Abstract
In this paper, we study the symmetric travelling wave solutions of the b-family of the Novikov equation. We show that the b-family of the Novikov equation can provide symmetric travelling wave solutions, such as peakon, kink and smooth soliton solutions. In particular, the single peakon, two-peakon, stationary kink, anti-kink, two-kink, two-anti-kink, bell-shape soliton and hat-shape soliton solutions are presented in an explicit formula.
1. Introduction
The b-family of the Camassa–Holm equation
where b is an arbitrary constant and is fluid velocity. Equation (1) was first proposed by Holm and Stanley in studying the exchange of stability in the dynamics of solitary waves under changes in the nonlinear balance in a evolutionary PDE related to shallow water waves and turbulence [1,2]. In the case of , peakon solutions of Equation (1) were discussed in [1,2]. In the case of , Xia and Qiao showed that Equation (1) provides N-kink, bell-shape and hat-shape solitary solutions [3]. For , Equation (1) becomes the well-known Camassa–Holm (CH) equation
which was originally implied in Fokas and Fuchssteiner in [4], but became well-known when Camassa and Holm [5] derived it as a model for the unidirectional propagation of shallow water over a flat bottom. The CH equation was found to be completely integrable with a Lax pair and associated bi-Hamiltonian structure [4,5,6]. The famous feature of the CH equation is that it provides peaked soliton (peakon) solutions [4,5], which present an essential feature of the travelling waves of largest amplitude [7,8,9]. For , Equation (1) becomes the Degasperis–Procesi (DP) equation
which can be regarded as another model for nonlinear shallow water dynamics with peakons [10,11]. The integrability of the DP equation was shown by constructing a Lax pair, and deriving two infinite sequences of conservation laws in [12].
In this paper, we are concerned with the b-family of the Novikov equation
where b is an arbitrary constant. It is easy to see that the b-family of the Novikov Equation (4) has nonlinear terms that are cubic, rather than quadratic, of the b-family of CH Equation (1). The Cauchy problem of the b-family of the Novikov Equation (4) was studied in [13].
For , Equation (4) becomes the Novikov equation
which was discovered by Vladimir Novikov [14] in a symmetry classification of nonlocal PDEs with quadratic or cubic nonlinearity. In [15,16], it was shown that the Novikov equation provides peakon solutions such as the CH and DP equations. Additionally, the Novikov Equation (5) has a Lax pair in matrix form and a bi-Hamiltonian structure. Moreover, it has infinitely many conserved quantities.
The purpose of this paper is to investigate the solutions of the b-family of the Novikov Equation (4) in the case of and . We will show that Equation (4) possesses symmetric travelling wave solutions, such as peakon, kink and smooth soliton solutions. In particular, the single peakon, two-peakon, stationary kink, anti-kink, two-kink, two-anti-kink, bell-shape soliton and hat-shape soliton solutions are presented in an explicit formula and plotted.
2. Peakon Solutions
In this section, we derive the N-peakon solutions in the case of . We assume the N-peakon solution as the form
where and are to be determined. The derivatives of (6) do not exist at , thus (6) can not satisfy Equation (4) in a classical sense. However, in the distribution, we have
Substituting (6)–(10) into (4) and integrating against the test function with compact support, we obtain that and evolve according to the dynamical system:
For , (11) is reduced to
Thus, the single peakon solution ( See Figure 1 ) is
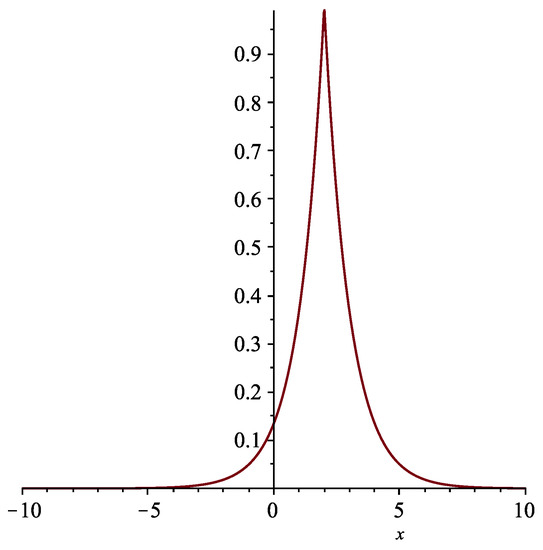
Figure 1.
The positive single peakon solution determined by (12) with at time .
For , (11) is reduced to
Solving (13), we have
In particular, for , the solution (See Figure 2) becomes
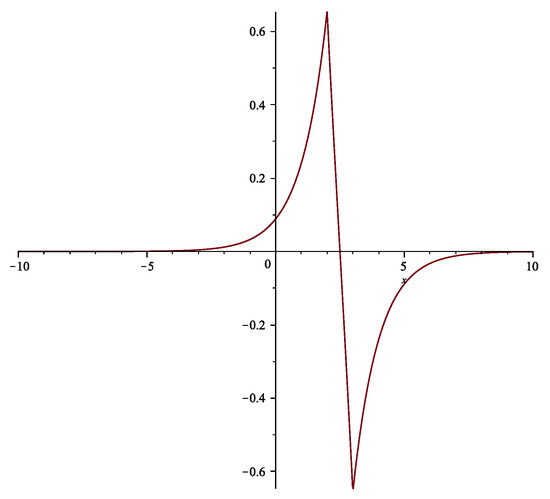
Figure 2.
The two-peakon solution (15) at time .
3. Kink and Smooth Soliton Solutions
In this section, we discuss the N-kink and smooth soliton solutions in the case of , namely
We suppose that the N-kink solution as the form
where are arbitrary constants and are to be determined. The derivatives of (17) do not exist at , thus (17) can not satisfy Equation (4) in a classical sense. However, in the distribution, we have
Substituting (17)–(20) into (16) and integrating against the test function with compact support, we obtain that evolves according to the dynamical system:
For , we have , which yields , where c is an arbitrary constant. Thus the single kink solution (See Figure 3 and Figure 4) is stationary and it reads
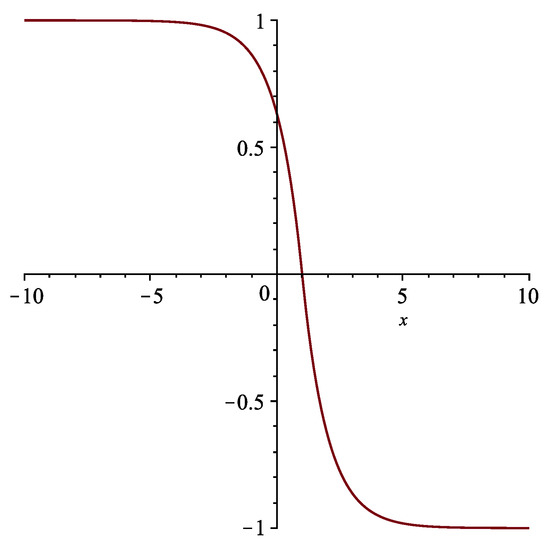
Figure 3.
The stationary kink solution determined by (22) with .
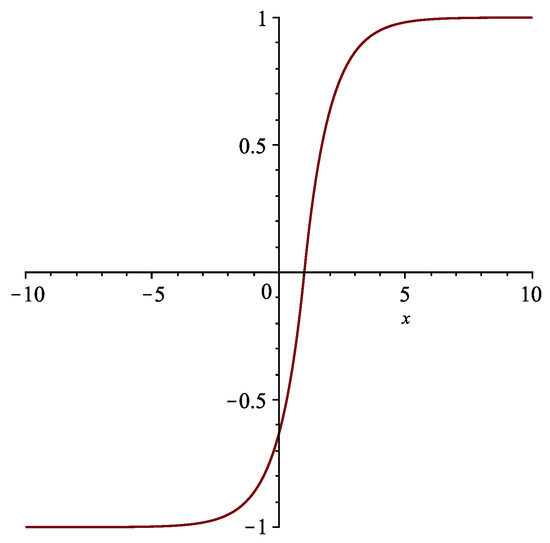
Figure 4.
The stationary anti-kink solution determined by (22) with .
For , (21) is reduced to
If , we obtain
where is an arbitrary constant. The solution (See Figure 5 and Figure 6) becomes
where and are given by (24).
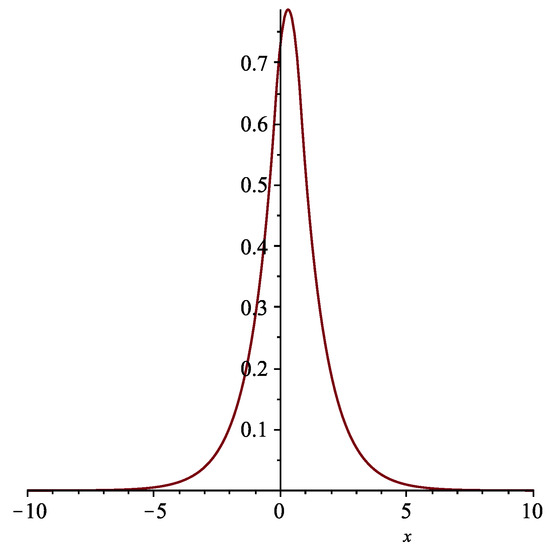
Figure 5.
The bell-shape solution determined by (25) with , at time .
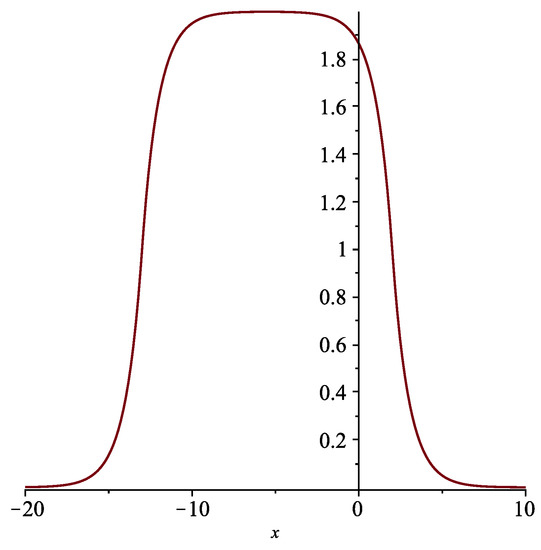
Figure 6.
The hat-shape solution determined by (25) with , , at time .
If , we obtain
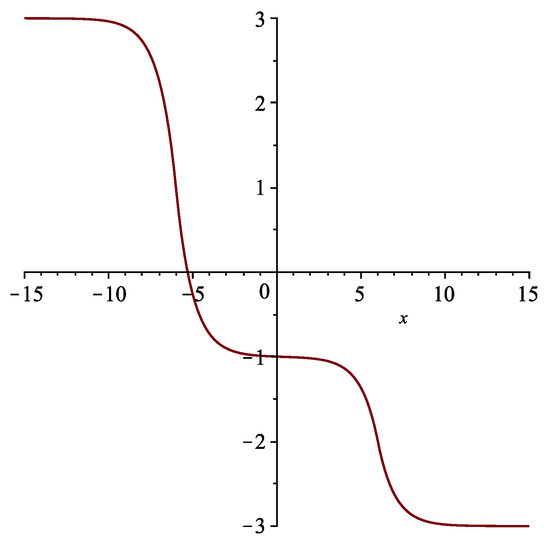
Figure 7.
The two kink solution determined by (27) with , at time .
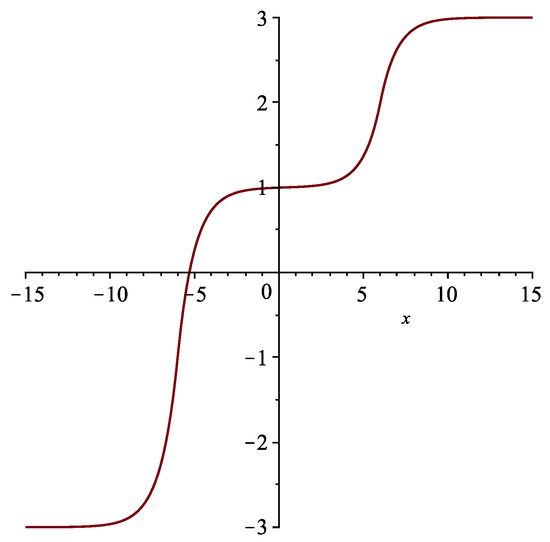
Figure 8.
The two anti-kink solution determined by (27) with , at time
Author Contributions
Investigation, T.W., X.H. and Y.L.; writing – review and editing, T.W., X.H. and Y.L.; funding acquisition, T.W., X.H. and Y.L. The authors contributed equally and significantly in writing this article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11461037).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the anonymous referees for their constructive comments and suggestions, which have greatly improved this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Holm, D.; Staley, M. Nonlinear balance and exchange of stability of dynamics of solitons, peakons, ramps/cliffs and leftons in a 1 + 1 nonlinear evolutionary PDE. Phys. Lett. A 2003, 308, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holm, D.; Staley, M. Wave structure and nonlinear balance in a family of 1 + 1 evolutionary PDE’s. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 2003, 2, 323–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, B.; Qiao, Z. The N-kink, bell-shape and hat-shape solitary solutions of b-family equation in the case of b = 0. Phys. Lett. A 2013, 377, 2340–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokas, A.; Fuchssteiner, B. Symplectic structures, their Bäklund transformation and hereditary symmetries. Physica D 1981, 4, 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Camassa, R.; Holm, D. An integrable shallow water equation with peaked solitons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 71, 1661–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher, M.; Fisher, J. The Camassa-Holm equation: Conserved quantities and the initial value problem. Phys. Lett. A 1999, 259, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Constantin, A. The trajectories of particles in Stokes waves. Invent. Math. 2006, 166, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, A.; Escher, J. Particle trajectories in solitary water waves. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 2007, 44, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Constantin, A.; Escher, J. Analyticity of periodic traveling free surface water waves with vorticity. Ann. Math. 2011, 173, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degasperis, A.; Procesi, M. Asymptotic Integrability. In Symmetry and Perturbation Theory; World Scientific Publishing: River Edge, NJ, USA; Rome, Italy, 1998; pp. 23–37. [Google Scholar]
- Constantin, A.; Lannes, D. The hydrodynamical relevant of the Camassa-Holm and Degasperis-Procesi equations. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 2009, 192, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degasperis, A.; Holm, D.; Hone, A. A new Integrable equation with peakon solutions. Theor. Math. Phys. 2002, 133, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mi, Y.; Mu, C. On the Cauchy problem for the modified Novikov equation with peakon solutions. J. Differ. Equ. 2013, 254, 961–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, V. Generalizations of the Camassa-Holm equation. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2009, 42, 342002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hone, W.; Wang, J. Integrable peakon equations with cubic nonlinearity. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2008, 41, 372002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hone, W.; Lundmark, H.; Szmigielski, J. Explicit multipeakon solutions of Novikov cubically nonlinear integrable Camassa-Holm type equation. Dyn. Partial Differ. Equ. 2009, 6, 253–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).