Selection and Characterization of Single-Domain Antibodies for Detection of Lassa Nucleoprotein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Selection and Production of sdAb
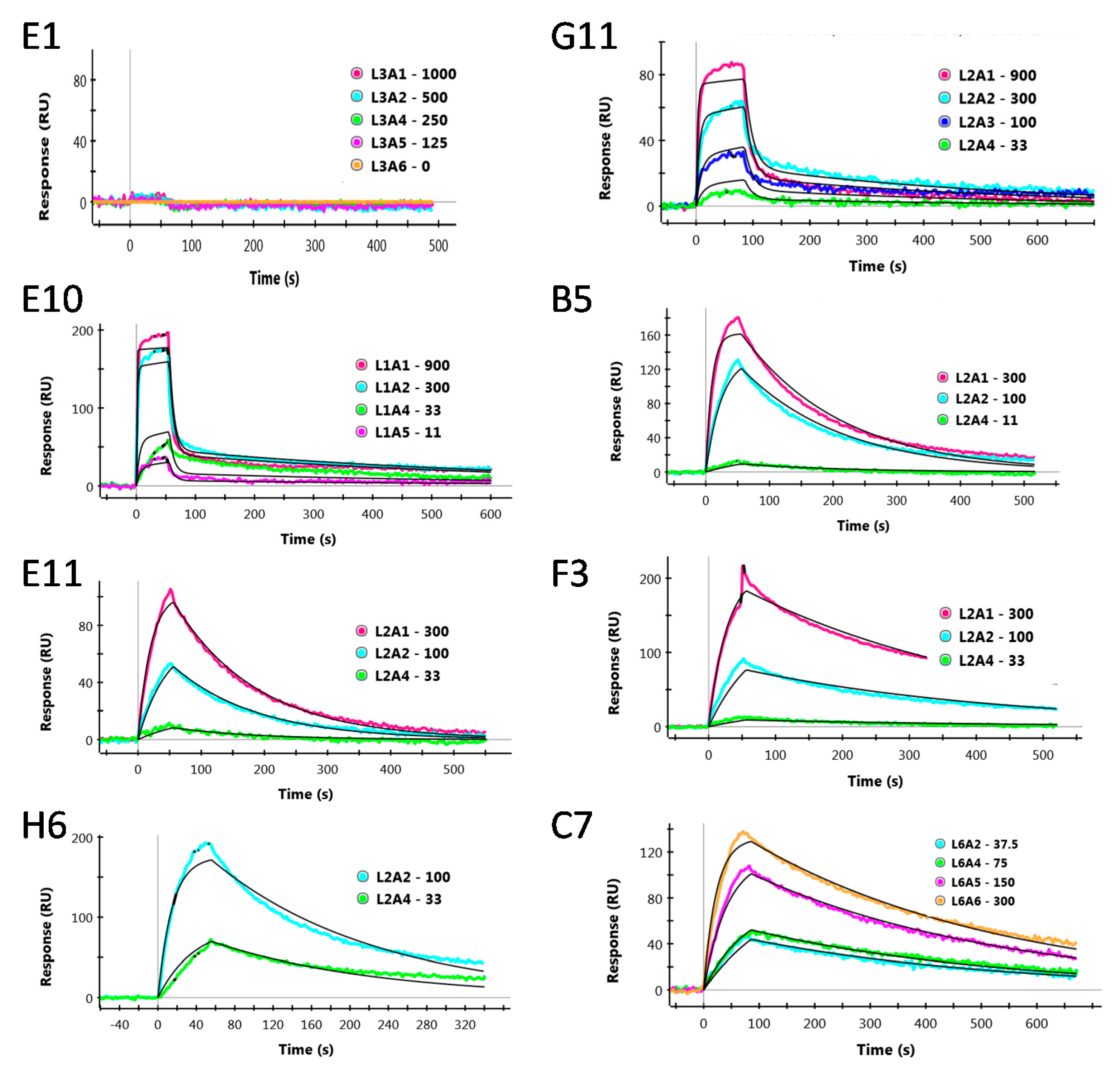
2.3. Surface Plasmon Resonance
2.4. Determining Melting Temperature and Refolding by Circular Dichroism
2.5. MagPlex Direct Binding and Homogeneous Sandwich Assays
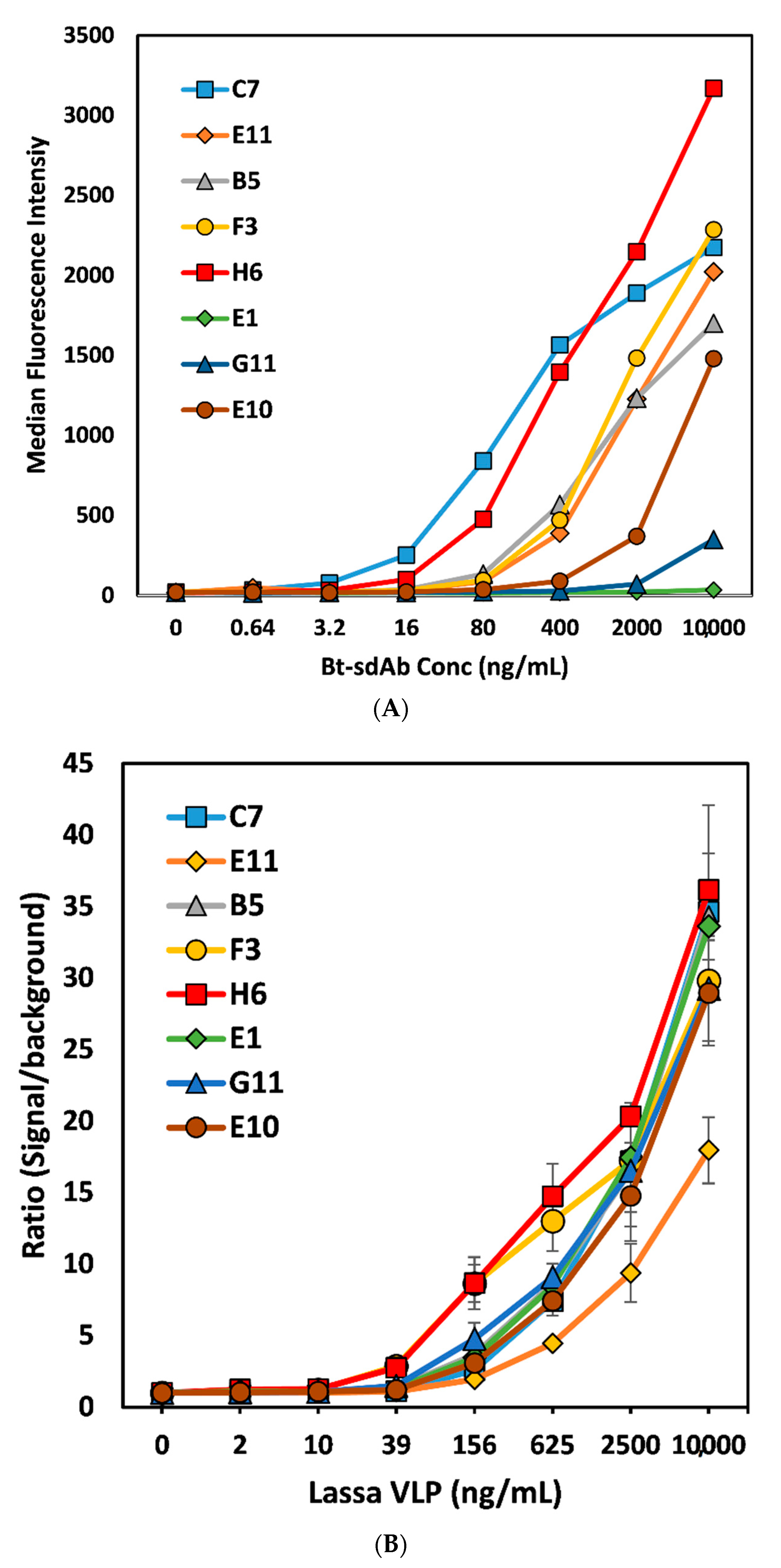
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Yun, N.E.; Walker, D.H. Pathogenesis of Lassa fever. Viruses 2012, 4, 2031–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, L.M.; Boisen, M.L.; Andersen, K.G.; Grove, J.N.; Moses, L.M.; Muncy, I.J.; Henderson, L.A.; Schieffellin, J.S.; Robinson, J.E.; Bangura, J.J.; et al. Lassa hemorrhagic fever in a late term pregnancy from northern sierra leone with a positive maternal outcome: Case report. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.E.; Fisher-Hoch, S.P.; Craven, R.B.; McCormick, J.B. A prospective study of maternal and fetal outcome in acute Lassa fever infection during pregnancy. BMJ 1988, 297, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, M.D.; Rollin, P.E.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Hustad, H.L.; Bausch, D.G.; Demby, A.H.; Bajani, M.D.; Peters, C.J.; Nichol, S.T. Genetic Diversity among Lassa Virus Strains. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6992–7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raabe, V.; Koehler, J. Laboratory Diagnosis of Lassa Fever. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisen, M.L.; Hartnett, J.N.; Shaffer, J.G.; Goba, A.; Momoh, M.; Sandi, J.D.; Fullah, M.; Nelson, D.K.S.; Bush, D.J.; Rowland, M.M.; et al. Field validation of recombinant antigen immunoassays for diagnosis of Lassa fever. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisen, M.L.; Uyigue, E.; Aiyepada, J.; Siddle, K.J.; Oestereich, L.; Nelson, D.K.S.; Bush, D.J.; Rowland, M.M.; Heinrich, M.L.; Eromon, P.; et al. Field evaluation of a Pan-Lassa rapid diagnostic test during the 2018 Nigerian Lassa fever outbreak. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahrling, P.; Niklasson, B.; McCormick, J. Early Diagnosis of Human Lassa Fever by ELISA Detection of Antigen and Antibody. Lancet 1985, 325, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausch, D.G.; Rollin, P.E.; Demby, A.H.; Coulibaly, M.; Kanu, J.; Conteh, A.S.; Wagoner, K.D.; McMullan, L.K.; Bowen, M.D.; Peters, C.J.; et al. Diagnosis and clinical virology of Lassa fever as evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, indirect fluorescent-antibody test, and virus isolation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2670–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, L.M.; Grove, J.N.; Boisen, M.L.; Shaffer, J.G.; Goba, A.; Fullah, M.; Momoh, M.; Grant, D.S.; Garry, R.F. Emerging trends in Lassa fever: Redefining the role of immunoglobulin M and inflammation in diagnosing acute infection. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, J.N.; Branco, L.M.; Boisen, M.L.; Muncy, I.J.; Henderson, L.A.; Schieffellin, J.S.; Robinson, J.E.; Bangura, J.J.; Fonnie, M.; Schoepp, R.J.; et al. Capacity building permitting comprehensive monitoring of a severe case of Lassa hemorrhagic fever in Sierra Leone with a positive outcome: Case report. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamers-Casterman, C.; Atarhouch, T.; Muyldermans, S.; Robinson, G.; Hamers, C.; Songa, E.B.; Bendahman, N.; Hamers, R. Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature 1993, 363, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies: Natural Single-Domain Antibodies. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 775–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Marco, A. Recombinant expression of nanobodies and nanobody-derived immunoreagents. Protein Expr. Purif. 2020, 172, 105645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Shriver-Lake, L.C.; Anderson, G.P.; Zabetakis, D.; Goldman, E.R. Selection, characterization, and thermal stabilization of llama single domain antibodies towards Ebola virus glycoprotein. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriver-Lake, L.C.; Liu, J.L.; Zabetakis, D.; Sugiharto, V.A.; Lee, C.-R.; Defang, G.N.; Wu, S.-J.L.; Anderson, G.P.; Goldman, E.R. Selection and Characterization of Anti-Dengue NS1 Single Domain Antibodies. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, E.R.; Anderson, G.P.; Liu, J.L.; Delehanty, J.B.; Sherwood, L.J.; Osborn, L.E.; Cummins, L.B.; Hayhurst, A. Facile generation of heat-stable antiviral and antitoxin single domain antibodies from a semisynthetic llama library. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 8245–8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walper, S.A.; Liu, J.L.; Zabetakis, D.; Anderson, G.P.; Goldman, E.R. Development and Evaluation of Single Domain Antibodies for Vaccinia and the L1 Antigen. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriver-Lake, L.C.; Zabetakis, D.; Goldman, E.R.; Anderson, G.P. Evaluation of anti-botulinum neurotoxin single domain antibodies with additional optimization for improved production and stability. Toxicon 2017, 135, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walper, S.A.; Lee, P.A.B.; Goldman, E.R.; Anderson, G.P. Comparison of single domain antibody immobilization strategies evaluated by surface plasmon resonance. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 388, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyldermans, S.; Atarhouch, T.; Saldanha, J.; Barbosa, J.A.; Hamers, R. Sequence and structure of VH domain from naturally occurring camel heavy chain immunoglobulins lacking light chains. Protein Eng. 1994, 7, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmsen, M.M.; Ruuls, R.C.; Nijman, I.J.; Niewold, T.A.; Frenken, L.G.J.; de Geus, B. Llama heavy-chain V regions consist of at least four distinct subfamilies revealing novel sequence features. Mol. Immunol. 2000, 37, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpet, F. Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical-clustering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 10881–10890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlapschy, M.; Grimm, S.; Skerra, A. A system for concomitant overexpression of four periplasmic folding catalysts to improve secretory protein production in Escherichia coli. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2006, 19, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriver-Lake, L.C.; Goldman, E.R.; Zabetakis, D.; Anderson, G.P. Improved production of single domain antibodies with two disulfide bonds by co-expression of chaperone proteins in the Escherichia coli periplasm. J. Immunol. Methods 2017, 443, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, E.R.; Liu, J.L.; Zabetakis, D.; Anderson, G.P. Enhancing Stability of Camelid and Shark Single Domain Antibodies: An Overview. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, Y.; Mine, S.; Uegaki, K. Stabilization of an immunoglobulin fold domain by an engineered disulfide bond at the buried hydrophobic region. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 36489–36495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govaert, J.; Pellis, M.; Deschacht, N.; Vincke, C.; Conrath, K.; Muyldermans, S.; Saerens, D. Dual Beneficial Effect of Interloop Disulfide Bond for Single Domain Antibody Fragments. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, E.R.; Broussard, A.; Anderson, G.P.; Liu, J.L. Bglbrick strategy for the construction of single domain antibody fusions. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasniqi, A.; Bialkowska, M.; Xavier, C.; Van der Jeught, K.; Muyldermans, S.; Devoogdt, N.; D’Huyvetter, M. Pharmacokinetics of radiolabeled dimeric sdAbs constructs targeting human CD20. New Biotechnol. 2018, 45, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrath, K.E.; Lauwereys, M.; Wyns, L.; Muyldermans, S. Camel single-domain antibodies as modular building units in bispecific and bivalent antibody constructs. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7346–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.L.; Zabetakis, D.; Brozozog Lee, P.A.; Goldman, E.R.; Anderson, G.P. Single Domain Antibody Alkaline Phosphatase Fusion Proteins for Antigen Detection—Analysis of Affinity and Thermal Stability of Single Domain Antibody. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 393, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.L.; Zabetakis, D.; Walper, S.A.; Goldman, E.R.; Anderson, G.P. Bioconjugates of rhizavidin with single domain antibodies as bifunctional immunoreagents. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 411, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tanha, J.; Hirama, T.; Khieu, N.H.; To, R.; Tong-Sevinc, H.; Stone, E.; Brisson, J.-R.; MacKenzie, C.R. Pentamerization of Single-domain Antibodies from Phage Libraries: A Novel Strategy for the Rapid Generation of High-avidity Antibody Reagents. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 335, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, M.D.; Anderson, G.P.; Serrano-Gonzalez, J.; Liu, J.L.; Zabetakis, D.; Goldman, E.R. Immunodiagnostic reagents using llama single domain antibody-alkaline phosphatase fusion proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 417, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, C.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Z. Construction of multiform scFv antibodies using linker peptide. J. Genet. Genom. 2008, 35, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| sdAb | Yield (mg/L) | Tm (°C) | % Refold | pI | #SS Bonds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | 8.4 | 59 | 56 | 7.18 | 1 |
| G11 | 5.2 | 60 | 30 | 8.01 | 1 |
| E10 | 16.4 | 48 | 15 | 8.64 | 1 |
| E11 | 0.8 | 64 | 93 | 7.95 | 2 |
| B5 | 1.4 | 63 | 52 | 7.96 | 2 |
| H6 | 3.5 | 64 | 30 | 8.74 | 2 |
| F3 | 2.7 | 65 | 59 | 7.89 | 2 |
| C7 | 1.9 | 66 | 83 | 7.96 | 2 |
| Clone | ka (1/Ms) | kd (1/s) | KD (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | - | - | NBO * |
| G11 | 3.8 × 105 | 7.0 × 10−2 | 184 |
| E10 | 1.9 × 106 | 1.3 × 10−1 | 69 |
| E11 | 1.5 × 105 | 7.6 × 10−3 | 57 |
| B5 | 3.2 × 105 | 6.1 × 10−3 | 19 |
| H6 | 6.1 × 105 | 5.7 × 10−3 | 9.3 |
| F3 | 4.0 × 105 | 3.0 × 10−3 | 7.5 |
| C7 | 5.1 × 105 | 3.8 × 10−3 | 7.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anderson, G.P.; Liu, J.L.; Shriver-Lake, L.C.; Goldman, E.R. Selection and Characterization of Single-Domain Antibodies for Detection of Lassa Nucleoprotein. Antibodies 2020, 9, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040071
Anderson GP, Liu JL, Shriver-Lake LC, Goldman ER. Selection and Characterization of Single-Domain Antibodies for Detection of Lassa Nucleoprotein. Antibodies. 2020; 9(4):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040071
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnderson, George P., Jinny L. Liu, Lisa C. Shriver-Lake, and Ellen R. Goldman. 2020. "Selection and Characterization of Single-Domain Antibodies for Detection of Lassa Nucleoprotein" Antibodies 9, no. 4: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040071
APA StyleAnderson, G. P., Liu, J. L., Shriver-Lake, L. C., & Goldman, E. R. (2020). Selection and Characterization of Single-Domain Antibodies for Detection of Lassa Nucleoprotein. Antibodies, 9(4), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040071





