Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis: A Cross-Sectional Study to Investigate Clinical Features and Patients’ Quality of Life
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Questionnaire
2.1.1. Clinical Information
2.1.2. Patient-Reported Outcomes
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Information
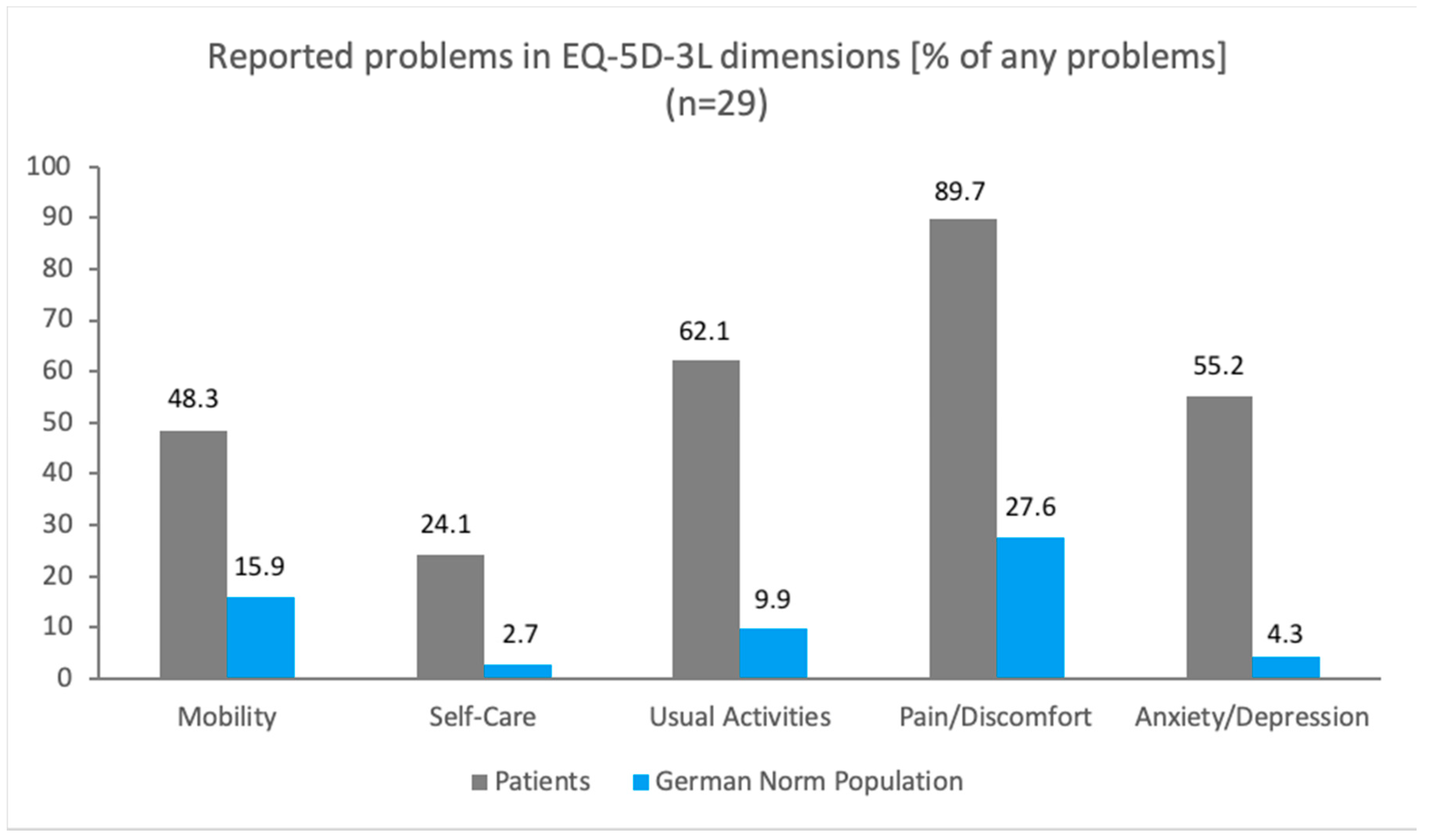
3.2. EQ-5D-3L
3.3. Patient-Benefit-Index-Lymphedema
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Enzi, G.; Busetto, L.; Ceschin, E.; Coin, A.; Digito, M.; Pigozzo, S. Multiple symmetric lipomatosis: Clinical aspects and outcome in a long-term longitudinal study. Int. J. Obes. 2002, 26, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enzi, G. Multiple symmetric lipomatosis: An updated clinical report. Medicine 1984, 63, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiltz, D.; Anker, A.; Ortner, C.; Tschernitz, S.; Koller, M.; Klein, S.; Felthaus, O.; Schreml, J.; Schreml, S.; Prantl, L. Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis: New Classification System Based on the Largest German Patient Cohort. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2018, 6, e1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzi, G.; Busetto, L.; Sergi, G.; Coin, A.; Inelmen, E.M.; Vindigni, V.; Bassetto, F.; Cinti, S. Multiple symmetric lipomatosis: A rare disease and its possible links to brown adipose tissue. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez Aragon, F.; Morales Puebla, J.M.; Corzon Pereira, T. Madelung’s disease. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2013, 64, 166–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, C.I.; Carvalho, P.J.; Correia, M.M. Madelung’s Disease: Revision of 59 Surgical Cases. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2017, 41, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prantl, L.; Schreml, J.; Gehmert, S.; Klein, S.; Bai, X.; Zeitler, K.; Schreml, S.; Alt, E.; Gehmert, S.; Felthaus, O. Transcription Profile in Sporadic Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis Reveals Differential Expression at the Level of Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 137, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzicka, T.; Vieluf, D.; Landthaler, M.; Braun-Falco, O. Benign symmetric lipomatosis Launois-Bensaude. Report of ten cases and review of the literature. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1987, 17, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donhauser, G.; Vieluf, D.; Ruzicka, T.; Braun-Falco, O. Benign symmetric Launois-Bensaude type III lipomatosis and Bureau-Barriere syndrome. Der Hautarzt Z. Dermatol. Venerol. Verwandte Geb. 1991, 42, 311–314. [Google Scholar]
- Brea-Garcia, B.; Cameselle-Teijeiro, J.; Couto-Gonzalez, I.; Taboada-Suarez, A.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, E. Madelung’s disease: Comorbidities, fatty mass distribution, and response to treatment of 22 patients. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2013, 37, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, P.; Prosdocimi, M.; Carpenedo, F.; Caparrotta, L.; Tessari, F.; Enzi, G. Multiple symmetric lipomatosis. A defect in adrenergic stimulated lipolysis II. Pharmacol. Res. Commun. 1980, 12, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzi, G.; Inelmen, E.M.; Baritussio, A.; Dorigo, P.; Prosdocimi, M.; Mazzoleni, F. Multiple symmetric lipomatosis: A defect in adrenergic-stimulated lipolysis. J. Clin. Investig. 1977, 60, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Dou, J.; Yang, G.; Li, J.; Ba, J.; Lu, Z.; Mu, Y.; Lu, J. The endocrine and metabolic evaluation of benign symmetrical lipomatosis: A case report and literature review. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2010, 31, 446–450. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, Y.; Yao, P.; Xin, W.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; Yue, J.; Zhu, J. Recent progress on diagnosis and treatment of benign symmetric lipomatosis. J. Clin. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 24, 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.H.; Mottillo, E.P.; Granneman, J.G. Adipose tissue plasticity from WAT to BAT and in between. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naumann, M.; Schalke, B.; Klopstock, T.; Reichmann, H.; Lange, K.W.; Wiesbeck, G.; Toyka, K.V.; Reiners, K. Neurological multisystem manifestation in multiple symmetric lipomatosis: A clinical and electrophysiological study. Muscle Nerve 1995, 18, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, A.; Okada, Y.; Morita, E.; Tanaka, Y. Benign symmetric lipomatosis associated with alcoholism. Intern. Med. 2006, 45, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klopstock, T.; Naumann, M.; Schalke, B.; Bischof, F.; Seibel, P.; Kottlors, M.; Eckert, P.; Reiners, K.; Toyka, K.V.; Reichmann, H. Multiple symmetric lipomatosis: Abnormalities in complex IV and multiple deletions in mitochondrial DNA. Neurology 1994, 44, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawyer, S.L.; Cheuk-Him Ng, A.; Innes, A.M.; Wagner, J.D.; Dyment, D.A.; Tetreault, M.; Care4Rare Canada, C.; Majewski, J.; Boycott, K.M.; Screaton, R.A.; et al. Homozygous mutations in MFN2 cause multiple symmetric lipomatosis associated with neuropathy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 5109–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zolotov, S.; Xing, C.; Mahamid, R.; Shalata, A.; Sheikh-Ahmad, M.; Garg, A. Homozygous LIPE mutation in siblings with multiple symmetric lipomatosis, partial lipodystrophy, and myopathy. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2017, 173, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindner, A.; Marbach, F.; Tschernitz, S.; Ortner, C.; Berneburg, M.; Felthaus, O.; Prantl, L.; Kye, M.J.; Rappl, G.; Altmuller, J.; et al. Calcyphosine-like (CAPSL) is regulated in Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis and is involved in Adipogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nisoli, E.; Regianini, L.; Briscini, L.; Bulbarelli, A.; Busetto, L.; Coin, A.; Enzi, G.; Carruba, M.O. Multiple symmetric lipomatosis may be the consequence of defective noradrenergic modulation of proliferation and differentiation of brown fat cells. J. Pathol. 2002, 198, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiltz, D.; Tschernitz, S.; Ortner, C.; Anker, A.; Klein, S.; Felthaus, O.; Biermann, N.; Schreml, J.; Prantl, L.; Schreml, S. Adipose Tissue in Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis Shows Features of Brown/Beige Fat. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felthaus, O.; Schon, T.; Schiltz, D.; Aung, T.; Kuhlmann, B.; Jung, F.; Anker, A.; Klein, S.; Prantl, L. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells from affected and unaffected areas in patients with multiple symmetric lipomatosis show differential regulation of mTOR pathway genes. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2018, 69, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.J.; Chen, L.L.; Huarte, M. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, W.; Claes, C.; Busschbach, J.J.; von der Schulenburg, J.M. Validating the EQ-5D with time trade off for the German population. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2005, 6, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EuroQol Research Foundation. EQ-5D-3L User Guide. 2018. Available online: www.euroqol.org (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- Blome, C.; Augustin, M.; Behechtnejad, J.; Rustenbach, S.J. Dimensions of patient needs in dermatology: Subscales of the patient benefit index. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2011, 303, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blome, C.; Augustin, M.; Heyer, K.; Knofel, J.; Cornelsen, H.; Purwins, S.; Herberger, K. Evaluation of patient-relevant outcomes of lymphedema and lipedema treatment: Development and validation of a new benefit tool. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2014, 47, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szende, A.; Janssen, B. Socio-demographic indicators based on EQ-5D. In Self-Reported Population Health: An International Perspective Based on EQ-5D; Szende, A., Janssen, B., Cabases, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plummer, C.; Spring, P.J.; Marotta, R.; Chin, J.; Taylor, G.; Sharpe, D.; Athanasou, N.A.; Thyagarajan, D.; Berkovic, S.F. Multiple Symmetrical Lipomatosis--a mitochondrial disorder of brown fat. Mitochondrion 2013, 13, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, K.L. Subcutaneous adipose tissue diseases: Dercum disease, lipedema, familial multiple lipomatosis, and madelung disease. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Dungan, K., Grossman, A., Hershman, J.M., Kaltsas, G., Koch, C., Kopp, P., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, R.H.; Kim, B.; Choi, I.; Kim, H.; Choi, H.S.; Suh, K.; Bae, Y.C.; Jung, J.S. Characterization and expression analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow and adipose tissue. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 14, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, K.; Kahnert, S.; Mons, U. Alkoholatlas Deutschland 2017; Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum in der Helmholz-Gemeinschaft: Bonn, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
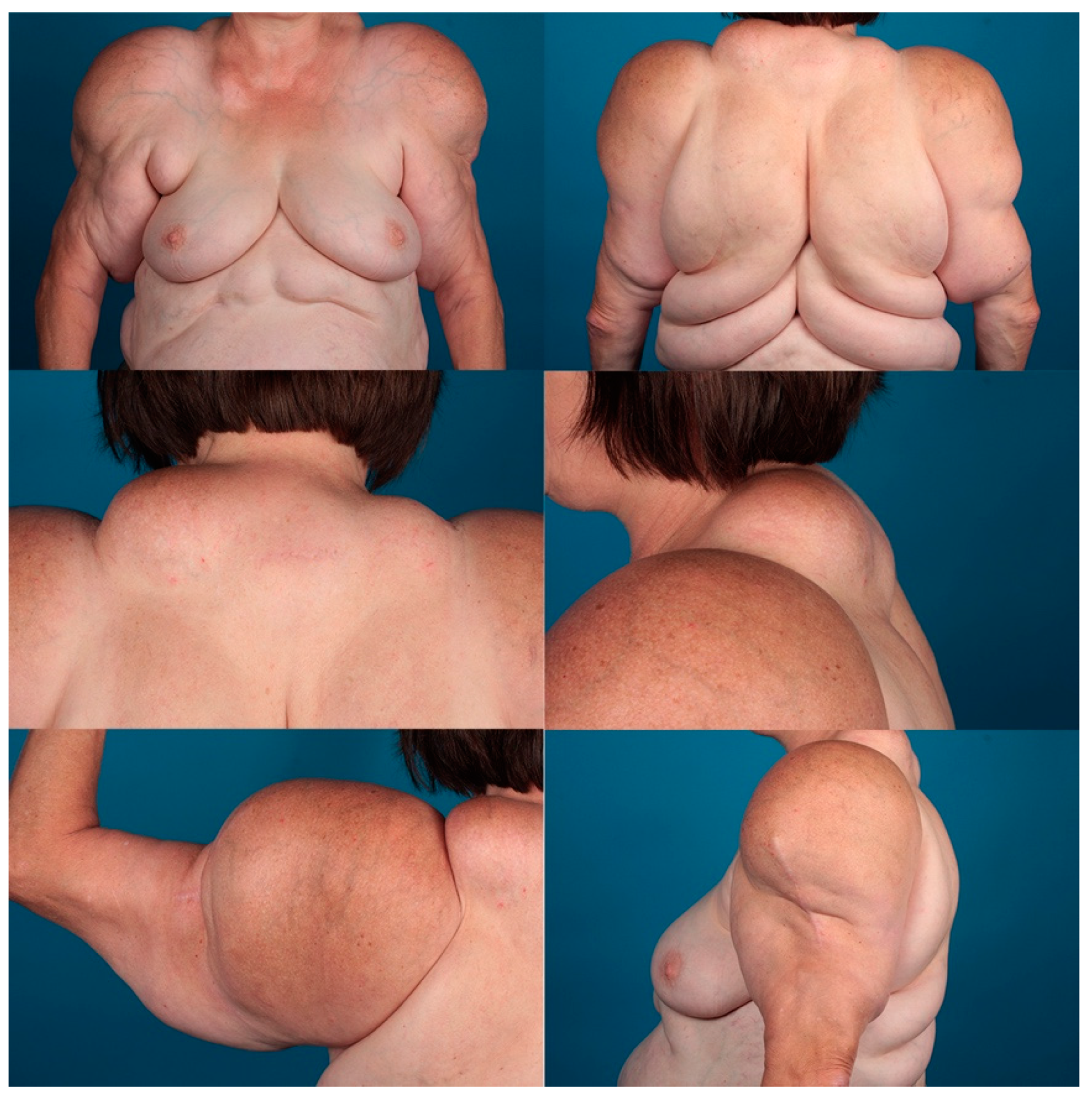


| Age in years mean ± (min–max) n = 29 | 58.5 ± 13 (31–77) |
| Sex | |
| male | 6 (21%) |
| female | 23 (79%) |
| Weight in kg mean ± (min–max) n = 27 | 88.9 ± 21 (53–130) |
| Occupation | |
| Trainee | 1 (3%) |
| Employee | 13 (45%) |
| Civil servant | 3 (10%) |
| Freelancer | 2 (7%) |
| Househusband/housewife | 1 (3%) |
| Pensioner | 2 (7%) |
| Missing | 7 (24%) |
| Height in cm mean ± (min–max) n = 29 | 164.9 ± 8 (148–188) |
| Body-Mass-Index (BMI) in kg/m2 mean ± (min–max) n = 27 | 32 ± 8 (21–53) |
| Normal weight | 4 (14%) |
| Overweight | 8 (28%) |
| Adipositas I (BMI 30–35) | 4 (14%) |
| Adipositas II (BMI 35–40) | 8 (28%) |
| Adipositas III (BMI > 40) | 3 (10%) |
| Missing | 2 (7%) |
| Weight changes in kg in last 5 years | |
| Stable | 14 (48%) |
| Weight gain (mean ± sd, min–max) | 13 (45%) (16 ± 12, 2–30) |
| Weight loss (mean) | 1 (3%) (7) |
| Missing | 1 (3%) |
| Permanent medication | |
| Yes | 23 (79%) |
| No | 6 (21%) |
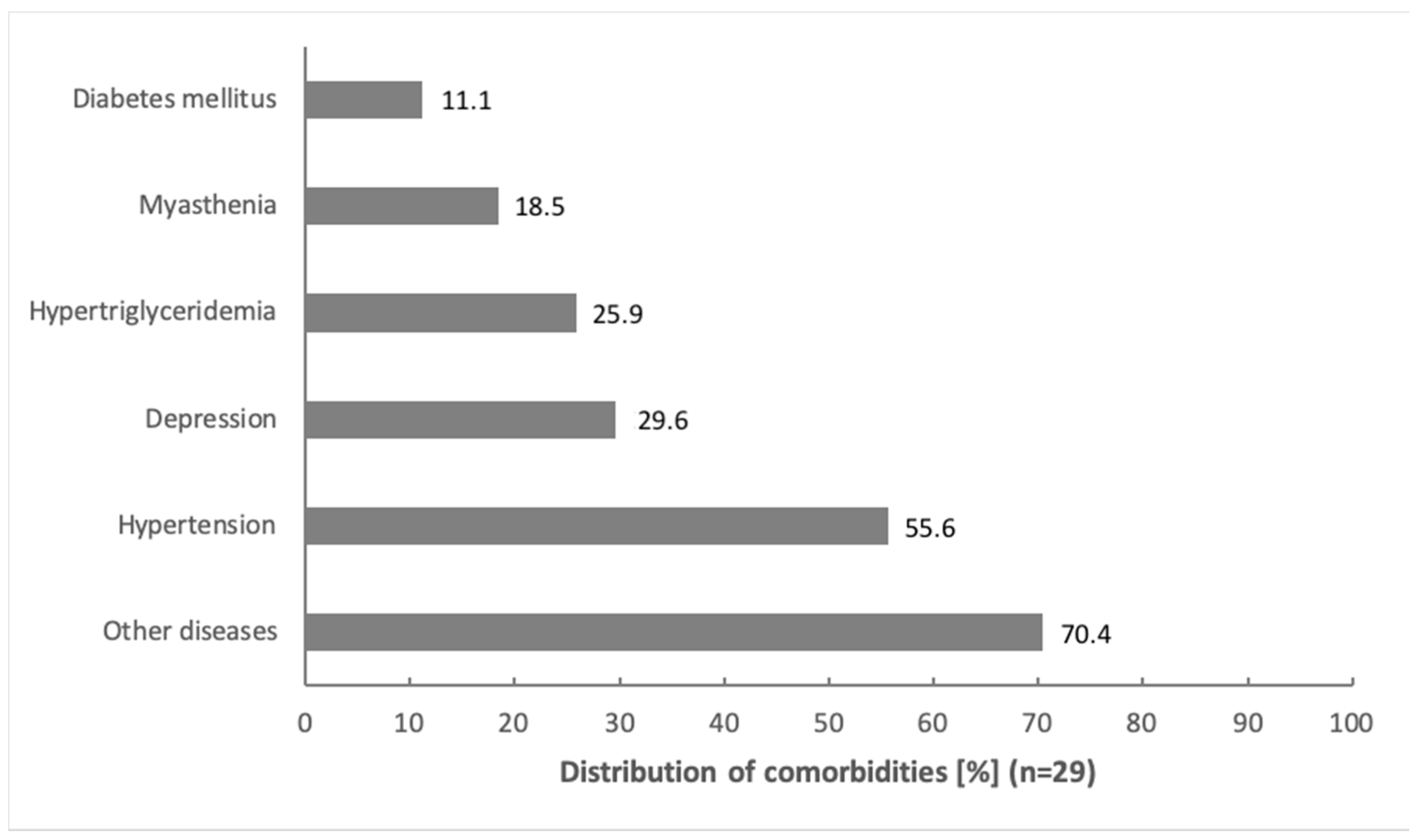
| Comorbidities mean ± (min–max) | 2 ± 2 (0–4) |
| Yes (hypertension n = 15, diabetes mellitus n = 3, hyperlipidemia n = 7, myasthemia n = 5, depression n = 8, other disease n = 19) | 27 (93%) |
| No | 2 (7%) |
| Alcohol consumption | |
| Yes, daily | 5 (17%) |
| Yes, not daily | 7 (24%) |
| No | 17 (59%) |
| Age of MSL onset in years mean ± (min–max) n = 29 | 37.0 ± 15 (14–70) |
| Pain | |
| Pain in affected areas | |
| Yes | 8 (28%) |
| No | 21 (72%) |
| Factors that ease pain | |
| Yes (movement n = 5, cold n = 3, warmth n = 4, lymphatic drainage n = 1, physiotherapy n = 2, massage n = 1) | 11 (38%) |
| No | 17 (59%) |
| Missing | 1 (3%) |
| Factors that increase pain | |
| Yes (movement n = 3, cold n = 4, warmth n = 3, long time standing n = 3) | 15 (52%) |
| No | 14 (48%) |
| Paraesthesia in affect areas | |
| Yes | 18 (62%) |
| No | 10 (34%) |
| Missing | 1 (3%) |
| Suspected factor in the last 6 months that triggered MSL | |
| Yes (diverticulosis + surgery n = 1, oral contraceptives n = 1, alcohol withdrawal n = 1, liver disease n = 1, surgery n = 1, pregnancy (clomifen) n = 1, stress n =1, increasing insulin resistance n = 1) | 8 (28%) |
| No | 19 (66%) |
| Missing | 2 (7%) |
| Family occurrence | |
| Yes | 10 (34%) |
| No | 10 (34%) |
| Unknown | 8 (28%) |
| Missing | 1 (3%) |
| Therapy | |
| Yes (liposuction n=16, lipectomy n=7) Number of treatments 1 2 3 4 5 | 23 (79%) 7 (24%) 8 (28%) 3 (10%) 4 (14%) 1 (3%) |
| No | 6 (21%) |
| Medication | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Allopurinol | 2 | 2.4 |
| Amlodipin | 2 | 2.4 |
| Anastrozol | 1 | 1.2 |
| ASS | 2 | 2.4 |
| Bimatoprost | 1 | 1.2 |
| Bisoprolol | 3 | 3.6 |
| Candesartan | 2 | 2.4 |
| Cetirizin | 1 | 1.2 |
| Citalopram | 1 | 1.2 |
| Clomipramin | 1 | 1.2 |
| Coumarin | 1 | 1.2 |
| Dapagliflozin | 1 | 1.2 |
| Diclofenac | 1 | 1.2 |
| Digoxin | 1 | 1.2 |
| Diltiazem | 1 | 1.2 |
| Enalapril | 2 | 2.4 |
| Esomeprazol | 1 | 1.2 |
| Euthyrox | 1 | 1.2 |
| Ferrosanol | 1 | 1.2 |
| Formoterol | 1 | 1.2 |
| Furosemid | 1 | 1.2 |
| Gestagen | 4 | 4.8 |
| Ginkgo | 1 | 1.2 |
| Hydrochlorothiazid | 1 | 1.2 |
| Ibuprofen | 1 | 1.2 |
| Insulin | 1 | 1.2 |
| L-Thyroxin | 4 | 4.8 |
| Liponsäure | 1 | 1.2 |
| Lorazepam | 1 | 1.2 |
| Mesalazin | 1 | 1.2 |
| Metformin | 1 | 1.2 |
| Methylprednisolon | 1 | 1.2 |
| Metoprolol | 4 | 4.8 |
| Moxonidin | 1 | 1.2 |
| Naproxen | 1 | 1.2 |
| Paroxetin | 1 | 1.2 |
| PPI | 5 | 6.0 |
| Pravastatin | 1 | 1.2 |
| Pregabalin | 2 | 2.4 |
| Propanolol | 1 | 1.2 |
| Ramipril | 6 | 7.2 |
| Raniditid | 1 | 1.2 |
| Rivaroxaban | 1 | 1.2 |
| Salmeterol +Fluticasonpropionat | 2 | 2.4 |
| Simvastatin | 2 | 2.4 |
| Thiazid + Pyrazinkarbonylguanidin | 1 | 1.2 |
| Tilidin | 1 | 1.2 |
| Timolol und Dorzolamid | 1 | 1.2 |
| Torasemid | 2 | 2.4 |
| Tyronajod | 1 | 1.2 |
| Valsartan | 2 | 2.4 |
| Venlafaxin | 1 | 1.2 |
| Zopiclon | 1 | 1.2 |
| Total | 83 | 100.0 |
| Relative Person 1 | Relative Person 2 | Relative Person 3 | Relative Person 4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient | Who | Age * | Who | Age * | Who | Age * | Who | Age * |
| 1 | Daughter | 25 | Daughter | 37 | Mother | Brother | ||
| 2 | Sister | 25 | Mother | 40 | Uncle–maternal | Grandmother-maternal | ||
| 3 | Son | 11 | Aunt | Aunt | Aunt | |||
| 4 | Grandmother | 50 | Mother | 50 | Sister | 30 | ||
| 5 | Mother | Daugther | 35 | Niece | ||||
| 6 | Mother | Grandmother | Aunt | |||||
| 7 | Sister | 40 | Mother | 40 | ||||
| 8 | Brother | 50 | ||||||
| 9 | Brother | |||||||
| 10 | Father | 30 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schiltz, D.; Mueller, K.; Ortner, C.; Tschernitz, S.; Anker, A.; Felthaus, O.; Schreml, J.; Koller, M.; Prantl, L.; Schreml, S. Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis: A Cross-Sectional Study to Investigate Clinical Features and Patients’ Quality of Life. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101823
Schiltz D, Mueller K, Ortner C, Tschernitz S, Anker A, Felthaus O, Schreml J, Koller M, Prantl L, Schreml S. Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis: A Cross-Sectional Study to Investigate Clinical Features and Patients’ Quality of Life. Symmetry. 2021; 13(10):1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101823
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchiltz, Daniel, Karolina Mueller, Christine Ortner, Sebastian Tschernitz, Alexandra Anker, Oliver Felthaus, Julia Schreml, Michael Koller, Lukas Prantl, and Stephan Schreml. 2021. "Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis: A Cross-Sectional Study to Investigate Clinical Features and Patients’ Quality of Life" Symmetry 13, no. 10: 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101823
APA StyleSchiltz, D., Mueller, K., Ortner, C., Tschernitz, S., Anker, A., Felthaus, O., Schreml, J., Koller, M., Prantl, L., & Schreml, S. (2021). Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis: A Cross-Sectional Study to Investigate Clinical Features and Patients’ Quality of Life. Symmetry, 13(10), 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101823








