A Reweighted Symmetric Smoothed Function Approximating L0-Norm Regularized Sparse Reconstruction Method
Abstract
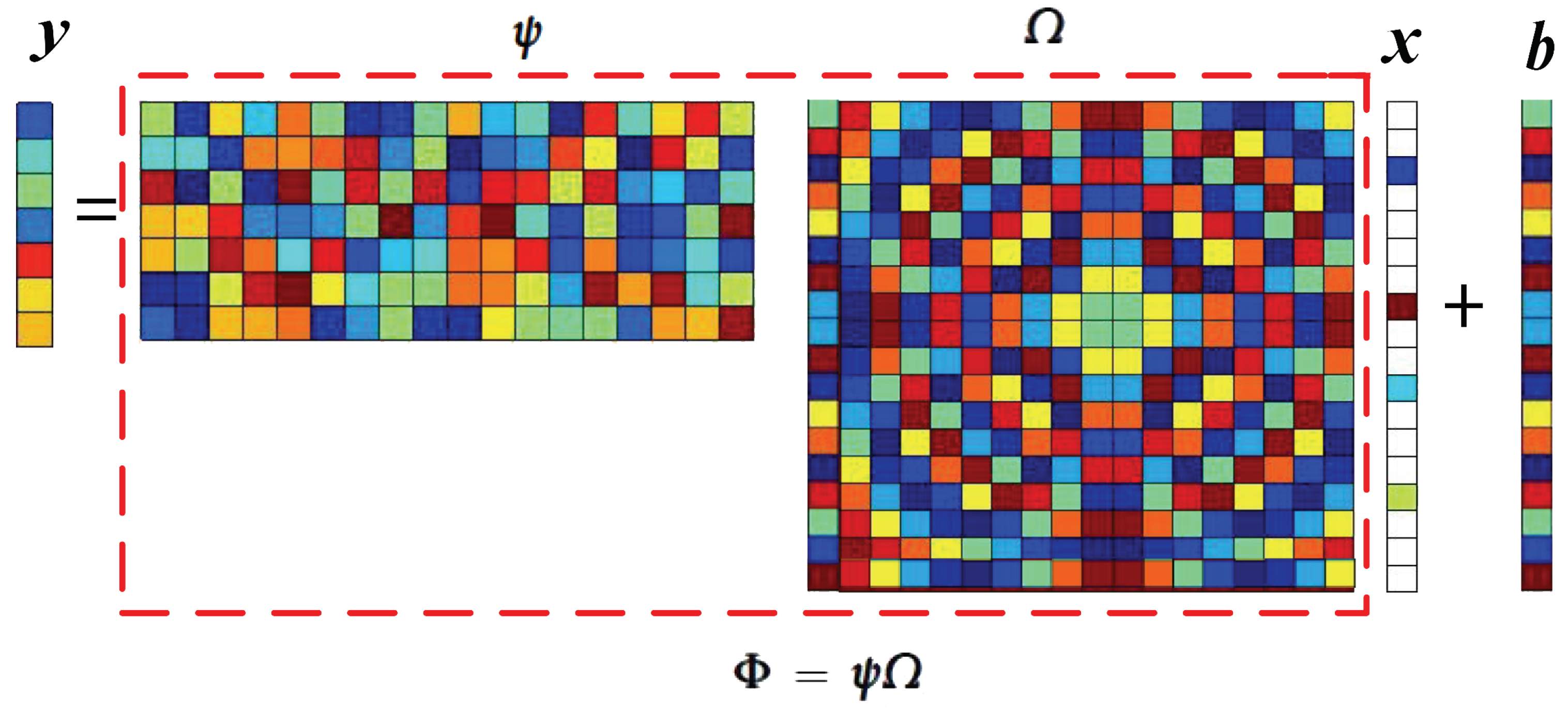
1. Introduction
- Greedy algorithms with sparsity as a prior condition;
- Relaxation method.
- (1)
- For -RLS, the value of p cannot be too small because, the smaller p is, the less smooth is, which makes the optimization effect worse [25], so cannot closely approach the norm, and reconstruction accuracy cannot be further improved;
- (2)
- For -SL0, although the algorithm can more closely approach the -norm, the convergence of the adopted optimization method is not good, resulting in limited reconstruction accuracy.
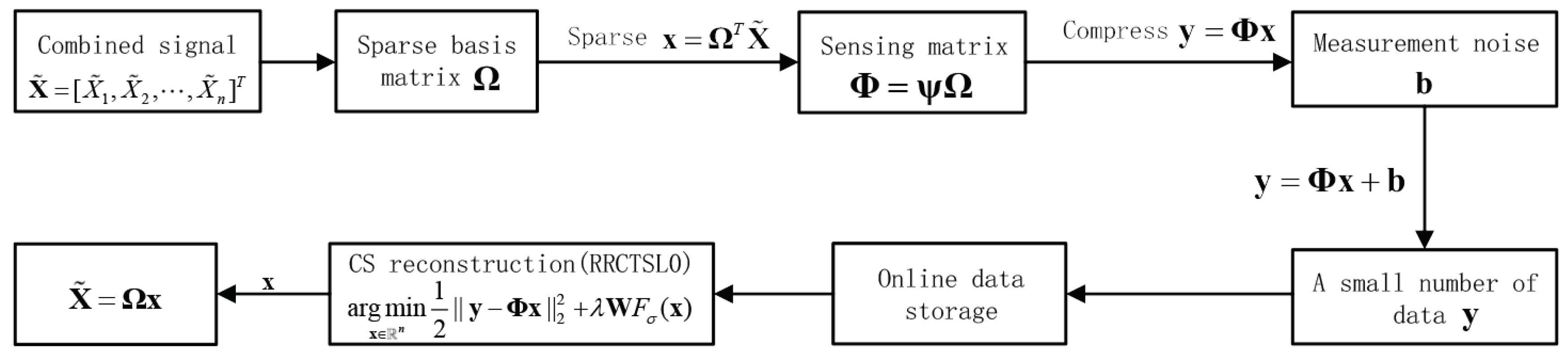
2. RRCTSL0 Algorithm
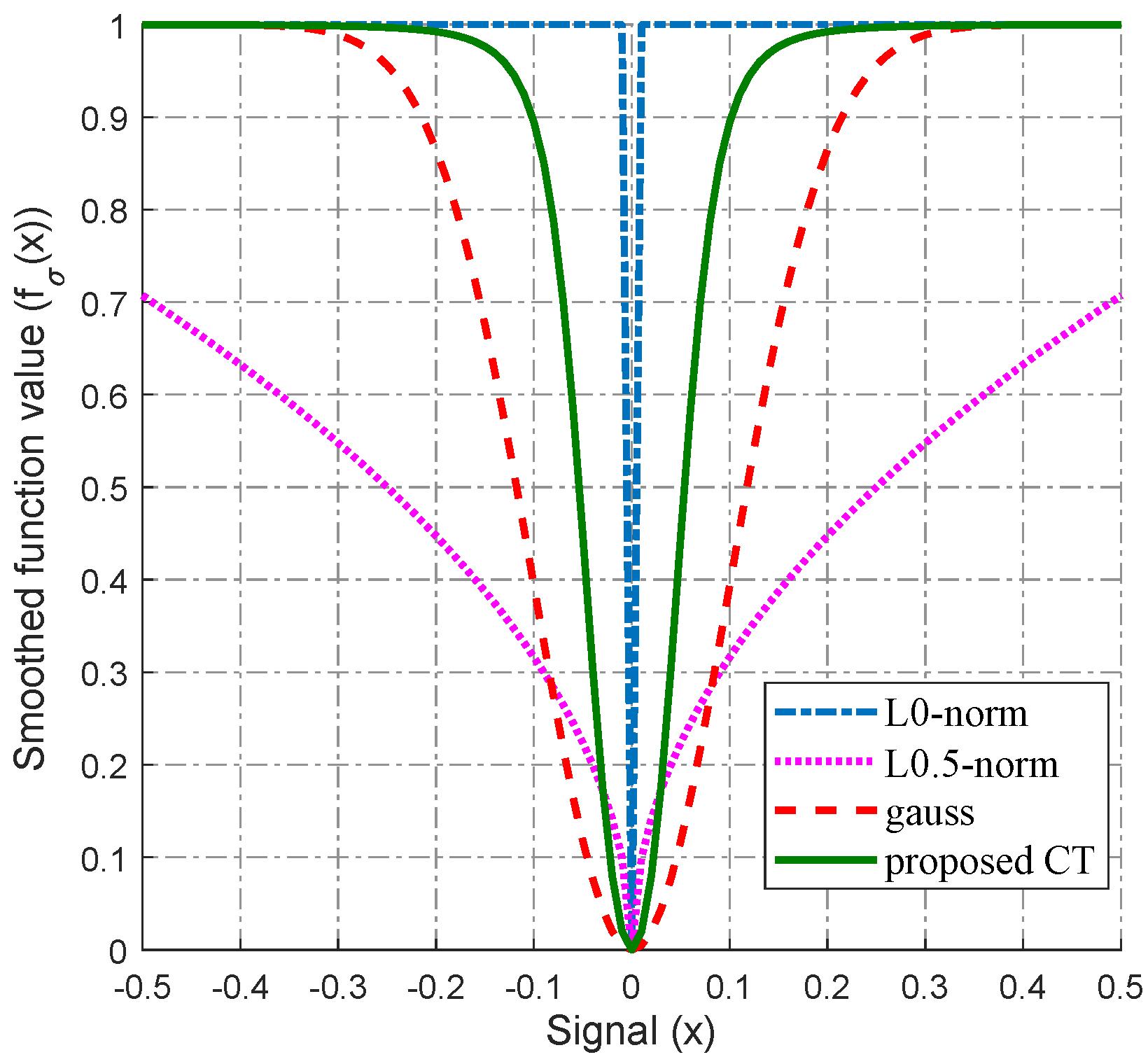
2.1. New Smoothed -Norm Function Model
2.2. New Reweighted Function Design
- It has a proper range that can give each signal component a proper reweighted value, and, when the signal component is close to zero, the reweighted value is not too large.
- It does not need the adjustment of parameters like , and the denominator does not equal to zero.
2.3. New Proposed RRCTSL0 Algorithm and Its Steps
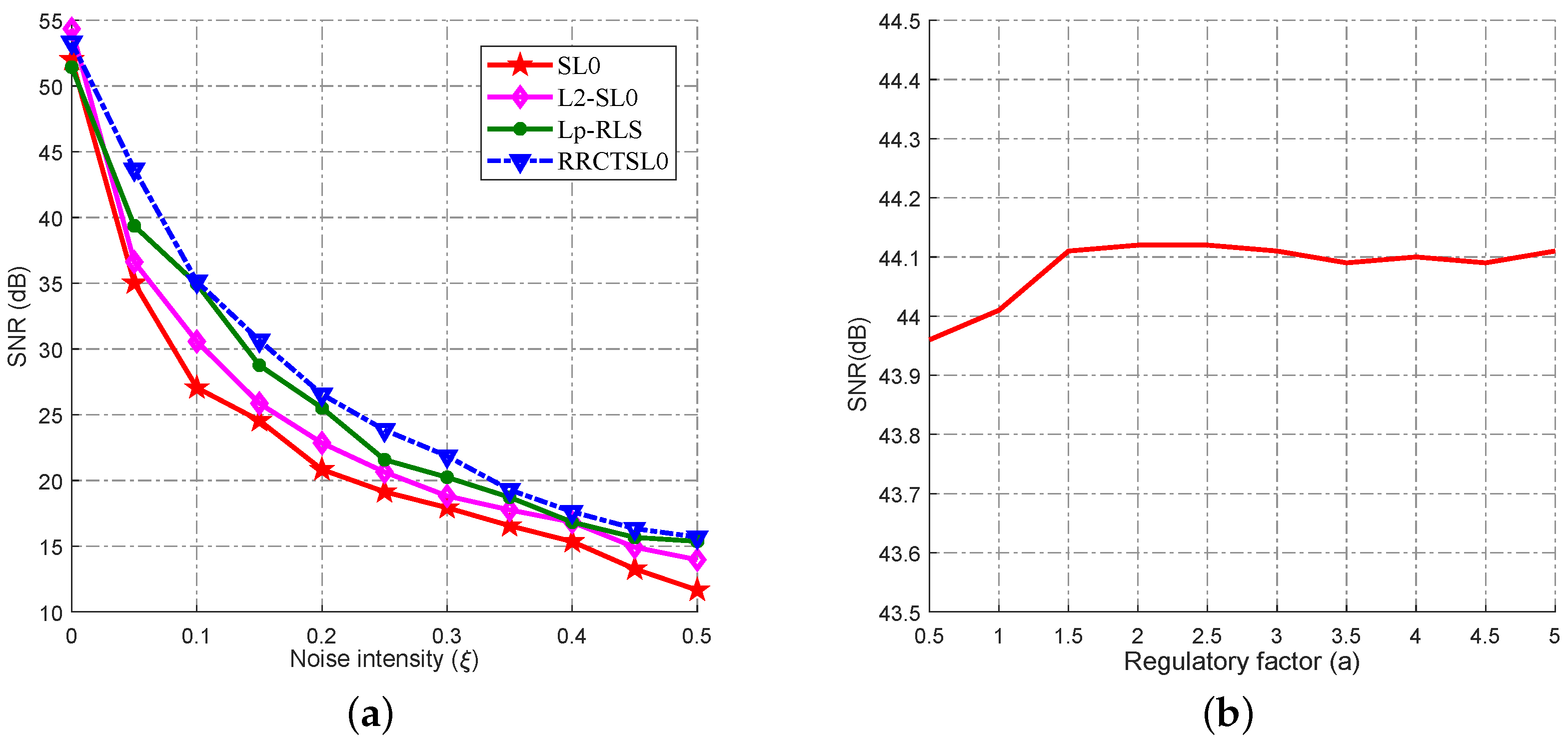
2.4. Selection of Parameters and
3. Numerical Simulation and Analysis
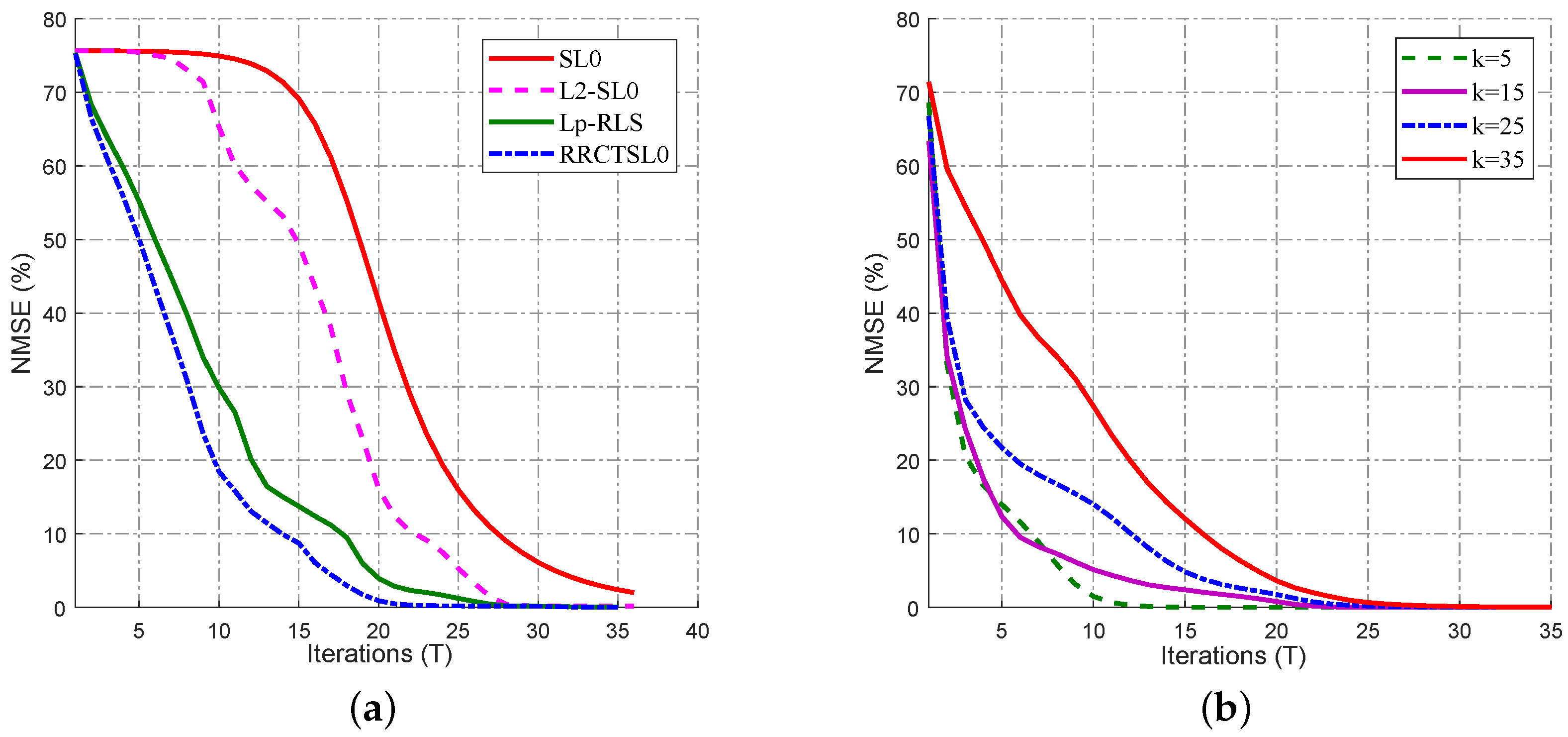
3.1. Convergence-Performance Comparison of the Algorithms
3.2. Accuracy Performance Comparison of the Algorithms
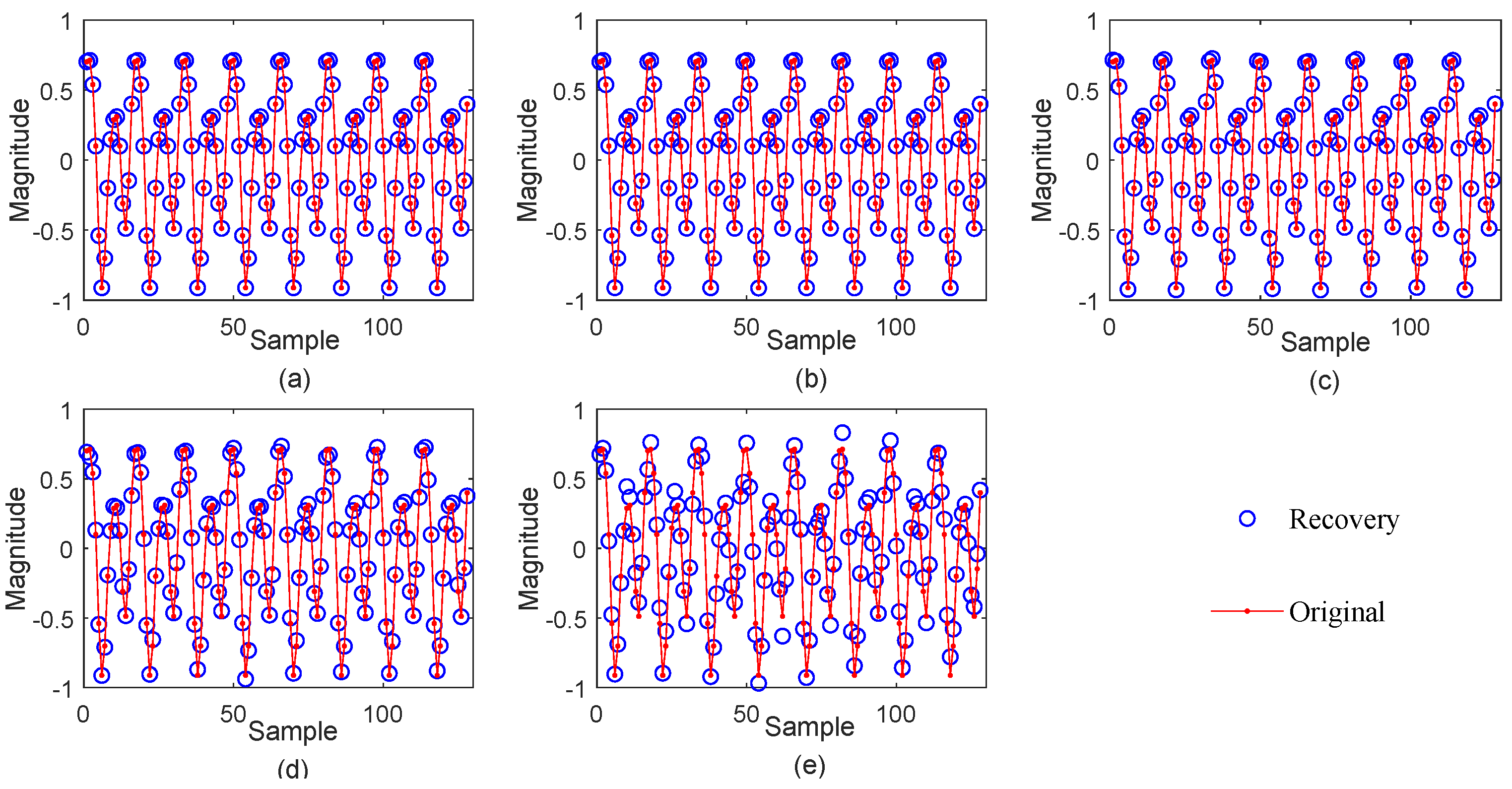
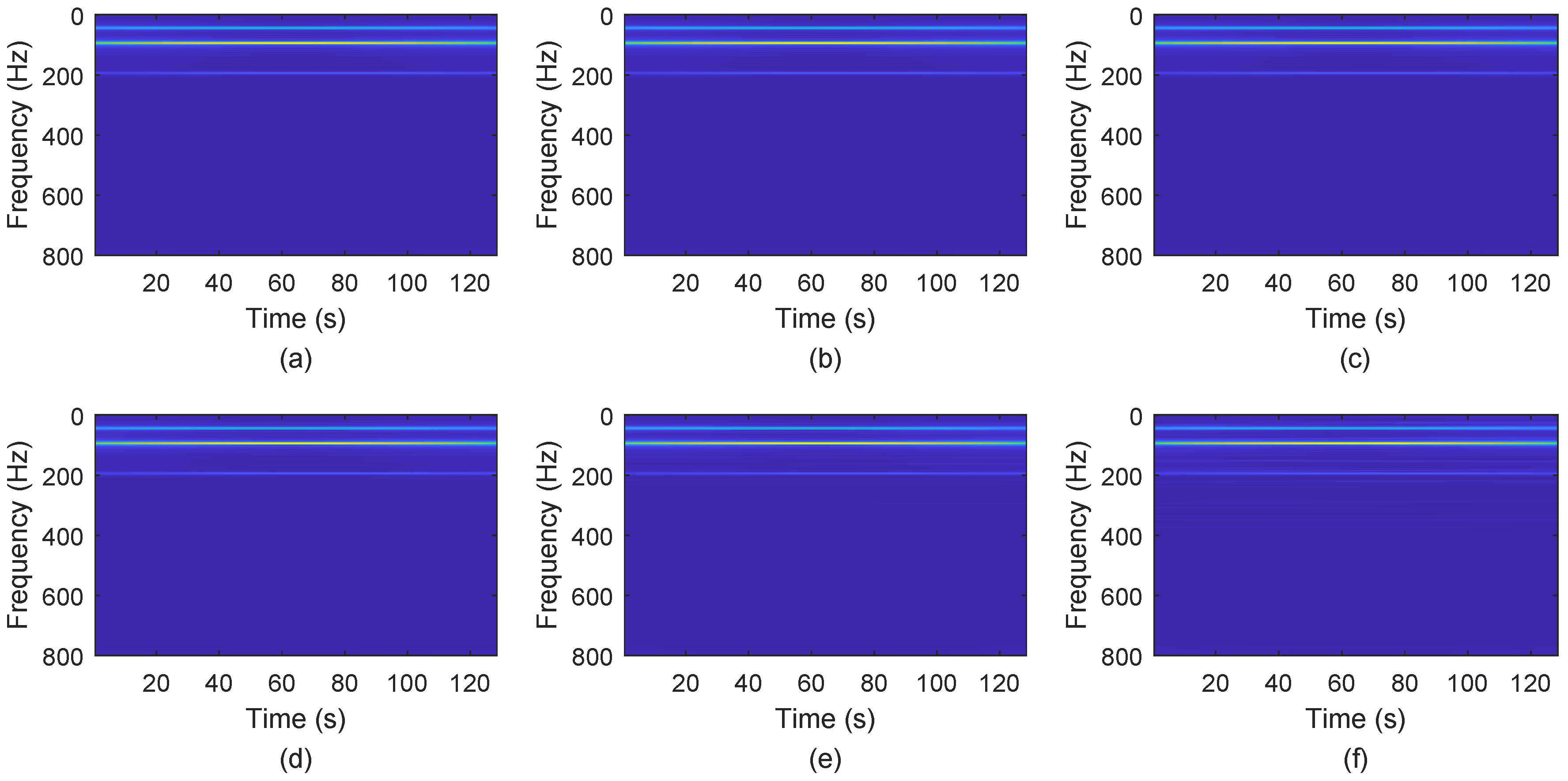
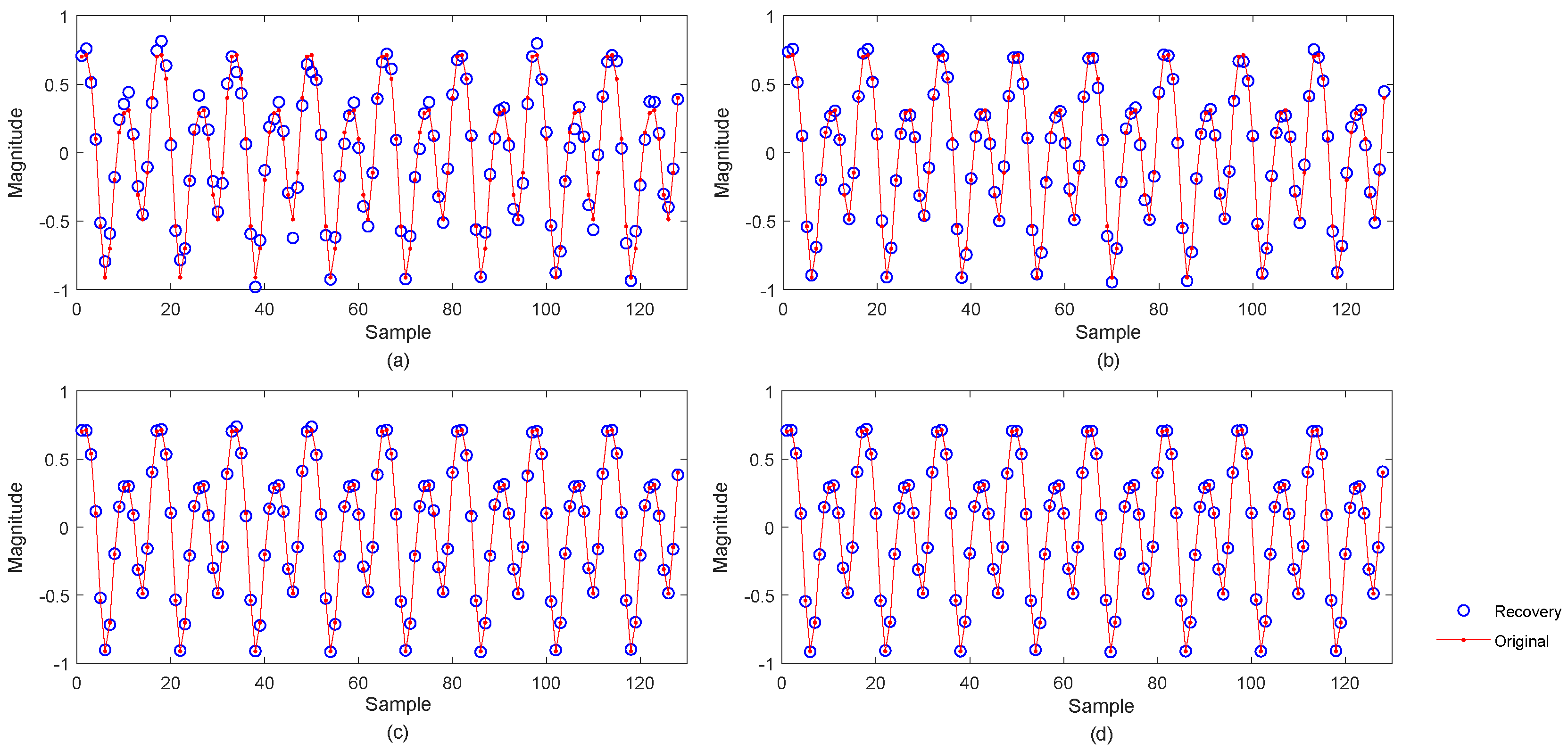
3.3. Applications of the Proposed RRCTSL0 Algorithm
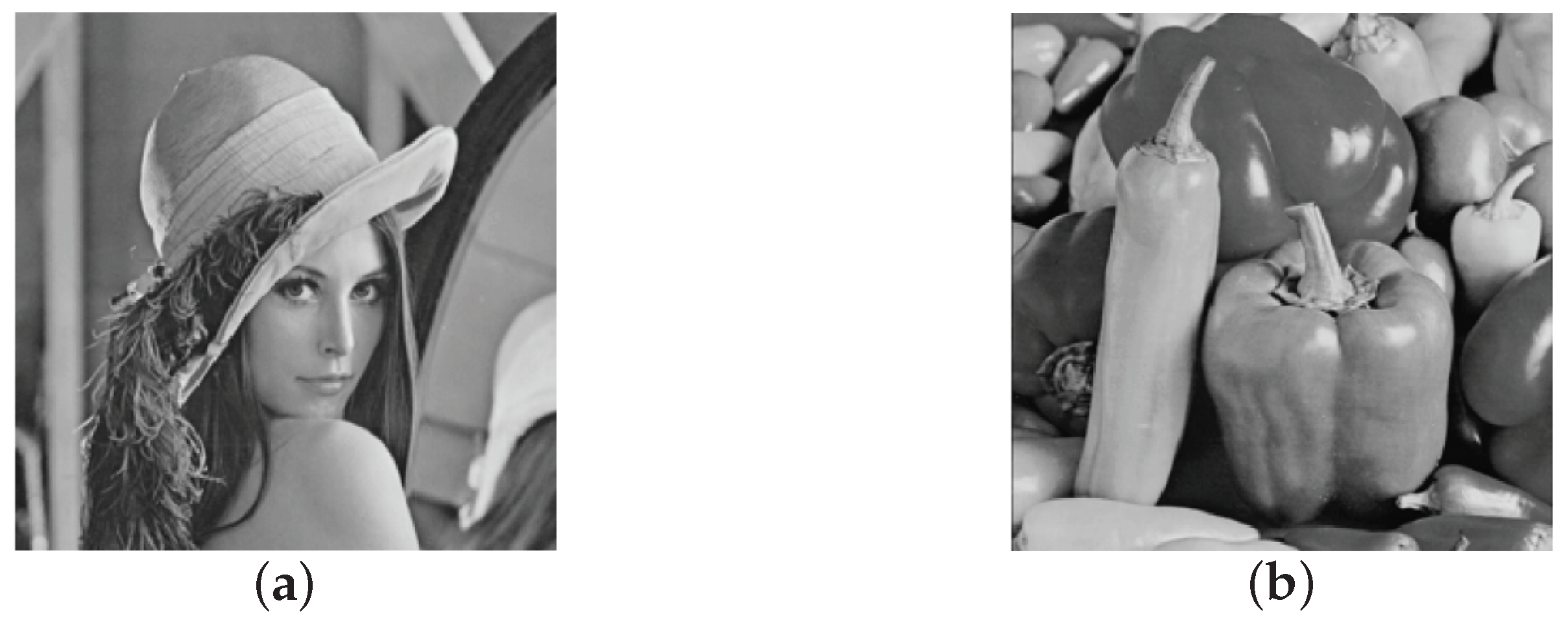
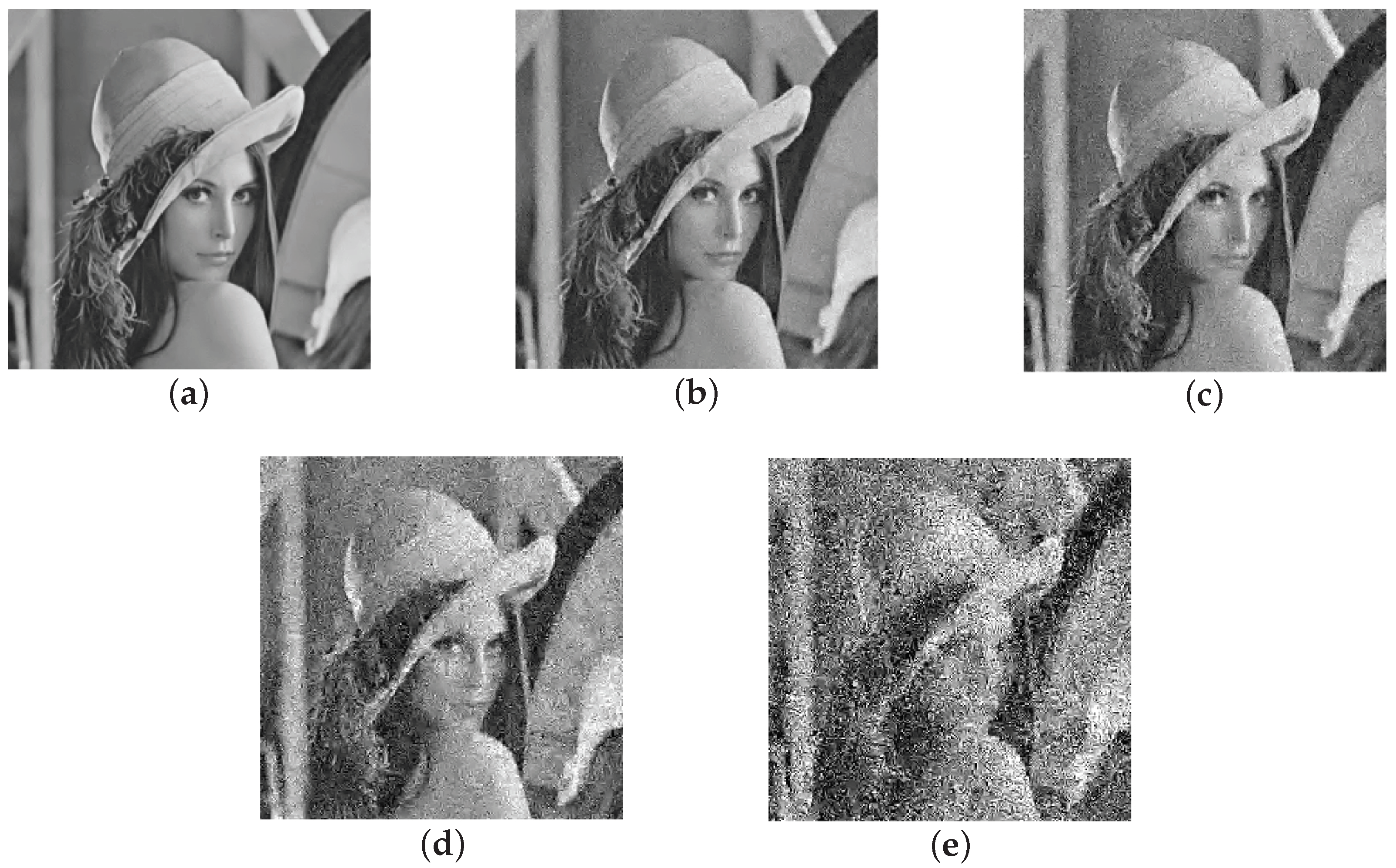
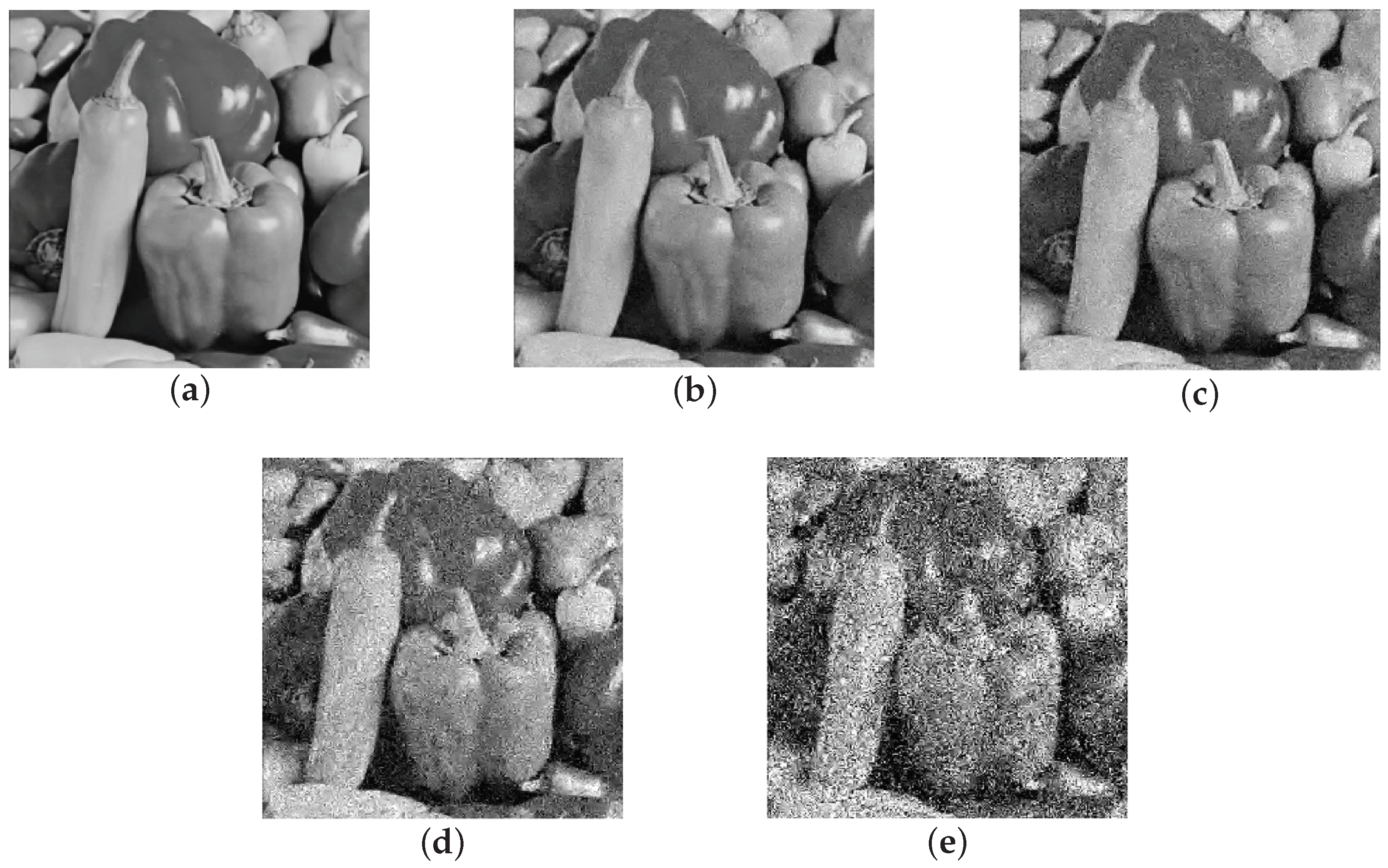
3.3.1. Real Sparse Signal Recovery
3.3.2. Real-Image Recovery
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donoho, D.L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cand’es, E.J.; Wakin, M.B. An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 2, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badeńska, A.; Błaszczyk, L. Compressed sensing for real measurements of quaternion signals. J. Frankl. Inst. 2017, 354, 5753–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routray, S.; Ray, A.K.; Mishra, C. MRI Denoising Using Sparse Based Curvelet Transform with Variance Stabilizing Transformation Framework. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2017, 7, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, S.; Chen, C.; Han, J.; Yang, W. Gabor convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 4357–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Tran, T.D. Sparse Signal Recovery via Generalized Entropy Functions Minimization. arxiv, 2017; arXiv:1703.10556. [Google Scholar]
- Tropp, J.A.; Gilbert, A.C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2007, 12, 4655–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Tang, X.; Mo, Q. A sharp condition for exact support recovery with orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 6, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, W.; Seokbeop, K.; Byonghyo, S. Generalized orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 12, 6202–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kwon, S.; Li, P.; Shim, B. Recovery of sparse signals via generalized orthogonal matching pursuit: A new analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 4, 1076–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needell, D.; Tropp, J.A. CoSaMP: Iterative signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples. Commun. ACM 2010, 12, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Milenkovic, O. Subspace pursuit for compressive sensing signal reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2009, 5, 2230–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Pan, C. Priori-information hold subspace pursuit: A compressive sensing-based channel estimation for layer modulated tds-ofdm. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2018, 99, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanadham, C.; Tranchina, D.; Simoncelli, E.P. Recovery of Sparse Translation-Invariant Signals with Continuous Basis Pursuit. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 10, 4735–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, T.; Studer, C. Phasemax: Convex phase retrieval via basis pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2018, 4, 2675–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Qureshi, I.M.; Haider, H.; Zaman, F.; Shoaib, B. Diagnosis of faulty sensors in phased array radar using compressed sensing and hybrid IRLS–SSF algorithm. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2016, 91, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Lai, X.; Hong, X.; Lin, Z. A matrix-based IRLS algorithm for the least Lp-norm design of 2-d fir filters. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ewald, K.; Schneider, U. Uniformly valid confidence sets based on the lasso. Statistics 2018, 12, 1358–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.J.; Nowak, R.D.; Figueiredo, M.A.T. Sparse reconstruction by separable approximation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 7, 2479–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Sparse regularization for force identification using dictionaries. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 368, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, A.; Meng, Q. Sparse channel estimation in MIMO-OFDM systems based on an improved sparse reconstruction by separable approximation algorithm. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2013, 10, 609–619. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Gao, C.; Yirong, W.U. An efficient data compression technique based on BPDN for scattered fields from complex targets. Sci. China (Inf. Sci.) 2017, 60, 109302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Li, Z.C. Accelerated 3D blind separation of convolved mixtures based on the fast iterative shrinkage thresholding algorithm for adaptive multiple subtraction. Geophysics 2018, 83, V99–V113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Fessler, J.A. Another look at the fast iterative shrinkage/thresholding algorithm (FISTA). Siam J. Optim. 2018, 28, 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, J.K.; Lu, W.S.; Antoniou, A. New Improved Algorithms for Compressive Sensing Based on ℓp Norm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2014, 61, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhu, W.P.; Zhang, A.; Yan, J. Sparse channel estimation of MIMO-OFDM systems with unconstrained smoothed L0-norm-regularized least squares compressed sensing. Eurasip J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2013, 2013, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohimani, H.; Babaie-Zadeh, M.; Jutten, C. A Fast Approach for Overcomplete Sparse Decomposition Based on Smoothed ℓ0 Norm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek-Mohammadi, M.; Koochakzadeh, A.; Babaie-Zadeh, M.; Jansson, M.; Rojas, C.R. Successive concave sparsity approximation for compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 5657–5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Ruan, G.; Liao, Y. A time-frequency domain underdetermined blind source separation algorithm for mimo radar signals. Symmetry 2017, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candès, E.J.; Wakin, M.B.; Boyd, S.P. Enhancing sparsity by reweighted L1 minimization. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 2008, 14, 877–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z. A Weighted Block Dictionary Learning Algorithm for Classification. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.F.; Zhang, J.S.; Li, Y.Q. Sparse Signal Reconstruction Based on Multiparameter Approximation Function with Smoothed Norm. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.H.; Huang, Z.T.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Wang, F.H. Robust sparse recovery based on approximate l0 norm. Acta Electron. Sin. 2012, 40, 1185–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Del-Blanco, C.R.; Cuevas, C.; García, N. Fast image decoding for block compressed sensing based encoding by using a modified smooth l0-norm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Consumer Electronics, Berlin, Germany, 5–7 September 2016; pp. 242–244. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Zhu, W.P. Sparse channel estimation of pulse-shaping multiple-input–multiple-output orthogonal frequency division multiplexing systems with an approximate gradient L2-SL0 reconstruction algorithm. Iet Commun. 2014, 8, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Li, D. Sparse flight array SAR downward-looking 3-d imaging based on compressed sensing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C. Hyperspectral image classification with spatial filtering and ℓ2,1 norm. Sensors 2017, 17, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, C.; Weiss, P.; Vignaud, A.; Ciuciu, P. An empirical study of the maximum degree of undersampling in compressed sensing for T2*-weighted MRI. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 53, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Lu, C.W. Adaptive integration of the compressed algorithm of CS and NPC for the ECG signal compressed algorithm in VLSI implementation. Sensors 2017, 17, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.T.; Zhao, H.; Peng, X.; Fang, M.; Qin, Z.; Goh, R.S.M. Transfer hashing: From shallow to deep. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 99, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Initialization: , and |
|---|
| Step 1: Set ; |
| Step 2: Compute using (7), for using Equation (15); |
| Step 3: For |
| (1) Set |
| (2) Compute Residual , and iterative termination threshold |
| (3) While |
| (a) Compute using Equations (16)–(23), using Equation (7) |
| (b) Set |
| (c) Compute |
| (4) Set |
| Step 4: Output |
| CR | PSNR (dB) | SSIM (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL0 | -SL0 | -RLS | RRCTSL0 | SL0 | -SL0 | -RLS | RRCTSL0 | |
| 0.4 | 29.075 | 29.255 | 32.369 | 34.825 | 98.24 | 98.28 | 99.16 | 99.53 |
| 0.5 | 30.379 | 30.688 | 34.664 | 36.669 | 98.70 | 98.77 | 99.51 | 99.69 |
| 0.6 | 33.140 | 30.232 | 36.699 | 36.789 | 99.31 | 98.64 | 99.69 | 99.70 |
| CR | PSNR (dB) | SSIM (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL0 | L2-SL0 | -RLS | RRCTSL0 | SL0 | L2-SL0 | -RLS | RRCTSL0 | |
| 0.4 | 21.811 | 26.343 | 33.887 | 34.673 | 93.13 | 97.33 | 99.53 | 99.61 |
| 0.5 | 28.405 | 29.769 | 34.588 | 35.046 | 98.35 | 98.80 | 99.60 | 99.64 |
| 0.6 | 32.276 | 33.188 | 34.872 | 35.160 | 99.33 | 99.45 | 99.63 | 99.65 |
| Photo | PSNR (dB) | SSIM (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Lena | 38.492 | 99.80 |
| Peppers | 39.367 | 99.87 | |
| 0.05 | Lena | 29.203 | 98.28 |
| Peppers | 28.826 | 97.53 | |
| 0.1 | Lena | 24.272 | 94.78 |
| Peppers | 24.305 | 95.64 | |
| 0.2 | Lena | 18.727 | 83.43 |
| Peppers | 19.782 | 86.07 | |
| 0.5 | Lena | 12.489 | 49.50 |
| Peppers | 13.416 | 55.34 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, J.; Yue, H.; Yin, X.; Ruan, G. A Reweighted Symmetric Smoothed Function Approximating L0-Norm Regularized Sparse Reconstruction Method. Symmetry 2018, 10, 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10110583
Xiang J, Yue H, Yin X, Ruan G. A Reweighted Symmetric Smoothed Function Approximating L0-Norm Regularized Sparse Reconstruction Method. Symmetry. 2018; 10(11):583. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10110583
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Jianhong, Huihui Yue, Xiangjun Yin, and Guoqing Ruan. 2018. "A Reweighted Symmetric Smoothed Function Approximating L0-Norm Regularized Sparse Reconstruction Method" Symmetry 10, no. 11: 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10110583
APA StyleXiang, J., Yue, H., Yin, X., & Ruan, G. (2018). A Reweighted Symmetric Smoothed Function Approximating L0-Norm Regularized Sparse Reconstruction Method. Symmetry, 10(11), 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10110583





