Chronic Liver Disease Classification Using Hybrid Whale Optimization with Simulated Annealing and Ensemble Classifier
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
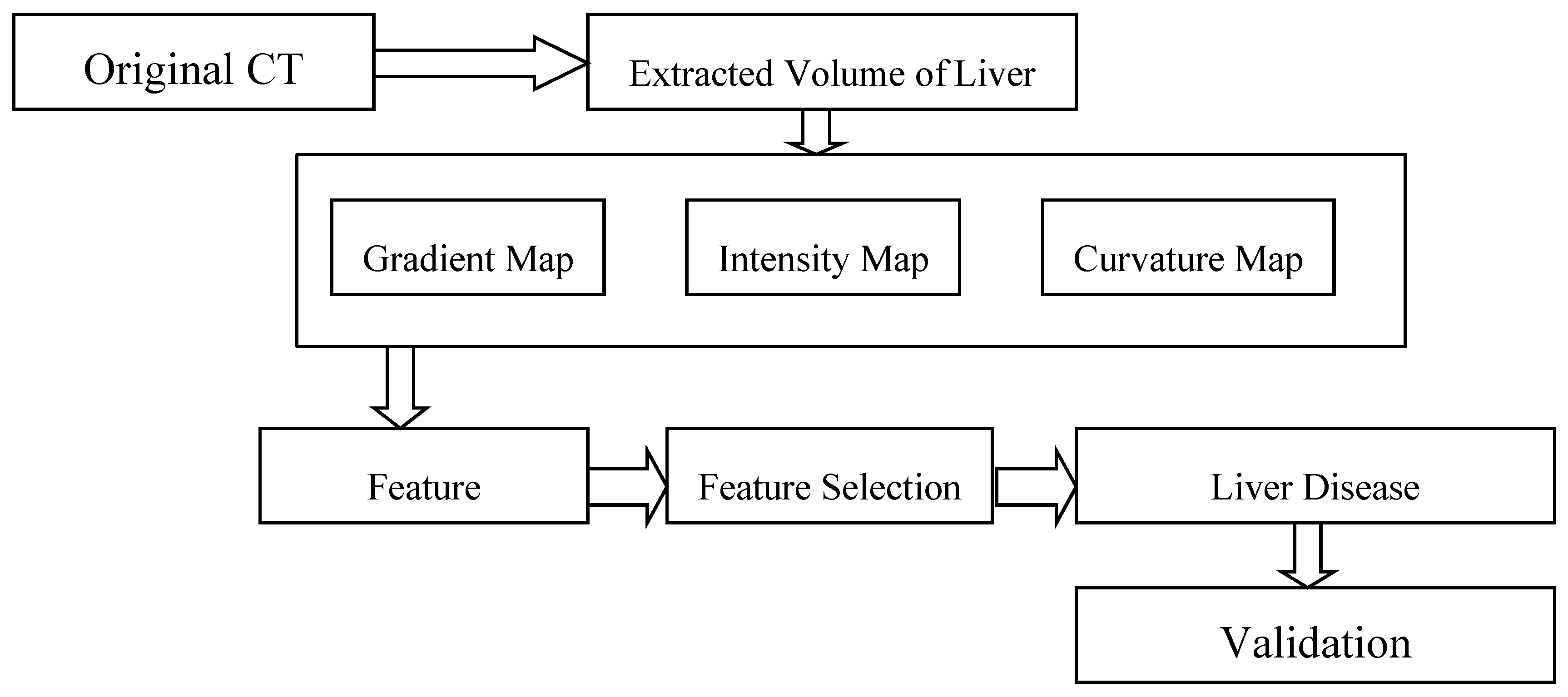
2.2. Overview of the Proposed Method
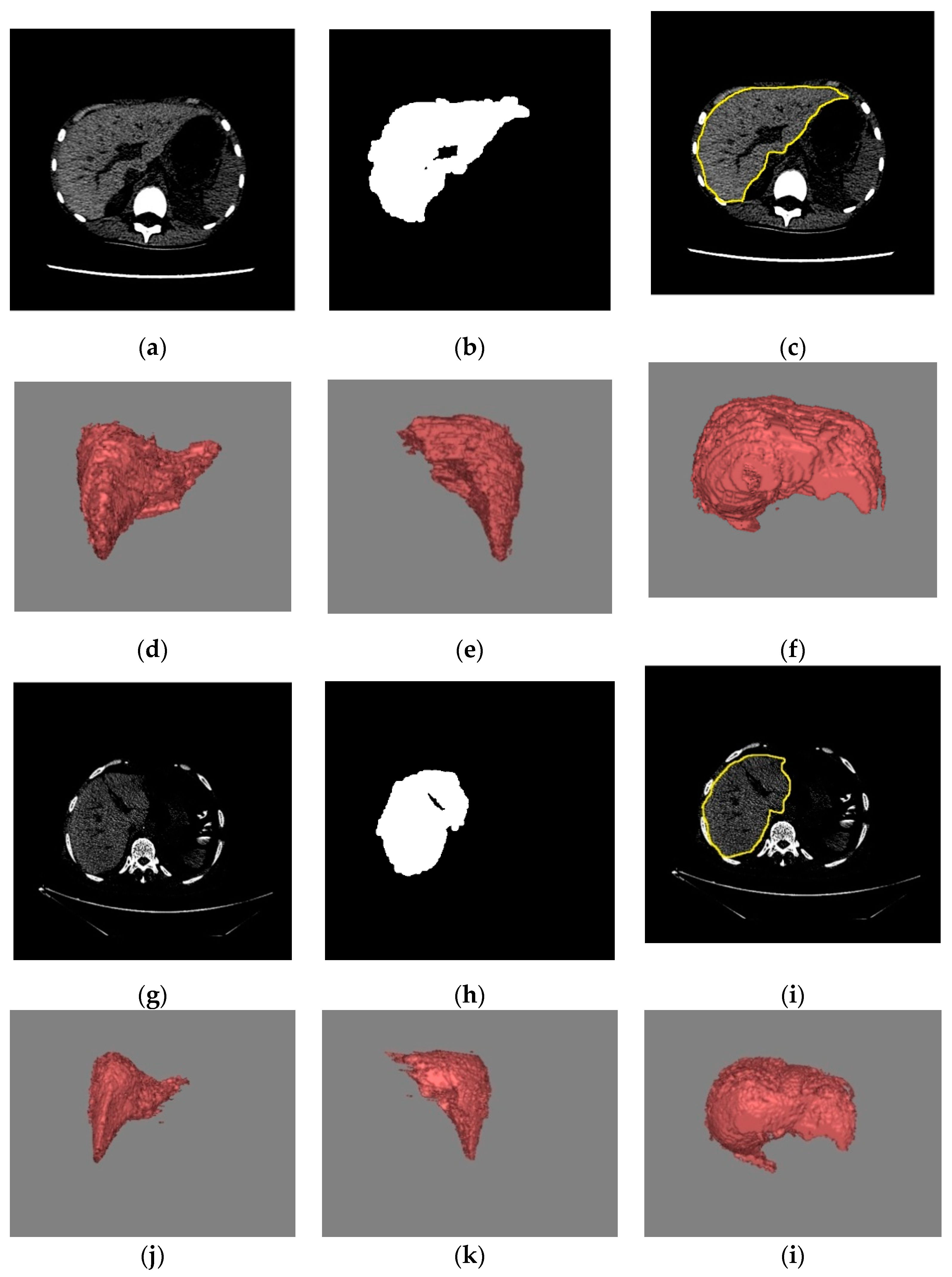
2.2.1. Volume Extraction of Liver
2.2.2. Feature Extraction
Texture Features of Four Groups: GLCM, GLGCM, GLCCM, and Tamura
Texture Features of Three Groups: NGTDM, NGTGDM, and NGTCDM
2.2.3. Feature Selection
2.2.4. Hybrid WOA-SA
Hybrid WOA-SA for Optimal Feature Selection
2.2.5. Class Prediction Based on Ensemble Classifier with WMV: SVM, k-NN, RF
Ensemble Approach
2.2.6. Tumor Burden
2.3. Performance Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
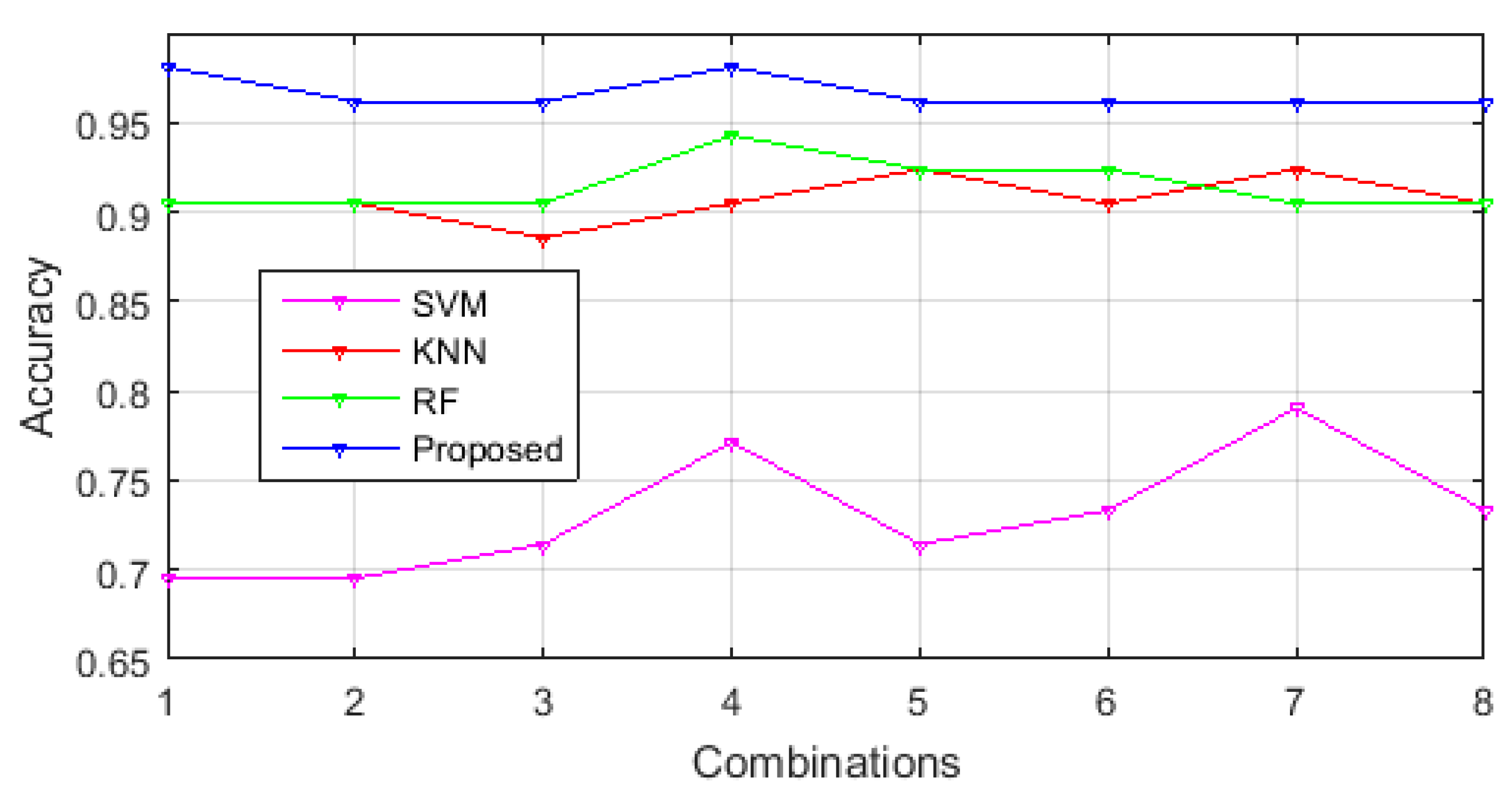
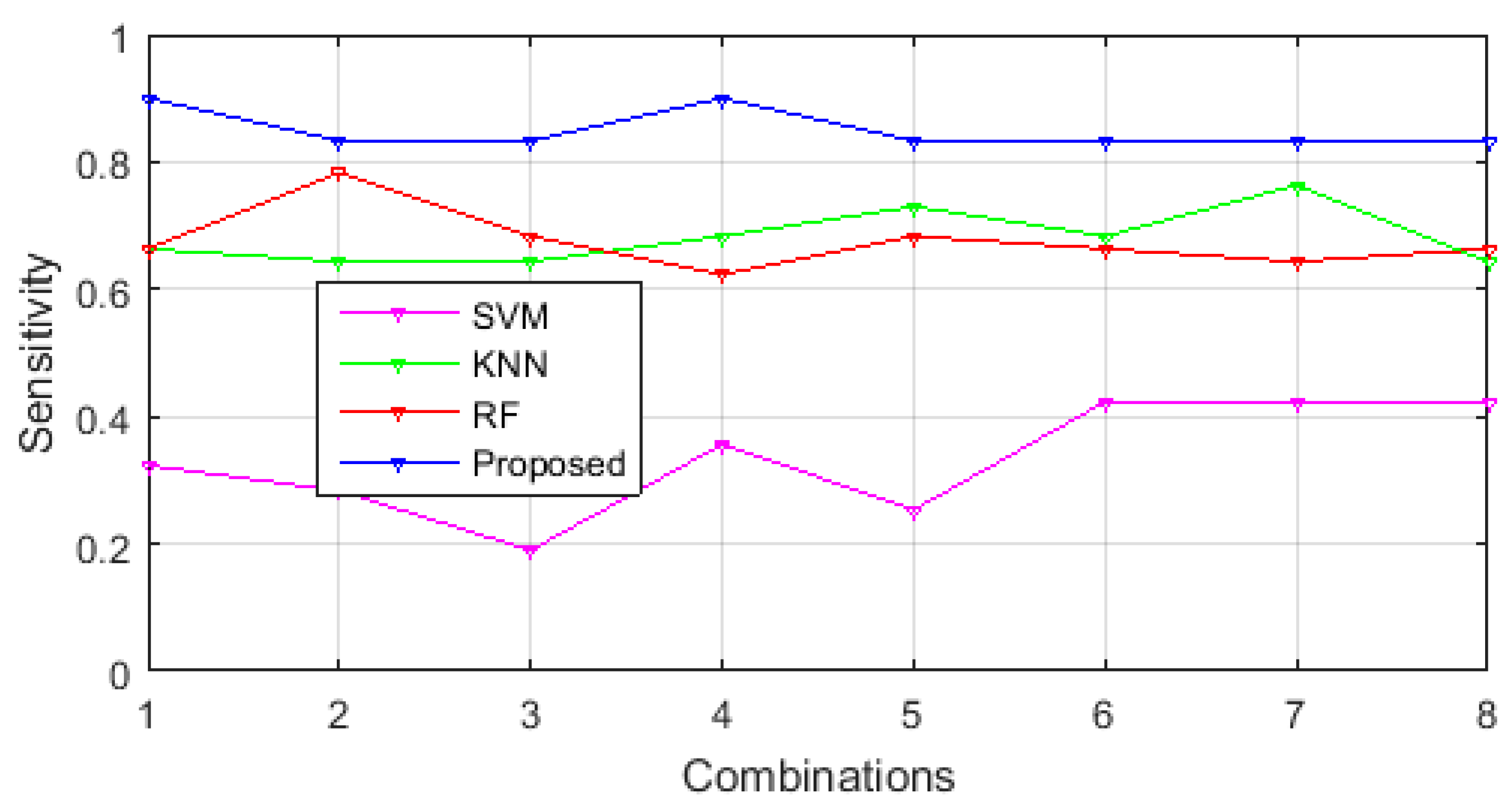
3.1. Performance Comparison of Selected Feature Sets in Different Classification Methodologies
3.2. Classification Error Percentage
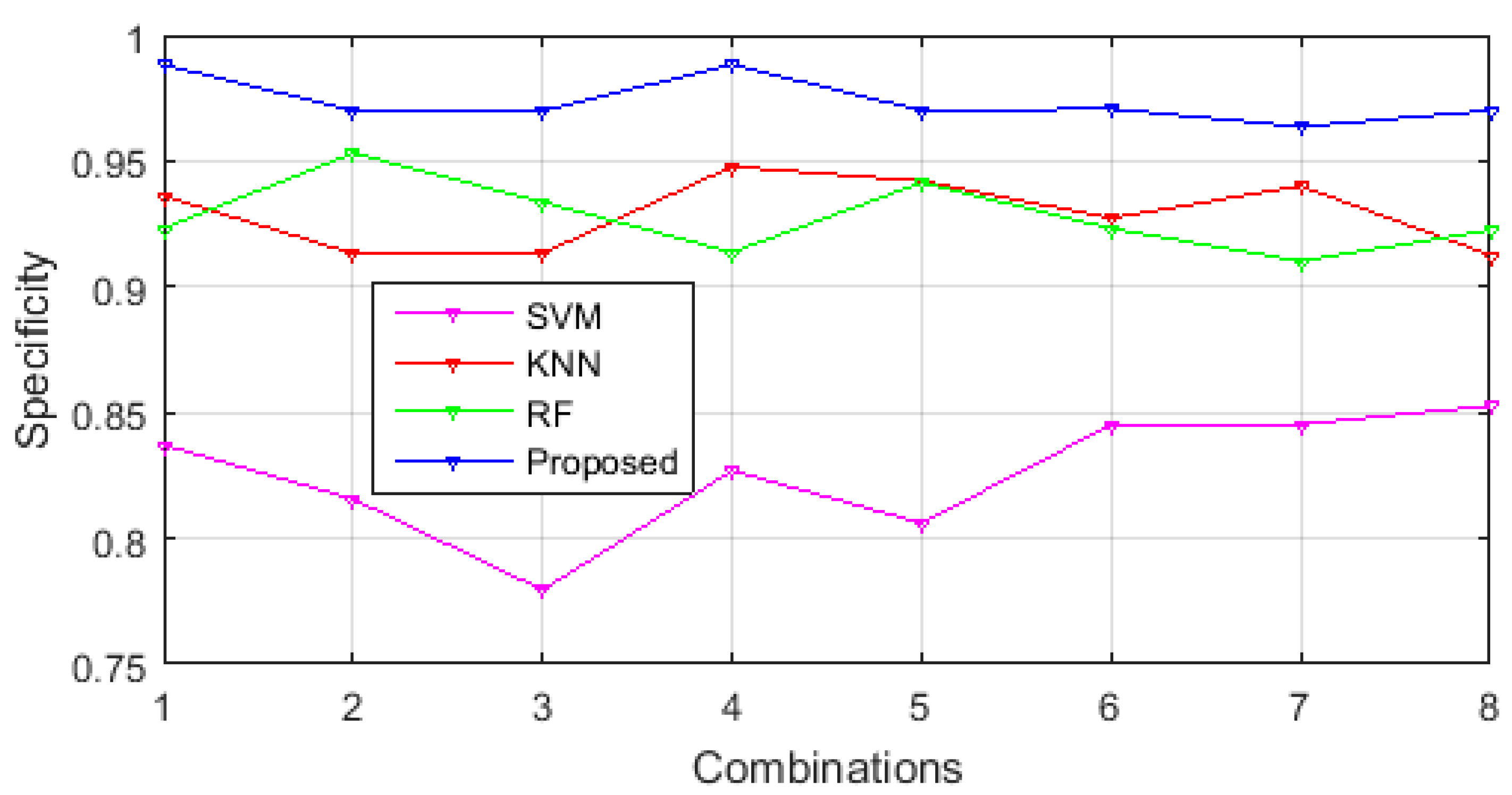
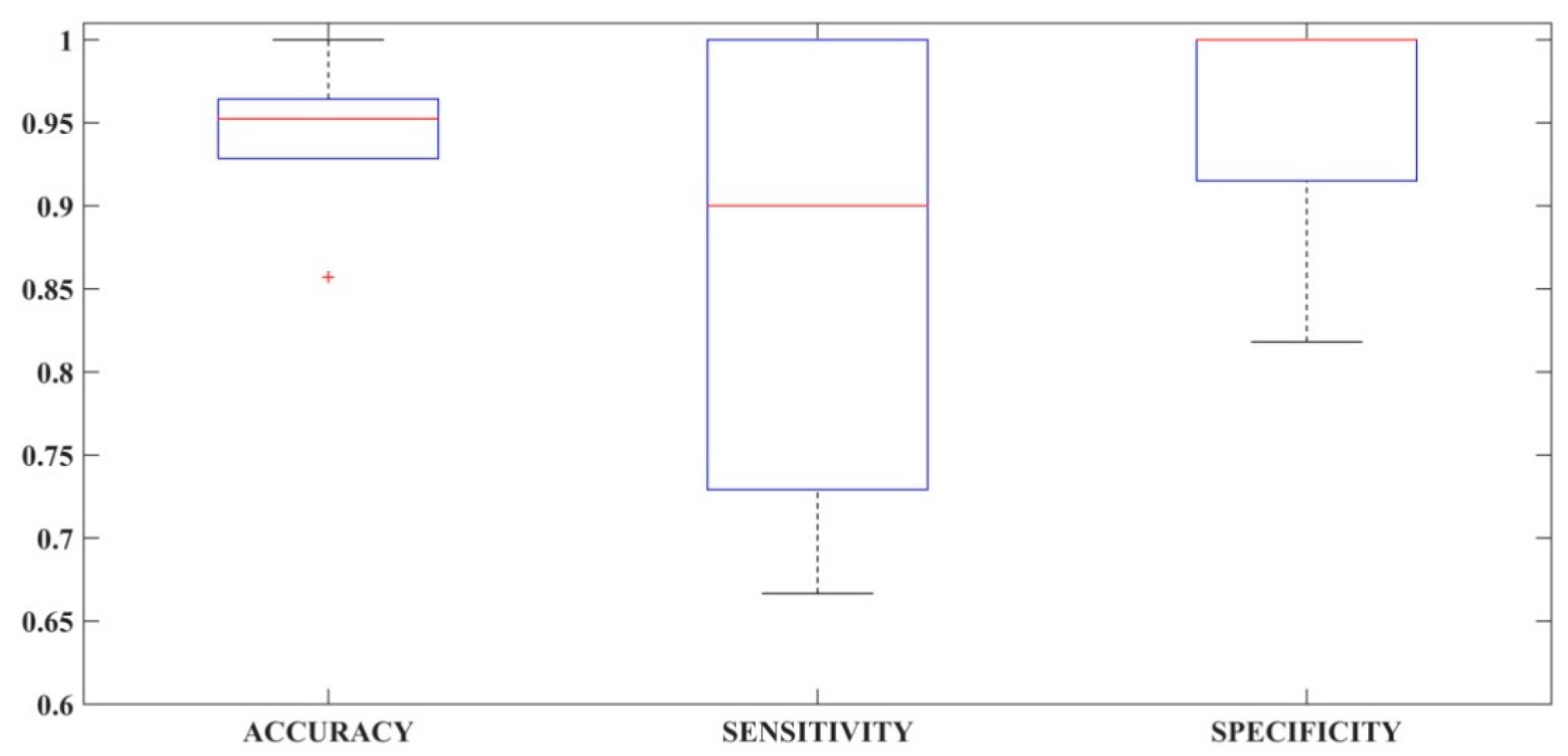
3.3. Comparison of Classification Performance
3.4. Clinical Feasibility
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdar, M.; Zomorodi-Moghadam, M.; Das, R.; Ting, I.H. Performance analysis of classification algorithms on early detection of liver disease. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 67, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatos, I.; Tsantis, S.; Spiliopoulos, S.; Karnabatidis, D.; Theotokas, I.; Zoumpoulis, P.; Loupas, T.; Hazle, J.D.; Kagadis, G.C. A Machine-Learning Algorithm Toward Color Analysis for Chronic Liver Disease Classification, Employing Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 1797–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, Y.; Cohen, D.E. Mechanisms of hepatic triglyceride accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis B. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 14 December 2018).
- Health24. Health Cirrhosis of the Liver. Available online: https://www.health24.com/Medical/Liver-Health/Cirrhosis-of-the-liver/Cirrhosis-of-the-liver-2012072 (accessed on 14 December 2018).
- Liver Metastasis. Available online: https://www.healthline.com/health/liver-metastases (accessed on 14 December 2018).
- Metastatic Cancer. Available online: http://www.cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-type/metastatic-cancer/liver-metastases/?region=on (accessed on 14 December 2018).
- Miriam, E. Tucker The Liver Meeting 2013: American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). Medscape. 2013. Available online: https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/813788 (accessed on 14 December 2018).
- Campbell, A. Alcohol-related deaths in the UK: Registered in 2015. Available online: https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/healthandsocialcare/causesofdeath/bulletins/alcoholrelateddeathsintheunitedkingdom/registeredin2015 (accessed on 12 December 2018).
- Banerjee, R.; Pavlides, M.; Tunnicliffe, E.M.; Piechnik, S.K.; Sarania, N.; Philips, R.; Collier, J.D.; Booth, J.C.; Schneider, J.E.; Wang, L.M.; et al. Multiparametric magnetic resonance for the non-invasive diagnosis of liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.J.; Aguilar, M.; Cheung, R.; Perumpail, R.B.; Harrison, S.A.; Younossi, Z.M.; Ahmed, A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.C.; Heba, E.; Wolfson, T.; Ang, B.; Gamst, A.; Han, A.; Erdman, J.W.; O’Brien, W.D.; Andre, M.P.; Sirlin, C.B.; et al. Noninvasive Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Andquantification of Liver Fat Using a New Quantitative Ultrasound Technique. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, G.; Cova, L.; De Beni, S.; Ierace, T.; Tondolo, T.; Cerri, A.; Goldberg, S.N.; Solbiati, L. Real-Time US-CT/MRI Image Fusion for Guidance of Thermal Ablation of Liver Tumors Undetectable with US: Results in 295 Cases. CardioVascular Int. Radiol. 2015, 38, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thian, Y.L.; Riddell, A.M.; Koh, D.M. Liver-specific agents for contrast-enhanced MRI: Role in oncological imaging. Cancer Imaging 2013, 13, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Mir, F.; Naranjo, V.; Angulo, J.; Alcañiz, M.; Luna, L. Liver segmentation in MRI: A fully automatic method based on stochastic partitions. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 114, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechichia, R.; Valette, S.; Desvignes, M.; Prost, R. Shortest-Path Constraints for 3D Multiobject Semiautomatic Segmentation via Clustering and Graph Cut. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 4224–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Fishbein, M.H.; Rigsby, C.K.; Zhang, G.; Schoeneman, S.E.; Donaldson, J.S. Quantitative MRI for hepatic fat fraction and T2* measurement in pediatric patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Pediatr. Radiol. 2014, 44, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, C.S.; Stolzmann, P.; Husmann, L.; Burger, I.A.; Von Schulthess, G.K.; Veit-haibach, P. Protocol requirements and diagnostic value of PET/MR imaging for liver metastasis detection. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imajing 2014, 41, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, S.; Motosugi, U.; Morisaka, H.; Sano, K.; Ichikawa, T.; Tatsumi, A.; Enomoto, N.; Matsuda, M.; Fujii, H.; Onishi, H. Comparison of the diagnostic accuracies of magnetic resonance elastography and transient elastography for hepatic fibrosis. Magn. Resonance Imaging 2015, 33, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HA, S.; AH, A.-R. Liver biopsy remains the gold standard for evaluation of chronic hepatitis and fibrosis. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2007, 16, 425–426. [Google Scholar]
- Castera, L. Invasive and non-invasive methods for the assessment of fibrosis and disease progression in chronic liver disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 25, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beuthan, J.; Minet, O.; Müller, G. Quantitative optical biopsy of liver tissue ex vivo. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 1996, 2, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuppan, D.; Afdhal, N.H. Seminar Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2008, 371, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurie, Y.; Webb, M.; Cytter-Kuint, R.; Shteingart, S.; Lederkremer, G.Z. Non-invasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11567–11583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gletsos, M.; Mougiakakou, S.G.; Matsopoulos, G.K.; Nikita, K.S.; Nikita, A.S.; Kelekis, D. A Computer-Aided Diagnostic System to Characterize CT Focal Liver Lesions: Design and Optimization of a Neural Network Classifier. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2003, 7, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.M. An identification method of malignant and benign liver tumors from ultrasonography based on GLCM texture features and fuzzy SVM. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 6737–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougiakakou, S.G.; Valavanis, I.K.; Nikita, A.; Nikita, K.S. Differential diagnosis of CT focal liver lesions using texture features, feature selection and ensemble driven classifiers. Artif. Intell. Med. 2007, 41, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybernet. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, K.N.B.; Ramakrishnan, A.G.; Member, S.; Suresh, S.; Chow, T.W.P. Fetal lung maturity analysis using ultrasound image features. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2002, 6, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chen, Y.; Member, S.; Hsieh, K. Texture Features for Classification of Ultrasonic Liver Images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1992, 11, 141–152. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, S.S.; Salama, M.M.A. Computer-aided diagnosis for prostate cancer using support vector machine. Proceedings 2005, 5744, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Caldwell, C.; Mah, K.; Mozeg, D. Coregistered FDG PET/CT-Based Textural Characterization of Head and Neck Cancer for Radiation Treatment Planning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2009, 28, 374–383. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, M.; Besa, C.; Ayache, J.B.; Yasar, T.K.; Bane, O.; Fung, M.; Ehman, R.L.; Taouli, B. Magnetic resonance elastography of the liver: Qualitative and quantitative comparison of gradient echo and spin echo echoplanar imaging sequences. Investig. Radiol. 2016, 51, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooden, B.; Goossens, N.; Hoshida, Y.; Friedman, S.L. Using Big Data to Discover Diagnostics and Therapeutics for Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 53–67.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.D.; Ping, X.O.; Tseng, Y.J.; Huang, G.T.; Lai, F.; Yang, P.M. Recurrence predictive models for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation using support vector machines with feature selection methods. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 117, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, H.H.; Hsu, C.Y.; Lin, Y.A.; Atique, S.; Fuad, A.; Wei, L.M.; Hsu, M.H. Development of a web-based liver cancer prediction model for type II diabetes patients by using an artificial neural network. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 125, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özşen, S.; Güneş, S. Attribute weighting via genetic algorithms for attribute weighted artificial immune system (AWAIS) and its application to heart disease and liver disorders problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.R.; Faust, O.; Molinari, F.; Sree, S.V.; Junnarkar, S.P.; Sudarshan, V. Ultrasound-based tissue characterization and classification of fatty liver disease: A screening and diagnostic paradigm. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 75, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghesh Krishnan, K.; Radhakrishnan, S. Hybrid approach to classification of focal and diffused liver disorders using ultrasound images with wavelets and texture features. IET Image Process. 2017, 11, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, M.; Shi, H.; Zheng, Z. Early detection of liver disease using data visualisation and classification method. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2014, 11, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chen, H.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Yang, M.Y.; Lo, C.M.; Ko, W.C.; Lee, Y.F.; Liu, K.L.; Chang, R.F. Computer-aided diagnosis of liver tumors on computed tomography images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 145, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Peng, L. An automated diagnosis system of liver disease using artificial immune and genetic algorithms. J. Med. Syst. 2013, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mala, K.; Sadasivam, V.; Alagappan, S. Neural network based texture analysis of CT images for fatty and cirrhosis liver classification. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2015, 32, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Cui, G.; Meng, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, T.; Yang, Z.; et al. Three-dimensional texture features from intensity and high-order derivative maps for the discrimination between bladder tumors and wall tissues via MRI. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamecker, H.; Lange, T.; Seebass, M. Segmentation of the Liver Using a 3D Statistical Shape Model; Technical Report; Zuse Institute Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Badakhshannoory, H.; Member, S.; Saeedi, P. A Model-Based Validation Scheme for Organ Segmentation in CT Scan Volumes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 2681–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, J.; Deng, K.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Construction, A.S. Automatic Liver Segmentation Using a Statistical Shape Model With Optimal Surface Detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 2622–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, L.; Delingette, H.; Malandain, G.; Montagnat, J.; Ayache, N.; Koehl, C.; Dourthe, O.; Malassagne, B.; Smith, M.; Mutter, D.; et al. Fully automatic anatomical, pathological, and functional segmentation from CT scans for hepatic surgery. Comput. Aided Surg. 2001, 6, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.; Aurich, V. HepaTux—A Semiautomatic Liver Segmentation System. 2007. Available online: http://sliver07.org/data/2007-10-24-2338.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2018).
- Rusko, L.; Bekes, G.; Nmeth, G.; Fidrich, M. Fully Automatic Liver Segmentation for Contrast-Enhanced CT Images. 2007. Available online: http://mbi.dkfz-heidelberg.de/grand-challenge2007/web/p143.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2018).
- Foruzan, A.H.; Aghaeizadeh, R.; Hori, M.; Sato, Y. Liver segmentation by intensity analysis and anatomical information in multi-slice CT images. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2009, 4, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, D.; Tanahashi, N. Neural-Network-Based Boundary Detection of Liver Structure in CT Images for 3-D Visualization. In Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Orlando, FL, USA, 28 June–2 July 1994; pp. 3484–3489. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, M.; Susomboon, R.; Disney, T.; Raicu, D.; Furst, J. A Comparison of Texture Models for Automatic Liver Segmentation. 2007. Available online: https://www.spiedigitallibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie/6512/1/A-comparison-of-texture-models-for-automatic-liver-segmentation/10.1117/12.710422.short?SSO=1 (accessed on 15 November 2018).
- Heimann, T.; van Ginneken, B.; Styner, M.A.; Arzhaeva, Y.; Aurich, V.; Bauer, C.; Beck, A.; Becker, C.; Beichel, R.; Bekes, G.; et al. Comparison and Evaluation of Methods for Liver Segmentation From CT Datasets. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2009, 28, 1251–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Song, H.; Zhou, W. Active contours with selective local or global segmentation: A new formulation and level set method. Image Vis. Comput. 2010, 28, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H.; Mori, S.; Yamawaki, T. Textural Features Corresponding to Visual Perception. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1978, 8, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zhang, G.; Lu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhu, W.; Pickhardt, P.J. Volumetric texture features from higher-order images for diagnosis of colon lesions via CT colonography. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2014, 9, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, R. Textural features corresponding to textural properties. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1989, 19, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. S-shaped versus V-shaped transfer functions for binary Particle Swarm Optimization. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2013, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafarja, M.M.; Mirjalili, S. Hybrid Whale Optimization Algorithm with simulated annealing for feature selection. Neurocomputing 2017, 260, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elton, R.J.; Vasuki, P.; Mohanalin, J. Voice activity detection using fuzzy entropy and support vector machine. Entropy 2016, 18, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.N.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Shin, E.S.; Kim, S.M. Characterization of coronary plaque regions in intravascular ultrasound images using a hybrid ensemble classifier. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 153, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, E.M.; Mabrouk, M.S. A Study of Support Vector Machine Algorithm for Liver Disease Diagnosis. Am. J. Intell. Syst. 2014, 4, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, K.R.; Aljabar, P.; Heckemann, R.A.; Hammers, A.; Rueckert, D. Random forest-based similarity measures for multi-modal classification of Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 2013, 65, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, L.; Suen, C.Y.; Ieee, F. Application of Majority Voting to Pattern Recognition: An Analysis of Its Behavior and Performance. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 1997, 27, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linguraru, M.G.; Richbourg, W.J.; Liu, J.; Watt, J.M.; Pamulapati, V.; Wang, S.; Summers, R.M. Tumor burden analysis on computed tomography by automated liver and tumor segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2012, 31, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Du, G. 3D Segmentation in the Clinic: A Grand Challenge II—Liver Tumor Segmentation. 2008. Available online: http://www.midasjournal.org/browse/journal/45 (accessed on 22 October 2018).
- Hossin, M.; Sulaiman, M. A review on evaluation metrics for data classification evaluations. Int. J. Data Min. Knowl. Manag. Process 2015, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gunasundari, S.; Janakiraman, S.; Meenambal, S. Velocity Bounded Boolean Particle Swarm Optimization for improved feature selection in liver and kidney disease diagnosis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 56, 28–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Feature Groups | Extracted Features | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GLCM | Angular second moment | |
| Contrast | ||
| Correlation | ||
| Inverse Different Moment | ||
| Homogeneity | ||
| Sum Average | ||
| Sum Variance | ||
| Sum entropy | ||
| Entropy | ||
| Difference variance | ||
| Difference Entropy | ||
| The information measure I of correlation | ||
| Information measure II of correlation | ||
| The range of the Features | ||
| GLGCM | 13 Haralick features of GLGCM | |
| GLCCM | 13 Haralick features of GLCCM | |
| Tamura | Coarseness | |
| Contrast | ||
| Directionality | ||
| Line-likeness | ||
| Regularity | ||
| Roughness |
| Feature Group | Extracted Features | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NGTDM | Coarseness | |
| Contrast | ||
| Busyness | ||
| Complexity | ||
| Texture strength | ||
| NGTGDM | Coarseness | |
| Contrast | ||
| Busyness | ||
| Complexity | ||
| Texture strength | ||
| NGTCDM | Coarseness | |
| Contrast | ||
| Busyness | ||
| Complexity | ||
| Texture strength |
| Feature Groups | Range of Features | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GLCM | 1 to 13 | Angular second moment, Contrast, Correlation, Inverse Different Moment, Homogeneity, Sum Average, Sum Variance, Sum entropy, Entropy, Difference variance, Difference Entropy, Information measure of correlation 1, Information measure of correlation 2. |
| 14 to 26 | Range of corresponding GLCM features from 1 to 13 (listed above) | |
| GLGCM | 27 to 39 | Autocorrelation, Contrast, Energy, Entropy, Homogeneity, Maximum-probability, sum-average, Sum-variance, Sum-entropy, Difference-variance, Difference-entropy, Information measure of correlation 1, Information measure of correlation 2 |
| GLCCM | 40 to 52 | Autocorrelation, Contrast, Energy, Entropy, Homogeneity, Maximum-probability, sum-average, Sum-variance, Sum-entropy, Difference-variance, Difference-entropy, Information measure of correlation 1, Information measure of correlation 2 |
| NGTDM | 53 to 57 | Coarseness, contrast, busyness, complexity, strength |
| NGTCDM | 58 to 62 | Coarseness, contrast, busyness, complexity, strength |
| NGTGDM | 63 to 67 | Coarseness, contrast, busyness, complexity, strength |
| Tamura | 68 to 73 | Coarseness, Contrast, Directionality, Line likeness, Regularity, Roughness |
| Sl. No | Feature Combinations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed | Rand_Comb1 | Rand_Comb2 | Rand_Comb3 | |
| 1 | 47 | 37 | 38 | 5 |
| 2 | 31 | 63 | 29 | 68 |
| 3 | 6 | 51 | 24 | 16 |
| 4 | 59 | 67 | 33 | 6 |
| 5 | 24 | 6 | 67 | 72 |
| 6 | 22 | 41 | 45 | 36 |
| 7 | 63 | 55 | 4 | 13 |
| 8 | 57 | 5 | 63 | 4 |
| 9 | 44 | 20 | 72 | 53 |
| 10 | 19 | 15 | 56 | 26 |
| 11 | 3 | 28 | 48 | 58 |
| 12 | 51 | 8 | 27 | 32 |
| 13 | 29 | 13 | 73 | 52 |
| 14 | 16 | 34 | 30 | 14 |
| 15 | 32 | 45 | 41 | 69 |
| 16 | 10 | 12 | 70 | 30 |
| 17 | 5 | 3 | 15 | 25 |
| 18 | 12 | 58 | 65 | 49 |
| 19 | 38 | 64 | 55 | 23 |
| 20 | 53 | 46 | 6 | 60 |
| 21 | 30 | 25 | 25 | 8 |
| 22 | 42 | 21 | 9 | 15 |
| 23 | 25 | 61 | 35 | 66 |
| 24 | 41 | 2 | 57 | 45 |
| 25 | 2 | 31 | 7 | 11 |
| Feature Combinations | 95% Confidence Interval—Performance Metrics | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | ||||||||||
| SVM | k-NN | RF | Proposed | SVM | k-NN | RF | Proposed | SVM | k-NN | RF | Proposed | |
| 1 | (0.50, 0.90) | (0.66, 0.99) | (0.66, 0.99) | (0.78, 1.00) | (0.21, 0.63) | (0.41, 0.83) | (0.41, 0.83) | (0.68, 1.00) | (0.61, 0.97) | (0.70, 1.00) | (0.69, 1.00) | (0.79, 1.00) |
| 2 | (0.50, 0.90) | (0.70, 1.00) | (0.64, 0.98) | (0.75, 1.00) | (0.07, 0.42) | (0.53, 0.92) | (0.39, 0.82) | (0.60, 0.96) | (0.59, 0.96) | (0.73, 1.00) | (0.69, 1.00) | (0.76, 1.00) |
| 3 | (0.50, 0.90) | (0.68, 1.00) | (0.70, 1.00) | (0.75, 1.00) | (0.10, 0.48) | (0.43, 0.85) | (0.53, 0.92) | (0.60, 0.96) | (0.61, 0.97) | (0.71, 1.00) | (0.72, 1.00) | (0.76, 1.00) |
| 4 | (0.50, 0.90) | (0.68, 1.00) | (0.66, 0.99) | (0.78, 1.00) | (0.17, 0.59) | (0.43, 0.85) | (0.41, 0.83) | (0.68, 1.00) | (0.61, 0.97) | (0.72, 1.00) | (0.69, 1.00) | (0.79, 1.00) |
| 5 | (0.42, 0.84) | (0.68, 1.00) | (0.70, 1.00) | (0.75, 1.00) | (0.05, 0.39) | (0.43, 0.85) | (0.45, 0.86) | (0.60, 0.96) | (0.54, 0.93) | (0.71, 1.00) | (0.72, 1.00) | (0.76, 1.00) |
| 6 | (0.46, 0.87) | (0.70, 1.00) | (0.70, 1.00) | (0.75, 1.00) | (0.07, 0.43) | (0.45, 0.86) | (0.45, 0.86) | (0.60, 0.96) | (0.58, 0.95) | (0.71, 1.00) | (0.74, 1.00) | (0.77, 1.00) |
| 7 | (0.59, 0.96) | (0.68, 1.00) | (0.66, 0.99) | (0.75, 1.00) | (0.36, 0.79) | (0.51, 0.91) | (0.41, 0.83) | (0.60, 0.96) | (0.67, 1.00) | (0.70, 1.00) | (0.69, 1.00) | (0.76, 1.00) |
| 8 | (0.46, 0.87) | (0.66, 0.99) | (0.68, 1.00) | (0.75, 1.00) | (0.07, 0.43) | (0.41, 0.83) | (0.43, 0.85) | (0.60, 0.96) | (0.57, 0.94) | (0.69, 1.00) | (0.70, 1.00) | (0.76, 1.00) |
| Liver Diseases | Tumor Burden Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Fatty | 14.87 |
| Metastasis | 11.23 |
| Cancer | 29.43 |
| Cirrhosis | 17.05 |
| Methods | Error Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| SVM | 17.14 ± 0.1321 |
| k-NN | 7.62 ± 0.0621 |
| RF | 11.43 ± 0.0522 |
| Proposed Method | 1.90 ± 0.0522 |
| Test Class Labels | Performance Metrics | Comparative Methods | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Existing Method [43] | Existing Method [69] | Proposed Method | |||||
| PNN | LVQ | BPN | PNN | SVM | Ensemble | ||
| Fatty | Accuracy | 0.76 (0.5226, 0.9170) | 0.80 (0.5641, 0.9431) | 0.80 (0.5641, 0.9431) | 0.61 (0.3787, 0.8073) | 0.85 (0.6184, 0.9733) | 0.90 (0.6760, 1.0000) |
| Sensitivity | 0.79 (0.5536, 0.9367) | 0.61 (0.3787, 0.8073) | 0.65 (0.4151, 0.8382) | 0.81 (0.5747, 0.9494) | 0.76 (0.5226, 0.9170) | 1.00 (0.8076, 1.0000) | |
| Specificity | 0.84 (0.6073, 0.9675) | 0.81 (0.5747, 0.9494) | 0.81 (0.5747, 0.9494) | 0.81 (0.5747, 0.9494) | 0.94 (0.7253, 1.0000) | 0.88 (0.6525, 0.9899) | |
| Metastasis | Accuracy | 0.95 (0.7382, 1.0000) | 0.14 (0.0362, 0.3551) | 0.85 (0.6184, 0.9733) | 0.95 (0.7382, 1.0000) | 0.95 (0.7382, 1.0000) | 0.95 (0.7382, 1.0000) |
| Sensitivity | 0.80 (0.5641, 0.9431) | 0.63 (0.3969, 0.8229) | 0.67 (0.4342, 0.8532) | 0.81 (0.5747, 0.9494) | 0.81 (0.5747, 0.9494) | 0.66 (0.4248, 0.8457) | |
| Specificity | 0.78 (0.5431, 0.9303) | 0.81 (0.5747, 0.9494) | 0.81 (0.5747, 0.9494) | 0.81 (0.5747, 0.9494) | 0.91 (0.6880, 1.0000) | 1.00 (0.8076, 1.0000) | |
| Cancer | Accuracy | 0.95 (0.7382, 1.0000) | 0.90 (0.6760, 1.0000) | 0.90 (0.6760, 1.0000) | 0.95 (0.7382, 1.0000) | 0.95 (0.7382, 1.0000) | 0.95 (0.7382, 1.0000) |
| Sensitivity | 0.72 (0.4825, 0.8895) | 0.64 (0.4061, 0.8306) | 0.68 (0.4437, 0.8606) | 0.83 (0.5963, 0.9616) | 0.78 (0.5431, 0.9303) | 0.50 (0.2834, 0.7166) | |
| Specificity | 0.89 (0.6642, 0.9952) | 0.81 (0.5747, 0.9494) | 0.83 (0.5963, 0.9616) | 0.83 (0.5963, 0.9616) | 0.88 (0.6525, 0.9899) | 1.00 (0.8076, 1.0000) | |
| Cirrhosis | Accuracy | 1.00 (0.8076, 1.0000) | 0.90 (0.6760, 1.0000) | 0.90 (0.6760, 1.0000) | 0.95 (0.7382, 1.0000) | 0.95 (0.7382, 1.0000) | 1.00 (0.8076, 1.0000) |
| Sensitivity | 0.78 (0.5431, 0.9303) | 0.61 (0.3787, 0.8073) | 0.66 (0.4248, 0.8457) | 0.85 (0.6184, 0.9733) | 0.75 (0.5124, 0.9103) | 1.00 (0.8076, 1.0000) | |
| Specificity | 0.91 (0.6880, 1.0000) | 0.79 (0.5536, 0.9367) | 0.85 (0.6184, 0.9733) | 0.85 (0.6184, 0.9733) | 0.90 (0.6760, 1.0000) | 1.00 (0.8076, 1.0000) | |
| Normal | Accuracy | 0.85 (0.6184, 0.9733) | 0.52 (0.3002, 0.7337) | 0.47 (0.2589, 0.6904) | 0.76 (0.5226, 0.9170) | 0.90 (0.6760, 1.0000) | 1.00 (0.8076, 1.0000) |
| Sensitivity | 0.75 (0.5124, 0.9103) | 0.64 (0.4061, 0.8306) | 0.67 (0.4342, 0.8532) | 0.85 (0.6184, 0.9733) | 0.82 (0.5855, 0.9555) | 1.00 (0.8076, 1.0000) | |
| Specificity | 0.85 (0.6184, 0.9733) | 0.79 (0.5536, 0.9367) | 0.85 (0.6184, 0.9733) | 0.85 (0.6184, 0.9733) | 0.92 (0.7002, 1.000) | 1.00 (0.8076, 1.0000) | |
| Parameter | Solution Methods | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Existing Method [43] | Existing Method [69] | Proposed Method | ||||
| PNN | LVQ | BPN | PNN | SVM | ||
| Accuracy | 0.90 (0.6760, 1.0000) | 0.65 (0.4154, 0.8382) | 0.79 (0.4154, 0.8382) | 0.84 (0.6073, 0.9675) | 0.92 (0.7002, 1.000) | 0.98 (0.7786, 1.0000) |
| Sensitivity | 0.77 (0.5328, 0.9237) | 0.65 (0.4154, 0.8382) | 0.69 (0.4154, 0.8382) | 0.77 (0.5328, 0.9237) | 0.87 (0.6410, 0.9845) | 0.96 (0.7513, 1.0000) |
| Specificity | 0.88 (0.6525, 0.9899) | 0.82 (0.5855, 0.9555) | 0.85 (0.6184, 0.9733) | 0.83 (0.5963, 0.9616) | 0.91 (0.6880, 1.0000) | 0.93 (0.7126, 1.0000) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajathi, G.I.; Jiji, G.W. Chronic Liver Disease Classification Using Hybrid Whale Optimization with Simulated Annealing and Ensemble Classifier. Symmetry 2019, 11, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11010033
Rajathi GI, Jiji GW. Chronic Liver Disease Classification Using Hybrid Whale Optimization with Simulated Annealing and Ensemble Classifier. Symmetry. 2019; 11(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajathi, G. Ignisha, and G. Wiselin Jiji. 2019. "Chronic Liver Disease Classification Using Hybrid Whale Optimization with Simulated Annealing and Ensemble Classifier" Symmetry 11, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11010033
APA StyleRajathi, G. I., & Jiji, G. W. (2019). Chronic Liver Disease Classification Using Hybrid Whale Optimization with Simulated Annealing and Ensemble Classifier. Symmetry, 11(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11010033




