Fast Pig Detection with a Top-View Camera under Various Illumination Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
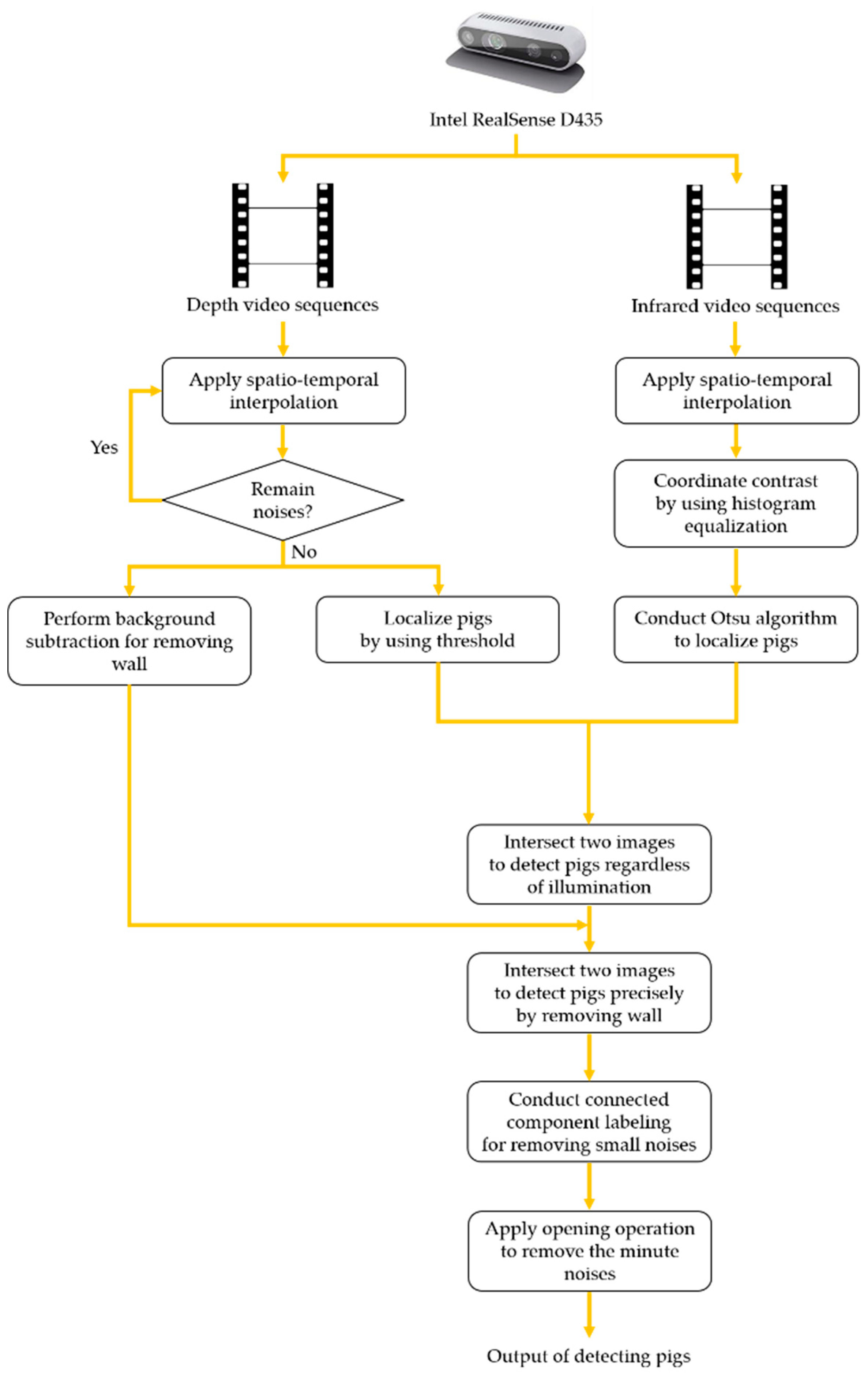
3. Proposed Method
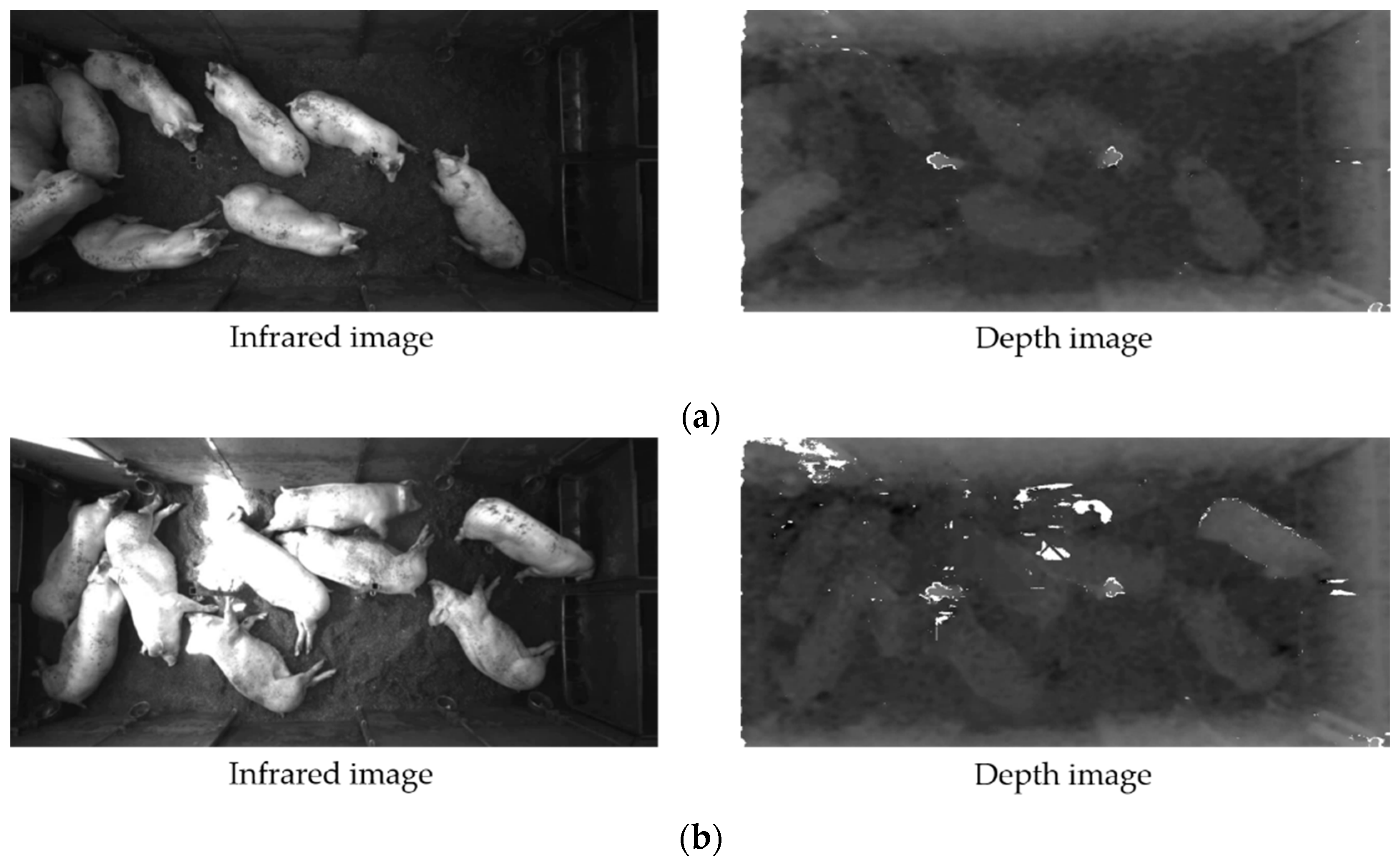
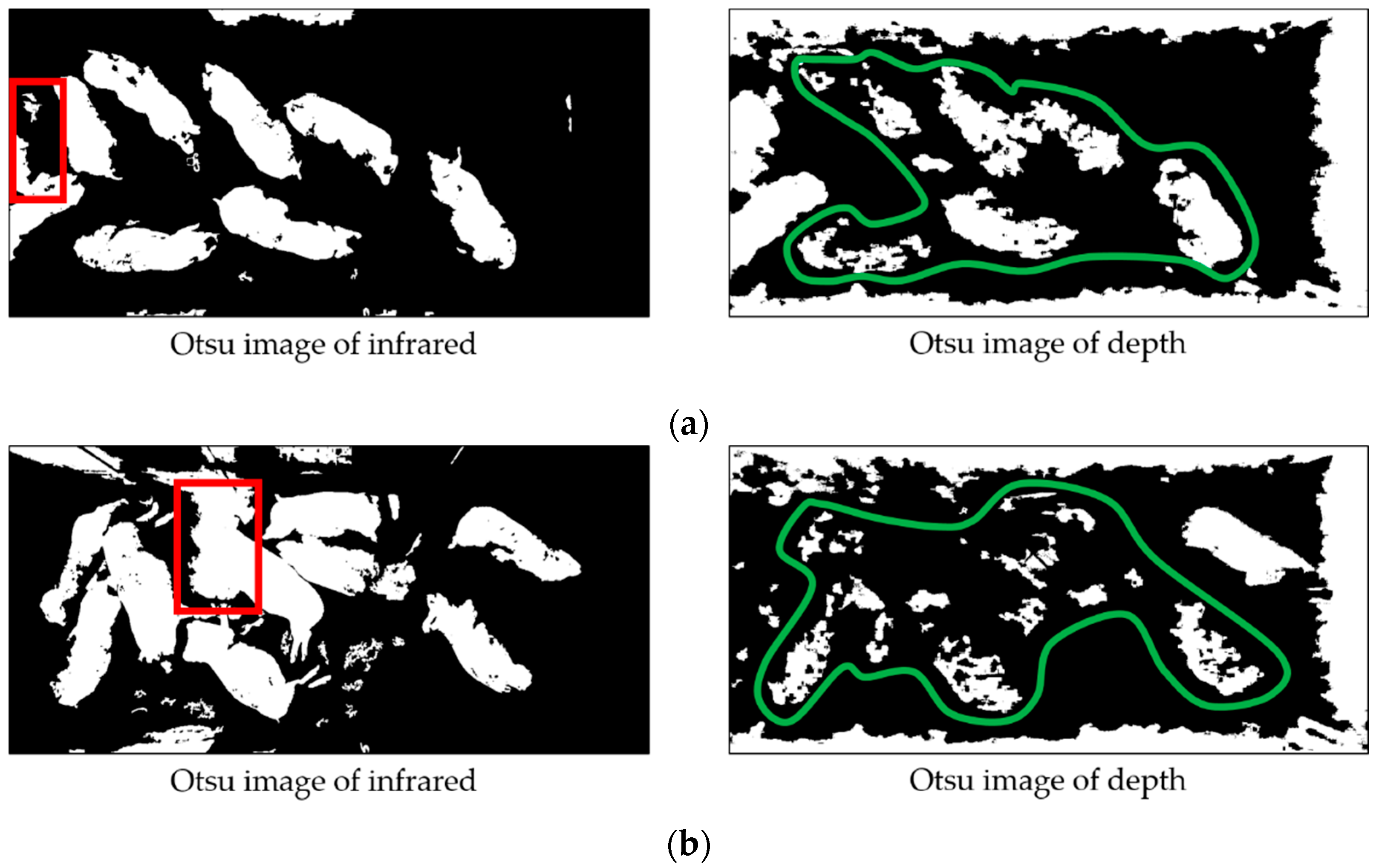
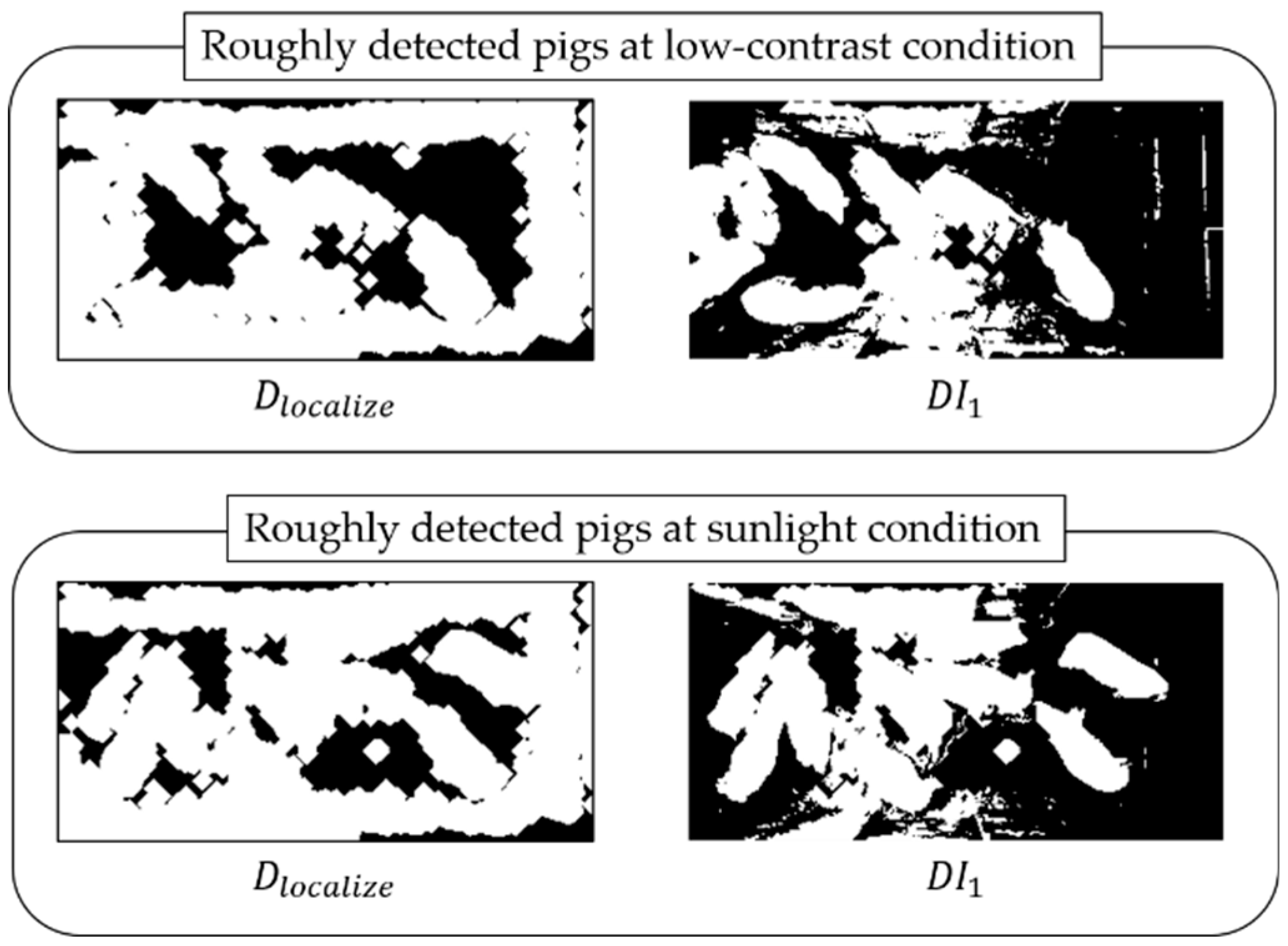
3.1. Removing Noises and Localizing Pigs
3.1.1. Procedure with Depth Information
3.1.2. Procedure with Infrared Information
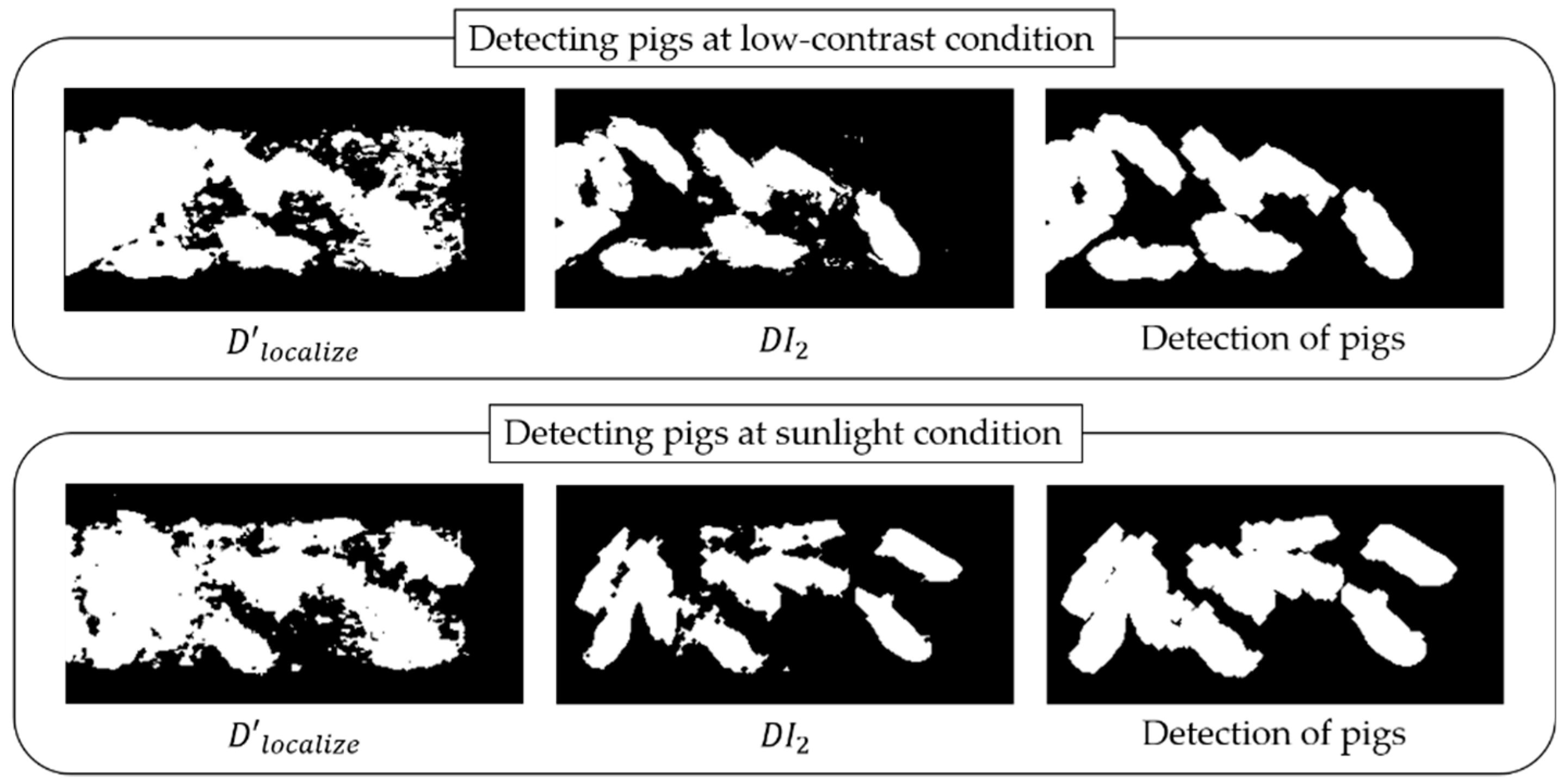
3.2. Detecting Pigs Using both Depth and Infrared Information
| Algorithm 1. Pig detection algorithm under various illumination conditions |
| Input: Depth and infrared images Output: Detected pig image Step 1: Removing noises and localizing pigs with depth and infrared information individually Procedure with depth information: Generate from modeling background during 24 h videos; for y = 0 to height: for x = 0 to width: : : ; Procedure with infrared information:; Step 2: Detecting pigs with depth and infrared information collectively Erode to remove and minimize noises; Conduct CCA to the minute noises in ; Dilate to recover shapes of the pigs; |
4. Experimental Results
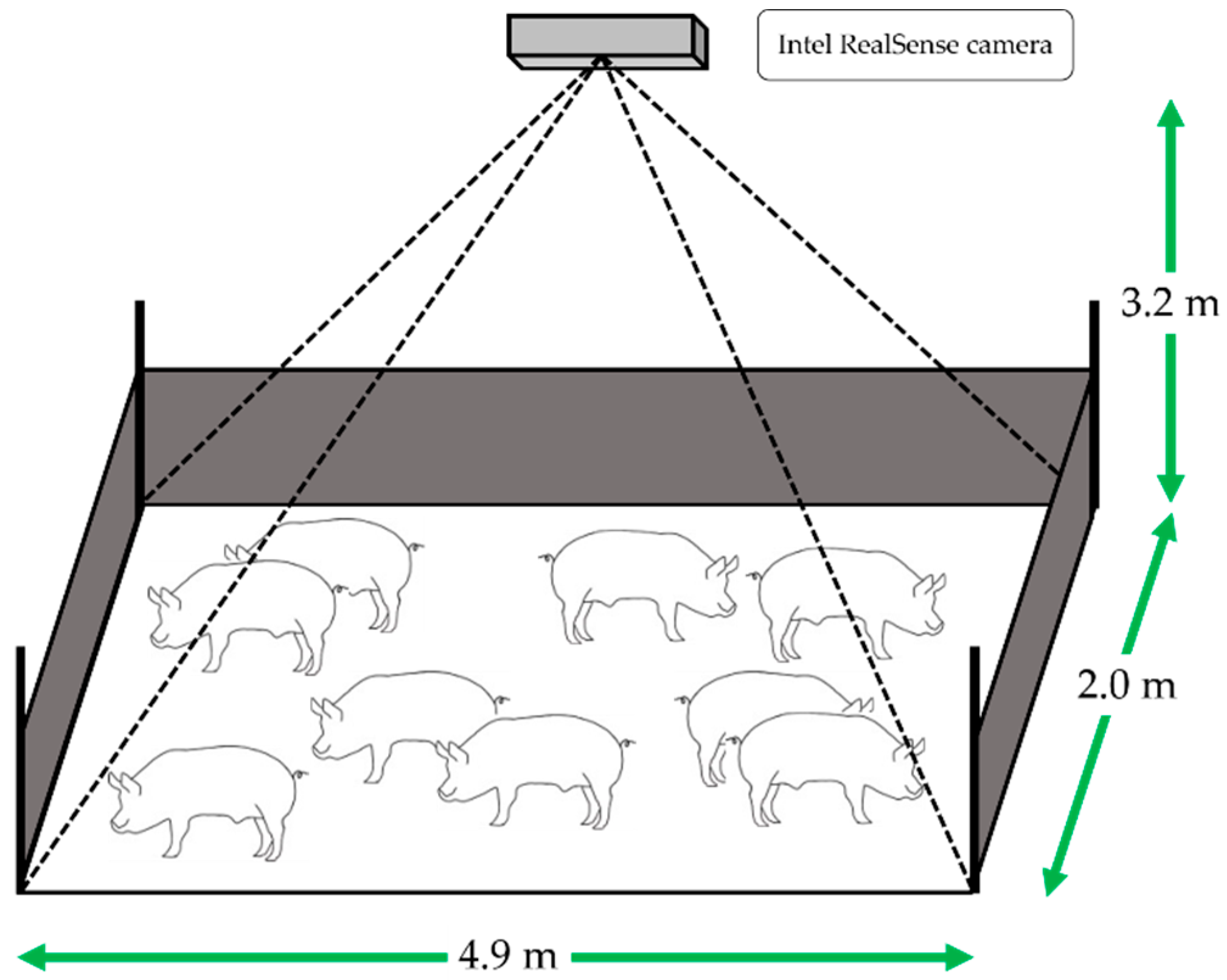
4.1. Experimental Setup and Resources for the Experiment
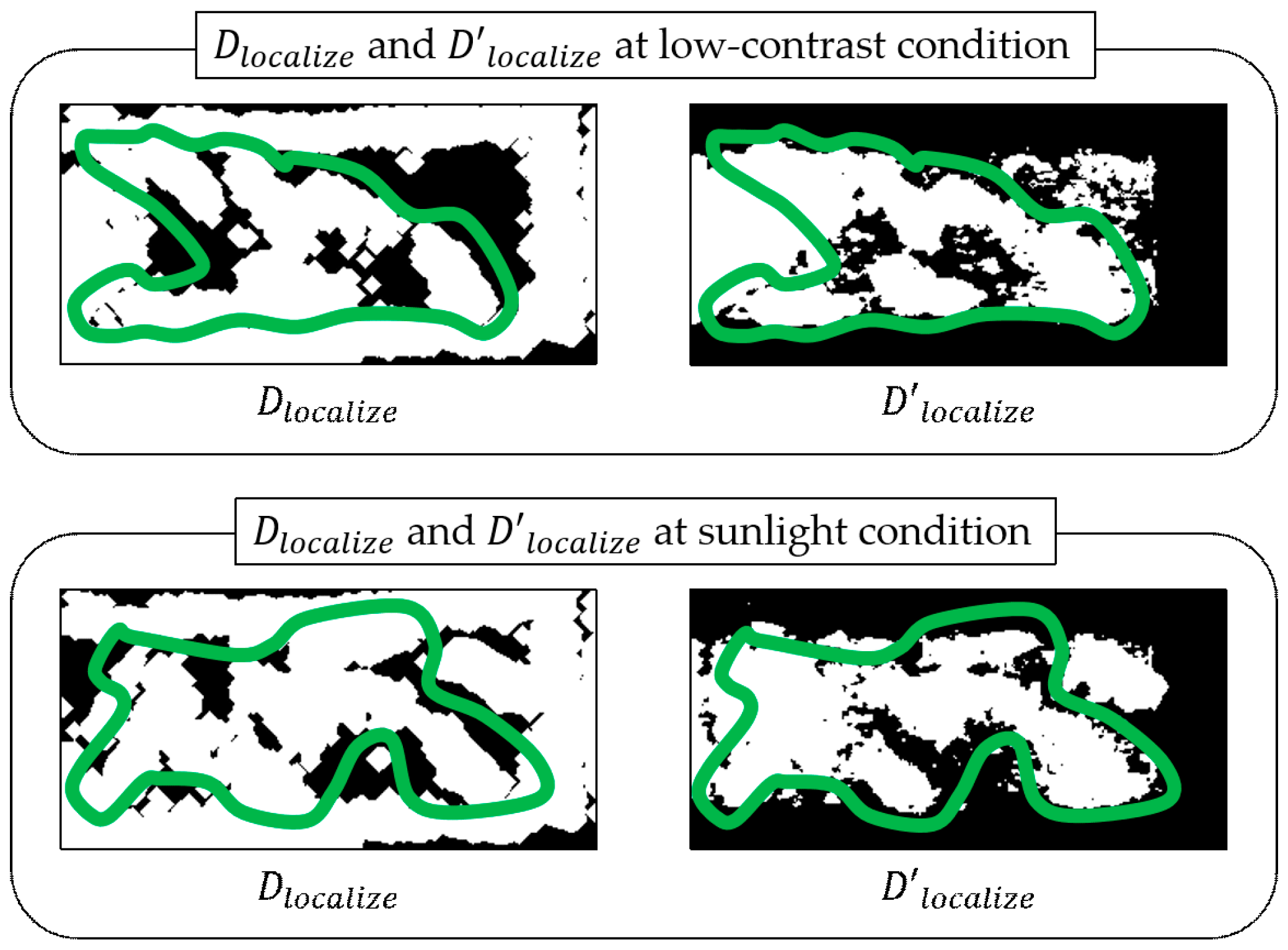
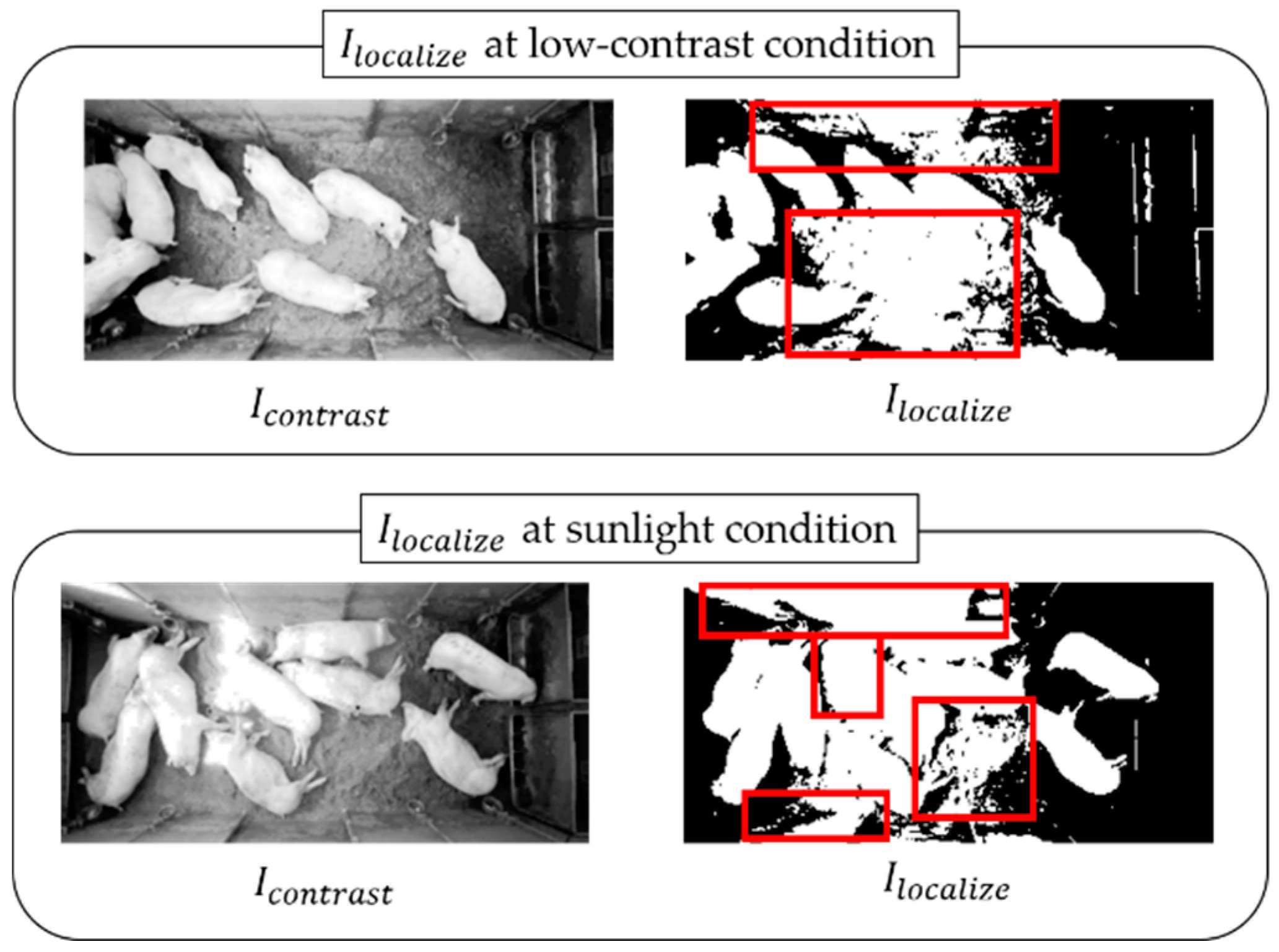
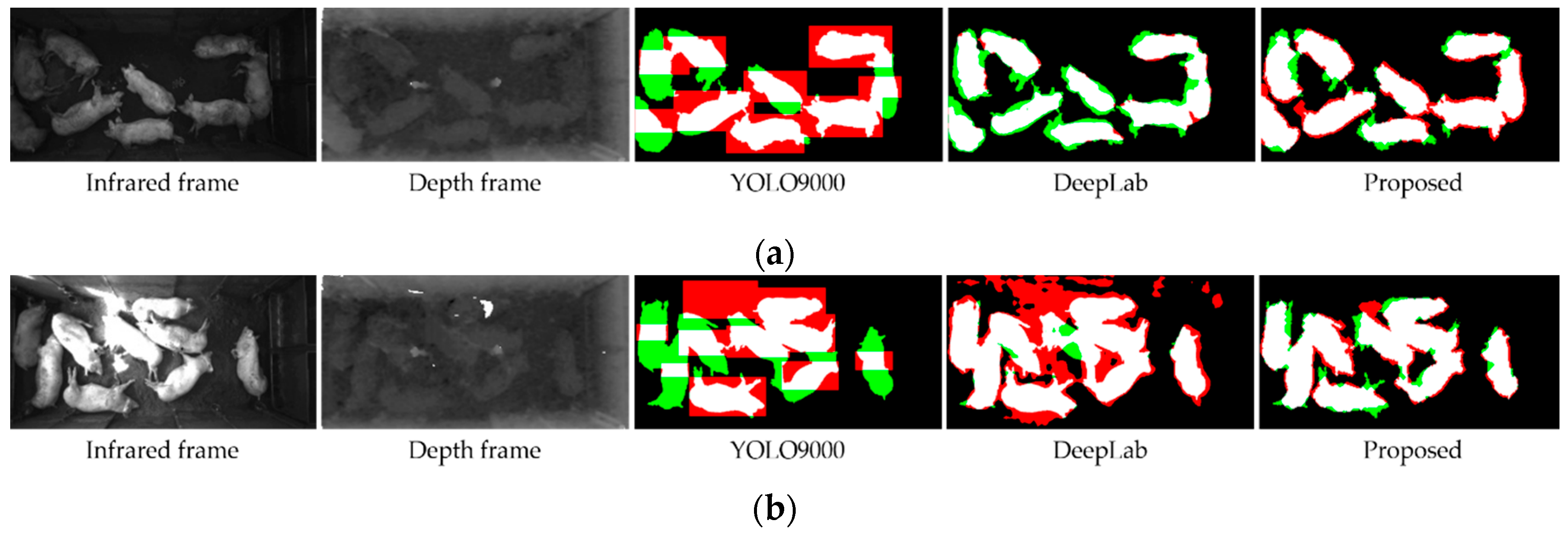
4.2. Detection of Pigs under Various Illumination Conditions
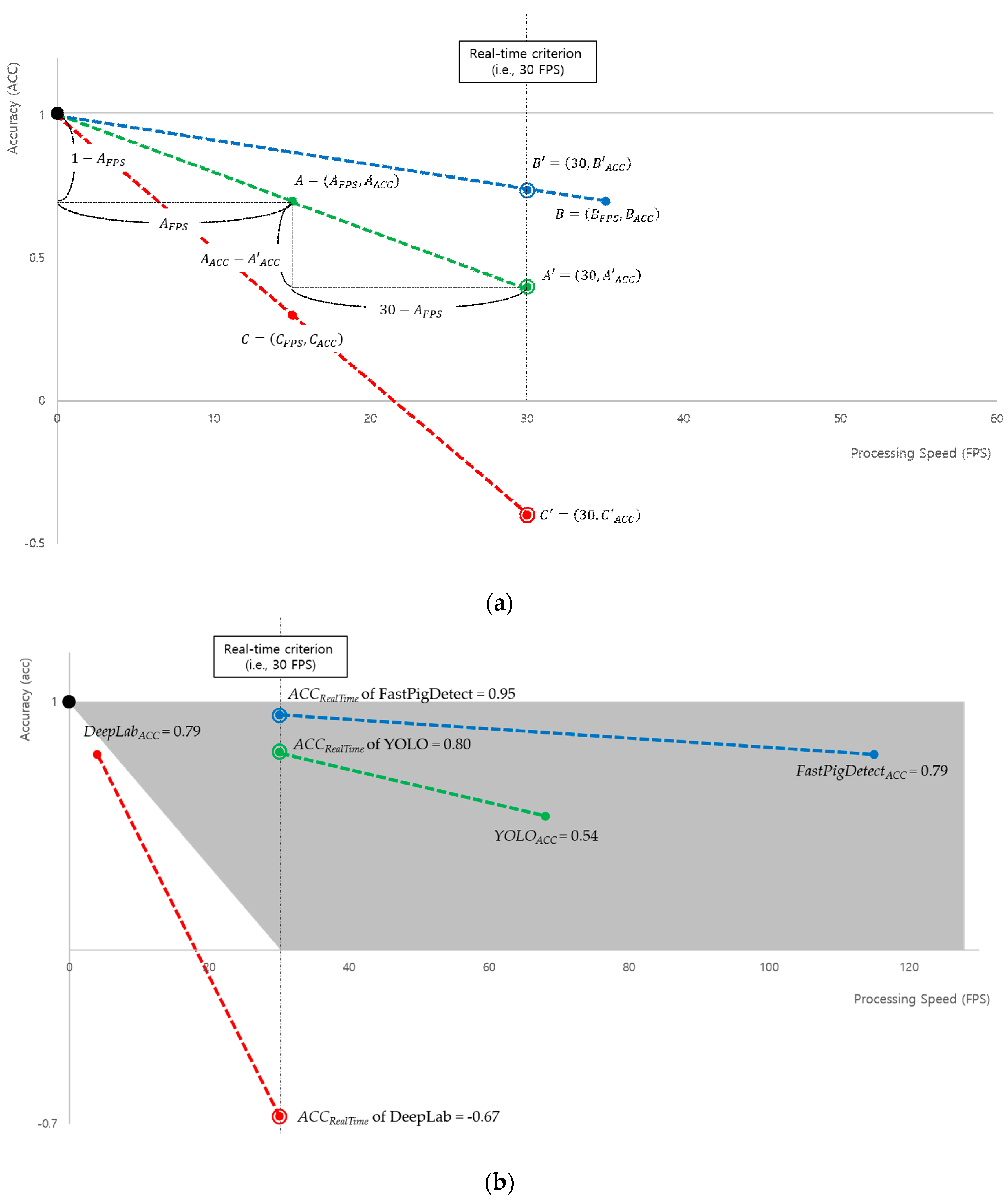
4.3. Evaluation of Detection Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banhazi, T.; Lehr, H.; Black, J.; Crabtree, H.; Schofield, P.; Tscharke, M.; Berckmans, D. Precision Livestock Farming: An International Review of Scientific and Commercial Aspects. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2012, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Neethirajan, S. Recent Advances in Wearable Sensors for Animal Health Management. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2017, 12, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tullo, E.; Fontana, I.; Guarino, M. Precision Livestock Farming: An Overview of Image and Sound Labelling. In Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Precision Livestock Farming (EC-PLF 2013), Leuven, Belgium, 10–12 September 2013; pp. 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, S.; Miller, A.; Clapp, J.; Plötz, T.; Kyriazakis, I. Early Detection of Health and Welfare Compromises through Automated Detection of Behavioural Changes in Pigs. Vet. J. 2016, 217, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tscharke, M.; Banhazi, T. A Brief Review of the Application of Machine Vision in Livestock Behaviour Analysis. J. Agric. Inform. 2016, 7, 23–42. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, M.; Wu, J.; Kong, F. Review of Automatic Detection of Pig Behaviours by using Image Analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on AEECE, Chengdu, China, 26–28 May 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.; Bench, C.; Liu, T.; Chabot, B.; Schaefer, A. The Automated Analysis of Clustering Behaviour of Piglets from Thermal Images in response to Immune Challenge by Vaccination. Animal 2018, 12, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunger, J.; Traulsen, I.; Koch, R. Model-based Detection of Pigs in Images under Sub-Optimal Conditions. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 152, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, G.; Karstoft, H.; Pedersen, L.; Jorgensen, E. Illumination and Reflectance Estimation with its Application in Foreground. Sensors 2015, 15, 12407–12426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, G.; Karstoft, H.; Pedersen, L.; Jorgensen, E. Segmentation of Sows in Farrowing Pens. IET Image Process. 2014, 8, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, G.; Karstoft, H.; Pedersen, L.; Jorgensen, E. Foreground Detection using Loopy Belief Propagation. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 116, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.; Herlin, A.; Ardo, H.; Guzhva, O.; Astrom, K.; Bergsten, C. Development of Automatic Surveillance of Animal Behaviour and Welfare using Image Analysis and Machine Learned Segmentation Techniques. Animal 2015, 9, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiha, M.; Bahr, C.; Ott, S.; Moons, C.; Niewold, T.; Tuyttens, F.; Berckmans, D. Automatic Monitoring of Pig Locomotion using Image Analysis. Livest. Sci. 2014, 159, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oczak, M.; Maschat, K.; Berckmans, D.; Vranken, E.; Baumgartner, J. Automatic Estimation of Number of Piglets in a Pen during Farrowing, using Image Analysis. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 151, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrendt, P.; Gregersen, T.; Karstoft, H. Development of a Real-Time Computer Vision System for Tracking Loose-Housed Pigs. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2011, 76, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoramshahi, E.; Hietaoja, J.; Valros, A.; Yun, J.; Pastell, M. Real-Time Recognition of Sows in Video: A Supervised Approach. Inf. Process. Agric. 2014, 1, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirahmadi, A.; Hensel, O.; Edwards, S.; Sturm, B. Automatic Detection of Mounting Behaviours among Pigs using Image Analysis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 124, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirahmadi, A.; Hensel, O.; Edwards, S.; Sturm, B. A New Approach for Categorizing Pig Lying Behaviour based on a Delaunay Triangulation Method. Animal 2017, 11, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasirahmadi, A.; Edwards, S.; Matheson, S.; Sturm, B. Using Automated Image Analysis in Pig Behavioural Research: Assessment of the Influence of Enrichment Subtrate Provision on Lying Behaviour. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2017, 196, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Jover, J.; Alcaniz-Raya, M.; Gomez, V.; Balasch, S.; Moreno, J.; Grau-Colomer, V.; Torres, A. An Automatic Colour-based Computer Vision Algorithm for Tracking the Position of Piglets. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2009, 7, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhu, W.; Jiao, P.; Chen, J. Foreground Detection of Group-Housed Pigs based on the Combination of Mixture of Gaussians using Prediction Mechanism and Threshold Segmentation. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 125, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhu, W.; Jiao, P.; Ma, C.; Yang, J. Multi-Object Extraction from Topview Group-Housed Pig Images based on Adaptive Partitioning and Multilevel Thresholding Segmentation. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 135, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buayai, P.; Kantanukul, T.; Leung, C.; Saikaew, K. Boundary Detection of Pigs in Pens based on Adaptive Thresholding using an Integral Image and Adaptive Partitioning. CMU J. Nat. Sci. 2017, 16, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Xiong, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, L.; Yan, L.; Ding, Y.; Lin, X.; Yang, X.; Shen, M. An Automatic Splitting Method for the Adhesive Piglets Gray Scale Image based on the Ellipse Shape Feature. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 120, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; He, J.; Chen, C.; Okinda, C.; Shen, M.; Liu, L.; Yao, W.; Norton, T.; Berckmans, D. An Automatic Ear Base Temperature Extraction Method for Top View Piglet Thermal Image. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 155, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, K.; Kim, S.; Ji, H. Estimating Pig Weights from Images without Constraint on Posture and Illumination. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 153, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, F.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Zong, Z. A Multiobjective Piglet Image Segmentation Method based on an Improved Noninteractive GrabCut Algorithm. Adv. Multimed. 2018, 2018, 108876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Huang, H.; Zhu, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, P.; Li, S.; Xue, Y. Automatic Recognition of Sow Nursing Behavious using Deep Learning-based Segmentation and Spatial and Temporal Features. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 175, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xiao, D.; Lin, S. Feeding Behavior Recognition for Group-Housed Pigs with the Faster R-CNN. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 155, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongsro, J. Estimation of Pig Weight using a Microsoft Kinect Prototype Imaging System. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 109, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, F.; Brown-Brandl, T.; Stinn, J.; Liu, K.; Teng, G.; Xin, H. Automatic Recognition of Lactating Sow Behaviors through Depth Image Processing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 125, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrakakis, S.; Li, W.; Guy, J.; Morgan, G.; Ushaw, G.; Johnson, G.; Edwards, S. Validity of the Microsoft Kinect Sensor for Assessment of Normal Walking Patterns in Pigs. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 117, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Ren, J.; Barclay, D.; McCormack, S.; Thomson, W. Automatic Animal Detection from Kinect Sensed Images for Livestock Monitoring and Assessment. In Proceedings of the ICCCIT, Liverpool, UK, 26–28 October 2015; pp. 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, V.; Khotskin, N.; Nikitin, S.; Lankin, V.; Kulikov, A.; Trapezov, O. Application of 3D Imaging Sensor for Tracking Minipigs in the Open Field Test. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 235, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Teng, G.; Li, Z. An Approach of Pig Weight Estimation using Binocular Stereo System based on LabVIEW. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 129, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.; Miller, A.; Plötz, T.; Kyriazakis, I. Automated Tracking to Measure Behavioural Changes in Pigs for Health and Welfare Monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Zhu, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Tu, S.; Xue, Y. Automatic Recognition of Lactating Sow Postures from Depth Images by Deep Learning Detector. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 147, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jin, L.; Park, D.; Chung, Y. Automatic Recognition of Aggressive Pig Behaviors using Kinect Depth Sensor. Sensors 2016, 16, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Chung, Y.; Choi, Y.; Sa, J.; Kim, H.; Chung, Y.; Park, D.; Kim, H. Depth-based Detection of Standing-Pigs in Moving Noise Environments. Sensors 2017, 17, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Park, D.; Jeon, T.; Chang, H. A Cost-Effective Pigsty Monitoring System based on a Video Sensor. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2014, 8, 1481–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, M.; Choi, Y.; Seo, J.; Sa, J.; Lee, S.; Chung, Y.; Park, D. A Kinect-based Segmentation of Touching-Pigs for Real-Time Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.; Jin, L.; Chung, Y.; Park, D. An Index Algorithm for Tracking Pigs in Pigsty. In Proceedings of the ICITMS, Hong Kong, China, 1–2 May 2014; pp. 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intel RealSense D435, Intel. Available online: https://click.intel.com/intelr-realsensetm-depth-camera-d435.html (accessed on 28 February 2018).
- Mallick, T.; Das, P.; Majumdar, A. Characterization of Noise in Kinect Depth Images: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Patel, S. Efficient Medical Image Enhancement using CLAHE and Wavelet Fusion. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2017, 167, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Eramian, M.; Mould, D. Histogram Equalization using Neighborhood Metrics. In Proceedings of the 2nd Canadian Conference on Computer and Robot Vision (CRV’05), Victoria, BC, Canada, 9–11 May 2005; pp. 397–404. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi, S.; Bhanu, B. Physics-based Models of Color and IR Video for Sensor Fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (MFI’03), Tokyo, Japan, 1 August 2003; pp. 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, S.; Scherer-Negenborn, N.; Thakkar, P.; Hübner, W.; Arens, M. The effects of camera jitter for background subtraction algorithms on fused infrared-visible video streams. In Proceedings of the Optics and Photonics for Counterterrorism, Crime Fighting, and Defence XII, Edinburgh, UK, 26–27 October 2016; p. 99950. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Luo, B.; Li, C.; Wang, G.; Tang, J. Fast Grayscale-Thermal Foreground Detection with Collaborative Low-rank Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 28, 2574–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmans, T.; Silva, C.; Marghes, C.; Zitouni, S.; Bhaskar, H.; Frelicot, C. On the Role and the Importance of Features for Background Modeling and Foreground Detection. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2018, 28, 26–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddalena, L.; Petrosino, A. Background Subtraction for Moving Object Detection in RGB-D Data: A Survey. J. Imaging 2018, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open Source Computer Vision, OpenCV. Available online: http://opencv.org (accessed on 18 December 2016).
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1612.08242. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Ross, A. A Multi-Task Convolutional Neural Network for Joint Iris Detection and Presentation Attack Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Winter Applications of Computer Vision Workshops (WACVW), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 15 March 2018; pp. 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on CVPR, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Buehler, M.; Iagnemma, K.; Singh, S. The DARPA Urban Challenge: Autonomous Vehicles in City Traffic; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 56. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Liang, Y.; Chen, L.; Ahmad, I.; Wu, D. Power-Rate-Distortion Analysis for Wireless Video Communication under Energy Constraint. IEEE Trans. Syst. Video Technol. 2005, 15, 645–658. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Cheng, W.; Zhao, X.; Moll, R.; Beringer, J.; Sartwell, J. Energy-Aware Portable Video Communication System Design for Wildlife Activity Monitoring. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2008, 8, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data Type | Data Size | Pig Detection Algorithm | Management of Various Illumination (Sunlight) | No. of Pigs in a Pen | Execution Time (seconds) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gray/Color | Not Specified | Thresholding | No (No) | Not Specified | Not Specified | [7] |
| 720 × 540 | CMA-ES | Yes (No) | 12 | 0.220 | [8] | |
| 768 × 576 | Wavelet | Yes (No) | Not Specified | 1.000 | [9] | |
| 768 × 576 | GMM | Yes (No) | Not Specified | 0.500 | [10] | |
| 150 × 113 | Texture | Yes (No) | Not Specified | 0.250 | [11] | |
| 640 × 480 | Learning | Yes (No) | 9 | Not Specified | [12] | |
| 720 × 576 | Thresholding (Otsu) | No (No) | 10 | Not Specified | [13] | |
| 1280 × 720 | Thresholding | No (No) | 7–13 | Not Specified | [14] | |
| Not Specified | GMM | Yes (No) | 3 | Not Specified | [15] | |
| 352 × 288 | ANN | No (No) | Not Specified | 0.236 | [16] | |
| 640 × 480 | Thresholding (Otsu) | No (No) | 22–23 | Not Specified | [17] | |
| 640 × 480 | Thresholding (Otsu) | No (No) | 22 | Not Specified | [18] | |
| Not Specified | Thresholding (Otsu) | No (No) | 17–20 | Not Specified | [19] | |
| 574 × 567 | Color | No (No) | 9 | Not Specified | [20] | |
| 256 × 256 | GMM/Thresholding | Yes (No) | Not Specified | Not Specified | [21] | |
| 1760 × 1840 | Global + Local Thresholding | Yes (No) | Not Specified | Not Specified | [22] | |
| 1280 × 720 | Global + Local Thresholding | Yes (No) | 23 | 0.971 | [23] | |
| Not Specified | Thresholding (Otsu) | No (No) | 2–12 | Not Specified | [24] | |
| 320 × 240 | Thresholding (Otsu) | No (No) | Not Specified | Not Specified | [25] | |
| 512 × 424 | Thresholding (Otsu) | Yes (No) | Not Specified | Not Specified | [26] | |
| 1440 × 1440 | Thresholding | Yes (No) | Not Specified | 1.606 | [27] | |
| 960 × 540 | Deep Learning | No (No) | 1 | Not Specified | [28] | |
| 2560 × 1440 | Deep Learning | No (No) | 4 | Not Specified | [29] | |
| Depth | Not Specified | Depth Thresholding | No (No) | 1 | Not Specified | [30] |
| 640 × 480 | Depth Thresholding | No (No) | Not Specified | Not Specified | [31] | |
| 512 × 424 | Depth Thresholding | No (No) | 1 | Not Specified | [32] | |
| 512 × 424 | Thresholding (Otsu) | No (No) | Not Specified | Not Specified | [33] | |
| 512 × 424 | Depth Thresholding | No (No) | 1 | Not Specified | [34] | |
| 1294 × 964 | Depth Thresholding | No (No) | 1 | Not Specified | [35] | |
| 512 × 424 | GMM | No (No) | 19 | 0.142 | [36] | |
| 512 × 424 | Deep Learning | Yes (No) | 1 | 0.050 | [37] | |
| 512 × 424 | Depth Thresholding | No (No) | 22 | 0.056 | [38] | |
| 512 × 424 | Depth Thresholding | No (No) | 13 | 0.002 | [39] | |
| Gray + Depth | 1280 × 720 | Infrared + Depth Fusion | Yes (Yes) | 9 | 0.008 | Proposed Method |
| Category | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | Depth input image | |
| Depth background image through modeling during 24 h videos | ||
| Depth interpolated image through spatiotemporal interpolation | ||
| Depth image where pigs are localized through threshold | ||
| Depth image where pigs are localized through background subtraction and Otsu | ||
| Infrared | Infrared input image | |
| Infrared interpolated image with spatiotemporal interpolation | ||
| Infrared image where the contrast is coordinated by histogram equalization | ||
| Infrared image where pigs are localized by Otsu algorithm | ||
| Depth + Infrared | Intersection image between and | |
| Intersection image between and |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sa, J.; Choi, Y.; Lee, H.; Chung, Y.; Park, D.; Cho, J. Fast Pig Detection with a Top-View Camera under Various Illumination Conditions. Symmetry 2019, 11, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11020266
Sa J, Choi Y, Lee H, Chung Y, Park D, Cho J. Fast Pig Detection with a Top-View Camera under Various Illumination Conditions. Symmetry. 2019; 11(2):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11020266
Chicago/Turabian StyleSa, Jaewon, Younchang Choi, Hanhaesol Lee, Yongwha Chung, Daihee Park, and Jinho Cho. 2019. "Fast Pig Detection with a Top-View Camera under Various Illumination Conditions" Symmetry 11, no. 2: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11020266
APA StyleSa, J., Choi, Y., Lee, H., Chung, Y., Park, D., & Cho, J. (2019). Fast Pig Detection with a Top-View Camera under Various Illumination Conditions. Symmetry, 11(2), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11020266






