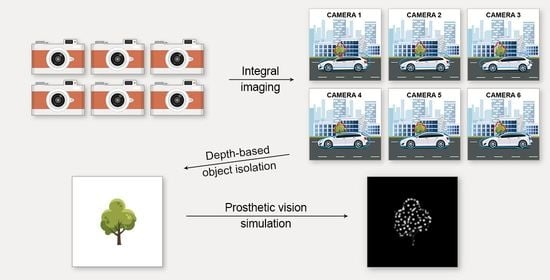
Effects of Depth-Based Object Isolation in Simulated Retinal Prosthetic Vision
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Scene Capture
2.2. Object Isolation Algorithm
2.3. Prosthetic Vision Simulation
3. Results
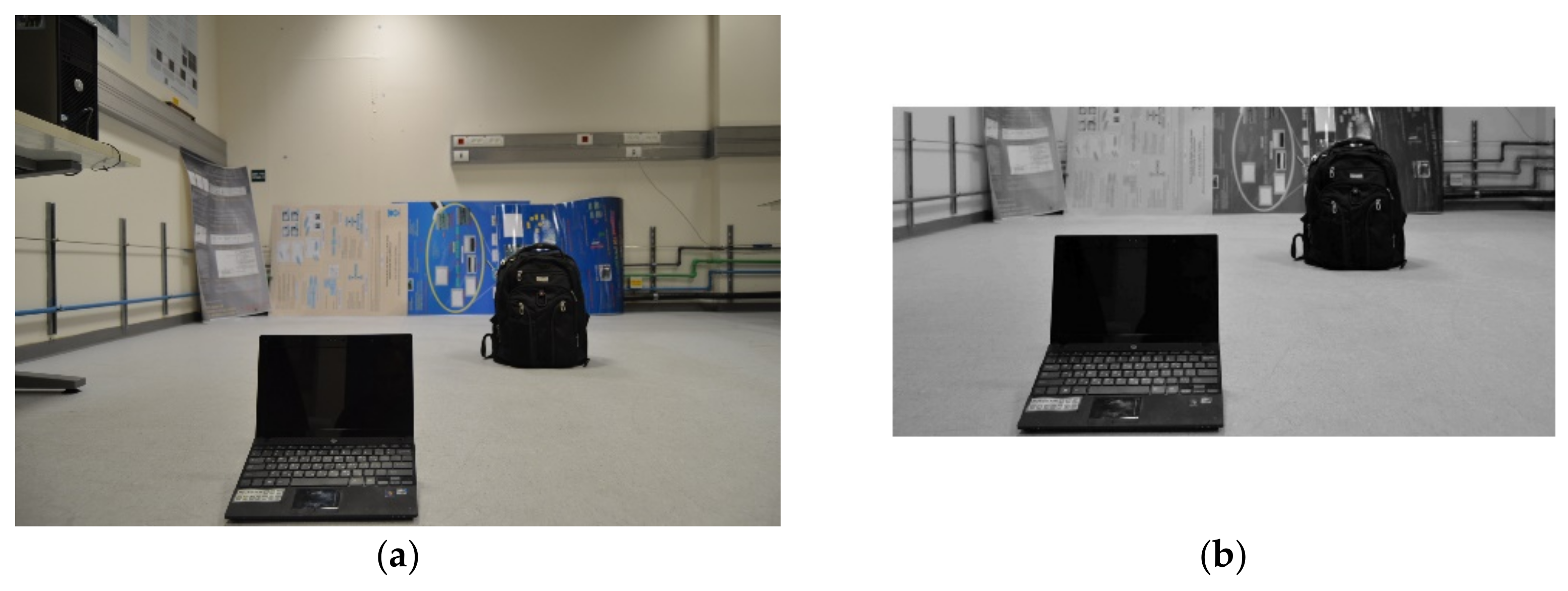
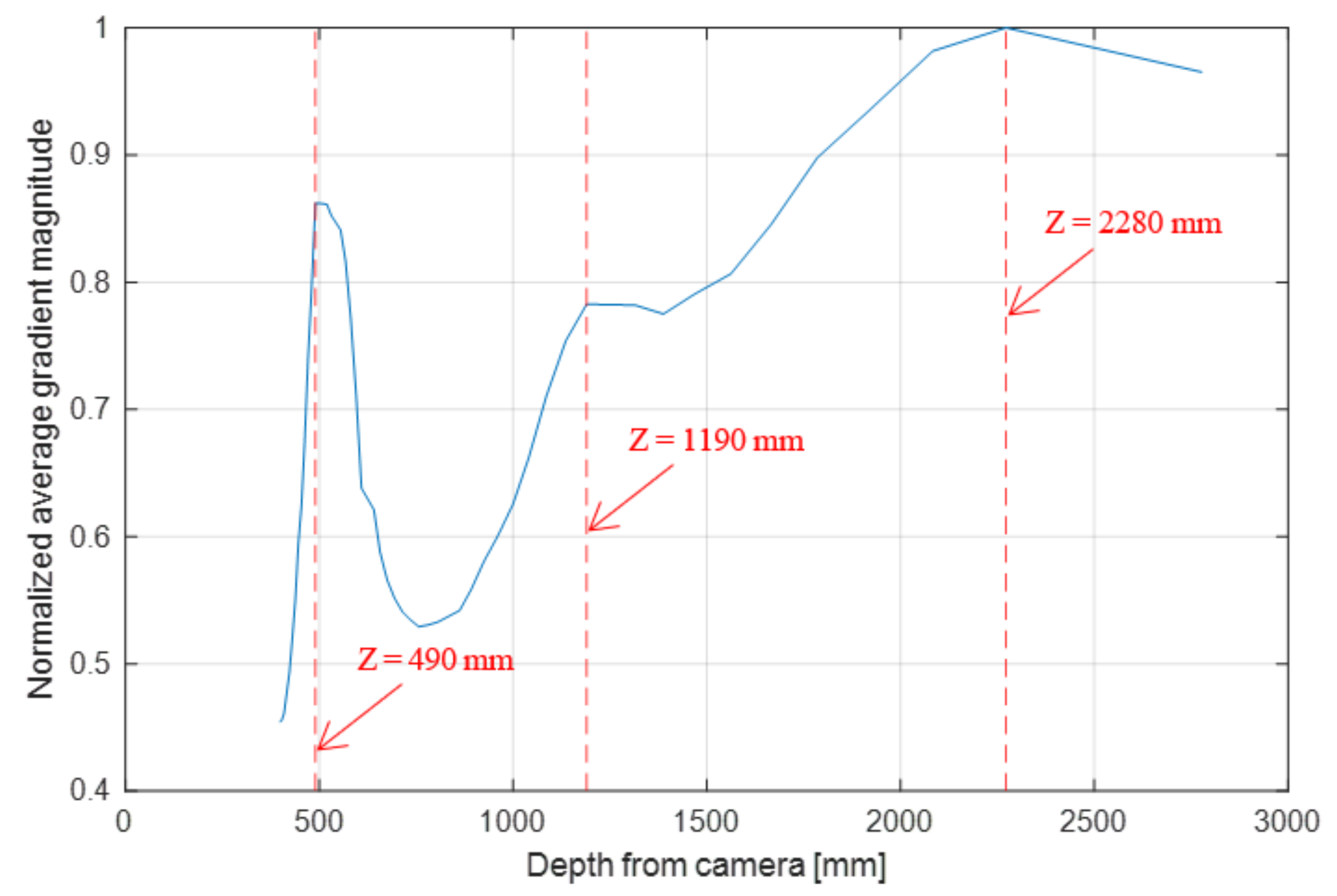
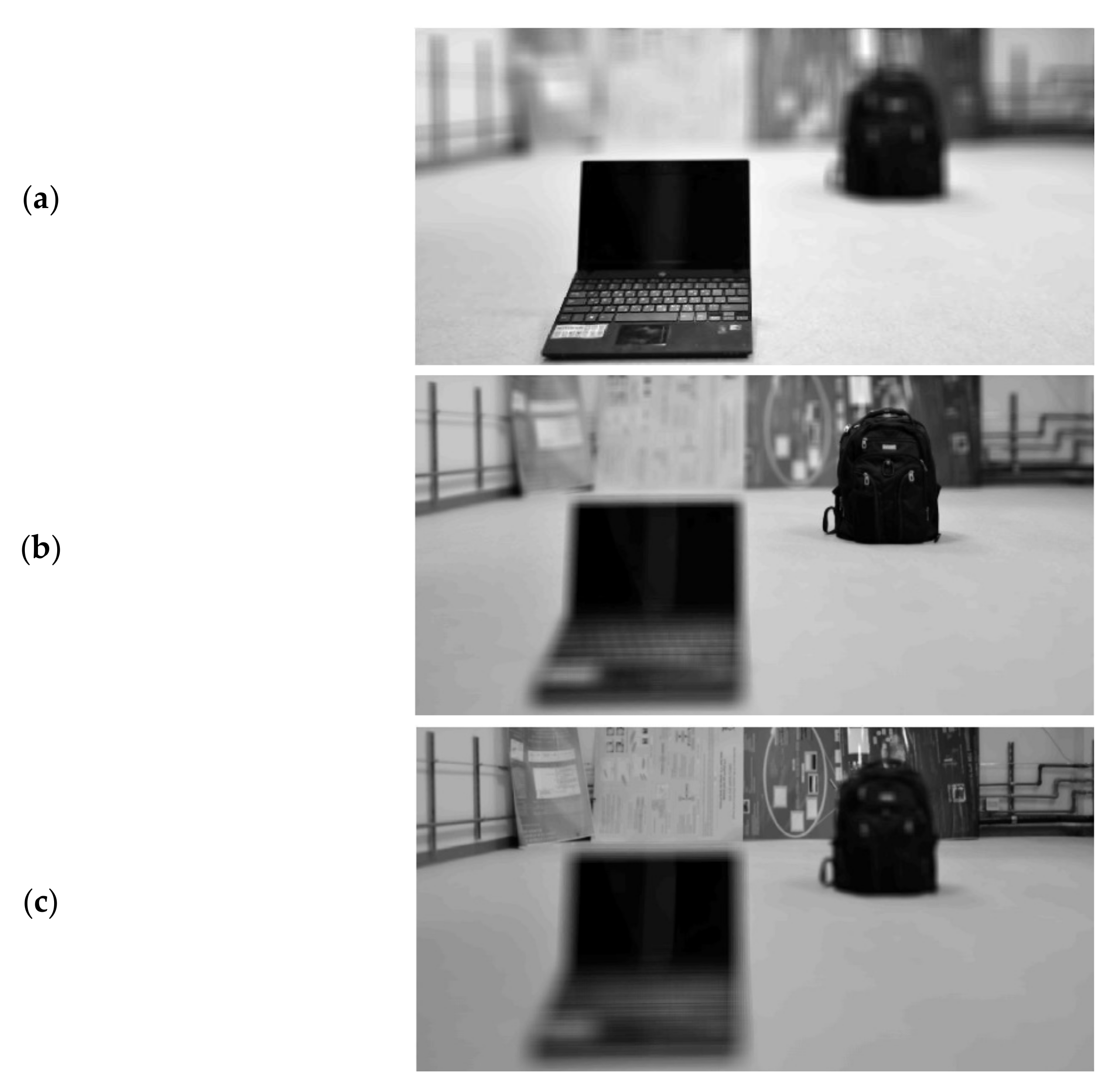
3.1. Object Isolation
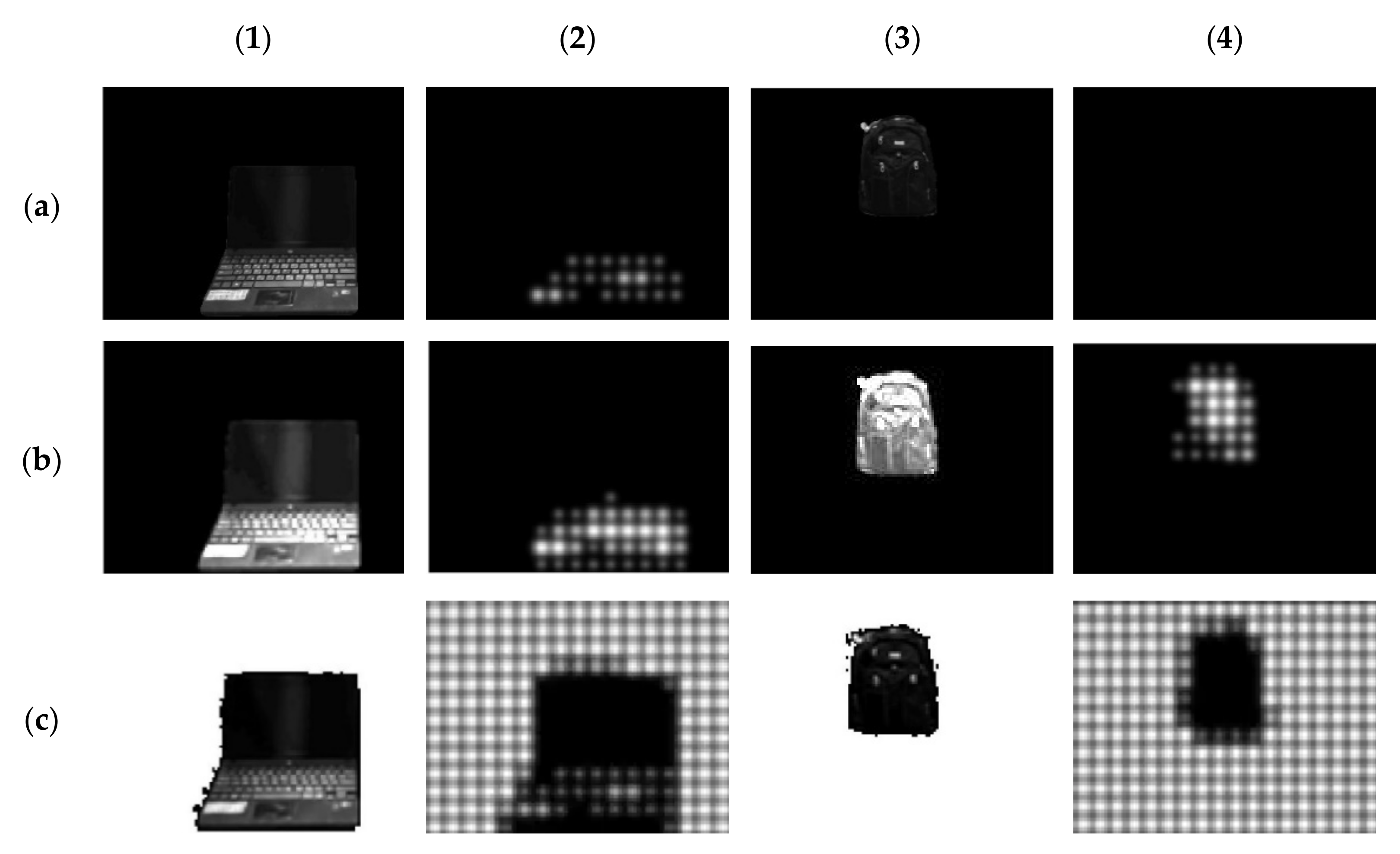
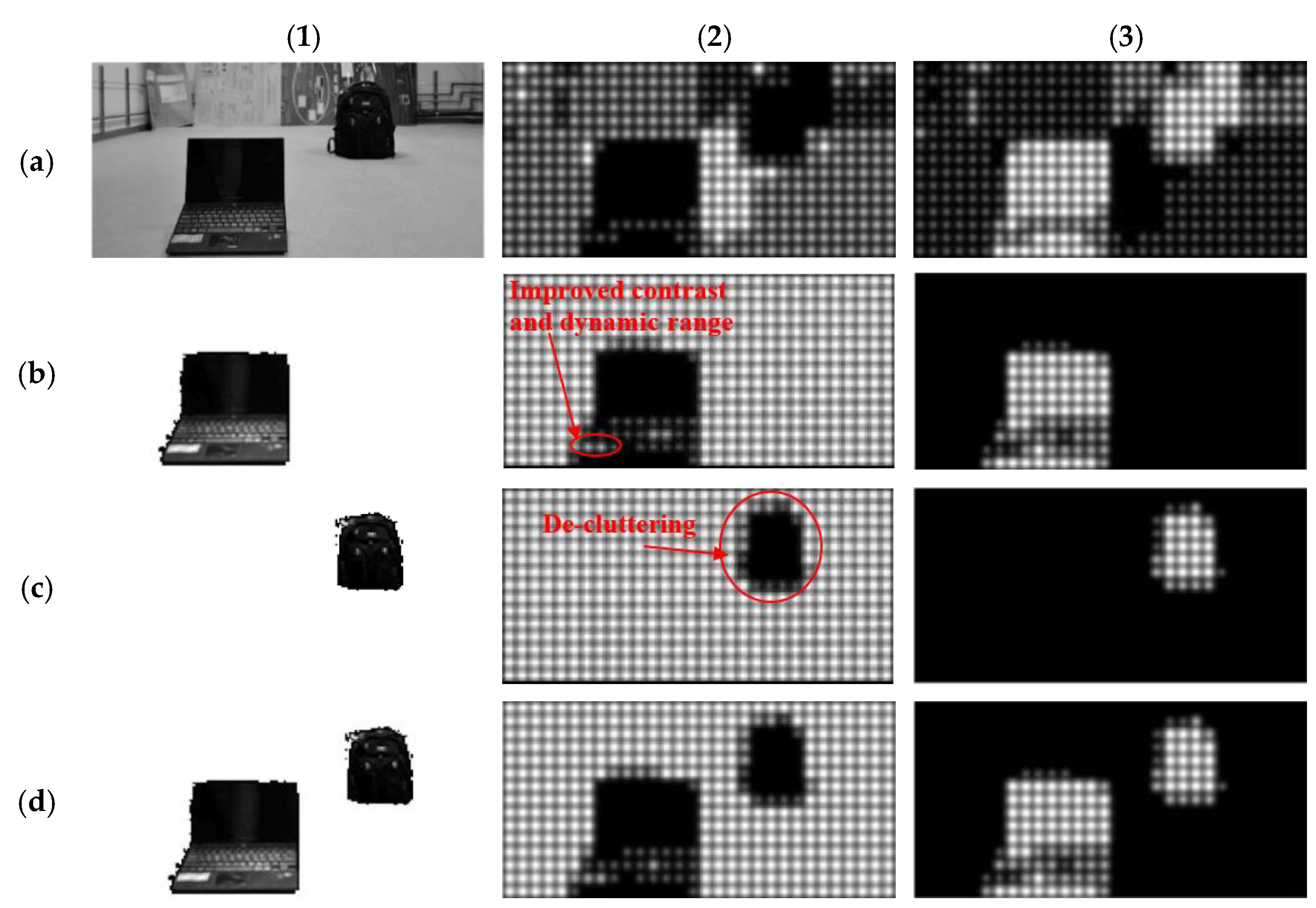
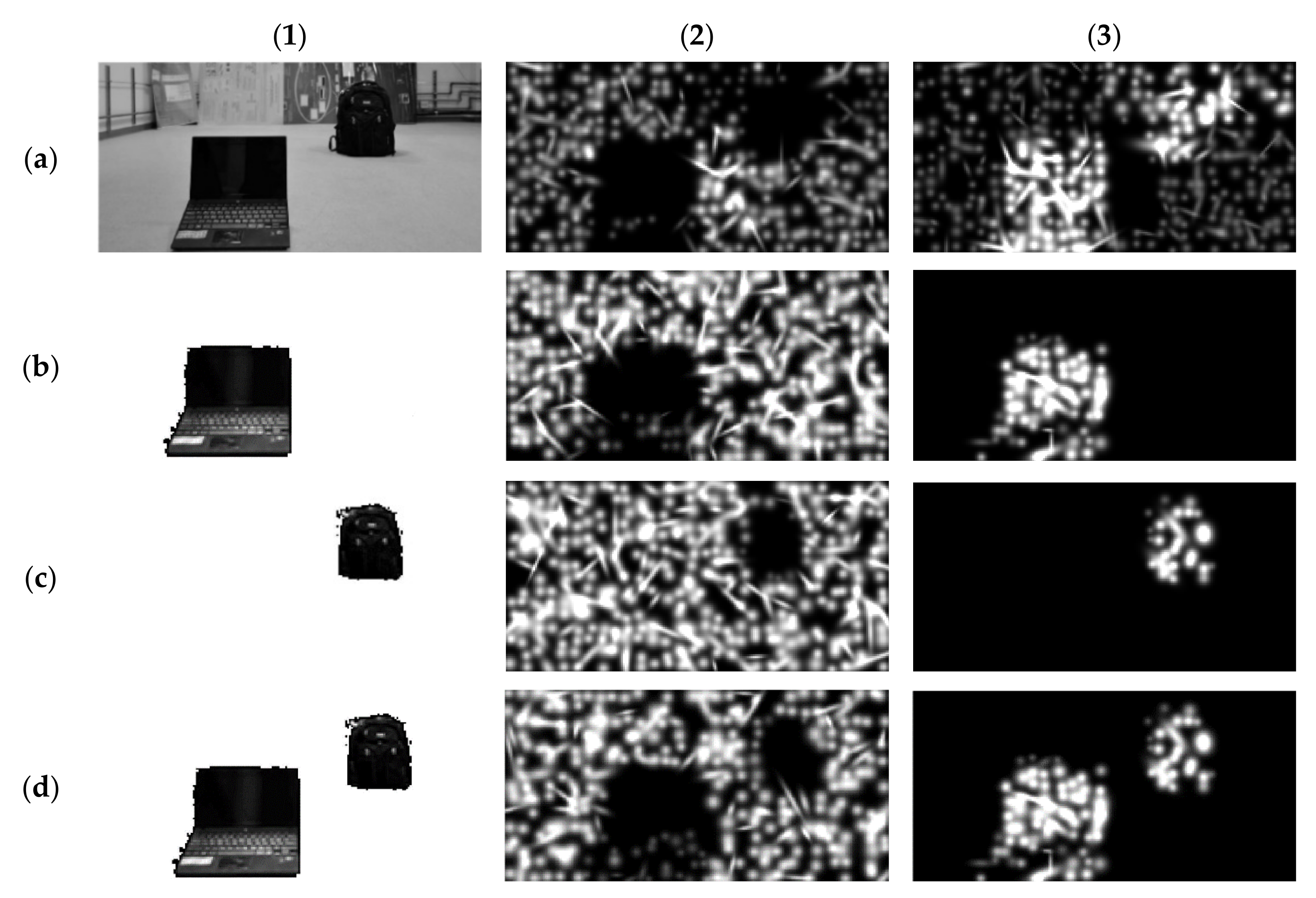
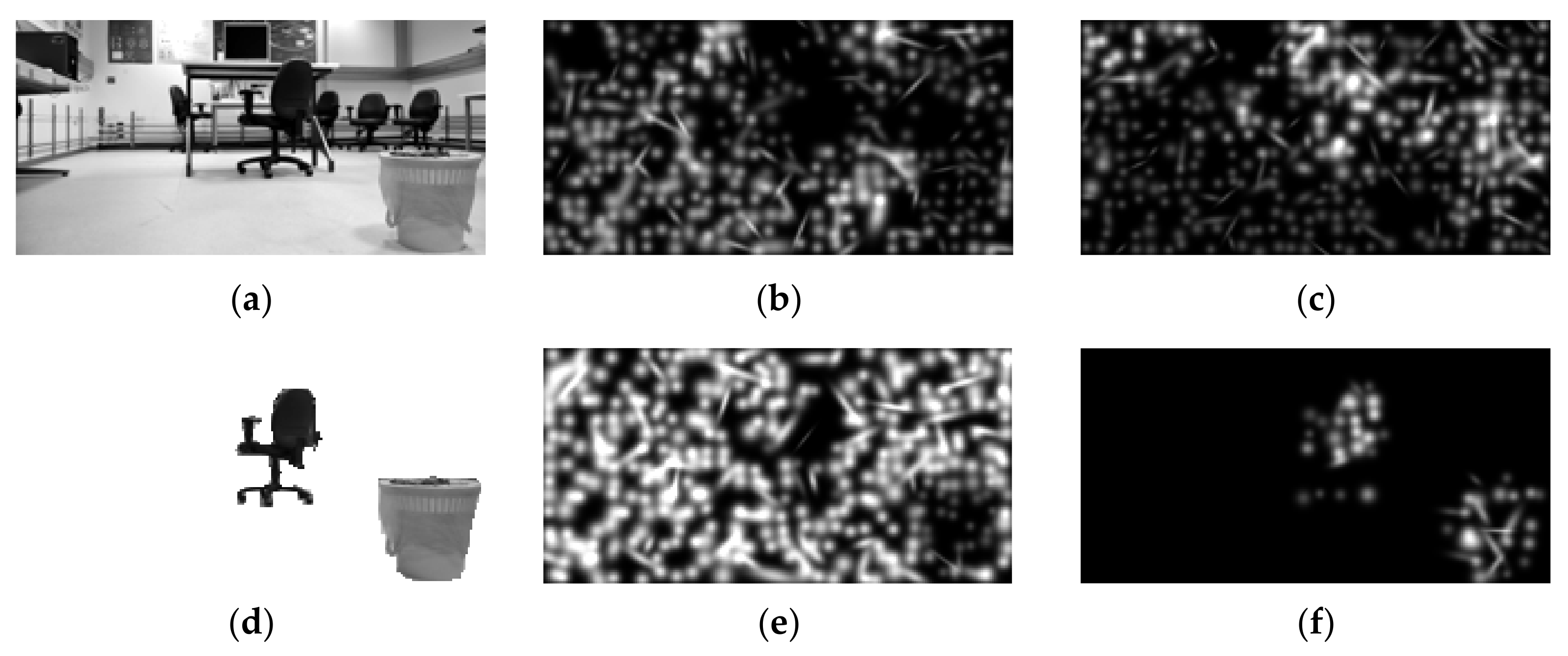
3.2. Prosthetic Vision Views of the Isolated Objects
3.3. Prosthetic Vision Views before and after Isolation
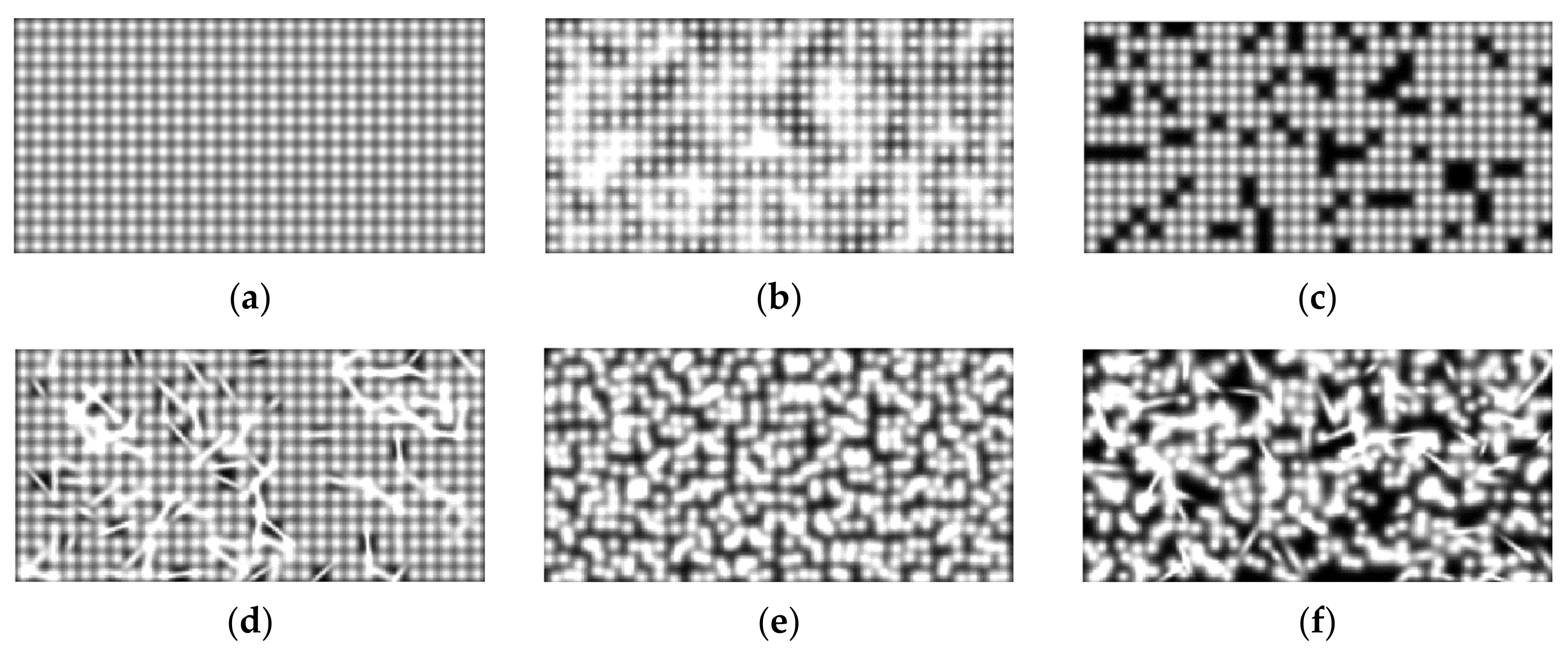
3.4. Prosthetic Vision Views before and after Isolation with Spatial Phosphene Variations
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, A.L.; Knight, D.K.; Vu, T.-T.T.; Mehta, M.C. Retinitis Pigmentosa: Review of Current Treatment. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 2019, 59, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holz, F.G.; Strauss, E.C.; Schmitz-Valckenberg, S.; Campagne, M.V.L. Geographic Atrophy. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, D.S.; Wood, J.P.M.; Chidlow, G.; Casson, R.J. A review of the mechanisms of cone degeneration in retinitis pigmentosa. Acta Ophthalmol. 2016, 94, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandello, F.; Silva, R. AMD: Age-Related Macular Degeneration; Théa: Loures, Lisbon, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Brindley, B.Y.G.S.; Lewin, W.S. The Sensations Produced by Electrical Simulation of the Visual Cortex. J. Physiol. 1968, 196, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornig, R.; Zehnder, T.; Velikay-Parel, M.; Laube, T.; Feucht, M.; Richard, G. The IMI Retinal Implant System. In Artificial Sight; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Humayun, M.S.; Weiland, J.; Fujii, G.Y.; Greenberg, R.; Williamson, R.; Little, J.; Mech, B.; Cimmarusti, V.; Van Boemel, G.; Dagnelie, G.; et al. Visual perception in a blind subject with a chronic microelectronic retinal prosthesis. Vis. Res. 2003, 43, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horsager, A.; Greenberg, R.J.; Fine, I. Spatiotemporal Interactions in Retinal Prosthesis Subjects. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stingl, K.; Bartz-Schmidt, K.U.; Besch, D.; Braun, A.; Bruckmann, A.; Gekeler, F.; Greppmaier, U.; Hipp, S.; Hörtdörfer, G.; Kernstock, C.; et al. Artificial vision with wirelessly powered subretinal electronic implant alpha-IMS. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20130077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.H.-L.; da Cruz, L. The Argus® II Retinal Prosthesis System. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2016, 50, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, G.; Laube, T.; Brockmann, C.; Kirschkamp, T.; Mazinani, B.; Goertz, M.; Koch, C.; Krisch, I.; Sellhaus, B.; Trieu, H.K.; et al. Implantation and Explantation of a Wireless Epiretinal Retina Implant Device: Observations during the EPIRET3 Prospective Clinical Trial. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 3003–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagnelie, G.; Barnett, D.; Humayun, M.S.; Thompson, R.W. Paragraph text reading using a pixelized prosthetic vision simulator: Parameter dependence and task learning in free-viewing conditions. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, K.; Horch, K.; Normann, R.A. Simulation of a phosphene-based visual field: Visual acuity in a pixelized vision system. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1992, 20, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, X.; Yu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, C.; Ren, Q. Recognition of Pixelized Chinese Characters Using Simulated Prosthetic Vision. Artif. Organs 2007, 31, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tong, S.; Zhu, Y.; Qiu, Y. Object Recognition Under Distorted Prosthetic Vision. Artif. Organs 2010, 34, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humayun, M.S.; de Juan, E., Jr.; Dagnelie, G.; Greenberg, R.J.; Propst, R.H.; Phillips, D.H. Visual Perception Elicited by Electrical Stimulation of Retina in Blind Humans. Clin Sci. 1996, 114, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, J.F.; Wyatt, J.; Loewenstein, J.; Kelly, S.; Shire, D. Perceptual Efficacy of Electrical Stimulation of Human Retina with a Microelectrode Array during Short-Term Surgical Trials. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 5362–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiland, J.; Yanai, D.; Mahadevappa, M.; Williamson, R.; Mech, B.; Fujii, G.; Little, J.; Greenberg, R.; de Juan, E.; Humayun, M. Electrical stimulation of retina in blind humans. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37439), Cancun, Mexico, 17–21 September 2004; Volume 3, pp. 2021–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nanduri, D.; Fine, I.; Horsager, A.; Boynton, G.M.; Humayun, M.S.; Greenberg, R.J.; Weiland, J. Frequency and Amplitude Modulation Have Different Effects on the Percepts Elicited by Retinal Stimulation. Invest. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beyeler, M.; Nanduri, D.; Weiland, J.D.; Rokem, A.; Boynton, G.M.; Fine, I. A model of ganglion axon pathways accounts for percepts elicited by retinal implants. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahadevappa, M.; Weiland, J.; Yanai, D.; Fine, I.; Greenberg, R.; Humayun, M. Perceptual thresholds and electrode impedance in three retinal prosthesis subjects. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehab. Eng. 2005, 13, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, D.; Weiland, J.D.; Mahadevappa, M.; Greenberg, R.J.; Fine, I.; Humayun, M.S. Visual Performance Using a Retinal Prosthesis in Three Subjects with Retinitis Pigmentosa. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 143, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Balthasar, C.; Patel, S.; Roy, A.; Freda, R.; Greenwald, S.; Horsager, A.; Mahadevappa, M.; Yanai, D.; McMahon, M.J.; Humayun, M.S.; et al. Factors Affecting Perceptual Thresholds in Epiretinal Prostheses. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 2303–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grosberg, L.E.; Ganesan, K.; Goetz, G.A.; Madugula, S.S.; Bhaskhar, N.; Fan, V.; Li, P.; Hottowy, P.; Dabrowski, W.; Sher, A.; et al. Activation of ganglion cells and axon bundles using epiretinal electrical stimulation. J. Neurophysiol. 2017, 118, 1457–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanduri, D.; Humayun, M.; Greenberg, R.; McMahon, M.; Weiland, J. Retinal prosthesis phosphene shape analysis. In Proceedings of the 2008 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–25 August 2008; Volume 2008, pp. 1785–1788. [Google Scholar]
- Caspi, A.; Dorn, J.D.; McClure, K.H.; Humayun, M.S.; Greenberg, R.J.; McMahon, M.J. Feasibility Study of a Retinal Prosthesis. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2009, 127, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinclair, N.C.; Shivdasani, M.; Perera, T.; Gillespie, L.N.; McDermott, H.J.; Ayton, L.; Blamey, P.; For the Bionic Vision Australia Consortium. The Appearance of Phosphenes Elicited Using a Suprachoroidal Retinal Prosthesis. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 4948–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humayun, M.S.; Dorn, J.D.; da Cruz, L.; Dagnelie, G.; Sahel, J.-A.; Stanga, P.E.; Cideciyan, A.V.; Duncan, J.L.; Eliott, D.; Filley, E.; et al. Interim Results from the International Trial of Second Sight’s Visual Prosthesis. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humayun, M.S.; de Juan, E., Jr.; Weiland, J.D.; Dagnelie, G.; Katona, S.; Greenberg, R.; Suzuki, S. Pattern electrical stimulation of the human retina. Vis. Res. 1999, 39, 2569–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, P.; Hu, J.; Peng, Y. Adaptation to Phosphene Parameters Based on Multi-Object Recognition Using Simulated Prosthetic Vision. Artif. Organs 2015, 39, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Chai, X. Prosthetic vision simulating system and its application based on retinal prosthesis. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Information Science, Electronics and Electrical Engineering, Sapporo, Japan, 26–28 April 2014; Volume 1, pp. 425–429. [Google Scholar]
- Ayton, L.N.; Blamey, P.; Guymer, R.; Luu, C.; Nayagam, D.; Sinclair, N.C.; Shivdasani, M.; Yeoh, J.; McCombe, M.F.; Briggs, R.J.; et al. First-in-Human Trial of a Novel Suprachoroidal Retinal Prosthesis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayton, L.N.; Barnes, N.; Dagnelie, G.; Fujikado, T.; Goetz, G.; Hornig, R.; Jones, B.W.; Muqit, M.M.; Rathbun, D.L.; Stingl, K.; et al. An update on retinal prostheses. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 1383–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stronks, C.; Dagnelie, G. The functional performance of the Argus II retinal prosthesis. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2014, 11, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.C.; Suaning, G.J.; Morley, J.W.; Lovell, N.H. Simulating prosthetic vision: I. Visual models of phosphenes. Vis. Res. 2009, 49, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lippmann, G. Épreuves Réversibles Donnant La Sensation Du Relief. J. Phys. Théor. Appl. 1908, 7, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, B.; Javidi, B.; Watson, E. Three dimensional visualization by photon counting computational Integral Imaging. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 4426–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloni, D.; Yitzhaky, Y. Detection of Object Existence from a Single Reconstructed Plane Obtained by Integral Imaging. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2014, 26, 726–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloni, D.; Yitzhaky, Y. Automatic 3D object localization and isolation using computational integral imaging. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 6717–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avraham, D.; Jung, J.; Yitzhaky, Y.; Peli, E. Retinal prosthetic vision simulation: Temporal aspects. J. Neural. Eng. 2021, 18, 460d9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornos, A.P.; Sommerhalder, J.; Da Cruz, L.; Sahel, J.-A.; Mohand-Said, S.; Hafezi, F.; Pelizzone, M. Temporal Properties of Visual Perception on Electrical Stimulation of the Retina. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 2720–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, J.-H.; Aloni, D.; Yitzhaky, Y.; Peli, E. Active confocal imaging for visual prostheses. Vis. Res. 2015, 111, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farahani, N.; Post, R.; Duboy, J.; Ahmed, I.; Kolowitz, B.J.; Krinchai, T.; Monaco, S.E.; Fine, J.L.; Hartman, D.J.; Pantanowitz, L. Exploring virtual reality technology and the Oculus Rift for the examination of digital pathology slides. J. Pathol. Inform. 2016, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Second Sight. Argus II Retinal Prosthesis System Device Fitting Manual; Second Sight: Pontotoc, MS, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Palanker, D.; Vankov, A.; Huie, P.A.; Baccus, S. Design of a high-resolution optoelectronic retinal prosthesis. J. Neural Eng. 2005, 2, S105–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moleirinho, S.; Whalen, A.J.; Fried, S.I.; Pezaris, J.S. The impact of synchronous versus asynchronous electrical stimulation in artificial vision. J. Neural. Eng. 2021, 18, 51001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loudin, J.D.; Simanovskii, D.M.; VijayRaghavan, K.; Sramek, C.K.; Butterwick, A.F.; Huie, P.; McLean, G.Y.; Palanker, D.V. Optoelectronic retinal prosthesis: System design and performance. J. Neural. Eng. 2007, 4, S72–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Behrend, M.R.; Ahuja, A.K.; Humayun, M.S.; Chow, R.H.; Weiland, J.D. Resolution of the Epiretinal Prosthesis is not Limited by Electrode Size. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehab. Eng. 2011, 19, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, N.; Srivastava, S.; Xu, A.; Klein, D.; Beyeler, M. Deep Learning—Based Scene Simplification for Bionic Vision. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.00297. [Google Scholar]
- Weiland, J.D.; Humayun, M.S. Retinal prosthesis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 1412–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brummer, S.B.; Turner, M.J. Electrical Stimulation with Pt Electrodes: II-Estimation of Maximum Surface Redox (Theoretical Non-Gassing) Limits. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1977, 24, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogan, S.F.; Troyk, P.R.; Ehrlich, J.; Plante, T.D. In Vitro Comparison of the Charge-Injection Limits of Activated Iridium Oxide (AIROF) and Platinum-Iridium Microelectrodes Stuart. In Vitro 2005, 52, 1612–1614. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, J.F.; Wyatt, J.; Loewenstein, J.; Kelly, S.; Shire, D. Methods and Perceptual Thresholds for Short-Term Electrical Stimulation of Human Retina with Microelectrode Arrays. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 5355–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Spatial Parameter | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Size variations | Random uniformly distributed variation of the phosphenes’ sizes between 30% smaller than nominal and 30% larger than nominal. | |
| Shape variations | Random change in the shape of 15% of the phosphenes into an ellipse with a random angle (0–180°) of rotation. | |
| Spatial Shifts | Random uniformly distributed shifts of phosphenes by 0–4 pixels with respect to the retinotopic position of their corresponding electrodes in the array, in both the vertical and horizontal directions. | |
| Dropout | Random elimination of 20% of the phosphenes. |
| (deg) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size variations | Disabled | 1 | ||||||
| Enabled | 0.5–1.5 | |||||||
| Shape variations | Disabled | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||||
| Enabled | 1–3 | 1/3–1 | 0–180 | |||||
| Spatial Shifts | Disabled | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Enabled | 0–4 | 0–4 | ||||||
| Dropout | Disabled | 0, 1/3, 2/3, 1 | ||||||
| Enabled | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avraham, D.; Yitzhaky, Y. Effects of Depth-Based Object Isolation in Simulated Retinal Prosthetic Vision. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101763
Avraham D, Yitzhaky Y. Effects of Depth-Based Object Isolation in Simulated Retinal Prosthetic Vision. Symmetry. 2021; 13(10):1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101763
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvraham, David, and Yitzhak Yitzhaky. 2021. "Effects of Depth-Based Object Isolation in Simulated Retinal Prosthetic Vision" Symmetry 13, no. 10: 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101763
APA StyleAvraham, D., & Yitzhaky, Y. (2021). Effects of Depth-Based Object Isolation in Simulated Retinal Prosthetic Vision. Symmetry, 13(10), 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101763