A Collection of Single-Domain Antibodies that Crowd Ricin Toxin’s Active Site
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. RiVax and VHH Production
2.2. Competition ELISA
2.3. Vero Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
2.4. Affinity Determinations
2.5. HX-MS
2.6. Data Analysis
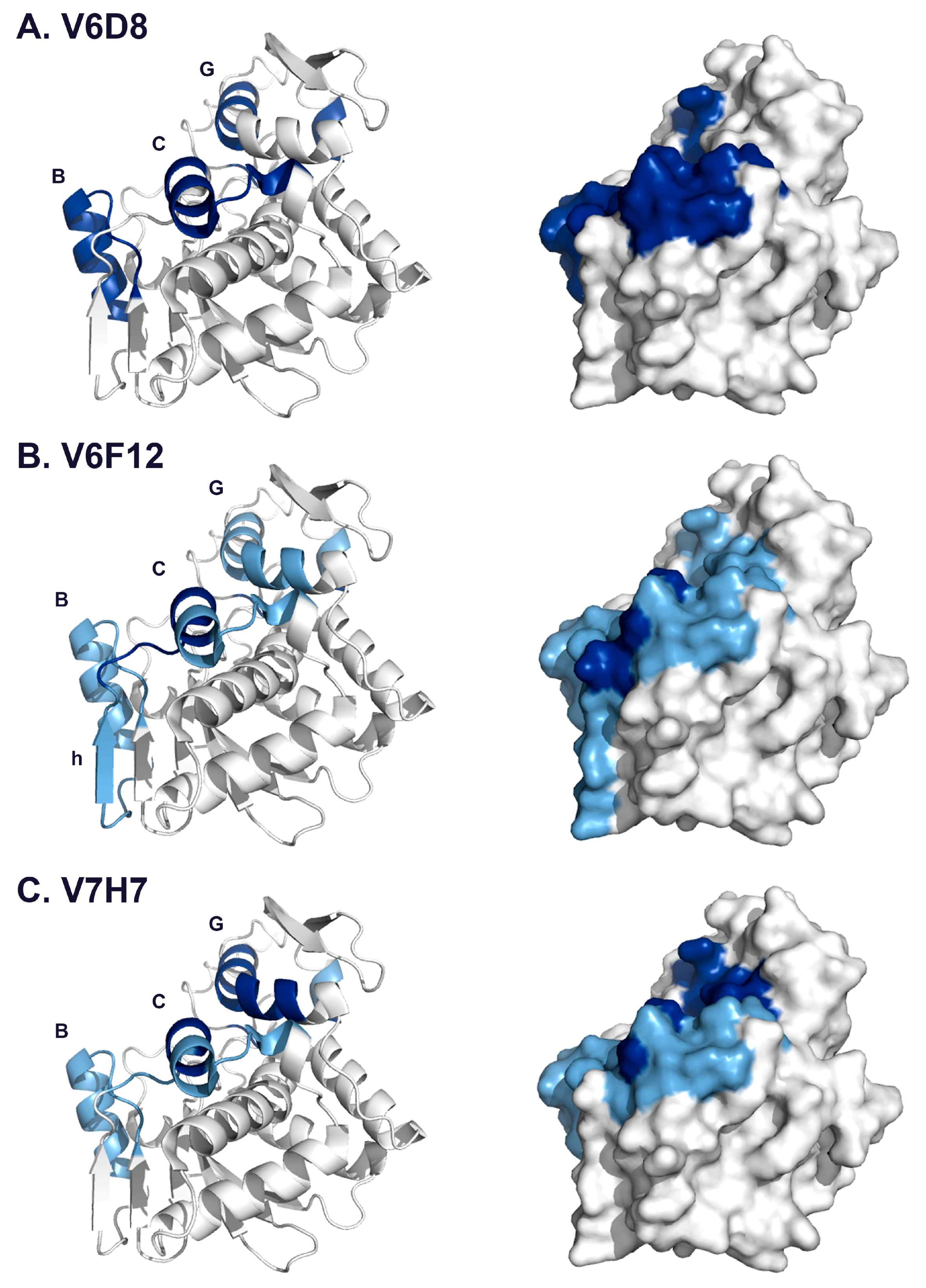
3. Results
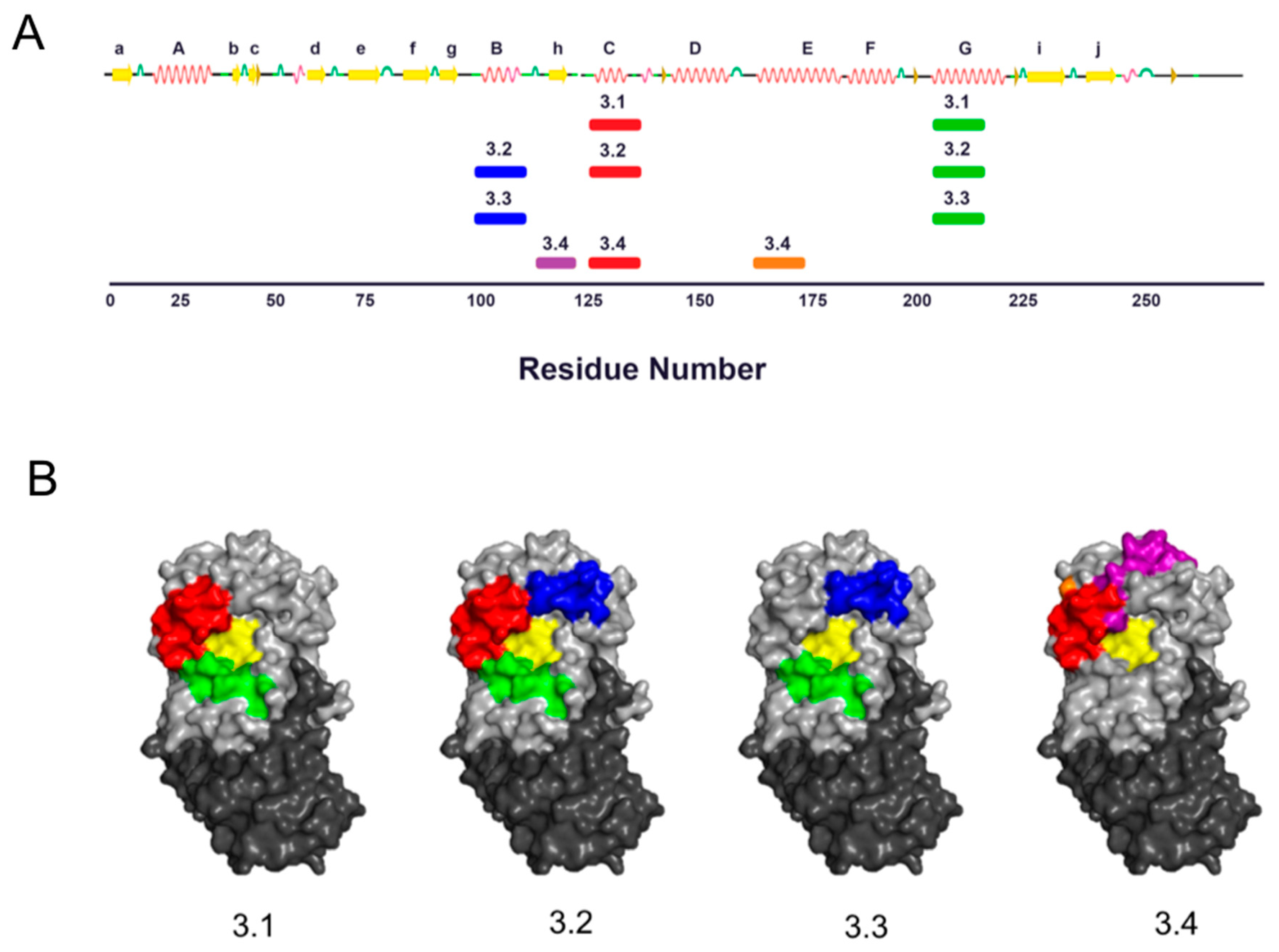
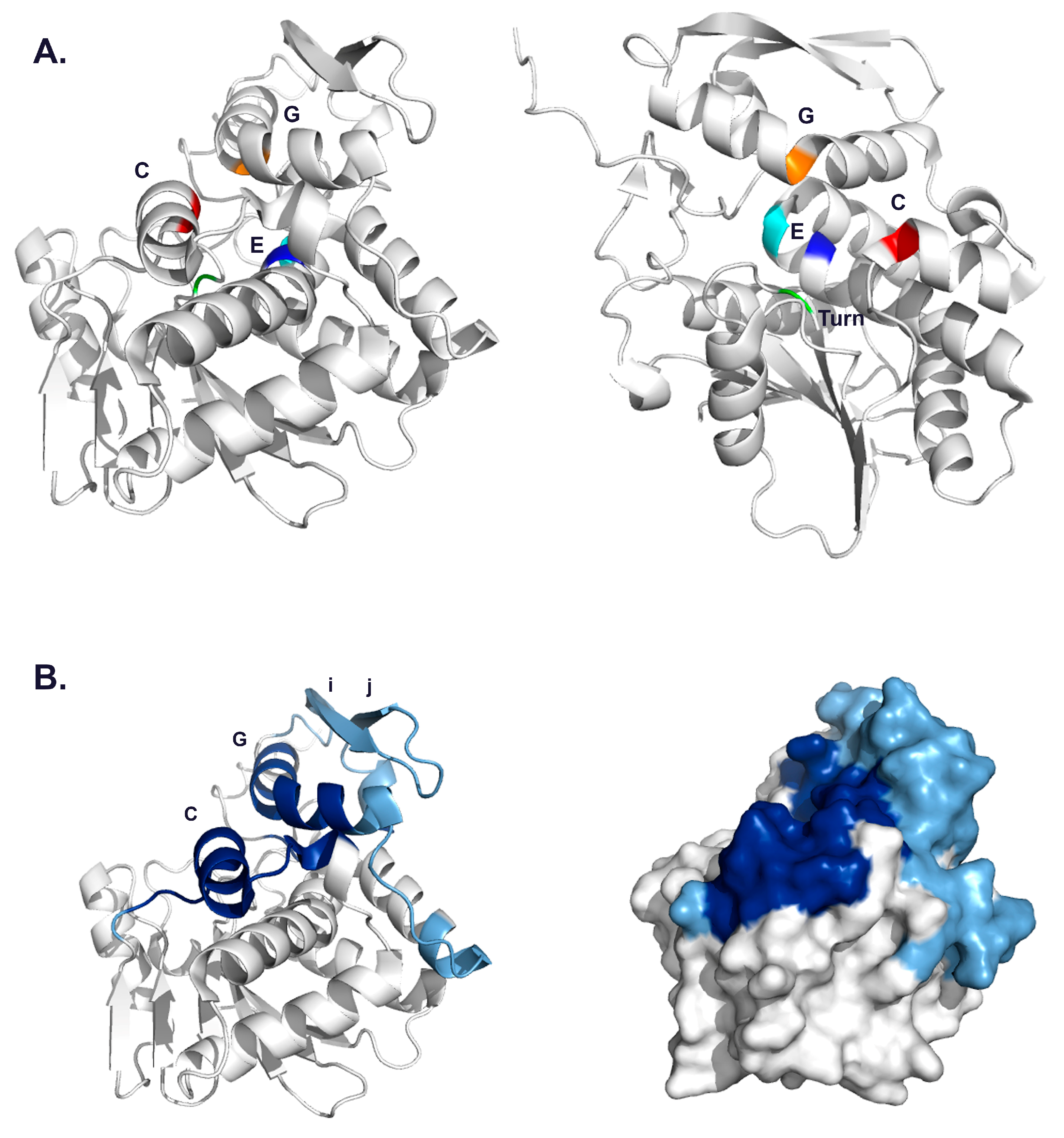
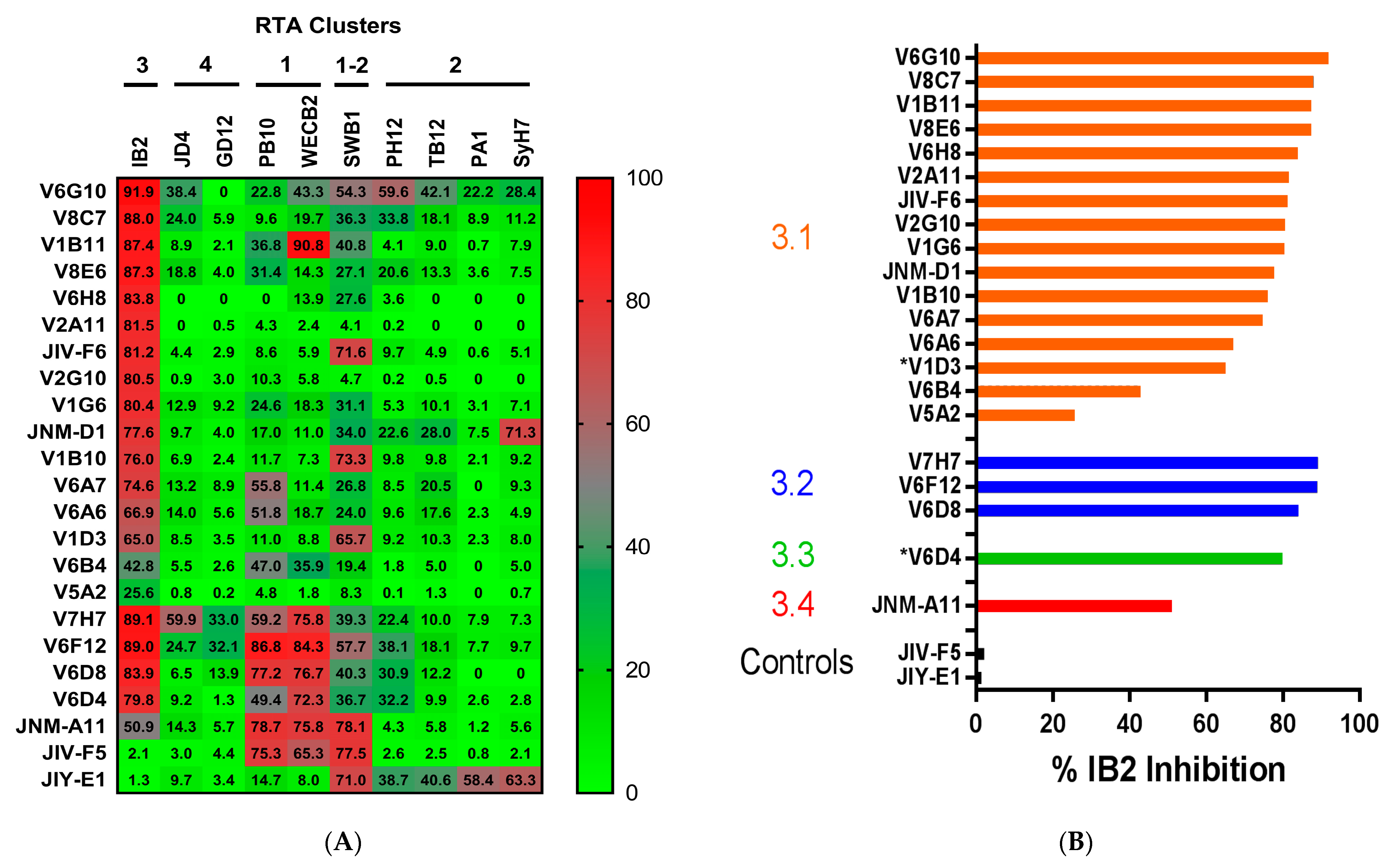
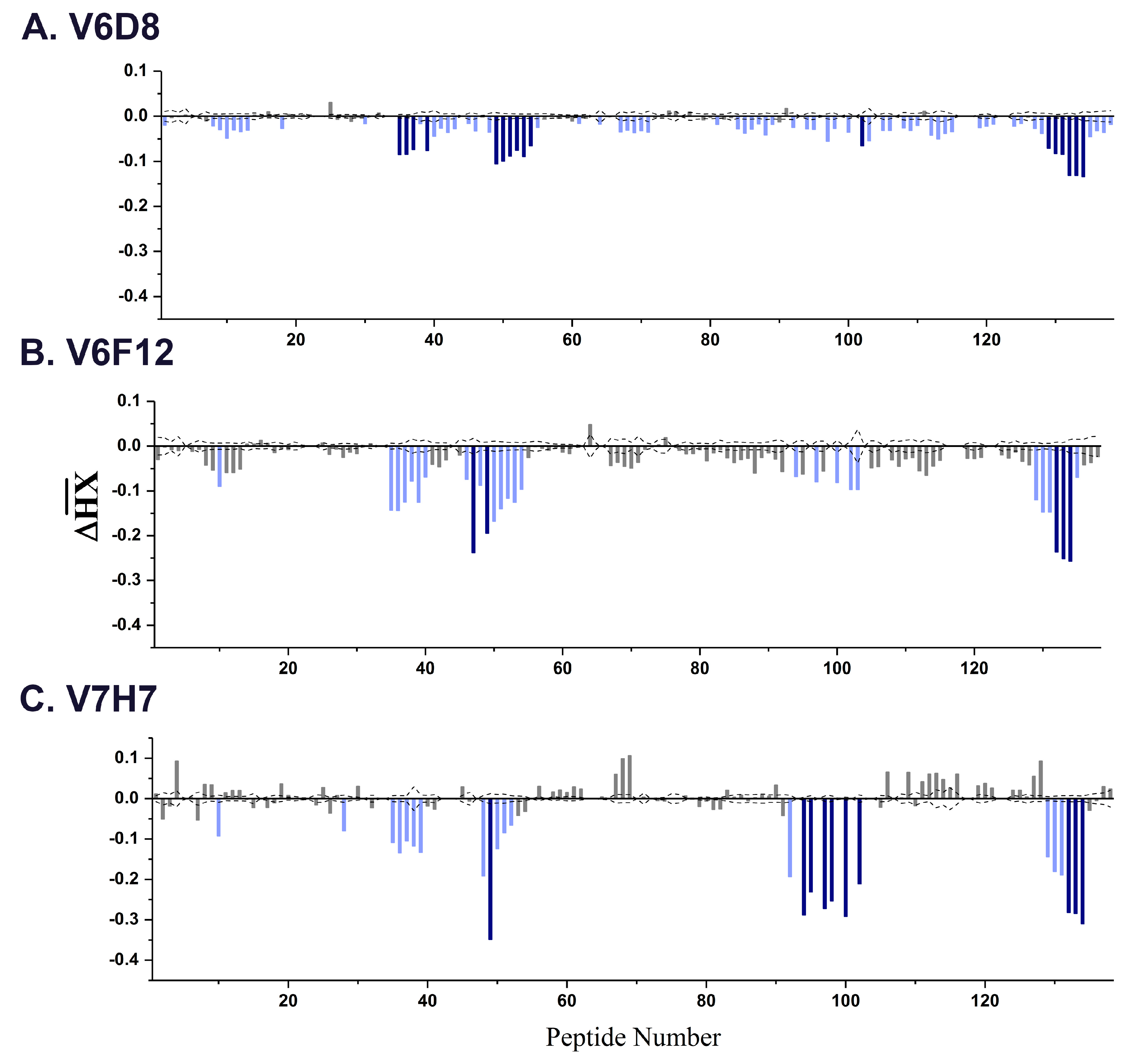
3.1. Identification and Characterization of Cluster 3 VHHs
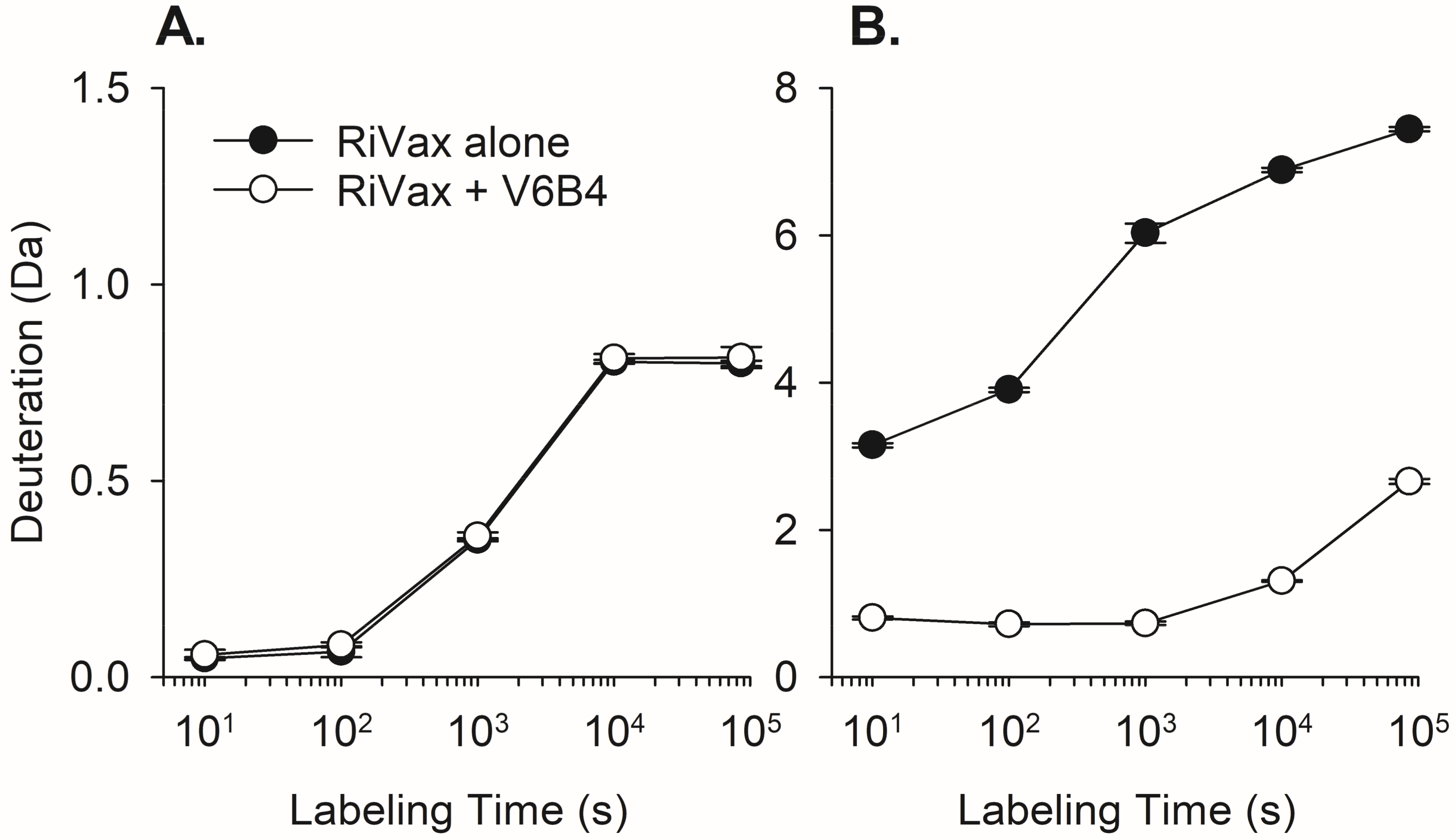
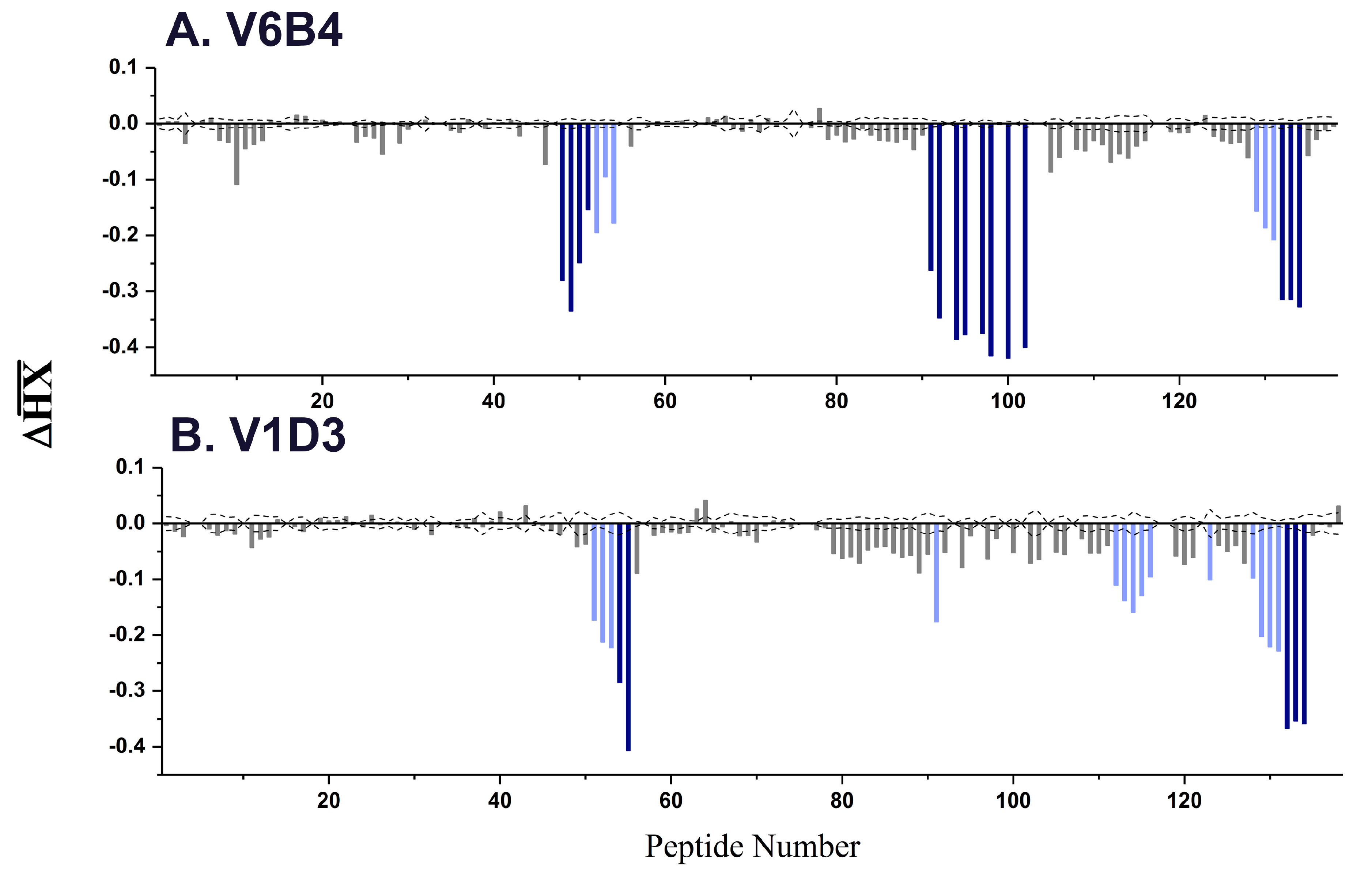
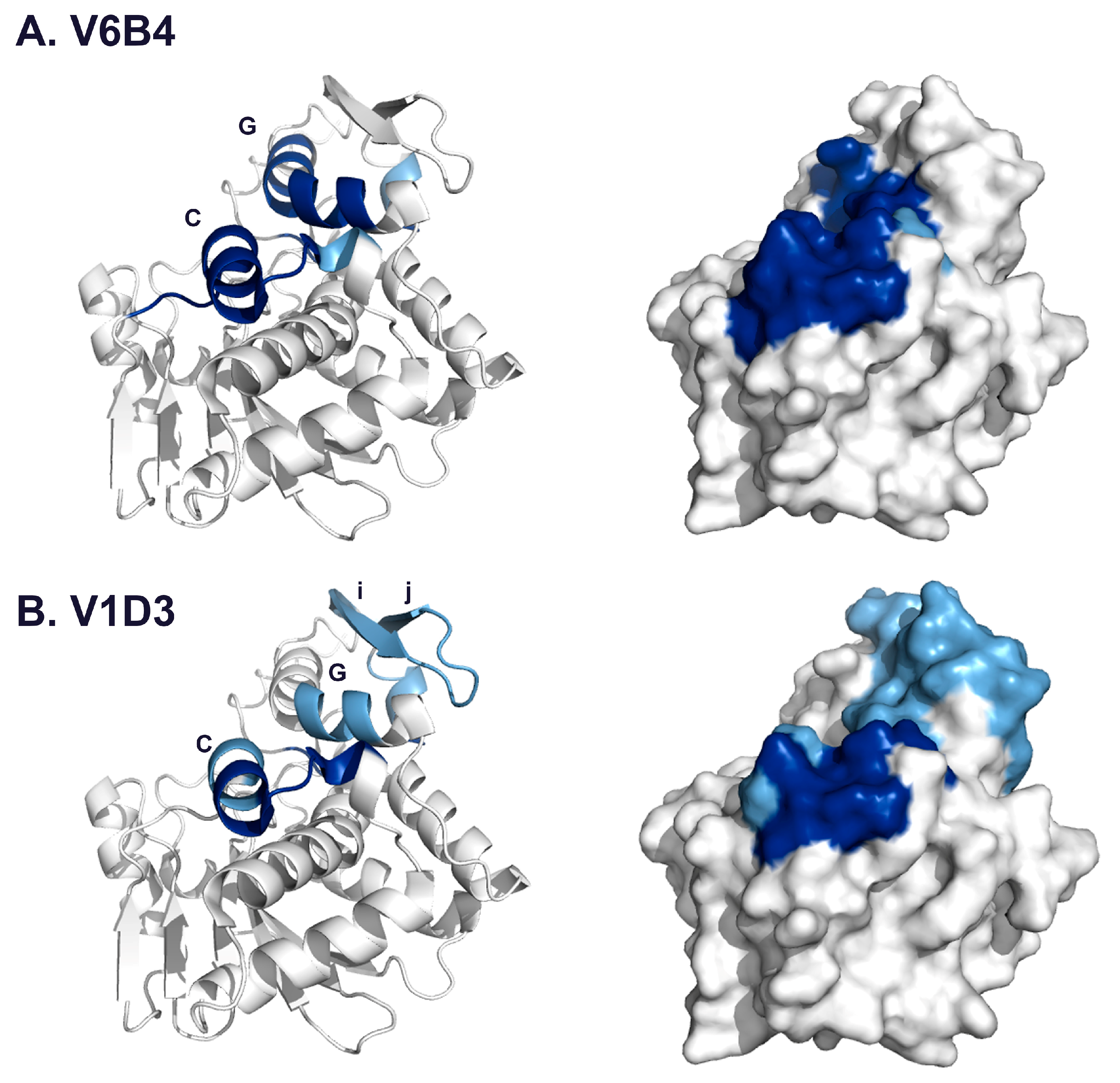
3.2. VHH Epitope Mapping by HX-MS
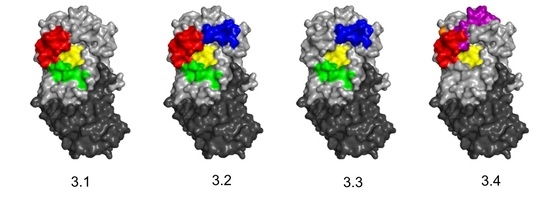
3.3. Identification of Epitope Subclusters
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gal, Y.; Mazor, O.; Falach, R.; Sapoznikov, A.; Kronman, C.; Sabo, T. Treatments for pulmonary ricin intoxication: Current aspects and future prospects. Toxins (Basel) 2017, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, G.D. Understanding ricin from a defensive viewpoint. Toxins (Basel) 2011, 3, 1373–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisler, R.B.; Smith, L.A. The need for continued development of ricin countermeasures. Adv. Prev. Med. 2012, 2012, 149737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutenber, E.; Ready, M.; Robertus, J.D. Structure and evolution of ricin b chain. Nature 1987, 326, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Mitsui, K.; Motizuki, M.; Tsurugi, K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 s ribosomal rna caused by the toxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 5908–5912. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Endo, Y.; Tsurugi, K. Rna n-glycosidase activity of ricin a-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 8128–8130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Montfort, W.; Villafranca, J.E.; Monzingo, A.F.; Ernst, S.R.; Katzin, B.; Rutenber, E.; Xuong, N.H.; Hamlin, R.; Robertus, J.D. The three-dimensional structure of ricin at 2.8 a. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 5398–5403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rutenber, E.; Katzin, B.J.; Ernst, S.; Collins, E.J.; Mlsna, D.; Ready, M.P.; Robertus, J.D. Crystallographic refinement of ricin to 2.5 a. Proteins 1991, 10, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzin, B.J.; Collins, E.J.; Robertus, J.D. Structure of ricin a-chain at 2.5 A. Proteins 1991, 10, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzingo, A.F.; Robertus, J.D. X-ray analysis of substrate analogs in the ricin a-chain active site. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 227, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, R.T.I.; Angalakurthi, S.K.; Van Slyke, G.; Vance, D.J.; Hickey, J.M.; Joshi, S.B.; Middaugh, C.R.; Volkin, D.B.; Weis, D.D.; Mantis, N.J. High-definition mapping of four spatially distinct neutralizing epitope clusters on rivax, a candidate ricin toxin subunit vaccine. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2017, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincus, S.H.; Bhaskaran, M.; Brey, R.N., 3rd; Didier, P.J.; Doyle-Meyers, L.A.; Roy, C.J. Clinical and pathological findings associated with aerosol exposure of macaques to ricin toxin. Toxins (Basel) 2015, 7, 2121–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallshaw, J.E.; Richardson, J.A.; Vitetta, E.S. Rivax, a recombinant ricin subunit vaccine, protects mice against ricin delivered by gavage or aerosol. Vaccine 2007, 25, 7459–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, C.J.; Brey, R.N.; Mantis, N.J.; Mapes, K.; Pop, I.V.; Pop, L.M.; Ruback, S.; Killeen, S.Z.; Doyle-Meyers, L.; Vinet-Oliphant, H.S.; et al. Thermostable ricin vaccine protects rhesus macaques against aerosolized ricin: Epitope-specific neutralizing antibodies correlate with protection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3782–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audi, J.; Belson, M.; Patel, M.; Schier, J.; Osterloh, J. Ricin poisoning: A comprehensive review. JAMA 2005, 294, 2342–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, D.J.; Mantis, N.J. Progress and challenges associated with the development of ricin toxin subunit vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2016, 15, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallshaw, J.E.; Richardson, J.A.; Pincus, S.; Schindler, J.; Vitetta, E.S. Preclinical toxicity and efficacy testing of rivax, a recombinant protein vaccine against ricin. Vaccine 2005, 23, 4775–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, J.M.; Kasten-Jolly, J.C.; Reynolds, C.E.; Mantis, N.J. Localization of non-linear neutralizing b cell epitopes on ricin toxin’s enzymatic subunit (rta). Immunol. Lett. 2014, 158, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, J.M.; Neal, L.M.; McCarthy, E.A.; Kasten-Jolly, J.A.; Brey, R.N., 3rd; Mantis, N.J. Folding domains within the ricin toxin a subunit as targets of protective antibodies. Vaccine 2010, 28, 7035–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, M.J.; Vance, D.J.; Cassidy, M.S.; Rong, Y.; Mantis, N.J. Structural analysis of single domain antibodies bound to a second neutralizing hot spot on ricin toxin’s enzymatic subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, M.J.; Vance, D.J.; Cassidy, M.S.; Rong, Y.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Mantis, N.J. Structural analysis of nested neutralizing and non-neutralizing b cell epitopes on ricin toxin’s enzymatic subunit. Proteins 2016, 84, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, M.J.; Vance, D.J.; Cheung, J.; Franklin, M.C.; Burshteyn, F.; Cassidy, M.S.; Gary, E.N.; Herrera, C.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Mantis, N.J. Crystal structures of ricin toxin’s enzymatic subunit (rta) in complex with neutralizing and non-neutralizing single-chain antibodies. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 3057–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, D.J.; Tremblay, J.M.; Rong, Y.; Angalakurthi, S.K.; Volkin, D.B.; Middaugh, C.R.; Weis, D.D.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Mantis, N.J. High-resolution epitope positioning of a large collection of neutralizing and nonneutralizing single-domain antibodies on the enzymatic and binding subunits of ricin toxin. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2017, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemley, P.V.; Amanatides, P.; Wright, D.C. Identification and characterization of a monoclonal antibody that neutralizes ricin toxicity in vitro and in vivo. Hybridoma 1994, 13, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westfall, J.; Yates, J.L.; Van Slyke, G.; Ehrbar, D.; Measey, T.; Straube, R.; Donini, O.; Mantis, N.J. Thermal stability and epitope integrity of a lyophilized ricin toxin subunit vaccine. Vaccine 2018, 36, 5967–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, J.M.; Mantis, N.J. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against ricin’s enzymatic subunit interfere with protein disulfide isomerase-mediated reduction of ricin holotoxin in vitro. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 395, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Slyke, G.; Angalakurthi, S.K.; Toth, R.T.; Vance, D.J.; Rong, Y.; Ehrbar, D.; Shi, Y.; Middaugh, C.R.; Volkin, D.B.; Weis, D.D.; et al. Fine-specificity epitope analysis identifies contact points on ricin toxin recognized by protective monoclonal antibodies. ImmunoHorizons 2018, 2, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.C.; O’Hara, J.M.; Hu, L.; Gao, F.P.; Joshi, S.B.; Volkin, D.B.; Brey, R.N.; Fang, J.; Karanicolas, J.; Mantis, N.J.; et al. Effect of single-point mutations on the stability and immunogenicity of a recombinant ricin a chain subunit vaccine antigen. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2013, 9, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smallshaw, J.E.; Firan, A.; Fulmer, J.R.; Ruback, S.L.; Ghetie, V.; Vitetta, E.S. A novel recombinant vaccine which protects mice against ricin intoxication. Vaccine 2002, 20, 3422–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Milne, J.S.; Mayne, L.; Englander, S.W. Primary structure effects on peptide group hydrogen exchange. Proteins 1993, 17, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzoli, A.; Vance, D.J.; Rudolph, M.J.; Rong, Y.; Angalakurthi, S.K.; Toth, R.T.t.; Middaugh, C.R.; Volkin, D.B.; Weis, D.D.; Karanicolas, J.; et al. Using homology modeling to interrogate binding affinity in neutralization of ricin toxin by a family of single domain antibodies. Proteins 2017, 85, 1994–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legler, P.M.; Brey, R.N.; Smallshaw, J.E.; Vitetta, E.S.; Millard, C.B. Structure of rivax: A recombinant ricin vaccine. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, M.J.; Vance, D.J.; Kelow, S.; Angalakurthi, S.K.; Nguyen, S.; Davis, S.A.; Rong, Y.; Middaugh, C.R.; Weis, D.D.; Dunbrack, R., Jr.; et al. Contribution of an unusual cdr2 element of a single domain antibody in ricin toxin binding affinity and neutralizing activity. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2018, 31, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankel, A.; Welsh, P.; Richardson, J.; Robertus, J.D. Role of arginine 180 and glutamic acid 177 of ricin toxin a chain in enzymatic inactivation of ribosomes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1990, 10, 6257–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ready, M.P.; Kim, Y.; Robertus, J.D. Site-directed mutagenesis of ricin a-chain and implications for the mechanism of action. Proteins 1991, 10, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahome, P.G.; Robertus, J.D.; Mantis, N.J. Small-molecule inhibitors of ricin and shiga toxins. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 357, 179–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weston, S.A.; Tucker, A.D.; Thatcher, D.R.; Derbyshire, D.J.; Pauptit, R.A. X-ray structure of recombinant ricin a-chain at 1.8 a resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 244, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, E.; Kose, N.; Edeling, M.A.; Adhikari, J.; Sapparapu, G.; Lazarte, S.M.; Nelson, C.A.; Govero, J.; Gross, M.L.; Fremont, D.H.; et al. Mouse and human monoclonal antibodies protect against infection by multiple genotypes of japanese encephalitis virus. MBio 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribenko, A.V.; Parris, K.; Mosyak, L.; Li, S.; Handke, L.; Hawkins, J.C.; Severina, E.; Matsuka, Y.V.; Anderson, A.S. High resolution mapping of bactericidal monoclonal antibody binding epitopes on staphylococcus aureus antigen mntc. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, X.X.; Chandramohan, A.; Lim, X.E.; Crowe, J.E., Jr.; Lok, S.M.; Anand, G.S. Epitope and paratope mapping reveals temperature-dependent alterations in the dengue-antibody interface. Structure 2017, 25, 1391–1402 e1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddaloni, M.; Cooke, C.; Wilkinson, R.; Stout, A.V.; Eng, L.; Pincus, S.H. Immunological characteristics associated with the protective efficacy of antibodies to ricin. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 6221–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noy-Porat, T.; Rosenfeld, R.; Ariel, N.; Epstein, E.; Alcalay, R.; Zvi, A.; Kronman, C.; Ordentlich, A.; Mazor, O. Isolation of anti-ricin protective antibodies exhibiting high affinity from immunized non-human primates. Toxins (Basel) 2016, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, D.J.; Mantis, N.J. Resolution of two overlapping neutralizing b cell epitopes within a solvent exposed, immunodominant alpha-helix in ricin toxin’s enzymatic subunit. Toxicon 2012, 60, 874–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, D.J.; Tremblay, J.M.; Mantis, N.J.; Shoemaker, C.B. Stepwise engineering of heterodimeric single domain camelid vhh antibodies that passively protect mice from ricin toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 36538–36547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Family | Members |
|---|---|
| V1D3 * | JIV-F6, V1B10 |
| V2A11 | V6H8 |
| V2G10 | V1G6 |
| V6D8 | V6F12 |
| V6A6 | V6A7, V6G10, V8C7, V8E6 |
| V6D4 * | V6B4 |
| VHH | Subcluster | IC50 (nM) | KD a (nM) | kon b | koff c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1D3 | 3.1 | 80 | 0.460 | 3.15 × 105 | 1.45 × 10−4 |
| V8C7 | - | 0.597 | 1.58 × 105 | 9.40 × 10−5 | |
| V6B4 | - | 0.652 | 1.70 × 105 | 1.11 × 10−4 | |
| V8E6 | - | 0.830 | 1.26 × 105 | 1.04 × 10−4 | |
| V1B10 | - | 0.917 | 8.29 × 104 | 7.60 × 10−5 | |
| V6A6 | - | 0.996 | 5.06 × 105 | 5.04 × 10−4 | |
| V6H8 | - | 1.150 | 6.63 × 104 | 7.66 × 10−5 | |
| V2G10 | - | 1.160 | 8.48 × 104 | 9.84 × 10−5 | |
| JNM-D1 | - | 1.190 | 1.80 × 105 | 2.15 × 10−4 | |
| V6G10 | - | 1.270 | 1.77 × 105 | 2.24 × 10−4 | |
| V5A2 | - | 1.460 | 2.15 × 105 | 3.14 × 10−4 | |
| V6A7 | - | 1.760 | 7.70 × 104 | 1.36 × 10−4 | |
| V2A11 | - | 1.820 | 2.97 × 104 | 5.41 × 10−5 | |
| JIV-F6 | - | 1.860 | 1.94 × 105 | 3.61 × 10−4 | |
| V1G6 | - | 5.340 | 3.05 × 104 | 1.63 × 10−4 | |
| V1B11 | - | 8.840 | 2.76 × 104 | 2.44 × 10−4 | |
| V7H7 | 3.2 | - | 0.507 | 1.65 × 105 | 8.36 × 10−5 |
| V6D8 | - | 1.130 | 2.14 × 105 | 2.41 × 10−4 | |
| V6F12 | - | 1.210 | 1.80 × 105 | 2.17 × 10−4 | |
| V6D4 | 3.3 | 200 | 0.222 | 1.44 × 105 | 3.21 × 10−5 |
| JNM-A11 | 3.4 | - | 0.212 | 4.20 × 105 | 8.91 × 10−5 |
| Strong and Intermediate Protected Elements in RiVax a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VHH | Subcluster | Peptides | Residues | Structure(s) |
| V6B4 | 3.1 | 48–51 | 119–133 | α-helix C |
| 91–102 | 205–217 | α-helix G | ||
| 132–134 | 249–255 | C-terminus | ||
| V1D3 * | 54,55 | 127–135 | α-helix C | |
| 91 | 205–210 | α-helix G | ||
| 112–116 | 226–243 | β-strands i, j | ||
| 132–134 | 249–255 | C-terminus | ||
| V6D8 | 3.2 | 35–39 | 92–107 | α-helix B |
| 49–54 | 123–135 | α-helix C | ||
| 102 | 211–217 | α-helix G | ||
| 129–134 | 247–255 | C-terminus | ||
| V6F12 | 35–40 | 92–107 | α-helix B | |
| 47,49 | 118–126 | α-helix C | ||
| 94,97,100,102–103 | 205–217 | α-helix G | ||
| 132–134 | 249–255 | C-terminus | ||
| V7H7 | 35–39 | 92–107 | α-helix B | |
| 49 | 123–126 | α-helix C | ||
| 94–95,97–98,100,102 | 205–217 | α-helix G | ||
| 129–131 | 249–255 | C-terminus | ||
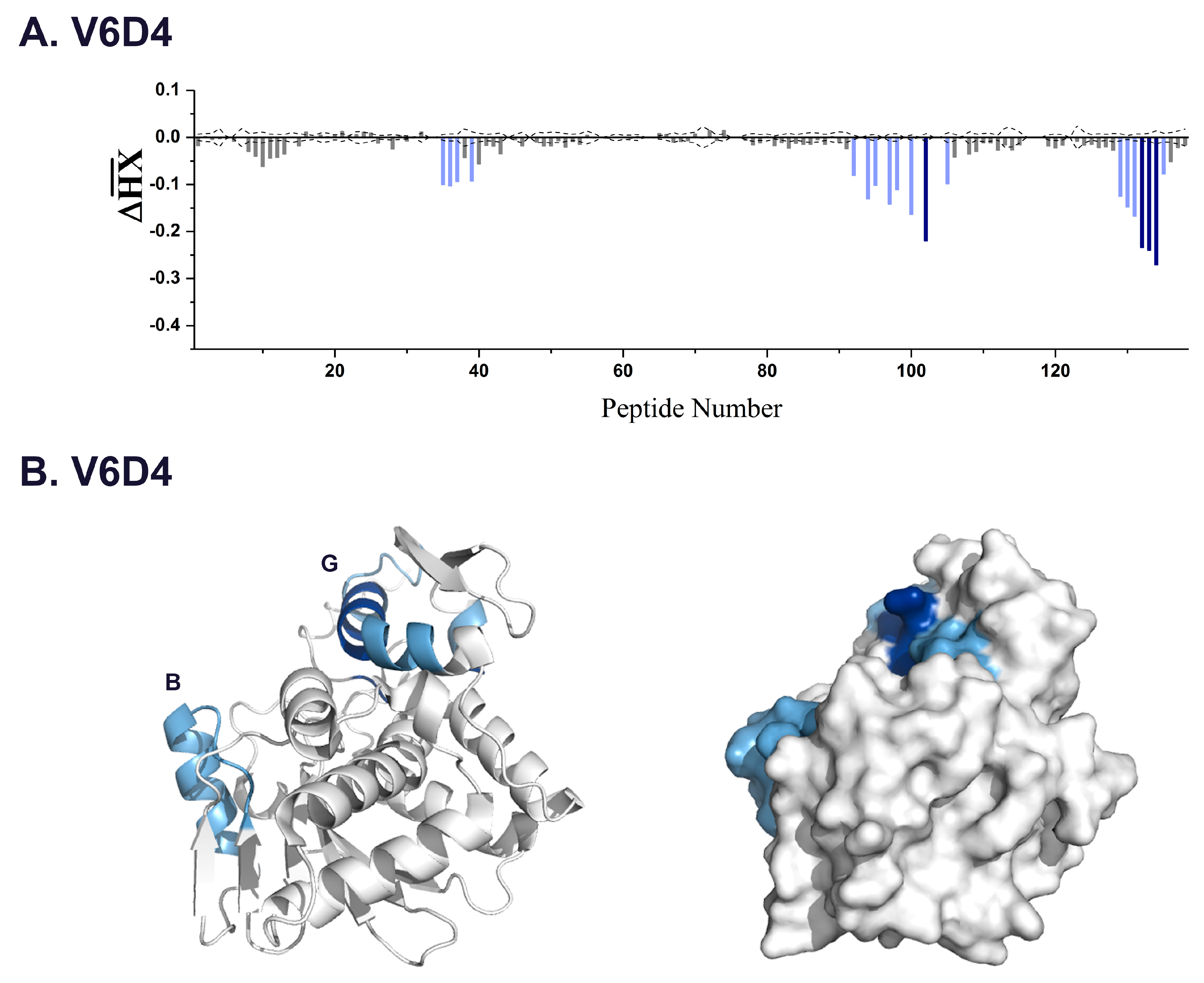
| V6D4 * | 3.3 | 35–37,39 | 92–107 | α-helix B |
| 102 | 211–217 | α-helix G | ||
| 132–134 | 249–255 | C-terminus | ||
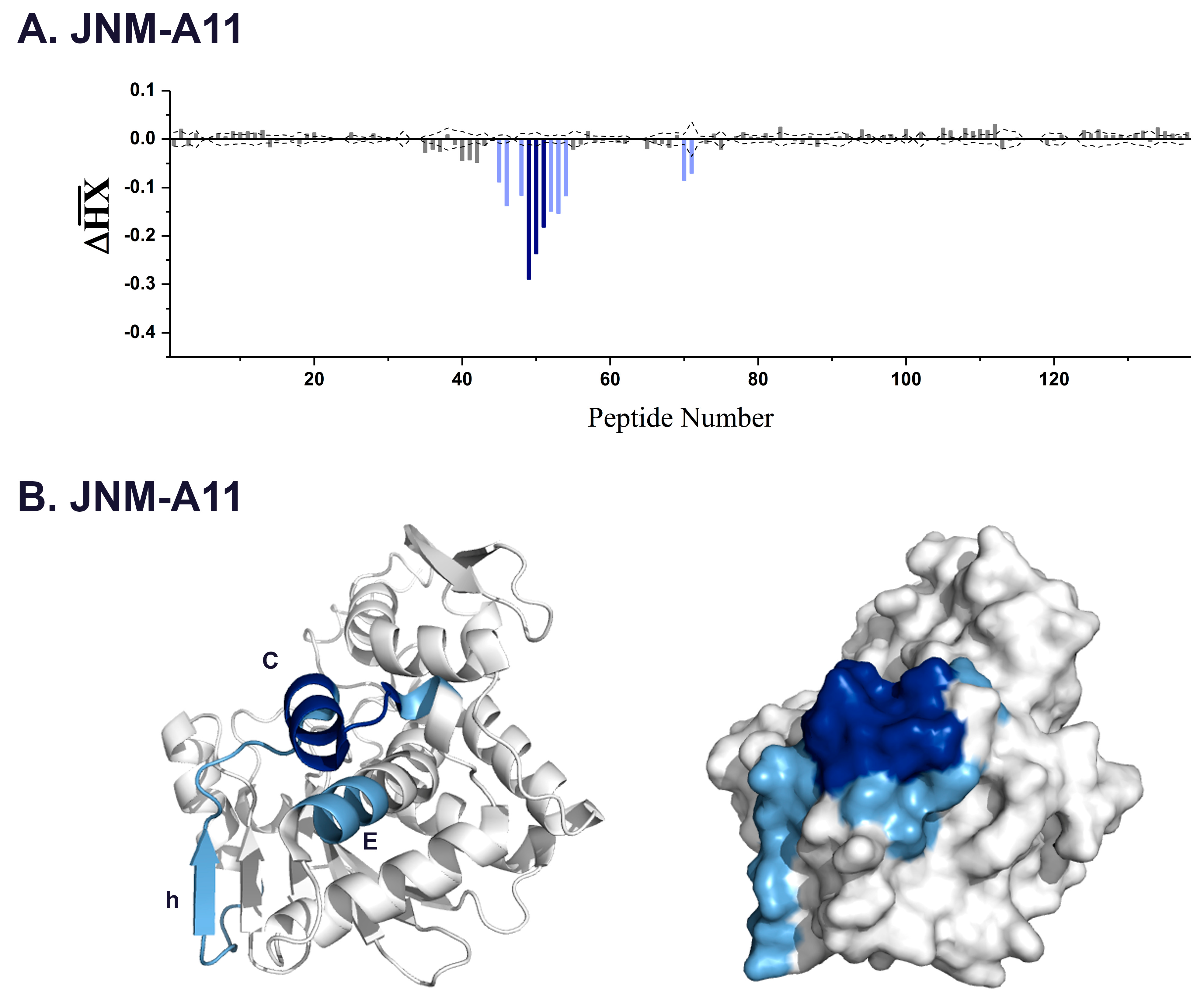
| JNM-A11 | 3.4 | 45,46 | 108–122 | β-strand h |
| 49–51 | 124–133 | α-helix C | ||
| 70,71 | 162–168 | α-helix E | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angalakurthi, S.K.; Vance, D.J.; Rong, Y.; Nguyen, C.M.T.; Rudolph, M.J.; Volkin, D.; Middaugh, C.R.; Weis, D.D.; Mantis, N.J. A Collection of Single-Domain Antibodies that Crowd Ricin Toxin’s Active Site. Antibodies 2018, 7, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib7040045
Angalakurthi SK, Vance DJ, Rong Y, Nguyen CMT, Rudolph MJ, Volkin D, Middaugh CR, Weis DD, Mantis NJ. A Collection of Single-Domain Antibodies that Crowd Ricin Toxin’s Active Site. Antibodies. 2018; 7(4):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib7040045
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngalakurthi, Siva Krishna, David J. Vance, Yinghui Rong, Chi My Thi Nguyen, Michael J. Rudolph, David Volkin, C. Russell Middaugh, David D. Weis, and Nicholas J. Mantis. 2018. "A Collection of Single-Domain Antibodies that Crowd Ricin Toxin’s Active Site" Antibodies 7, no. 4: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib7040045
APA StyleAngalakurthi, S. K., Vance, D. J., Rong, Y., Nguyen, C. M. T., Rudolph, M. J., Volkin, D., Middaugh, C. R., Weis, D. D., & Mantis, N. J. (2018). A Collection of Single-Domain Antibodies that Crowd Ricin Toxin’s Active Site. Antibodies, 7(4), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib7040045