Abstract
Electrocardiogram (ECG) signals have been used to monitor and diagnose signs of cardiovascular disease and abnormal signals about the human body. ECG signals are typically characterized by the PR, QRS, QT interval, ST-segment, and heart rate (HR) parameters. ECG devices are widely used for many applications, especially for the elderly. However, ECG signals are often affected by noises from the environment. There are mainly two types of noises that affect the ECG signals: low frequencies from muscle activity and 50/60 Hz from the electrical grid. Removing these noises is important for improving the quality of the ECG signal. A clear ECG signal makes it easy to diagnose cardiovascular problems. ECG signals with high sampling frequency are more accurate. However, the noises in the signal will be more obvious and it will be difficult to remove these noises with filters. We analyzed the symmetrical correlation between the sampling frequency of the signal and the parameters of the signal such as signal to noise ratio (SNR) and signal amplitude. This study will compare characterization of ECG signals performed at different sampling frequencies before and after applying infinite impulse response (IIR) and symmetric finite impulse response (FIR) filters. Therefore, it is critical that the sampling frequency is consistent at the same frequency of the ECG signal for accurate diagnosis. Furthermore, the approach can be also important for the device to help reduce the device’s computing power and hardware resources. Our results were tested with the MIT/ BIH database at 360 Hz sampling frequency with 11-bit resolution. We also experimented with the device operating in real-time with a sampling frequency from 100 Hz to 2133 Hz and a 24-bit resolution. The test results show the advantages of the symmetric FIR filter over IIR when applied to the filtering of ECG signals. The study’s conclusions can be applied to real-world devices to improve the quality of ECG signals.
1. Introduction
According to WHO statistics, the number of people with cardiovascular problems is increasing, especially among the elderly [1]. Therefore, the monitoring of cardiovascular issues has become more and more urgent and important [2,3,4]. The electrocardiogram is a common non-invasive measurement method in the screening and diagnosing of various diseases [5,6,7,8]. One of the critical applications is in health monitoring and diagnosis [9,10]. It provides one of the essential pieces of information supporting the diagnosis of stroke. Electrocardiogram monitoring helps in the early detection and identification of the cause of stroke [11]. The quality of the ECG signal plays a direct role in the diagnostic outcome [12]. The components of the ECG signal include the Q, R, S, and T wave [13], where the R peaks play an essential role in calculating the patient’s heart rate [9]. Distinguishing the components of an ECG signal will yield more helpful information [14].
Typically, the recording of an electrocardiogram is conducted by attaching electrodes to the patient’s body, and the device will receive electrical signals from these electrodes [15]. Therefore, the contact between the electrodes and the user’s skin will directly affect the quality of the obtained ECG signal. In addition, when the user is near the equipment that uses alternating current (AC) power, the human body is also affected by interference from the power grid [16,17,18]. This interference has a frequency equal to the 50/60 Hz grid frequency, depending on the country [19]. These are two types of noise that directly affect the quality of the received ECG signal. Therefore, it is necessary to eliminate these two types of interference [20,21,22]. There are two methods of noise removal: using analog filters designed on hardware and digital filters designed on software. Analog filters are made up of three basic elements—resistor (R), inductor (L) and capacitor (C)—and have fixed parameters [15,23]. The digital filters are designed based on the computing power of the central processing unit (CPU), so the parameters can be changed more flexibly [24]. To completely eliminate the two types of noise in the ECG signal, designing both low-pass (LP) and high-pass (HP) filters is necessary [25]. Therefore, the choice of filter design method plays an essential role in signal quality [16,22]. Recently, dedicated filter architectures, such as adaptive filters or machine learning algorithm (autoencoders) were developed [26,27,28]. For our case, we utilized the simple filter topology for reduced design complexity to filter out unwanted ECG noises.
Along with advanced semiconductor technology, there have been many analog Front end (AFE) for ECG applications, produced by created manufacturers, serving biological measurement, such as TI, Maxim Integrated and Analog Devices, and the more compact and precise form of these components makes the design of wearable devices faster and easier [3,24,29,30]. The streamlined design process accelerates the commercial product launch process [24,31]. These bio-sensors usually have a variable sampling frequency [32]. For ECG signal, the higher the sampling frequency, the more accurate the signal, and vice versa. However, a high sampling frequency will create an extensive database that makes it difficult to calculate and transmit data to other devices. The BIT/ MIH database has a sampling frequency of 360 Hz [33]. Sensor ADS1293 from TI has a sampling frequency of up to 2133 Hz [34], sensor MAX86150 from Maxim Integrated has a frequency of 3200 Hz [35], and sensor ADAS1000 from Analog Devices has a sampling frequency of 8000 Hz. Therefore, surveying the ECG signal at different sampling frequencies plays a vital role in reducing the amount of data to be collected but still ensuring the correctness of the signal. The basic structure of a wearable device includes bio-sensor and system-on-chip module (microcontroller unit (MCU), Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, battery management, etc.,) [32,36,37,38]. Since most ECG wearable devices use batteries, reducing the amount of computation on the data is also an effective method to save energy consumption and prolong usage time [24,32].
Usually, there is a correlation between sampling frequency and signal quality. The higher the sampling frequency, the more faithful the components of the signal will be. However, ECG signal parameters need to be considered, such as heart rate (60–150 beats/min) and P, QRS and T wave amplitude. We analyzed the asymmetries in the ECG signal at different frequencies, from which to draw conclusions.
Overall, our study has the following contributions:
- We analyzed the crucial components in the ECG signal. Noise factors affect the signal and how to design filters to remove noise.
- We investigated ECG signals from BIT/ MIH database with different sampling frequencies. We apply filters to compare the difference between the received signals.
- We proposed an ECG signal acquisition model based on large production components to collect real-time signals. We also apply filters to remove noise with different sampling frequencies of the device. We compare the parameters and draw conclusions.
The rest of this article is presented as follows: the Materials and Methods section will analyze the related works and implementation methods. The subsequent sections will show the implementation results. In the last part of the paper, we will present the conclusions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ECG Characteristic Analysis and Related Works
In this section, we review related works by other authors to further clarify the meaning of the ECG signal and the obtained results of applied analysis. Figure 1 describes a reasonably typical ECG signal with the P wave, the QRS complex, and the T wave [39]. The P waves are generated by muscle activation of both atria. The left-to-right ventricular activation produces a QRS complex. Finally, ventricular muscle activation produces T waves. Therefore, the P, QRS, and T wave are essential parts of the electrocardiogram that should be observed and evaluated because they have a lot of helpful information [13,40].
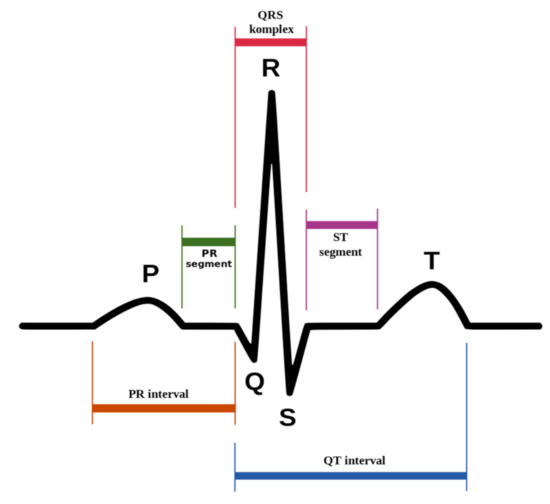
Figure 1.
ECG signal with typical segment [39].
Wenliang Zhu and colleagues have studied cardiac arrhythmias based on abnormal cardiac electrical activity to correct cardiac arrhythmias. The study analyzed the electrocardiogram P-QRS-T segment and the shape features of the P-QRS-T wave to identify arrhythmias [2]. Dengao Li et al. used a novel neural network structure based on the 12 most common electrocardiographic leads proposed to classify 9 arrhythmias [5]. Piotr Augustyniak used a time-independent QRS detection method [10]. We applied a graph data representation and applied a heterogeneous time-scale transform finding the exact P, QRS and T wave demarcation points. J. P. V. Madeiro used the mathematical model of Gaussian and Rayleigh Functions to compare the modeling and segmentation of P and T waves in the electrocardiogram [13]. The root mean square (RMS) evaluated between models and characteristics wave. In addition, the author also applied wavelet transform to estimate the P peak and T wave. Khaleel Husain and colleagues presented their study on the architecture of an ECG signal acquisition system including hardware and software [24]. Regarding the software, they analyze factors such as noise reduction, machine learning and privacy protection. With the result, it is possible to provide details regarding the components of the ECG signal.
From the studies of the above authors, we found that there are no studies focused on analyzing the sample frequency of the ECG signal and the quality of the signal. We focused on complementing the new knowledge and results related to ECG signal acquisition and analysis.
2.2. Design a High-Pass and Low-Pass Filter
It is necessary to design both high-pass and low-pass filter to remove high-pass and low-pass noises from the grid for ECG signal [41]. The FIR and IIR filters are usually utilized for two types of filtering: the Formulas (1) and (2) describe the FIR filter and the IIR filter, respectively.
is output signal (ECG signal after applied filter), is input signal (ECG signal before applied filter), n is the orders of filter.
The characteristic of the symmetrical FIR filter is that it is always stable and the signal is not distorted. However, the symmetrical FIR has a substantial computation, so it needs to be selected appropriately for the intended use. Besides, a symmetric FIR filter with an odd number of coefficients has an integer delay. This means that the original signal and the filtered signal are delayed by shifting an integer number. The integer numbers shift follows the formula below.
n is the orders of filter, d is the shifting delay interval.
The IIR filter has a much smaller order number than the FIR filter. However, the signal, after passing through the IIR filter, is distorted and needs to be designed to ensure stability. The high-pass filter was applied to the ECG signal to eliminate noise with a cutoff frequency in the 0.01 Hz to 0.05 Hz. The FIR filter requires dedicated computations. Therefore, applying the FIR high-pass filter would not be appropriate. Therefore, we only use the IIR high-pass filter. The purpose of a low-pass filter is to remove multiple harmonic supply/ground-bouncing noises from power lines. The noise frequency is equal to the frequency of the power grid, which is 50/60 Hz depending on the power-delivery network in the system. We recommend the filter structure, as shown in Figure 2. The structure includes the combination of low-pass filter (IIR/ FIR) and high-pass filter (IIR).
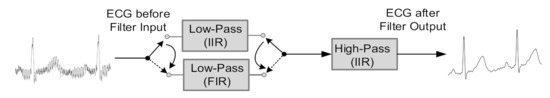
Figure 2.
The structure of filter applied to ECG signal.
Detailed information on the design of high-pass and low-pass filter applied to ECG signals is presented in Table 1. We chose to design the IIR filter according to the Elliptic method and the FIR filter according to the Equiripple method to minimize the number of calculations in the filters.

Table 1.
The Characteristics of Filter Design.
2.3. Standard Evaluation ECG Signal before and after Applied Filter with Different Sampling Frequencies
As we mentioned above, the BIT/ MIH database data has a sampling frequency of 360 Hz. In this section, we will examine the ECG signal extracted from this database with smaller sampling frequencies. The new sampling frequency is chosen as follows = (30, 45, 72, 90, 120, 180) Hz. The evaluation of new data generated from the BIT/ MIH database was performed as follows.
- We created new databases from the MIT/BIT database with sampling frequencies.
- We performed the filter on both new and old data.
- We selected the data after filtering at 360 Hz as the original data and the data at the new sampling frequencies as the comparison data.
- The standards for comparison included: signal to noise ratio of the signal. We compared the amplitudes of the P wave, QRS wave and T wave at different sampling frequencies.
The signal to noise ratio (SNR) of the ECG signal is shown below:
According to the Formulas (1) and (2), the total number of multiplication and addition calculations for the FIR/ IIR filter is as follows:
The total number of multiplication and work performed by the FIR/ IIR filter on the entire data are as follows:
where: L is the length of data, M is the order of FIR and N is the order of IIR filter
3. Results
In this section, we evaluated the effect of filters on ECG signals at different sampling frequencies. We used ECG signals from the MIT/ BIH database, and the signals were collected directly from volunteers. The electrocardiogram sample from the MIT/BIH database is fixed at a sampling rate of 360 Hz. However, the electrocardiogram signals from the volunteers had a dynamic sampling frequency of 100 Hz to 2133 Hz.
3.1. Testing the Filter with the MIT/BIH Database
We used five ECG signals from the MIT/ BIH database to evaluate the high-pass and low-pass filters. This data are then used to generate seven new ECG signals with sample frequencies of less than (30, 45, 60, 72, 90, 120 and 180) Hz. For our proposed design, we chose the lowest possible sampling rate suitable for a heart rate monitor application because the reduced size of data could increase the computation efficiency and overall power overhead in the system. The minimum sampling frequency suitable for ECG applications with P wave and QRS wave needed to be evaluated.
3.1.1. Analysis of the Minimum Sampling Frequency Choice for Heart Rate Applications
We also used five ECG signals from the MIT/ BIH database with sample frequencies below (30, 45 and 60) Hz. The results show that for the frequency of 30 Hz, the value on the R peak of the signal is decreased significantly, so it is not suitable for the application to calculate the heart rate using the data from the R peak of the ECG signal. For the sampling frequency of 45 Hz, there is still some loss of peak R. Therefore, we find that the minimum sampling frequency of 45 Hz is suitable for ECG applications that calculate heart rate with R peak of ECG signal. In Figure 3, we described these signals.
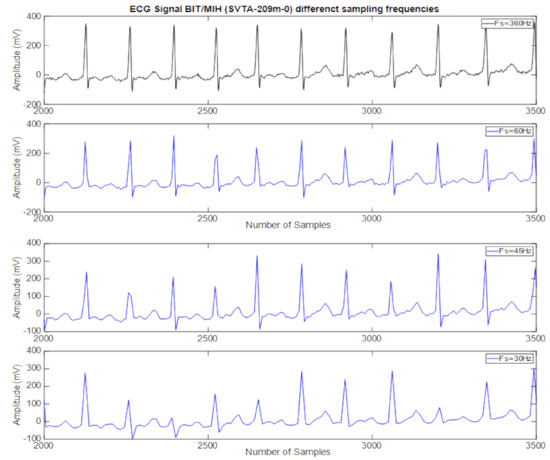
Figure 3.
The comparison ECG with different low sampling frequencies (first plot with black color lines for original data and second three plots with blue color lines for regenerated waveforms with 30, 45 and 60 Hz).
3.1.2. Analysis of the Minimum Sampling Frequency for P, QRS, T Wave Applications
We examine five ECG signals from the MIT/ BIH database with sample frequencies below (60, 72, 90, 120 and 180) Hz. The results show that for frequencies of less than 90 Hz, the determinants Q and S values might be usually wrong. Therefore, we choose the value of the minimum sampling frequency suitable for applications where the P, QRS, and T waveforms are considered to be 90 Hz. In Figure 4, we described the ECG signals with different sample frequencies and S and Q positions.
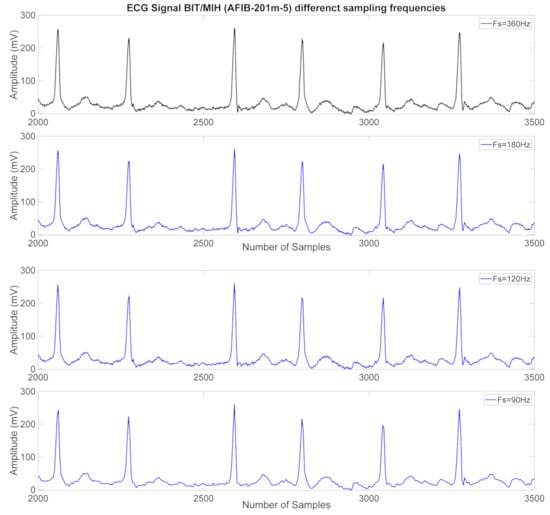
Figure 4.
The comparison ECG signal with different sampling frequencies for P, QRS, T wave detection (first plot with black color lines for original data and second three plots with blue color lines for regenerated waveforms with 90, 120 and 180 Hz).
Figure 5 describes the original ECG signal in the time domain and noise spectrum with a sampling rate of 360 Hz. Figure 5b clearly shows that the filtered signals such as low-pass FIR (blue) and low-pass IIR (red) could provide sufficient noise suppression against the original signals, which could improve the accurate processing of ECG signals.
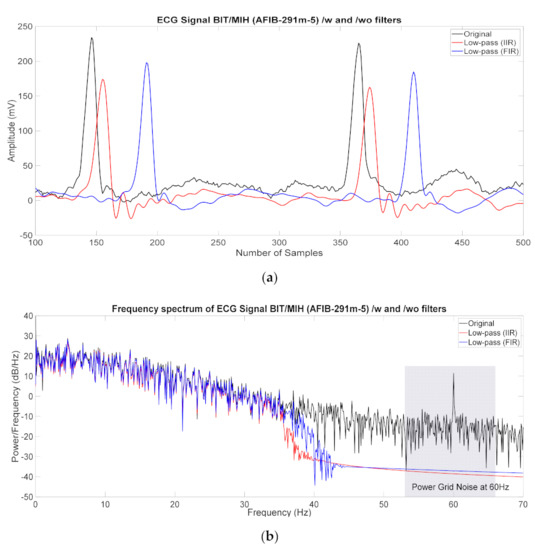
Figure 5.
(a) ECG signal in the time domain and (b) ECG spectral signal with original (black) and filtered signals (red (IIR), blue (FIR)) for noise suppression.
Next, we will investigate the effect of filters on ECG signals with different sampling frequencies as 90, 120, 180 and 360 Hz. For ECG signals with sampling frequencies 90 and 120 Hz, we do not apply a low-pass and high-pass filter because the noise in these ECG signals is noise from the power grid with a frequency 60 Hz. The 90 Hz and 120 Hz sampling frequencies are not large enough to evaluate the effect of this noise. The results are described in Table 2.

Table 2.
The comparison SNR, P, QRS, T wave of ECG from MIT/ BIH Database before and after Filter.
The results described in Table 2 include: the SNR of the signal before and after applying the filter, the amplitude of the P, QRS and T wave before and after the filter, and the number of calculations corresponding to each filter.
- (a)
- Analysis of SNR without filter and with the proposed filters.
When we change the sampling frequency, we see that the SNR of the signal changes. The SNR of the ECG signals tends to increase, and at 90 Hz, many data have the largest SNR (AFIB-201m(5), NSR-100m(5)). We can clearly see that the smaller sampling frequency could reduce the effect of spectral noises from power delivery networks at 60 Hz.
For the 90 Hz and 120 Hz sampling frequencies for reconstructing ECG signals, we only apply the IIR low-pass filter because the low-pass IIR filter could provide the lower order of filtering and greatly improve computation efficiency of the FIR low-pass filter. We see that the SNR of the ECG signal at the sampling frequencies at 90 and 120 Hz is smaller than the SNR of the original signal because the IIR filter has distorted the ECG signals, leading to the reduction in the SNR of the reconstructed ECG signals in the 35 to 45 Hz frequency range. At 180 Hz and 360 Hz sampling frequencies, we also investigated and analyzed the SNR characteristics depending on a wide range of combinations of filters. The SNR of the ECG signal with combined high-pass and low-pass IIR/ FIR filters could provide the best performance among all combinations of filters such as high-pass (HP) and low-pass (LP) IIR/ FIR, HP-LP (IIR-IIR), and HP-LP (IIR-FIR). At the lower sampling frequencies of less than 120 Hz, we found that there is no need to apply any filters to improve the ECG signals.
In terms of amplitude at different ECG sampling frequencies, for the ECG signals at sampling frequencies 180 Hz and 360 Hz, the amplitudes of the P, QRS and T waves of the symmetric FIR filter signal are higher than those of the IIR filter. The IIR filter could more significantly reduce the signal amplitude than the FIR filter, which also can lead to increased difficulty of positioning of the peak S of ECG signal. The FIR filter makes quite easy to decide on the implement and the amplitude of the QRS wave is the same in the original signal. However, the IIR filter might cause unwanted signal ringing, as shown in Figure 5b. Therefore, the choice of filter combination and optimization of filter orders is the most important factor in terms of SNR, amplitude and computation complexity.
- (b)
- Optimal number of filter orders
The results in Table 2 also show massive differences in the number of calculations that need to be performed between the IIR and symmetric FIR filters at different frequencies.
At 180 Hz sampling frequency, the order of the symmetric FIR filters with an odd order of filter is 45, while that of the IIR filter is 15. However, at different sampling frequencies (i.e., 360 Hz), the computation complexity can be increased significantly, because the orders of FIR filter should be changed from 45 to 91. Hence, we could determine that the selection of the sampling frequency at 180 Hz can be the most suitable for the ECG signals because the low-pass FIR could significantly remove noises from power delivery networks operating with 50 and 60 Hz frequencies.
3.2. Experiment with Volunteers
We made a test model to measure the ECG signal from the volunteers, as shown in Figure 6. The hardware architecture includes the ECG integrated circuit (ADS1293) and the evaluation board (ESP32). The ADS1293 board connects to the volunteer body by electrodes [42] and communicates with the ESP32 board by a serial peripheral interface (SPI). The connection signals of the ESP32 board and the ADS1293 module include such key components as (GPIO23-MOSI), (GPIO19-MISO), (GPIO18-SCK), (GPIO17-ADS1293_CS) and (GPIO16-ADS1293_INT. For the ADS1293 chip, the configured signals include the following (IN0-RA), (IN1-LA), (IN2-LL) and (IN3-RL). Operation configuration as well as other parameters are described in detail here [19]. The implementation code for this system uses the Arduino library. The sampling frequency of the ADS1293 can be adjusted to make our tests suitable. In the evaluation tests, the sampling frequencies of the ECG signals were chosen to be 100 Hz, 200 Hz, 400 Hz and 2133 Hz, respectively. With different sampling frequencies, we can perform monitoring in order to eliminate the effects of different types of noises effective the ECG signal. We applied the proposed filter architecture to our system, as depicted in Figure 3, to remove any unwanted noises from the ECG signals collected from volunteers. The software to collect and display the ECG signals is programmed based on MATLAB. The key results including SNR and ECG amplitudes, and utilized filter orders are summarized in Table 3.
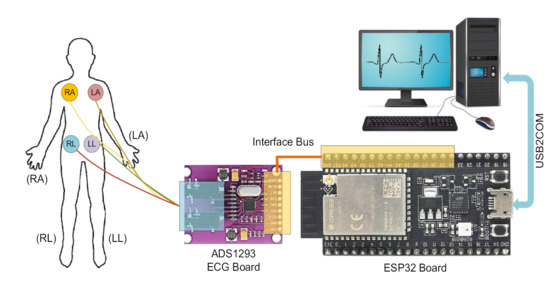
Figure 6.
Real-time ECG measurement system.

Table 3.
The comparison SNR, P, QRS, T wave of ECG signals from volunteers (with/without applied filtering).
Table 3 shows the measured SNR of ECG signals at different sampling frequencies, such as 2133, 400, 200, 100 Hz. We can reconstruct the (30, 40, 60, 90, 120, 180) Hz from the original MIB data (330 Hz). We used sampling frequencies for our system that were similar to reconstructed signal frequencies (i.e., measured 100 Hz signal for the reconstructed 90 Hz). This comes from the limitation of the fixed frequency of utilized chips (i.e., 2333 Hz of ADS1293).
From the analysis of the ECG signals, such as SNR and amplitude, we could find that no filter is needed for P, QRS, and T waves at the 100 Hz sampling frequency. However, as the sampling frequency was increased, we could see that the SNR of the original ECG signals degraded, as shown in Figure 7a,c and Figure 8a. In terms of measured amplitude of the P, QRS and T waves from the ECG signals, we found that the amplitude of the symmetric FIR filter was higher than that of the IIR filter. In terms of needed number of filters, the low-pass IIR filter could provide same order of filter until 2133 Hz. However, the order of needed filter was increased significantly when the sampling frequency increased to more than 2133 Hz.
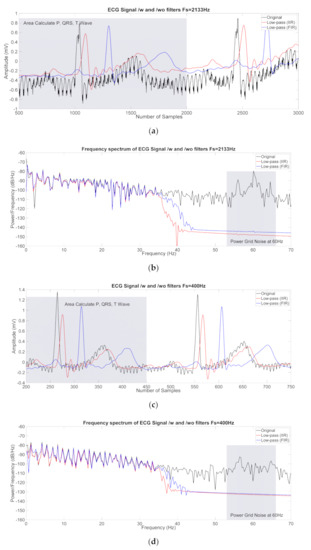
Figure 7.
ECG signal in the time domain and ECG spectral signal with original (black) and filtered signals (red (IIR), blue (FIR)) for noise suppression: (a,b) at sampling frequency 2133 Hz; (c,d) at sampling frequency 400 Hz.
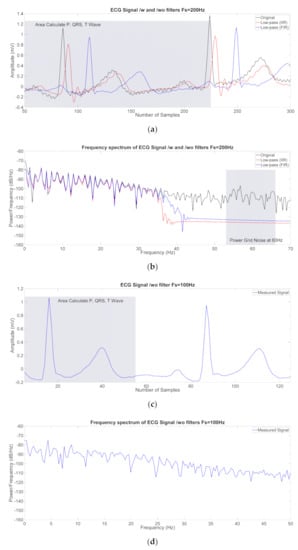
Figure 8.
ECG signal in the time domain and ECG spectral signal with original (black) and filtered signals (red (IIR), blue (FIR)) for noise suppression: (a,b) at sampling frequency 200 Hz; (c,d) at sampling frequency 100 Hz.
4. Discussion
Through our proposed ECG system, we could reconstruct the ECG signal from the MIT/ BIH database to accurately calculate heart rate at 45 Hz. We could significantly reduce the computation complexity (i.e., eight times lower than the original sampling frequency from the MIT/ BIH database) by using optimal low-pass and high-pass FIR/ IIR filters. In particular, in the case of ECG application system that required P, QRS and T wave evaluation, the best sampling frequency could be 90 Hz for optimal performance. Furthermore, the ECG signal does not need any filtering operation to suppress any potential noises from hardware and the human body from 90 Hz to 120 Hz sampling frequencies. We also found that the low-pass symmetric FIR filtering of ECG signals at 180 Hz sampling frequency could provide much better performance than IIR filtering, including reduced noise suppression from power delivery networks. Furthermore, when the sampling frequencies are higher than 360 Hz, low-pass IIR filtering could significantly reduce the computation complexity, leading to fast data processing (i.e., reduced mathematical calculation of MCU). In the measured SNR, our proposed ECG system with the 100 Hz sampling frequency could also improve performance in ECG application areas (i.e., 10 times better than the original 2133 Hz sampling frequency). In terms of noise performance, the measured SNR of our proposed ECG system, which required P, QRS and T wave evaluation at 100 Hz sampling frequency, also needed no additional filters to reject unwanted noises from hardware and the human body, leading to the significantly reduced computation and real-time data processing of ECG signals.
Eliminating interference with the ECG signal is always a top priority because it directly affects clinical applications and diagnostics. Usually, a good combination of hardware and software could be the best solution to filter out unwanted noises because the dedicated combination of filters might increase the cost of the device and the design complexity. High-quality ECG pads between the patient body and ECG sensor also could improve the signal quality in terms of hardware. The ECG signal quality could also be further enhanced by utilizing adaptive filters.
5. Conclusions
We analyzed, designed, and implemented the electrocardiogram systems with optimal filters to suppress two types of unwanted noises from hardware, such as power delivery networks and miscellaneous peripherals, and from the human body, such as muscle activities. From our analysis and design of the proposed ECG filter system, the reduction in sampling frequency could improve performance in ECG application areas, for example, by enhancing power and computation efficiency, thus leading to real-time ECG data processing and measurement. Furthermore, our proposed system also could reduce design complexity and provide low-cost solutions for ECG signal processing.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.-T.B. and G.-s.B.; methodology, N.-T.B.; software, N.-T.B.; validation, G.-s.B.; formal analysis, N.-T.B.; investigation, G.-s.B.; resources, N.-T.B.; data curation, N.-T.B.; writing—original draft preparation, N.-T.B.; writing—review and editing, G.-s.B.; visualization, G.-s.B.; supervision, G.-s.B.; project administration, G.-s.B.; funding acquisition, G.-s.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Inha University Research Grant under Grant INHA-00000.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Moody GB, Mark RG. The impact of the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database. IEEE Eng in Med and Biol 20(3):45-50 (May-June 2001). (PMID: 11446209).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Chen, X.H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Arrhythmia Recognition and Classification Using ECG Morphology and Segment Feature Analysis. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2019, 16, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magsi, H.S.; Sodhro, A.H.; Al-Rakhami, M.S.; Zahid, N.; Pirbhulal, S.; Wang, L. A Novel Adaptive Battery-Aware Algorithm for Data Transmission in IoT-Based Healthcare Applications. Electronics 2021, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, U.Z.M.; Moon, K.S.; Lee, S.Q. Extraction and Analysis of Respiratory Motion Using a Comprehensive Wearable Health Monitoring System. Sensors 2021, 21, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.W.; Wu, H.; Zhao, J.; Tao, Y.; Fu, J. Automatic Classification System of Arrhythmias Using 12-Lead ECGs with a Deep Neural Network Based on an Attention Mechanism. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.T.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wu, H. Classification of Congestive Heart Failure from ECG Segments with a Multi-Scale Residual Network. Symmetry 2020, 12, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S. Emery-Dreifuss FHL1 Mutation: A Credo for a Better ECG Definition in Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Mod. J. Med. Biol. 2021, 1, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, X.A.; Abdala, A.K.; Kamavuako, E.N. Estimation of the Respiratory Rate from Localised ECG at Different Auscultation Sites. Sensors 2021, 21, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hua, W.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Gao, X. Heartbeat classification using projected and dynamic features of ECG signal. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 31, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustyniak, P. Diagnostic Interpretation of Non-Uniformly Sampled Electrocardiogram. Sensors 2021, 21, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.Z. Intelligent and Real-Time Data Acquisition for Medical Monitoring in Smart Campus. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 74836–74846. [Google Scholar]
- Bashar, S.K.; Ding, E.; Walkey, A.J.; Mcmanus, D.D.; Chon, K.H. Noise Detection in Electrocardiogram Signals for Intensive Care Unit Patients. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 88357–88368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeiro, J.P.V.; Santos, E.M.B.; Cortez, P.C.; Felix, J.H.S.; Schlindwein, F.S. Evaluating Gaussian and Rayleigh-Based Mathematical Models for T and P-waves in ECG. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2017, 15, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, J.; Torres, A.M.; Aparicio, A.; Santos, J.L. An efficient method for ECG beat classification and correction of ectopic beats. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2016, 53, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, N.T.; Phan, D.T.; Nguyen, T.P.; Hoang, G.; Choi, J.; Bui, Q.C.; Oh, J. Real-Time Filtering and ECG Signal Processing Based on Dual-Core Digital Signal Controller System. IEEE Sens. 2020, 20, 6492–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.; Jais, R.; Hota, M.K. Removal of Powerline Interference from ECG Signal using FIR, IIR, DWT and NLMS Adaptive Filter. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Chennai, India, 4–6 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Levkov, C.; Mihov, G.; Ivanov, R.; Daskalov, I.; Christov, I.; Dotsinsk, I. Removal of power-line interference from the ECG: A review of the subtraction procedure. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2005, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mateoa, J.; Sánchez-Morla, E.M.; Santos, J.L. A new method for removal of powerline interference in ECG and EEG recordings. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2015, 45, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, N.T.; Nguyen, T.M.T.; Park, S.; Choi, J.; Vo, T.M.T.; Kang, Ye.; Kim, By.; Oh, J. Design of a nearly linear-phase IIR filter and JPEG compression ECG signal in real-time system. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 67, 102431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhatte, A.S.; Ghongade, R.; Tekale, S.V. Noise Analysis of ECG Signal Using Fast ICA. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Advances in Signal Processing (CASP), Pune, India, 9–11 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nevi, J.; Shakya, D.K. Denoising Baseline Wander Noise from Electrocardiogram Signal using Fast ICA with Multiple Adjustments. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2014, 99, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kher, R. Signal Processing Techniques for Removing Noise from ECG Signals. J. Biomed. Eng. Res. 2019, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Pisani, B. Digital Filter Types in Delta-Sigma ADCs. Texas Instrument: USA. 2017. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwio1frwuvPxAhWPwpQKHfAFCAYQFjAAegQIAxAD&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.ti.com%2Flit%2FSBAA230&usg=AOvVaw20EnmELqUtCkeuJau3m1qv (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Husain, K.; Zahid, M.S.M.; Ul Hassan, S.; Hasbullah, S.; Mandala, S. Advances of ECG Sensors from Hardware, Software and Format Interoperability Perspectives. Electronics 2021, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohaddes, F.; da Silva, R.L.; Akbulut, F.P.; Zhou, Y.; Tanneeru, A.; Lobaton, E.; Lee, B.; Misra, V. A Pipeline for Adaptive Filtering and Transformation of Noisy Left-Arm ECG to Its Surrogate Chest Signal. Electronics 2020, 9, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poungponsri, S.; Yu, X.-H. An. adaptive filtering approach for electrocardiogram (ECG) signal noise reduction using neural networks. Neurocomputing 2013, 117, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuradha, P.; Arabelli, R.; Rajkumar, K. Noise removal of ECG signals with adaptive filtering. Mater. Today Proc. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasan, E.; Panneerselvam, I. A novel dimensionality reduction approach for ECG signal via convolutional denoising autoencoder with LSTM. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 63, 102225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B. Delta-Sigma ADCs in a Nutshell. Texas Instrument: USA. 2007. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjTgIGPu_PxAhXpFqYKHRShD8MQFjAAegQIAxAD&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.rpi.edu%2Fdept%2Fecse%2Frta%2FLMS%2FDelta-Sigma_ADCs.pdf&usg=AOvVaw1gtlqld4N66_n8O7rOVKuv (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Kumngern, M.; Auphithak, N.; Khateb, F.; Kulej, T. 0.5 V Fifth-Order Butterworth Low-Pass Filter Using Multiple-Input OTA for ECG Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zompanti, A.; Sabatini, A.; Grasso, S.; Pennazza, G.; Ferri, G.; Barile, G.; Chello, M.; Lusini, M.; Santonico, M. Development and Test of a Portable ECG Device with Dry Capacitive Electrodes and Driven Right Leg Circuit. Sensors 2021, 21, 2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, N.T.; Vo, T.H.; Kim, B.-k.; Oh, J. Design of a Solar-Powered Portable ECG Device with Optimal Power Consumption and High Accuracy Measurement. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plawiak, P. ECG Signals (1000 Fragments). 2017. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/7dybx7wyfn/3 (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Instruments, T. ADS1293 24-bit, 3-ch, Low-Power Analog Front-End (AFE) for ECG Applications. Texas Instrument: USA. 2014. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiHsYuhu_PxAhUmyIsBHXCUDJ4QFjABegQIBBAD&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.ti.com%2Flit%2Fgpn%2Fads1293&usg=AOvVaw1Hg-0ApG7NF92PtKp3VDnE (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Integrated, M. MAX86150 Integrated Photoplethysmogram and Electrocardiogram Bio-Sensor Module for Mobile Health. Integrated, M., Ed.; 2018. Available online: https://www.maximintegrated.com/en/products/interface/sensor-interface/MAX86150.html (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Beach, C.; Krachunov, S.; Pope, J.; Fafoutis, X.; Robert, J.P.; Craddock, I.; Alexander, J.C. An Ultra Low Power Personalizable Wrist Worn ECG Monitor Integrated with IoT Infrastructure. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 44010–44021. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8432430 (accessed on 1 July 2021). [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, T. A Battery-Less Portable ECG Monitoring System with Wired Audio Transmission. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2019, 13, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Deng, G.; Wei, W.; Wang, H.; Ming, Z. Design of a Real-Time ECG Filter for Portable Mobile Medical Systems. IEEE Access 2016, 5, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The McGill Physiology Virtual Lab. Electrocardiogram Waveform. 2021. Available online: https://www.medicine.mcgill.ca/physio/vlab/cardio/introECG.htm (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- Bae, T.W.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, K.K. An Adaptive Median Filter Based on Sampling Rate for R-Peak Detection and Major-Arrhythmia Analysis. Sensors 2020, 20, 6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Sheng, V.S.; Ding, X. An ECG Signal De-Noising Approach Based on Wavelet Energy and Sub-Band Smoothing Filter. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Song, Y.; Gou, L.; Zou, Y. A Novel Wearable Flexible Dry Electrode Based on Cowhide for ECG Measurement. Biosensors 2021, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).