | L | −18 | −4 | 2 | 7.66 |
| Precentral Gyrus | 29 | R | 36 | −10 | 53 | 7.56 |
| Superior Frontal Gyrus | R | 27 | −1 | 62 | 7.52 | |
| Inferior Frontal Gyrus (opercular part) | 4 | R | 51 | 17 | 32 | 6.79 |
| Postcentral Gyrus | 15 | R | 42 | −31 | 50 | 6.72 |
| Supplementary Motor Area | 1 | L | −18 | −4 | 65 | 6.33 |
| Mid Cingulate Cortex | 2 | L | −12 | −16 | 47 | 6.27 |
| Inferior Parietal Lobule | 1 | R | 30 | −46 | 50 | 6.18 |
| LETTERS > FIXATION | ||||||
| Fusiform Gyrus | 731 | R | 27 | −55 | −13 | 11.91 |
| Middle Occipital Gyrus | R | 39 | −76 | 8 | 9.40 | |
| Inferior Occipital Gyrus | R | 39 | −76 | −1 | 8.34 | |
| Superior Occipital Gyrus | R | 24 | −82 | 23 | 7.88 | |
| Inferior Temporal Gyrus | R | 48 | −55 | −13 | 7.75 | |
| Cuneus | R | 12 | −79 | 29 | 7.60 | |
| Lingual Gyrus | R | 15 | −70 | −4 | 7.50 | |
| Precuneus | L/R | −6/6 | −73/−67 | 41/41 | 6.51/7.14 | |
| Lingual Gyrus | 916 | L | −18 | −64 | −7 | 11.86 |
| Superior Occipital Gyrus | L | −18 | −76 | 26 | 8.98 | |
| Cerebellum | L | −12 | −61 | −10 | 8.96 | |
| Middle Occipital Gyrus | L | −36 | −79 | 5 | 8.95 | |
| Superior Parietal Lobule | L | −24 | −58 | 47 | 8.37 | |
| Inferior Temporal Gyrus | L | −45 | −61 | −7 | 8.31 | |
| Fusiform Gyrus | L | −42 | −58 | −19 | 8.00 | |
| Postcentral Gyrus | L | −42 | −31 | 50 | 7.94 | |
| Inferior Occipital Gyrus | L | −39 | −70 | −7 | 7.92 | |
| WHOLE BRAIN ANALYSES | Brain Region | Cluster Size | L/R | MNI Coordinates (x,y,z) | t-Value | ||
| LETTERS > OBJECTS | |||||||
| Angular Gyrus | 1749 | R | 45 | −55 | 32 | 9.25 | |
| Middle Frontal Gyrus | R | 30 | 23 | 44 | 8.17 | ||
| Superior Frontal Gyrus | R | 24 | 38 | 41 | 7.03 | ||
| Supramarginal Gyrus | R | 57 | −25 | 29 | 5.66 | ||
| Precentral Gyrus | R | 48 | 5 | 41 | 5.53 | ||
| Superior Temporal Gyrus | R | 51 | −46 | 20 | 5.43 | ||
| Postcentral Gyrus | R | 33 | −34 | 59 | 4.85 | ||
| Precuneus | 683 | L/R | −3/12 | −64/−49 | 47/38 | 5.52/6.72 | |
| Mid Cingulate Cortex | L/R | −3/3 | −28/−28 | 41/41 | 4.22/4.05 | ||
| Supramarginal Gyrus | 269 | L | −51 | −19 | 35 | 5.51 | |
| Postcentral Gyrus | L | −45 | −22 | 41 | 5.26 | ||
| Rolandic Operculum | L | −45 | −16 | 20 | 3.68 | ||
| Superior Temporal Gyrus | 77 | L | −57 | −43 | 20 | 4.96 | |
| Middle Temporal Gyrus | L | −51 | −64 | 17 | 4.96 | ||
| Insula | 72 | L | −42 | −13 | 2 | 4.27 | |
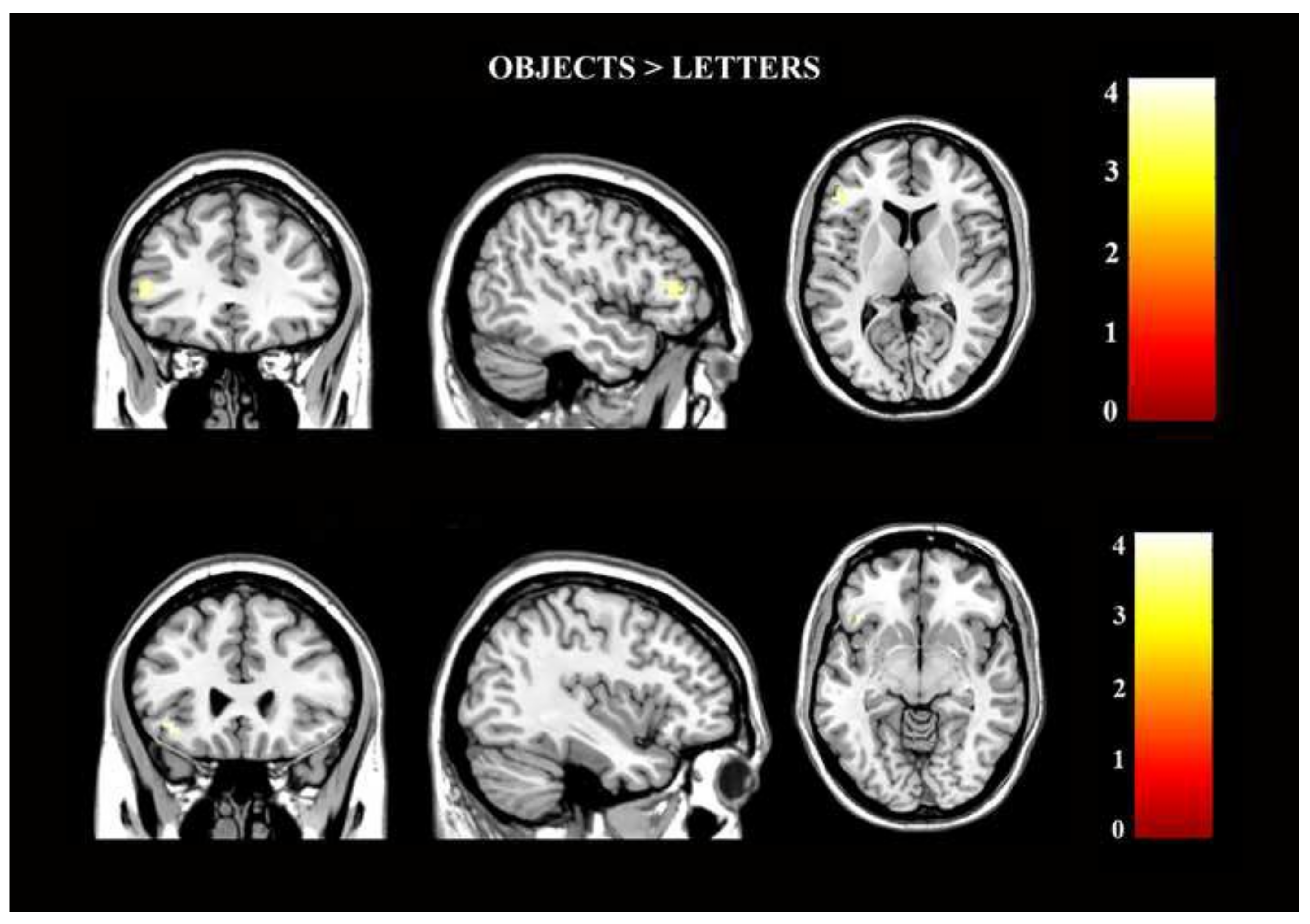
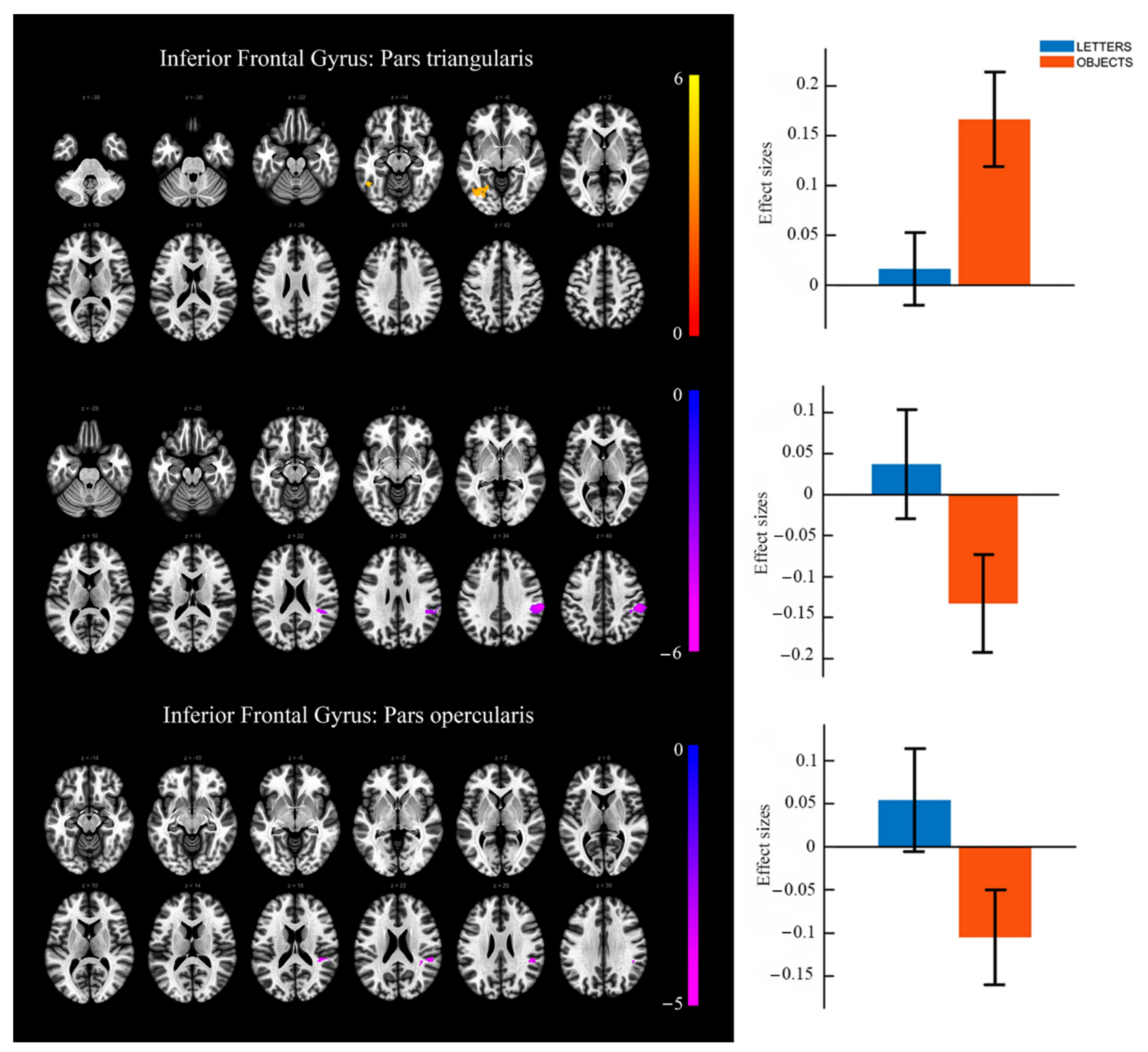
| ROI ANALYSES | Brain region | Clustersize | L/R | MNI Coordinates (x,y,z) | t-value | ||
| OBJECTS > LETTERS | |||||||
| Inferior Frontal Gyrus (triangular part) | 15 | L | −48 | 32 | 8 | 4.24 | |
| Inferior Frontal Gyrus (orbital part) | 6 | L | −39 | 26 | −10 | 3.89 | |
| Brain Region | Cluster Size | L/R | MNI Coordinates (x,y,z) | t-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OBJECTS > LETTERS | ||||||
| Inferior Occipital Gyrus | 241 | L | −36 | −72 | −4 | 5.21 |
| Inferior Temporal Gyrus | L | −48 | −54 | −14 | 5.10 | |
| Lingual Gyrus | L | −30 | −64 | −2 | 4.62 | |
| Fusiform Gyrus | L | −28 | −72 | −6 | 4.49 | |
| Supramarginal Gyrus | 539 | R | 54 | −30 | 40 | −5.97 |
| Brain region | Clustersize | L/R | MNI Coordinates (x,y,z) | t-value | ||
| OBJECTS > LETTERS | ||||||
| Superior Temporal Gyrus | 117 | R | 52 | −36 | 24 | −4.40 |
| Supramarginal Gyrus | R | 46 | −38 | 30 | −3.74 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivas-Fernández, M.Á.; Varela-López, B.; Cid-Fernández, S.; Galdo-Álvarez, S. Functional Activation and Connectivity of the Left Inferior Frontal Gyrus during Lexical and Phonological Retrieval. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13091655
Rivas-Fernández MÁ, Varela-López B, Cid-Fernández S, Galdo-Álvarez S. Functional Activation and Connectivity of the Left Inferior Frontal Gyrus during Lexical and Phonological Retrieval. Symmetry. 2021; 13(9):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13091655
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivas-Fernández, Miguel Ángel, Benxamín Varela-López, Susana Cid-Fernández, and Santiago Galdo-Álvarez. 2021. "Functional Activation and Connectivity of the Left Inferior Frontal Gyrus during Lexical and Phonological Retrieval" Symmetry 13, no. 9: 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13091655
APA StyleRivas-Fernández, M. Á., Varela-López, B., Cid-Fernández, S., & Galdo-Álvarez, S. (2021). Functional Activation and Connectivity of the Left Inferior Frontal Gyrus during Lexical and Phonological Retrieval. Symmetry, 13(9), 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13091655





