Abstract
Lorentz symmetry is an important concept in modern physics. Precision pulsar timing was used to put tight constraints on the coefficients for Lorentz violation in the pure-gravity sector of the Standard-Model Extension (SME). We extend the analysis to Lorentz-violating matter-gravity couplings, utilizing three small-eccentricity relativistic neutron star (NS)—white dwarf (WD) binaries. We obtain compelling limits on various SME coefficients related to the neutron, the proton, and the electron. These results are complementary to limits obtained from lunar laser ranging and clock experiments.
1. Introduction
The theory of general relativity (GR) and the Standard Model (SM) of particle physics represent our contemporary condensed wisdom in the search of fundamental laws in physics. Nevertheless, there exist various motivations to look for new physics. Among them, the possibility of Lorentz violation is a well developed concept [1]. Lorentz violation could be resulted from a deep underlying theory of quantum gravity [2]. At low energy, it is believed to be described by an effective field theory (EFT). An EFT framework, the so-called Standard-Model Extension (SME), systematically incorporates all Lorentz-covariant, gauge-invariant, energy-momentum-conserving operators that are associated with GR and SM fields [3,4,5]. Field operators are sorted according to their mass dimension, and, for some certain species, operators of arbitrary mass dimensions are classified [6,7,8,9].
The SME is supposed to be an effectively low-energy theory for the quantum gravity, thus, the gravitational aspect of the SME is of particular interest. Kostelecký [5] presented the general structure of the SME when the curved spacetime is considered. Bailey and Kostelecký [10] worked out different kinds of observational phenomena associated with the minimal operators in the pure-gravity sector of the SME, whose mass dimension . After that, Kostelecký and Tasson [11] investigated in great detail the theoretical aspects of the matter-gravity couplings, whose mass dimension . Phenomenological aspects and relevant experiments are identified. Moreover, the nonminimal SME with gravitational operators, whose mass dimension , was studied and gained global interests during the past few years [12,13,14].
Due to the advances on the theoretical side [5,10,11,12], phenomenological and experimental studies of the gravitational SME became a hot topic [15,16,17,18]. Hees et al. [19] have a comprehensive summary on this topic—see also the Data Tables for Lorentz and CPT Violation, compiled by Kostelecký and Russell [20]. In the pure-gravity sector, binary pulsars turn out to be among the best experiments in constraining (i) the minimal Lorentz-violating operators [21,22]; (ii) dimension-5 CPT-violating operators [23]; as well as (iii) dimension-8 cubic-in-the-Riemannian-tensor operators, which are related to the leading-order violation of the gravitational weak equivalence principle [24]. In a closely related metric-based framework, the so-called parameterized post-Newtonian formalism [25,26], binary pulsars similarly outperform many Solar-system-based experiments [27,28,29,30].
In this work, we investigate the matter-gravity couplings in the SME and their signals in binary pulsars [11,31]. In particular, we use small-eccentricity binary pulsars—PSRs J0348+0432 [32], J0751+1807 [33], and J1738+0333 [34]—to put stringent constraints on various matter-gravity coupling coefficients. The limits are compelling, and complementary to other experiments. They contribute to the research field on the experimental examination of the SME.
The paper is organized as follows. In the next section, we review the matter-gravity couplings in the SME [11]. Then, in Section 3, the orbital dynamics for a binary pulsar [31] are provided. In particular, the secular change of the eccentricity vector (decomposed into the two Laplace–Lagrange parameters [35]), and the secular change of the pulsar’s projected semimajor axis are discussed. Constraints on the matter-gravity coupling coefficients are given in Section 4. The last section discusses constraints from other experiments, the strong-field aspects of pulsars, and the prospects in improving the limits on the Lorentz-violating matter-gravity couplings.
2. Matter-Gravity Couplings in the SME
In order to incorporate fermion-gravity couplings, we use the vierbein formalism [5]. In the SME, the action for a massive Dirac fermion reads [11]
where, for spin-independent cases,
Here, is the vierbein with e as its determinant; m is the mass of the fermion; is the Dirac matrix; , , and are species-dependent, spin-independent coefficient fields for Lorentz violation (see Equations (7) and (8) in [11] for spin-dependent terms).
While being kept to the leading order, a field redefinition via a position-dependent component mixing in the spinor space can be used to show that the CPT-odd coefficients and always appear in the combination [11]
Therefore, we shall consider only and in the following.
At leading order, the point-particle action is [11],
where . For a macroscopic composite object, the action Equation (5) is still applicable with the replacements [11],
where w denotes the particle species and is the number of particles of type w. We have neglected the contribution from binding energies which could be at most for neutron stars (NSs), unless some unknown nonperturbative effects take place (see discussions in Section 5) [30]. In general, the role of binding energy could further aid the analysis of signals for Lorentz violation, see Section VI B in [11] for more details. Hereafter, for simplicity we only consider three types of fermions—(i) the electron , (ii) the proton , and (iii) the neutron . In Table 1, we list the estimated composition of these three species for NSs and white dwarfs (WDs), and their corresponding composite coefficient fields for Lorentz violation.

Table 1.
Estimated composition for neutron stars (NSs) and white dwarfs (WDs). Composite coefficient fields for Lorentz violation are estimated according to Equations (6)–(8). In the table, and are the masses for NS and WD, respectively, and () is the mass for a neutron (proton) particle. We define and .
In general, the coefficient fields, and , are dynamical fields. In the Riemann–Cartan spacetime, the Lorentz violation often needs to be spontaneous [36], instead of explicit [5]. The coefficient fields obtain their vacuum expectation values via the Higgs-like spontaneous symmetry breaking mechanism. We denote the vacuum expectation values of and as and , respectively. The barred quantities are also known as the coefficients for Lorentz violation [20]. In asymptotically inertial Cartesian coordinates, they are assumed to be small and satisfy [11]
The coefficients for Lorentz violation, and [20], are the quantities that we want to investigate with pulsar timing experiments [37,38] in this work.
3. Binary Pulsars with Lorentz-Violating Matter-Gravity Couplings
Jennings et al. [31] worked out the osculating elements for a binary system, composed of masses and , in the presence of the Lorentz-violating matter-gravity couplings. We consistently use the subscript “1” to denote the pulsar; and use the subscript “2” to denote the companion which is a WD in our study. We define and . To simplify some expressions, we also define , then, .
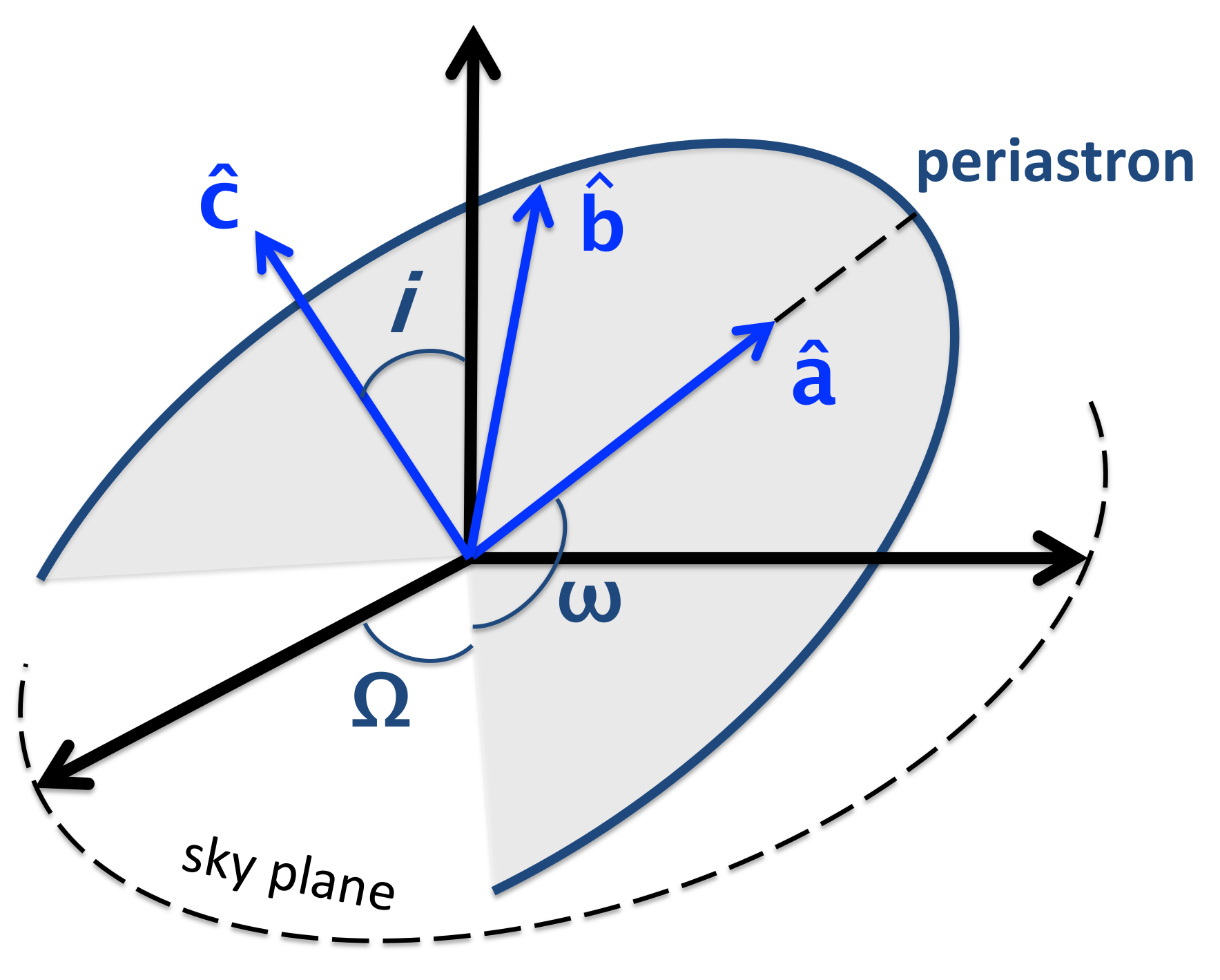
Neglecting the finite-size effects, the Newtonian relative acceleration for a binary is , where is the relative separation and . In the Newtonian gravity, a two-body system with a negative total orbital energy forms an elliptical orbit. An elliptical orbit in the celestial mechanics is usually described by six orbital elements—(i) the semimajor axis a; (ii) the orbital eccentricity e; (iii) the epoch of periastron passage ; (iv) the inclination of orbit i; (v) the longitude of periastron ; and (vi) the longitude of ascending node . The last three angles are illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Pulsar orbit and the coordinate system [10,22,23].
When there is a perturbing acceleration to , say, , the orbit is changed perturbatively. In the osculating-element approach, one assumes that at any instant moment, the orbit is still an ellipse, but the six orbital elements become functions of the time t [39]. The time derivatives of these six functions are derived from the extra acceleration [39]. In the current case, after averaging over an orbital period , the secular changes read [31]
where we have defined , , and . From Equation (11), we can see that the energy of the orbit is conserved at leading order, which is compatible with the action formulation of the system in the absence of gravitational waves. The expressions for and are not important in the present context, and thus not shown. The 3-vector and the tensor are defined as [31],
where are defined in Equation (9) of [31], and their approximated values for NS–NS and NS–WD binaries are given in Table 2 for convenience.

Table 2.
Expressions of (; ) for NS–NS and NS–WD systems (see Equation (9) in [31]), where . Results in Table 1 are adopted for the calculation here.
We can easily obtain the following conclusion from the above two equations. (I) The sensitivity to and (compared with and , respectively) is suppressed by the mass ratio of the electron to the proton , while the sensitivity to (compared with ) is not suppressed. (II) We have no sensitivity to nor from binary pulsars in this simplified situation. This is similar to the case of (the time–time component of the Lorentz-violating field ) in the pure-gravity sector of the SME with dimension 4 operators [10,21], nevertheless, these coefficients can be probed with the help of the “boost effect” introduced by the systematic velocity of the binary () with respect to the Solar system [22]. We defer the investigation along this line to future studies.
In Equations (11)–(14), and are projected to the coordinate system [10,22,23], where is the unit vector points from the center of binary towards the periastron, is the unit vector points along the orbital angular momentum, and (see Figure 1).
We are interested in the small-eccentricity binaries. In the limiting case of small eccentricity , we have
We can convert the derivatives of e, i, and into derivatives of the projected semimajor axis of the pulsar orbit , and the Laplace–Lagrange parameters, and into
where we have used .
4. Bounds on the SME Coefficients
We use the time derivatives of , , and in Equations (24)–(26) to constrain the coefficients for Lorentz violation. It is clear that the more relativistic the binary (namely, the larger ), the better the tests. Therefore, we use three well-timed NS–WD binaries whose orbital periods are shorter than half a day [32,33,34]. Relevant parameters of these binaries are collected in Table 3. Due to the binary interaction and matter exchange in the evolutionary history, these NS–WD binaries have small orbital eccentricity , thus, Equations (24)–(26) are sufficient to perform the tests.

Table 3.
Relevant parameters for PSRs J0348+0432 [32], J0751+1807 [33], and J1738+0333 [34]. Parenthesized numbers represent the 1- uncertainty in the last digit(s) quoted. The parameter is the intrinsic value, after subtraction of the contribution from the Shapiro delay [35]. Masses are derived without using information related to , , nor for consistency. For PSRs J0348+0432 and J1738+0333, masses were derived independently of gravity theories [32,34], while for PSR J0751+1807 we have used observed quantities related to the Shapiro delay and orbital decay, assuming the validity of general relativity (GR) [33].
From Table 3, we see that the time derivatives of and are not reported in literature, as well as the time derivative of for PSR J0348+0432. The reason is usually the following. In fitting the times of arrival of pulse signals, these quantities would be measured to be consistent with zero if they were included in the timing formalism. To have a simpler timing model, these quantities are considered unnecessary for a good fit. Actually, the insignificance of these quantities is consistent with the spirit of our tests to put upper limits on the Lorentz violation. We estimate the upper limits for these quantities using [21], where is the measured uncertainty for the quantity X and is the observational span of the data from where these quantities were derived. The factor “” approximately takes a linear-in-time evolution of the quantity X into account [21]. It is verified that this approximation works reasonably well [21,23]. For PSRs J0751+1807 and J1738+0333, was measured to be nonzero. As the proper motion of the binary in the sky could contribute to a nonzero for nearby pulsars [37,40], we use the measured value of as an upper limit for the effects from Lorentz violation. For nearby pulsars, the contribution to from the proper motion depends sinusoidally on [37,40]—although is not measured, we do not expect the Nature’s conspiracy in assigning certain values of case-by-case to different binary pulsars, in order to hide the Lorentz symmetry breaking. Therefore, we believe the above treatments introduce uncertainties no larger than a multiplicative factor of a few.
In order to use Equations (24)–(26), one also needs the absolute geometry of the orbit to properly project the vector and the tensor onto the coordinate system . In general, the longitude of the ascending node is not observable in pulsar timing [37]. Nevertheless, the procedure to randomize the value of and to systematically project vectors and tensors onto was worked out in [21]. It was successfully applied to binary pulsars in previous studies [21,22,23,24]. Since here (i) we have already introduced an uncertainty with a factor of a few, and (ii) we are interested in the “maximal-reach” limits in absence of the Lorentz violation, we take a simplified approach and treat these projections as operators. The “maximal-reach” approach [18] assumes that only one component of Lorentz-violating coefficients is nonzero in a test. We think our approach is reasonable at the stage of setting upper limits to the coefficients for Lorentz violation. Nevertheless, when people start to discover some evidence for the Lorentz violation, it is absolutely needed to take into account more sophisticated analysis, for example, to use the 3-D orientation of the orbit (possibly in a probabilistic way with an unknown ) as was done in [21,22,23,24]. In addition, if one wants to explore the correlation between different coefficients for Lorentz violation, more sophisticated analysis is needed as well. These improvements lay beyond the scope of this work.
In Table 4, we list the “maximal-reach” [18] limits on the coefficients for Lorentz violation with matter-gravity couplings obtained from binary pulsars. As we can see, the best limits on come from PSR J1738+0333 due to its very good measurement on the [34]. For and , the best limits come from PSR J0751+1807 due to its good measurement of the Lagrange–Laplace parameters [33].

Table 4.
“Maximal-reach” limits from binary pulsars on the coefficients for Lorentz violation with matter-gravity couplings, where only one component is assumed to be nonzero at a time. The limits on come from ; while the limits on and come from or , and only the stronger one is listed in the table. For each row, the strongest limit is shown in boldface.
5. Discussion
Besides the streamlined theoretical analysis, the maximal-reach limits in Table 4 are the main results of this paper. As far as we are aware, Altschul [41] was the first to put preliminary limits on the SME neutron-sector coefficients with pulsar rotations. The pure-gravity sector of the SME at different mass dimensions was systematically tested with binary pulsars in [21,22,23,24]. Early limits on were given with K/He magnetometer and torsion-strip balance [42,43], but these limits, while constraining different linear combinations of the Lorentz violating coefficients, are rather weak. Later, the maximal-reach limits on were obtained systematically with superconducting gravimeters [44] and lunar laser ranging (LLR) experiments [45]. The former got ; while the latter got . Our best limits from PSR J0751+1807 for the proton and the electron are weaker than the LLR limits, while our limit for the neutron is slightly better. There is also a limit from the observation of gravitational waves, but being weaker than our limits by almost 30 orders of magnitude [46]. The limits on were cast by analyzing nuclear binding energy, Cs interferometer, torsion pendulum, and weak equivalence principle experiments [11,47,48,49]. The analysis with binary pulsars in this work could not bound these SME coefficients. The limits on from other experiments (e.g., clock experiments [50]) are much better than the limits from binary pulsars [20]. However, our limits are the best ones from gravitational systems. In a short summary, our limits are compelling, and complementary to limits obtained from other experiments.
In using the SME, we have assumed the validity of the effective field theory (EFT) and the smallness of the Lorentz violation. This is true for most ordinary objects. However, we shall be aware of a caveat for NSs, because of the possible nonperturbative behaviors which might be triggered by their strongly self-gravitating nature [38]. It was shown explicitly that, in a class of scalar-tensor theories, highly nonlinear phenomena are possible within NSs and they may result in large deviations from GR [51,52]. Although the nonperturbative behaviors were constrained tightly with binary pulsars and the binary neutron star inspiral GW170817 [34,53,54], the possibility is not completely ruled out yet [55,56,57]. With this caveat in mind, conservatively speaking, the tests in this paper are basically testing the strong-field counterparts of the weak-field SME coefficients. Usually, when the strong-field effects are considered, the constraints become even tighter. Therefore, we treat the limits here as conservative ones [30].
The tests of Lorentz violation with binary pulsars improve with a longer baseline for data [21]. Specifically, even pessimistically assuming no advance in the quality of binary-pulsar observation for the future, the tests in Equations (24)–(26) improve as , where is the total observational span. In reality, the quality of observation improves rapidly, especially with the newly built and upcoming telescopes, like the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST), the MeerKAT telescope, and the Square Kilometre Array (SKA) [58,59,60,61]. Therefore, we expect better tests than the scaling in testing the Lorentz violation in the future.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11975027), the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by the China Association for Science and Technology (2018QNRC001), and partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11721303), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences through the Grant No. XDB23010200, and the European Research Council (ERC) for the ERC Synergy Grant BlackHoleCam under Contract No. 610058.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Jay Tasson for the invitation and stimulating discussions. We thank Norbert Wex for carefully reading the manuscript, and Adrien Bourgoin, Zhi Xiao, and Rui Xu for communication.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| EFT | Effective Field Theory |
| GR | General Relativity |
| LLR | Lunar Laser Ranging |
| NS | Neutron Star |
| SM | Standard Model |
| SME | Standard-Model Extension |
| WD | White Dwarf |
References
- Tasson, J.D. What Do We Know About Lorentz Invariance? Rept. Prog. Phys. 2014, 77, 062901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostelecký, V.A.; Samuel, S. Spontaneous Breaking of Lorentz Symmetry in String Theory. Phys. Rev. D 1989, 39, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colladay, D.; Kostelecký, V.A. CPT violation and the standard model. Phys. Rev. D 1997, 55, 6760–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colladay, D.; Kostelecký, V.A. Lorentz violating extension of the standard model. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 58, 116002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostelecký, V.A. Gravity, Lorentz violation, and the standard model. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 69, 105009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostelecký, V.A.; Mewes, M. Electrodynamics with Lorentz-violating operators of arbitrary dimension. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 015020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostelecký, V.A.; Mewes, M. Neutrinos with Lorentz-violating operators of arbitrary dimension. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 096005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostelecký, A.; Mewes, M. Fermions with Lorentz-violating operators of arbitrary dimension. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 096006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostelecký, V.A.; Li, Z. Gauge field theories with Lorentz-violating operators of arbitrary dimension. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 056016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, Q.G.; Kostelecký, V.A. Signals for Lorentz violation in post-Newtonian gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostelecký, V.A.; Tasson, J.D. Matter-gravity couplings and Lorentz violation. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 016013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, Q.G.; Kostelecký, V.A.; Xu, R. Short-range gravity and Lorentz violation. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 022006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.G.; Tan, Y.-J.; Tan, W.-H.; Yang, S.-Q.; Luo, J.; Tobar, M.E.; Bailey, Q.G.; Long, J.C.; Weisman, E.; Xu, R.; et al. Combined search for Lorentz violation in short-range gravity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 071102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostelecký, V.A.; Mewes, M. Lorentz and Diffeomorphism Violations in Linearized Gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 779, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasson, J.D. Gravitational Searches for Lorentz Violation with Matter and Astrophysics. In Proceedings of the 7th Meeting on CPT and Lorentz Symmetry (CPT 16), Bloomington, IN, USA, 20–24 June 2016; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, Q.G. Recent Developments in Spacetime-Symmetry tests in Gravity. In Proceedings of the 8th Meeting on CPT and Lorentz Symmetry (CPT’19), Bloomington, IN, USA, 12–16 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, L. Pulsar Tests of the Gravitational Lorentz Violation. In Proceedings of the 8th Meeting on CPT and Lorentz Symmetry (CPT’19), Bloomington, IN, USA, 12–16 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tasson, J.D. Maximal Tests in Minimal Gravity. In Proceedings of the 8th Meeting on CPT and Lorentz Symmetry (CPT’19), Bloomington, IN, USA, 12–16 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hees, A.; Bailey, Q.G.; Bourgoin, A.; Bars, H.P.L.; Guerlin, C.; Le Poncin-Lafitte, C. Tests of Lorentz symmetry in the gravitational sector. Universe 2016, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostelecký, V.A.; Russell, N. Data Tables for Lorentz and CPT Violation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2011, 83, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L. Tests of local Lorentz invariance violation of gravity in the standard model extension with pulsars. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 111103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L. New pulsar limit on local Lorentz invariance violation of gravity in the standard-model extension. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 122009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Bailey, Q.G. Testing velocity-dependent CPT-violating gravitational forces with radio pulsars. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 084049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Bailey, Q.G. Testing the Gravitational Weak Equivalence Principle in the Standard-Model Extension with Binary Pulsars. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 084017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, C.M. The Confrontation between General Relativity and Experiment. Living Rev. Rel. 2014, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Will, C.M. Theory and Experiment in Gravitational Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, L.; Wex, N. New tests of local Lorentz invariance of gravity with small-eccentricity binary pulsars. Class. Quant. Grav. 2012, 29, 215018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Caballero, R.N.; Kramer, M.; Wex, N.; Champion, D.J.; Jessner, A. A new limit on local Lorentz invariance violation of gravity from solitary pulsars. Class. Quant. Grav. 2013, 30, 165019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Wex, N. New limits on the violation of local position invariance of gravity. Class. Quant. Grav. 2013, 30, 165020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Wex, N. Tests of gravitational symmetries with radio pulsars. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2016, 59, 699501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, R.J.; Tasson, J.D.; Yang, S. Matter-Sector Lorentz Violation in Binary Pulsars. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 125028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, J.; Freire, P.C.; Wex, N.; Tauris, T.M.; Lynch, R.S.; van Kerkwijk, M.H.; Kramer, M.; Bassa, C.; Dhillon, V.S.; Driebe, T.; et al. A Massive Pulsar in a Compact Relativistic Binary. Science 2013, 340, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desvignes, G.; Caballero, R.N.; Lentati, L.; Verbiest, J.P.W.; Champion, D.J.; Stappers, B.W.; Janssen, G.H.; Lazarus, P.; Osłowski, S.; Babak, S.; et al. High-precision timing of 42 millisecond pulsars with the European Pulsar Timing Array. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2016, 458, 3341–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, P.C.C.; Wex, N.; Esposito-Farèse, G.; Verbiest, J.P.W.; Bailes, M.; Jacoby, B.A.; Kramer, M.; Stairs, I.H.; Antoniadis, J.; Janssen, G.H. The relativistic pulsar-white dwarf binary PSR J1738+0333 II. The most stringent test of scalar-tensor gravity. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2012, 423, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.; Camilo, F.; Wex, N.; Kramer, M.; Backer, D.C.; Lyne, A.G.; Doroshenko, O. Precision timing measurements of psr j1012+5307. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2001, 326, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluhm, R.; Bossi, H.; Wen, Y. Gravity with explicit spacetime symmetry breaking and the Standard-Model Extension. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.13209. [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer, D.R.; Kramer, M. Handbook of Pulsar Astronomy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wex, N. Testing Relativistic Gravity with Radio Pulsars. In Frontiers in Relativistic Celestial Mechanics: Applications and Experiments; Kopeikin, S.M., Ed.; Walter de Gruyter GmbH: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 2, p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- Poisson, E.; Will, C.M. Gravity: Newtonian, Post-Newtonian, Relativistic; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeikin, S.M. Proper Motion of Binary Pulsars as a Source of Secular Variations of Orbital Parameters. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1996, 467, L93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, B. Limits on Neutron Lorentz Violation from Pulsar Timing. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 023001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasson, J.D. Lorentz violation, gravitomagnetism, and intrinsic spin. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 124021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjwani, H.; Carbone, L.; Speake, C.C. Laboratory Searches for Preferred Frame Effects: Ongoing Work and Results at Birmingham. In Proceedings of the 5th Meeting on CPT and Lorentz Symmetry (CPT 10), Bloomington, IN, USA, 28 June–2 July 2010; pp. 194–198. [Google Scholar]
- Flowers, N.A.; Goodge, C.; Tasson, J.D. Superconducting-Gravimeter Tests of Local Lorentz Invariance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 201101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgoin, A.; Le Poncin-Lafitte, C.; Hees, A.; Bouquillon, S.; Francou, G.; Angonin, M.C. Lorentz Symmetry Violations from Matter-Gravity Couplings with Lunar Laser Ranging. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 201102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreck, M. Fermionic Lorentz violation and its implications for interferometric gravitational-wave detection. Class. Quant. Grav. 2017, 34, 135009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostelecký, V.A.; Tasson, J. Prospects for Large Relativity Violations in Matter-Gravity Couplings. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 010402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohensee, M.A.; Chu, S.; Peters, A.; Mueller, H. Equivalence Principle and Gravitational Redshift. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 151102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohensee, M.A.; Mueller, H.; Wiringa, R.B. Equivalence Principle and Bound Kinetic Energy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 151102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihan-Le Bars, H.; Guerlin, C.; Lasseri, R.D.; Ebran, J.P.; Bailey, Q.G.; Bize, S.; Khan, E.; Wolf, P. Lorentz-symmetry test at Planck-scale suppression with nucleons in a spin-polarized 133Cs cold atom clock. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 075026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damour, T.; Esposito-Farèse, G. Nonperturbative strong field effects in tensor-scalar theories of gravitation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 70, 2220–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damour, T.; Esposito-Farèse, G. Tensor-scalar gravity and binary pulsar experiments. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 54, 1474–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Sennett, N.; Buonanno, A.; Kramer, M.; Wex, N. Constraining nonperturbative strong-field effects in scalar-tensor gravity by combining pulsar timing and laser-interferometer gravitational-wave detectors. Phys. Rev. X 2017, 7, 041025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shao, L.; Cao, Z.; Ma, B.Q. Reduced-order surrogate models for scalar-tensor gravity in the strong field and applications to binary pulsars and GW170817. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.00780. [Google Scholar]
- Yunes, N.; Yagi, K.; Pretorius, F. Theoretical Physics Implications of the Binary Black-Hole Mergers GW150914 and GW151226. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 084002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyaprakash, B.S.; Buonanno, A.; Lehner, L.; Van Den Broeck, C.; Ajith, P.; Ghosh, A.; Chatziioannou, K.; Pani, P.; Puerrer, M.; Sotiriou, T.; et al. Extreme Gravity and Fundamental Physics. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.09221. [Google Scholar]
- Carson, Z.; Seymour, B.C.; Yagi, K. Future Prospects for Probing Scalar-Tensor Theories with Gravitational Waves from Mixed Binaries. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.03897. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, M.; Backer, D.C.; Cordes, J.M.; Lazio, T.J.W.; Stappers, B.W.; Johnston, S. Strong-field tests of gravity using pulsars and black holes. New Astron. Rev. 2004, 48, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Stairs, I.H.; Antoniadis, J.; Deller, A.T.; Freire, P.C.C.; Hessels, J.W.T.; Janssen, G.H.; Kramer, M.; Kunz, J.; Lämmerzahl, C.; et al. Testing Gravity with Pulsars in the SKA Era. In Proceedings of the Advancing Astrophysics with the Square Kilometre Array, Giardini Naxos, Italy, 9–13 June 2014; Volume AASKA14, p. 042. [Google Scholar]
- Bull, P.; Camera, S.; Kelley, K.; Padmanabhan, H.; Pritchard, J.; Raccanelli, A.; Riemer-Sørensen, S.; Shao, L.; Andrianomena, S.; Athanassoula, E.; et al. Fundamental Physics with the Square Kilometre Array. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.02680. [Google Scholar]
- Bailes, M.; Barr, E.; Bhat, N.D.R.; Brink, J.; Buchner, S.; Burgay, M.; Camilo, F.; Champion, D.J.; Hessels, J.; Janssen, G.H.; et al. MeerTime—The MeerKAT Key Science Program on Pulsar Timing. In Proceedings of the MeerKAT Science: On the Pathway to the SKA (MeerKAT2016), Stellenbosch, South Africa, 25–27 May 2016; Volume MeerKAT2016, p. 011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).