Predictions of Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Ray Propagation in the Context of Homogeneously Modified Special Relativity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Homogeneously Modified Special Relativity
2.1. Geometric Structure: Hamilton/Finsler Geometry
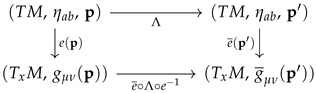
2.2. HMSR Standard Model Extension
2.3. HMSR Modified Kinematics
3. Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays Propagation and GZK Cut-Off Effect
4. LIV Introduced Phenomenology in UHECR Propagation
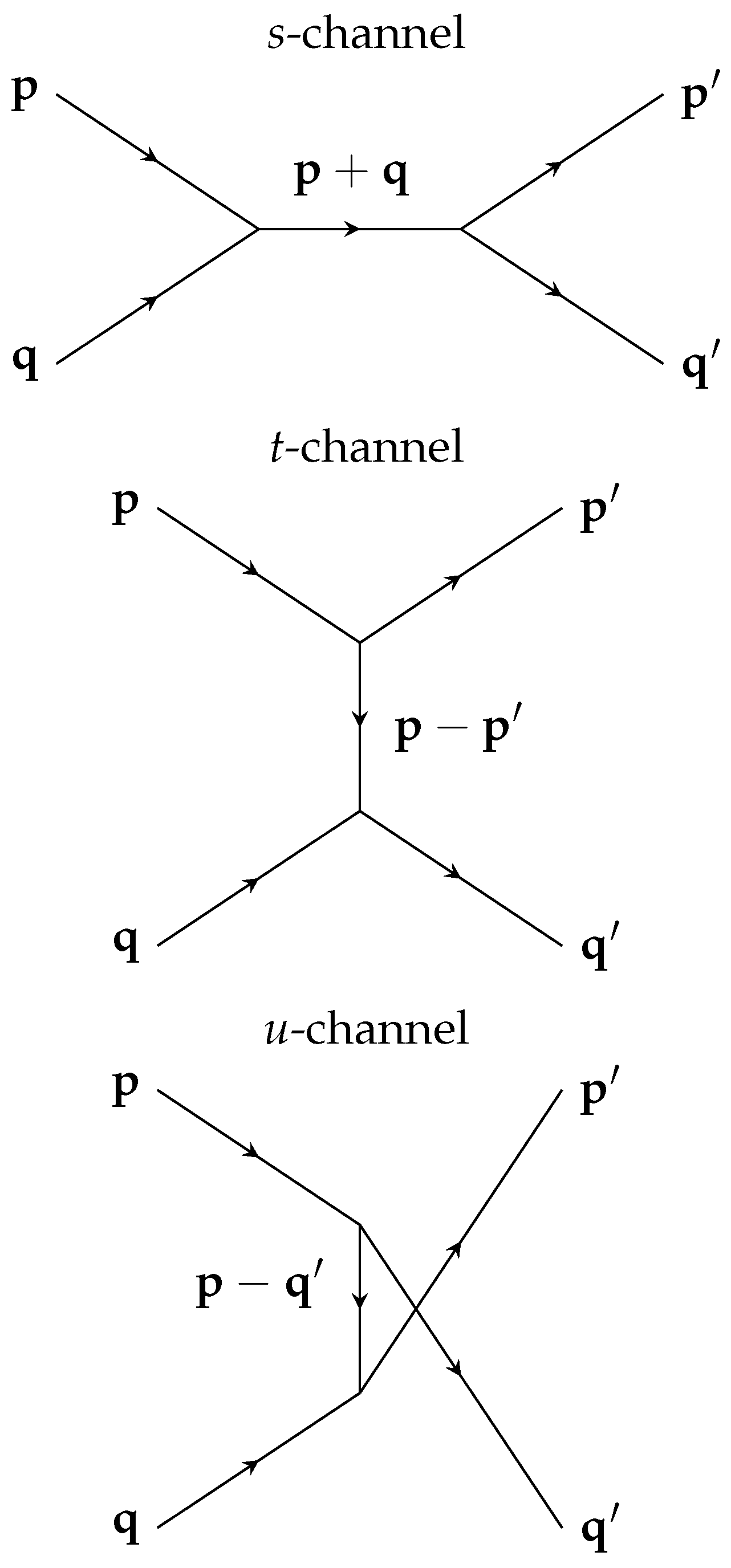
4.1. Resonance Creation Constraint
4.2. Reduced Phase Space and Modified Inelasticity
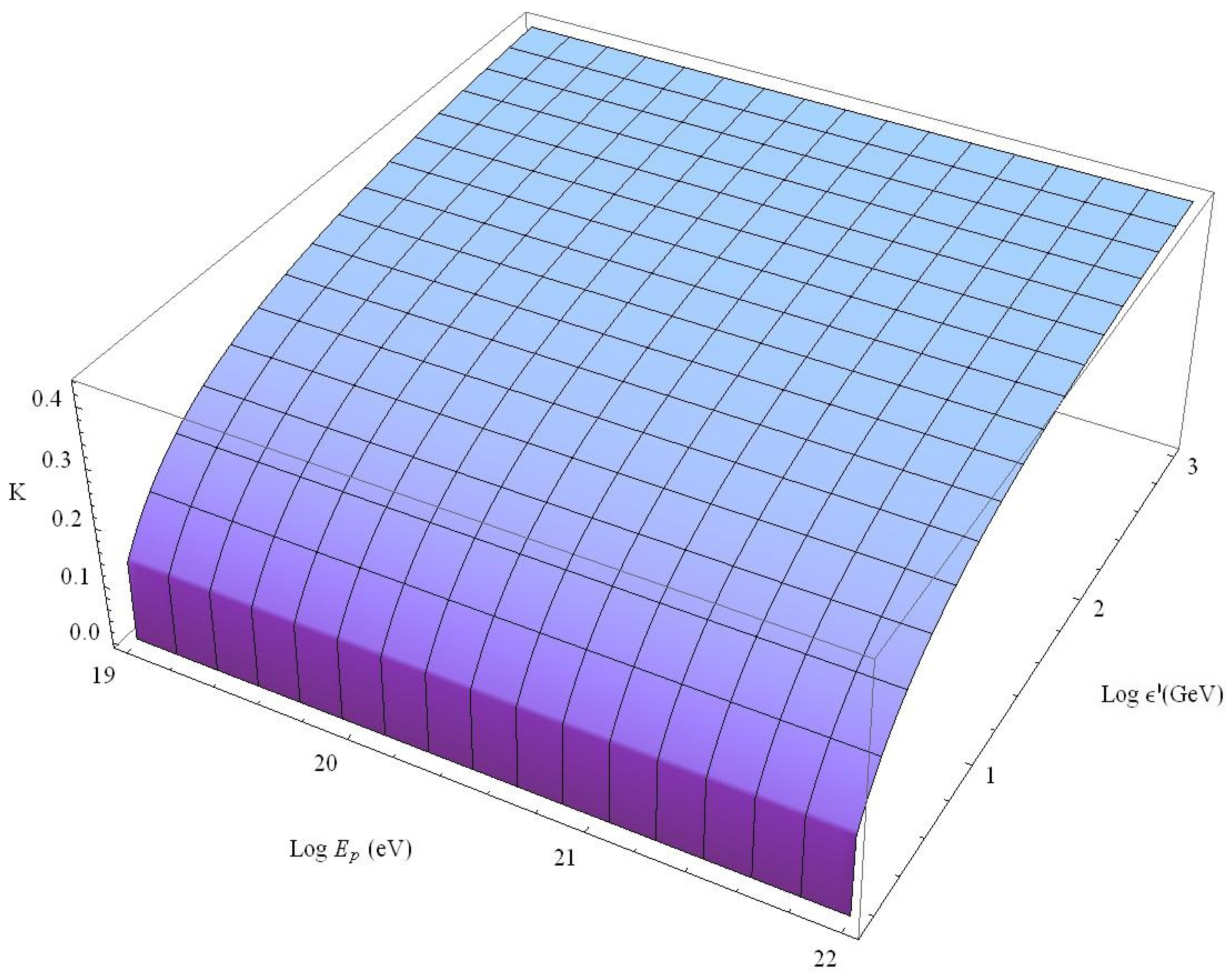
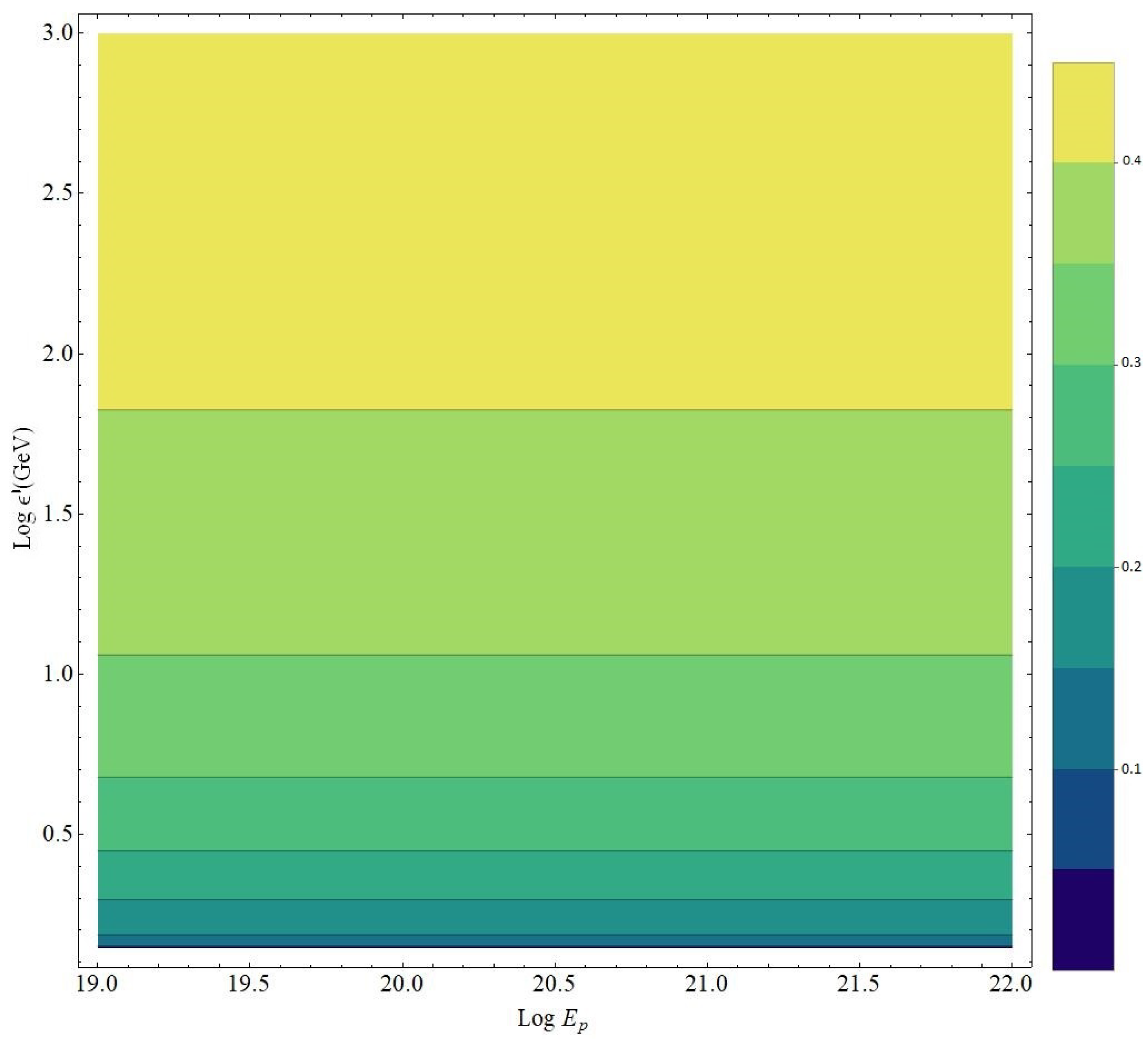
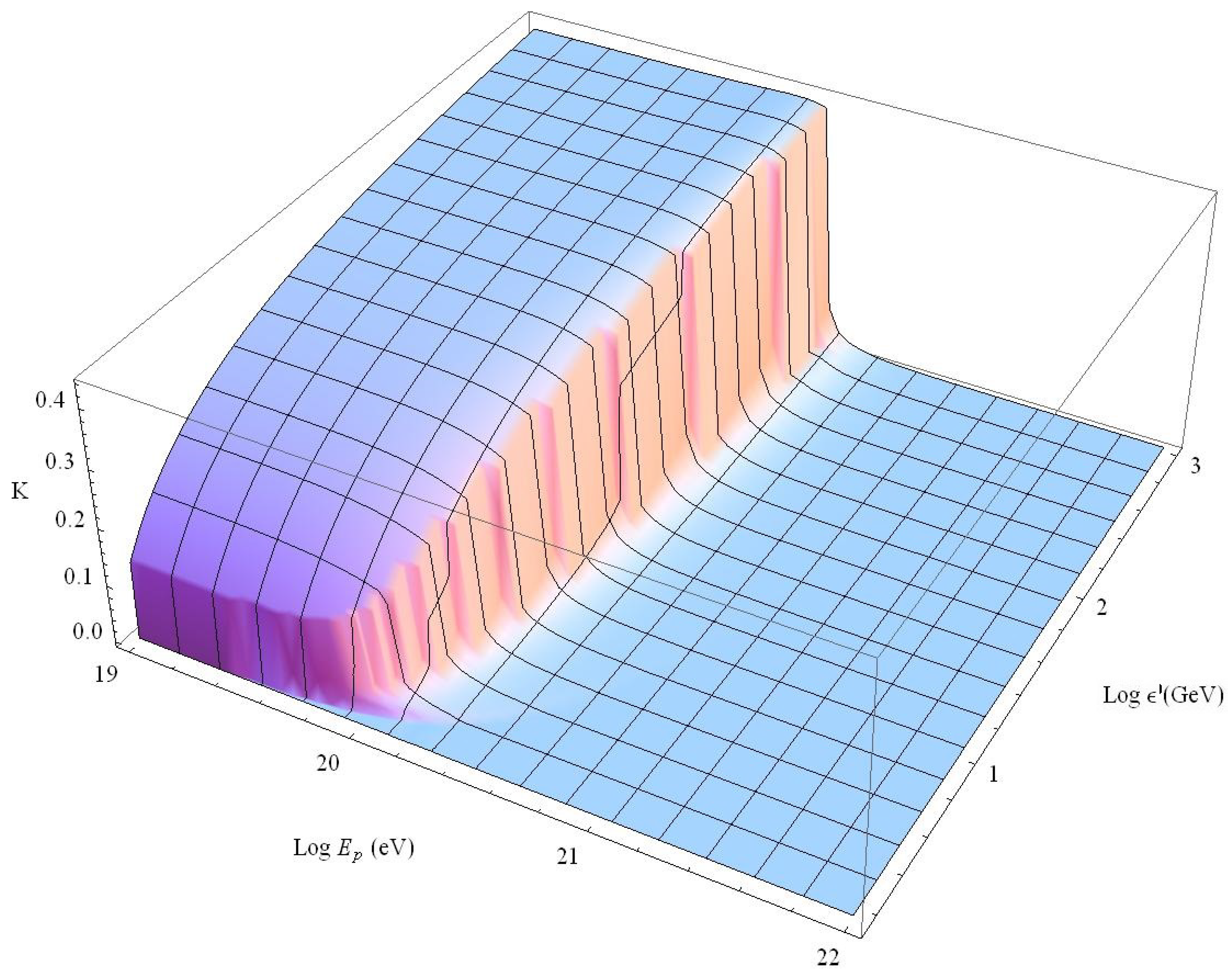
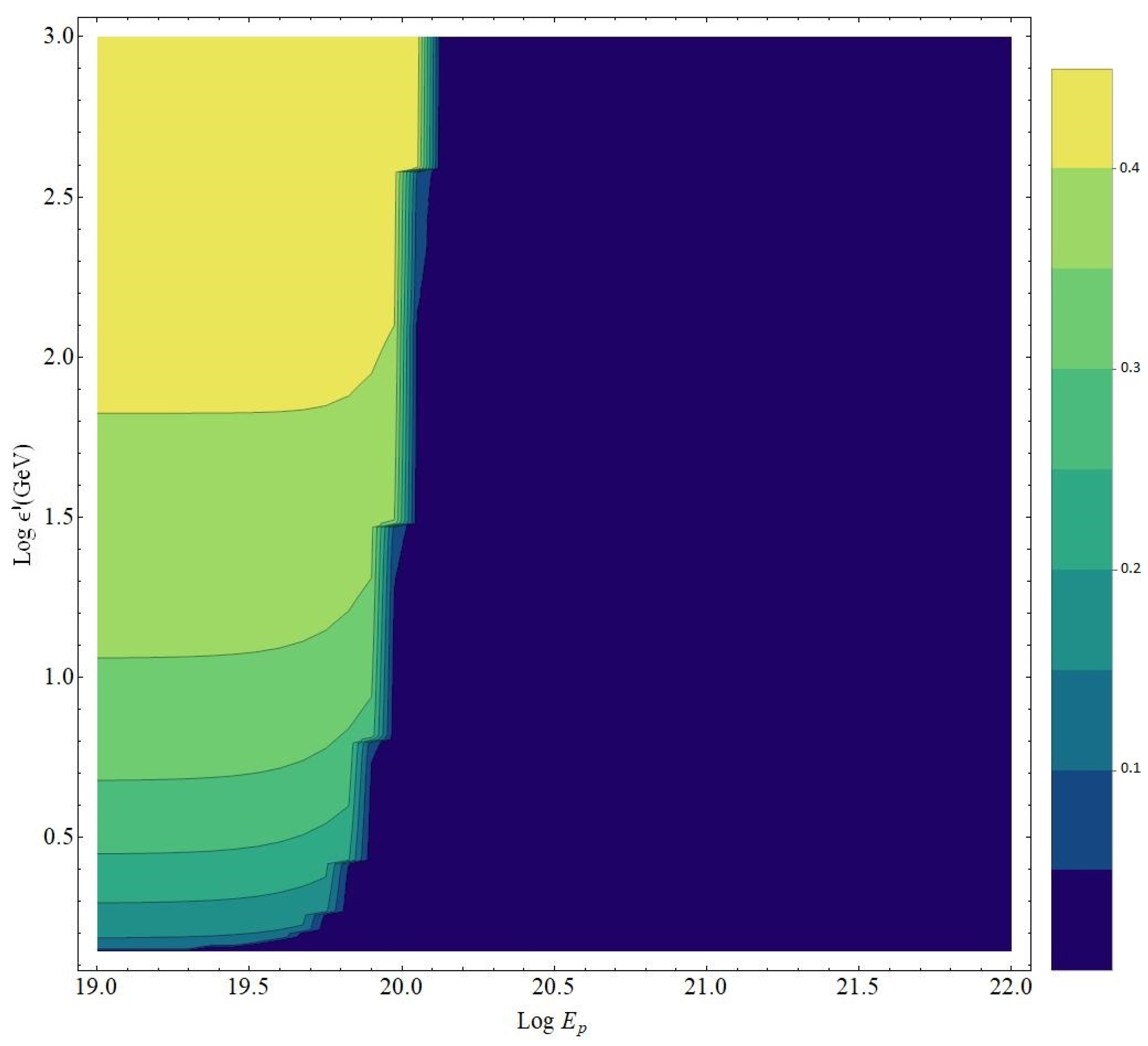
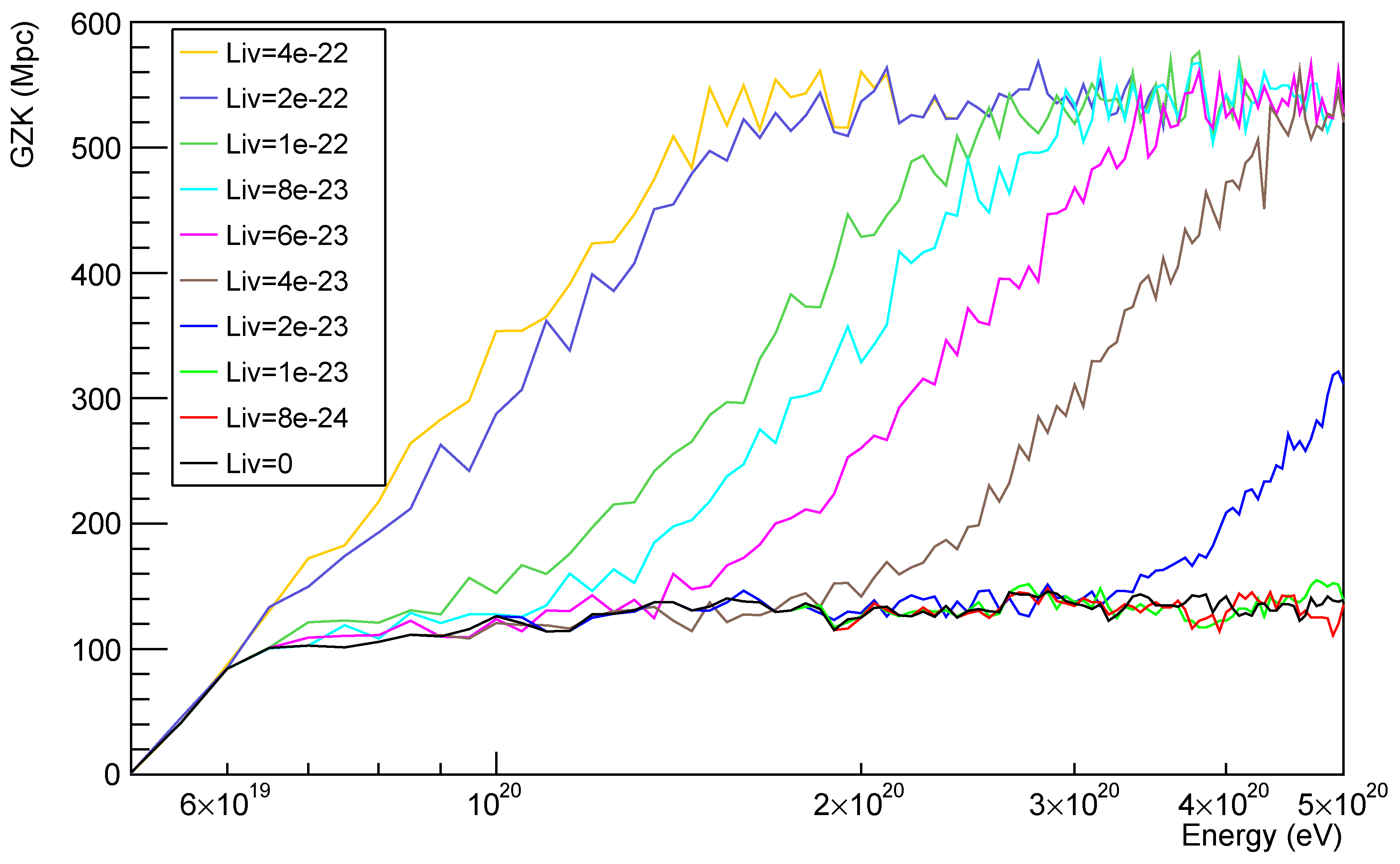
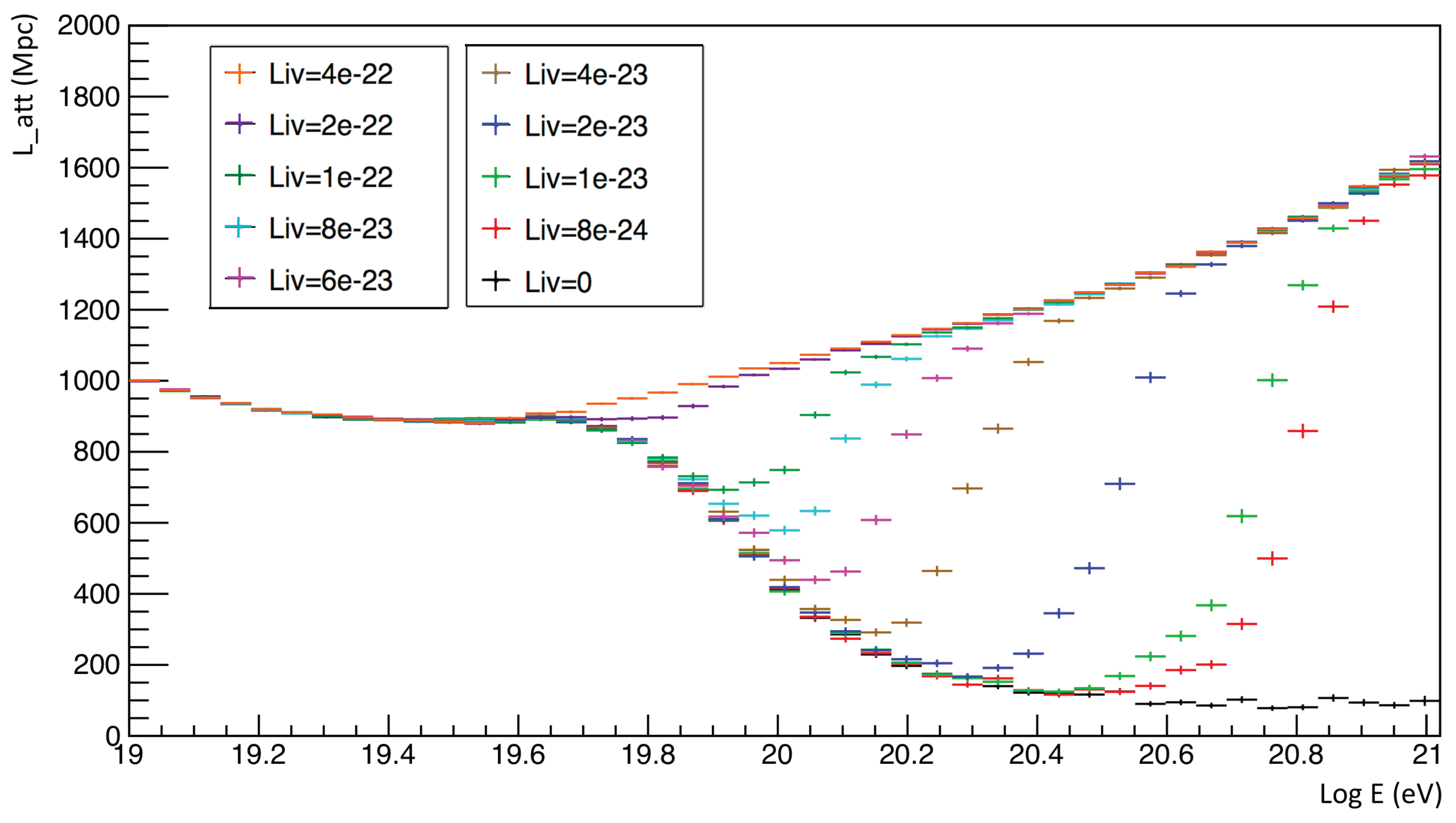
5. Simulations on LIV Modified Propagation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UHECR | Ultra High Energy Ccosmic Ray |
| CR | Cosmic Rays |
| LIV | Lorentz Invariance Violation |
| HMSR | Homogeneously Modified Special Relativity |
| SM | Standard Model |
| SME | Standard Model extension |
| VSR | Very Special Relativity |
| DR | Dispersion Relation |
| MDR | Modified Dispersion Relation |
| MLT | Modified Lorentz Transformation |
Appendix A. Derivative of the 0 Degree Homogeneous Function
References
- Pierre Auger Collaboration. Observation of a Large-scale Anisotropy in the Arrival Directions of Cosmic Rays above 8 × 1018 eV. Science 2017, 357, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierre Auger Collaboration. Constraints on the origin of cosmic rays above 1018 eV from large scale anisotropy searches in data of the Pierre Auger Observatory. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2012, 762, L13. [Google Scholar]
- Tinyakov, P.G.; Urban, F.R.; Ivanov, D.; Thomson, G.B.; Tirone, A.H. A signature of EeV protons of Galactic origin. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 460, 3479–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, R.U.; Abe, M.; Abu-Zayyad, T.; Allen, M.; Azuma, R.; Barcikowski, E.; Belz, J.W.; Bergman, D.R.; Blake, S.A.; Cady, R.; et al. Search for EeV Protons of Galactic Origin. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 86, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, P. Origin of very high- and ultra-high-energy cosmic rays. C. R. Physique 2014, 15, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greisen, K. End to the cosmic ray spectrum? Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 16, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatsepin, G.; Kuzmin, V. Upper limit of the spectrum of cosmic rays. JETP Lett. 1966, 4, 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, S.R.; Glashow, S.L. High-energy tests of Lorentz invariance. Phys. Rev. D 1999, 59, 116008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W.; Scully, S.T. Searching for New Physics with Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 085003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, S.; Stecker, F. Lorentz Invariance Violation and the Observed Spectrum of Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 31, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torri, M.D.C.; Bertini, S.; Giammarchi, M.; Miramonti, L. Lorentz Invariance Violation effects on UHECR propagation: A geometrized approach. J. High Energy Astrophys. 2018, 18, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torri, M.D.C. Lorentz Invariance Violation Effects on Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays Propagation, a Geometrical Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, Milan University, Milan, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Colladay, D.; Kostelecký, V.A. Lorentz violating extension of the standard model. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 58, 116002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.G.; Glashow, S.L. Very special relativity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 021601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelino-Camelia, G. Doubly special relativity. Nature 2002, 418, 34–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelino-Camelia, G. Doubly special relativity: First, results and key open problems. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2002, 11, 1643–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelino-Camelia, G.; Freidel, L.; Kowalski-Glikman, J.; Smolin, L. The principle of relative locality. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 084010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelino-Camelia, G.; Bianco, S.; Rosati, G. Planck-Scale-Deformed Relativistic Symmetries and Diffeomorphisms on Momentum Space. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 026018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torri, M.; Antonelli, V.; Miramonti, L. Homogeneously Modified Special relativity (HMSR). Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloisio, R.; Boncioli, D.; Grillo, A.; Petrera, S.; Salamida, F. SimProp: A Simulation Code for Ultra High Energy Cosmic Ray Propagation. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magueijo, J.; Smolin, L. Gravity’s rainbow. Class. Quant. Grav. 2004, 21, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magueijo, J.; Smolin, L. Lorentz invariance with an invariant energy scale. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 190403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, C.; Wohlfarth, M.N.R. Finsler geometric extension of Einstein gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 064009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, M.; Pfeifer, C.; Voicu, N. Finsler gravity action from variational completion. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 064035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, C. Finsler spacetime geometry in Physics. Int. J. Geom. Meth. Mod. Phys. 2019, 16, 1941004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaloyes, M.A.; Sánchez, M. On the definition and examples of cones and Finsler spacetimes. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.06978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, A.; Javaloyes, M.Á.; Sánchez, M. Foundations of Finsler spacetimes from the Observers’ Viewpoint. Universe 2020, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, O. Why is CPT fundamental? Found. Phys. 2006, 36, 1535–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, O. CPT violation implies violation of Lorentz invariance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 231602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, V.; Miramonti, L.; Torri, M.D.C. Phenomenological Effects of CPT and Lorentz Invariance Violation in Particle and Astroparticle Physics. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichian, M.; Dolgov, A.D.; Novikov, V.A.; Tureanu, A. CPT Violation Does Not Lead to Violation of Lorentz Invariance and Vice Versa. Phys. Lett. B 2011, 699, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tureanu, A. CPT and Lorentz Invariance: Their Relation and Violation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 474, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichian, M.; Fujikawa, K.; Tureanu, A. Electromagnetic interaction in theory with Lorentz invariant CPT violation. Phys. Lett. B 2013, 718, 1500–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duetsch, M.; Gracia-Bondia, J.M. On the assertion that PCT violation implies Lorentz non-invariance. Phys. Lett. B 2012, 711, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, O. Remarks on a Challenge to the Relation between CPT and Lorentz Violation. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1105.0927. [Google Scholar]
- Antonelli, V.; Miramonti, L.; Torri, M.D.C. Neutrino oscillations and Lorentz Invariance Violation in a Finslerian Geometrical model. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torri, M.D.C. Neutrino Oscillations and Lorentz Invariance Violation. Universe 2020, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostelecky, A. Riemann-Finsler geometry and Lorentz-violating kinematics. Phys. Lett. B 2011, 701, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, F.; Liberati, S.; Sindoni, L. Planck-scale modified dispersion relations and Finsler geometry. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 064015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, B.R.; Kostelecky, V.A. Riemann-Finsler geometry and Lorentz-violating scalar fields. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 786, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lämmerzahl, C.; Perlick, V. Finsler geometry as a model for relativistic gravity. Int. J. Geom. Meth. Mod. Phys. 2018, 15, 1850166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lämmerzahl, C.; Perlick, V. Axiomatic formulations of modied gravity theories with nonlinear dispersion relations and Finsler Lagrange Hamilton geometry. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 969. [Google Scholar]
- Schreck, M. Classical Lagrangians and Finsler structures for the nonminimal fermion sector of the Standard-Model Extension. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 105017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W. Photodisintegration of ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays by the universal radiation field. Phys. Rev. 1969, 180, 1264–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boncioli, D.; di Matteo, A.; Salamida, F.; Aloisio, R.; Blasi, P.; Ghia, P.L.; Grillo, A.; Petrera, S.; Pierog, T. Future prospects of testing Lorentz invariance with UHECRs. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1509.01046. [Google Scholar]
- Boncioli, D.; Pierre Auger Collaboration. Probing Lorentz symmetry with the Pierre Auger Observatory. In Proceedings of the ICRC17, Busan, Korea, 10–20 July 2017; Volume 561. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, R.G.; Pierre Auger Collaboration. Testing Lorentz Invariance Violation at the Pierre Auger Observatory. In Proceedings of the ICRC19, Madison, WI, USA, 24 July–1 August 2019; p. 327. [Google Scholar]
- Bietenholz, W. Cosmic Rays and the Search for a Lorentz Invariance Violation. Phys. Rep. 2011, 505, 145–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattingly, D. Modern tests of Lorentz invariance. Living Rev. Rel. 2005, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostelecky, V.A.; Russell, N. Data Tables for Lorentz and CPT Violation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2011, 83, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre Auger Collaboration. Depth of maximum of air-shower profiles at the Pierre Auger Observatory. II. Composition implications. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 122006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.S.; Klinkhamer, F.R.; Risse, M. Changes in extensive air showers from isotropic Lorentz violation in the photon sector. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 085025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkhamer, F.R.; Niechciol, M.; Risse, M. Improved bound on isotropic Lorentz violation in the photon sector from extensive air showers. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 116011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.G.; Martínez-Huerta, H.; de Souza, V. Limits on the Lorentz Invariance Violation from UHECR astrophysics. Astrophys. J. 2018, 853, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torri, M.D.C.; Caccianiga, L.; di Matteo, A.; Maino, A.; Miramonti, L. Predictions of Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Ray Propagation in the Context of Homogeneously Modified Special Relativity. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12121961
Torri MDC, Caccianiga L, di Matteo A, Maino A, Miramonti L. Predictions of Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Ray Propagation in the Context of Homogeneously Modified Special Relativity. Symmetry. 2020; 12(12):1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12121961
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorri, Marco Danilo Claudio, Lorenzo Caccianiga, Armando di Matteo, Andrea Maino, and Lino Miramonti. 2020. "Predictions of Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Ray Propagation in the Context of Homogeneously Modified Special Relativity" Symmetry 12, no. 12: 1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12121961
APA StyleTorri, M. D. C., Caccianiga, L., di Matteo, A., Maino, A., & Miramonti, L. (2020). Predictions of Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Ray Propagation in the Context of Homogeneously Modified Special Relativity. Symmetry, 12(12), 1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12121961







